
BEARZ Attack FALCON: Implementation Attacks with Countermeasures
on the FALCON Signature Scheme
Sarah McCarthy
1
, James Howe
2,†
, Neil Smyth
3,‡
, Séamus Brannigan
1
and Máire O’Neill
1
1
Centre for Secure Information Technologies (CSIT), Queen’s University Belfast, U.K.
2
PQShield Ltd., Oxford, U.K.
3
Allstate NI, Belfast, U.K.
Keywords:
Lattice-based Cryptography, Fault Attacks, FALCON, Digital Signatures, Post-quantum Cryptography,
BEARZ, Countermeasures.
Abstract:
Post-quantum cryptography is an important and growing area of research due to the threat of quantum comput-
ers, as recognised by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recent call for standardisation.
FALCON is a lattice-based signature candidate submitted to NIST, which has good performance but lacks in
research with respect to implementation attacks and resistance. This research proposes the first fault attack
analysis of FALCON and finds its lattice trapdoor sampler is as vulnerable to fault attacks as the GPV sampler
used in alternative signature schemes. We simulate the post-processing component of this fault attack and
achieve a 100% success rate at retrieving the private-key. This research then proposes an evaluation of coun-
termeasures to prevent this fault attack and timing attacks of FALCON. We provide cost evaluations on the
overheads of the proposed countermeasures which shows that FALCON has only up to 30% deterioration in
performance of its key generation, and only 5% in signing, compared to runtimes without countermeasures.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital signature schemes are an important crypto-
graphic primitive, used for data authentication, in-
tegrity, and non-repudiation across the Internet and
in secure computer systems. However, the discov-
ery of Shor’s algorithm (Shor, 1999) has the potential
to break all currently used signature schemes, such
as ECDSA. This threat has led to a new era of cryp-
tography which is built to withstand quantum com-
puting attacks, known as post-quantum, or quantum-
safe, cryptography. This threat has also prompted a
standardisation effort by NIST (2016a) through their
call for quantum-safe primitives. One of the most
promising types of post-quantum solutions is lattice-
based cryptography, which makes up almost half of
the round 2 candidates. Many problems based on
lattice assumptions provide the appealing property
of worst-case to average-case hardness (Ajtai and
Dwork, 1997) and lattices have yet to be hindered by
†
Most of this research was completed while the author was
at the University of Bristol.
‡
Most of this research was completed while the author was
at the Centre for Secure Information Technologies (CSIT),
Queen’s University Belfast.
a serious cryptanalytic break. They also benefit from
extended functionality, with primitives such as fully-
homomorphic encryption (Gentry and Boneh, 2009)
and identity-based encryption (Ducas et al., 2014).
This research focuses on lattice-based signatures,
which have been shown to perform well in com-
parison to classical signature schemes (Howe et al.,
2015). They also have relatively small key sizes, offer
cryptographic agility, and most importantly offer pro-
tection from quantum attacks. There are three lattice-
based signatures in round 2 of the NIST standardisa-
tion process, and we analyse the performance and at-
tack resistance of one of these, FALCON (Prest et al.,
2017).
Despite being resistant to quantum computing at-
tacks, lattice-based cryptographic schemes are sus-
ceptible to the same side-channel attacks as alterna-
tive primitives used today, as summarised by Hodgers
et al. (2016) and Khalid et al. (2018). Thus, consider-
ing attacks and possible countermeasures is important
during standardisation and implementation. This re-
search focuses on countermeasures of types of attack
that have been considered to date for lattice-based
signatures, namely timing and fault analysis attacks.
Examples of these types of attacks and countermea-
McCarthy, S., Howe, J., Smyth, N., Brannigan, S. and O’Neill, M.
BEARZ Attack FALCON: Implementation Attacks with Countermeasures on the FALCON Signature Scheme.
DOI: 10.5220/0007834800610071
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2019), pages 61-71
ISBN: 978-989-758-378-0
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
61

sures are given in (Roy et al., 2014; Bruinderink et al.,
2016; Howe et al., 2016; Espitau et al., 2016; Bindel
et al., 2016; Karmakar et al., 2018).
This research considers timing and fault attacks
and countermeasures of the lattice-based signature
FALCON, including the first fault attack on the
scheme. This is an important contribution to the NIST
standardisation effort, as NIST (2016b) have stressed
for the need for side-channel analysis (SCA) and ef-
ficient countermeasures. In NIST’s report on the sec-
ond round candidates (Alagic et al., 2019), their com-
ments for FALCON were that “more work is needed
to ensure that the signing algorithm is secure against
side-channel attacks” and this is the gap we hope to
address in this paper. We review existing implemen-
tation attacks, propose the first fault attack on FAL-
CON, and implement the signature scheme with ap-
propriate countermeasures in place. The impact on
performance with these countermeasures is thus also
provided. The proposed attack, BEARZ, is a modifi-
cation of the attack on the DLP (Ducas et al., 2014)
hash-and-sign scheme by Espitau et al. (Espitau et al.,
2016) (Espitau et al., 2018). The origins of FALCON
are somewhat based on DLP, but it employs a novel
recursive form of the GPV sampler in the FFT do-
main. We find that the FALCON sampler is still vul-
nerable to fault attacks and we are able to retrieve the
private-key; however we show that it still performs
competitively with countermeasures in place, incur-
ring only a 5% decrease in performance. The zero-
check countermeasure is effective against the pro-
posed fault attack, and causes a 16% decrease in per-
formance on the high security parameter set. Fur-
thermore, we compare our results to those of signa-
ture schemes Dilithium (Lyubashevsky et al., 2017)
and BLISS-B (Ducas, 2014) with similar countermea-
sures applied.
The contributions of this paper are as follows:
• The first fault attack on FALCON using a Ba-
sis Extraction by Aborting Recursion or Zeroing
(BEARZ) technique.
• Novel portable ANSI C design of FALCON, with
competitive performance (as part of libSAFE-
crypto
1
). Features include constant-time compo-
nents and use of the CDT (Gaussian) sampler.
• The first proposed design of FALCON with coun-
termeasures against known side-channel attacks.
• A thorough overhead bench marking and com-
parison of FALCON with alternative state of the
art signature schemes incorporating side-channel
countermeasures.
1
https://github.com/safecrypto/libsafecrypto
The structure of the paper is as follows. Section 2 in-
troduces lattice-based cryptography and describes the
signature schemes discussed in this research. Section
3 outlines timing attacks on FALCON and proposed
countermeasures. Section 4 presents the first fault at-
tack on FALCON, followed by appropriate counter-
measures to prevent this attack. Section 5 presents
performance figures for our software implementa-
tions of the signature scheme, with and without attack
countermeasures, followed by evaluations. The paper
is then concluded in Section 6.
2 LATTICE-BASED DIGITAL
SIGNATURE SCHEMES
This section describes preliminaries on lattice-based
cryptography and introduces the FALCON signature
scheme (Prest et al., 2017) and its relation to the DLP
IBE (Ducas et al., 2014) scheme.
2.1 Preliminaries
Lattices are specified by a collection of vectors,
x
i
, which form their basis, B, which can be de-
fined as: L(B) =
{
∑
i
a
i
x
i
|a
i
∈ Z, x
i
∈ B,1 ≤i ≤ n
}
.
