
A Flow Measurement Instrument to Test the Students’ Motivation in
a Computer Science Course
Nour El Mawas and Jean Heutte
CIREL (EA 4354), University of Lille, Lille, France
Keywords: Learning, Students’ Motivation, Computer Science, Flow, Optimal Experience.
Abstract: Motivate students is a top research aspect for many research communities, schools, universities, and
institutions. In this context, motivation has an important role in the leaning process and particularly in the
students’ success and the drop-out avoidance. This paper proposes a flow measurement instrument in order
to test the students’ motivation in a Computer Science course. The experimental study involved 33 students
that answer a same questionnaire twice in a period of one week. The temporal stability, internal consistency
and convergent validity of the first English version of the Flow in education scale (EduFlow) were examined.
The results show that autotelic experience (well-being provided by the activity itself) is significantly
positively correlated with academic achievement. This research work is dedicated to Education and Computer
Science active communities and more specifically to directors of learning centres / pedagogy departments,
and the service of information technology and communication for education (pedagogical engineers) who
meet difficulties in evaluate students’ motivation in a specific course.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, education is facing big changes based on
concepts, theories, principles, and methods.
Motivation is one of the most important factor that
universities/institutions/teachers need to target in
order to improve students' learning (Bhoje 2015).
Palmer (2007) reviews the student motivation as an
essential element that is necessary for the education
quality.
According to Weiner (1992), motivation is the
study of the determinants of thought and action—it
addresses why behaviour is initiated, persists, and
stops, as well as what choices are made. In general,
most teachers are aware of the importance of keeping
students motivated. According to Goleman (1996),
“The extent to which emotional upsets can interfere
with mental life is no news to teachers. Students who
are anxious, angry, or depressed don’t learn; people
who are caught in these states do not take in
information efficiently or deal with it well.”
The efforts of teachers to motivate their students
are not always successful, probably due to lack of
training and deep understanding of all the issues
involved in the class. The motivation behind this
work is the teachers’ difficulty to evaluate students’
motivation in instructional situations.
Optimal experience (or Flow) “is a gratifying
state of deep involvement and absorption that
individuals report when facing a challenging activity
and they perceive adequate abilities to cope with it”
(EFRN 2014). The phenomenon is described by
Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi in 1975 in order to explain
why people perform activities for the activity itself,
without extrinsic rewards. During flow state, people
are deeply motivated to persist in their activities and
to perform such activities again (Csikszentmihalyi,
1975). The experience is triggered by a balance
between a person’s skills in an activity and the
challenges afforded by the lifelong learning
environment. Flow has been shown to promote
learning and personal development because deep and
total concentration experiences are intrinsically
rewarding, and they motivate students to repeat an
activity at progressively higher levels of challenge
(Csikszentmihalyi et al., 2005). Potentially due to its
positive consequences, flow research is further
growing in the new millennium, and there is a
plethora of empirical articles dedicated to this
phenomenon.
In this paper, we are focusing on a flow
measurement instrument in order to test the students’
motivation in a Computer Science course. We choose
the Research in Computing course in a Master
El Mawas, N. and Heutte, J.
A Flow Measurement Instrument to Test the Students’ Motivation in a Computer Science Course.
DOI: 10.5220/0007771504950505
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2019), pages 495-505
ISBN: 978-989-758-367-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
495

programme entitled Cloud Computing because
students in this field do not see the immediate benefit
to have this course in their curriculum. Note that, in
our context, ‘instrument’ is a novel psychometric
scale to assess optimal experience in educational
situations.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2
presents some research work done in the area of flow
and motivation to learn, focusing on flow in
education. Section 3 describes our flow measurement
instrument. Section 4 highlights our case study in an
engineering school in Dublin. Section 5 presents the
results of the case study. Section 6 summarizes the
conclusion of this paper and presents its perspectives.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Flow and Motivation to Learn
As Csikszentmihalyi and LeFevre (1989) noted,
“when both challenges and skill are high, the person
is not only enjoying the moment, but is also stretching
his or her capabilities with the likelihood of learning
new skills and of increasing self-esteem and personal
complexity”. In this manner, the concept of flow is
inherently relevant to learning and particularly
important within educational settings.
According to (Culbertson et al., 2015), research
findings regarding flow within learning contexts have
demonstrated that flow is associated with heightened
creativity, persistence in studies (Nakamura 1988),
and overall learning and academic performance
(Csikszentmihalyi et al., 1993). In addition, there is
evidence that flow is related to teaching effectiveness
and that flow within the classroom can crossover
from one individual to others (e.g., from teacher to
students);.
Optimal motivation and learning occur when
perceived challenge and perceived skill are balanced
and high. An imbalance between perceived challenge
and skill can lead to decreased motivation, such as
boredom when skills exceed challenge, or anxiety
when challenge is higher than skill (Csikszentmihalyi
2014). Optimal motivation promote the most positive
psychological / developmental / behavioural
outcomes and psychological well-being (Deci and
Ryan, 2002).
High perceived skill is especially advantageous
when perceived difficulty is high. Learners who
perceive that their skills are high and matched with
the level of challenge report higher enjoyment,
interest, and positive affect (Shernoff et al., 2003),
and are more likely to persist or wish to continue with
a task (Csikszentmihalyi et al., 1993).
The main topic of flow in education was the link
of flow with motivational indicators. Beside
motivation, some studies related flow to (a)
engagement (Mesurado et al., 2016); (b) goal
orientation (Oertig et al., 2014), (c) achievement
motives (Engeser and Rheinberg, 2008), (d) interest
(Bachen et al., 2016). This is not surprising because
many authors consider flow experience as a state of
the optimal motivation (Deci and Ryan, 2002; Heutte
2017).
The topic of flow in education has often been
studied in combination with other theories. Many
previous studies have examined the connection
between flow and intrinsic motivation (Keller et al.,
2011). Intrinsic motivation involves doing a
behaviour because the activity itself is interesting and
spontaneously satisfying (Deci and Ryan, 2002).
