
An Integrated Data Platform for Agricultural Data Analyses based on
Agricultural ISOBUS and ISOXML
Franz Kraatz, Heiko Tapken, Frank Nordemann, Thorben Iggena, Maik Fruhner and Ralf T
¨
onjes
Faculty of Engineering and Computer Science, Osnabr
¨
uck University of Applied Siences,
Albrechtstr. 30, Osnabr
¨
uck, Germany
Keywords:
Agricultural Data Platform, Data Integration, Data Warehouse, Data Lake.
Abstract:
Over the last years many different agricultural online management portals got to market. The focus of these
portals is on documentation, accounting and task planning. Data analyses and process planning are often not
considerd. For this reason, the existing data in the data platforms of present portals is often badly integrated
and consequently not designed for data analyses. This paper introduces a new architecture concept for an
integrated agricultural data platform. With this new data platform agricultural data analyses for precision
farming become possible. Furthermore, the integration of the agricultural devices and external sources into
one platform changes task planning for one machine into a process planning for cooperated machines. Several
challenges for the integration of agricultural data and data types for agricultural data analyses are discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
The agricultural industry is still in an extreme state
of change. Since electronic equipment on the agri-
cultural machinery is established, the digital develop-
ment of equipment progresses. One of the essential
development steps was the launch of ISOBUS, stan-
dardised in ISO11783 (ISO, 2007).
Parallel to ISOBUS a huge variety of sensor sys-
tems got to market. Two well-known systems are
the ISARIA sensor for mineral fertilising (Fritzmeier
Umwelttechnik, 2018) and the NIRS sensor for dry
substance measurement used for maize harvesting
(Maschinenfabrik Bernard Krone, 2015).
To handle this digital data, the farmer can organ-
ise inventory and build tasks in farm management in-
formation systems (FMIS). For task planning service
providers or web services, like weather forecast or
precision farming providers, are connected to FMIS.
Machinery logged process data is archived and can be
displayed for evaluation and documentation.
Most available FMISs are not designed for anal-
yses, process planning and process automation. The
main issue is the separate handling of heterogeneous
data. FMISs are often not based on an integrated
database, storing information, like soil and yield in-
formation, in a common way for data analyses. For
that reason the potential of collected process data is
not fully used to optimise agricultural processes.
New electronic equipment and partial area based
documentation enable precision farming. With this
method the field is not considered as a homogeneous
area. The field is divided into subareas and can be
farmed individually. As a result the harvest rises with
the same resource input or less resources are needed
for the same output. In both cases the efficiency rises
and the environmental damage is decreased. Precision
farming will be the future direction for agricultural
development because there is an increased demand for
food to feed the growing population and to handle the
reduction of available farmland. In Germany agricul-
tural used areas shrank from 53.5% in 2000 to 51.6%
in 2015 (Umweltbundesamt, 2018). At the other hand
the population stays nearly constant at 82 million peo-
ple (Federal Agency for Civic Education, 2015). In
comparison the worlds population raised from 6.1 bil-
lion to 7.3 billion in this period (Federal Agency for
Civic Education, 2017).
The research project OPeRAte - ”Orchestration of
Process Chains for data-driven Resource Optimisa-
tion in Agricultural Business and Engineering” (OP-
eRAte, 2018) addresses these topics for the next step
in farming 4.0. To realise data analyses and process
optimisation in agriculture one project target is an in-
tegrated data platform. The existing inventory and
log data are combined with heterogeneous informa-
tion from web services, service providers and other
external data portals.
422
Kraatz, F., Tapken, H., Nordemann, F., Iggena, T., Fruhner, M. and Tönjes, R.
An Integrated Data Platform for Agricultural Data Analyses based on Agricultural ISOBUS and ISOXML.
DOI: 10.5220/0007760304220429
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security (IoTBDS 2019), pages 422-429
ISBN: 978-989-758-369-8
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
This paper introduces an architectural concept for
an integrated agricultural data platform designed for
data analyses and distributed mobile data. Chap-
ter 2 discusses the FMIS, the agricultural data for-
mat ISOXML and different data sources for precision
farming. This is followed by the state of the art on
data lake and Internet of Things (IoT). Afterwards it
is shown how IoT functionality can be provided on
the agricultural machine. The challenges of data inte-
gration into the data platform are discussed in chapter
5. Before concluding the paper with the summary,
chapter 6 presents the new architecture concept of the
integrated agricultural data platform in detail.
