
The Influence of Various Text Characteristics on the Readability and
Content Informativeness
Nina Khairova
1a
, Anastasiia Kolesnyk
1b
, Orken Mamyrbayev
2c
and Kuralay Mukhsina
3d
1
National Technical University ”Kharkiv Polytechnic Institute”, 2, Kyrpychova str., 61002, Kharkiv, Ukraine
2
Institute of Information and Computational Technologies, 125, Pushkin str., 050010, Almaty, Republic of Kazakhstan
3
Al-Farabi Kazakh National University, 71 al-Farabi Ave., Almaty, Republic of Kazakhstan
Keywords: Text Quality, Readability Indexes, Linguistic Features, Statistical Characteristics of a Document, Simple
Wikipedia, Enterprise Information Systems.
Abstract: Currently, businesses increasingly use various external big data sources for extracting and integrating
information into their own enterprise information systems to make correct economic decisions, to understand
customer needs, and to predict risks. The necessary condition for obtaining useful knowledge from big data
is analysing high-quality data and using quality textual data. In the study, we focus on the influence of
readability and some particular features of the texts written for a global audience on the texts quality
assessment. In order to estimate the influence of different linguistic and statistical factors on the text
readability, we reviewed five different text corpora. Two of them contain texts from Wikipedia, the third one
contains texts from Simple Wikipedia and two last corpora include scientific and educational texts. We show
linguistic and statistical features of a text that have the greatest influence on the text quality for business
corporations. Finally, we propose some directions on the way to automatic predicting the readability of texts
in the Web.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, industry, government and businesses
increasingly use various external big data sources in
order to extract and integrate information into their
own enterprise information systems (Cai, 2015).
By analyzing a massive amount of information
and knowledge from various external sources, a
decision-maker has benefits for making correct
financially significant economic decisions,
understanding customer needs, predicting and
preventing any risks.
However, the necessary condition for obtaining
useful knowledge from big data is analysing data
high-quality, in particular, using qualitative textual
data. At the same time, the Internet is flooded with
different texts that convey no useful information for
business purposes. It can be not only meaningless
blogs and obvious computer-generated spam but also
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9826-0286
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5817-0844
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8318-3794
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8627-1949
such texts that, at first glance, are from reliable and
serious sources.
Although today the concept of the quality of the
text information is quickly modified depending on the
type of information, its style, and field of
applications, and besides, the universal method for
conducting a full assessment of the quality of textual
material has not been developed yet, mainly, the
estimating of the text information is based on
traditional quality assessment standards of
information generally relevant to actual business
needs. It is believed that such text information quality
dimensions are аvailability, usability, reliability,
relevance and presentation quality.
In our study, we focus on the last dimension,
which we can divide into such elements associated
with it as readability, structural and linguistic
correctness. We strive to reveal parameters to identify
462
Khairova, N., Kolesnyk, A., Mamyrbayev, O. and Mukhsina, K.
The Influence of Various Text Characteristics on the Readability and Content Informativeness.
DOI: 10.5220/0007755004620469
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2019), pages 462-469
ISBN: 978-989-758-372-8
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

these elements of the text quality and develop a tool
for testing it.
At the same time, in many cases, text sources,
which are used by enterprise information systems,
address a global audience. That is, they are written in
English and then receive worldwide distribution. For
these Internet resources, in order to estimate its
readability, we offer to add such linguistic features to
traditional readability level indexes as the use of one-
word verbs instead of a verb phrase or the use of only
international writing of terms.
As an example of the texts intended for the
worldwide audience, we employ our corpus of
Wikipedia articles. Currently, there are sufficient
approaches to quality assessment of Wikipedia
articles (Lewoniewski, 2017). The issue of Wikipedia
texts quality assessment has become the subject of
studies in various fields of science. In 2006 one of the
co-founders of the online non-profit encyclopedia
Wikipedia suggested concentrating on the quality of
the articles instead of their number (Giles, 2005).