However, some authors introduce confusion by
considering flow as intrinsic motivation. Indeed, it is
quite possible to have an optimal experience during
an activity that has not been chosen for intrinsic
reasons (which is not a free choice). This is often the
case like the first time a student performs a task to
respond to a teacher's request without any intrinsic
motivation. It is thus possible to see that sometimes it
can be the challenge (complexity or task
requirements) imposed by a prescribed task that goes
in a completely unexpected way (for the student) to
induce the state of flow, as if the flow literally fell on
him without his expectation. In this case, it is during
the activity that the student will find himself or herself
gradually absorbed by the task and it is this
absorption, combined with the fact of realizing that he
or she is progressing (sometimes beyond what he or
she thought he or she was capable of), that will bring
pleasure to the work. Of course, it is this phenomenon
that may induce the desire to re-engage in the task,
this time for intrinsic reasons. Therefore, it would be
more accurate to say that intrinsic motivation can be
a consequence of flow (because the opposite is not
always true). Thus, even if obviously all forms of
autonomous motivation can promote flow, the fact
remains that the confusion between intrinsic
motivation and flow is indeed a conceptual error
(Heutte 2017).
Other studies on motivation and flow are more
linked to self-efficacy (Bandura 1997). Results
highlight that self-efficacy is linked to flow
frequency, higher levels of challenge, and skills.
These results also show that self-efficacy predicts
flow over time (Heutte et al, 2016). High efficacy
beliefs levels have a positive impact on flow
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
496

Table 1: Some instruments examples used to study flow in an educational context.
Scales
Authors
Items
nb
Dim
nb
Flow Questionnaire* (Flow Q)
Csikszentmihalyi and Csikszentmihalyi (1988)
3
n.a.
Flow in Human-Computer Interaction
Ghani and Deshpande (1994)
15
4
Flow in Online Environments
Novak et al (2000)
66
13
Flow State Scale-2 (FSS-2)
Jackson and Eklund (2002)
36
9
Flow-Kurzskala (FKS)
Rheinberg et al (2003)
10
1
EGameFlow
Fu et al (2009)
42
8
Échelle de mesure du flow en éducation
(EduFlow)
Heutte et al (2014)
12
4
Échelle de mesure du flow en éducation-2
(EduFlow-2)
Heutte et al (2016)
12
4
Note. * only for qualitative study
experiences in academic settings (Heutte et al., 2016;
Salanova et al., 2006). Various aspects of Bandura's
(1986) self-regulation learning model were shown to
exert a significant and positive effect on flow state
(Chen and Sun, 2016). Higher congruence between
one’s implicit motives and self-attributed motives is
associated with better self-regulation, goal
attainment, and flow (Rheinberg and Engeser, 2012).
Some studies highlight collective (or social)
motivational conditions of flow: collective efficacy
beliefs predict collective flow over time (Salanova et
al., 2014).
In any case, most studies show that the relation
between flow and learning is complex because the
learning process is not simple. Flow predicts
motivational outcomes (intrinsic motivation, interest,
self-efficacy, self-regulation, persistence, etc.), but
not always task performance (Durik and Matarazzo,
2009).
2.2 EduFlow
Various instruments have long been used to study
flow in educational contexts (Table 1). However,
according to Csikszentmihalyi, before the
development of the Flow in education model
(EduFlow) (Heutte et al., 2014), there was no short
multidimensional scale designed and dedicated
specifically for education (some generic scales were
applied in education without being initially designed
for this domain). “The understanding of flow within
educational settings, however, is limited by the
methodological approaches to date. For example,
most research on the correlates of flow has been
cross-sectional and therefore incapable of
establishing the causal nature of the relationships
between the potential antecedents and consequences
of flow. In addition, cross-sectional studies must rely
on measures assessing recalled flow as opposed to
direct measures of flow at the times of the activities”
(Culbertson et al., 2015). Note that in table 1, nb
refers to number and dim to dimension.
In order to carry out a convergent validity test
with this first English version of the Flow in
Education Scale (EduFlow), we have selected two
standardized measurement instruments whose main
characteristics are: (1) short scales and (2) scales very
regularly used in international scientific work. In our
context, we use the Flow Short Scale (Rheinberg et
al., 2003) and the General Self-Efficacy Scale
(Schwarzer, and Jerusalem, 1995).
3 OUR FLOW MEASUREMENT
INSTRUMENT
3.1 An Overview of Our Approach
Figure 1 shows an overview of our design and
evaluation approaches. Three actors are involved in
the design of our flow measurement instrument: the
psychologist researcher who designs the instrument,
the learning psychologist who uses the proposed
instrument in order to contextualize it, and the teacher
who validates the contextualized instrument based on
the course and the vocabulary used in the class.
Regarding the use of the instrument, the learning
psychologist puts the contextualized instrument in the
dedicated learning environment (for example lime
survey) and the teacher runs it in the class where
students answer the questions of the contextualized
instrument. Then, the learning psychologist
anonymizes and analyzes student’s answers via a
statistical analysis software like SPSS statistic, R, etc.
