
Visual Schedule: A Mobile Application for
Autistic Children - Preliminary Study
Joana Muchagata and Ana Ferreira
CINTESIS - Center for Health Technology and Services Research, Faculty of Medicine, University of Porto, Portugal
Keywords: Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Autistic Children, Visual Schedules, Mobile Applications, User Interface
Design (UI).
Abstract: Children with autism often experience considerable challenges and one of them is the difficulty in
understanding, structuring and predicting their daily life activities and routines. Several methodologies have
been studied and implemented to help autistic children with these routine activities and tasks, and one of those
methods is the use of visual schedules. For this, mobile apps and related technology have been considered as
an excellent tool in supporting autistic children’s development. But despite the technological resources and
the variety of mobile apps available today, the authors could not find such needed resources available for the
Portuguese speaking autistic children population, especially in relation to visual schedules/routines, which are
considered very important for the child’s development. Therefore, based on the literature and in some apps
available in other countries for autistic children, the authors propose a set of mock-ups of a visual schedule
application for smartphone. The visual mock-ups represent the idea of the app that we intend to implement in
a near future to be used by Portuguese autistic children aged between 4 to 10 years old to support them in
their daily routine and the performance of related tasks.
1 INTRODUCTION
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a developmental
disorder of the brain characterized by deficits in three
major areas of behaviour: social, communicative, and
repetitive behaviours and restricted interests and
activities. The social problems include less eye
contact, less attention and difficulty in learning and
using the social skills needed to function in society
(Sorensen, 2009). As a result, it impacts how a child
perceives and socializes with others, causing
difficulties in communication and interaction with
other people (Lubetsky et al, 2011). Also, because of
the disorder of social interaction, many autistic
children do not have the concept of time management.
Therefore, it is very difficult for them to understand
what they need to do as daily tasks (Niwa et al, 2014).
Several approaches have been made to assist
education of autistic children as well as several
methods have been implemented in different
countries to help children in their daily lives, with
their routines and tasks. One of the methods
considered by several authors as an effective
intervention technique for helping children with ASD
is the use of visual schedules. By providing a
structure, visual schedules support children to be
more independent (Hayes et al, 2010). And although
many special support education tools still use
traditional methods such as picture cards and
whiteboards (Niwa et al, 2014), technologies have
also been considered as an excellent tool in
supporting education and inclusion for children with
disabilities, including those with autism (Laabidi et
al, 2014; Rani et al, 2014).
But despite the various studies and methods
implemented in other countries, we have noticed that
in Portugal, there is a gap in educational methods
based on mobile technology for children with autism.
Therefore, this study aims to develop a set of mock-
ups for a new visual schedule application for
Portuguese autistic children. Our goal is that through
this method, children will be able in a simpler, more
engaging and independently way, to accomplish their
daily routines.
Since there is not much work available in this area
in our country, we need to start designing and
developing interactive methods and interfaces to face
this gap. This work is such a first step in this area.
This paper is organized as follows: section 2
presents the related work and section 3 describes the
452
Muchagata, J. and Ferreira, A.
Visual Schedule: A Mobile Application for Autistic Children - Preliminary Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0007732804520459
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2019), pages 452-459
ISBN: 978-989-758-372-8
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

methods used to design the mock-ups of an
interactive visual schedule for autistic children.
Section 4 describes our use-case and proposed mock-
ups, section 5 discusses the obtained results while
section 6 concludes the paper and provides future
research steps.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Visual Schedules
Most adults naturally make plans for their daily
behaviours and routines but autistic children have
several difficulties to make such plans for themselves.
Children with autism often experience considerable
challenges in understanding, structuring, and
predicting their daily life activities. Also, they need a
constant confirmation of their behaviours (Niwa et al,
2014).
There are many conventional therapies that work
for autistic children, and according with Azahari et
al., (Azahari et al, 2016) one of the most effective
educational approach is the visual method. More
precisely visual schedules have been shown to be an
effective intervention technique for helping
individuals with ASD (Hirano et al, 2010). Through
symbols such as pictures, words, and other visual
elements, visual schedules describe activities, and
what task will be happening, in what order, and where
(Hayes et al, 2010) (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Paper-based visual schedules. Individual student
schedules include representations for each activity of the
day (Hayes et al, 2010).