The best articles of Wikipedia must follow the
specific style guidelines, the rating system of which
depends on a specific language. For example, in
English Wikipedia articles, which we examine in the
study, the system of Wikipedia articles quality has 9
grades: FA (Featured Article), A, GA (Good Article),
B, C, Start, Stub, FL (Featured List), List. Each of
these grades has special criteria. For instance, to those
criteria, we can include the relevance,
informativeness and encyclopedicness (Khairova,
2018) of the information, the correctness of texts
spelling and grammar and some others. However, to
date, all of these criteria are assessed manually by the
Wikipedia communities.
In our study, we will consider the influence of
readability and some particular features of the texts
written for a global audience on the texts quality
assessment.
In order to estimate the influence of different
linguistic and statistical features on the text
readability, we decided to use five different text
corpora.
2 RELATED WORK
The readability concept was introduced in the 1920s
and it means the ability to read a text. Until the late
1980s, the readability concept was used by educators
in order to identify the complexity of tutorials and
textbooks. The educators discovered a way to use
vocabulary difficulty and sentence length to predict
the difficulty level of a text (DuBay, 2004).
At the present time, readability is one of the
dimensions of the text information quality and it
matters in every profession where people need
qualitative information and knowledge. Now, the
most known ways of representation of readability
level are 5 indexes, such as Flesch Reading Ease
(Cotugna, 2005), Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level, ARI
(Oosten, 2010), SMOG (Hedman, 2008) and FOG
(Walsh, 2008).
Generally, more modern methods are based on the
data of well-known indexes and do not give a reliable
advantage to any of them.
For instance, Pitler and Nenkova (Pitler, 2008)
ranged the influence of various readability factors on
predicting readability of a text and the text quality
Schwarm and Ostendorf (Schwarm, 2005)
proposed to develop new method appropriate for
finding English texts of a certain readability level on
the basis of the widely known readability indexes to
combine them with statistical language models,
support vector machines and other language
processing tools. Their research showed that
сombining information from statistical LMs with
other features using support vector machines
provided the best results.
Authors of the next study (Oosten, 2010) used 4
corpora in two languages, Dutch and English to find
the correspondences between the readability formulas
and variables that are used in them.They made a
conclusion that it was not reasonable to expect that
formulas based on language-independent features can
precisely predict the readability level.
It is interesting, that many studies dedicated to
readability analyze the text readability on the basis of
the texts devoted to health care. In our opinion, that's
because such texts must be understandable to as many
readers as possible. In medicine, it is extremely
important that texts with such information correspond
to the average level of the reader. The United States
Department of Health and Human Services identified
that the reader of this level is in the 7th-grade
(D'alessandro, 2001).
According to the article (D'alessandro, 2001), the
average reading level is eighth-ninth grade, in the
USA. But all medical education materials are too
complex for average adults. It means that such
materials should have a lower grade to be
understandable. Their conclusion was based on the
result of 2 most widely used indexes: The Flesch
Reading Ease score and Flesch-Kincaid that
evaluated one hundred documents from 100 different
Web sites. The result was that pediatric patient
education materials on the Internet were not written
at an appropriate reading level for the average adult.
The Influence of Various Text Characteristics on the Readability and Content Informativeness
463

One more article that also affected health topic
(Walsh, 2008) confirmed that the average readability
of Internet-based consumer health information had
exceeded the recommended 7th-grade reading level.
They assessed articles with 3 readability indexes:
FOG, SMOG and Flesch-Kincaid.
The second element, which associated with the
presentation quality of textual information, is
structural and linguistic correctness of a text. The
most universal criteria for grammatical, punctuation,
and style evaluation of technical and scientific texts
are offered by The Microsoft Manual of Style
(Microsoft, 2012).
The glossary of the international version of the
terminology spelling developed by the INTECOM
International Language Project Group is very useful
in this regard (Intecom, 2003).
