Experimental Implementation of Time-varying Input Shaping on UR
Robots
∗
Dan Kielsholm Thomsen
1,2
, Rune Søe-Knudsen
2
, David Brandt
2
and Xuping Zhang
1
1
Aarhus University Dept. of Engineering, Inge Lehmanns Gade 10, DK-8000 Aarhus C, Denmark
2
Universal Robots A/S, Energivej 25, DK-5260 Odense S, Denmark
Keywords:
Input Shaping, Industrial Robots, Time-varying Input Shaping, Configuration Dependency, Fractional Delay
Finite Impulse Response.
Abstract:
Lightweight design leads to the unwanted vibration of industrial robot manipulators. Input Shaping (IS)
has been proven to be an effective vibration suppression method. However, applying IS to suppress the
vibration of industrial robots faces a challenging problem: time-varying dynamics. To address the time-varying
dynamics of robot manipulators, this paper presents a novel and practical solution to vibration suppression
based on Time-Varying Input Shaping Technology (TVIST). Our focus in this paper is to develop a practical
implementation strategy that can be applied in discrete time. A Fractional Delay Finite Impulse Response filter
is employed to design and implement TVIST. This solution makes TVIST more useful in practice because it can
be combined with online and discrete-time trajectory generation. It can also be implemented in combination
with position control using feed-forward velocity and torque. The performance of the new approach is validated
through experimental implementation on a lightweight robot from Universal Robots A/S. Experimental results
are analyzed to demonstrate significant vibration suppression and increased productivity of the robot with
the proposed solution. The proposed method can be extended to the vibration suppression of other types of
industrial robotic manipulators with serial links as well as other time-varying dynamic systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
In order to meet the requirements of increased pro-
ductivity, safety and energy efficiency, manufacturers
tend to develop robots with light weight design com-
pared to traditional robots. Light weight design leads
to mechanical flexibility of the robotic system due
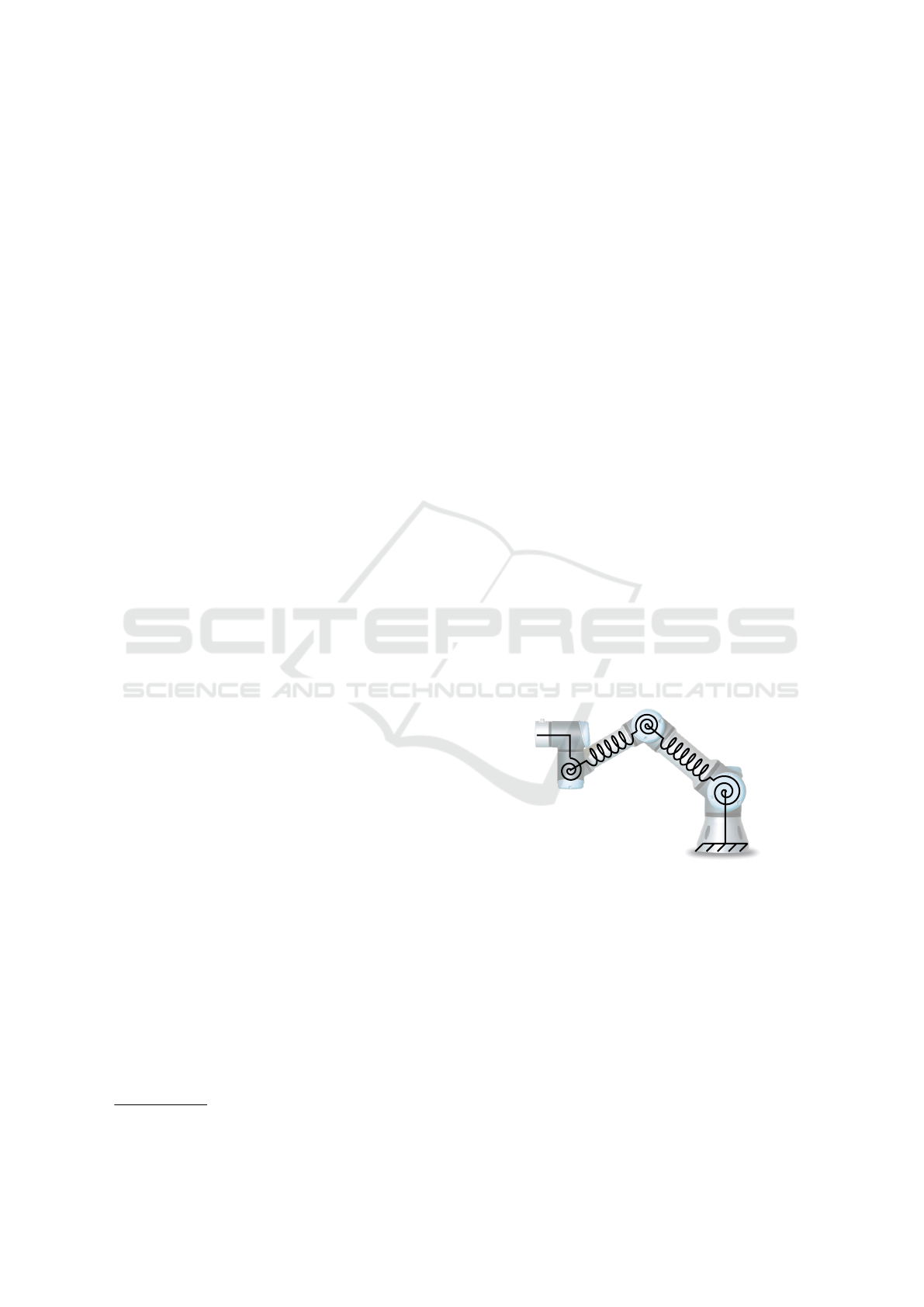
to reduced stiffness and damping. A visualization of
primary mechanical flexibility in a light weight col-
laborative robot from Universal Robots A/S (UR) is
presented in Figure 1.
As shown in the Figure 1, mechanical flexibility
comes primarily from gear flexibility in the joints
(strain wave gears) and link flexibility in the two long
links. In addition to mechanical flexibility, reduced
impedance resulting from control algorithms and elec-
trodynamics decreases the total system stiffness. The
mechanical and the electrical flexibility cause the robot
manipulator to be subject to unwanted mechanical vi-
brations during motions with high acceleration. These
mechanical vibrations are unwanted, because they af-
∗
Patent pending, PCT/EP2018/068934
Figure 1: Mechanical flexibility visualized in a UR3 robot.
fect robot precision, accuracy, wear, power consump-
tion and productivity in a negative way.