2 INTRODUCTION OF
AGRICULTURAL DOMAIN
2.1 Farm Management Information
Systems
Farm management information systems have been es-
tablished to organise a farm with machinery, fields,
resources, and task planning as a desktop software.
During the last years many FMIS online portals got to
market (NEXT Farming, 2019), (365FramNet, 2019).
Thereby the farmer can access the FMIS with a com-
puter, mobile device and other electronic equipment.
In Germany the number of agricultural companies
decreases about 20 - 30 times faster (Federal Institute
for Population Research, 2018) than the agricultural
surface (Umweltbundesamt, 2018). Consequently the
remaining farmers need the assistance of an FMIS to
handle the additional ground and work economically.
In order to achieve a suitable workload of the large
and expensive machines, FMISs allow the farmer to
plan tasks digitally. Afterwards the tasks can be trans-
ferred to and integrated in to the machinery. Finished
tasks combined with logged process data are the re-
sult of these jobs and will be transferred to the FMIS
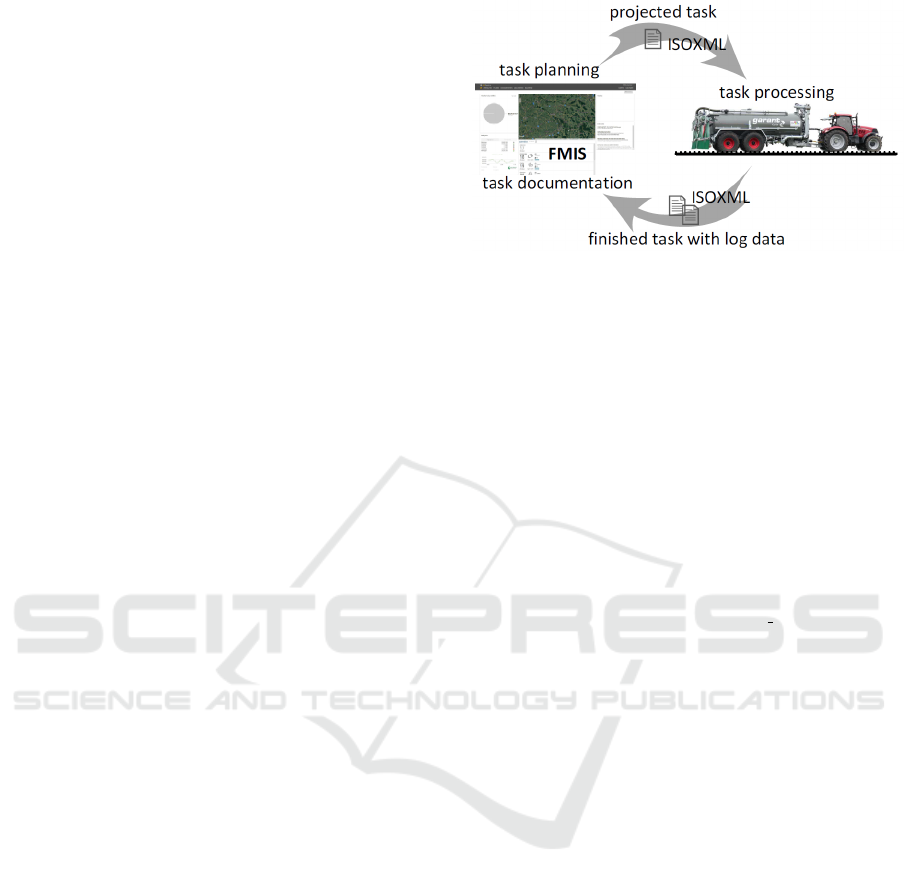
for documentation and interpretation (Figure 1).
The information exchange between FMISs and
machinery is based on the ISOXML format and is not
prepared for a data exchange during task runtime. A
summary of this format follows in section 2.2. Most
of the time the physical transport is realised by mobile
storage mediums. The transfer via mobile communi-
cation and internet is not provided by every system.