The objective of INTECOM’s International
Language Project Group was to identify which
spelling and usage it should recommend for
documentation that would be written in English and
would receive worldwide distribution.
Additionally, nowadays a lot of web-resources
provide online services to assess the readability of a
text. Site ReadablePro
5
, website Online-Utility.org
6
,
textalyzer
7
tools are the best-known type of such
resources. However, a detailed examination of such
resources revealed that the results of their work are
different when one and the same text is checked on
readability. So it can be said that the resources the
Internet offers us today can provide non-
representative and unreliable results.
3 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
3.1 Experiments Description
Generally, the readability of the texts, submitted on
the Internet, is affected by many factors. For example,
it can be rhythmics of the text, the complexity of the
used words and sentences, website logical structure (a
background, types of fonts, the sizes of columns,
etc.). Neglecting any of these parameters can
significantly reduce the readability of the Web article.
Besides, the readability level (or the complexity
of text perception) is influenced by such linguistic
features of the text as length of words and sentences;
the complexity of syntactic constructions; the rate of
5
Measure readability: https://readable.io/
6
Test document readability: https://www.online-utility.
org/english/readability_test_and_improve.jsp.
7
Improve text readability: https://www.textalyzer.xyz
words; the level of abstractness of lexicon; the large
number of terms; the use of neologisms and jargons;
active or passive voice.
These indicators are used for formulation of
various formulas of readability indexes calculation. In
our experiments, we calculate a few main coefficients
of readability that can be used to compute readability
of any texts types: scientific, education, encyclopedic
and some others.
Fog Index is calculated by the following equation:
FOG= 0.4
+100
,
(1)
where w is the number of words, s is the number of
sentences and cw is the number of complex words.
The SMOG index doesn’t need the entire text to
be assessed. It requests 10 sentences in a row near the
beginning, 10 in the middle, and 10 in the end:
SMOG=1.0430
∗
+3.1291,
(2)
where NPS is the number of polysyllables and
s is the
number of sentences.
ARI index outputs a number that approximates
the age needed to understand the text.
ARI = 4.71
+ 0.5
– 21.43,
(3)
where c is characters (the number of letters and
numbers), w is the number of words and s is the
number of sentences
To determine the readability level of the scientific,
educational, encyclopedic Web resources addressed
to a world audience, we add the linguistic features to