A Flow Measurement Instrument to Test the Students’ Motivation in a Computer Science Course
497
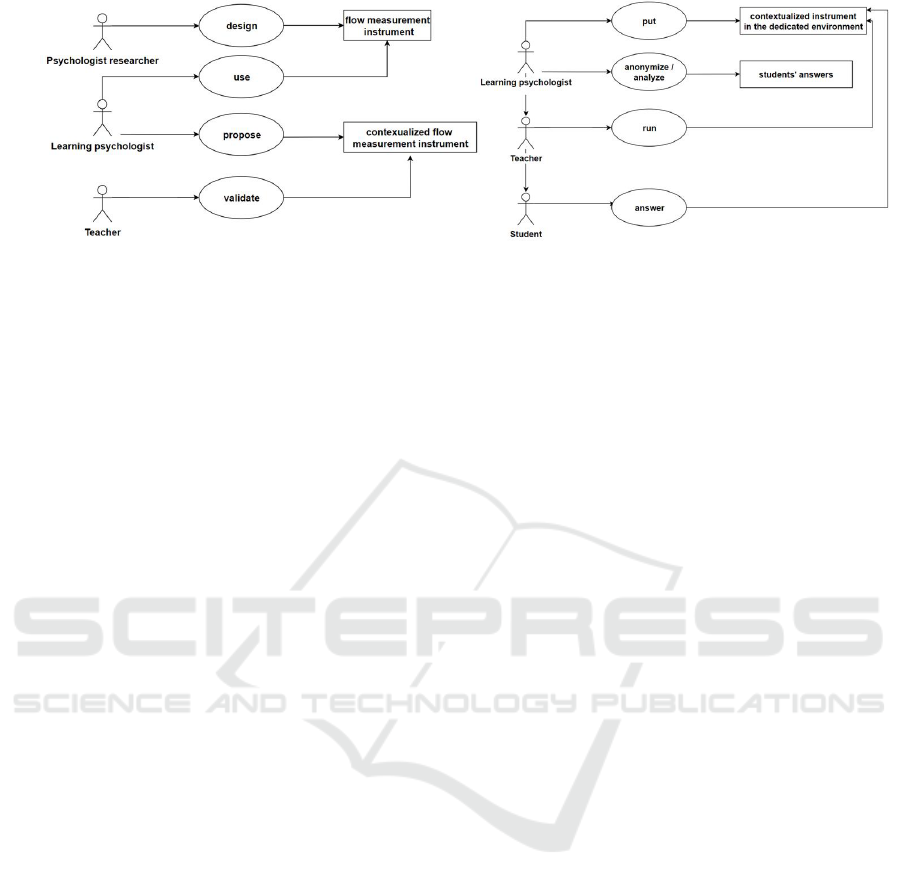
Figure 1: An overview of our approach from the design side (on the left) and the evaluation/use side (on the right).
3.2 Instruments
The Flow in education scale version 2 (EduFlow-2) is
a twelve-item scale and it differentiates 4 flow
dimensions (there are three items per dimension):
- FlowD1-Cognitive Control: a strong feeling of
control, specifically over one’s actions,
characterized by a feeling of ability to deal with
the situation and a feeling that the student knows
how to deal with whatever comes next (“I feel
completely in control of my actions”);
- FlowD2-Immersion and Time Transformation:
alteration in the perception of time, sometimes
leading to a lengthened duration of immersion in
the task (“I am wholly absorbed in what I am
doing”);
- FlowD3-Loss of Self-Consciousness: lack of self-
concern related to an increase in importance of the
psycho-social dimension of learning (“I don’t care
about what others may think of me”);
- FlowD4-Autotelic Experience: well-being
provided by the activity itself enhances
persistence and the desire to engage in the activity
again (“This activity brings me a sense of well-
being”).
When tested via Confirmatory Factor Analysis, the
EduFlow-2 showed significant improvement in all fit
indices (Heutte et al., 2016). We have consequently
gathered FlowD1, FlowD2 and FlowD3, namely
Cognitive Control, Immersion and Time
Transformation, and Loss of Self-Consciousness, under
Cognitive Absorption (Figure 2).
The EduFlow has three main advantages:
- It suits flow measurement in various educational
contexts;
- It is a short instrument (reducing respondent
burden);
- It highlights the difference between four
dimensions of flow that are related to a cognitive
process.
This scale was used to measure flow after
classrooms activities (7-point scale).
Flow was complementary measured with the
Flow Short Scale (Rheinberg et al., 2003). This scale
measures all components of flow experience with ten
items (“My mind is completely clear”) and was used
to measure flow after classrooms activities (7-point
scale). The first flow model (Csikszentmihalyi 1975)
proposes that flow occurs when the actor perceives a
balance between the challenge of the activity and his
or her own skill. Due to theoretically inconsistent
results, this model was reformulated: the revised
model proposes that flow is experienced only when
challenge and skill are both high (Csikszentmihalyi
and Csikszentmihalyi, 1988), that’s why according to
(Engeser and Rheinberg, 2008), we add three
additional items to measure the perceived importance
(‘‘Something important to me is at stake here’’, ‘‘I
won’t make any mistakes here’’, and ‘‘I am worried
about failing’’). The experienced difficulty of the
task, perceived skill and perceived balance were
measured on a 7-point scale.
Many studies on motivation and flow are linked
to Social Cognitive Theory (Bandura, 1986). Results
highlighting that self-efficacy is linked to flow
frequency and have a positive impact on optimal
experiences in academic settings (Heutte et al., 2016;
Salanova et al., 2006). The German version of
General Self-Efficacy Scale (GSES) developed in
1979 by Jerusalem and Schwarzer and later revised
(Schwarzer, and Jerusalem, 1995), and adapted to 26
other languages by various co-authors. GSES is a ten
items scale; (“It is easy for me to stick to my aims and
accomplish my goals”) created to assess a general
sense of perceived self-efficacy with the aim in mind
to predict coping with daily hassles as well as
adaptation after experiencing all kinds of stressful life
events. This scale was used to measure flow after
classrooms activities (7-point scale).
