
Review of Cognitive Energy Flow Model Concept for Virtual Student
Viktors Zagorskis
a
and Atis Kapenieks
Distance Education Study Centre, Riga Technical University, Kronvalda 1, Riga, Latvia
Keywords:
Cognitive Energy, E-leaning Quality, Computer Agent, Virtual Student.
Abstract:
Data analysis in Virtual Learning Environment deepens the understanding of cognition processes in real stu-
dent’s brain. The challenge is the evaluation of the quality of e-learning courses before the large-scale im-
plementation. With this aim, we formulate the concept for a computer model for Virtual Student’s evolution.
We combine knowledge elements explored from learners behavior data and cognitive theories. We assume
that some of the brains energy flow expenses in learning and memorization are due to energy extraction for
applying existing skills, analysis of accumulated knowledge, and adaptation of newly available information.
We argue that the proposed Virtual Student model can perform cognitive energy flow modeling by extracting
energy from the environmental learning objects and losing the power in a tedious learning process. The re-
search shows that Cognitive Energy Flow model can be computerized to produce synthetic data to improve
e-learning courses and predict real student’s behavior.
1 INTRODUCTION
Intelligent Agents introduced a breakthrough in com-
puter science because of autonomy, ubiquity, human
centric orientation and, what is essential, human-like
behavior. Among the number of different agents cat-
egories, Learning Agents are more advanced because
they have the human-similar ability to learn from ex-
perienced interaction with the host learning system.
Since 1950th, intelligent agents used to use almost
in all of the computer systems with the aim to get
the system objects information, to rethink and pro-
vide local feedback or public actions. Usually, intel-
ligent agents follow some road-map: (1) Perception,
(2) Cognition, and (3) Actuation. These are functional
properties of almost all the independent autonomous
agents.
In the current research, we propose to invent
new features shrinking the gap between improved
intelligent agent namely Virtual Student (VS) and real
on-line learner behavioral properties. We reflect the
concept of improved Learning Agent Model with the
following additional properties: (1) emotional states,
(2) ability to forget the learned facts, (3) need for rest,
and (4) agent’s energy flow. Concerning that, we pro-
pose the improved learning agent model based on the
agent’s energy flow modeling is the crucial point of
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6155-0570
our interest in a proposal of a new Learning
Agent model.
We aim to create the preliminary model as a con-
cept that would further help to computerize and sim-
plify real learners’ behavior classification problems.
We assume to apply traditional predictive analytics
methods on outcomes of Virtual Student operation
where either (1) usage of Machine Learning Methods
are not cost-efficient or (2) the environment has new
- not approved learning courses and learners have not
produced any data yet.
Such, the Virtual Student’s cognitive energy flow
model-based approach improves computerized agent
model to be applicable for Predictive Analytics (PA)
methods applied to real learners without uneconom-
ical Machine Learning (ML) operations. This state-
ment is the current research question.
The research organized as follows: Section 2 -
the reflexion of related theories, methods, and ap-
proaches. In Section 3, that is the most important
in the research we propose the concept of the Virtual
Student’s Cognitive Energy Flow Model. In Section
4 we provide a discussion of results and conclude the
paper.
542
Zagorskis, V. and Kapenieks, A.
Review of Cognitive Energy Flow Model Concept for Virtual Student.
DOI: 10.5220/0007768205420549
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2019), pages 542-549
ISBN: 978-989-758-367-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 RELATED WORK
The large-scale picture on human-like Cognition ap-
pliances in a Computer-intelligence success like Ar-
tificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), or
particularly in VLEs has the roots based on some his-
torical conclusions expressed in learning theories.
2.1 Theories of Cognitive Development
Undoubtedly, any learning process aims to gain
knowledge results. Mainly, the learning process is
cognitive because the learner develops itself regard-
less of supervised or unsupervised learning style.
The most influential theories of Cognitive Develop-
ment categorized as: (1) Piaget’s theory, (2) So-
ciocultural theories, (3) Core-knowledge theories,
and (4) Information-processing theories. The last
- Information-processing theories are well adaptable
and known in a computer applications domain.
About 1920, Piaget developed the first ”Cognitive
theory” mapped on child cognitive development. At
that time, Piaget’s the revolutionary idea was to con-
sider a child as a scientist providing experiments on
their (Piaget and Campbell, 1976).
Three of Piaget’s main essential processing cate-
gories (Piaget, 2005) are: (1) construct own learner
knowledge from experimenting on the world, (2)
learn many things on their own without the interven-
tion of helpers, and (3) to stay intrinsically motivated
to learn and do not require rewards to incentivize
learning.
