
A Mobile Health Application to Assist Health Professionals: A Case
Study in a Portuguese Nursing Home
Márcia Esteves
1 a
, Marisa Esteves
2 b
, António Abelha
2 c
and José Machado
2 d
1
Universidade of Minho, Campus Gualtar, 4470 Braga, Portugal
2
Algoritmi Research Center, University of Minho, Campus Gualtar, 4470 Braga, Portugal
Keywords: Health Information and Communication Technology, Mobile Health, Health Professionals, Elders, Nursing
Home, Ethical Issues in Medicine.
Abstract: The rapidly aging population has been a matter of concern over years since this problematic has been posing
several challenges to healthcare systems worldwide. In Portugal, which is one of the countries with the largest
aging population, nursing homes have been getting a higher demand, and health professionals are overloaded
with work. Furthermore, the fact that few nursing homes use health information and communication
technology (ICT) resorting to paper to record information and clinically manage their residents is a
tremendous problem, since this method is more prone to errors and time-consuming. Thus, this paper proposes
the design and development of a mobile application for health professionals working in a Portuguese nursing
home with the intention of assisting them at the point-of-care, by recording and providing all the necessary
information, and helping them to schedule, perform, and digitally record their tasks. This solution will help
health professionals to provide better care, by reducing time-waste and errors, and, consequently, to improve
elders’ quality of life. A mobile solution was chosen since a hand-held device, which can be used anywhere
and anytime, is able to give access and store all the needed information at the point-of-care.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the last few years, the rapidly aging population
has been a matter of concern, namely because of the
challenges this situation is posing to healthcare
systems in many countries all over the world (Kuo et
al. 2016, Mostaghel 2016). In fact, the statistics
regarding the aging population are alarming:
comparatively to the growth of the whole population,
it is estimated the elderly population is growing twice
as fast (Mostaghel 2016). Consequently, this
demographic change leads to several problems,
namely to the increase in the costs of elderly care
(Mostaghel 2016) and of the number of elders in
nursing homes.
In Portugal, which is one of the countries with the
largest aging population in the world (UN DESA
2015), the increasing number of elders in nursing
homes has been one of the major challenges caused
by the aging population (Pereira 2018, RTP 2019). In
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4770-5502
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9710-847X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6457-0756
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4121-6169
fact, finding a place in a nursing home in Portugal has
been a tremendous challenge for several elders since
the demand is higher, and the vacancies are filling up
quickly (Pereira 2018, RTP 2019). On the order hand,
health professionals are overloaded with work since
the number of elderly people is high compared to the
number of health professionals (Borja-Santos 2015,
DN/Lusa 2018), which can lead to the decrease of the
quality of the nursing care delivered, and, more than
not, nursing homes use rudimentary methods, i.e.
paper, to record information and clinically manage
residents, which can be time-consuming (Alexander
and Wakefield 2009, Broughton et al. 2013).
Therefore, there is an urgent need to face these
challenges and improve elders’ quality of life and the
care delivered in nursing homes. Thus, with these
problems in mind, this project emerged and consists
in designing and developing a mobile application for
health professionals, i.e. nurses and doctors, working
in a Portuguese nursing home that can assist them at
338
Esteves, M., Esteves, M., Abelha, A. and Machado, J.
A Mobile Health Application to Assist Health Professionals: A Case Study in a Portuguese Nursing Home.
DOI: 10.5220/0007809203380345
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2019), pages 338-345
ISBN: 978-989-758-368-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

the point-of-care and help them to schedule, perform,
and digitally record their tasks.
In order to have a better understanding of the
relevance of this project, it is essential to present the
main challenges faced by the nursing home for which
this project is being developed. Firstly, there is no
electronic health records to clinically manage the
residents, whereby all the information is gathered in
papers which make the record and the access to this
information a lot more time-consuming, especially at
the point-of-care, since the professionals constantly
need to go back to the nursing station in order to
retrieve or record information. This situation makes
the risk of misplacing, losing, or forgetting
information much higher.