In the recent decades, many different strategies have
been investigated to reduce the unwanted mechanical
vibrations in light weight robotic systems. Generally,
the different strategies can be divided into hardware
design, trajectory optimization, feedback control, and
feed-forward control methods.
One type of feed-forward vibration suppression is
Input Shaping (IS) (Singer and Seering, 1990). IS has
gained a lot of attention for its simplicity and efficiency.
488
Thomsen, D., Søe-Knudsen, R., Brandt, D. and Zhang, X.
Experimental Implementation of Time-varying Input Shaping on UR Robots.
DOI: 10.5220/0007834504880498
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2019), pages 488-498
ISBN: 978-989-758-380-3
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
The basic principle of IS is to convolve a reference
signal with a well-designed impulse train to generate a
modified (shaped) reference signal, that introduces a
reduced amount of unwanted mechanical vibrations in
the robotic system.
The conventional IS assumes that the system is
time invariant, i.e. the system frequency and damping
do not change with time. Applying IS to an industrial
robot manipulator faces a significant challenge as in-
dustrial robots have configuration dependent dynamics
(time-varying dynamics), i.e. the natural frequency
and damping of an industrial robot often vary with
configuration and payload. This behavior arises mainly
from time-varying mass distribution, i.e. inertia, as
illustrated in Figure 2. Here, the actuator of the illus-
trated 1DOF robot will experience a position dependent
mass moment of inertia, which will result in position
dependent natural frequency and damping ratio of the
system.
q = 150
◦
Decreased
inertia
q = 90
◦
q = 30
◦
Increased
inertia
Actuator with
flexibility
Figure 2: 1DOF manipulator with configuration dependent
inertia.
Taking a UR5e robot as an example, the damped
natural frequency varies as much as from 6Hz to 15Hz
with a constant 5kg payload. The Robust IS method
was developed to accommodate slight deviations in sys-
tem frequencies and damping (Singh and Vadali, 1993;
Kim and Croft, 2018), but it is not capable of handling
the large deviation of the frequencies and damping in
industrial robot manipulators (Thomsen et al., 2018).
The Time-Varying Input Shaping Technology (TVIST)
is a promising method for handling the time-varying
dynamics and providing efficient vibration suppression
throughout the workspace of the robot for any desired
motion (Cho and Park, 1995; Chang and Park, 2005;
Kivila, 2017). However, TVIST methods in existing
literature on are not directly applicable in commercial-
ized industrial robots, since the reported research is
limited to very flexible robot manipulators, or have no
practical implementation strategies.
A new type of TVIST, which utilizes Fractional
Delay FIR filtering has been suggested for industrial
robots (Thomsen et al., 2019). While simulations have
been published to support the new principles, practical
implementation and experimental validation have not
yet been presented.
The main contribution of this paper is to develop
and validate the practical and effective implementation
strategy of TVIST on typical industrial robots with six
joints. The detailed principles and procedures of imple-
menting TVIST on a UR robot are presented together
with preliminary experimental results. A set of test
motions are performed, and the experimental results
are analyzed. The experimental results validate the ef-
ficiency of the proposed experimental implementation
strategy.
2 OVERVIEW ON INPUT
SHAPING
Input Shaping (IS) is a vibration suppression method,
which aims to avoid introducing vibrations in a dy-
namic system by convolving the reference signal with a
set of vibration free impulses in order to obtain a modi-
fied (shaped) reference signal. The shaped reference
signal will solve the desired task without introducing
vibrations in the system.
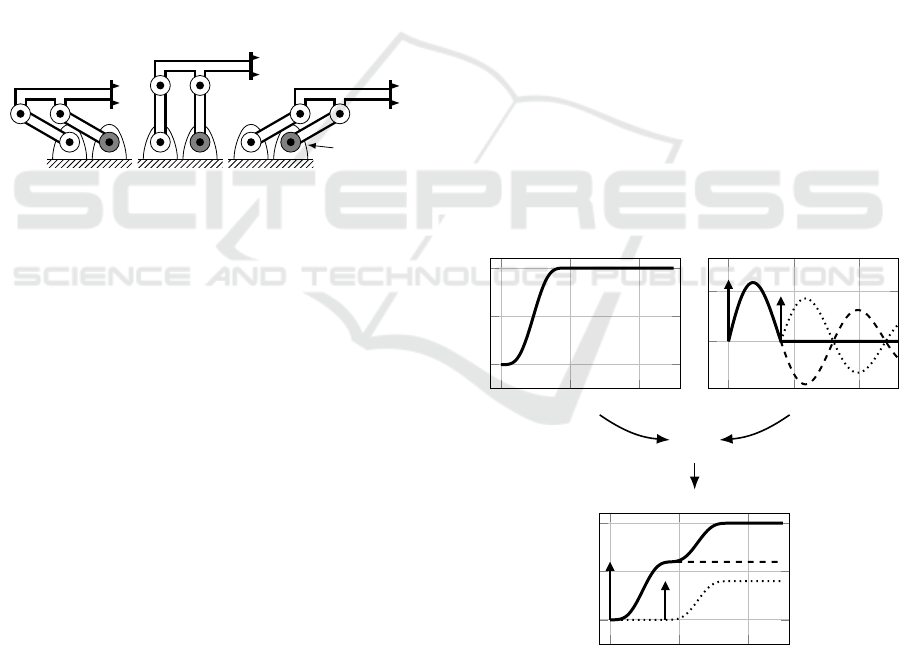
The fundamental principle of input shaping is illus-
trated in Figure 3. Here it is shown how an impulse,
A
1
, will cause a dynamic response in the system, and
how the response of a second impulse,
A
2
, will cancel
out this response if applied with the correct timing and
amplitude.
∗
A
1
A
2
Time,
ˆ
t
System response
Impulse sequence, I(
ˆ
t)
∆
1
∆
2
Time, t
Reference signal
Reference, x(t)
A
1
A
2
Total
From A
1
From A
2
Time, t
Reference signal
Shaped reference, x
∗
(t)
∆
1
∆
2
Figure 3: Convolution of Zero Vibration (ZV) shaper.
In general, the impulse sequence,
I(
ˆ
t)
, can be ex-
pressed as shown in
(1)
-
(3)
, where
ˆ
t
is internal filter
time,
~
A
is impulse amplitudes, and
~
∆
is impulse timings
for a shaper with N impulses.