Among the criticisms of Piaget’s Theory the most
strong are: (1) learners’ thinking process is affected
by social interactions (Vygotsky’s Theory), (2) young
children have and use much inborn mental machinery
for complex abstract thought (Core-Knowledge The-
ories), (3) thinking is not as consistent as the theory
suggests, and (4) thinking is a computational process.
The last two criticisms belong to authors of Contem-
porary Theories. The most relevant example adopted
from contemporary theories is the Information Pro-
cessing approach considering child development as
a computer model development. Therefore, we con-
clude that modern methods of Cognitive Development
are pointing again back to the discussions about the
Child cognition.
The full theory of intelligence is not yet in ex-
istence, although we assume that Master Theory of
Cognitive Development should exist in the future
(Domingos, 2015), and is applicable in a Human or
Artificial World.
2.2 Sense, Perception, Cognition, and
Semantics
Overall, Artificial Intelligence (AI) held on a cou-
ple of key concepts: Sensing, Perception, Cognition,
and Semantic (Sheth et al., 2015). Such processes
came into AI systems view to delegate computers to
solve human-specific sensing, perception, and think-
ing problems. Also, we have to consider that a real
person does not perceive the real world, the person
first interprets what he/she sees and then simulate the
next event in their mind. The magic is still, how we
learn and get the subconscious to do things effort-
lessly.
Assuming that Computer-Agent (as a computer
program) have Senses to receive various data from the
digital learning environment host, the next conscious
process in a computational sequence is the Percep-
tion: a cyclic process of interpreting data. Percep-
tion involves both interpretation and exploration with
a firm reliance on background knowledge patterns of
the domain of application (Gregory, 1997).
Cognitive computing follows the Perception and
aims to develop a coherent, unified, and universal
mechanism for understanding problems around the
Computer-Agent. Cognition utilizes all the data re-
ceived from a Perception act. Similarly like in a per-
ception process, cognitive computing context is pro-
vided by the existing knowledge base (Modha et al.,
2011). Overall, the cognition is the process of gaining
knowledge.
Finally, Semantics layer involves mapping obser-
vations from various stimuli on Computer-Agent in-
put, such as tactile, speech, or visual signals, to con-
cepts and relationships as humans would interpret and
communicate them. Semantics stays out of current re-
search scope.
2.3 Cognitive Learning and Cognitive
Engineering
Cognitive Engineering is a method of study using
cognitive psychology to design and develop engineer-
ing systems aimed to support the cognitive learning
processes of users (learners). A person starts with
goals and intentions that are psychological variables.
Although, Psychological Variables differ from Phys-
ical Variables used in engineering systems (Norman,
1987).
In the case of real learner modeling, the computer
agent must interpret the learning object physical vari-
ables into terms relevant to the psychological goals
and must translate the mental intentions into physi-
cal actions upon the application algorithms. Overall,
Review of Cognitive Energy Flow Model Concept for Virtual Student
543

the Cognition Engineering challenge is to study and
design the process of acquiring knowledge through
Agent’s thoughts, experiences, and senses. Cogni-
tive Learning involves obtaining knowledge through
experience, study, and being taught by Computer-
Agents (Brown and Fehige, 2017). At the same time
Computer- Agents can be used as Agents that learn.
Learning and Cognition are two almost identical
concepts, although cannot occur without each other:
Learning requires Cognition, and Cognition involves
Learning.
Cognitive Process. Of full value, cognitive pro-
cess implementation serves goals to complete match-
ing micro-architectures: Senses (Intensity of Sensa-
tion), Affection (Weber’s Law - quantifying the per-
ception of change in a given stimulus), Attention
(Rate, Duration, Degree, Inertia), Perception (Tempo-
ral, Qualitative, Quantitative(Simple, Complex)), As-
sociation (Law of Association), Memory & Imagina-
tion (Cache Operative(a couple of seconds), Middle,
Long Term Storage Network), and Action (Emotions
& Thoughts). Individual cognitive system require-
ments can cause simplification of the whole architec-
ture or more detailed research and design of the spe-
cific item.
Levels of Cognitive Learning. An ordering of cogni-
tive skills usually are arranged based on Bloom’s tax-
onomy (first edition 1956) contemporary transformed
into a new version. The revisited version (Anderson
et al., 2001) includes six levels: (1) Remembering,
(2) Understanding, (3) Applying, (4) Analyzing, (5)
Evaluating, and (6) Creating. Although, we find an
applicable reduced version of taxonomy: (1) Memo-
rization, (2) Understanding, (3) Application.
Despite the reduction, the minimized approach in-
cludes all the skills above the Application level as the
ability to apply the knowledge. For the proposed Vir-
tual Student model, we find three knowledge levels
acceptable.
