
Performance Evaluation of "Dynamic Double Trickle Timer
Algorithm" in RPL for Internet of Things (IoT)
Muneer Bani Yassein, Ismail Hmeidi, Haneen Shehadeh, Waed Bani Yaseen, Esra’a Masadeh,
Wail Mardini, Yaser Khamayseh and Qanita Bani Baker
Department of Computer Science, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid, Jordan
{masadeh, hmeidi, hhshehadeh16, wabaniyaseen17, emasadeh, mardini, yaser, qmbanibaker}@ just.edu.jo
Keywords: Internet of Things, LLN, Trickle Timer, RPL Protocol.
Abstract: Internet of Things (IoT) is a modern technology which used to support a variety of domains and applications
in life. It is based on connecting various devices which can communicate with each other without the need
for human intervention. Low Power and Lossy Networks (LLN), which already used IOT techniques, suffer
from limited energy and resources. Special protocols have been designed for LLN, like RPL which uses the
Trickle Timer algorithm, it turns to the act as a router and organizer for transmission of messages in the
network. However, the trickle algorithm suffers from performance deficiency problems such as prolonged
time and high power consumption. Therefore, there are such efforts to develop Trickle Timer algorithm to
solve performance shortcomings in the algorithm. This work is an attempt to enhance the trickle timer
algorithm to overcome delay and energy consumption problems, using dynamic doubling technique.
Researchers used Cooja 2.7 simulator to evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm by using several
metrics: packet delivery ratio, convergence time and power consumption. The simulation examined under
different scenarios. It also showed better results in performance and lower energy consumption of the
proposed algorithm.
1 INTRODUCTION
Internet of Things (IoT) is a technology that based on
any object in life which enable to communicate with
other objects and formation of wireless networks with
each other; in other words, they communicate with
each other and exchange information without the
need for human intervention (Madakam, 2015).
These objects need sensors, to be connected with each
other within wireless Sensor networks (Madakam,
2015). This technology has opened up an area for
many services and applications in various fields such
as healthcare systems, agriculture systems, smart
cities systems, and so on. Low Power and Lossy
Networks (LLN), are one form of networks which
used IOT techniques. Routing Protocol for Low
Power and Lossy Networks (RPL) is a routing
protocol for LLN, RPL which used to choose the best
path to transfer data within the network by using IPV6
distance vector proactive routing protocol (Winter et
al., 2012)(Abuein et al., 2016). RPL consist of a set
of algorithms, each algorithm has specific tasks. The
main algorithm in RPL is the trickle timer algorithm.
The major goal of the trickle timer algorithm is to
manage the transmission process in the network,
while trickle organizes and routes the data between
nodes in the network in an efficient manner to reduce
the collision between the data during the messaging
in the network, and to reduce the dissemination of
messages that do not need to resent as repeated
messages in the network. This is done by using two
mechanisms. The first one when an asymmetric state
occurs in the network, the algorithm increases the
signaling rate of control and return to the harmonic
mode in the network. The second one when repeating
the same message in the network and nodes aren't
longer needed to it; because it's connected to its
neighbors, then the algorithm suppresses its
transmission and this helps to reduce the messages
spread to the network and the provision of energy
(Djamaa and Richardson, 2015). Trickle timer
algorithm assigns the main interval for each node in
the network, this main interval starts from lmin and
ends at Imax, lmin and Imax are variables. The node
divides its own main interval to a group of
subintervals, each subinterval starts from Istart and
ends at Iend, Istart and Iend are variables. The start
of the subinterval is at Istart = Imin and it ends with
430
Yassein, M., Hmeidi, I., Shehadeh, H., Yaseen, W., Masadeh, E., Mardini, W., Khamayseh, Y. and Baker, Q.
Performance Evaluation of "Dynamic Double Trickle Timer Algorithm" in RPL for Internet of Things (IoT).
DOI: 10.5220/0007780004300437
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security (IoTBDS 2019), pages 430-437
ISBN: 978-989-758-369-8
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Iend = Istart* 2 as shown in (Yassein and Aljawarneh,
2017). The execution starts from the first subinterval
in the node, when the first subinterval finishes, next
subinterval starts, and so on until ends up with all
subintervals when the timer arriving into Imax value
(Yassein et al., 2016), as shown in below Figure 4.