Experimental Implementation of Time-varying Input Shaping on UR Robots
489
~
A =
A
1
A
2
··· A
N
(1)
~
∆ =
∆
1
∆
2
··· ∆
N
(2)
I(
ˆ
t) =
(
A
j
if
ˆ
t = ∆
j
0 otherwise
(3)
For the Zero Vibration (ZV) shaper,
~
A
and
~
∆
can
be determined as described by
(4)
-
(7)
, where
K
is a
helping constant,
ζ
is damping ratio,
ω
n
is natural
frequency in rad/s, and
f
d
is damped frequency in Hz
(Singer and Seering, 1990).
K = e
ζπ
√
1−ζ
2
(4)
f
d
=
ω
n
2π
q
1 −ζ
2
(5)
~
A =
1
1 + K
K
1 + K
(6)
~
∆ =
0 0.5/ f
d
(7)
Once all parameters of
I(
ˆ
t)
are known, the shaped
reference command,
x
∗
(t)
, can be obtained by convolv-
ing the reference command,
x(t)
, and
I(
ˆ
t)
as presented
in (8). This operation is called shaping.
x
∗
(t) = (x ∗I)(t) ≡
N
∑
j=1
(A
j
·x(t −∆
j
)) (8)
The shaping can be performed on any reference
signal for the controlled system, such as a position,
velocity, acceleration, torque, or current reference sig-
nal. The convolution of a position reference is also
illustrated in Figure 3. Here it is seen that convolving
x(t)
with
I(
ˆ
t)
corresponds to splitting
x(t)
into two
parts, which are scaled by
A
1
and
A
2
and delayed by
∆
1
and
∆
2
, respectively, before being added together
as
x
∗
(t)
. If
x
∗
(t)
is given to the system as reference,
this will result in zero vibration in the system.
3 TIME-VARYING INPUT
SHAPING
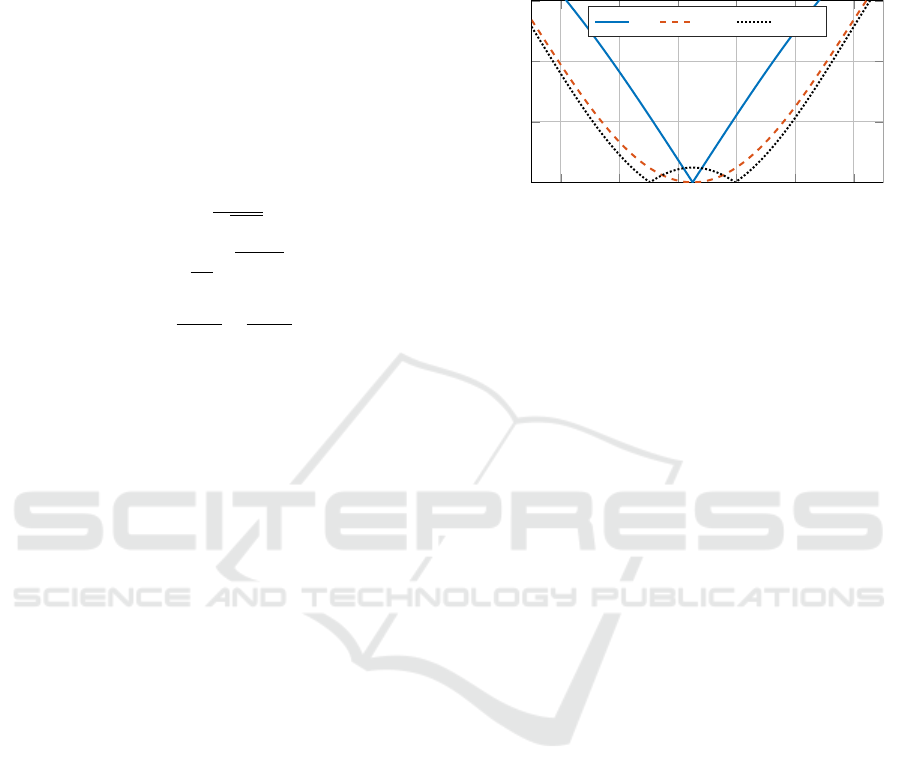
While IS has proved efficient for suppressing vibrations
system with time-invariant dynamics, it is not robust
enough to variations in
f
d
and
ζ
to provide acceptable
vibration suppression for time-varying dynamic sys-
tems such as serial link robots. This is clearly seen, by
inspecting a sensitivity curve for the Zero Vibration
Derivative (ZVD) and Extra Insensitive (EI) shapers as
presented in Figure 4. It is seen, that an EI shaper can
not guarantee vibration suppression to a level of less
than 36% for the span of
f
d
from 6 to 15Hz, which
is seen in a UR5e robot. This is even without taking
damping variations into account.
6
8 10 12 14
16
0
20
40
60
Frequency (Hz)
Percent Residual Vibration (%)
ZV ZVD
EI 5%
Figure 4: Sensitivity plot of ZV, ZVD, and EI shapers.
It is possible to increase robustness, but this comes
at the expense of increased shaper delay, which is unde-
sirable. It is desired to increase vibration suppression
capabilities and decrease shaper delay for systems with
time-varying dynamics. Thus, a demand for taking
time-varying dynamics into account exists for light
weight robots. This section elaborates on how to extend
the IS methods to TVIST.
For a system with time-varying dynamics, i.e. time-
varying damping ratio,
ζ(t)
, and damped frequency,
f
d
(t)
, the impulse train can be updated as presented in
(9)
, which is an expansion of
(3)
. Here
I(
ˆ
t, f
d
(t),ζ(t))
is updated continuously as
f
d
(t)
and
ζ(t)
varies with
time.
I(
ˆ
t, f
d
(t),ζ(t)) =
(
A
j
(ζ(t)) if
ˆ
t = ∆
j
( f
d
(t))
0 otherwise
(9)
When introducing the impulse sequence as
I(
ˆ
t, f
d
(t),ζ(t))
, it is necessary to expand
(8)
as pre-
sented in (10).
x
∗
(t) =
N
∑
j=1
(A
j
(ζ(t)) ·x (t −∆
j
( f
d
(t)))) (10)
The formulation of TVIST in
(10)
is the idealized
principle, which can be used in systems, where: 1)
The analytical description of the reference signal is
known, and 2) The system does not have multiple
reference signals, which are dependent on each other,
such as position and velocity signals. The next section
elaborates on the shortcomings of this formulation, and
propose a way to overcome them in the implementation
in UR robots.