Proprietary telematic systems (Claas E-Systems,
2019) are able to collect and store parameters of the
machinery during task runtime for the manufacturers.
In a portal the farmer has access to this information
for live monitoring and parameter evaluation.
Figure 1: Data exchange between FMIS and agricultural
machine.
2.2 Agricultural Data Format
Based on the ISO11783 standard, called ISOBUS,
the ISOXML structure is the agricultural data ex-
change format between machinery and FMISs. Each
XML element has several mandatory and optional at-
tributes. Representative for each attribute name a
character is defined. Similar to this, the element name
in the xml schema is represented by a shortcut of three
characters. Some of the attributes hold references to
other elements in the structure.
In the following ISOXML example a farm called
Hof Herrmann and a field called Exx Platz is shown.
1:<FRM A="FRM1" B="Hof Herrmann"/>
2:<PFD A="PFD1" C="Exx_Platz" F="FRM1">
3: <PLN A="1">
4: <LSG A="1">
5: <PNT A="2" C="52.28.." D="8.02.."/>
6: <PNT A="2" C="52.28.." D="8.02.."/>
7: <PNT A="2" C="52.28.." D="8.02.."/>
8: <PNT A="2" C="52.28.." D="8.02.."/>
9: <PNT A="2" C="52.28.." D="8.02.."/>
10: </LSG>
11: </PLN>
12:</PFD>
The field (line 2) has a reference to the farm (line
1) at the attribute F. Part of the field element is a poly-
gon (line 3) with a line element (line 4) and five points
(line 5-9) for the field border. All elements inside the
field do not have an additional identification as they
are assigned inside the field element.
Main problem is the interpretation of the stan-
dard by the manufacturers. For example, optional at-
tributes are defined as mandatory attributes. A sec-
ond problem is the data exchange between different
FMISs without user interaction because of the unique
identification only inside the transfer file. For this rea-
son only information of executed tasks from machin-
ery can be automatically imported, if the planed task
was generated by this FMIS before. For an automatic
integration in every situation a comparison of selected
An Integrated Data Platform for Agricultural Data Analyses based on Agricultural ISOBUS and ISOXML
423

descriptive string attributes has to be made. This does
not preclude duplicate records in the database and
rises the amount of redundant linked data from the
external sources discussed in the next section.
2.3 External Data Sources for Precision
Farming
To realise precision farming different data sources
have to be used to represent the influencing factors
for crop production. An example is a combination of
yield information of the last years to get a yield poten-
tial map. To improve quality an additional combina-
tion with the soil type map (State Office for Mining,
Energy and Geology, 2019) is used in practice.
A large part of external data sources are geo-
graphic data, like historical weather data (Deutscher
Wetterdienst, 2018), weather forecasts, soil maps,
topological maps and process data. Furthermore
satellite images (German Aerospace Center, 2019)
provide information of crop growth and the condition
outside of the field, e.g. water bodies. To get match-
able geographic data for analyses, the granularity of
the data must be dissolved.
Important external data sources are legal re-
quirements of the government for nitrate (European
Comission, 2019) and pesticide (European Comis-
sion, 2018) application. Failure to comply will result
in penalties and compromise the environment. Only
in combination with a geographic map and the apply-
ing product it is usable for precision farming.
Furthermore data sheets of the agricultural ma-
chinery are external data sources used for precision
farming. A precision farming application can also be
optimised for the properties of the machinery or for
required absolute values for application rates adapted
to the product.
3 STATE OF THE ART
3.1 Data Lake
A data warehouse (Inmon et al., 2008) combines data
from different sources in an integrated schema based
on requirements of defined analyses, evaluation, and
reporting tasks. Distributed data is combined for anal-
yses, evaluation and reporting tasks in a data lake.
This approach is defined as a non fixed coupling of
structured, semi structured and unstructured data in a
central data management system (Maccioni and Tor-
lone, 2017), (Tomcy and Pankaj, 2017) and is able
to apply the data warehousing concept. The main
components of a data lake are the connectors with
different quantity and complexity levels. This set-
ting is mostly chosen at semantic-aware big data sys-
tems (Nadal et al., 2017) and context-aware data lakes
(Ahmed et al., 2017) for the data management.