Figure 1: Standard Trickle Algorithm for Each Node
(Yassein and Aljawarneh, 2017).
The standard trickle algorithm has three basic
parameters:
1. Imax: maximum interval size
2. Imin: minimum interval size
3. K: redundancy constant
Furthermore, three variables are maintained by
the algorithm (Levis et al., 2011):
1. I: size of the current interval
2. C: counter
3. T: specific time within the current
interval
Whatever, the general goal Standard Trickle
algorithm provides flow control of messages, by
sending Hello messages. The main problem of the
trickle timer algorithm is in the short listen period,
that maybe not enough to receive all message requests
from neighbors. There are some solutions that
developed to solve this problem, but these solutions
resulted in greater consumption of power and time.
Therefore, the studies have continued on the
algorithm to reduce the consumption of resources like
power and time, especially since this algorithm
supports networks with limited resources. This study
is an attempt to improve the performance of the
trickle timer algorithm. The proposed idea has
developed an elastic algorithm that assigns the
resources according to the node need, as resulted to
reduce energy consumption and time to receive and
transmit messages.
This paper is organized as follows: Section II
provides an overview of related work. Section III
presents the proposed dynamic double trickle timer
algorithm. Section IV shows the evaluation of the
performance. Section V provides average results, and
section VI provides the conclusion and future work.
2 RELATED WORK
Tickle timer algorithm has developed to manage and
control messages deployment in wireless sensor
networks. There are a lot of studies which focused on
enhancing the performance of the trickle timer
algorithm, to achieve optimal messages deployment
between nodes, especially in the low power and the
lost network's environment.
The authors in (Lin and Wang, 2015) proposed to
change default parameters values when
predetermined threshold value change the remaining
power in the node change to be less than a threshold
value, and when network condition has changed. In
(Clausen and Herberg, 2011), the authors provided a
set of notes and experiences when building RPL
prototype products, and how to do the evaluation for
products in the real world.
In (Meyfroyt et al., 2015), the authors proposed to
use a Markov chain to manage messages broadcast
process in the network by using Markov. They proved
expectation the effect of a listen-only period and
some mathematical analysis for the network. In
(Vallati and Mingozzi, 2013)(Abdulraziq et al.,
2018), the authors provided to perform an evaluation
for RPL by using different Trickle parameters. The
result was in the nondeterministic nature which leads
to select a non-optimal path.
The authors of (Meyfroyt, 2013) (Park et al.,
2016) (Shehadeh et al., 2018) studied the
performance for the trickle timer algorithm based on
parameter settings, they build mathematical models
and analyze it. In (Meyfroyt et al., 2015) the authors
continued to explore and discover in computing for a
wireless sensor network.
The authors in (Meyfroyt et al., 2015) (Bani
Yassein et al., 2018) detected the problem in load
balancing between nodes inside the network, also
there is no main cause to assign default parameters
values for suppression mechanism, and they proposed
to assign the suppression mechanism based on node
density.
In (Ghaleb et al., 2015) (Yassein et al., 2017)
(Yassein and Aljawarneh, 2017), the authors focused
on a short listen problem in the trickle timer
algorithm, they proposed a new version of the trickle
to solve a Short-listen problem without a listen-only
period. In (Ghaleb et al., 2016) (Abuein et al., 2016),
Performance Evaluation of "Dynamic Double Trickle Timer Algorithm" in RPL for Internet of Things (IoT)
431

the authors proposed a new version of trickle called
Trickle-Plus which increase elastic property in
parameters value selection, to reduce time
convergence and power consumption with better
performance.
The authors of (Vučinić et al., 2017), the authors
proposed a fairness problem solution, to achieve load
balancing between all nodes with keeping the whole
message count. The proposed idea is based on two
steps. The first step is by simulating the network to
detect parameters performance, and the second step is
by building a new algorithm to adapt the redundancy
parameter to achieve high load balancing. Recently,
in (Yassein and Aljawarneh, 2017) the authors
proposed elastic trickle algorithm to fix listen to the
only problem, the proposed algorithm provided an
elastic selection for listen-only was period based on
the density of node. The result showed improvement
in convergence time and power consumption with the
same level in the packet delivery ratio.