3.1 Implementation of TVIST
This section elaborates on the implementation of
TVIST in the control structure of a UR robot. The
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
490

original control structure is illustrated in Figure 5. As il-
lustrated, a trajectory generator provides reference joint
positions,
~q
, reference joint velocities,
˙
~q
, and reference
joint accelerations,
¨
~q
, to an inverse dynamic model,
which computes reference joint torques,
~
τ
. Then
~q
,
˙
~q
and
~
τ
are provided to the joint controllers, which also
utilize sensor feedback about actual joint positions,
~q
a
,
and actual joint velocities,
˙
~q
a
, to generate actual motor
voltages,
~u
a
, which are applied in the joints. Thus
each joint controller should be seen as a feedforward-
feedback controller with 3 reference inputs, 2 feedback
measurements and 1 controller output.
Trajectory
generator
Inverse
dynamics
Joint
controllers
Electro-mechanical
dynamic system
~q
˙
~q
¨
~q
~
τ
~q
a
˙
~q
a
~u
a
Figure 5: Control structure of a UR robot.
By shaping
~q
,
˙
~q
, and
¨
~q
simultaneously, it would be
possible to handle the multiple reference inputs in the
classic time-invariant shaper presented in
(8)
. However,
once introducing time-varying shaping, as presented in
(10)
, the relation between
~q
and its derivatives becomes
non-linear.
Thus it is not an option to shape
~q
,
˙
~q
, and
¨
~q
simulta-
neously using identical shapers. Others (Beazel, 2004;
Chatlatanagulchai et al., 2006) suggest averaging the
non-linear dynamics of the robot over the motion and
treat them like linear dynamics. Then
~
τ
is shaped, and
weighted to fit the linearized dynamics. Then
¨
~q
is de-
termined and integrated twice to obtain
˙
~q
and
~q
. This
process requires that the analytic description of the
whole motion is known in advance, and that the motion
is completed before starting a new motion. Hence this
method does not suit a system with online trajectory
generation. Also, the method is computationally ex-
pensive because complex dynamic models need to be
evaluated.
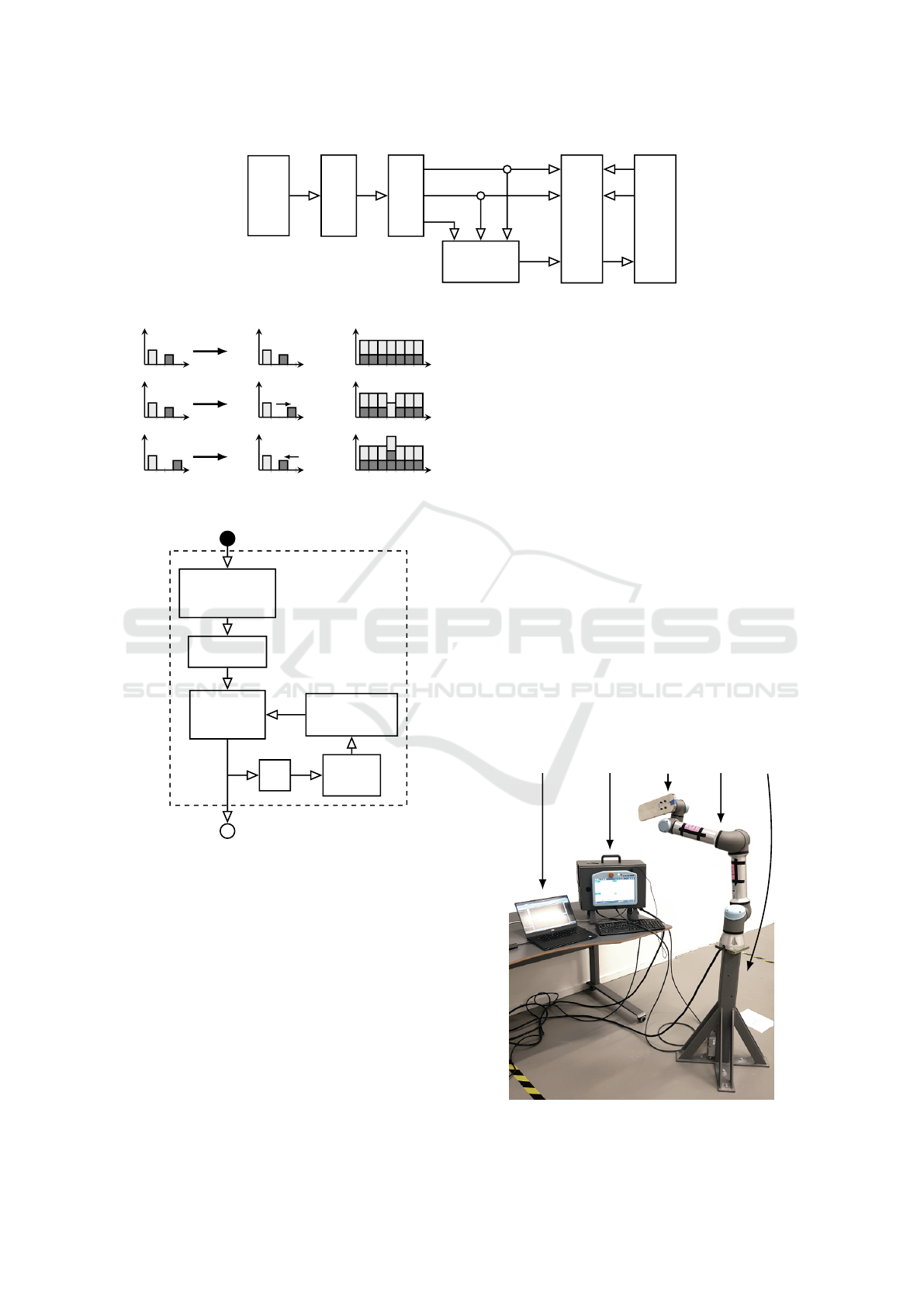
Instead it is proposed to implement the method
in discrete time and to shape
~q
while performing nu-
merical differentiation in order to obtain
˙
~q
and
¨
~q
, like
illustrated in Figure 6.
By implementing the TVIST filter as a discrete
time filter, the robot will be able to perform filtering on
any trajectory, which can be generated online or even
provided by a 3
rd
party PC or software, which sends
discrete reference commands to the robot.