For data management at data lakes, extract, trans-
form and load (ETL) tools are used (Zhu, 2017). If
there are already different kinds of data silos avail-
able, methods of machine learning fit for the data in-
tegration (Wibowo et al., 2017). Additional concepts
load all data in the data lake and do the integration
and organisation of the data lake afterwards (Terriz-
zano et al., 2015).
Figure 2: Architecture of mediator-wrapper technology.
With the mediator-wrapper technology (Figure 2)
external, heterogeneous data can be connected to a
data lake (Wiederhold, 1992). The wrapper adapts
the data and communication from external sources to
the mediator and provides a unified access to a data
source. The mediator combines the adapted data from
wrappers at the same domain as a single data source to
higher applications. To have an efficient implemented
mediator it is fundamental to get the right balance at
service level and domain level. An example for wrap-
per design is web wrapper.
After connecting the external sources to the data
lake, the distribution of data can be handled by a
publish/subscribe system in combination with a mes-
sage passing system. Published data will be automati-
cally forwarded to the subscribed users. For handling
the data flow from a publisher to the subscribers a
message passing system like kafka (Apache Software
Foundation, 2019) can be used.
3.2 Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) combines several tech-
nologies to connect cyber physical systems with each
other. The systems provide their information in a
open format to the network. A lot of information
and functions combined with a interface description
are available as commercial or open source solutions.
IoTBDS 2019 - 4th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
424

By using ontologies (Bermudez-Edo et al., 2016) it is
possible to automatically process and integrate these
interface descriptions.
The heterogeneity and variety of IoT also includes
the individual system properties, e.g. the currency or
reliability of information. In the end, you have to
trust the provided description or merge several sys-
tems with identical information to derive information
about the individual system properties.
For information exchange, message bus systems
are used in the IoT. The information is published on a
mesage bus, like Message Queuing Telemetry Trans-
port protocol (MQTT) (Stanford-Clark and Nipper,
2019), to reach the subscribed system. The exchange
of sensitive information in IoT is realised by access
control to the message bus.
4 IoT ENABLED SMART
FARMING
For an independent integration of the different sensor
systems of a modern agricultural machine in an FMIS,
a self description of the machinery is needed. With
the description additional standalone sensor systems
can be used as Internet of Things devices to support
the agricultural application.
In the research project OPeRAte such a universal
valid description to handle a machine like an Internet
of Things device has been developed. To get the avail-
able process data from the machine during a running
agricultural process, an essential function is missing.
The data exchange between machinery and FMIS
is currently only possible before and after an agricul-
tural task is processed. An extension of the ISOBUS
standard with a streaming protocol for data stream-
ing during application is still an ongoing task (Harris,
2018). For process regulation or adaptation there is
no controlling function available.
To solve this problem, the OPeRAte project is de-
veloping a separate ISOBUS module. An individ-
ual adaptation of the task processing unit (Task Con-
troller) on the machine is too complex. With a Task
Controller (TC) client the module can have a direct
online connection and a peer-control connection via
ISOBUS to the implement. Similarly, the client can
be commissioned by the TC for the recording of the
log data. This client is much easier to adapt to new re-
quirements and can still take over almost all functions
from the TC. Only a simplified part of a task needs to
be integrated into the TC.
5 CHALLENGES FOR THE DATA
ENRICHMENT IN
AGRICULTURAL AREA
5.1 Different Level of Granularity
Data analyses at the finest level of granularity often
do not show all relationships. A first abstract view
at higher granularity level opens up new insights for
detailed analyses at finer resolution. An example is
a summary of the different agricultural resources to
categories. At the first step winter and spring barley
together make up the category barley. Barley together
with wheat and rye forms the next category cereals.
Similar a temporal summary of information can be
useful for analyses. A good example is the water sup-
ply for plants over the full growth phase and the im-
pact on work planning and the resulting yield.
For realising data analyses at these different levels
of granularity, information must be available in the
smallest granularity level, if possible. The summary
in a higher level of granularity takes place via sepa-
rately stored filters, categorization or linkage.