Moreover, there are few health professionals
comparatively to the high amount of elderly people.
Lastly, due to the lack of time and the overload of
work experienced by the health professionals, some
clinical information is not properly or not at all
recorded. Thus, in order to solve these problems,
there is a need to design and develop a solution that
can help these health professionals at the point-of-
care and, subsequently, enhance the care delivered
and the elders’ quality of life.
Therefore, the proposed solution consists of a
mobile application that would allow health
professionals to:
Have access and manage the personal and
clinical information of the residents at the
point-of-care as well as add and disable
residents when necessary;
Create clinical and nursing notes, and consult
the clinical and nursing notes’ history of each
resident;
Schedule nursing interventions, e.g. wound
care, nasogastric tube and urinary catheters
replacement, periodic evaluations, and
tracheostomy care, among others, and confirm
their execution;
Record the evaluations made by them, and
consult the history of these evaluations for each
resident;
Record new wounds and their treatment and
evolution via images and observations, and
consult the wound history of each resident;
Consult the history of the medical records of
each resident, and add new medical records;
Have a simplified plan of the nursing home to
identify which resident is in each room and bed.
The novelty of this project lies in the fact that few
nursing homes use health ICT, which consists in any
form of electronic solution that allows to retrieve,
store, manage, manipulate, and transmit digital
information in a healthcare setting, despite their great
potential and well-known advantages (Alexander and
Wakefield 2009, Broughton et al. 2013, Ko et al.
2018, Wei and Courtney 2018). In fact, they can
enhance the quality of care, reduce time-waste, e.g.
by accessing and recording the information at the
point-of-care, and improve the sharing of
information, e.g. by making the information more
accessible and legible (Alexander and Wakefield
2009, Rouleau et al. 2015). Moreover, the lack of
literature and of an integrated body of knowledge on
the use of ICT in nursing homes show that there is
still much work that needs to be done in this area.
Concerning the structure of this paper, the state of
the art related to this project is presented in Section 2.
Subsequently, Section 3 discusses the research
strategies selected to design and develop this project.
Thereafter, in Section 4, a brief description of the case
study, i.e. of the Portuguese nursing home for which
the proposed solution is being developed, is presented
with the intention of having a better understanding of
the main challenges encountered in the institution
and, thus, affirm and validate the relevance of this
project. Then, in Section 5, the results achieved are
presented. Finally, to conclude this paper, a
discussion of the results attained is presented in
Section 6, and, lastly, in Section 7, the main
conclusions of the project are explained, and future
work is suggested.
2 STATE OF THE ART
2.1 Mobile Health
Over the last few years, the implementation and rapid
expansion of mobile technology, which refers to all
the technology that can be used “on-the-move”, have
been impacting several industries, and the healthcare
industry is not an exception (Aungst 2013, Ventola
2014). In fact, the use of mobile health (mHealth), i.e.
of mobile devices and applications in a health and
clinical context (Nouri et al. 2018), to help health
professionals to execute their daily tasks, namely to
manage and monitor patients, to access and manage
health records and other types of data, and to enhance
the decision-making process, among others, has been
transforming several aspects of the health industry
(Prgomet et al. 2009, Ventola 2014, O’ Connor and
O’ Reilly 2018).
In this context, the use of mobile devices in
healthcare settings has been rapidly growing and,
consequently, the development of mobile
applications for these devices, thus leading to the
A Mobile Health Application to Assist Health Professionals: A Case Study in a Portuguese Nursing Home
339

rapid integration of mobile devices in healthcare
settings (Ventola 2014, O’ Connor and O’ Reilly
2018). Furthermore, the adoption of mobile
technology by health professionals can be explained
by the need to have a better and easier communication
and access to the information at the point-of-care
since a single device, which is portable, light, and
small, can gather and give access to all the needed
information anywhere and anytime (Prgomet et al.
2009, Ventola 2014, O’ Connor and O’ Reilly 2018).