3.2 TVIST in Discrete Time
When IS is implemented in discrete time, it is nec-
essary to use a discrete time impulse sequence,
I [i]
,
i.e. to discretize
I(
ˆ
t)
from continuous time to discrete
time domain (Rappole, 1992; Murphy and Watanabe,
1992; Cole, 2011). The traditional method of imple-
menting IS in discrete time is to use a Finite Impulse
Response (FIR) filter to convolve the discrete time
reference signal
x [i]
with
I [i]
(Singer, 1989). However,
a major challenge in Discrete Time Time-Varying In-
put Shaping Technology (DT-TVIST) is that the FIR
convolution operation results in significant defects in
x
∗
, when
f
d
is varying such that the position of an im-
pulse is moving from one discrete time step to another
(Magee and Book, 1992; Magee, 1996).
The discretization problem is illustrated in Figure 7.
Here it is seen how a change in
f
d
results in a time shift
of the second impulse. When the time shift becomes
large enough, the impulse will jump from one discrete
time step to the next, and this will cause defects in
the convolved signal (Murphy and Watanabe, 1992;
Magee, 1996).
In the proposed implementation, the described chal-
lenges are handled by maintaining a buffer of previous
filter inputs and perform an interpolation in order the
obtain an estimate of
x(t)
, as illustrated in Figure 8.
The figure illustrates that at time step
i
, the reference
command,
x
i
, is stored in a buffer of length
M
. An esti-
mate of
x(t)
is established through interpolation of the
buffered reference commands. Then
x(t)
is convolved
with the impulse sequence of current time step,
I
i
(
ˆ
t)
,
to compute the shaped reference command,
x
∗
i
.
I
i
(
ˆ
t)
is
established based on an estimate of
f
d
and
ζ
based on
the shaped reference command of the previous time
step, x
∗
i−1
, as described in section 3.3.
This type of convolution filter, which includes in-
terpolation of discrete reference commands, is called a
Fractional Delay Finite Impulse Response (FD-FIR) fil-
ter (Laakso et al., 1996). The option to utilize FD-FIR
filters in IS has recently been presented and analyzed
(Thomsen et al., 2019).
3.3 Estimating Time-varying Dynamics
In order to validate the effect of the proposed TVIST
design, it is required to have a method of estimating
the robot dynamics, i.e.
f
d
(t)
and
ζ(t)
. This can be
achieved using different types of dynamic modeling
(Book, 1993; Chang and Park, 2005; Sayahkarajy et al.,
2016; Kivila, 2017), system identification (Pham et al.,
2002; Khalil and Dombre, 2004), or lookup tables
(Hearne, 2009).
The most accurate estimate seems to be achieved
Experimental Implementation of Time-varying Input Shaping on UR Robots
491
Trajectory
generator
TVIST filter
Differentiator
Inverse
dynamics
Joint
controllers
Electro-mechanical
dynamic system
~q ~q
∗
~q
∗
˙
~q
∗
¨
~q
∗
~
τ
∗
~q
a
˙
~q
a
~u
a
Figure 6: Control structure of a UR robot with TVIST.
0 1 2 3
i
I[n]
0 1 2 3
i
I[n]
Constant
f
d
⇒
i
x
∗
[n]
0 1 2 3
i
I[n]
0 1 2 3
i
I[n]
Decrease
f
d
⇒
i
x
∗
[n]
0 1
2 3
i
I[n]
0 1 2 3
i
I[n]
Increase
f
d
⇒
i
x
∗
[n]
Figure 7: The discretization problem of TVIST.
x
i
Input buffer
[x
i−M
··· x
i
]
Interpolation
Convolution
Estimated x(t)
Update
~
A(ζ) and
~
∆( f
d
)
Estimate
f
d
and ζ
I
i
(
ˆ
t)
x
∗
i
z
−1
x
∗
i−1
TVIST filter
Figure 8: UR TVIST filter design.
from a combination of dynamic modeling and sys-
tems identification. However, a representative dynamic
model would need to include a large number of param-
eters in describing mechanical, electrical and software
non-linear dynamics.
Before engaging in developing such a complex and
computationally intensive estimator, it seems reason-
able to try a simple method and see, if this can provide
a useful estimate for the given application.
Thus, for this work it was decided to make a lookup
table based on measurements in multiple different
configurations over the workspace of the robot. This
lookup table was fitted to two multi-variable polyno-
mials, which are evaluated to estimate
f
d
(~q(t))
and
ζ(~q(t)).
4 EXPERIMENT
To validate the performance of the proposed TVIST im-
plementation in UR robots, experiments are performed
on a UR5e robot. Section 4.1 presents the experimental
setup, section 4.2 presents the results of the experiment
together with the performance parameters of interest,
and section 4.3 presents a discussion on the results.
4.1 Experimental Setup
In the experimental setup, a UR5e robot is mounted on
a steel stand, which is deemed very rigid compared to
the flexibility of the robot itself. A rigid steel payload
of 5kg is installed on the robot tool flange. This corre-
sponds to the rated payload of the robot. The test setup
is illustrated in Figure 9.
5kg
payload
PC for data
logging
UR robot
controller
UR5e
robot
Steel
stand
Figure 9: Test setup with UR5e robot on stand.
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
492

All test data is logged from the robot’s Real Time
Client (Universal Robots A/S Support, 2018) at 500Hz.
This includes reference joint positions,
~q
, reference
joint accelerations,
¨
~q
, actual joint positions,
~q
a
, and
tool accelerometer readings,
~
α .
It has been chosen to use a ZV shaper for evaluating
the performance of the proposed TVIST implementa-
tion. There are two reasons for this choice, 1) The ZV
shaper has a short time-delay, 2) The ZV is sensitive,
i.e. not robust, to errors in estimated
f
d
and
ζ
. Both of
these characteristics are seen as strengths, when it is
sought to validate the performance and applicability
of the method. In practice, it would probably make
sense to implement a Zero Vibration Derivative (ZVD)
shaper for increased robustness, but this depends on
the application.
Test motions are performed with and without shap-
ing for evaluating the TVIST method. Motions are
performed between configurations
Q
1
,
Q
2
, and
Q
3
,
which are listed in Table 1.
Between these configurations, three different joint
space motions are used for evaluation, namely
Q
1
→Q
2
,
Q
1
→Q
3
, and
Q
3
→Q
1
. Visualizations of these mo-
tions are presented in Figure 10 and Figure 11. The
configurations and motions are chosen such that the
Q
1
→Q
2
motion will have non-varying dynamic prop-
erties, while
Q
1
→Q
3
and
Q
3
→Q
1
motions will have
varying dynamic properties.