3 DYNAMIC DOUBLE TRICKLE
TIMER ALGORITHM
The interval, in the standard trickle timer algorithm,
is divided into two halves: the listen-only period in
the first half and the second half. During listen the
only period a node stays listening and receiving
messages from their neighbors and having no ability
to transmit any message. When a new consistent
message is received during listen the only period,
there exist counter c for the node incremented by one.
After the first half of the interval has spent, a random
number t is chosen, so a node can transmit. Node first
checks if the counter c that includes the number of
receiving consistent messages is equal or greater than
a threshold value k it, the node does not transmit.
Otherwise, if counter c is less than k it transmits
messages. Then the interval is doubled.
As mentioned above in the previous sections, the
double value in trickle timer algorithm assigns as a
static value, Idouble= 2 in all cases. This concept does
not match in continuously changing environments,
especially in networks environment which has
different parameters and principles depends on the
type of network and the goal from it. Double value is
an important issue in the trickle timer algorithm
because it has an influence on the whole execution
performance. In this work, we attempt to find if there
is an actual relationship between the double value and
node status, as a number of neighbors for the node,
which called node density. Performance evaluation
for the trickle timer algorithm shows problems in
performance, like high power consumption and long
convergence time, one of these problems reasons is
static doubling value. In the trickle algorithm,
doubling value for subintervals always assigned for
two value, Idouble =2, regardless of the status of the
node if it's on high density or low density. Actually,
if the node in high density, its needs for high doubling
value, and vice versa. In the standard algorithm, in
low density when sub interval doubles to two without
need, it's caused low utility problem, and wasted
power and time.
After the executed number of experiments, we
have reached the double value was affected by the
number of neighbors for the node, which is known as
node density. The proposed algorithm has
implemented to add more dynamically to the standard
timer algorithm. In basic, the proposed algorithm
developed to provide an elastic selection for the
appropriate double value based on the node density.
The node density should be measured in each node
starts working (Yassein and Aljawarneh, 2017).
Assuming the first subinterval double value is d1,
then the second subinterval double value is d2 and so
on, and assuming the number of neighbors for the
first subinterval is n1, then the number of neighbors
for the second subinterval is n2 and so on, n1<n2<n3..
etc., that means d1<d2<d3 and so on. In other words,
whenever the number of neighbors for the node is
higher, double values that that node need is higher
also, and vice versa. This idea helps to reduce waste
in time and power, each node takes enough double
value.
But, when the node need for doubling? for each
message arrived at the node during listening only
period, the counter increase by 1, when the node
needs to transmit the message, it does the following:
its check if the neighbors count value C is less than or
equal threshold value K, if yes, transmit, if no, the
node waiting for ends the current interval and
doubling the new interval. Below is the proposed
double dynamic trickle timer algorithm.
As shown in Algorithm 1, all parameters of trickle
assign at the beginning of the main interval, the
counter (counter of consistent messages which
received) is set to zero at the beginning of each
subinterval and after an inconsistent state. After the
listen-only period is dynamically random chosen
between [I start, I end], the node will spend listening
time and checking if it is in a consistent state or
inconsistent. After listen-only period finish, trickle
check the counter c is less than the threshold value, k,
if yes, the node will transmit messages, if no and
counter c is more than or equal k value the node will
IoTBDS 2019 - 4th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
432

Algorithm 1: Dynamic Double Trickle Timer Algorithm.
Input: Imin, Imax, threshold value (K),
nodes.
Output: control message flow
Imin = 2^12, Imax = 2^20, K=1, nodes
density= 20, 40
Istart = Imin
for (Imin ; Imin < = Imax ; Imin = Imin
* Dynamic_double())
{
count=0
Iend = Istart * Dynamic_double()
for (Istart ; ⌊ Istart ⌋ < = Iend ; ⌊
Istart ⌋ +1 )
{
Receiving ( )
t = random number chosen over [ Istart
, Iend ]
Sending( )
}
Istart = Iend
}
…………………………
Dynamic_double( nodes, neighbor ,
current, min)
{
If ((neighbor > -1) && (neighbor <
nodes /6 -1)) {
I=I*2 }
Else If ((neighbor > nodes /6 ) &&
(neighbor< nodes /3-1)){
I=I*4 }
Else If ((neighbor > nodes /3 ) &&
(neighbor< nodes /2-1)){
I=I*8 }
Else If ((neighbor > nodes /2 ) ){
I=I*16 }
}
…………………………
Receiving ( )
{
if a message is the newest
{
C=C+1
else
break
}
}
………………………….