In fact, mHealth has been proving to be quite
promising and to offer several benefits, such as
(Prgomet et al. 2009, West 2012, Ventola 2014):
Faster accessibility and better management of
the data since all the data is gathered in a single
source, which can be used anywhere and at the
time of need, making the access to information
much more convenient;
Faster and better decision-making process,
since it provides access to information at the
point-of-care where the decisions are being
made, thus leading to a lower error rate;
And, consequently, an enhancement of the
quality of the care delivered and of the elders’
life, among other advantages.
In some cases mobile applications are developed
without truly understanding, assessing, and meeting
the needs of health professionals, thus resulting in
their under-utilization (Nouri et al. 2018, O’ Connor
and O’ Reilly 2018). Therefore, a better evaluation of
the needs of health professionals should be done
before developing these applications. Nevertheless,
the benefits of mHealth are undeniable and a higher
investment should be done in this area since it can
improve the quality of the care delivered and of the
patients’ quality of life.
2.2 Ethical Issues in Medicine
Without a doubt, the use of health ICT and mHealth
in healthcare settings provides many benefits to the
clinical practice having the potential to enhance the
care delivered, as mentioned previously. However,
despite the advantages offered by these technologies,
challenges and issues may arise from the use of
solutions based on them. In fact, one of the main
challenges associated with the introduction of any
form of technology in healthcare settings are ethical
issues.
In this context, one of the problems that can be
pointed is the fear and distrust that the confidentiality
and privacy of the electronic health records and data
of the patients are compromised and not guaranteed,
since, comparatively to the traditional paper-based
method, technological advancements made access to
data and the break of the privacy of health
information easier (Wallace 2015, Nouri et al. 2018).
Additionally, despite the many advantages and
benefits provided by mHealth, some health
professionals still remain hesitant regarding its use,
since mHealth applications are currently being used
without having a complete understanding about their
effectiveness, accuracy, quality, and associated risks
(Ventola 2014, Nouri et al. 2018).
Therefore, during the design, development, and
implementation of mHealth applications, a set of
best-practice standards should be thoughtfully
followed in order to ensure their quality, accuracy,
and safety (Misra et al. 2013, Ventola 2014, Nouri et
al. 2018). Moreover, after their development, these
applications should be subjected to a proper and
rigorous set of validation and evaluation methods as
a way to guarantee their quality, accuracy, correct
use, safety, and importance in a healthcare setting
(Misra et al. 2013, Ventola 2014, Nouri et al. 2018).
3 RESEARCH STRATEGIES
In order to have well-defined standards and an
organized path to follow, this project is being
sustained by a set of methods with the intention of
ensuring its success. Firstly, extensive research was
made with the aim of identifying a broad range of
options. Then, after analysing the available options, a
choice was made based on the method that was the
most effective to meet the established objectives and
adequate according to the scope of this project.
Therefore, the main research strategy that is being
followed during the course of this project is design
science research (DSR). DSR was chosen since it is
suitable for ICT research projects, which is the case
of this study (Hevner et al. 2004, Peffers et al. 2007).
The main purpose of the DSR strategy is to create and
evaluate objects know as artefacts, i.e. solutions, in
order to solve organizational problems (Hevner et al.
2004). Thus, in a simplified way, DSR corresponds to
a rigorous science research method that offers a set of
techniques, principles, and procedures that must be
followed in order to design and develop successful
solutions (Peffers et al. 2007).
The DSR methodology can be divided into the
steps shown in Figure 1.
In order to perform the first three steps – “Problem
Identification and Motivation”, “Definition of the
Solution’s Objectives”, and “Design and
Development of the Solution” – focus groups, semi-
structured interviews, and questionnaires were made
ICT4AWE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
340

Figure 1: Schematic representation of the steps composing
the design science research strategy.
with the health professionals working in the nursing
home for which this project is being developed. The
information given by these professionals was
fundamental and valuable since it allowed to identify
and understand the main challenges encountered by
them. Thus, it was then possible to identify and
motivate the problems that needed to be solved, to
define the objectives and benefits of the proposed
solution, and, finally, to design the architecture of the
solution, which is currently being developed.