Q
1
Q
2
Figure 10: Q
1
→ Q
2
motion.
By varying dynamic properties, it is understood
that
Q
1
→Q
3
yields increasing
f
d
and decreasing
ζ
,
while
Q
3
→Q
1
goes in the opposite direction and yields
decreasing
f
d
and increasing
ζ
. In the test motions, the
kinematic limitations of the double S velocity profile
trajectory (Biagiotti and Melchiorri, 2008), is set as
max(
˙
~q) = 1.5
rad/s,
max(
¨
~q) = 2.0
rad/s
2
, and a jerk
time, i.e. acceleration ramp up time, of 20ms.
4.2 Experimental Results
The results of performing the three different motions
are presented in Figures 12-14. Here it has been chosen
to present shaped reference accelerations
(
¨
~q
∗
(t))
, Carte-
sian distance to attained position (
E
), tool accelerome-
ter amplitude (
|
~
α|
), estimated damped frequency in Hz
( f
d
), and estimated damping ratio (ζ).
Q
3
Q
1
Figure 11: Q
1
→ Q
3
motion.
E
is interesting because it is used to determine a set
of key performance parameters in (ISO 9283, 1998),
such as stabilization time (
t
stb
) and overshoot (
e
os
).
The attained position is the actual Tool Center Point
(TCP) position after the motion has finished, and after
the position has been stabilized.
E
is defined as the
Cartesian distance from actual TCP position to the
attained position. Actual TCP position should ideally
be measured by external 3D tracking equipment. How-
ever, for the scope of this paper, which is to determine
the relative impact of TVIST on mechanical vibrations,
it has been chosen to use
~q
a
and perform a calibrated
forward kinematics to determine actual TCP position.
This makes it possible to obtain all data from the robot
itself.
In this work, three performance parameters are
established based on
E
, namely
t
stb
,
e
os
, and
t
cycle
. The
definition of these parameters will be given here.
In this work, cycle time,
t
cycle
, denotes the time
span from when the reference motion starts, until the
last time, where
E
takes value higher than the repeata-
bility of the robot. For the UR5e robot, the repeatability
is specified as 0.03mm. The stabilization time,
t
stb
,
is the time span from the first time, where
E
takes
value lower then the repeatability of the robot (
t
enter
),
until
t
cycle
(ISO 9283, 1998). The overshoot,
e
os
, is the
maximum value of
E
after
t
enter
(ISO 9283, 1998). If
this value is lower than the repeatability, the overshoot
is 0. Another metric of interest is the shaper delay
(
∆
n
).
∆
n
,
t
stb
,
e
os
,
t
enter
, and
t
cycle
are all illustrated in
Figure 15, and the actual values for the test motions
are listed in Table 2. Here the listed values are average
values from 10 runs of the test motions.
Experimental Implementation of Time-varying Input Shaping on UR Robots
493

Table 1: Listed test configurations.
Conf. q
0
(rad) q
1
(rad) q
2
(rad) q
3
(rad) q
4
(rad) q
5
(rad) f
d
(Hz) ζ (-)
Q
1
0 −π 0 −π/2 0 0 6.7 0.34
Q
2
π/2 −π 0 −π/2 0 0 6.7 0.34
Q
3
π/2 −π/2 5π/6 −π/2 0 0 15.0 0.14
Table 2: Performance evaluation of TVIST, average of 10 repetitions.
Delay (ms) Stabil. Time (ms) Cycle Time (ms) Overshoot (m) Res. Vibration (m/s
2
)
∆
n
t
stb
t
cycle
e
os
RV
Q
1
→ Q
2
Unshaped 0 548.8 2368.9 5.5E-04 1.11
Shaped 74.1 167.0 2229.5 3.1E-05 0.13
Impact - -69.6% -5.9% -94.3% -88.6%
Q
1
→ Q
3
Unshaped 0 70.8 2821.4 3.7E-05 0.80
Shaped 33.6 7.2 2820.4 1.0E-05 0.17
Impact - -89.8% 0.0% -72.4% -78.5%
Q
3
→ Q
1
Unshaped 0 1049.2 3707.8 1.3E-04 1.14
Shaped 74.2 816.7 3596.0 6.4E-05 0.22
Impact - -22.2% -3.0% -50.3% -80.8%
The UR5e robot has an accelerometer in the tool
flange. Analyzing the measured accelerations is consid-
ered the most reliable way of quantifying the amount
of residual vibrations in of the motion without using
external 3D tracking equipment. When determining
the amount of residual vibration, the amplitude of the
total acceleration
|
~
α|
with gravity compensation is con-
sidered. Then the amount of Residual Vibration (RV)
is found by identifying the peaks of the acceleration
signal and fitting them to an exponential decay. RV
is the amplitude of the fitted curve at the time, where
the reference motion stops (Kozak et al., 2006). RV is
also listed in Table 2. Figure 16 is introduced for easy
comparison of |
~
α| with and without IS.
4.3 Discussion on Results
From the
Q
1
→Q
2
motion presented in Figure 12 it
is seen that the estimated dynamics are constant at
f
d
= 6.7Hz
and
ζ = 0.34
during the motion. It is seen
from
|
~
α|
that mechanical vibrations are present dur-
ing and after the unshaped motion. When comparing
with the shaped motion, it is seen, how oscillations
are clearly reduced during the motion, while residual
vibrations are practically eliminated. It appears that IS
is performing well, but there are other contributions
to mechanical vibrations, which can not be eliminated
by IS. This is believed to be a result of mechanical
imperfections, such as kinematic error in the gears
(Tuttle, 1992) and bearing imperfections.
The same tendency for residual vibration is seen
for
E
. When comparing the shaped and unshaped
motions, it may be noticed how the introduced de-
lay seems to pay off well, as the TCP comes to rest
faster than originally. The promising results for the
Q
1
→Q
2
motion tells us that IS can provide effective
vibration suppression in the system, when dynamics
are invariant.
By inspecting the
Q
1
→Q
3
motion in Figure 13
and
Q
3
→Q
1
in Figure 14. It is found that effective
vibration suppression is also possible, when
f
d
and
ζ
vary over time. These are really good results, especially
since the TVIST is implemented with the simple ZV
shaper. Achieving good vibration suppression using a
time-invariant robust shaper would require two or three
times more delay and would not give as good results.
f
d
is varying between 15Hz and 6.7Hz, while
ζ
varies
between 0.14 and 0.34. This huge span would not be
possible to cover appropriately with one robust shaper.