Computationally hard lattice problems, such as the
Shortest Vector Problem (SVP), Short Integer Solu-
tion (SIS), and Learning With Errors (LWE) (Regev,
2005, 2009) can form security assumptions for cryp-
tographic primitives. In this research, we examine
schemes which use module or ideal lattices, which
progressively add more structure to the basis. The
hardness assumption of FALCON’s key generation is
based on a variant of the NTRU problem, which states
that, given polynomial ring element A = g · f
−1
, it is
difficult to recover f and g. The hardness of the sign-
ing procedure depends on the SVP, which states that
if we are given the public basis of the lattice, it is a
hard to find a short vector in the lattice.
We denote by N the dimension of the ring, q the
modulus, and we operate in the polynomial ring R
q
=
Z
q
[x]/(x
n
+1). The elements in R
q
can be represented
as polynomials of degree N or vectors of dimension
N. These parameters for FALCON are given in Table
1, as well as the (equivalent) security levels of each
parameter set.
2.2 The FALCON Signature Scheme
The FALCON signature scheme was proposed by Prest
et al. (Prest et al., 2017). Its notable character-
istics are that it is a hash-and-sign type signature
SECRYPT 2019 - 16th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
62

Table 1: The proposed parameters (Prest et al., 2017) for the FALCON signature scheme.
Parameter NIST Security Dimension Modulus
Set Level Level (N) (q)
Set 1 Level 1 AES128 512 12289
Set 2
Level 4 SHA384 1024 12289
Level 5 AES256 1024 12289
scheme (in contrast to Dilithium, a Fiat-Shamir sig-
nature scheme) and is secure in the random oracle
model. It is based on the DLP identity-based en-
cryption scheme proposed by Ducas et al. (2014),
together with fast Fourier sampling techniques pro-
posed Ducas and Prest (2016). These techniques im-
prove the compactness of the private key and speed of
the sampling procedure. The key generation process,
shown in Algorithm 1, produces NTRU polynomials,
where f and g become the private keys, and h = g f
−1
is the public key. For the signing process, shown in
Algorithm 2, the f f Sampling algorithm (Algorithm
3) finds a short vector in the NTRU lattice, using the
private key. The public key is used to verify the sig-
nature by checking the modulus lies beneath the re-
quired bound β in the verification algorithm, given in
Algorithm 4.
2.3 The DLP Signature Scheme
Espitau et al. (2016, 2018) present an attack on the
GPV-based DLP hash-and-sign signature scheme. In
their fault model, the attacker is able to abort a loop
early in the GPV Gaussian lattice-sampling stage in
the signing algorithm. Whilst sampling vector coef-
ficients of a signature polynomial of degree 2n, they
force the process to terminate at some iteration m ≤n,
and obtain a faulty signature in the sub-lattice of rank
m. After producing around m + 3 faulty signatures,
they can generate the original lattice and recover a
short vector with probability 86%, thereby recovering
enough of the NTRU lattice structure to obtain the pri-
vate key. Espitau et al. recommend checking the va-
lidity of the DLP signature before sending, by running
the verification algorithm. In Section 4, we construct
a variant of this attack which targets the FALCON sig-
nature scheme.
3 TIMING ATTACKS ON
FALCON
3.1 Gaussian Sampler
Gaussian samplers are used in FALCON to sam-
ple short lattice vectors. Generally in lattice-based
Algorithm 1: FALCON key generation (adapted
from (Prest et al., 2017)).
Data: N,q
Result: B ∈ Z
2N×2N
q
, h ∈ R
q
1 σ
f
= 1.17
q
q
2N
2 f ,g,← D
N,σ
f
3 Norm
← max
||g,−f ||,
q
¯
f
f ∗
¯
f +g∗¯g
,
q ¯g
f ∗
¯
f +g∗¯g
4 if Norm > 1.17
√
q then go to Step 2;
5 Compute ρ
f
,ρ
g
∈ R and R
f
,R
g
∈ Z such
that: ρ
f
· f = R
f
and ρ
g
·g = R
g
6 if GC D(R
f
,R
g
) 6= 1 or GCD(R
f
,q) 6= 1 then
go to Step 2;
7 Compute u,v ∈ Z such that:
u ·R
f
+ v ·R
g
= 1
8 F ← qvρ
g
and Q ← −quρ
f
9 k =
j
F∗
¯
f +G∗¯g
f ∗
¯
f +g∗¯g
m
∈ R
10 F ← F −k ∗ f and G ← G −k ∗g
11 h = g ∗ f
−1
mod q
12 B =
g −f
G −F
13
ˆ
B =
FFT (g) −F FT ( f )
FFT (G) −FFT (F)
14 T=ffLDL*(G)
15 σ ← 1.55
√
q
16 for each leaf of T, leaf.value = σ/
√
leaf.value
17 sk ← (
ˆ
B,T),pk = h
18 return sk, pk
cryptography, Gaussian samplers are known to be vul-
nerable to timing analysis attacks and constant-time
samplers can be expensive. Bruinderink et al. (Bruin-
derink et al., 2016) proposed the first timing attack on
a lattice-based signature scheme, BLISS, and recov-
ered the private key by targeting the scheme’s Gaus-
sian sampler. Because of this, there has been signif-
icant research on designing the Gaussian sampler to
operate in independent time (Saarinen, 2015; Khalid
et al., 2016; Howe et al., 2016; Micciancio and Wal-
ter, 2017).
BEARZ Attack FALCON: Implementation Attacks with Countermeasures on the FALCON Signature Scheme
63
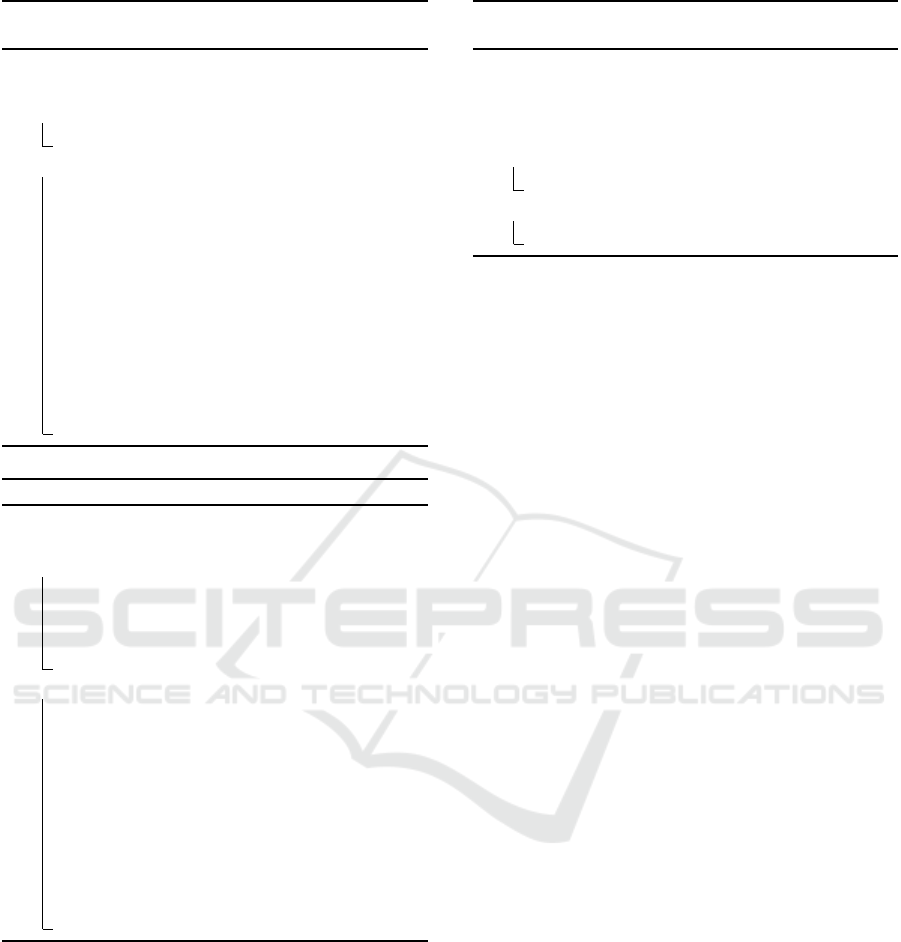
Algorithm 2: FALCON signing (adapted from (Prest
et al., 2017)).
