
A Hierarchical Planner based on Set-theoretic Models: Towards
Automating the Automation for Autonomous Systems
Bernd Kast
1 a
, Vincent Dietrich
1 b
, Sebastian Albrecht
1 c
, G. Wendelin Feiten
1 d
,
and Jianwei Zhang
2
1
Siemens AG, Corporate Technology, Otto-Hahn-Ring 6, 81739 Munich, Germany
2
University of Hamburg, Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural Sciences,
Vogt-K
¨
olln-Str. 30, 22527 Hamburg, Germany
Keywords:
Hierarchy, Planning, Autonomy.
Abstract:
The complexity of today’s autonomous systems renders the manual engineering of control strategies or be-
haviors for all possible system states infeasible. Therefore, planning algorithms are required that match the
capabilities of the system to the tasks at hand. Solutions to typical problems with robotic systems combine
aspects of symbolic action planning with sub-symbolic motion planning and control. The problem complexity
of this combination currently prohibits online planning without task specific, manually defined heuristics. To
counter that we use a set-theoretic approach to model declarative and procedural knowledge which allows for
flexible hierarchies of planning tasks. The coordination of the planning tasks on different levels, the classifi-
cation of information and various views on data are the core functions of hierarchical planning. We propose
suitable graph structures to capture all relevant information and discuss the elements of our hierarchical plan-
ning algorithm in this paper. Furthermore, we present two use-cases of an autonomous manufacturing system
to highlight the capabilities of our system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Setting up autonomous systems still requires huge in-
tegration and engineering efforts. In order to make
them widely applicable, we need a holistic approach
that even considers aspects of component integration.
This is especially important in production, where a
higher degree of automation, notably for small lot
sizes, can account for changing customer demands.
A limiting factor of today’s automation strate-
gies is the interwoven product and production design
which requires costly manual effort even for small
changes of some component (Hitomi, 2017), (Bryan
et al., 2007). To reduce this effort, the design process
of the product and the production system have to be
decoupled (Hu et al., 2011) and then matched again
by an autonomous system. Thus, the autonomous sys-
tem has to solve on its own certain engineering tasks
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7838-3142
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0568-9727
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3647-4043
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7593-6298
Figure 1: Images of the robotic system (upper right) and
the hat-rail with components (left) and the box next to its
lid (lower right).
that these days are addressed manually when automat-
ing a production system, i.e. the automation of au-
tomation (Schmitz et al., 2009) is necessary for flexi-
ble autonomous systems.
This requires general models which character-
ize objects by their properties (declarative knowl-
edge) and describe actions modifying them (proce-
dural knowledge). These models define domains for
Kast, B., Dietrich, V., Albrecht, S., Feiten, G. and Zhang, J.
A Hierarchical Planner based on Set-theoretic Models: Towards Automating the Automation for Autonomous Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0007840702490260
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2019), pages 249-260
ISBN: 978-989-758-380-3
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
249

suitable planners. Real-world manufacturing domains
suffer from a huge computational complexity due to
their mixed continuous and discrete nature. Dis-
crete symbolic action planning and scheduling bring
in the problem of combinatorial explosion while sub-
symbolic tasks such as motion planning or control in-
troduce time, accuracy and stability constraints. A
common approach to address this curse of dimension-
ality is to use abstractions or hierarchies to decom-
pose the problem. This allows to extract smaller sub-
problems that are easier to handle. It is especially im-
portant to deduce those hierarchies for both, proce-
dural and declarative knowledge, automatically from
the models in order to keep the task and plant descrip-
tion separate. Additionally, assumptions that limit the
flexibility of the system have to be avoided. One ex-
ample is the downward refinement property which de-
mands that each coarse plan can be refined on all more
detailed levels. This is in general not viable for real-
world problems with decoupled models for the prob-
lem and the plant. This becomes obvious for task spe-
cific sub-symbolic properties, such as possible grasp
positions, which can for the general case not be mod-
eled on an abstract, purely symbolic level.