Table 2 lists the performance metrics for the shaped
and unshaped motions, as well as the relative impact
from shaping. Here, it is seen that
t
stb
,
e
os
, and residual
vibration are reduced for all three test motions. This
was also expected from introducing IS. However, it
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
494
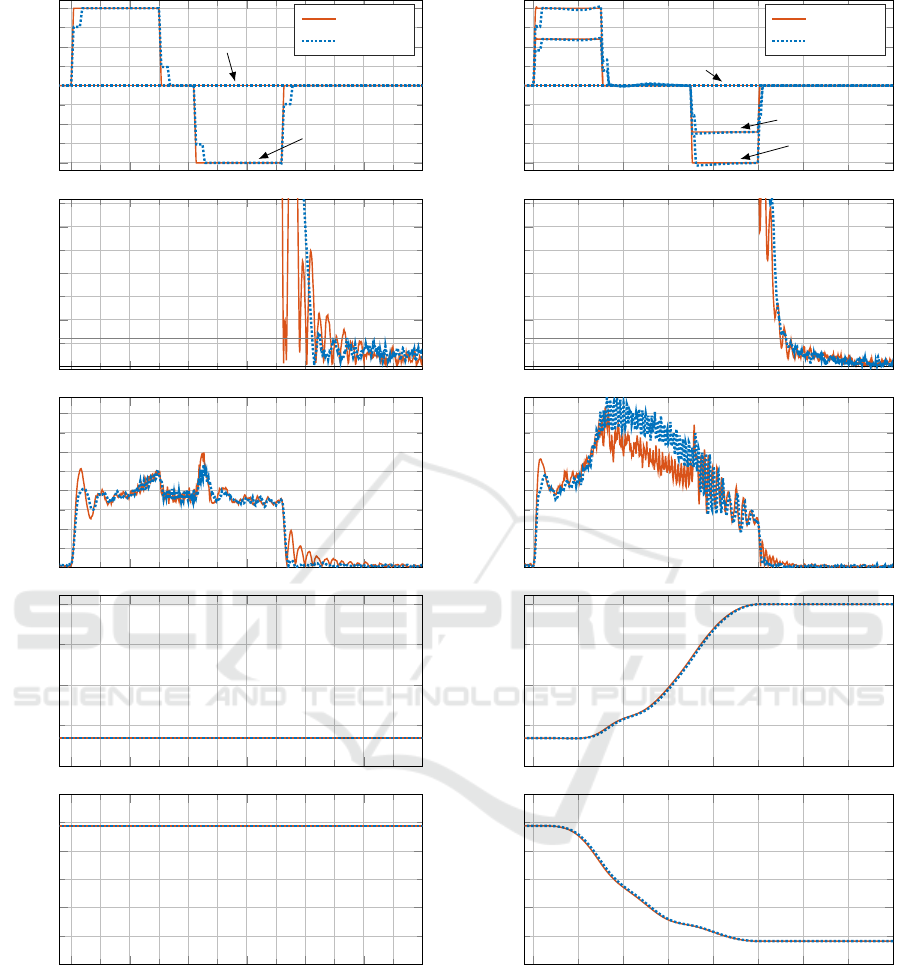
−2
−1
0
1
2
¨q
0
¨q
1
, ¨q
2
, ¨q
3
, ¨q
4
, ¨q
5
¨
~q (rad/s
2
)
Unshaped
Shaped
0
0.5
1
1.5
·10
−4
E (m)
0
1
2
3
4
|
~
α| (m/s
2
)
5
10
15
Estimated f
d
(Hz)
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
Time (s)
Estimated ζ (-)
Figure 12: Recorded data from Q
1
→ Q
2
motion.
is impressive to see, that the absolute reduction in
stabilization time is larger, than the introduced time
delay, meaning that the total cycle time can be reduced
by up to 5.9%. In other words, the productivity of the
robot can be increased by up to 6.3%.
−2
−1
0
1
2
¨q
0
, ¨q
1
¨q
2
¨q
3
, ¨q
4
, ¨q
5
¨
~q (rad/s
2
)
Unshaped
Shaped
0
0.5
1
1.5
·10
−4
E (m)
0
1
2
3
4
|
~
α| (m/s
2
)
5
10
15
Estimated f
d
(Hz)
0 1 2 3 4
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
Time (s)
Estimated ζ (-)
Figure 13: Recorded data from Q
1
→ Q
3
motion.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, a need for efficient vibration reduction
methods in light weight robots has been identified.
It was found that Input Shaping (IS) had great po-
tential, but lacked on the ability to handle the time-
varying dynamics of industrial robots with the serial
Experimental Implementation of Time-varying Input Shaping on UR Robots
495

−2
−1
0
1
2
¨q
0
, ¨q
1
¨q
2
¨q
3
, ¨q
4
, ¨q
5
¨
~q (rad/s
2
)
Unshaped
Shaped
0
0.5
1
1.5
·10
−4
E (m)
0
1
2
3
4
|
~
α| (m/s
2
)
5
10
15
Estimated f
d
(Hz)
0 1 2 3 4
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
Time (s)
Estimated ζ (-)
Figure 14: Recorded data from Q
3
→ Q
1
motion.
link configuration. IS has previously been extended
to Time-Varying Input Shaping Technology (TVIST),
for dealing with time varying dynamics. This paper
focuses on the strategy of implementing TVIST on
a UR5e robot from Universal Robots A/S (UR). It
was found that it is necessary to change its present for-
mulation to implement TVIST on an industrial robot
manipulator.
t
stb
Limit
Time, t
Distance from attained position, E
x
x
∗
x
a
t
cycle
t
b
t
∗
b
t
enter
∆
n
e
os
Figure 15: Visualization of delay (
∆
n
), stabilization time
(t
stb
), cycle time (t
cycle
), and overshoot (e
os
).
1.8 2 2.2 2.4
2.6
0
0.5
1
1.5
RV: 1.16 m/s
2
RV: 0.09 m/s
2
|
~
α| (m/s
2
)
Q
1
→ Q
2
Unshaped
Shaped
t
b
t
∗
b
2.6
2.8 3 3.2
0
0.5
1
RV: 0.78 m/s
2
RV: 0.22 m/s
2
|
~
α| (m/s
2
)
Q
1
→ Q
3
t
b
t
∗
b
2.6
2.8 3 3.2
0
0.5
1
1.5
RV: 1.15 m/s
2
RV: 0.17 m/s
2
Time (s)
|
~
α| (m/s
2
)
Q
3
→ Q
1
t
b
t
∗
b
Figure 16: Tool accelerometer amplitude.