Data: sk, H : {0, 1}
∗
→ Z
N
q
, m, β
Result: SIG
m
1 if SK
m
is in local storage then
2 return Output SIG
m
to message m
3 else
4 r ← Unif({0,1}
320
)
5 c ← H(r||m) ;
6 t ← (FFT (c),FFT (0)) ·
ˆ
B
−1
z ← ffSampling(t,T )
7 s = (t −z)
ˆ
B
8 while ||s|| > β
9 (s
1
,s
2
) ← invFFT (s)
10 s
2
= Compress(s
2
)
11 SIG
m
← (r,s
2
)
12 return Output SIG
m
associated to
message m and keep in local storage
Algorithm 3: ffSampling (Prest et al., 2017).
Data: t = (t
0
,t
1
) in FFT format , T
Result: z = (z
0
,z
1
) in FFT format
1 if n = 1 then
2 σ
0
← T.value
3 z
0
← D
Z,t
0
,σ
0
4 z
1
← D
Z,t
1
,σ
0
5 return z = (z
0
,z
1
)
6 else
7 (l, T
0
,T
1
) ←
(T.value,T.leftchild,T.rightchild)
8 t
1
← splitfft(t
1
)
9 z
1
← ffSampling(t
1
,T
1
)
10 z
1
← mergefft(z
1
)
11 t
0
0
←t
0
+ (t
1
−z
1
) ·l
12 t
0
← splitfft(t
0
0
)
13 z
0
← ffSampling(t
0
,T
0
)
14 z
0
← mergefft(z
0
)
15 return z = (z
0
,z
1
)
3.2 Number Theoretic Transform
The NTT is commonly used in lattice-based cryptog-
raphy, such as FALCON, to speed up multiplication
of ring polynomials. However, it involves a lot of
modular arithmetic, which is difficult to implement
in constant-time, as described by Scott (2017), and
so is a potential risk. There has also been signifi-
cant research on attacking the NTT, as well as making
the module run in constant-time (Longa and Naehrig,
2016; Alkim et al., 2016; Primas, 2017).
Algorithm 4: FALCON verifying (adapted from
(Prest et al., 2017)).
Data: pk = h ∈ R
q
, (SIG
m
,m), β
Result: Accept or Reject
1 c ← H(r||m)
2 s
2
= Decompress(s
2
),s
1
← c −s
2
h mod q
3 if ||(s
1
,s
2
)|| < β and H(r||m) = c then
4 return Accept
5 else
6 return Reject
3.3 HashtoPoint
The HashtoPoint function hashes the message to a
point in the polynomial ring. The authors of FALCON
note that this “may be difficult to efficiently imple-
ment in a constant-time way”. If the message is to be
kept secret, this could pose a problem.
3.4 Proposed Countermeasures to
Timing Attacks
We now discuss existing countermeasures in the liter-
ature which we incorporate into our FALCON imple-
mentation, as well as novel designs of constant-time
components.
Roy et al. (2014) introduced shuffling of the
Gaussian-distributed vector as a countermeasure to
timing attacks, which was also extended by Howe
et al. (2016). The Fisher-Yates shuffling algorithm
(Fisher et al., 1938) is typically used to effectively
randomly permute these vector coefficients. How-
ever, Pessl (2016) suggested that this countermea-
sure is not sufficient on its own. The BlindVector al-
gorithm introduced by Saarinen (2017) extended the
use of the Fisher-Yates shuffling procedure to en-
hance random shuffles for side-channel protection.
We utilise this algorithm and ensure a constant-time
implementation to further increase the attack com-
plexity. The algorithmic loops are not data dependent
and the operations are such that regardless of whether
a value is swapped or not they are always performed.
We introduce sample discard, the process whereby
extra cache reads from random addresses are per-
formed, in an attempt to distort statistics used in SCA.
These extra reads are then thrown away. In this imple-
mentation, where it has been added as an extra pre-
ventative layer, we have used a range of discard rates
at 6.25%, 12.5%, and 25%.
Our designs use a novel, efficient constant-time
design of the CDT Gaussian sampling technique as
this is much more simple to adapt for multiple param-
eter sets than other contenders. An exact number of
SECRYPT 2019 - 16th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
64

look-up reads are performed each time, with the com-
parison being computed using arithmetic logic using
the same operations regardless of the branch which
we want to take according to the CDT algorithm. The
upper bound for the number of look-ups required is
dlog
2
Ne and so each call of the sampler is padded out
to the nearest power-of-two to take this same amount
of clock cycles. For the required values of the stan-
dard deviation, this CDT sampler gives better per-
formance than the Knuth-Yao, discrete Ziggurat, and
Bernoulli samplers when operated in constant-time.
The NTT and FFT functions are also made
constant-time in our designs. The modular reduction
part of NTT can leak timing information (Scott, 2017)
and so our implementation is made constant-time by
avoiding branch operations at the cost of some per-
formance. This is done by processing all required
branch variables and eschewing logic for more time
consuming arithmetic operations. Performance is in-
creased by employing lazy reduction to reduce the
number of modular reductions that occur and using
SIMD vectorisation. Point-wise modulo multiplica-
tion computes each element independently, allowing
a multiplication of two polynomial rings in the NTT
domain. As the operations are sequential and uncon-
ditional, it is constant-time.
The transform routinely utilises the Cooley-Tukey
NTT algorithm with some small optimisations de-
signed to increase performance, enable automatic
vectorisation, and ensures that no conditional branch
operations are used. The inverse NTT operation is
the mirrored operation of the forward NTT, but ad-
ditionally requires shuffling of the output coefficients
and the use of both forward and inverse roots of unity
coefficient tables. Automatic vectorisation of the fi-
nal shuffle of the inverse NTT was not possible as
the loop conditions were considered too complex and
therefore it is performed separately to the modular re-
duction in order to improve performance. Our mod-
ular reduction design is a simplified range restriction
that avoids the use of logical operations and instead
opts to use arithmetic operations, in particular the
constant time less than comparison function.
4 BEARZ ATTACK FALCON
This section proposes a new fault attack on the FAL-
CON digital signature scheme, which uses Basis Ex-
traction by Aborting Recursion or Zeroing, named
BEARZ. The attack exerts and then exploits faults in
the FALCON signature scheme in order to learn pri-
vate key information, following a similar attack used
on DLP. We utilise a different attack model, assuming
that the attacker is able to skip instructions and to zero
variables as assumed by Bindel et al. (2016, 2017).