For the representation of such information in dif-
ferent levels of granularity so-called data cubes are
used (Totok, 2000). Here the data is arranged in
a multi-dimensional cube and the user can analyse
within the different planes. Most of the time the data
itself is already stored as a data cube in order to be
quickly available during analyses.
5.2 Data Identification at ISOXML
For ISOXML files, a simplified example shown in
section 2.2, no unique identification is defined. Only
a manufacturer given machine identification ISON-
AME is included. Alternatively, the coordinates of
the field can be used for identification. For the other
data only an identification with the available links to
the machines and fields or a string comparison of de-
scription is possible.
Figure 3: Two different field borders for the same field.
An Integrated Data Platform for Agricultural Data Analyses based on Agricultural ISOBUS and ISOXML
425

A problem of identification by location is the dis-
crepancy in locations at the different FMISs shown
in Figure 3 with green and red colour. To solve that
problem, a variation rate has to be defined. For ex-
ample, a difference for the field area matching of five
percent.
5.3 Process Data Cleansing
The sensor value recording takes place during task
processing without observing the working state for a
defined interval or by threshold values. Yield record-
ing is carried out, for example, position according to
a distance interval. If a machine turns at the end of
the field during harvest, a yield of 0 is recorded. The
same recording problem occurs for start-up, run out
and back ride. These errors must be removed, other-
wise the average yield, for example, is falsified.
Manually collected data, that has subsequently
been digitised, is still used in agricultural. To use
these data, overlaps, gaps or self-intersects of poly-
gons have to be removed.
The five coordinated steps of data cleansing take
place with saving all raw data. Thereafter, the require-
ments of the data are derived from the properties of
the data. If the requirements for the data are present,
an analysis shows which data meets the requirements.
Before the data is cleaned up, the data goes through
standardisation to resolve remediable errors.
5.4 Runtime Data Handling
Agricultural machinery record large numbers of sen-
sor values. To provide this captured information di-
rectly to the system during processing, the previously
presented treatment steps have to be integrated di-
rectly into the provisioning process.
Thus the records can be included directly in new
analyses. In order to reduce the resulting queries of
the external data sources, the data sources should be
subdivided into the following categories.
• local available with online connection
• only local available
• access only with online connection
To avoid expensive queries from external sources,
a local part for the existing datasets or the entire ex-
ternal source is the better solution. The information
of the source is available in the prepared state during
task processing and is updated at a fixed interval or at
a new dataset. Sources without an online connected
interface have to read locally in the system.
The different levels of granularity can be used for
an additional optimisation of source queries. Assign-
ing the information of an external source to a higher
granularity level also requires queries only for records
at that level. The data in the underlying levels can be
added to the dataset without a source query.
6 AN AGRICULTURAL DATA
PLATFORM FOR DATA
ANALYSES
6.1 Provided Characteristics of the
Agricultural Data Platform
The data platform has to support different character-
istics focused on FMIS functionality and data anal-
yses. For task management and process planning a
data pool with user, resource, yard, and field man-
agement is needed. The logged process data has to
be integrated during task execution and prepared for
analyses, process optimisation and the required docu-
mentation.
Second, the platform has to connect the distributed
external sources and mobile devices to a common ex-
change layer. The exchange layer enables the avail-
ability of the external sources at the agricultural de-
vice without data lake interaction and a data access
from process management for process controlling.
6.2 Concept of the Agricultural Data
Lake
The main component of the data platform, the data
lake, works as a single point of truth and supports dis-
tributed data subsets on mobile devices like agricul-
tural machinery. In the opposite direction the device
transfers the process data back. The data will be en-
riched with additional information from external data
sources during the integration process. The runtime
integration process is necessary to provide the data
for reactive process optimisation across machines per-
formed by a connected process management.
The core of the data lake is build on the ISOXML
format described in section 2.2. Therefore, the archi-
tecture is following the data warehouse approach with
a database, ETL processes and a data warehouse. The
database is realised with relational database technol-
ogy and an extension for spatial functions.