Cognitive Cycles. Neuroscientists have indepen-
dently proposed ideas similar to the cognitive cycle:
cascading cycles of recurring brain events. (Fuster,
2002; Baars and Franklin, 2007). Notably, that re-
search results in psychology (Franklin and Graesser,
1997; Anderson et al., 2004) show that cognition
in autonomous agents, whether artificial, animal or
human, can be thought of as consisting of repeated
perception-understanding-action cycles.
Cognitive Cycles Timing. Results from studies in
neurosciences determine the length of time taken by
each of the phases of the cognitive cycle also, are well
known. Some results successfully adopted for spe-
cific architectures, for instance: LIDA (Learning In-
telligent Distribution Agent) (Madl et al., 2011). We
also integrate Cognitive Cycles Timing results to later
proposed Virtual Student’s model.
2.4 Thoughts on Energy in Learning
Process
2.4.1 Mental Energy
The idea of energy associated with mental activity
dates far back in human History and cultures. For-
mulation of Mental Energy (a hard mental effort) in
scientific magazines belong to Julian Huxley (Hux-
ley, 1944). The problem complexity relies on the ori-
gins of Human Mental Energy correlation to physical,
social, and mental health impacting the real learning
process. It is a generally recognized truth physical
events considering in two ways: from the mechanistic
and from the energic standpoint (JUNG, 1969).
2.4.2 Time and Energy
The fundamental principle of causality and a propor-
tional (linearity is not the obligation) connection be-
tween time and energy is acceptable for later use to
build the Virtual Student Energy Flow model.
2.5 Intelligent Agents
A very simple agent model (Eq. 1) is an abstract con-
cept that can be defined mathematically as an agent
function:
f : P
∗
decision
−−−−→ A (1)
If P
∗
is a data set of perception on input of model,
and A is defined as action on model output, then f is
by function defined simple agent.
In general, an agent receives information through
its sensors. Decision making is an internal functional
facility of Intelligent Agent Model. Such a simplified
definition gives insight into concerns about the possi-
ble complexity of concise and valuable intelligence of
models.
Overall, exist more than one Intelligent Agents
classification schemes proposed by Russel (Russell
and Norvig, 2003) and Weiss (Weiss, 2013). We fol-
low Russel classification, where group agents divided
into five classes based on their degree of perception
and capability. Russel evolves five agent groups: (1)
simple reflex agents,(2) model-based reflex agents,
(3) goal-based agents, (4) utility-based agents, and
(5) learning agents. Any other proposed models have
variations based on classical concepts of agents ar-
chitecture, their ability to perceive, control the action
reasoning, and to act on sensing networks.
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
544

Intelligent Agents can act either as a single in-
stance or in groups: multi-agent systems. In the cur-
rent paper, we discuss a single instance model.
3 DISCUSSION AND OUTCOMES
The current research question is: The cognitive en-
ergy flow model-based approach shows another way
to evaluate empty learning course in a digital learning
environment where learners have not produced any
data yet.
The new approach goal is to create the preliminary
model that would help simplify real learners’ behav-
ior forecast and classification problems using tradi-
tional predictive analytical methods in a digital learn-
ing environment.
Based on the essential concepts revealed in the
previous section, we propose a new learning agent
model named Virtual Student The new model takes
into account such quite complicated to explore com-
mon human emotional conditions like relaxation,
boredom, excitement, and anxiety to explore human
emotional conditions.
We specify some crucial principles we follow cre-
ating Virtual Student’s model: (1) reliable Mental En-
ergy Flow Model for Virtual Student is the primary
interest of our research, (2) Virtual Student’s Learn-
ing Process is a Mental Energy Flow expressed as a
consummation of Internal Energy or gain from inher-
ited Learning Objects, (3) every single mental activity
is a transition along the learning path rewarded with
a specified but finite Energy Portion - Energy Token
if the change has a direction to the comfortable emo-
tional condition, (4) if the transition has a direction to
the uncomfortable emotional condition, Virtual Stu-
dent becomes fined by Energy Token Decreasing, (5)
Virtual Student initially has enough Energy Tokens to
overcome threshold level to join the Learning Course,
or to start to explore specific Learning Object, (6) Vir-
tual Student runs based on the principle of causality
and a proportional (linearity is not the obligation) re-
lation between time and energy.
On the research roadmap, firstly we draft the
Learning Energy flow boundaries for Virtual Stu-
dent’s evolution model. Then, we specify Virtual Stu-
dent’s properties. Finally, we propose the Virtual Stu-
dent Learning Model concept ready for operational
implementation.