Even though, visual support has always been
typically made of paper in supporting autistic
children’s learning and development (Hayes et al,
2010), it has also been reported, by many parents and
caregivers, that this is a good methodology when used
with the support of new technology that involves
visual communications (Rani et al, 2014). Even more,
and according with several authors, mobile devices
could play a significant role in enhancing the quality
of life for children with ASD and their families
(Vlachou and Drigas, 2017)
2.2 Visual Schedule Mobile
Applications for Autistic Children
Studies have shown that autistic children are
enthusiast with technology, in particular with mobile
technology. This is especially because the touch
screen interface makes it appealing and simple to use
and learn everyday. It also helps the interaction
between children and other people (Vlachou and
Drigas, 2017). Besides, mobile devices are able to
assist them to be more concentrated and motivated to
learn and apply what they have learnt (Azahari et al,
2016). And beyond their strong interest in mobile
technology, autistic children are enthusiastic to use a
certain type of applications (Niwa et al, 2014).
During our research, we found various mobile
applications for children with autism and Asperger’s
syndrome, but taking into account our study’s
objective, the applications mentioned below are only
those related to visual schedules for autism.
Niwa et al. (Niwa et al, 2014) developed
“Smiley”, a schedule application to help autistic
children to do something by themselves without
instructions from teachers or parents. Many special
education schools in Japan have already adopted
“Smiley” as a primer of a schedule application.
Hayes et al. (Hayes et al, 2010) created “vSked”,
a prototype visual support which assists teachers in
managing their classrooms by providing interfaces
for creating, facilitating, and viewing progress of
classroom activities based on an interactive visual
schedule. It can be also used at home.
Song et al. (Song and Yusof, 2010) talks about
“PECS”, which allows the child to move the images
around to form sentences by touching the mobile
device screen. It gives the ability to easily customize
the images based on the needs, interests and
preferences of each child (Figure 2).
Figure 2: The smartphone app “PECS” (Song and Yusof,
2010).
Visual Schedule: A Mobile Application for Autistic Children - Preliminary Study
453

Another mobile assistive application is
“MOSOCO”, proposed by Escobedo et al. (Escobedo
et al, 2012). This app uses augmented reality and
visual supports to help children with autism to
practice social skills in real-life situations. This study
was tested in a public school in Southern California
and the results demonstrated that “MOSOCO”
facilitates the practice and learning of social skills.
In addition to the applications mentioned above,
on Apple App Store (iOS system), we found a few
paid apps related with our study such as: “Children
with Autism: A visual schedule”, “Visual Schedule
Planner” (Figure 3), “Birdhouse for Autism”,
“Choiceworks”, “First Then Visual Schedule”, and
“PictogramAgenda”. Besides not being free, these
applications are not available in the Portuguese
language and most of them are only developed for
iPad.
Figure 3: Image from the “Visual Schedule Planner” app.
In its turn, on Google Play Store (Android system)
there are several apps free for downloading. But
despite this variety of apps, the authors could not find
many resources available in Portuguese, to be used by
Portuguese speaking autistic children, especially
relating to visual schedules/routines.
On Google Play Store we looked for free apps that
matched the following English and Portuguese search
terms: “schedule routine for autism”, “visual routine
for autism”, “visual schedule autism”, “visual timer
autism” and “rotina autismo”. Therefore, we found
eight free apps available for downloading. And even
though, three of them are available in Portuguese
language, none of them were developed in Portugal.
The apps “Minha Rotina Lite” and “Autismo Projeto
Integrar” (Figure 4) were made in Brasil, and “Lista
visual - Visual Schedule” was made in Canada.