To enrich the core data, different additional data
sources are integrated, e.g. historical weather infor-
mation of Germany (Deutscher Wetterdienst, 2018),
IoTBDS 2019 - 4th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
426

raw data
MD1
MD3
MD4
MD5
S1D1
S2D1
S3D1
S1D2
S2D2
publish/subscribe + messaging
M
W
MD6
W
W
M
M
M
W
W
W
W
W
W
FMIS
M
W
W
W
analysis
data
AgriRouter
FMIS
process management
AgriRouter
transform
load
process
storage
Sources /
Domains
Mobile
Device
Agricultural Data Lake
MW
extract
W
MD2
Figure 4: Architecture of the data platform with agricultural data lake.
soil types of Germany (Federal Institute for Geo-
sciences and Natural Resources, 2019), field borders
of Lower Saxony (Servicezentrum Landentwicklung
und Agrarf
¨
orderung, 2019) and sentinel2 satellite im-
ages (German Aerospace Center, 2019). The different
categories of enriched data are as follow:
• Spatio temporal data: A significant proportion of
data in agricultural has a spatial and temporal cor-
relation. For example the recorded yield with the
position and associated time stamp is used in anal-
yses, separated in subareas for each year.
• Spatial data: If the time factor disappears from
the data, the data only provides information about
a specific location. Here you can call soil maps as
examples. Once captured, this data is used with-
out any time limit.
• Meta data: In order to get properties of resources,
consumables and plants, additional information
needs to be collected, if it is not supplied by the
product. An interface for machine-specific prop-
erties for the manufacturers database for business
and service purposes would help. Meta data on
mineral fertilizers and pesticides can often be ob-
tained from the central licensing authority.
In parallel to the fixed linked data, temporal linked
data is possible too, for example weather forecasts.
The forecast is linked to the core to include the in-
formation into decision making. If the process plan-
ning is not finished or cancelled, the weather forecast
is deleted like a garbage collector. Only permanent
linked data stays in the data lake to keep the growth
of data small. This ensures to keep important correla-
tions for decision reconstruction and evaluation.
The measured data from the agricultural ma-
chineries is transferred to the data lake during applica-
tion execution. This data is enriched by the following
integration with additional data in real time. Missing
additional data for this dataset as well is reloaded in
real time from the external data source.
The technical architecture is built-up with classic
data warehouse technology. There is a multi-layer
mediator/wrapper in combination with a publish sub-
scribe system shown in Figure 4. With the publish
subscribe system other applications can get enriched
data from the data lake or directly from external data
sources. The integrated topic structure enables a se-
lective access to sensitive data.
The functions of wrappers are divided into differ-
ent adaptation aspects, which handle the granularity
levels. One function solves the temporal issues like
time zone and resolution. Another function solves
the different spatial issues, e.g. the adaptation be-
tween different geographical coordinate systems and
formats. Wrappers for the machinery also contain
a function to perform data cleansing of the process
and sensor data. At the next level the mediator com-
bines different external data sources with similar in-
formation. By this procedure a temporarily not reach-
able external data source is compensated. In addi-
An Integrated Data Platform for Agricultural Data Analyses based on Agricultural ISOBUS and ISOXML
427

tion to the combination mechanism the different quo-
rum (Ozsu and Valduriez, 1991) techniques best vote,
weighted vote and majority vote are implemented.
The prepared information is available at the pub-
lish subscribe system by the mediator as a publisher.
All different connected players such as the core data
base, the data lake or third party actors, like mobile
devices on the field, can register to the available ser-
vices at the publish subscribe system. This technique
reduces the complexity of the architecture and allows
a flexible mapping to new agricultural applications.
For the integration of new ISOXML data from
agricultural machinery a trigger for validation of ex-
isting enriched data in the data lake is performed.
For this purpose, a message-passing system is used,
which receives the new ISOXML data and sum-
marises the data to data sets on the same reference.
Thereby, the verification of enriched data must be per-
formed only for the summary and the identification
problem, shown in section 5.2, is dissolved.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The need for an increasing resource efficiency in agri-
culture, for farm economics and to feed the world’s
growing population, is shown in the introduction. The
establishment of electronic systems such as sensors
and farm management information systems in agri-
culture contributes to this as well as precision farm-
ing. However, the available FMISs, with their badly
integrated data platforms, have limited scope for data
analyses and cross-machine process planning for col-
laborative machines.