3.1 Virtual Student Learning Energy
Centered Ecosystem
3.1.1 Learning Energy Network
Here, we invent the isolated learning network with
boundaries for Virtual Student operations when sens-
ing, and declare rules for reasoning (perception, cog-
nition) and acting. Learning network bounds energy
consumption or production. In other words - the
amount of internal energy U in the ecosystem is con-
stant. Equation (2) formalize this assumption. Each
component in the ecosystem holds their energy de-
noted as E
i
. Under such a restriction the only way to
keep U constant and simultaneously provide energy
flow is the process of energy redistribution among
system components. We follow the simple princi-
ple: no energy - no action. Therefore, to operate,
the model system energy should be greater than zero:
U > 0.
U =
∑
i
E
i
= Const. (2)
We specify three top class energy-related objects
for the ecosystem and their properties:
• System Energy Depot - E
D
,
• Virtual Student’s Energy Buffer - E
V S
,
• Learning Object Energy Storage - E
LO
.
In the model, learning network Enthalpy we specify
as:
U =
∑
i
E
D
i
+
∑
j
E
V S
j
+
∑
k
E
LO
k
(3)
3.1.2 Initial Energy Flow Considerations
Invented Initial Energy Depot holds a certain amount
of energy distributed among other components on
system simulation start. For our experiment, we use
one System Energy Depot, one Virtual Student’s in-
stance, and a specified number of Learning Object
with various but specified learning related energy
value. As follows, for one Virtual Student Equation
(3) transforms into:
U = E
D
+ E
V S
+
∑
k
E
LO
k
(4)
Equation (4) depicted in Fig. 1 applying di-
rections of possible energy flow. Firstly, at the
learning process initialization, each Learning Object
(LO
1
. . . LO
k
) receives specific initial energy portion
(E
LO
1
. . . E
LO
k
). Next, Virtual Student’s Energy Buffer
(VS) receives their initial amount of energy sufficient
Review of Cognitive Energy Flow Model Concept for Virtual Student
545

Figure 1: Energy Flow Model for Virtual Student’s Ecosys-
tem: System Energy Depot (Depot), Virtual Student’s En-
ergy Buffer (VS), and k Energy Storages for Learning Ob-
jects (LO
1
. . . LO
k
).
to start the simulation based on some algorithmic con-
siderations.
3.1.3 Energy Flow Control Algorithm
After the Virtual Student’s simulation start, their in-
stance sequentially interacts with Learning Objects
imitating all the phases of the cognition process. In
the case of success, indicated as the corresponding
flag in the algorithm, Virtual Student receives energy
portion from the Learning Object it communicated.
Learning fortune path transfers energy tokens as re-
wards from Learning Objects to Virtual Student. A
decision regarding learning fortune rewards amount
depends on the Virtual Student: (1) Virtual Student’s
self-assessment score, (2) Virtual Student’s assess-
ment by Learning Object requirements gathered from
submission, (3) Virtual Student’s emotional condi-
tions after the task finishing, and (4) on time spent
for learning. Learning fortune path is active only at
favorable emotional conditions like excitement or re-
laxation. Similarly, indications of negative emotions
(anxiety, boredom) lead to energy tokens loss from
Virtual Student’s Energy Buffer. As mentioned be-
fore, the ecosystem model assures energy is return-
ing to system depot. Also, we argue that Virtual Stu-
dent’s energy reduction is a consequence of effort in
a conventional learning process. Thinking on ecosys-
tem model parameters, we consider that real average
learner can hold approximately two or three learning
tasks in their attention at the same time, or one com-
plex task. Task complexity metrics in the ecosystem
the point of interest. Here, we identify learning ob-
jects as tasks.
3.1.4 Initial Energy Flow Conditions
In the beginning, sufficient initial energy amount E
V S
can be assigned to Virtual Student. If energy assigned
to Learning Object E
LO
i
> E
V S
, we say that this is
border condition not to start a learning process di-
rected to specific Learning Object. If all the Learning
Objects in a system have energy level bigger than spe-
cific Virtual Student’s energy, learning cannot start at
all. Such simple rules allow modeling various
initial learners’ conditions.
3.1.5 Optimal Energy Flow Conditions
Energy awareness is a central interest point of energy
flow control algorithm. That is to say, a Virtual Stu-
dent with a capability of estimating its energy flow
in the cognitive learning process can determine the
potential points for energy optimization. Such an ap-
proach requires both (1) sensing data and (2) compu-
tational schemes based on the learning model.
3.1.6 Final Energy Flow Conditions
During the model runtime, energy control algorithm
follows the energy balance principle. As we stated
above, final conditions lead to process termination
based on energy comparing rules.
3.2 Virtual Student Properties
We invent the following groups of static and dynamic
properties that characterize Virtual Student: (1) need
the rest property, (2) ability to forget the learned facts,
(3) emotional states, and (4) cycling through motiva-
tional sequences. The cycling through motivational
sequences depending on real student’s emotions is
crucial for the Virtual Student model proposal and
later discussed in details.