The original attack is on the GPV sampling compo-
nent in DLP, however there are two major differences
between this sampler and the FALCON sampler: re-
cursion and FFT domain.
4.1 DLP Attack
We begin with a recap of the attack on DLP by Es-
pitau et al. (2016). In the GPV lattice trapdoor sam-
pler, coefficients of the n-dimensional vectors (R,r)
are sampled in a 2n-length loop in reverse, from the
last coefficient r
n
to the first coefficient R
0
. This is
converted to a short Gaussian-distributed lattice vec-
tor by multiplying the vector (R,r) by the basis:
B =
A(g) −A( f )
A(G) −A(F)
,
where A(F) is the anti-circulant matrix associated
with the degree-n polynomial, F. We are con-
cerned with second half of the signature, denoted
s
2
= (R, r) (−A( f ),−A(F)) = R. f + r.F, which is a
2n-dimensional vector.
The fault attack is a loop abort on the 2n-loop
which samples the (R, r) coefficients. It causes
the loop to abort at the m
th
iteration, where m ≤
n. This effectively eradicates the vector R, so s
2
becomes: s
2
= (0,.. .,0,r
0
,.. .,r
m−n
)F, or alterna-
tively the polynomial s
2
= r
0
x
n−1
F + r
1
x
n−2
F + ···+
r
m−1
x
n−m
F, which is in the sub-lattice of L(A(F)).
With a certain number of faulty signatures, l ≈m, one
will obtain a set spanning the lattice. From this, lat-
tice reduction can be used to find a short vector, which
should be one of the signed shifts of F, from which
the private basis can be recovered. We now propose a
similar attack which works for FALCON.
4.2 Recursion of FALCON
The FALCON sampling algorithm, shown in Algo-
rithm 3, can be viewed as a recursive form of the GPV
sampler. We change the attack notation to match that
in FALCON’s specifications (Prest et al., 2017), where
(R,r) in the DLP scheme becomes z = (z
0
,z
1
). The
DLP attack inserts a loop abort fault at some itera-
tion, m, of the 2n loop (Espitau et al., 2016, Fig. 2),
however in FALCON this translates to aborting the re-
cursive call early (Prest et al., 2017, Alg. 18). To do
this, we need to examine the structure of the recur-
sion. There are two recursive calls in the top level
of the f f Sampling algorithm, given the target vec-
tor (t
0
,t
1
), it acts first on t
1
, recursively, from right
to left, and then on t
0
. Each of t
1
, and then t
0
, con-
tinuously splits into two vectors of length n := n/2
BEARZ Attack FALCON: Implementation Attacks with Countermeasures on the FALCON Signature Scheme
65

until n = 2, and then samples the coefficients from a
Gaussian distribution, before building back up to give
sample vector (z
0
,z
1
). Hence, there are two recursive
branches within the top level algorithm. Also, this is
all performed within the FFT domain. For a vector
of length n, the first n/2 values represent the real co-
efficients and the second n/2 represent the imaginary
coefficients. So, the initial approach would be to ter-
minate the recursive call at the required point so that
only m −n spaces would be filled, but this would not
work due to the nature of the FFT functions.
4.3 FFT: Merging and Splitting
The sampling algorithm calls merging and splitting
functions as subroutines. These functions do not sim-
ply break up and concatenate the polynomial ring ele-
ments. The split function separates a polynomial into
its even and odd coefficients and is performed in the
FFT domain. Operating in the FFT domain causes is-
sues for the fault attack, since a zero input does not
translate to zero in the FFT domain. Thus, we have
to track the coefficients of the samples as they move
up through the recursive tree of the algorithm. This is
done by manually examining the pseudocode. Once
the lattice vector has been obtained from the Gaus-
sian sample, the FFT
−1
function is applied to it, and
the signing and verifying procedures are the same as
in DLP. This means the same post-processing can be
used from the DLP attack, however we need to ensure
that the signature is not in the FFT domain by apply-
ing the inverse FFT function.
We now present different methods of attack, dif-
ferentiated by the point at which the abortion occurs,
this being the m positions from the end of the vector.
This depends on where the attacker decides to abort
the sample generation. All attack methods lead to the
same output vector format for z; the first (2n −m) co-
efficients of z = (z
0
,z
1
) are forced to zero.
4.3.1 Abort Second Recursion (for m = n)
This attack can be performed in a straightforward
manner. Simply abort at the top sampling algorithm
call, after the first recursive call, after Line 10 of Al-
gorithm 3. Therefore z
1
gets filled with sampled co-
efficients, yet z
0
remains all zeros. This fault abortion
is also performed for the case where m ≤ n, in order
to zero the first n coefficients.
4.3.2 Zeroing or Skipping Attack (for m ≤ n)
There are two options for this attack. First, at the
penultimate merge (n = 256 to 512), set the required
coefficients (e.g., the first half if m = n/2) of the out-
put coefficients to zero by skipping operations or later
zeroing the corresponding coefficients. The skipped
operations are f [(u << 1) + 0] = t_re and f [(u <<
1) + 1] = t_re, from the reference code
2
(Prest et al.,
2017). Otherwise, one can set the first required num-
ber of coefficients of z
1
to zero before computing
the corresponding lattice vector, that is, overwrite the
sampler output z
1
.
4.3.3 Aborting Mid-recursion (m ≤ n)
dimension This attack is more sophisticated, as we
must track the coefficients throughout the tree. Al-
though this requires a prior one-off computation, it
allows the fault to be applied at the one-dimensional
Gaussian sampler stage, which is an easier point to
physically exploit.
Suppose the target is m = n/2; we want the left
half of z
1
to be zero. For this to occur, the left-hand
side (LHS) vector in the final merge_fft() call has to
have its first half equal to zero, and the right-hand side
(RHS) vector has to have the first half of its coeffi-
cients equal to the second half. We generate each real
coefficient (the first half) of the z
1
vector by z
1
[2u] =
f
0
[u] + ( f
1
[u] − f
1
[u + n/4]) andz
1
[2u + 1] = f
0
[u] −
( f
1
[u] − f
1
[u + n/4]), where n is the dimension of the
higher-level vector, and u ∈ {0,.. .,n/4 −1). Note
that constants have been removed from the equations
as they are irrelevant for the result.
For z
1
[2u] and z
1
[2u + 1] to be zero, we can
set f
0
[u] = 0 and f
1
[u] = f
1
[u + n/4] for each u ∈
{0,.. .,n/4 −1). So for n = 512, the first n/4 = 128
coefficients of the LHS 256-dimension vector are set
to equal zero, and the first 128 coefficients of the RHS
256-dimension vector are set to equal the second 128
coefficients.
For the LHS 256-dimension vector, the first half
of its coefficients must equal zero. The LHS 128-
dimension vector must have its first half equal to zero,
and the RHS 128-dimension vector must have the first
half of its values equal to the second half of its values.
This process is repeated on the LHS. The RHS 256-
dimension vector must have the first half coefficients
equal to the second half. For this to occur, the LHS
128-dimension vector must have the real values equal
to the imaginary values, and the RHS 128-dimension
vector must equal zero.
2
Specifically, the merge_fft() function in falcon_fft.c
SECRYPT 2019 - 16th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
66

This conclusion is reached by considering the fact
we want f [2u] = f [2u + n/2] (first real/imaginary
computation per iteration) and f [2u + 1] = f [2u +1 +
n
2
] (second real/imaginary) equal for each iteration of
u.