the traditional coefficients described above. Then we
divide these features into three group potential
mistakes. In our research, we use three types of these
mistakes that can influence the text quality. These are
punctuation mistakes, grammar mistakes and style
mistakes.
Table 1 shows the distributions of some linguistic
features according to these groups of mistakes.
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
464
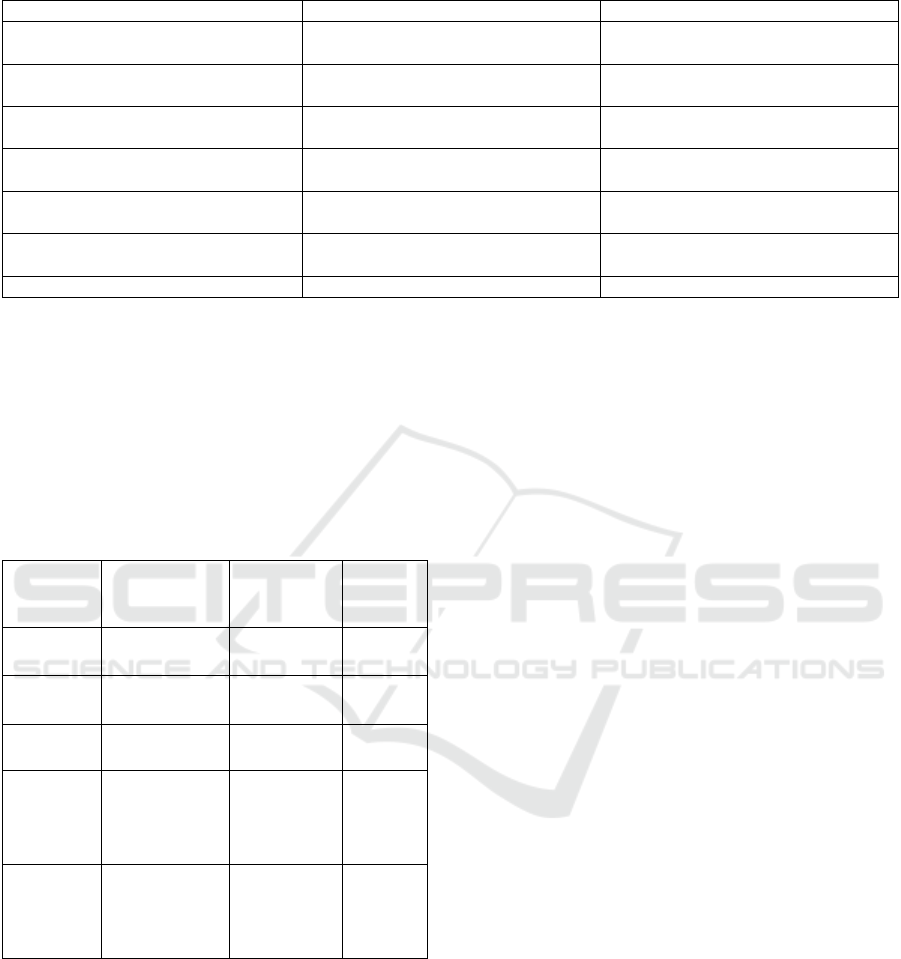
Table 1: The distributions of some linguistic features according to the types of mistakes.
Style mistakes Grammar mistakes Punctuation mistakes
Writing of digits from 1 through 9 in
words
Use of one-word verbs instead of a
verb phrase
Use of only one gap after the
punctuation mark.
Use of numerals for 10 and greater Use of only international writing of
terms
There is no coma in MMMM YYYY
date format
Use of numerals for all measurements,
even if the number is less than 10
Use a punctuation mark without an
extra gap
Use of (from і through) instead of
(between і and)
Slash cannot be a substitute of “or”,
for example he/she
Use of MMMM DD, YYYY date
format
Use of italic formatting instead of
upper-case
No abbreviation of months
3.2 Source Data
The dataset of our research includes 5 corpora of three
styles, namely, educational, scientific and
encyclopedic. Table 2 shows the distributions of the
analyzed articles
according to our corpora.
Table 2: The distribution of analyzed articles according to
our corpora.
Corpus
name
Categories
Items in
each
category
The
number
of words
Good-
Enough
FA
GA
53
37
358454
Needs-
Work
C
Stub
49
41
189885
Simple-
Wikipedia
15 8611
Education
Astronomy
Biology
Chemistry
Physics
5
5
5
5
31755
Science Astronomy
Biology
Chemistry
Physics
5
5
5
5
33024
Three of our corpora consist of articles from
English Wikipedia. This Web-resource was chosen
for our experiment because nowadays Wikipedia is
the biggest public universal encyclopedia. And it
means that Wikipedia’s articles must be well-written
and must follow style guidelines. But Wikipedia isn’t
a static resource. Anyone can make changes and it can
well affect the article quality. All experts admit that
there are some difficulties in determining the
Wikipedia articles quality. In our research, we intend
to estimate their quality and check their readability
level. To obtain the texts from Wikipedia, we have
created own special software for automatic parsing of
the websites.
The first corpus, “GoodEnough” consists of 90
articles that belong to such quality classes of English
Wikipedia as Featured articles (FA) and Good articles
(GA). All of these articles must have correct grammar
and spelling.
For the second corpus, “NeedsWork”, we chose
also 90 articles from such quality classes as C and
Stub, that are very underworked and need further
completion.