The first app is only available for tablet and it is
not the full version (the full version is paid). The
version available has limited tasks and, in addition,
some terms used are not the same as those used in
Portuguese language, from Portugal. In the second
app, the images and the sequence are predefined and
customization is not possible while the third app does
not contain a distinction of users (a different profile
for the child and their parents/teachers) and so it can
become confusing due to all available options and
functionalities each time the child accesses the app.
Figure 4: Some images of “Autismo Projeto Integrar” app
(Krause, 2016).
3 METHODS
Taking into consideration our research in terms of the
availability of visual schedule apps for autistic
children, we may conclude that, in Portugal, there is
a clear gap for this type of mobile apps. Children are
increasingly using computers for a variety of
activities, however, designing for children can be
extremely challenging, particularly for children with
special needs (Hayes et al, 2010). So we decided to
analyse the existing visual schedule mobile apps
developed in other countries, and understand what are
the successful functionalities and which must be
avoided, when developing such an app. Beyond the
apps, we also analysed the existing literature on the
subject to help us define our app’s main requirements
and avoid common mistakes right from the
beginning. The combination of all recommendations
and a set of User Interface Design (UI) principles for
designing and developing a mobile-based learning
application are summarized in Table 1 and explained
in Section 4.
4 REQUIREMENTS & USE-CASE
Based on the literature review and in some apps
available in other languages rather than Portuguese
from Portugal, our idea focuses on the development
of visual mock-ups of a visual schedule application
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
454
for smartphone. The visual mock-ups represent the
idea of the app that we intend to implement in a near
future. Our goal is to have a very simple design to be
easily understandable and used by children and
prepared to be customized by parents/teachers. And
although it is intended to be used independently by
the child, at the beginning, it may be necessary the
help of an adult to use the tools and complete the
tasks.
4.1 Requirements
According with Hussain et al. (Hussain et al, 2016),
numerous apps for autistic children are difficult to
use, particularly in terms of user-interface design.
Instead of what happens in many available
applications for children, Niwa et al. (Niwa et al,
2014) suggested that applications must have simple
functions and operations, focused on basic
manipulations which will allow autistic children to
understand what to do next, easily. The same authors
also refer that such apps must also have an attractive
design.
Another important characteristic that many apps
do not have is related with customization of images.
Parents or teachers should be able to customize the
app with personal photos of real situations and
activities, based on the needs, interests and
preferences of each child (De Leo and Leroy, 2008;
Song, 2012; Voon et al, 2015). All this can facilitate
the learning process. Some apps lack on a good
structure which may cause anxiety (Fletcher-Watson
et al, 2016). Others have only one login mode which
may be confusing and the child could easily reset the
settings (Voon et al, 2015).
The design and development of a learning mobile
application for educating children implies essential
elements to guarantee that the user will easily and
effectively use the application. Since in this phase we
could not engage the final user (the children with
ASD), our design process of visual mock-ups was
mainly based on the literature review, the analysis of
existing apps and also on a set of User Interface
Design (UI) principles for designing and developing
a mobile-based learning application proposed by
Hussain et al. (Hussain et al, 2016) and Hashim et al.
(Hashim et al, 2010). Thus, with the proposed design
we intend to have a combination of the benefits found
in some tested apps and in the results demonstrated in
the studies of our review. At the same time, we tried
to avoid already encountered problems. Moreover,
we intend to suggest some design decisions to provide
an app which better fits the target group’s needs. The
list of found recommendations is available in Table 1.