Need for the Rest property involves relatively
slow action modeling daily workout process. Just as
the human need rest and recuperation the Virtual Stu-
dent must re-stock on vital energy from system depot.
Such an approach allows simulating long-term inac-
tivity gaps like housekeeping, sleeping, and vacations.
”Need the Rest” property simulation results lead to
the opportunity to study memorization and forgetting
depending on Virtual Student’s idleness and leisure.
We suggest that current property activation would im-
prove the Virtual Student’s conformity to a real one.
Albeit forgetting is a human-like property, we use
Forgetting property to add a new research vector.
Forgetting curve, adopted from Murre follows the Ex-
ponential Distribution, whereas Memorization mod-
eled as the Poisson Arrival Process (Murre et al.,
2013) and is useful for Virtual Student’s memory
model. For Virtual Student model, we apply three-tier
memory architecture: sensory, short-term, and long-
term memory. We also accept The 24-hour point of
upward jump in Ebbinghaus’ forgetting curve (Murre
and Dros, 2015).
Also, in the further development of memory pro-
cess control algorithm, we propose to include the
module for memorization processes’ volume control
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
546
- an option for the Virtual Student to practice the
memory and become smarter. For further references
let’s name the memorization processes’ volume con-
trol module as MVC.
Emotional States. With this property, we under-
stand real learners’ emotional conditions playing a
specific role in the learning modeling confidence.
In the next section, we discuss, specify, and utilize
four emotional categories classified as follows: very
pessimistic, skeptical, confident, and very confident.
Considering correlation to Virtual Student’s energy
model, we elaborated the Emotional States factors.
Positive emotions incentivize learners subconsciously
growing their energy, although negative sentiment -
lead to stuck, depression, energy loss to learn.
Motivational Sequences. To form Virtual Student
emotionally motivated interactions with ecosystem
layers and components required for cognitive learning
process modeling, we adopt a commonly occurring
Apter’s Motivational Sequence model (Apter, 1989).
Fig. 2 depicts adopted Motivational Sequence model
mapped to the timeline. Virtual Student’s attempts to
catch and hold certain pleasant states like excitement
or relaxation are alternating with unpleasant ones like
flat, tiresome states.
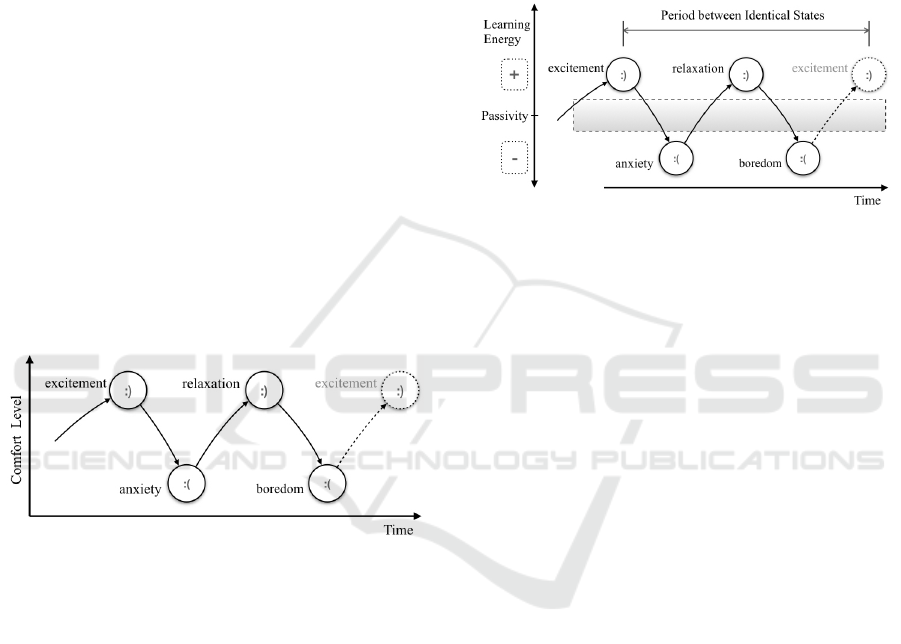
Figure 2: Van der Molen Motivational Cycling model trans-
formed into Motivational Sequence model by mapping to
timeline.
In the amended Motivational Sequences model
(Fig. 2), we define the excitement state as the ini-
tial one, therefore indicating Virtual Student’s addic-
tion to learning. We argue that a tendency to begin
to learn at the emotional excitement phase correlates
with the real learners’ motivation keen to learn. By
standing anxiety as the next position in the sequence,
we realize that in reality, human behavior follows the
same path: positive emotions and negative emotions
are in the constant cycling process. Therefore, we
simplify the Motivational Sequences model avoiding
the direct transition to any other state except catego-
rized as emotionally opposite.