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
498
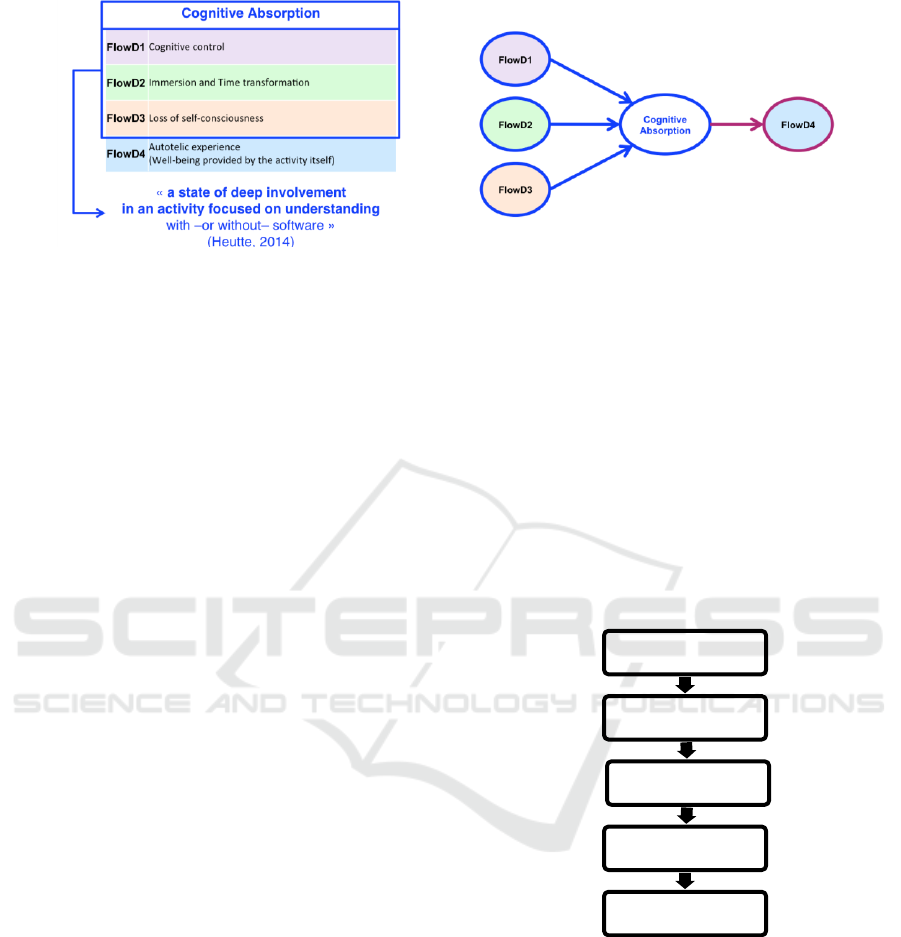
Figure 2: Cognitive Absorption Modelling (Heutte 2017).
4 CASE STUDY
The goal of this research study was to investigate
learner motivation in a Computer Science course.
This section presents the evaluation methodology
applied and case study set-up.
The evaluation included a group of master
students who were taught the Research in Computing
course. In this course, learners acquire the
fundamental computing research skills in Cloud
computing of an MSc programme in order to set up
the foundations of a research project via a major
literature review and a project plan. In the course,
there is an assessment about writing a research paper
(~20 pages). This paper must be submitted at the end
of the course.
The evaluation took place in class, during the
normal hours of study. A total of 33 students (21.2%
woman and 78.8% man) of average age 25.7 years
(Standard Deviation = 2.3 years) with a range from
21 to 30, from an engineering school located in
Dublin, Ireland took part in the case study. Team
members from the school and the Université de Lille
(in France) have prepared and helped perform the
tests. The students volunteered to participate in a
study that required them to complete two surveys for
an average test–retest interval of about seven days.
Once the assessment is corrected, we compare the
grades with the motivation indicators.
The evaluation meets all Ethics requirements.
Prior to running the case study, all required forms
were provided to the students including informed
consent form, informed assent form, plain language
statement and data management plan. These
documents include a detailed description of the
testing scenario, as well as information on study
purpose, data processing and analysis, participant
identity protection, etc.
The evaluation process is illustrated in Figure 3
that presents in details the steps followed by the
researchers. It can be seen that prior to beginning the
evaluation, the consent forms signed by students were
collected. Then the students were introduced to the
research case study and asked to review and sign the
assent form. The students had roughly 20 minutes to
answer the questionnaire (see appendix).
The learner motivation questionnaire assessing
student motivation was collected. After 1 week of this
evaluation, the students were asked to answer the
same questionnaire in order to verify the temporal
stability and internal consistency of our flow
measurement instrument. This instrument is the first
English version of the Flow in education scale.
Figure 3: Evaluation process.
5 CASE STUDY RESULTS
ANALYSIS
The analyses were carried out in two stages: (1) verify
certain psychometric qualities of our novel
instrument EduFlow, and (2) study links between
academic success and different psychological
determinants of motivation highlighted by this new
measurement instrument. Note that all statistical
Collection of the consent
forms (signed by the students)
Description of the research
study
Collection of assent forms
Learning experience
Survey
A Flow Measurement Instrument to Test the Students’ Motivation in a Computer Science Course
499

analyses were performed using the Statistical
Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), version 23.
5.1 Quality of the Eduflow
Table 3 presents the test and retest means, standard
deviations, and test–retest stability coefficients for the
12 items of EduFlow. The results of this first analysis
highlight that there is no significant difference in the
answers at one week interval for each of the 12 items.
This confirms the temporal stability of the EduFlow.
Cronbach’s alpha (Cronbach 1951) is so far the
most frequently reported reliability coefficient. Table
1 presents the internal consistency coefficient alphas
for each dimension of the EduFlow. According to
(Hinton et al., 2014), coefficient alphas .50 to .70
shows moderate reliability, .70 to .90 shows high
reliability, .90 and above shows excellent reliability.
According to Moss and colleagues (1998, cited by
Hair et al., 2006), the .60 level of Cronbach´s alpha is
acceptable.
The coefficient alphas (Table 1) shows excellent
reliability for FlowD3-Loss of Self-Consciousness
(.93), high reliability for FlowD1-Cognitive Control
(.84) and FlowD4-Autotelic Experience (.83),
moderate reliability for FlowD2-Immersion and Time
Transformation (.60).