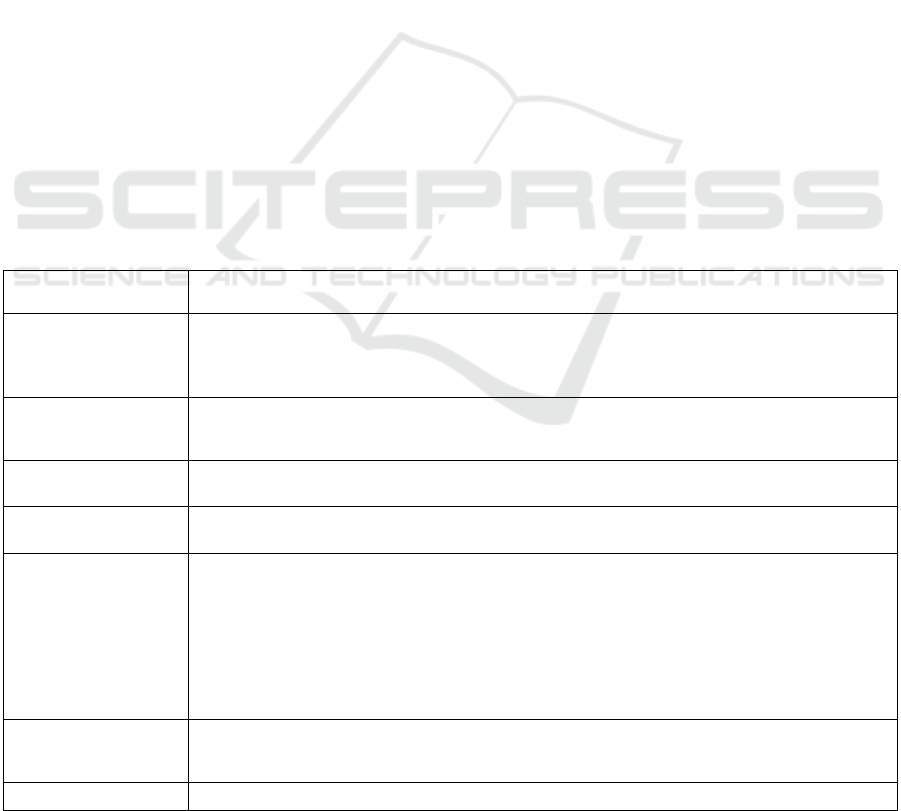
Table 1: The combination of all recommendations and design principles to design a visual schedule app for autistic children.
Design Principle
Suitable Design
Structure
Simple structure and sequence (Fletcher-Watson et al, 2016; Niwa et al, 2014)
Two login modes - the child login and the parent/teacher login which makes the layout
simpler and more perceptible for the child (Voon et al, 2015)
The admin section should be protected with a password (Hussain et al, 2016)
Navigation
Simple navigation, easy to understand and use (Hussain et al, 2016; Niwa et al, 2014)
Should always be consistent (Hashim et al, 2010)
Similar actions and similar buttons located in similar positions (Hashim et al, 2010)
Interface
Simple and attractive (Hussain et al, 2016; Niwa et al, 2014)
Should be user friendly (Hashim et al, 2010)
Content
Information must be small and consistent and unnecessary information should be avoided
(Hashim et al, 2010)
Images
The customization of images should be available and must be at the parental login mode
(De Leo and Leroy, 2008; Hussain et al, 2016; Song, 2012; Voon et al, 2015)
Images must be identical to real life (personal and real photographs of the child) because it
facilitates the recognition and allows children to learn more efficiently and effectively (De
Leo and Leroy, 2008; Hussain et al, 2016; Song, 2012; Voon et al, 2015)
Through their own login, children must have access to all images corresponding to the
activities previous organised by their parents/teachers (De Leo and Leroy, 2008; Song,
2012; Voon et al, 2015)
Text, video and
audio
Options to add text, audio and video to each task and for all the steps should be available
(Song, 2012; Voon et al, 2015)
The audio should correspond to the images and must be user-friendly (Hussain et al, 2016)
Colours
Dark colours such as black should be avoided (Hussain et al, 2016)
Visual Schedule: A Mobile Application for Autistic Children - Preliminary Study
455

4.2 Use-case
The proposed app’s name is “My Routine” and it is
designed to be used by Portuguese autistic children
aged between 4 to 10 years old to support them in
their daily routine and for the performance of related
different tasks. Activities such as “use the bathroom”,
“get dressed” or “eat breakfast” can be supported by
the app because it contains each step for the
accomplishment of the task. Through pictures, words
and sounds it is shown the sequence of steps within
each activity. It is also designed to be used by parents,
teachers and special educators, once they are
responsible to organize all the activities (names and
descriptions) taking into account the child’s routine,
upload real photos of the child, record audio an even
upload videos in the app related with each child’s
task.