Throughout this paper, we illustrate our approach
with an industrial assembly use-case, cf. Figure 1,
which is modeled for maximal flexibility. This means
in particular, that not only the actions of the robot,
but even the interplay between software components
is planned, cf. section 8. We present a planner that
benefits from models that integrate declarative and
procedural knowledge and allow for an automatic cal-
culation of abstractions. This planner uses the graph
structures of our models on different abstraction lev-
els to factorize the problem, integrates special single-
level planners for individual subproblems but does not
depend on the downward refinement property.
The paper is structured as follows: In section 2
we present related work regarding hierarchical sym-
bolic planning, combined task and motion planning in
robotics and autonomous production systems. After
that, we discuss a set-theoretic approach for declara-
tive and procedural models that natively enables the
deduction of hierarchical structures in section 3. The
data structures for the single-level planning are de-
scribed in section 4 and the respective single-level
planner is discussed in section 5. In section 6 we
extend these concepts for the hierarchical planning
context. Finally, we present the hierarchical planning
method in section 7 and demonstrate its features on
two examples in section 8.
2 RELATED WORK
Planning algorithms are often tailored to modeling
languages and rely on their expressiveness. In this
section we discuss both symbolic and sub-symbolic
planning, as well as the application specific aspects
related to for autonomous production systems.
2.1 (Hierarchical) Action Planning
The key for flexible systems is a modeling language
that formalizes the description of the domain. On
the symbolic level, there are many languages such as
PDDL (McDermott et al., 1998) and its dialects that
focus on the procedural knowledge of a domain. A
long series of planning competitions have resulted in
a large set of fast planners for PDDL domains such
as (Helmert, 2006). Extensions to PDDL add sup-
port for certain sub-symbolic properties such as time.
An example is PDDL+ (Fox and Long, 2002) that
introduces events and processes to model exogenous
change and support domains with mixed discrete and
continuous dynamics. Corresponding solvers, such as
(Cashmore et al., 2016) or (Piotrowski et al., 2016),
make use of this representation and handle domains
with nonlinear continuous change. They approximate
the dynamics of the system and handle the result-
ing discretized model with uniform time steps and
step functions. Other PDDL dialects, e.g. (Dornhege
et al., 2009), extend the formalism by using seman-
tic attachments that allow for an evaluation of exter-
nally specified functions. Though, this requires mod-
ifying standard PDDL planners and to create domain-
specific PDDL action choosing the specific external
functions.
Another approach is partial-order planning (POP)
(Young et al., 1994) which involves partially spec-
ified action decompositions. In this approach, the
planner is only allowed to fill in missing pieces of a
fixed plan template which hugely reduces the search
space. However, it is difficult to ensure the separation
of hardware and task description with this approach,
which reduces the flexibility.
A large community addresses hierarchical task
networks (HTN) that refine each abstract skill by a
network of sub-methods, e.g. (Castillo et al., 2006),
(Goldman, 2006), (Nau et al., 2003). In their ba-
sic form they were state-oriented and could not deal
with time constraints or concurrent actions. Never-
theless, the formalism is more expressive than that of
first principle planners (Erol et al., 1994), HTN meth-
ods can improve planning times (Nau et al., 2003)
and even support plan reparation (Gateau et al., 2013).
In (Bercher et al., 2016) an overview of HTN meth-
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
250

ods is provided that discusses the expressiveness of
hierarchical planning formalisms as well as implica-
tions of preconditions and effects of abstract meth-
ods. A mandatory and limiting condition for HTNs
is the downward refinement property that enforces re-
finements to all abstract solutions (Bacchus and Yang,
1994). Yet, the generation of suitable abstract models
for a domain is a challenging or even impossible task
and often results in a coupling between task and hard-
ware description.
This becomes obvious in (Marthi et al., 2008).
They propose expressive models, which allow for the
definition of domains with the downward refinement
property. In this approach, an underlying semantic
that defines preconditions and effects even for abstract
tasks, ensures that abstract plans can always be re-
fined to a primitive solution. However, this demands
that all relevant effects and preconditions of the prim-
itives have to be considered even on the most abstract
level. This is only possible if all properties can be de-
scribed symbolically and hugely limits the benefits of
the hierarchical abstractions.