Additionally, observation of the case study was also
necessary since it allowed to have a better
understanding of the conditions of the nursing home.
The fourth and fifth steps – “Demonstration” and
“Evaluation”, respectively – are currently being
executed: the design of the proposed solution was
demonstrated to the target audience, i.e. the health
professionals, and as the solution is being developed,
the professionals are being consulted to assess if the
established objectives are being met and if changes
need to be done. It must be mentioned that in order to
evaluate the usefulness and accuracy of the proposed
solution, a proof of concept (PoC) was made.
Finally, the last step of the DSR methodology –
“Communication” – is currently being performed.
This step consists of diffusing the importance of the
problem and the novelty of the proposed solution,
which is the aim of this paper.
It must be mentioned that during all stages of the
design and development of this project, ethical issues
are being taken into account and safeguarded to
guarantee the quality, accuracy, and safety of the
solution and that confidentiality issues do not arise.
4 CASE STUDY
The case study for which the proposed solution is
being developed corresponds to a Portuguese nursing
home, which is being managed by a Portuguese
hospital. Thus, in this section, a brief description of
the case study will be presented in order to identify
the main issues of the nursing home and the
challenges faced by the health professionals.
As mentioned before, focus groups, semi-
structured interviews, and questionnaires were
performed with the health professionals in order to
identify their needs and the main challenges faced by
them. Additionally, the case study was subjected to
observation to assess the conditions of the nursing
home. Thus, it is possible to identify a set of
challenges and issues that need to be solved:
The nursing home does not use health ICT or
any other form of technological progress. There
is only one computer in the nursing station, and
it is not being used to record or document
clinical information. Additionally, there are not
electronic health records or any other form of
digital information to clinically manage the
residents. Therefore, the professionals use
handwritten charts and medical records, and all
the information is stored and recorded in
papers. This situation makes the access and
record of information a lot more time-
consuming, especially at the point-the-care,
since the professionals constantly need to go
back to the nursing station in order to retrieve
or document information. On the other hand,
this situation makes the risk of losing,
misplacing, forgetting, and documenting the
information in the wrong place higher;
All the tasks performed by the health
professionals are scheduled and documented in
handwritten charts or boards, which can lead to
errors since its more confusing and less
organized than to digitally schedule and
document tasks;
There is no wireless internet connection in the
nursing home. The only internet connection
available is in the nursing station where the
computer is located. This situation makes it a
lot more difficult to implement any kind of
mHealth solution since the nursing home does
not have the necessary needs;
A Mobile Health Application to Assist Health Professionals: A Case Study in a Portuguese Nursing Home
341
There are few health professionals
comparatively to the high amount of elderly
people. Thus, at times, the health professionals
are overloaded with work. This situation
combined with the fact that all the information
is documented through papers poses the risk of
some clinical information not being properly or
at all recorded.
During the realization of these interviews and
focus groups, it was also mentioned that the nursing
home tried to implement a web application but
without success. This web application had the intent
of converting all the information recorded in papers
to the digital form, allowing the health professionals
to schedule tasks, document them, and record clinical
information. However, this application was
abandoned because it was time-consuming and not
user-friendly: the health professionals constantly
needed to return to the nursing station, where the
computer was, to use the application, thus spending
too much time with it, e.g. scheduling tasks and
documenting information.
Moreover, the health professionals manifested
their wish of needing a mobile application that would
allow them to be anywhere in the nursing and still
have access to information and schedule and
document their daily tasks. Therefore, there is a need
to design and develop a mobile solution, i.e. a
mHealth application, that would help these health
professionals at the point-of-care by allowing them to
have access, document, consult, and manipulate
information anywhere in the nursing home and,
subsequently, enhance the care delivered and the
elders’ quality of life.