Therefore, the following images are in English for
the sake of understanding of a wider audience, but the
idea is to have the app developed and implemented in
Portuguese.
4.2.1 Child’s Profile
As suggested by a few authors (De Leo and Leroy,
2008; Hussain et al, 2016; Song, 2012; Voon et al,
2015), an application must be customizable with
images, texts and audio. Thus, in the design process
we thought that the application could be more
appealing if it started with the child’s photo and
name. Figure 5 (left), represents the child’s profile
and what s/he sees as soon as s/he runs the application
(his/her name and photo). This corresponds to the
child’s login mode but we considered the idea of
having two login modes very relevant, being one for
the child and the other for the parent or teacher (Voon
et al, 2015). This helps the layout to be simple and
more perceptible for the child.
In the child layout, it is possible to switch to the
parent/teacher profile through the button in the lower
right corner. The parent/teacher profile is protected
with a password to avoid any confusion in the child’s
understanding and perception.
By choosing to continue in the child profile and
after clicking on the photo, Figure 5 (right) represents
the following menu. This menu consists of several
buttons with the days of the week. Taking into
account the ideas proposed by Niwa et al. (Niwa et al,
2014), and also the potential group users of our
application, we decided the best would be to have a
very simple structure and navigation. Beyond the
days of the week (from Monday to Sunday), the
authors thought that it might be important have two
more options, “Holidays” and “Special days”. These
options allow parents to personalize specific activities
taking into account different occasions of the year.
The month of the year is also presented, in this case
“January” accompanied by a customizable
background image. For a better identification and
because this is a visual schedule, each day is
combined with a symbol with the corresponding day
of the month, and the current day is highlighted. For
the school days we choose a school board, and for the
other days we chose different symbols that may
represent different activities. The next step is the
choice of the day of the week. The colours used are
the type of shade used in other apps for children, not
too light and not too dark (Hussain et al, 2016).
Figure 5: The beginning of the app “My Routine” with the
child's profile image (left), followed by the first menu to
choose the day of the week (right).
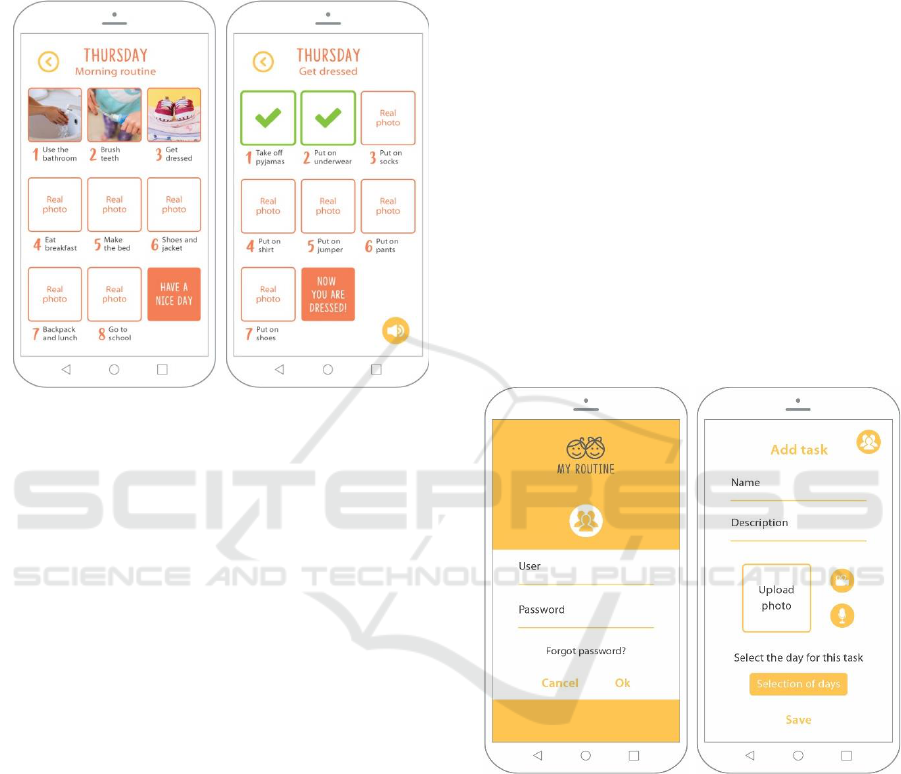
When choosing the day of the week the various
morning activities/tasks are visualized (Figure 6 -
left): use the bathroom, brush teeth, get dressed, eat
breakfast, make the bed, shoes and jacket, backpack
and lunch, go to school. These activities/tasks were
chosen based on real activities performed by
Portuguese children during their school days. Our
layout was inspired by the combination of schedule
apps such as “Visual Schedule Planner” and “Minha
Rotina Lite” as, for each day of the week, they have
several organised images representing the planned
activities. Moreover, these two apps are completely
audio-visual customizable.