Although the coefficient for FlowD2 is a little bit
low, the analyses show that the reliability of the scale
is acceptable. This confirms the internal consistency
of each dimension of the EduFlow.
Bartlett’s test of sphericity and the Kaiser–
Meyer–Olkin (KMO) measure of sampling adequacy
(Kaiser 1974) were used to evaluate the strength of
the linear association between the items in the inter-
item correlation matrix (Table 2). Bartlett’s Test was
significant (Chi-Square = 380.55, p < .000) and KMO
value was .76, which is good (if >.70). The number of
students in the case study was too small to conduct an
exploratory factor analysis.
The convergent validity test (Table 3) highlights
that all dimensions of EduFlow are significantly
positively highly correlated (r=.56 to r=.88, p < .01)
with Flow Short Scale (Rheinberg et al., 2003) and
the General Self-Efficacy Scale (Schwarzer and
Jerusalem, 1995). These results are fully in line with
expectations. All these analyses confirm the good
quality of the first English version of the EduFlow.
5.2 Results Focused on Motivation
First of all, we can see in table 4 that all mean score
of motivation indicators (evaluated with 7-point
Likert scale) are particularly high overall, both for all
dimensions of the EduFlow (5.03 to 5.76), the Flow
Short Scale (4.93) and the General Self-Efficacy
Scale (5.56). We also notice that in all selected
indicators, the one relating to difficulty has the lowest
score (4.24).
Contrary to expectations, the results (Table 5)
show that there is no significant link between the
students' self-efficacy and their academic success
(final grade obtained at the end of the course). Among
all the flow indicators, there is only FlowD4-
Autotelic Experience that is significantly related to
academic success (r = .38, p< .05).
Some unexpected results, particularly regarding
flow, may be due to the fact that students did not feel
they were having a difficult experience. Indeed, in
free fields of expression, many students emphasized
the quality of the teacher's pedagogical support,
particularly the time spent even outside the classroom
to ensure that they had understood the requirements
of the prescribed tasks (Prof. Nour El Mawas helped
us a lot. Prof. made us understand things in a very
simple format by giving multiple example. Prof. used
to repeat until we understand the concept clearly. I
thoroughly enjoyed the lecture given by Prof. Nour El
Mawas. I truly appreciate the way you had cleared
Table 1: Reliability Statistics (Cronbach’s Alpha Based
on Standardized Items).
Cronbach’s
Alpha
N of
Items
FlowD1
.835
3
FlowD2
.602
3
FlowD3
.926
3
FlowD4
.831
3
Table 2: KMO and Bartlett’s Test.
Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of
Sampling Adequacy
.764
Bartlett’s Test of
Sphericity
Approx.
Chi-Square
380.554
df
66
Sig.
.000
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
500

Table 3: Paired Samples T-test Output.
Paired Differences
t
df
Sig.
(2-
tailed)
Mean
Std.
Dev.
Std.
Error
Mean
95%
Confidence
Interval of the
Difference
Inf.
Sup.
Pair 1
FlowD1a (t1 vs t2)
-.273
1.153
.201
-.682
.136
-1.359
32
.184
Pair 2
FlowD2a (t1 vs t2)
-.030
1.357
.236
-.512
.451
-.128
32
.899
Pair 3
FlowD3a (t1 vs t2)
.129
2.109
.379
-.645
.903
.341
30
.736
Pair 4
FlowD4a (t1 vs t2)
-.061
1.638
.285
-.641
.520
-.213
32
.833
Pair 5
FlowD1b (t1 vs t2)
.030
1.649
.287
-.554
.615
.106
32
.917
Pair 6
FlowD2b (t1 vs t2)
.091
1.646
.287
-.493
.675
.317
32
.753
Pair 7
FlowD3b (t1 vs t2)
.188
1.635
.289
-.402
.777
.649
31
.521
Pair 8
FlowD4b (t1 vs t2)
-.485
1,889
.329
-1.155
.185
-1.474
32
.150
Pair 9
FlowD1c (t1 vs t2)
-.091
1.721
.300
-.701
.519
-.304
32
.763
Pair 10
FlowD2c (t1 vs t2)
-.152
1.839
.320
-.804
.501
-.473
32
.639
Pair 11
FlowD3c (t1 vs t2)
-.030
2.468
.430
-.906
.845
-.071
32
.944
Pair 12
FlowD4c (t1 vs t2)
-.269
1.845
.362
-1.015
.476
-.744
25
.464
Note: t1: test ; t2: retest (at one week interval); FlowD1, FlowD2, FlowD3 and FlowD4 are dimensions of EduFlow Scale
(Heutte et.al., 2016), for more information about all items please see appendix.
Table 4: Descriptive Statistics.
Motivation (7-point Likert scale)
Mean
S.D.
N
Cognitive Control (FlowD1)
5.76
1.35
33
Immersion and Time Transformation (FlowD2)
5.03
1.12
33
Loss of Self-Consciousness (FlowD3)
5.45
1.81
33
Autotelic experience (FlowD4)
5.12
1.60
33
Flow Short Scale (FSS)
4.93
1.15
33
Perceived importance (FSS-Imp)
4.48
1.86
33
Experienced difficulty (FSS-Diffic)
4.24
2.05
33
Perceived skill (FSS-Skill)
5.45
1.54
33
Perceived challenge-skill balance (FSS-Balance)
4.90
1.51
31
General Self-Efficacy Scale (GSES)
5.56
1.19
33
Grade (0 à 100)
Mean
S.D.
N
Grade
72.27
13.87
33
Note: FlowD1, FlowD2, FlowD3 and FlowD4 are dimensions of EduFlow scale (Heutte et.al., 2016); FSS-Imp, FSS-Diffic,
FSS-Skill and FSS-Balance are additional factors include in Flow Short Scale (FSS, Rheinberg, et al., 2003), GSES
(Schwarzer, and Jerusalem, 1995).