5 RESULTS
As mentioned previously, the nursing home for which
this project is being developed does not have any
form of technological progress and, naturally, any
database implemented. Therefore, before designing
the architecture of the mHealth application, a
database had to be defined to support it and to allow
the storage of the necessary data.
Thus, a MySQL database, which is a highly
secure, reliable, and scalable relational database, was
designed and created. Thereafter, once the database
created, it had to be deployed and implemented in the
server of the Portuguese hospital that is managing the
nursing home. A MySQL database was chosen
because the server was already configured for this
type of database. Additionally, it must be mentioned
that although the database has been successfully
implemented in the server, it remains to be populated
with real data, i.e. residents’ and health professionals’
information.
On the other hand, the proposed solution is being
developed using React Native, which is a JavaScript
framework that allows the development of native
mobile applications (Facebook Inc. 2019). React
Native was chosen since the same code can deploy on
both iOS and Android, thus saving a lot of time in the
development process. Moreover, React Native has an
optimal performance for mobile environments.
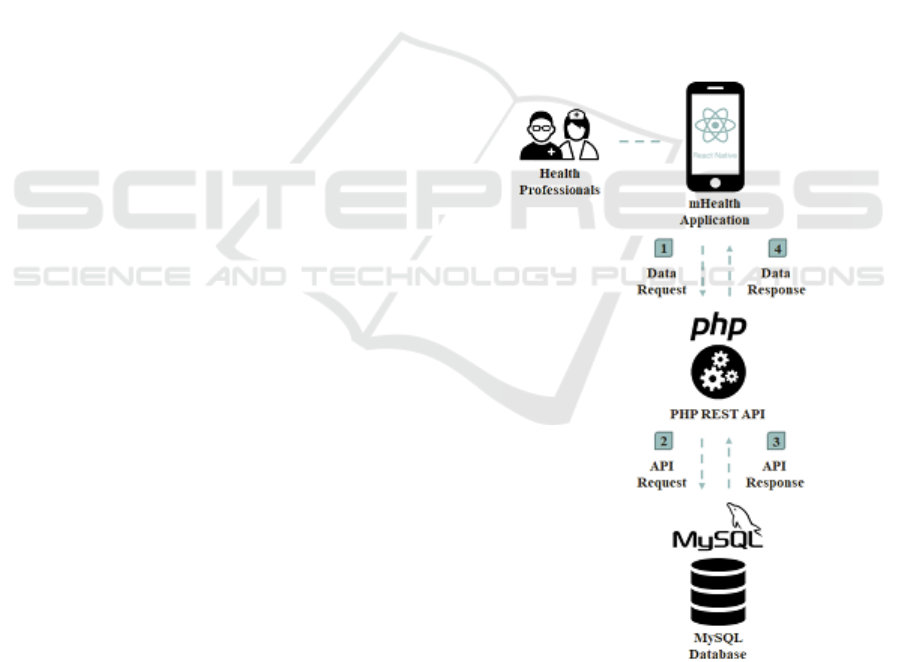
Additionally, a REST API written in PHP with
SQL queries is being developed in order to allow the
sharing of data between the frontend, i.e. the mobile
application, and the backend, i.e. the database. PHP
was chosen since the server in which the database was
implemented is only configured for this programming
language.
In Figure 2, a schematic representation of the
interactions between the different elements of the
proposed solution is presented.
Figure 2: Schematic representation of the interactions
between the different elements of the proposed solution.
Firstly, the user, i.e. the health professional, needs
to sign up for an account in the mobile application.
Then, all the data provided by the user, i.e. his login
credentials and his personal data, is stored into the
ICT4AWE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
342

database. Alternatively, if the user already has an
account, he needs to sign in into the mobile
application with his login credentials.
Once the user is successfully registered into the
application, the following features are provided to
him:
Profile: the user can have access and edit his
personal data;
Management of the residents: the user can view
and edit the personal data of each resident.
Additionally, the user can add new residents
when needed or disactivate a given resident.