Therefore, the space we have for images identified
with “Real photo” must be customized with personal
photographs of the child (De Leo and Leroy, 2008;
Hussain et al, 2016; Song, 2012; Voon et al, 2015).
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
456
As previously mentioned, the customization with
personal and real photographs of the child facilitates
the recognition and allows children to learn more
efficiently and effectively (De Leo and Leroy, 2008;
Hussain et al, 2016; Song, 2012; Voon et al, 2015).
Figure 6: All the tasks that are planned to be performed by
the child (left) and details of the task “Get dressed” (right).
The app “Autismo Projeto Integrar” helped us in
the organization of the tasks and how to organise each
task steps. When a task is chosen, all the steps related
with that task are displayed (Figure 6 - right). The
space designed for images are accompanied with a
small text to support each step, if necessary (Song,
2012; Voon et al, 2015). In this case, the chosen task
is “Get dressed” and all the steps that the child will
have to perform are displayed. After the child
completes each step s/he will have to click on the
corresponding image in order to confirm that a
particular step is completed and the green check mark
symbol will appear. Each step can also have audio
combined, preferably personalized with a voice of
someone the child knows well (Hussain et al, 2016).
The sound button (present in the lower right corner)
gives the child the opportunity to listen the several
steps previously recorded. As soon as the task “Get
dressed” is completed the menu with all the activities
reappears and this specific task appears with a green
check mark symbol (similar to Figure 6 - left).
As recommended by several authors, we tried to
design a simple structure, sequence and navigation
(Fletcher-Watson et al, 2016; Hussain et al, 2016;
Niwa et al, 2014). And as referred by Hashim el al.
(Hashim et al, 2010), we also tried to maintain the
consistence needed for autistic children. Also, we
placed similar actions in similar positions because it
will help the child to understand the content, the
sequence and it will be easier to use.
4.2.2 Parental Profile
In addition to the child's profile, there is also the adult
profile. Thus, parents, teachers and special educators
must login into the app in order to structure, organise
and customize the child’s tasks (Figure 7). The
authors agree with Hussain et al. (Hussain et al,
2016), that this area should be protected with a
password in order to avoid the child to feel confused
or even to reset the settings (Voon et al, 2015).
Right after signing in, tasks can be introduced. On
“Add task” menu (Figure 7 - right) a task name and
description should be inserted; a real photo of the
child performing the task must be uploaded; recorded
audio and video can be uploaded (if desirable).
Parents/teachers should also choose the days on
which the task must be performed. Multiple days may
be chosen as various activities can be repeated on
different days.
Figure 7: The adult login mode (left) followed by the menu
to start introducing tasks (right).
Each task can be composed by several steps.
Figure 8 illustrates the introduction of several steps as
well as the possibility of its sequential organization.
The button on the lower right corner allows adding
steps.
The authors also proposed a “Share” button which
may allow the information exchange between parents
and teachers or special educators.
Visual Schedule: A Mobile Application for Autistic Children - Preliminary Study
457

Figure 8: The customization of the task “Get dressed”.