The third corpus includes 15 articles from the
Simple English Wikipedia. The Simple Wikipedia is
a resource that is much easier to understand for
children and adults who are learning English (Coster,
2011). It is free and all articles are based on basic
English vocabulary and grammar and shorter
sentences.
In order to compare the readability of Wikipedia
articles and texts from other information sources, we
have produced two further corpora, which also
comprise educational and scientific texts.
The first one is called “Education” and includes
20 different texts from school books (from 6th
through 12th grades) and college books (all years of
education) on such topics: Physics, Astronomy,
Biology, Chemistry.
The second supplementary corpus, which is
called “Science”, is created on the basis of scholarly
articles from GoogleScholar and other scientific
internet resources. It includes 20 different texts on
Physics, Astronomy, Biology and Chemistry
subjects.
The Influence of Various Text Characteristics on the Readability and Content Informativeness
465

3.3 Experimental Evaluation
In order to estimate the readability of our corpora
texts, we determine three groups of features. The first
one comprises three traditional indexes of readability.
These are FOG (1), SMOG (2) and ARI (3).
The second group of the features that in our
opinion can impact on a level of readability of a text,
which is addressed to a global audience, includes
linguistic mistakes in the text. The three types of
them, which we have identified above, are shown in
Table 1.
The third group of the features that affect
readability text level comprises conventional
statistical characteristics, such as the number of
nouns, the number of pronouns, the number of unique
words, the number of sentences that includes more
than 30 syllables etc. To calculate the third group of
features, we carried out the POS-tagging of our
corpora using the nltk
8
package of Python.
Table 3 shows values of the features of all these
three groups for our five corpora. Additionally, based
on the Corpus Linguistics approaches (McEnery,
2012), (Rizun, 2018) in order to compare the
frequencies of linguistic features occurrence in the
different corpora, we normalized their frequencies per
10 thousand words. All numbers in tables, graphs and
figures represent the normalized frequencies of the
emergence of these features in the text corpus.
Every readability index has its own assessment
scale with different values. For example, SMOG
depends on the number of words with three or more
syllables and this number is compared with a grade
level. FOG index is based on a grade level and ARI
depends on age. In order to compare the results of our
research on 5 corpora, we created a universal scale