The presented data platform for agriculture ad-
dresses this problem. The data lake architecture
already considers the integration of different data
sources as well as the connection of the agricultural
machine itself. For the integration of an agricultural
machine to the data platform, a new ISOBUS module,
comparable to an IoT device, is introduced. Within
the architecture the integration of the external data
source and the agricultural machines takes place by
mediator-wrapper method.
The data exchange between the connected compo-
nents within the data platform is realised via a mes-
sage bus according to the publish/subscribe principle.
With this method, external data sources are available
to the agricultural machinery for assistance in task
processing. Topics in the message bus system are
used for selected access to sensitive data.
The challenges of data processing in the compo-
nents of the new agricultural data platform are dis-
cussed. For example, the data often has a different
granularity, has to be cleaned up for further process-
ing and must be available for new analyses or process
optimisation at runtime. In order to ensure data pro-
vision at runtime, a different integration of external
data sources according to their characteristics has to
be considered additionally.
The distributed and modular design of the new
agricultural data platform ensures adaptation and ex-
tension capabilities for future topics. For an easier
integration of external sources, a partially to fully au-
tomatic integration process would make sense.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The project is supported by funds of the Federal Min-
istry of Food and Agriculture (BMEL) based on a
decision of the Parliament of the Federal Republic
of Germany via the Federal Office for Agriculture
and Food (BLE) under the innovation support pro-
gramme.
REFERENCES
365FramNet (2019). 365FarmNet - the innovative software
solution for your entire agricultural holding. https://
www.365farmnet.com/en/ accessed 20/01/19.
Ahmed, E., Yaqoob, I., Hashem, I. A. T., Khan, I., Ahmed,
A. I. A., Imran, M., and Vasilakos, A. V. (2017). The
role of big data analytics in Internet of Things. Com-
puter Networks, 129(Part 2):459 – 471. Special Issue
on 5G Wireless Networks for IoT and Body Sensors.
Apache Software Foundation (2019). Apache kafka - adis-
tributed strstream platform. https://kafka.apache.org/
25/01/19.
Bermudez-Edo, M., Elsaleh, T., Barnaghi, P., and Taylor, K.
(2016). Iot-lite: A lightweight semantic model for the
internet of things. In 2016 Intl IEEE Conferences on
Ubiquitous Intelligence & Computing, Advanced and
Trusted Computing, Scalable Computing and Commu-
nications, Cloud and Big Data Computing, Internet of
People, and Smart World Congress.
Claas E-Systems (2019). How TELEMATICS
works. http://www.claas-e-systems.com/en/oem-
products/telematics/ accessed 30/01/19.
Deutscher Wetterdienst (2018). Climate Data Center. https:
//www.dwd.de/EN/ourservices/cdcftp/cdcftp.html ac-
cessed 22/12/18.
European Comission (2018). Agriculture and pesticides.
https://ec.europa.eu/agriculture/envir/pesticides\ en
accessed 29/12/18.
European Comission (2019). Agriculture and nitrates.
https://ec.europa.eu/agriculture/envir/nitrates\ en ac-
cessed 29/01/19.
Federal Agency for Civic Education (2015). Deutsche
Bev
¨
olkerungsentwicklung. http://www.bpb.de/
IoTBDS 2019 - 4th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
428

nachschlagen/zahlen-und-fakten/soziale-situation-in-
deutschland/61541/altersstruktur accessed 15/12/18.
Federal Agency for Civic Education (2017). Globale
Bev
¨
olkerungsentwicklung. http://www.bpb.de/
nachschlagen/zahlen-und-fakten/globalisierung/
52699/bevoelkerungsentwicklung accessed 12/12/18.
Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources
(2019). Boden
¨
ubersichtskarte. https://www.bgr.
bund.de/DE/Themen/Boden/Projekte/
Informationsgrundlagen-laufend/BUEK200/
BUEK200.html accessed 20/02/19.
Federal Institute for Population Research (2018). Agri-
cultural holdings. https://www.destatis.de/EN/
FactsFigures/EconomicSectors/AgricultureForestry
Fisheries/AgriculturalHoldings/Tables/Agricultural
HoldingsandUtilisedAgriculturalAreabySizeofthe
UtilisedAgriculturalArea.html accessed 11/12/18.