From the merge_fft() function, this
means f
0
[u] + ( f
1
[u] − f
1
[u + n/4]) =
f
0
[u + n/4] + ( f
1
[u] + f
1
[u + n/4]) and f
0
[u] −
( f
1
[u] − f
1
[u + n/4]) = f
0
[u + n/4] −
( f
1
[u] + f
1
[u + n/4]). To satisfy the components
of the equations, we can set f
0
[u] = f
0
[u + n/4],
that is the first half of coefficients equal to second
half, and for the second component, we can set
f
1
[u] = f
1
[u + n/4] = 0. Therefore the equations will
simply depend on the LHS feed-in vector.
For the RHS, every branch below can be set equal
to zero. Take the LHS 128-dimension vector. It fol-
lows the same conditions as the level above, that is
the LHS 64-dimension vector must have its real and
imaginary values equal, and the RHS must be zero.
Any vector equalling zero must have both feed-in vec-
tors equalling zero, so the branches below this can be
zeroed. This method can be applied for any m such
that m = 2
k
, where k ∈ Z.
4.4 Post-attack Processing
The final step of the attack involves recovery of the
private basis from the faulty signatures. Suppose we
have the first 2n −m coefficients of vector (z
0
,z
1
)
equal to zero. Then, according to the signing algo-
rithm (Algorithm 2) of FALCON, we compute the sig-
nature s
2
as:
s = t −z
ˆ
B,
where
ˆ
B is the basis matrix in the FFT domain. But
we only need the second half of s, that is s
2
, where
s
2
= t
1
−z
−A( f )
−A(F)
,
and since t
1
is set to zero,
s
2
= −z
−A( f )
−A(F)
.
Furthermore, the first m −n coefficients of z are zero,
which further implies:
s
2
= −z
1
(−A(F)) ,
and since some of the coefficients of z
1
are zero, we
finally have:
s
2
= (z
1
[m −1]x
n−m
F + ···+ z
1
[0]x
n−1
F).
This leaves us with a sub-lattice of the lattice gener-
ated by F, akin to that obtained in the DLP attack.
The only difference is that we are in the FFT do-
main, which we overcome by applying the inverse
FFT function to the output. Thus, with multiple faulty
signatures, the lattice spanned by F (where F is a
short vector in this lattice) can be found, where the
BKZ algorithm can be used to retrieve it. Then G, f ,
and g can be deduced from the public key h, and thus
the private NTRU lattice basis can be found.
4.5 Attack Results
The aim of this research is to show that if this fault at-
tack is applied successfully, the the output can reveal
the private key. The technicalities of the fault injec-
tion are left as future work. Thus, to verify this attack
model, we first tested each method of attack through
software simulation and ensured the output signature
gave the expected number of zeros. This was success-
ful for all attack methods and parameter sets. We then
collected l faulty signatures for the values of m zeros
given in Table 2, and ran the BKZ algorithm (FPLLL
Development Team, 2016) to obtain the private key
polynomial F. The timings in seconds for the BKZ
algorithm to obtain F are given in Table 2. The as-
sumptions and attack model are similar to that used
by Espitau et al. (2016), in particular for estimating
the number of faults required.
4.6 Fault Model
The physical attack methods required for BEARZ are
early abortion and zeroing. Side-channel analysis
may be used to detect the window between the first
call and the second recursive call, within which the
algorithm can be aborted, as in the original DLP at-
tack. A zeroing attack can be performed as a memory-
based attack, during storage of the vector in RAM,
by setting the required bits to zero (Naccache et al.,
2005). Alternatively, skipping lines of code can be
performed by CPU clock glitching (Blömer et al.,
2014). With respect to the fault models guide (Ver-
bauwhede et al., 2011), we can classify the BEARZ
fault attack models as being on the processing part
(for zeroing) and program flow (for skipping and
aborting). These are high precision attacks, where the
adversary has the ability to bit flip/set, and targets the
cryptographic primitive.
4.7 Countermeasures to BEARZ
Bindel et al. (2017) discuss countermeasures rele-
vant to BEARZ. A straightforward method of detect-
ing fault attacks (such as by Bruinderink and Pessl
BEARZ Attack FALCON: Implementation Attacks with Countermeasures on the FALCON Signature Scheme
67
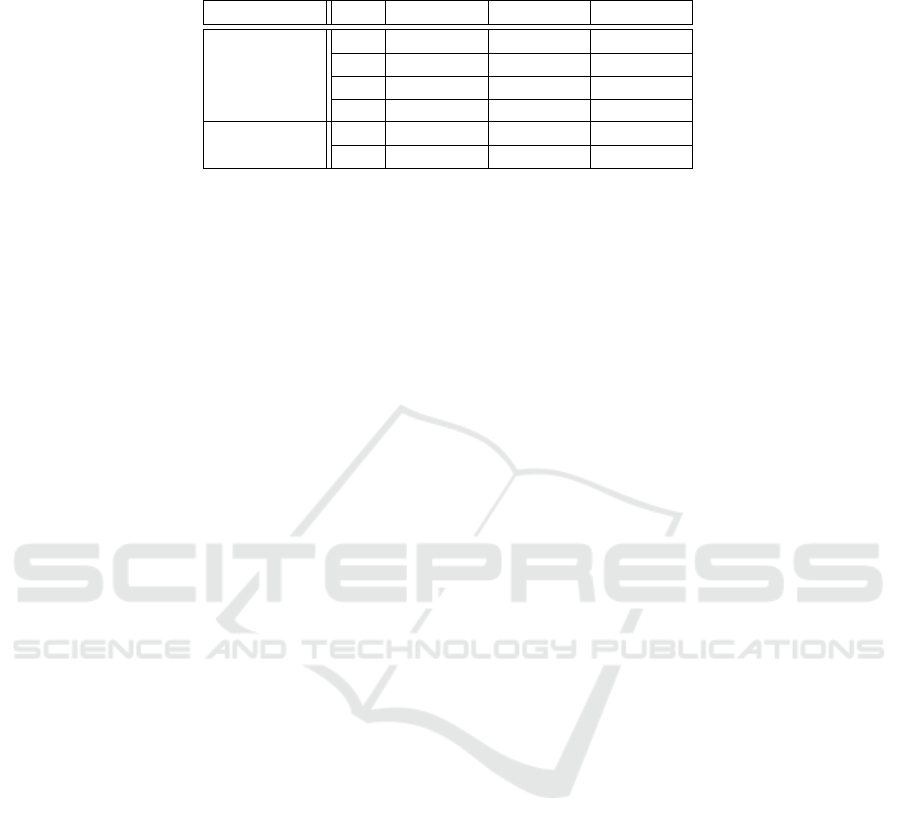
Table 2: Timings (in seconds) to run the BKZ algorithm on l faulty signatures to obtain the basis polynomial F running on a
single core of an Intel Core i7-6700HQ CPU at 2.60 GHz.
Parameters m l = m + 1 l = m +2 l = m + 3
Set 1
64 0.07 0.07 0.08
128 0.35 0.30 0.36
256 2.17 2.80 2.36
385 10.9 12.8 11.8
Set 2
128 0.28 0.29 0.35
256 2.24 2.55 2.67
(2018)) is to compute the signature twice. The dou-
ble computation method works for non-deterministic
schemes by fixing the randomness. A conservative
estimate of this is doubling the signing time. Run-
ning the verification process immediately after sign-
ing can give the signer confidence that their hardware
has not been subject to fault attacks (Bruinderink and
Pessl, 2018). A simple, efficient method of detecting
the BEARZ attack is checking that the sampled vector
does not go to zero at some point along its length at
the end of the f f Sampler algorithm.