Sending ( )
{
if (C < K )
{
Transmit
else
Suppress
}
}
be suppressed message until the end of the current
subinterval and call the dynamic double function. The
interval is doubled to new subinterval by choosing
one of four classes are provided based on node
density. Below is the flowchart for the proposed
double dynamic trickle timer algorithm.
Figure 2: Proposed Double Dynamic Function.
4 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
AND DISCUSSION
This section will present the results of simulation
experiments for the proposed algorithm, dynamic
doubling algorithm, based on 3 measure parameters,
power consumption, convergence time, and packet
delivery ratio (PDR). Each measured parameter will
present two sides, a standard trickle timer algorithm,
and dynamic doubling algorithm. The simulator that
used is Cooja 2.7 on the Contiki operating system,
with random topology, and the sink placed in the
center. Densities that used is 20 and 40, each type runs
on 3 different Rx values, 20, 60, and 100, to take more
reliable average results. Table I will present the
specifications of computers that had run a simulation
on it, and parameters values that used.
Performance Evaluation of "Dynamic Double Trickle Timer Algorithm" in RPL for Internet of Things (IoT)
433

Below, it shows the simulation experiments
results, for network density=20, depending on the
three comparative parameters, convergence time,
power consumption and PDR, The same thing goes
for second network density=40.
Table 1: Simulation Parameters.
Parameter
value
Simulator
Cooja 2.7
Operating System
Contiki
Computer
8 RAM, 64 bit
Simulation Time
15 minute
Network Density
40,20 Nodes
Imin, Imax
2
12
,2
20
Respectively
Reception Ratio , Rx
20, 60, 100
Transmission Ratio, Tx
100
Transmission Rang
30
Interference Range
30
Network Topology
Randomly
Radio Medium
UDGM
Objective Function
MRHOF
4.1 Convergence Time
This section presents the result of convergence time
in simulation experiments when network density=20
and density=40, with random topology, sink in the
center location, along with different Rx values, 20,
60, and 100.
4.1.1 Density 20
Figure 3 presents the convergence time for the
proposed algorithm vs. the standard algorithm. As
shown, the standard trickle algorithm takes more
convergence time than dynamic double trickle
algorithm. The cause of this long convergence time is
when the node being in low density, its need for short
double value, but in standard algorithm always
doubling it to 2, the node uses short period and waste
the remaining time, and the node waits for the end of
this unused time.
Figure 3: Convergence time for 20 nodes with different RX
ratios.
4.1.2 Density 40
Figure 4 shows the convergence time for density= 40
nodes, as Figure 4 is shown, dynamic double also
shows a less convergence time than the standard
algorithm. Note that the whole convergence time is
less than when density was 20, the cause of that when
the number of nodes is larger, it be nearer to each
other, this helps to receive the same messages by
more neighbors.
Figure 4: Convergence time for 40 nodes with different RX
ratios.
4.2 Power Consumption
This section presents the result of power consumption
in simulation experiments when network density=20
and density= 40, with random topology, sink in the
center location, along with different Rx values, 20,
60, and 100.
4.2.1 Density 20
Figure 5 shows power consumption for density =20
nodes, as shown, when RX values under 100 and 60,
power consumption is better or almost remained the
same value of the standard algorithm. But when RX
values under 20, power consumption are worse in
IoTBDS 2019 - 4th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
434

some experiments, increase low-value on power
consumption compared with the standard algorithm.
In performance evaluation, dynamic double
considered as good, because it gives better or same
power of standard, but when RX=20, it's better to
achieve high improvement for time besides a low
increase in power.
Figure 5: Power consumption for 20 nodes with different
RX ratios.
4.2.2 Density 40
Figure 6 shows the power consumption for 40 nodes,
as Figure 6 is shown, the dynamic double algorithm
power consumption is better than or almost the same
as the standard algorithm in all different RX ratios.
Also, can be noted that the power consumption is
higher than when density=20, this is due to more
nodes need to more connections between them, this is
caused more power.