Fritzmeier Umwelttechnik (2018). ISARIA -
Your system for intelligent crop management.
http://fritzmeier-umwelttechnik.com/isaria/?lang=en
accessed 15/12/18.
German Aerospace Center (2019). Copernicus Data and
Exploitation Platform – Deutschland (CODE-DE).
https://code-de.org/en accessed 17/01/19.
Harris, T. (2018). AEF takes on automation,
machine-to-machine communication. https://
www.farmprogress.com/technology/aef-takes-
automation-machine-machine-communication
accessed 20/01/19.
Inmon, W., Strauss, D., and Neushloss, G. (2008). DW
2.0: The Architecture for the Next Generation of Data
Warehousing. Morgan Kaufmann.
ISO (2007). ISO 11783 Tractors and machinery for agricul-
ture and forestry - Serial control and communications
data network.
Maccioni, A. and Torlone, R. (2017). Crossing the finish
line faster when paddling the Data Lake with KAYAK.
In Proceedings of the 43rd International Conference
on Very Large Data Base, volume 10, pages 1853 –
1856, Munich, Germany.
Maschinenfabrik Bernard Krone (2015). DLG rates Krone
NIR sensor ’good’. http://landmaschinen.krone.de/
english/news/news-archive/news-archive-2015/dlg-
rates-krone-nir-sensor-good/ accessed 14/12/18.
Nadal, S., Herrero, V., Romero, O., Abell, A., Franch, X.,
Vansummeren, S., and Valerio, D. (2017). A software
reference architecture for semantic-aware Big Data
systems. Information and Software Technology, 90:75
– 92.
NEXT Farming (2019). Farm management at the touch
of a button. https://www.nextfarming.de/en/products/
next-farming-live/ accessed 23/01/19.
OPeRAte (2018). OPeRAte - Orchestration of Pro-
cess Chains for data-driven Resource Optimization in
Agricultural Business and Engineering. http://operate.
edvsz.hs-osnabrueck.de/ accessed 18/12/18.
Ozsu, T. M. and Valduriez, P. (1991). Principles of dis-
tributed database systems (2nd ed.). Prentice-Hall,
Inc.
Servicezentrum Landentwicklung und Agrarf
¨
orderung
(2019). Schlaginfo-Portal. https://sla.
niedersachsen.de/agrarfoerderung/schlaginfo/ ac-
cessed 15/02/19.
Stanford-Clark, A. and Nipper, A. (2019). Message queuing
telemetry transport protocol. http://mqtt.org/ accessed
28/01/19.
State Office for Mining, Energy and Geology (2019).
Lower Saxony Soil Information System NIBIS.
https://www.lbeg.niedersachsen.de/kartenserver/
nibis/niedersaechsisches-bodeninformationssystem-
nibis-841.htmlengl\ 0503 accessed 10/01/19.
Terrizzano, I. G., Schwarz, P. M., Roth, M., and Colino,
J. E. (2015). Data Wrangling: The Challenging Your-
ney from the Wild to the Lake. In CIDR.
Tomcy, J. and Pankaj, M. (2017). Data Lake for Enterprises
- Leveraging Lambda Architecture for building Enter-
prise Data Lake. Packt Publishing Ltd.
Totok, A. (2000). Modellierung von OLAP- und Data-
Warehouse-Systemen. Deutscher Universit
¨
atsverlag.
Umweltbundesamt (2018). Struktur der Fl
¨
achennutzung.
https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/daten/flaeche-
boden-land-oekosysteme/flaeche/struktur-der-
flaechennutzung accessed 13/12/18.
Wibowo, M., Sulaiman, S., and Shamsuddin, S. M. (2017).
Machine Learning in Data Lake for Combining Data
Silos, pages 294–306. Springer International Publish-
ing.
Wiederhold, G. (1992). Mediators in the architecture of fu-
ture information systems. Computer, 25(3):38–49.
Zhu, D. (2017). Large Scale ETL Design, Optimization
and Implementation Based On Spark and AWS Plat-
form. Master’s thesis, KTH, School of Information
and Communication Technology (ICT).
An Integrated Data Platform for Agricultural Data Analyses based on Agricultural ISOBUS and ISOXML
429