5 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
This section analyses the performance results of the
optimised software design of the FALCON signature
scheme, as well as the three countermeasures dis-
cussed in the previous section. Clearly, as with any
attack countermeasure, we expect some performance
degradation, however we are more concerned with
their relative impacts on performance. Unless oth-
erwise stated, performance figures were obtained on
Intel E5-1620 CPU @ 3.7GHz, with hyperthreading
disabled, running on a single CPU. The platform of
the reference figures are also stated. Any results with
“-” mean the results are unchanged, thus not being af-
fected by the countermeasure(s).
Our libSAFEcrypto implementation consists of
portable C code that is written to permit a compiler
(gcc) to generate AVX-2 assembler (or any other type
of SIMD code) without having to revert to writing
assembler code by hand. It can also be ported to
other target processors (like ARM) without having
to re-write the code; this portability was set out as
one of our major design goals in the project to pro-
vide for wide adoption. This portability comes at a
performance cost, but is advantageous if one wants
to support various systems (embedded or server),
quickly adapt to changing algorithms (like a NIST
post-quantum scheme), or are looking for wide sup-
port. Therefore our performance is lower than the ref-
erence implementation by Prest et al. (2017).
5.1 FALCON with Countermeasures
Results for our FALCON optimised designs and the
effects of our countermeasures are shown in Table 3.
Parameter sets for FALCON slightly changed for the
second round of NIST’s post-quantum standardisa-
tion. Specifically, the second set of parameters, thus
we have omitted these from our results and perfor-
mance analysis and focus on parameter sets 1 and 2.
Interestingly, FALCON’s performance is not
largely affected by the countermeasures. Applying
verify-after-sign to protect against BEARZ does not
significantly slow performance (∼ 5%), and the key
generation only drops significantly with a high sam-
ple discard rate. The recommended combination of
countermeasures together slow the key generation and
signing down by less than 5% for Parameter Set 1.
Sample discard has less than a 5% effect on key gen-
eration, and the effect of the 6.5% rate on Parameter
Set 1 is so minimal that the effect of fluctuation causes
an increase from the rate without discard. This small
effect on performance is due to the sampling and ver-
ification processes being efficient.
5.2 Effectiveness of Countermeasures
5.2.1 Timing Attacks
To verify our timing attack countermeasure, we ran
the signing procedure 100 times and found for Set 1,
it fell within a range of 50 operations per second, and
for Set 2 within 20 operations per second. This sug-
gests it is effective against timing attacks.
5.2.2 BEARZ Attack
If the same fault is successfully implemented twice,
then double computation will not suffice. The verify-
after-sign may not detect a fault attack which targets
the sampling, this has been shown previously by Espi-
tau et al. (2016), thus it still may produce a valid sig-
nature and go undetected. However, the zero-check
countermeasure should detect the attack with 100%
SECRYPT 2019 - 16th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
68
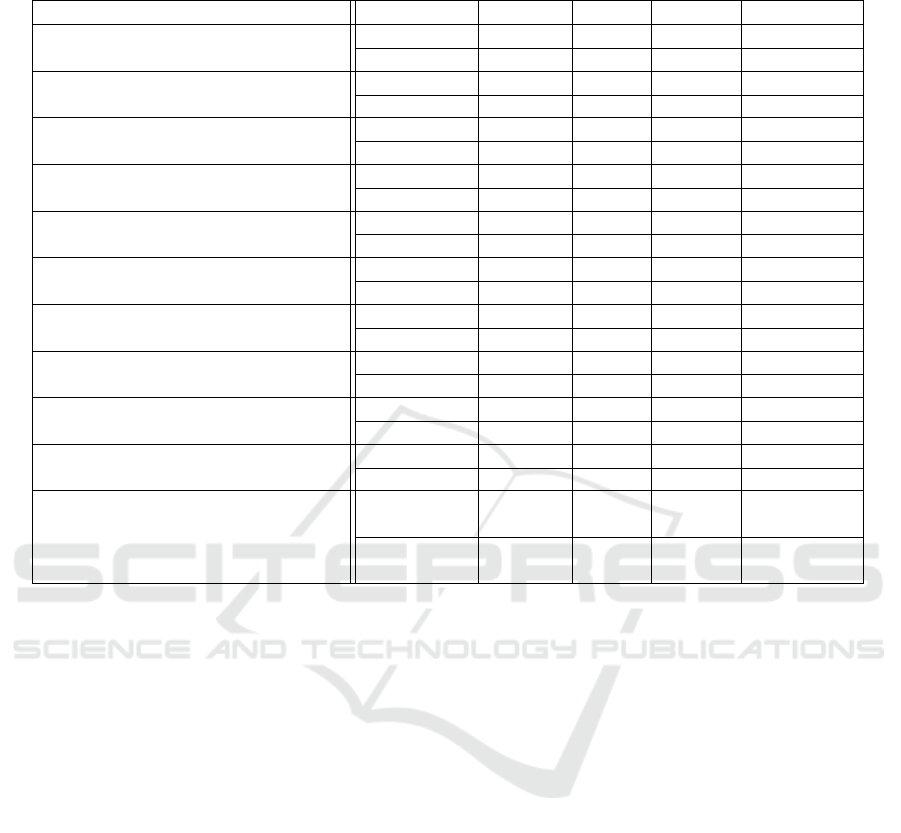
Table 3: Performance results (ops/sec) for FALCON with SCA countermeasures, including % decrease in affected components,
on Intel E5-1620 @ 3.7GHz unless otherwise stated.
Implementation Parameters KeyGen Sign Verify % decrease
Reference (Prest et al., 2017)
Intel Core i7-6567U @ 3.3GHz
Set 1 143 6081.9 37175.3 -
Set 2 50.9 3072.5 17697.4 -
Baseline
+constant-time NTT
Set 1 29.8 1484 29002 -
Set 2 11.1 734 14366 -
+Verify-after-sign
Set 1 - 1412 - 5
Set 2 - 699 - 5
+Zero-check
Set 1 - 1006 - 32
Set 2 - 489 - 16
+Double Computation
+Verify after sign
Set 1 - 706 - 52
Set 2 - 350 - 76
+Sample Discard (Low) (6.25%)
Set 1 26.3 - - 12
Set 2 12.0 - - +8
+Sample Discard (Medium) (12.5%)
Set 1 24.9 - - 16
Set 2 10.2 - - 8
+Sample Discard (High) (25%)
Set 1 27.7 - - 7
Set 2 8.0 - - 28
+Fisher-Yates Shuffling
Set 1 23.87 - - 20
Set 2 10.9 - - 2
+BlindVector
Set 1 27.03 - - 9
Set 2 8.7 - - 49
+Verify-after-sign
+Sample Discard (Low) (6.25%)
+Fisher-Yates Shuffling
Set 1 29.0 1426 - 4
Set 2 10.7 706 - 4
success rate. We therefore recommend this as a mini-
mum, sufficient countermeasure.