5 DISCUSSION
The more we delved into this research work the more
we realized that there is a gap that has to be fulfilled
in terms of Portuguese mobile applications for autistic
children. Moreover, the lack of data from testing of
existing mobile apps within this domain, in other
countries, does not help to provide adequate means to
evolve this specific technology at a more desirable
faster pace.
Nevertheless, with our study, we have learnt some
recommendations to be used as a first step to
implement the aimed visual schedule app, so we do
not reinvent the wheel, but start from existing
knowledge, even if it is scarce.
Consequently, the authors decided to propose
mock-ups of a visual schedule aiming to start
bridging that gap and help improving those children’s
skills within a domain that is very relevant to children
and their families, on a daily basis.
Simple mock-ups have been defined, which
although still incipient, can already achieve/model a
variety of tasks and activities and so, once these are
tested and enhanced by the autistic children as well as
their community of family, friends and educators, can
be easily reused for many similar actions that
comprise daily routine activities.
Focusing on the proposed mock-ups, for the child
profile, we realize that the main parts of the app are
the first page and the one that summarizes all
activities and from where all functionalities can be
accessed. For children, having simple and obvious
data, and also their own photo and name can help in
creating a “good” relation with an app that they may
be using everyday, several times a day. Also, the use
of simple functionalities such as pressing
buttons/images in a similar fashion and within the
same sequence can again create a routine of use in
itself. Other interesting customizations can be added
depending on the taste and personality of the child.
The simple action of earning points or receiving an
encouragement message when an activity is
concluded can help improve the engagement in using
the app and, therefore, enhancing the learning of the
required activities. Giving this flexibility of choice
within the parental profile can better help the parents
or other relatives to adapt the app to the child’s needs.
As already mentioned, this is only the first phase
of this project which we intend to develop and test in
the future. There are obviously several characteristics
of our proposal that need to be discussed with
professionals which work with autistic children
everyday as well as study the interactions and feel of
the children themselves.
Finally, and according with the application of the
new General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
(European Union, 2016) in the European Union, there
are some privacy and security concerns related with
the children’s information (photos and some other
personal information), which need to be addressed
while developing the proposed app.
Limitations. Despite the variety of apps available for
autistic children, the authors could not find many
digital resources in Portuguese for special education
particularly related with visual schedules/routines
applications to be used by Portuguese speaking
autistic children. Three visual schedules apps were
found on Google Play Store but none of them were
implemented in native Portuguese and, for one of
them, it was not possible to access its full version.
Furthermore, during this research, the authors could
not engage the final user (the children with ASD).
However, the visual mock-ups proposed were
designed based on the literature review, the analysis
of existing apps in other countries and also on a set of
User Interface Design principles. Nonetheless, in
future work, we will address these issues and connect
with entities related with our study in order to
implement our app and perform tests with end users
to improve it and make it useful to the community. In
this phase, we may experience some difficulty in
establishing the first contacts and finding available
people interested in working with us as well as we
may face some barriers in our approach to autistic
children. However, we will make every possible
effort to have success in our future work and to
achieve all our goals.
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
458

6 CONCLUSION
Visual supports can enable children with ASD to
learn and communicate more easily with their family,
friends and teachers. Traditional tools, however, are
challenging to create, use, and maintain. Furthermore,
they provide little or no ability to document and
monitor use and progress over time. This way, and
taking into account the Portuguese reality, it would be
very significant for autistic children (and for children
with special educational needs in general) if there was
a combination of efforts from autistic organizations
and teachers, designers and developers to provide
easy means to support such community.
This work aims to be such first step in this
direction with the development of mock-ups of a
visual schedule mobile app, in Portuguese, from
Portugal, to support ASD children in their daily
routine tasks.
Future work includes the engagement with the
ASD related community and especially the children
that can highly benefit from such efforts, to test and
improve the proposed app.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This article was supported by FCT through the
Project TagUBig - Taming Your Big Data
(IF/00693/2015) from Researcher FCT Program
funded by National Funds through FCT - Fundação
para a Ciência e a Tecnologia.