A Flow Measurement Instrument to Test the Students’ Motivation in a Computer Science Course
501

Table 5: Correlation among motivational indicators and academic performance (grade).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1
EduFlow
2
Cognitive
Abs.
.958**
3
FlowD1
.899**
.878**
4
FlowD2
.810**
.845**
.712**
5
FlowD3
.808**
.889**
.628**
.596**
6
FlowD4
.743**
.520**
.629**
.440*
.333
7
FSS
.832**
.820**
.797**
.700**
.668**
.564**
8
FSS-Imp
.452**
.433*
.332
.385*
.409*
.334
.331
9
FSS-Diffic
.387*
.440*
.312
.437*
.406*
.127
.191
.129
10
FSS-Skill
.792**
.814**
.679**
.774**
.697**
.460**
.782**
.391*
.192
11
FSS-
Balance
.501**
.512**
.477**
.585**
.340
.294
.460**
.253
.570**
.434*
12
GSES
.875**
.795**
.816**
.697**
.603**
.752**
.781**
.442*
.270
.703**
.535**
13
Grade
.304
.226
.290
.028
.233
.380*
.259
.076
-.064
.019
-.098
.240
** Correlation is significant at the .01 level (2-tailed).
* Correlation is significant at the .05 level (2-tailed).
Note: FlowD1, FlowD2, FlowD3 and FlowD4 are dimensions of EduFlow Scale (Heutte et.al., 2016); Cognitive absorption
= FlowD1+FlowD2+FlowD3; FSS-Imp, FSS-Diffic, FSS-Skill and FSS-Balance are additional factors include in Flow Short
Scale (FSS, Rheinberg, et al., 2003), GSES: General Self-Efficacy Scale (Schwarzer and Jerusalem, 1995).
everybody’s doubts and was amazed when I found out
that you have made a lot of contributions in the field
of RIC. Will be happy to get a professor like Nour El
Mawas in future. We are really glad to have prof.
Nour for our RIC subject. I haven’t met professor like
Nour in my life ever. I am sure that the notes given
by you will definitely be helpful to us during our
project and I am sure that I am going to score well in
RIC. Thanks Professor.) Note that RIC refers to
Research in Computing.
To summarize the above analysis, we can deduce
that:
(1) All our tests confirm the good quality of the first
English version of the EduFlow: temporal stability,
internal consistency, and convergent validity.
(2) The relation between flow and learning is
complex because the learning process is not simple.
Flow predicts students’ motivation, particularly self-
efficacy, but not always academic performance.
(3) It is better to use a multidimensional
measurement instrument, as EduFlow, to study
students’ motivation in learning situations, because it
allows to highlight some components of the optimal
experience, which is not possible with a
unidimensional scale.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this research paper, we investigate the motivation
in a Computer Science course. A flow measurement
instrument was designed and tested with students
from a Dublin-based engineering school. This
instrument is the first English instrument to assess
flow in education. The case study proves that the
students’ academic achievement is significantly
correlated with the autotelic experience which
presents the well-being provided by the activity itself.
Future work will aim to expand the research study
on our flow measurement tool by increasing the
number of participants (learners) in order to follow
researchers’ recommendations on exploratory and
confirmatory analyses (Hair et al., 2006). Further
research will include a scale to assess student's
feelings of relatedness (Deci and Ryan, 2014; Richer
and Vallerand, 1998). The motivation and the social
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
502

belonging impact on the learning will also be
evaluated.
We also want to increase students’ motivation by
promoting an optimal learning environment. In fact,
researchers have shown the benefits of integrating
interpersonal relations on the motivation (Deci and
Ryan, 2002, 2014, Heutte 2017).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is supported by the Dig-e-Lab project
(https://dig-e-lab.eu/fr/) funded under the Interreg
European Union.
REFERENCES
Bhoje, G. (2015). The Importance of Motivation in an
Educational Environment. Lulu. com.
Bachen, C. M., Hernández-Ramos, P. Raphael, C., and
Waldron, A. (2016). How do presence, flow, and
character identification affect players’ empathy and
interest in learning from a serious computer game?
Computers in Human Behavior, 64, 77-87.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and
action. Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control.
Worth Publishers.
Chen, L.X. and Sun, C.T. (2016). Self-regulation influence
on game play flow state. Computers in Human
Behavior, 54, 341-350
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal
structure of tests. psychometrika, 16(3), 297-334.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1975). Beyond boredom and
anxiety: experiencing flow in Work and play. San
Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2014). Applications of Flow in
Human Development and Education. Springer,
Dordrecht: Netherlands
Csikszentmihalyi, M., Abuhamdeh, S., and Nakamura, J.
(2005). Flow. In A.- J. Elliot and C.- S. Dweck (eds.)
Handbook of competence and motivation, 598-608.
New York: Guilford Press.
Csikszentmihalyi, M., and Csikszentmihalyi, I. (1988).
Optimal experience: Psychological studies of flow in
consciousness. New York : Cambridge University, 251–
265.
Csikszentmihalyi, M., and LeFevre, J. (1989). Optimal
experience in work and leisure. Journal of Personality
and Social Psychology, 56(5), 815-822.
Csikszentmihalyi, M., Rathunde, K., and Whalen, S.
(1993). Talented teenagers: The roots of success and
failure. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Culbertson, S. S., Fullagar, C. J., Simmons, M. J., and Zhu,
M. (2015). Contagious Flow: Antecedents and
Consequences of Optimal Experience in the Classroom.
Journal of Management Education, 39(3), 319–349
Deci, E. L., and Ryan, R. M. (2002). Handbook of self-
determination research. University Rochester Press.