Figure 6: Power consumption for 40 nodes with different
RX ratios.
4.3 PDR
Packet delivery ratio, known as PDR, expresses of the
ratio of packets that successfully delivered, the
mathematical expression for it is:
𝑃𝐷𝑅 =
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑖𝑣𝑒
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑖𝑣𝑒 + 𝐷𝑢𝑝𝑠 + 𝐿𝑜𝑠𝑡
(1)
This section presents the result of PDR in
simulation experiments when network density=20
and density=40, with random topology, sink in the
center location, along with different Rx values, 20,
60, and 100.
4.3.1 Density 20
Figure 7 shows the PDR for 20 nodes, as shown,
under RX=100 and 40, PDR in dynamic double is
better or almost the same of the standard algorithm,
but when RX=20, dynamic double shows decreasing
in PDR. Performance evaluation for proposed
algorithm considered good, because it gives bad
results in limited cases when RX=20, just, compared
with improvement in all remaining cases. In addition,
the high improvement in time with a low decrease in
PDR when RX=20 can balance.
Figure 7: PDR for 20 nodes with different RX ratios.
4.3.2 Density 40
Figure 8 shows the PDR for 40 nodes, as shown,
under RX=100, 40 and 20, PDR in dynamic double is
better or almost the same of standard algorithm.
Performance evaluation for proposed algorithm
depends on RX value; when it equals 100, no
probability to lost packets. In overall, dynamic double
algorithm considered good.
Figure 8: PDR for 40 nodes with different RX ratios.
Performance Evaluation of "Dynamic Double Trickle Timer Algorithm" in RPL for Internet of Things (IoT)
435
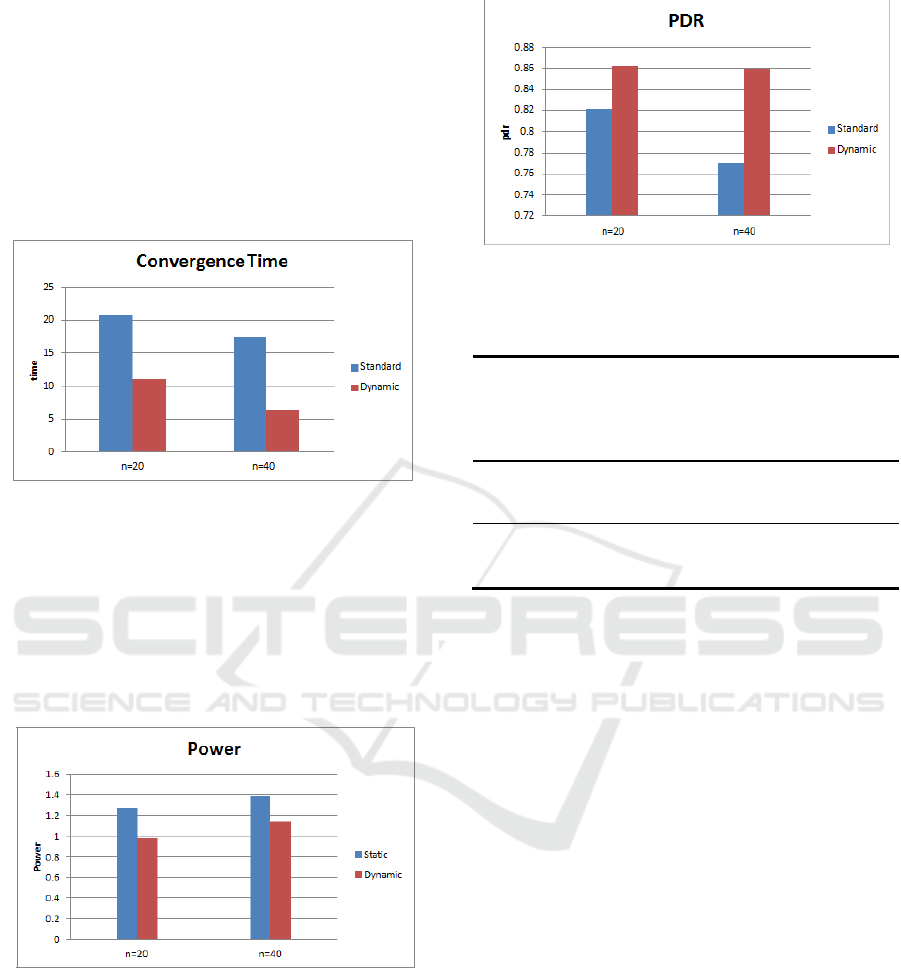
5 AVERAGE RESULTS
5.1 Convergence Time
Figure 9 shows the whole average for convergence
time of different scenarios. As shown, in overall
dynamic double algorithm best from the standard
algorithm in terms of convergence time and obvious
improvement.