based on the grade levels and factual values of our
indexes. Table 4 shows our universal scale of the
readability index.
Table 3: The values of the features of three groups (the traditional indexes, linguistic characteristics, statistical characteristics)
for our five corpora.
Criterion GoodEnough NeedsWork Simple
Wikipedia
Science Education
Punctuation mistakes 3.16 3.09 4.72 4,71 0,84
Grammar mistakes 2.24 2.12 2.98 4,42 7,37
Style mistakes 6.84 7.28 9.44 4,48 1,95
Sentences > 30 syllables 50.7 50.4 31.5 58,6 45,1
Words (4 syllables) 76.9 72.4 81.0 73,8 83,8
Words (12 letters) 76.9 72.4 81.0 73,8 83,8
Passive voice 31.6 30.4 34.8 35,3 41,4
The number of unique words 124.0 190.0 153.1 340,6 326,3
The number of adjectives 169.5 170.5 196.4 252,3 222,1
The number adverbs 64.2 64.9 86.7 80 89,5
The number of nouns 830.1 836.6 806.9 638,5 683,2
The number of conjunctions 45.9 51.4 47.2 44,6 56,2
The number of verbs 353.6 335.2 360.3 302,4 347,8
The number of prepositions 252.2 247.2 256.1 250,8 253,4
The number of pronouns 20.3 20.9 30.8 23,6 37,5
The number of determiners 213.2 210.2 264.1 221,8 253,4
ARI
10.9 11.8 7.6 13,9 9
SMOG
115 128 58 187 122
FOG
9.614 10.57 8.548 12,71 9,622
8
Natural Language Toolkit: https://www.nltk.org/
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
466
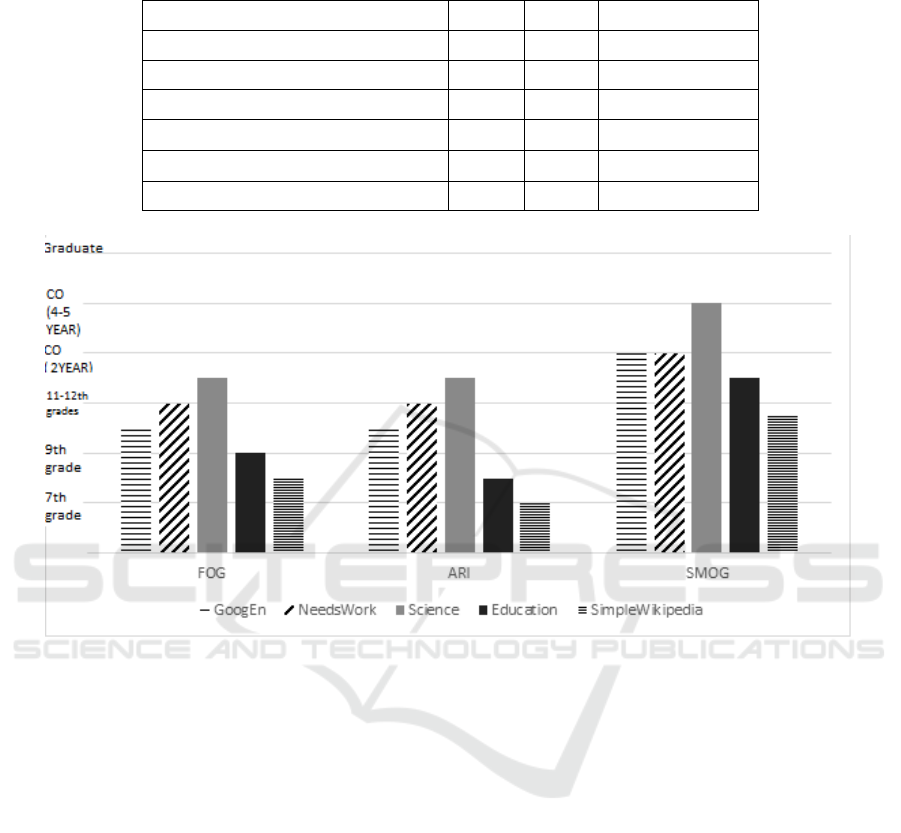
Table 4: The universal scale of the readability index based on the grade levels and factual values of FOG, ARI and SMOG
indexes.
Grade level FOG ARI SMOG
Graduate 17 14 211-240
College student (4-5 year) 15-16 13 157-210
College student (2 year) 13-14 12 111-156
High school (11
th
- 12
th
grades) 12-10 11 43-90
Secondary school (9
th
-8
th
grades) 9-8 10-9 21-42
Secondary school (6
th
-7
th
grades) 7-6 8-7 7-20
Figure 1: The values of FOG, ARI and SMOG indexes for GoodEnough Wikipedia, NeedsWork Wikipedia, Simple
Wikipedia, Science, Educational corpora.
According to the table, we built a histogram that
combines all researched indexes in conformity with
their factual values and allows demonstrating clearly
differences between our corpora.
Figure 1 shows the values of FOG, ARI and
SMOG indexes for our five corpora, namely for
GoodEnough Wikipedia, NeedsWork Wikipedia,
Simple Wikipedia, Science, Educational.
Our experiments show that the dependence of
FOG and ARI on types of the texts corresponds to
intuitively expected. According to the values of these
indexes, texts that have the smallest level of
complexity are the texts from SimpleWikipedia and
Education corpora. By the complexity level, these
texts correspond to the high and middle school level.
Scientific texts and texts from NeedsWorkWikipedia
corpus are the most difficult for reading. These texts
are intended for college students.