Four alternating model states represent cycling
through comfort levels: excitement, anxiety, relax-
ation, boredom mapped to the timeline. The comfort
cycling model mapping to energy-based model fol-
lows a simple idea: if the emotional state classified as
negative, Virtual Student does not receive the energy
and starts to lose one proportional to the time spent
in such a condition. By replacing a single emotional
Comfort Level vector (Fig. 2) with two Learning En-
ergy vectors beginning at the point of ”Passivity” we
invent the Energy Fluctuation model (Fig. 3). The far-
ther from middle (”Passivity”) level resides the emo-
tional state, the more energy we associate with such a
condition.
Figure 3: Four alternating model states represent emotional
cycling: a) adopted to timeline model, b) proposed Energy
Fluctuation model as a function of emotional cycling in
time.
In the figure, the shaded area considered as low
energy region or ”No Flow!” zone. Such an area
indicates Virtual Student being close to shut-off or
dropout in reality.
Alternating Emotional states represent emotional
cycling process having an impact on Energy Fluctua-
tion in the Virtual Student Learning Model. Follow-
ing diagram (Fig. 4 ) depicts one of the possible sce-
narios of possible strategic trends in Virtual Student’s
Energy Fluctuation model. Learning Energy gaining
in the next simulation step denoted as a ”FUTURE.”
Also, we invent the ”Comfort Zone” bounding Energy
Flow gulf for Virtual Student.
Overall, comparing of classified emotional states
is the beginning point to start to compare simulations’
outcomes and real learners’ classification results. A
computerized model can apply such consequences in
a blended learning process for comparing real and vir-
tual students operating in one shared virtual learning
environment.
3.3 Virtual Student Learning Model
From Franklin’s results (Franklin and Graesser,
1997), we take into consideration the existence of uni-
versal cognitive cycling paradigm: cognition in au-
tonomous agents is subject independent - whether ar-
tificial, animal or human. This cycling paradigm is
the crucial concept point to follow.
At first, we find that Stringer’s Action Spiral
model (Nasrollahi, 2015; Stringer, 2013) stated the
Review of Cognitive Energy Flow Model Concept for Virtual Student
547
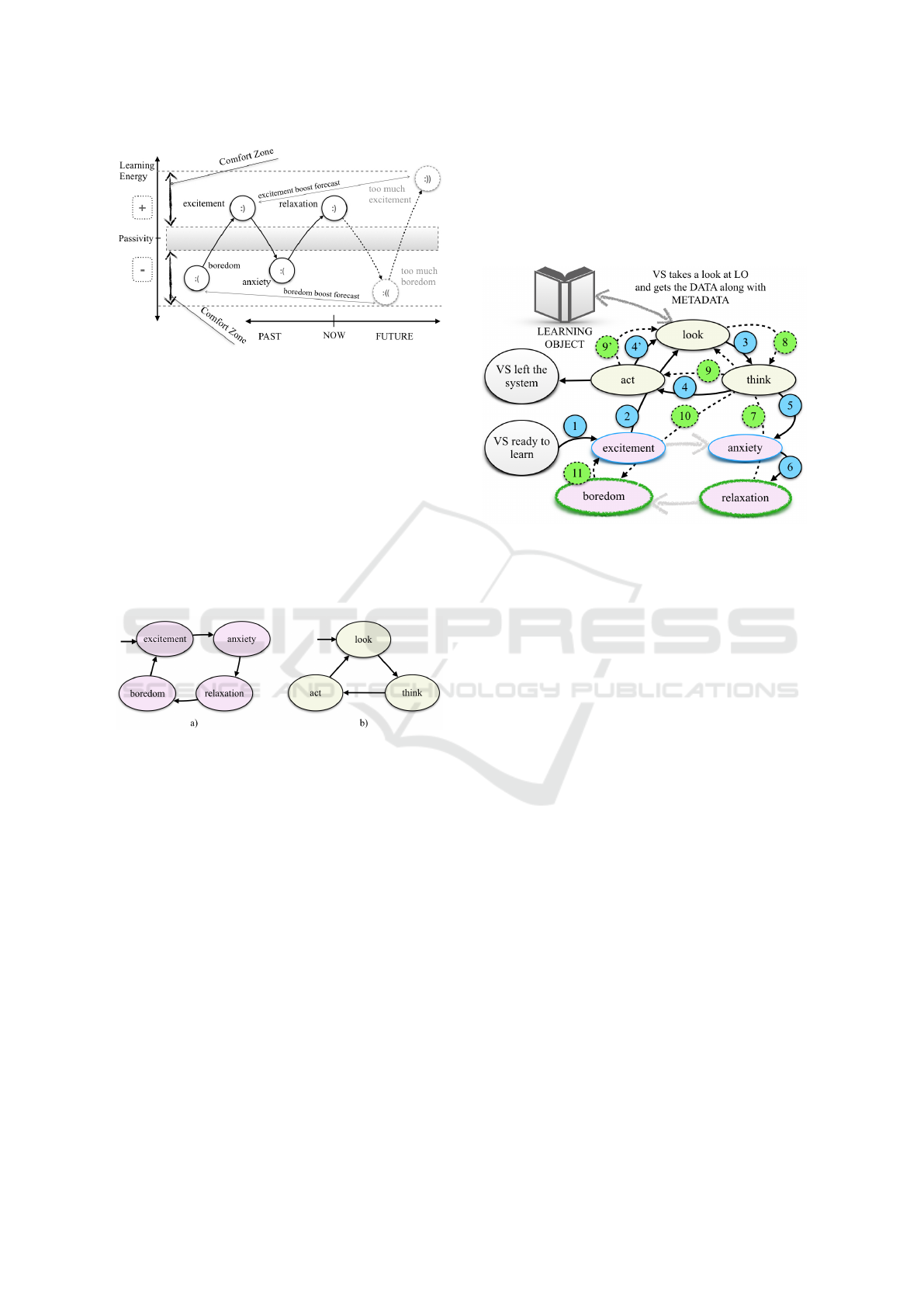
Figure 4: Energy Fluctuation model. Scenario: Suspicious
Energy boosting in both directions leaving a Comfort Zone
moving towards extreme threshold levels: hidden subburn-
ing (too much boredom) and overexpectations (too much
excitement).
existence of look-think-act cycles in cognitive learn-
ing correlate with similar results proposed by An-
derson (Anderson et al., 2004). Next, we conclude
that Anderson uses nouns: perception-understanding-
action, although Stringer applies verbs: look-think-
act to describe the same paradigm.
In our conceptual Virtual Student model, we apply
both emotions related and look-think-act cycles (Fig.
5).
Figure 5: Virtual Student Learning model Components:
subplot a) - Motivational Cycling (MC) model, and subplot
b) - Stringer’s Action Spiral (SAS) model.
Finally, by adding operation control logic, we
combine both motivational cycling and cognition cy-