5.3 Comparison to Other Lattice-based
Signature Schemes
We compare our results to our implementation of
Dilithium (Lyubashevsky et al., 2017) and Bliss-B
(Ducas, 2014) signature schemes with countermea-
sures in place. Interestingly, the performance of FAL-
CON is not as adversely affected as much as its NIST
competitor scheme Dilithium when the verify-after-
sign countermeasure is added, as shown in Figure
1b. Even at high security levels, it does not suffer
as much of a slowdown as BLISS-B, shown in Fig-
ure 1a. This is due to the efficiency of the FALCON
components. Similar countermeasures on Dilithium
that prevent the fault attack proposed by Bruinderink
and Pessl (2018), cause its performance to deterio-
rate by almost 20%. BLISS-B has a larger range of
countermeasures available in order to protect against
those proposed by Pessl et al. (2017), meaning the ef-
fect on performance can range between an additional
10% and 50%, depending on the instance. Dilithium
has the advantage of being immune to Gaussian sam-
pler attacks, however its protection from the fault at-
tacks by Bruinderink and Pessl (2018) remain an open
problem. Its performance is slowed down by nearly
20% with countermeasures in place and has greater
degradation than BLISS-B with a protected Gaussian
sampler.
6 CONCLUSION
In this research, we have proposed a new attack on
the FALCON signature scheme, BEARZ. We have
shown that FALCON is vulnerable to fault attacks on
its Gaussian sampler and so consideration of physical
attacks should be addressed when implementing for
real world use. We also provide possible countermea-
sures, including the verify-after-sign countermeasure,
as the faulty signature will not pass the norm bound
test, and the zero-check. Furthermore, we implement
double computation, a costly but reliable method, as-
suming the attacker only has access to the hardware
during one of the signing processes. Additionally,
we review timing attack vulnerabilities and counter-
measures and compare the impact on performance to
other lattice-based schemes, deducing that FALCON is
BEARZ Attack FALCON: Implementation Attacks with Countermeasures on the FALCON Signature Scheme
69
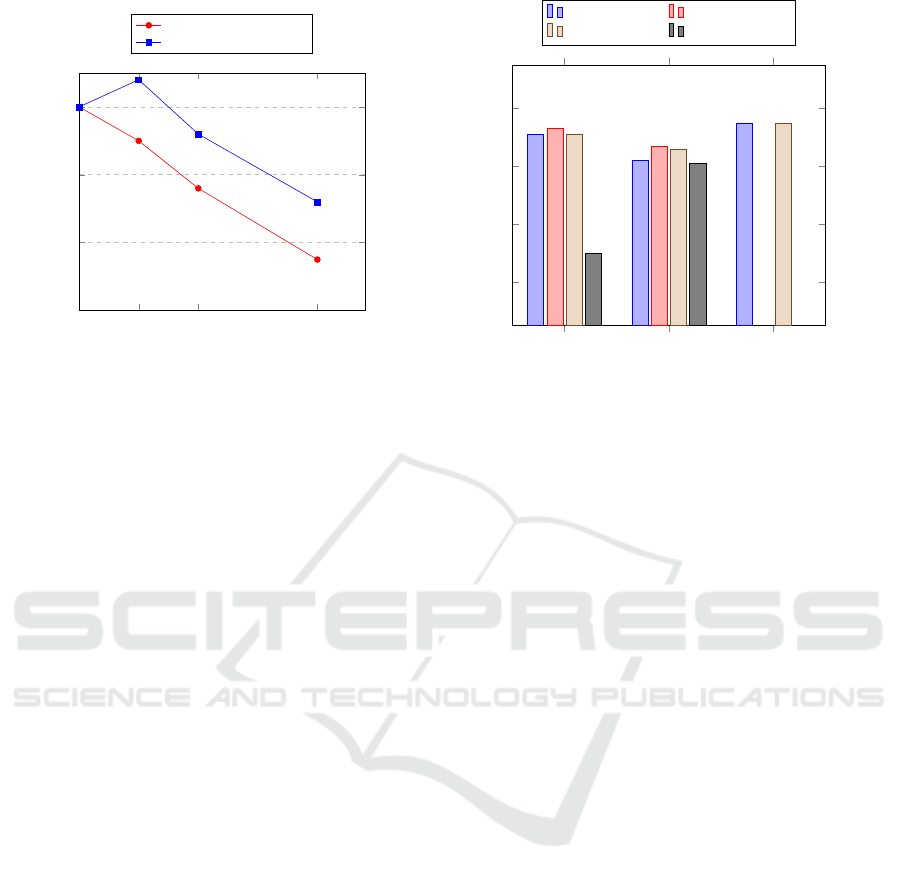
0
6.25 12.5 25
40
60
80
100
110
Sample discard rate (%)
Degredation of performance (%)
BLISS-B Signing (Set-IV)
FALCON KeyGen (Set 2)
(a) Sample Discard countermeasure effect
on BLISS-B and FALCON for equivalent
(192-bit) security levels.
BLISS-B Dilithium
FALCON
40
60
80
100
91
82
95
93
87
91
86
95
50
81
Degredation of performance (%)
Parameter Set-I Parameter Set-II
Parameter Set-III Parameter Set-IV
(b) Verify-after-sign effect on BLISS-B,
Dilithium, and FALCON.
Figure 1: Performance analysis of the proposed SCA countermeasures for the FALCON, Dilithium, and BLISS-B signatures.
a still a competitive second-round candidate.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Thomas Prest and the
anonymous reviewers of T-CHES 2019 and COSADE
2019 for their careful reading of the paper and their
diligent comments. The authors would also like to
acknowledge that this work was supported in part
by the European Union Horizon 2020 SAFEcrypto
project (grant no. 644729) and the EPSRC via grant
EP/N011635/1.
REFERENCES
Ajtai, M. and Dwork, C. (1997). A public-key cryptosystem
with worst-case/average-case equivalence. In STOC
’97 Proceedings of the twenty-ninth annual ACM sym-
posium on Theory of computing, pages 284–293.
Alagic, G., Alperin-Sheriff, J., Apon, D., Cooper, D., Dang,
Q., Liu, Y.-K., Miller, C., Moody, D., Peralta, R.,
Perlner, R., Robinson, A., and Smith-Tone, D. (2019).
Status Report on the First Round of the NIST Post-
Quantum Cryptography Standardization Process.
http://aiweb.techfak.uni-bielefeld.de/content/bworld-
robot-control-software/. [Online; accessed February
2019].
Alkim, E., Ducas, L., Pöppelmann, T., and Schwabe, P.
(2016). Post-quantum key exchange-a new hope. In
USENIX Security Symposium, volume 2016.
Bindel, N., Buchmann, J., and Krämer, J. (2016). Lattice-
based signature schemes and their sensitivity to fault
attacks. In Fault Diagnosis and Tolerance in Cryp-
tography (FDTC), 2016 Workshop on, pages 63–77.
IEEE.
Bindel, N., Kramer, J., and Schreiber, J. (2017). Special ses-
sion: hampering fault attacks against lattice-based sig-
nature schemes-countermeasures and their efficiency.
In Hardware/Software Codesign and System Synthe-
sis (CODES+ ISSS), 2017 International Conference
on, pages 1–3. IEEE.
Blömer, J., Silva, R. G. D., Günther, P., Krämer, J., and
Seifert, J.-P. (2014). A practical second-order fault
attack against a real-world pairing implementation.
In Fault Diagnosis and Tolerance in Cryptography
(FDTC), 2014 Workshop on, pages 123–136. IEEE.