Deci, E. L., and Ryan, R. M. (2014). Autonomy and need
satisfaction in close relationships. In N. Weinstein
(Dir.). Human motivation and interpersonal
relationships (pp. 53-73). Springer, Dordrecht.
Durik, A. M., and Matarazzo, K. L. (2009). Revved up or
turned off? How domain knowledge changes the
relationship between perceived task complexity and
task interest. Learning and Individual Differences,
19(1), 155-159.
EFRN (2014). What is Flow? – Current Definition of the
European Flow Researchers Network (EFRN).
Retrieved from: http://efrn.webs.com/about-us
(19.01.2019).
Engeser, S., and Rheinberg, F. (2008). Flow, performance
and moderators of challenge-skill balance. Motivation
and Emotion, 32(3), 158-172.
Fu, F. L., Su, R. C., and Yu, S. C. (2009). EGameFlow: A
scale to measure learners’ enjoyment of e-learning
games. Computers and Education, 52(1), 101-112.
Ghani, J. A., and Deshpande, S. P. (1994). Task
characteristics and the experience of optimal flow in
human-computer interaction. Journal Of Psychology-
Worcester Massachusetts-, 128, 381–381
Goleman, D. (1996). Emotional intelligence: Why it can
Matter more than IQ. Boomsbury, London. First
published by Bantam Books, New York, 1996.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., and
Tatham, R. L. (2006). Multivariate data analysis (Vol.
6). Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Heutte, J. (2017). Motivations, volition et expérience du
flow : quelques références théoriques pour l’étude des
communautés d’apprenance. Dans O. Las Vergnas
(dir.), Le e-learning informel ? Des apprentissages
diffus, noyés dans la participation en ligne (p. 199-
214). Paris, France : Archives contemporaines.
Heutte, J., Fenouillet, F., Boniwell, I., Martin-Krumm, C.
and Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2014). Optimal learning
experience in digital environments: theoretical
concepts, measure and modelisation. Proceedings of
Symposium Digital Learning in 21st Century
Universities. Atlanta, GA : Georgia Institute of
Technology.
Heutte, J., Fenouillet, F., Kaplan, J., Martin-Krumm, C. and
Bachelet, R. (2016). The EduFlow model – Ac
ontribution toward the study of optimal learning
environments. In, L. Harmat, F. Ø. Andersen, F. Ullén,
J. Wright and G. Sadlo (dir.). Flow Experience :
Empirical Research and Applications (p. 124-143).
Cham, Suisse : Springer.
Heutte, J., Fenouillet, F., Martin-Krumm, C., Boniwell, I.,
and Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2016). Proposal for a
conceptual evolution of the flow in education
(EduFlow) model. Proceedings of 8th European
Conference on Positive Psychology (ECPP 2016),
Angers, France.
A Flow Measurement Instrument to Test the Students’ Motivation in a Computer Science Course
503

Hinton, P. R., McMurray, I., and Brownlow, C. (2014).
SPSS explained.[online] Routledge.
Jackson, S. A., and Eklund, R. C. (2002). Assessing flow in
physical activity: The Flow StateScale-2 and
Dispositional Flow State Scale-2. Journal of Sport and
Exercise Psychology, 24, 133–115.
Kaiser, H. F. (1974). An index of factorial simplicity.
Psychometrika, 39(1), 31-36.
Keller, J., Ringelhan, S. and Blomann, F. (2011). Does
skills-demands compatibility result in intrinsic
motivation? Experimental test of a basic notion
proposed in the theory of flow-experiences. Journal of
Positive Psychology, 6, 408-417
Mesurado, B., Richaud, M.C. and Mateo, N.J. (2016).
Engagement, Flow, Self-Efficacy, and Eustress of
University Students: A Cross-National Comparison
Between the Phillipines and Argentina. Journal of
Psychology, 150, 281-299
Nakamura, J. (1988). Optimal experience and the uses of
talent. In M. Csikszentmihalyi and I. S.
Csikszentmihalyi (Eds.), Optimal experience:
Psychological studies of flow in consciousness (pp.
319-326). New York, NY, US: Cambridge University
Press.
Novak, T. P., Hoffman, D. L., and Yung, Y. F. (2000).
Measuring the flow construct in online environments:
A structural modeling approach. Marketing Science,
19(1), 22–42.
Oertig, D., Schüler, J., Brandstätter, V., and Augustine, A.
A. (2014). The Influence of Avoidance Temperament
and Avoidance‐ Based Achievement Goals on Flow.
Journal of personality, 82(3), 171-181.
Palmer, D. (2007), What is the best way to motivate in
science teaching. The Journal of the Australian Science
Teachers Association. 53(1).
Preckel, F., Götz, T., and Frenzel, A. (2010). Ability
grouping of gifted students: Effects on academic self‐
concept and boredom. British Journal of Educational
Psychology, 80(3), 451-472.
Rheinberg, F. and Engeser, S. (2012). Motivational
competence. In D. Leontiev (Dir.) Motivation,
consciousness, and self- regulation (pp. 79-87). New
York, NY: Nova Science Publishers
Rheinberg, F., Vollmeyer, R., and Engeser, S. (2003). Die
Erfassung des Flow-Erlebens. Diagnostik von
Motivation und Selbstkonzept, 261–279.
Richer, S. F., and Vallerand, R. J. (1998). Construction et
validation de l’échelle du sentiment d’appartenance
sociale (ÉSAS). European review of applied
psychology, 48(2), 129-138.
Salanova, M., Bakker, A. B., and Llorens, S. (2006). Flow
at Work: Evidence for an Upward Spiral of Personal
and Organizational Resources. Journal of Happiness
Studies, 7(1), 1-22
Salanova, M., Rodriguez-Sanchez, A. M., Schaufeli, W. B.,
and Cifre, E. (2014). Flowing Together: A Longitudinal
Study of Collective Efficacy and Collective Flow
Among Workgroups. The Journal of Psychology, 148
(4), 435-455
Schwarzer, R., and Jerusalem, M. (1995). Generalized Self-
Efficacy scale. In J. Weinman, S. Wright, and M.