Moreover, it is also possible to view and edit
the contacts of each resident as well as add and
remove contacts;
Clinical notes: if the user is a doctor, he can
create new clinical notes and consult the
clinical notes’ history of each resident.
However, if he is a nurse, the user is only able
to consult the clinical notes’ history;
Nursing notes: if the user is a nurse, he can
create new nursing notes and consult the
nursing notes’ history of each resident.
However, if he is a doctor, the user is only able
to consult the nursing notes’ history;
Management of the clinical information of the
residents: the user can consult and edit the
clinical information of each resident;
Management of wounds: the user can record
new wounds as well as consult and document
their evolution for each resident. Additionally,
the user can consult the wounds’ history of
each resident;
Periodic evaluations: the user can add a new
periodic evaluation and consult the periodic
evaluations’ history of each resident;
Periodic evaluations of the capillary blood
glucose: the user can add new periodic
evaluations of the capillary blood glucose for
residents with diabetes. Moreover, it is also
possible to consult the history of the periodic
evaluations of the capillary blood glucose of
each resident with diabetes;
Medical records: the user can add new medical
records or consult the medical records’ history
of each resident;
Planning: the user can schedule nursing
interventions for each resident;
Plan of the nursing home: the user can consult
which resident is in each room and bed;
Calendar: the user has a calendar in which he
can consult the nursing interventions scheduled
as well as cancel a nursing intervention or
confirm its execution;
Sign out: the user can sign out of his account.
6 DISCUSSION
In order to demonstrate the potential, quality, utility,
and practicality of the proposed solution, a PoC was
made. Therefore, in this section, a SWOT analysis is
performed to identify the main strengths and
weaknesses, which are internal factors, and
opportunities and threats, which are external factors,
of the proposed solution.
The main strengths of the proposed solution are
as follow:
Reduces time-waste since health professionals
can have access and record information at the
point-of-care;
Reduces errors since it decreases the risk of
misplacing, losing, or forgetting information;
Enhances the nursing care delivered and the
elders’ quality of life since less errors are being
made and health professionals have more time
to perform their tasks;
Makes the scheduling of tasks less confusing
and more organized;
Reduces the amount of paper that is being
generated with hand-written charts;
Has high usability due to its user-friendly
design with well-defined paths and decision
points and organized information;
Has high adaptability since the proposed
solution was designed to allow its easy
implementation in other nursing homes;
Has high scalability since new features can be
easily added.
However, some weaknesses can be pointed to the
proposed solution:
Need of a wireless internet connection, which
is not currently available in the nursing home;
Need of mobile devices such as mobile phones
and tablets to use the solution;
Need to populate the database with real data,
i.e. residents’ and health professionals’
information, which will require time resources;
Need to train the health professionals to use the
solution.
On the other hand, the opportunities of the
proposed solution are as follow:
Technological improvement of the nursing
home, which can lead to the demand for
improving other processes;
Elimination of the paper-based method used by
the nursing home, which is rudimentary and
more prone to errors, having clinical data
A Mobile Health Application to Assist Health Professionals: A Case Study in a Portuguese Nursing Home
343

stored in databases. This data could be used to
complement the mobile application with
business intelligence (BI) clinical indicators,
which can enhance the decision-making
process and the care delivered;
Implementation of the mobile application in
other nursing homes.
Lastly, the following threats can be highlighted
for the proposed solution:
Potential issues may arise if the necessary
needs are not provided to the nursing home,
namely if the wireless internet connectivity is
not reliable and if there are not any mobile
device. In these cases, the health professionals
would not be able to use mobile application.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In conclusion, this paper shows that, in Portugal,
nursing homes need several improvements, more
specifically, technological improvements, in order to
solve some of the problems faced by them, e.g. the
overload of work faced by health professionals. Thus,
in this context, this project emerged and consists in
designing and developing a mobile solution that
would help and assist the health professionals of a
Portuguese nursing home at the point-of-care.
As mentioned throughout this paper, with this
solution, it is intended to allow these professionals to
have access, document, consult, and manipulate
information anywhere in the nursing home.