We proposed a new and practical implementation
strategy of TVIST on a UR robot. The new implemen-
tation of TVIST is a discrete time filter that performs
IS in a reference position signal and numerically dif-
ferentiates the shaped position reference in order to
obtain shaped reference velocity and acceleration be-
fore performing inverse dynamics to compute shaped
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
496

reference torques. Experiments are conducted on a
UR5e robot with the proposed TVIST implementation
to validate its effectiveness.
Preliminary experimental results demonstrate that
the new TVIST implementation yields effective vibra-
tion suppression in the UR5e robot, and reduces the
residual vibrations by 78.5-88.6% in the tested cases.
In addition, experimental results show that it is possible
to increase the productivity of the robot by up to 6.3%
because the stabilization time is significantly reduced
through the proposed TVIST implementation strategy.
We can conclude that the proposed method facili-
tates practical implementation of TVIST for vibration
suppression on commercial industrial robots that has
online trajectory generation and position control with
feed-forward velocity and torque.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Universal Robots A/S
and Innovation Fund Denmark, through the Industrial
PhD program. We wish to thank Anders Skovgaard
Knudsen from Universal Robots A/S for his valuable
help in proofreading.
REFERENCES
Beazel, V. M. (2004). Command shaping applied to nonlin-
ear systems with configuration-dependent resonance.
PhD thesis, Purdue University.
Biagiotti, L. and Melchiorri, C. (2008). Trajectory Planning
for Automatic Machines and Robots. Springer-Verlag
Berlin Heidelberg.
Book, W. (1993). Controlled motion in an elastic world.
Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control,
Transactions of the ASME, 115(2B):252–261.
Chang, P. H. and Park, H.-S. (2005). Time-varying input
shaping technique applied to vibration reduction of
an industrial robot. Control Engineering Practice,
13(1):121 – 130.
Chatlatanagulchai, W., Beazel, V. M., and Meckl, P. H.
(2006). Command shaping applied to a flexible robot
with configuration-dependent resonance. In 2006 Amer-
ican Control Conference.
Cho, J.-K. and Park, Y.-S. (1995). Vibration reduction in
flexible systems using a time-varying impulse sequence.
Robotica, 13(3):305–313.
Cole, M. O. (2011). A discrete-time approach to impulse-
based adaptive input shaping for motion control without
residual vibration. Automatica, 47(11):2504 – 2510.
Hearne, J. (2009). Posture dependent vibration resistance of
serial robot manipulators to applied oscillating loads.
Master’s thesis, University of Waterloo.
ISO 9283 (1998). Manipulating industrial robots - perfor-
mance criteria and related test methods.
Khalil, W. and Dombre, E. (2004). Modeling Identification
and Control of Robots. Butterworth-Heinemann.
Kim, J. and Croft, E. A. (2018). Preshaping input trajectories
of industrial robots for vibration suppression. Robotics
and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 54:35 – 44.
Kivila, A. (2017). Modeling, estimation and control for
serial flexible robot arms. PhD thesis, Georgia Institute
of Technology.
Kozak, K., Singhose, W., and Ebert-Uphoff, I. (2006). Per-
formance measures for input shaping and command
generation. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement
and Control, Transactions of the ASME, 128(3):731–
736.
Laakso, T. I., Valimaki, V., Karjalainen, M., and Laine, U. K.
(1996). Splitting the unit delay - tools for the fractional
delay filter design. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,
13(1):30–60.
Magee, D. P. (1996). Optimal arbitrary time-delay filtering
to minimize vibration in elastic manipulator systems.
PhD thesis.
Magee, D. P. and Book, W. J. (1992). The application
of input shaping to a system with varying parameters.
In Japan/USA Symposium on Flexible Automation,
volume 1, pages 519–526.
Murphy, B. R. and Watanabe, I. (1992). Digital shaping fil-
ters for reducing machine vibration. IEEE Transactions
on Robotics and Automation, 8(2):285–289.
Pham, M. T., Gautier, M., and Poignet, P. (2002). Ac-
celerometer based identification of mechanical systems.
In Proceedings 2002 IEEE International Conference
on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No.02CH37292),
volume 4, pages 4293–4298 vol.4.
Rappole, B. W. (1992). Minimizing residual vibrations
in flexible systems. Master’s thesis, MIT Artificial
Intelligence Laboratory.
Sayahkarajy, M., Mohamed, Z., and Faudzi, A. A. M. (2016).
Review of modelling and control of flexible-link manip-
ulators. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical
Engineers, Part I: Journal of Systems and Control
Engineering, 230(8):861–873.
Singer, N. C. (1989). Residual vibration reduction in com-
puter controlled machines. PhD thesis, Massachusetts
Institute of Technology. Dept. of Mechanical Engineer-
ing.
Singer, N. C. and Seering, W. P. (1990). Preshaping
command inputs to reduce system vibration. Jour-
nal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control,
112(1):76–82.
Singh, T. and Vadali, S. (1993). Robust time-delay control.
Journal of dynamic systems, measurement, and control,
115(2A):303–306.
Thomsen, D. K., Søe-Knudsen, R., Brandt, D., Balling, O.,
and Zhang, X. (2018). Generating vibration free rest-to-
rest trajectories for configuration dependent dynamic
systems via 3-segmented input shaping. In IEEE
International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
Thomsen, D. K., Søe-Knudsen, R., Brandt, D., Balling, O.,
and Zhang, X. (2019). Smooth online time-varying in-
put shaping with fractional delay FIR filtering. Control
Engineering Practice, 88:21–37.
Experimental Implementation of Time-varying Input Shaping on UR Robots
497

Tuttle, T. D. (1992). Understanding and modeling the behav-
ior of a harmonic drive gear transmission. Technical
report, Massachusetts Inst of Tech Cambridge Artificial
Intelligence Lab.
Universal Robots A/S Support (2018). Overview of
client interfaces. Last accessed: 16/04/2018. URL:
https://www.universal-robots.com/how-tos-and-
faqs/how-to/ur-how-tos/overview-of-client-interfaces-
21744/.
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
498