cles approaches into one coherent system present-
ing the concept of Virtual Student Learning Model
(Fig.6).
For simplicity, the Virtual Learning Environment
on the proposed model depicted as a single simple
Learning Object (LO). The bi-directed line repre-
sents Virtual Student’s communication with LO. Vir-
tual Student’s requests for available data and retrieves
the next information portion proportional to the at-
tention quantity. Computerized VS model measures
such an effort and the time applied to the Learning
Object. The Learning Object’s response comes along
with LO’s specific METADATA set.
We suggest a real e-learning environment (VLE)
modification by implementing VS related META-
DATA in specific LO’s model. A METADATA should
include at least ENERGY-Specific credentials. We
propose to apply to use Energy Tokens. Also, META-
DATA represents a set of specific Learning Object pa-
rameters like size, complexity, expected learning ef-
fort, average forgetting parameters, and virtual learn-
ing path constraints to control the cognitive process.
Figure 6: Interaction of Virtual Student Learning model
Components with Learning Object in a Spatial Design.
Also, Fig. 6 depicts the Virtual Student Learning
model in dynamics. Each transition on the scheme
denoted as a colored circle object with a sequence
number inside. Blue colored transitions, and corre-
sponding solid directed arcs reveal a path for the first
stage of learning process switching from positive ex-
citement state to harmful one - anxiety. The route
goes via cognitive learning cycling (transitions 2, 3,
4, 4’). Transition 5 means a decision at a ”think”
state to get stuck. Next, after some arbitrary time
spent in state ”anxiety,” follows transition 6 return-
ing Virtual Student to a comfortable emotional level
- ”relaxation.” Green circles and dotted lines specify
the third phase in motivational sequences model lead-
ing to switching to the next uncomfortable - bore-
dom state. Finally, without discussions of reasons,
Virtual Student returns to the ”excited” state. Either
route goes through a decision-making component im-
plemented in the look-act-think module.
The main system algorithm controls the learning
process interacting with every module with the aim to
supervise ecosystem energy flow. On a condition of
insufficient enough energy, what is the worst scenario,
Virtual Student is dropped out of the course. In the
case of acceptable quality of interaction with learning
objects, the mission completed.
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
548

4 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
DIRECTIONS
Summarizing research results regarding energy as-
pects of the discussed model, we conclude: (1) Learn-
ing Energy redistribution flow among the system ob-
jects can be observed and controlled by the main
system algorithm, (2) Learning Energy Ecosystem
model’s Energy Quantity is constant for every sim-
ulation run, (3) proposed Learning Energy Ecosystem
for Virtual Student evolution has clear operating con-
ditions to simulate the learning process based on the
energy balance principles, (4) proposed Virtual Stu-
dent will produce more synthetic data ready for vali-
dation of correlation with real user behavior data.