Therefore, this solution will help to reduce time-
waste and errors made by health professionals and,
subsequently, enhance the nursing care delivered and
the elders’ quality of life.
In this paper, the architecture and the features of
the proposed solution were presented. However, as
future work, it is intended to continue the
development of the mobile application since,
currently, certain features remain to be implemented.
Thereafter, it is envisioned to populate the database
with real data, i.e. residents’ and health professionals’
information.
On the other hand, it is also planned to provide the
nursing home with the necessary needs, namely a
reliable wireless internet connection and mobile
devices such as tablets or mobile phones, for health
professionals to be able to use the mobile application.
Moreover, it is foreseen to test the application with
the health professionals to assess if the objectives are
being met and if changes need to be done.
Finally, in the future, when enough data will be
gathered throughout the use of this application, it is
hoped to complement it with BI clinical indicators
related to both the residents and the health
professionals. These indicators would help to obtain
useful knowledge to support the decision-making
process improving its outcomes, which can be proven
by previous and current work by the research team
(Esteves, Miranda, and Abelha 2018, Esteves,
Miranda, Machado, et al. 2018, Neves et al. 2018,
Esteves et al. 2019). Additionally, if the mobile
solution proves to be of quality, it is envisioned to
implement it in more nursing homes. This will be
possible since the mobile application was designed to
allow its adaptability according to the needs of similar
institutions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by FCT – Fundação
para a Ciência e Tecnologia within the Project Scope:
UID/CEC/00319/2019.
REFERENCES
Alexander, G.L. and Wakefield, D.S., 2009. Information
Technology Sophistication in Nursing Homes. Journal
of the American Medical Directors Association, 10 (6),
398–407.
Aungst, T.D., 2013. Medical Applications for Pharmacists
using Mobile Devices. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 47
(7–8), 1088–1095.
Borja-Santos, R., 2015. Falta de Profissionais de Saúde nos
Lares Coloca Idosos em Risco [online]. Available from:
https://www.publico.pt/2015/10/29/sociedade/noticia/
quase-20-dos-idosos-em-lares-cairam-pelo-menos-
uma-vez-em-meio-ano-1712731#gs.hJfTaLa5
[Accessed 20 Feb 2019].
Broughton, W., Lashlee, H., Marcum, C., and Wilson,
G.M., 2013. Health Information Technology: A New
World of Nursing Homes. Journal of Gerontology and
Geriatric Research, 2 (2).
DN/Lusa, 2018. Portugueses em Risco Devido à Falta de
Enfermeiros que Estão Exaustos [online]. Available
from: https://www.dn.pt/portugal/interior/portugueses-
em-risco-devido-a-falta-de-enfermeiros-que-estao-
exaustos---bastonaria-9075853.html [Accessed 20 Feb
2019].
Esteves, M., Abelha, A., and Machado, J., 2019. The
Development of a Pervasive Web Application to Alert
Patients based on Business Intelligence Clinical
Indicators: A Case Study in a Health Institution.
Wireless Networks, 1–7.
ICT4AWE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
344

Esteves, M., Miranda, F., and Abelha, A., 2018. Pervasive
Business Intelligence Platform to Support the Decision-
Making Process in Waiting Lists. In: Next-Generation
Mobile and Pervasive Healthcare Solutions. 186–202.
Esteves, M., Miranda, F., Machado, J., and Abelha, A.,
2018. Mobile Collaborative Augmented Reality and
Business Intelligence: A System to Support Elderly
People’s Self-care. In: Trends and Advances in
Information Systems and Technologies. Springer,
Cham, 195–204.
Facebook Inc., 2019. React Native - A Framework for
Building Native Apps using React [online]. Available
from: https://facebook.github.io/react-native/
[Accessed 20 Feb 2019].
Hevner, A.R., March, S.T., and Park, J., 2004. Design
Science in Information Systems Research. MIS
Quarterly, 28 (1), 75–105.