Figure 9: Average convergence time.
5.2 Power Consumption
Figure 10 shows the whole average for the power
consumption of different scenarios. As shown, in
overall dynamic double algorithm best from the
standard algorithm In terms of convergence time and
simple improvement.
Figure 10: Average Power Consumption.
5.3 PDR
Figure 11 shows the whole average for the PDR of
different scenarios. As shown, in overall dynamic
double algorithm best from the standard algorithm In
terms of convergence time and simple improvement.
Table 2 shows the average comparative
parameters along with the percentage of the
enhancement.
Figure 11: Average PDR.
Table 2: Average Convergence Time using Random
Topology.
Number of
nodes
Time
enhancement
percentage
Power
enhancement
percentage
PDR
enhancement
percentage
Total
node=20
51
.8
1
Total
node=40
42
.9
.9
6 CONCLUSION
RPL is routing protocol for low-power and lossy
network (LLN), RPL consists of a set of algorithms
that provides mechanisms to execute the various tasks
of protocol, Trickle Timer algorithm one of these
algorithms. The main goal of the trickle timer
algorithm regulates the flow of control messages
within the network (Yassein and Aljawarneh, 2017).
Trickle timer algorithm still has problems and effects
on the reduce performance, like high power
consumption, long time and so on. One of the causes
is static double value in the standard algorithm. In
trickle algorithm when the node needs to double its
own subinterval, trickle assign the value of double to
2 in all cases, regardless the node needs that may lead
to load balancing problems, nodes in high density
need to higher double value than nodes in low
density. The proposed trickle algorithm based on the
dynamic concept, assign an appropriate double value
that depends on the node density rather than 2 for
each. Performance evaluation was analyzed via three
various parameters, power consumption, time and the
PDR, the experiments had executed on Cooja 2.7
simulator. Simulation results revealed that the
proposed algorithm shows better results compared
IoTBDS 2019 - 4th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
436

with the standard algorithm, the best improvements
appeared in time, then a simple degree improves in
power and PDR. The best performance was observed
when RX value is high value, and some performance
problems when being low. In general, the proposed
helps great enhancement in time, at a rate of 51%
when total node=20 and 42% when total node =40,
for power consumption, proposed helps simple
enhancement, at a rate of .8% when total node=20 and
.9% when total node =40, for PDR, the proposed
helps simple enhancement, at a rate of 1% when total
node=20 and 9% when total node =40. For the future,
we aim to study the dynamic double trickle algorithm
with different topologies and noting the performance.
Furthermore, we aim to study the dynamic double
trickle algorithm in many different objective
functions. We also aim to combine a dynamic double
algorithm with other trickle timer optimization
algorithms in order to achieve more enhancement on
power consumption and PDR.
REFERENCES
Madakam, S., 2015. Internet of things: smart things.
International Journal of Future Computer and
Communication, 4(4), p.250.
Winter, T., Thubert, P., Brandt, A., Hui, J., Kelsey, R.,
Levis, P., Pister, K., Struik, R., Vasseur, J. P. and
Alexander, R., 2012. RPL: IPv6 routing protocol for
low-power and lossy networks (No. RFC 6550).
Djamaa, B. and Richardson, M., 2015. Optimizing the
trickle algorithm. IEEE Communications Letters, 19(5),
pp.819-822.
Yassein, M. B. and Aljawarneh, S., 2017. A new elastic
trickle timer algorithm for Internet of Things. Journal
of Network and Computer Applications, 89, pp.38-47.
Yassein, M. B., Aljawarneh, S. and Ghaleb, B., 2016,
September. A new dynamic trickle algorithm for low
power and lossy networks. In 2016 International
Conference on Engineering & MIS (ICEMIS) (pp. 1-6).