According to figure 1 SMOG index represents
less obvious results. The main reason of this is that
SMOG index is usually calculated on a limited
fragment of the text (30 sentences). Despite this
restriction, according to the values of this index texts
with the lowest level of readability are the texts of
SimpleWikipedia, and texts with the highest
readability level belong to the corpus with scientific
articles.
Accordingly, based on these indexes, we can infer
that, by the reading complexity level, our five corpora
can be arranged from the simplest to the most difficult
as follows:
• Simple Wikipedia,
• Education,
• GoodEnough Wikipedia,
• NeedsWork Wikipedia,
• Science
Based on the results of the table 3, we can
conclude that among statistical characteristics of the
The Influence of Various Text Characteristics on the Readability and Content Informativeness
467

text the frequency of emergence of the sentences
which have more than 30 syllables has the greatest
influence on the readability level. We can see that
SimpleWikipedia corpus has the smallest results
(31.5), and Education corpus has the highest results
(58.6).
At the same time, the number of long words (more
than 4 syllables or more than 12 letters) does not have
such great influence on the reading complexity as it
was considered earlier. Also, such feature as the
number of unique words in the text is interesting too.
There is the lower number of such words in
SimpleWikipedia than in texts from Science and even
Education corpora.
The large number of unique words in texts of
NeedsWork corpus is explained by the fact that these
texts don’t have a large size.
Reviewing the influence of the second group of
the analyzed factors, namely linguistic mistakes, on
the text readability, it is possible to see that
grammatical mistakes are the most linked to the text
complexity.
The number of such mistakes is much more in
Education corpus and less in the Wikipedia articles.
It is interesting that Wikipedia texts took a
midpoint position on the number of punctuation
mistakes.
The greatest percentage of style mistakes was
revealed in Wikipedia articles the number of which
does not depend on the user assessment of the article
quality. Generally, the discrepancy to the accepted
international way of writing of dates, numbers and
units of measure worsens style of the text and
therefore its readability.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In connection with the fast development of
information resources, a lot of enterprises and
corporations actively use big data sources not only for
obtaining information but also for extracting and
integrating information into their own enterprise
information systems. For making business decisions
it is necessary to be based on pure information and in
particular, take it from qualitative texts (information
texts).
The quality of texts includes a big number of
various characteristics, for example, usability,
reliability, relevance, availability and also readability.
Assessment of the text complexity is not
connected with a lack of knowledge of the subject or
material complexity. It is connected with the logical
organization of the text, linguistic characteristics, the
complexity of grammatical structures, vocabulary
and sentence construction.
In our study, we analyzed readability indexes for
English-language texts and revealed linguistic criteria
of text information quality. Such characteristics are
divided into 3 types: grammar, punctuation and style.
Our grammar criteria are based, for instance, on the
use of one-word verbs instead of a verb phrase and
the use of only international writing of terms.
Punctuation criteria consist of such items as the use
of only one gap after the punctuation mark, the
absence of coma in MMMM YYYY date format, the
use of a punctuation mark without an extra gap and
the use of “or” in structures specifying choice. (for
example he/she). Style criteria are responsible for the
writing of digits, measurements, date format and
abbreviations.
Results of the analysis were applied to
Wikipedia articles that belong to three classes
according to the assessment scale of the co-founders
Wikipedia, and to texts of the educational and
scientific direction. We consider that articles from
Wikipedia can really be assigned both to scientific
and to educational resources that correspond to its
rank of an encyclopedic resource.
According to the results of our research, it is
possible to make a conclusion that such indexes as
FOG and ARI evaluate texts on their complexity
more accurately. SMOG index gives rather accurate
results, but only on small fragments of the text that
can complicate the process of assessment.
Also, we suppose that grammatical mistakes are
the most connected with the text complexity because
grammar is responsible for sentence structure.
Therefore, we can claim that Wikipedia articles are
easier for reading than texts from the Education
corpora which contain the largest number of
grammatical mistakes. In turn, Wikipedia articles
have the highest percentage of style mistakes because
they consist of Americanisms. And they have an
average result on punctuation mistakes.