For future works, we consider the following con-
cept point: cognition for every autonomous agent is
subject independent. To approve such a concept we
consider: (1) tudy Virtual Student model computer
implementation depending on model Verification re-
sults on the model validation stages, (2) translate the
conceptual model to operational one and verify it by
implementation into real Virtual Learning Environ-
ment, (3) build the computerized model, (4) apply
the proposed model in a blended learning process for
comparing both real and virtual students operating in
one shared virtual learning environment.
Further research by applying validation to the pro-
posed model with an implementation in the Virtual
Learning Environment might clarify the aspect of Vir-
tual Student’s potential.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research has been supported by a grant
from the European Regional Development Fund
(ERDF/ERAF) project ”Technology Enhanced
Learning E-ecosystem with Stochastic Interdepen-
dences - TELECI”, Project No.1.1.1.1/16/A/154.
REFERENCES
Anderson, J. R., Bothell, D., Byrne, M. D., Douglass, S.,
Lebiere, C., and Qin, Y. (2004). An integrated theory
of the mind. Psychological review, 111(4):1036.
Anderson, L., Krathwohl, D., and Bloom, B. (2001). A tax-
onomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: a revi-
sion of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives.
Longman.
Apter, M. J. (1989). Reversal theory: A new approach to
motivation, emotion and personality. Anuario de Psi-
colog
´
ıa, 42(3):29.
Baars, B. J. and Franklin, S. (2007). 2007 special issue:
An architectural model of conscious and unconscious
brain functions: Global workspace theory and ida.
Neural Netw., 20(9):955–961.
Brown, J. R. and Fehige, Y. (2017). Thought experiments.
In Zalta, E. N., editor, The Stanford Encyclopedia
of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford
University, summer 2017 edition.
Domingos, P. (2015). The Master Algorithm: How the
Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake
Our World. Basic Books.
Franklin, S. and Graesser, A. (1997). Is it an agent, or just
a program?: A taxonomy for autonomous agents. In
Proceedings of the Workshop on Intelligent Agents III,
Agent Theories, Architectures, and Languages, ECAI
’96, pages 21–35, London, UK, UK. Springer-Verlag.
Fuster, J. M. (2002). Physiology of executive functions: The
perception-action cycle., page 96–108. New York:
Oxford University Press.
Gregory, R. L. (1997). Knowledge in perception and illu-
sion. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society
of London B: Biological Sciences, 352(1358):1121–
1127.
Huxley, J. (1944). On living in a revolution, by Julian Hux-
ley. Harper New York, [1st ed.] edition.
JUNG, C. G. (1969). Collected Works of C.G. Jung, Volume
8: Structure & Dynamics of the Psyche, pages 3–66.
Princeton University Press.
Madl, T., Baars, B., and Franklin, S. (2011). The timing of
the cognitive cycle. 6:e14803.
Modha, D. S., Ananthanarayanan, R., Esser, S. K., Ndi-
rango, A., Sherbondy, A. J., and Singh, R. (2011).
Cognitive computing. Commun. ACM, 54(8):62–71.
Murre, J., Chessa, A., and Meeter, M. (2013). A mathe-
matical model of forgetting and amnesia. Frontiers in
Psychology, 4:76.
Murre, J. M. J. and Dros, J. (2015). Replication and analysis
of ebbinghaus’ forgetting curve. PLOS ONE, 10(7):1–
23.
Nasrollahi, M. A. (2015). A closer look at using stringer’s
action research model in improving students’.
Norman, D. A. (1987). Interfacing thought: Cognitive as-
pects of human-computer interaction. chapter Cog-
nitive Engineering&Mdash;Cognitive Science, pages
325–336. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA.
Piaget, J. (2005). The Psychology Of Intelligence. Taylor &
Francis.
Piaget, J. and Campbell, S. (1976). Piaget Sampler: An
Introduction to Jean Piaget Through His Own Words.
Wiley.
Russell, S. J. and Norvig, P. (2003). Artificial Intelligence:
A Modern Approach. Pearson Education, 2 edition.
Sheth, A. P., Anantharam, P., and Henson, C. A. (2015).
Semantic, cognitive, and perceptual computing: Ad-
vances toward computing for human experience.
CoRR, abs/1510.05963.
Stringer, E. (2013). Action Research. SAGE Publications.
Weiss, G. (2013). Multiagent Systems. The MIT Press.
Review of Cognitive Energy Flow Model Concept for Virtual Student
549