Bruinderink, L. G., Hülsing, A., Lange, T., and Yarom, Y.
(2016). Flush, Gauss, and reload-a cache attack on
the BLISS lattice-based signature scheme. In Inter-
national Conference on Cryptographic Hardware and
Embedded Systems, pages 323–345. Springer.
Bruinderink, L. G. and Pessl, P. (2018). Differential fault at-
tacks on deterministic lattice signatures. IACR Trans-
actions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded
Systems, pages 21–43.
Ducas, L. (2014). Accelerating BLISS: the geometry of
ternary polynomials. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Re-
port 2014/874. https://eprint.iacr.org/2014/874.
Ducas, L., Lyubashevsky, V., and Prest, T. (2014). Efficient
identity-based encryption over ntru lattices. In Inter-
national Conference on the Theory and Application
of Cryptology and Information Security, pages 22–41.
Springer.
Ducas, L. and Prest, T. (2016). Fast fourier orthogonal-
ization. In Proceedings of the ACM on International
Symposium on Symbolic and Algebraic Computation,
pages 191–198. ACM.
Espitau, T., Fouque, P., G’erard, B., and Tibouchi, M.
(2018). Loop-abort faults on lattice-based signature
SECRYPT 2019 - 16th International Conference on Security and Cryptography
70

schemes and key exchange protocols. IEEE Transac-
tions on Computers, 67(11):1535–1549.
Espitau, T., Fouque, P.-A., Gérard, B., and Tibouchi, M.
(2016). Loop-abort faults on lattice-based fiat-shamir
and hash-and-sign signatures. In International Con-
ference on Selected Areas in Cryptography, pages
140–158. Springer.
Fisher, R. A., Yates, F., et al. (1938). Statistical tables for
biological, agricultural and medical research. Statis-
tical tables for biological, agricultural and medical
research.
FPLLL Development Team, O. T. (2016). fplll,
a lattice reduction library. Available at
https://github.com/fplll/fplll.
Gentry, C. and Boneh, D. (2009). A fully homomorphic
encryption scheme, volume 20. Stanford University
Stanford.
Hodgers, P., Regazzoni, F., Gilmore, R., Moore, C., and
Oder, T. (2016). State-of-the-art in physical side-
channel attacks and resistant technologies. Technical
report.
Howe, J., Khalid, A., Rafferty, C., Regazzoni, F., and
O’Neill, M. (2016). On practical discrete Gaussian
samplers for lattice-based cryptography. IEEE Trans-
actions on Computers.
Howe, J., Pöppelmann, T., O’Neill, M., O’Sullivan, E.,
and Güneysu, T. (2015). Practical lattice-based digital
signature schemes. ACM Transactions on Embedded
Computing Systems (TECS), 14(3):41.
Karmakar, A., Roy, S. S., Reparaz, O., Vercauteren, F., and
Verbauwhede, I. (2018). Constant-time discrete gaus-
sian sampling. IEEE Transactions on Computers.
Khalid, A., Howe, J., Rafferty, C., and O’Neill, M.
(2016). Time-independent discrete gaussian sampling
for post-quantum cryptography. In 2016 Interna-
tional Conference on Field-Programmable Technol-
ogy (FPT), pages 241–244. IEEE.
Khalid, A., Oder, T., Valencia, F., O’Neill, M., Güneysu,
T., and Regazzoni, F. (2018). Physical protection of
lattice-based cryptography: Challenges and solutions.
In Proceedings of the 2018 on Great Lakes Symposium
on VLSI, pages 365–370. ACM.
Longa, P. and Naehrig, M. (2016). Speeding up the number
theoretic transform for faster ideal lattice-based cryp-
tography. In International Conference on Cryptology
and Network Security, pages 124–139. Springer.
Lyubashevsky, V., Ducas, L., Kiltz, E., Lepoint, T.,
Schwabe, P., Seiler, G., and Stehle, D. (2017).
CRYSTALS-Dilithium. Technical report, National
Institute of Standards and Technology. avail-
able at https://csrc.nist.gov/projects/post-quantum-
cryptography/round-1-submissions.
Micciancio, D. and Walter, M. (2017). Gaussian sampling
over the integers: Efficient, generic, constant-time. In
Annual International Cryptology Conference, pages
455–485. Springer.
Naccache, D., Nguyen, P. Q., Tunstall, M., and Whelan,
C. (2005). Experimenting with Faults, Lattices and
the DSA. In International Workshop on Public Key
Cryptography, pages 16–28. Springer.
NIST (2016a). Post-quantum crypto project.
http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/ST/post-quantum-crypto/.
NIST (2016b). Submission requirements and
evaluation criteria for the post-quantum
cryptography standardization process.
https://csrc.nist.gov/csrc/media/projects/post-
quantum-cryptography/documents/call-for-proposals-
final-dec-2016.pdf.
Pessl, P. (2016). Analyzing the shuffling side-channel coun-
termeasure for lattice-based signatures. In Interna-
tional Conference in Cryptology in India, pages 153–
170. Springer.
Pessl, P., Bruinderink, L. G., and Yarom, Y. (2017). To
BLISS-B or not to be: Attacking strongSwan’s Imple-
mentation of Post-Quantum Signatures. In Proceed-
ings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Com-
puter and Communications Security, pages 1843–
1855. ACM.
Prest, T., Fouque, P.-A., Hoffstein, J., Kirchner, P., Lyuba-
shevsky, V., Pornin, T., Ricosset, T., Seiler, G., Whyte,
W., and Zhang, Z. (2017). Falcon. Technical re-
port, National Institute of Standards and Technol-
ogy. available at https://csrc.nist.gov/projects/post-
quantum-cryptography/round-1-submissions.
Primas, R. (2017). Side-channel attacks on efficient lattice-
based encryption. Master’s thesis, Graz University of
Technology, Graz.
Regev, O. (2005). On lattices, learning with errors, ran-
dom linear codes, and cryptography. In Proceedings of
the 37th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Com-
puting, Baltimore, MD, USA, May 22-24, 2005, pages
84–93.
Regev, O. (2009). On lattices, learning with errors, random
linear codes, and cryptography. Journal of the ACM
(JACM), 56(6):34:1–34:40.
Roy, S. S., Reparaz, O., Vercauteren, F., and Verbauwhede,
I. (2014). Compact and side channel secure discrete
Gaussian sampling. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive,
2014:591.
Saarinen, M.-J. O. (2015). Gaussian sampling precision
and information leakage in lattice cryptography. IACR
Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2015:953.
Saarinen, M.-J. O. (2017). Arithmetic coding and blind-
ing countermeasures for lattice signatures. Journal of
Cryptographic Engineering, pages 1–14.
Scott, M. (2017). A note on the implementation of the num-
ber theoretic transform. In IMA International Confer-
ence on Cryptography and Coding, pages 247–258.
Springer.
Shor, P. W. (1999). Polynomial-time algorithms for prime
factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum
computer. SIAM Review, 41(2):303–332.
Verbauwhede, I., Karaklajic, D., and Schmidt, J.-M. (2011).
The fault attack jungle-a classification model to guide
you. In 2011 Workshop on Fault Diagnosis and Toler-
ance in Cryptography, pages 3–8. IEEE.
BEARZ Attack FALCON: Implementation Attacks with Countermeasures on the FALCON Signature Scheme
71