Johnston, Measures in health psychology: A user’s
portfolio. Causal and control beliefs (pp. 35-37).
Windsor, UK: NFER-NELSON.
Shernoff, D. J., Csikszentmihalyi, M., Schneider, B., and
Shernoff, E. S. (2003). Student engagement in high
school classrooms from the perspective of flow theory.
School Psychology Quarterly, 18(2), 158–176.
Weiner, B. (1992). Human Motivation: Metaphors,
Theories, and Research. Sage Publications Inc.,
Newbury Park, London.
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
504
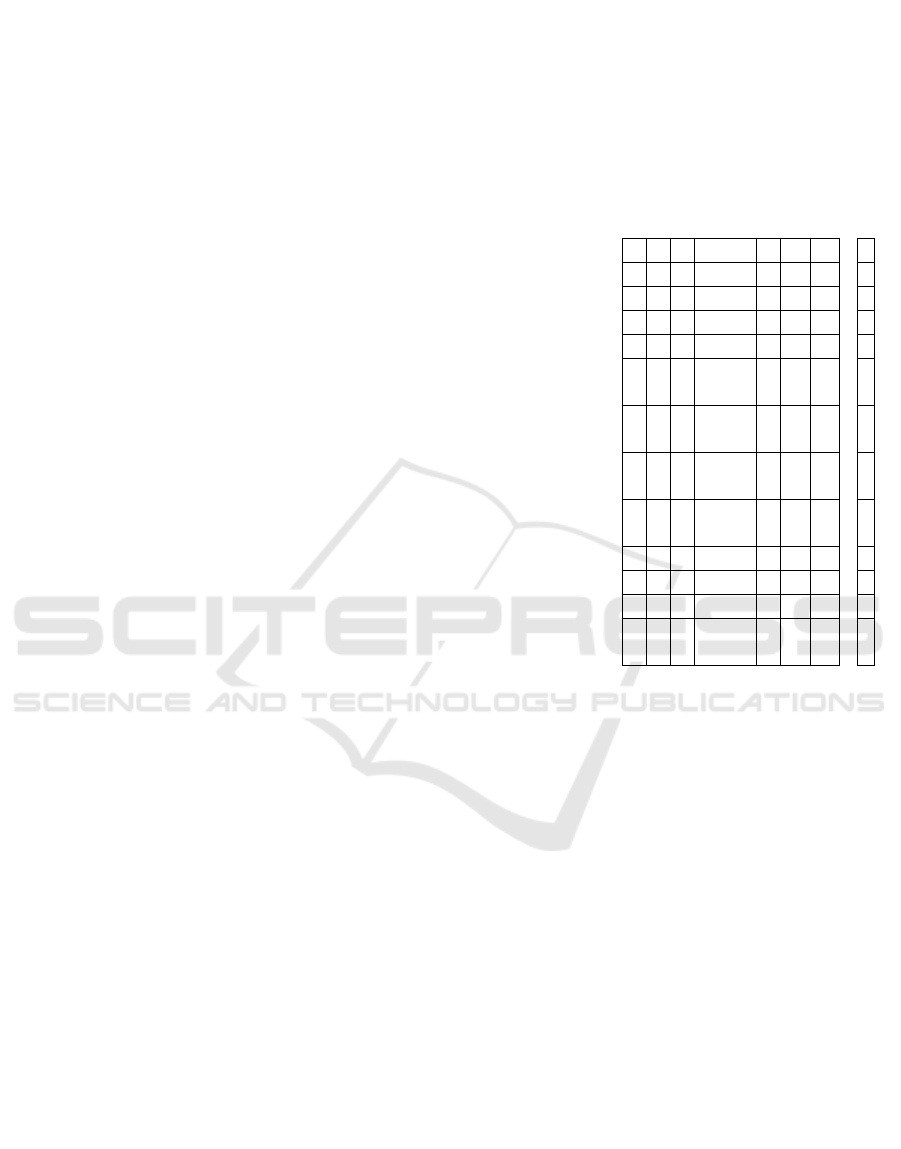
APPENDIX: EduFlow
Read each sentence carefully and answer, on the scale opposite, by checking a number that best
corresponds to what you think.
In general as part of activities related to the Research in Computing course...
Not
at
all
Partly
Very
much
I
don't
know
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
FlowD1a
I trust my ability to meet the high demands of the situation.
FlowD2a
I am wholly absorbed in what I am doing
FlowD3a
I don’t care about what others may think of me.
FlowD4a
I have the feeling I am living a very exciting experience.
FlowD1
b
I feel completely in control of my actions
FlowD2
b
I am deeply focused on what I am doing.
FlowD3
b
I am not concerned about the judgement of others.
FlowD4
b
This activity brings me a sense of well-being.
FlowD1c
At each step, I know exactly what I have to do
FlowD2c
I am losing track of time.
FlowD3c
I am not worried about what others might think of me.
FlowD4c
When I talk about this activity, I feel such a deep emotion that
I want to share it.
FlowD1: Cognitive control
FlowD2: Immersion and Time transformation
FlowD3: Loss of self-consciousness
FlowD4: Autotelic experience (well-being rooted in the
activity itself)
Note : FlowD1+FlowD2+FlowD3 = Cognitive absorption
Note that the elements written in red were only visible for the
teacher and the learning psychologist.
Please use this reference to cite the Flow in Education scale
(EduFlow)
Heutte, J., Fenouillet, F., Martin-Krumm, C., Boniwell, I., and Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2016).
Proposal for a conceptual evolution of the flow in education (EduFlow) model. 8th European
Conference on Positive Psychology (ECPP 2016), Angers, France.
A Flow Measurement Instrument to Test the Students’ Motivation in a Computer Science Course
505