Ko, M., Wagner, L., and Spetz, J., 2018. Nursing Home
Implementation of Health Information Technology:
Review of the Literature Finds Inadequate Investment
in Preparation, Infrastructure, and Training. The
Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and
Financing, 55, 1–10.
Kuo, M.-H., Wang, S.-L., and Chen, W.-T., 2016. Using
Information and Mobile Technology Improved Elderly
Home Care Services. Health Policy and Technology, 5
(2), 131–142.
Misra, S., Lewis, T.L., and Aungst, T.D., 2013. Medical
Application Use and the Need for Further Research and
Assessment for Clinical Practice. JAMA Dermatology,
149 (6), 661–662.
Mostaghel, R., 2016. Innovation and Technology for the
Elderly: Systematic Literature Review. Journal of
Business Research, 69 (11), 4896–4900.
Neves, J., Vicente, H., Esteves, M., Ferraz, F., Abelha, A.,
Machado, J., Machado, J., Neves, J., Ribeiro, J., and
Sampaio, L., 2018. A Deep-Big Data Approach to
Health Care in the AI Age. Mobile Networks and
Applications, 23 (4), 1123–1128.
Nouri, R., R Niakan Kalhori, S., Ghazisaeedi, M.,
Marchand, G., and Yasini, M., 2018. Criteria for
Assessing the Quality of mHealth Apps: a Systematic
Review. Journal of the American Medical Informatics
Association, 25 (8), 1089–1098.
O’ Connor, Y. and O’ Reilly, P., 2018. Examining the
Infusion of Mobile Technology by Healthcare
Practitioners in a Hospital Setting. Information Systems
Frontiers, 20 (6), 1297–1317.
Peffers, K., Tuunanen, T., Rothenberger, M., and
Chatterjee, S., 2007. A Design Science Research
Methodology for Information Systems Research.
Journal of Management Information Systems, 24 (3),
45–77.
Pereira, A.C., 2018. Os Centros de Dia Atraem Cada Vez
Menos Idosos, mas os Lares Estão Cheios [online].
Available from:
https://www.publico.pt/2018/12/15/sociedade/noticia/c
entros-dia-atraem-menos-lares-estao-cheios-
1854827#gs.lswiFrPB [Accessed 20 Feb 2019].
Prgomet, M., Georgiou, A., and Westbrook, J.I., 2009. The
Impact of Mobile Handheld Technology on Hospital
Physicians’ Work Practices and Patient Care: A
Systematic Review. Journal of the American Medical
Informatics Association, 16 (6), 792–801.
Rouleau, G., Gagnon, M.-P., and Côté, J., 2015. Impacts of
Information and Communication Technologies on
Nursing Care: an Overview of Systematic Reviews
(Protocol). Systematic Reviews, 4 (75).
RTP, 2019. Segurança Social Encerrou 109 Lares Ilegais
em 2018 [online]. Available from:
https://www.rtp.pt/noticias/pais/seguranca-social-
encerrou-109-lares-ilegais-em-2018_v1125675
[Accessed 20 Feb 2019].
UN DESA, 2015. World Population Prospects: The 2015
Revision, Key Findings and Advance Tables. New
York: United Nations Department of Economic and
Social Affairs.
Ventola, C.L., 2014. Mobile Devices and Apps for Health
Care Professionals: Uses and Benefits. Pharmacy and
Therapeutics, 39 (5), 356–364.
Wallace, I.M., 2015. Is Patient Confidentiality
Compromised with the Electronic Health Record?
Computers, Informatics, Nursing, 33 (2), 58–62.
Wei, Q. and Courtney, K.L., 2018. Nursing Information
Flow in Long-Term Care Facilities. Applied Clinical
Informatics, 9 (2), 275–284.
West, D., 2012. How Mobile Devices are Transforming
Healthcare. Issues in Technology Innovation, 18 (1).
A Mobile Health Application to Assist Health Professionals: A Case Study in a Portuguese Nursing Home
345