REFERENCES
Azahari, I. N. N. A., Ahmad, W. F. W., Jamaludin, Z. and
Hashim, A. S. (2016) The design of mobile social
application for children with autism, 2016 3rd
International Conference on Computer and
Information Sciences (ICCOINS). 15-17 Aug. 2016.
De Leo, G. and Leroy, G. (2008) Smartphones to facilitate
communication and improve social skills of children
with severe autism spectrum disorder.
Escobedo, L., Nguyen, D. H., Boyd, L., Hirano, S., Rangel,
A., Garcia-Rosas, D., Tentori, M. and Hayes, G. (2012)
MOSOCO: a mobile assistive tool to support children
with autism practicing social skills in real-life
situations, Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on
Human Factors in Computing Systems. Austin, Texas,
USA, 2208649: ACM, 2589-2598.
European Union (2016) Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the
European Parliament and of the Council L 119. Official
Journal of the European Union.
Fletcher-Watson, S., Pain, H., Hammond, S., Humphry, A.
and McConachie, H. (2016) Designing for young
children with autism spectrum disorder: A case study of
an iPad app. International Journal of Child-Computer
Interaction, 7, 1-14.
Hashim, A. S., Ahmad, W. F. W. and Rohiza, A. (2010) A
study of design principles and requirements for the m-
learning application development, 2010 International
Conference on User Science and Engineering (i-USEr).
13-15 Dec. 2010.
Hayes, G. R., Hirano, S., Marcu, G., Monibi, M., Nguyen,
D. H. and Yeganyan, M. (2010) Interactive visual
supports for children with autism. Personal and
Ubiquitous Computing, 14(7), 663-680.
Hirano, S. H., Yeganyan, M. T., Marcu, G., Nguyen, D. H.,
Boyd, L. A. and Hayes, G. R. (2010) vSked: evaluation
of a system to support classroom activities for children
with autism, Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on
Human Factors in Computing Systems. Atlanta,
Georgia, USA, 1753569: ACM, 1633-1642.
Hussain, A., Abdullah, A. and Husni, H. (2016) The design
principles of edutainment system for autistic children
with communication difficulties, 1761.
Krause, M. (2016) Autismo Projeto Integrar, 2016.
Available online: https://maicokrause.com/ [Accessed.
Laabidi, M., Jemni, M., Ayed, L. J. B., Brahim, H. B. and
Jemaa, A. B. (2014) Learning technologies for people
with disabilities. Journal of King Saud University -
Computer and Information Sciences, 26(1,
Supplement), 29-45.
Lubetsky, M. J., Handen, B. L. and McGonigle, J. J. (2011)
Autism Spectrum DisorderOxford University Press.
Niwa, T., Torii, I. and Ishii, N. (2014) Development of
Smart Devices Applications for Autistic Children, 2014
IIAI 3rd International Conference on Advanced
Applied Informatics. 31 Aug.-4 Sept. 2014.
Rani, N. M., Legino, R., Mudzafar, N. and Kamaruzaman,
M. F. (2014) Embedded visual schedule application
towards autistic children development: A prelimenary
study, 2014 IEEE 6th Conference on Engineering
Education (ICEED). 9-10 Dec. 2014.
Song, H. (2012) Mobile Technology for Children with
Autism Spectrum Disorder: Major Trends and Issue,
2012 IEEE Symposium on E-Learning, E-Management
and E-Services.
Song, H. and Yusof, A. (2010) A current review of the use
of mobile technology to enhance learning and
communication among children with developmental
disabilities.
Sorensen, L. (2009) Autism, Asperger’s and theory of
Mind. Cognition and Children’s Thinking Seminar.
Vlachou, J. and Drigas, A. (2017) Mobile Technology for
Students & Adults with Autistic Spectrum Disorders
(ASD), 11.
Voon, N. H., Bazilah, S. N., Maidin, A., Jumaat, H. and
Ahmad, M. Z. (2015) AutiSay: A Mobile
Communication Tool for Autistic Individuals Cham:
Springer International Publishing.
Visual Schedule: A Mobile Application for Autistic Children - Preliminary Study
459