IEEE.
Levis, P., Clausen, T., Hui, J., Gnawali, O. and Ko, J., 2011.
The trickle algorithm (No. RFC 6206).
Lin, Y. W. and Wang, P. H., 2015. Performance study of
an adaptive Trickle scheme for wireless sensor
networks. In Ubiquitous Computing Application and
Wireless Sensor (pp. 163-173). Springer, Dordrecht.
Clausen, T. H. and Herberg, U., 2011. Some considerations
on routing in particular and lossy environments
(Doctoral dissertation, INRIA).
Meyfroyt, T. M., Borst, S. C., Boxma, O. J. and Denteneer,
D., 2015. On the scalability and message count of
Trickle-based broadcasting schemes. Queueing
Systems, 81(2-3), pp.203-230.
Vallati, C. and Mingozzi, E., 2013, October. Trickle-F: Fair
broadcast suppression to improve energy-efficient route
formation with the RPL routing protocol. In 2013
Sustainable Internet and ICT for Sustainability
(SustainIT) (pp. 1-9). IEEE.
Meyfroyt, T. M. M., 2013. Modeling and analyzing the
Trickle algorithm. MsC, Eindhoven University of
Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
Park, J. J. J. H., Pan, Y., Chao, H. C. and Yi, G., 2016.
Ubiquitous Computing Application and Wireless
Sensor. Springer.
Meyfroyt, T. M., Stolikj, M. and Lukkien, J. J., 2015, June.
Adaptive broadcast suppression for Trickle-based
protocols. In 2015 IEEE 16th International Symposium
on A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia
Networks (WoWMoM) (pp. 1-9). IEEE.
Ghaleb, B., Al-Dubai, A. and Ekonomou, E., 2015, October.
E-trickle: Enhanced trickle algorithm for low-power and
lossy networks. In 2015 IEEE International Conference
on Computer and Information Technology; Ubiquitous
Computing and Communications; Dependable,
Autonomic and Secure Computing; Pervasive
Intelligence and Computing (pp. 1123-1129). IEEE.
Ghaleb, B., Al-Dubai, A., Ekonomou, E., Paechter, B. and
Qasem, M., 2016, April. Trickle-plus: Elastic trickle
algorithm for low-power networks and Internet of
Things. In 2016 IEEE Wireless Communications and
Networking Conference Workshops (WCNCW) (pp.
103-108). IEEE.
Vučinić, M., Król, M., Jonglez, B., Coladon, T. and
Tourancheau, B., 2017. Trickle-d: High fairness and
low transmission load with dynamic redundancy. IEEE
internet of things journal, 4(5), pp.1477-1488.
Shehadeh, H., Mardini, W., Yassein, M. B., Allah, D. H.
and Yaseen, W.B., 2018, June. Hop count dynamic
double trickle timer algorithm use case: data
aggregation in smart green house. In Proceedings of the
2nd International Conference on Future Networks and
Distributed Systems (p. 40). ACM.
Bani Yassein, M., Aljawarneh, S. and Al-Saad, M. 2018.
An Efficient On-Demand Constrained Application
Protocol for Internet of Things. International Journal
on Communications Antenna and Propagation
(IRECAP), 8(3), p.232.
Abdulraziq, R., Yassein, M. B. and Aljawarneh, S., 2018.
The Rise of Big Data, Cloud, and Internet of Things:
Three Trends to Watch. In Critical Research on
Scalability and Security Issues in Virtual Cloud
Environments (pp. 201-222). IGI Global.
Yassein, M. B., Aljawarneh, S., Al-Rousan, M., Mardini,
W. and Al-Rashdan, W., 2017, November. Combined
software-defined network (SDN) and Internet of Things
(IoT). In 2017 International Conference on Electrical
and Computing Technologies and Applications
(ICECTA) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Abuein, Q. Q., Yassein, M. B., Shatnawi, M. Q., Bani-
Yaseen, L., Al-Omari, O., Mehdawi, M. and Altawssi,
H., 2016. Performance evaluation of routing protocol
(RPL) for internet of Things. Performance Evaluation,
7(7).
Performance Evaluation of "Dynamic Double Trickle Timer Algorithm" in RPL for Internet of Things (IoT)
437