Besides, our analysis indirectly confirms that
Wikipedia articles are an academic resource. The
experiment entirely confirms a hypothesis of the
science paper (Biber, 1999) about the fact that in
academic prose nouns are by far the most frequent
word class; on average every fourth word is a noun.
Verbs are less frequent, on average every tenth word
is a verb, followed by adjectives or adverbs. In the
same time, it is obvious that the experiments show
almost full independence of readability from the
number of particular parts of speech in the text.
The study allows not only estimating the quality
and the readability of text information but also using
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
468

its result for further improvement of the text
information.
In future work, we plan to expand styles of text
corpora and the number of criteria for the text quality
assessment. These improvements will contribute to
the analysis of big data from Internet resources and
will allow creating the qualitative content of such
resources.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is supported by the Committee of
Science of the Ministry of Education and Science of
the Republic of Kazakhstan. The research was funded
by grant number AP05131073 — Methods, models of
retrieval and analyses of criminal contained
information in semi-structured and unstructured
textual arrays.
REFERENCES
Biber D. et al., 1999. Longman Grammar of Spoken and
Written English. Library of Congress Cataloging-in-
Publication Data.
Cai, L., Zhu, Y., 2015. The challenges of data quality and
data quality assessment in the big data era. In Data
Science Journal, 14.
Coster W., Kauchak D., 2011. Simple English Wikipedia:
A New Text Simplification Task. In Proceeding
HLT '11 Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the
Association for Computational Linguistics: Human
Language Technologies.
Cotugna N., Vickery C. E., Carpenter-Haefele K. M., 2005.
Evaluation of literacy level of patient education pages
in health-related journals. In Journal of Community
Health.
DuBay, William H., 2004. The Principles of Readability.
California: Impact Information
D'alessandro DM, Kingsley P., Johnson-West J., 2001. The
Readability of Pediatric Patient Education Materials on
the World Wide Web. In Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med.
Giles, G., 2005. Internet encyclopedias go head to head,. In
Nature, 438.P. 900-901. doi:10.1038/438900a
Hedman A.S., 2008. Using the SMOG formula to revise a
health-related document. American Journal of Health
Education.
Intecom International Language Project Group. 2003.
Guidelines for Writing English-Language Technical
Documentation for an International Audience. 1st. ed.
INTECOM.
Khairova, N., Lewoniewski, W., Węcel, K.,
Mamyrbayev O., Mukhsina, K., 2018. Comparative
analysis of the informativeness and encyclopedic style
of the popular web information sources. In Lecture
Notes in Business Information Processing. P. 333–347.
Lewoniewski W., 2017 Enrichment of Information in
Multilingual Wikipedia Based on Quality Analysis. In
Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing,
Microsoft Manual of Style 4th edition, 2012. Published by
Microsoft Press, 439 р.
McEnery, T. and Hardie, A, 2012. Corpus Linguistics:
Method, Theory and Practice. In Cambridge University
Press.
Oosten van P., Tanghe D., Hoste V., 2010. Towards an
Improved Methodology for Automated Readability
Prediction. In LREC 2010: seventh conference on
international language resources and evaluation.
Pitler E., Nenkova A., 2008. Revisiting Readability: A
Unified Framework for Predicting Text Quality. In
Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods
in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP '08).
Association for Computational Linguistics,
Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 186-195
Rizun N. and Taranenko Y., 2018. Methodology of
constructing and analyzing the hierarchical
contextually-oriented corpora. In Proceedings of
Federated Conference on Computer Science and
Information Systems.
Schwarm S. E., Ostendorf M., 2005. Reading Level
Assessment Using Support Vector Machines and
Statistical Language Models. In Proceedings of the
43rd Annual Meeting on Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Walsh T. M., Volsko T. A., 2008. Readability Assessment
of Internet-Based Consumer Health Information. In
Respiratory care.
The Influence of Various Text Characteristics on the Readability and Content Informativeness
469