To overcome the limitations induced by the down-
ward refinement property, several variants of HTN
planning and hybrid planning (Kambhampati et al.,
1998), (Schattenberg, 2009) have been proposed. The
hierarchical partial-order planner, introduced in (Be-
chon et al., 2014), uses additional knowledge that de-
scribes sets of abstract actions with optional methods
to increase flexibility during refinement. Another ap-
proach to improve versatility is the combination of
HTN and POP in a domain-specific planner with a
strict separation between several hierarchical levels
(Castillo et al., 2003). In both approaches the effects
of the downward refinement property are mitigated at
the cost of models which are dependent on the hard-
ware and the task at the same time.
Temporal reasoning within an HTN planner is dis-
cussed in (Castillo et al., 2006) and an HTN ex-
tension for (nonlinear) continuous temporal environ-
ments can be found in (Molineaux et al., 2010),
in which the SHOP2 planner (Nau et al., 2003) is
matched to features from PDDL+ (Fox and Long,
2002). Those approaches offer a suitable perfor-
mance even in domains with sub-symbolic properties
but don’t support general geometric constraints such
as collisions. An overview of HTN planning can be
found in (Georgievski and Aiello, 2015).
Each of those approaches extends the application
area. Summarizing we state that manually drafted hi-
erarchies, the strict requirement of the downward re-
finement property or a limited support of continuous
properties prevents an application in our general man-
ufacturing domain.
2.2 Combined Task and Motion
Planning in Robotics
A challenging and widely discussed subproblem for
autonomous systems in production is task and mo-
tion planning. In (Srivastava et al., 2014) existing
task planners and motion planners are combined by
the introduction of new symbolic abstractions. Mo-
tion planning is used to refine the plans from symbolic
planning to a sub-symbolic level. The general idea
is to add further abstract poses to the symbolic plan-
ning problem every time the refinement failed because
no collision-free path could be found. This allows
to consider continuous properties on an abstract level
without manual prior modeling. However, the com-
putational complexity is shifted to the abstract level.
The advantages of the hierarchy are additionally re-
duced by the limited number of abstractions that are
possible with this approach.
Instead of combining of two separate planners
(Garrett et al., 2015) extends the symbolic planners
and their heuristics to motion planning and thus lifts
the sub-symbolic world to the symbolic planning. The
heuristic is based on domain-dependent literals that
represent reachability for example, which can be eval-
uated lazily on demand. The planner maintains a
corresponding reachability graph of sampled config-
urations. Geometric constraint-satisfaction problems
(CSP) determine plan templates with unbound vari-
ables like robot and object poses (Lozano-P
´
erez and
Kaelbling, 2014). The central disadvantages of these
approaches are that a discretization has to be specified
in advance and that they run into scalability issues if
a fine discretization is needed.
Another possibility is to add the symbolic prop-
erties to the sub-symbolic path planning problem. If
a simple symbolic planner is used to generate action
sequences, large optimization problems can be for-
mulated that determine optimal intermediate and fi-
nal states (Toussaint, 2015). They demonstrated the
strength of their approach for a stacking problem in
which towers of cylinders and plates have to be as-
sembled. However, it is computationally too demand-
ing for online planning and scales exponentially with
the number of involved objects.
The ScottyActivity planner (Fernandez-Gonzalez
et al., 2018) is one of the few approaches that con-
sider dynamics and/or temporal constraints along the
manipulation problem. It combines strong heuristics
with convex optimization and relaxed plan graphs.
However, the absence of obstacles and the limitation
to linear dynamics for the robots prohibits the appli-
cability for real-world problems.
In (Schmitt et al., 2017) an asymptotically optimal
A Hierarchical Planner based on Set-theoretic Models: Towards Automating the Automation for Autonomous Systems
251
manipulation planner is proposed that considers both,
nonlinear dynamics and collisions. Without any hier-
archical decomposition or heuristics, their approach,
which extends sampling-based roadmap planners to
explore configuration spaces, scales exponentially.
2.3 Autonomous Production Systems
There are three main challenges for autonomous
robotics in production: planning to generate a coarse,
symbolic plan, mapping the plan to the actual hard-
ware and controlling it accordingly. The pioneering
system (Kaufman et al., 1996) is one of the few who
proposed an integrating approach to target all three
challenges at a time. However, this approach relied
on substantial task specific manual modeling of sub-
assemblies, which limits flexibility. Additionally, the
approach is tested in simulation only and therefore it
neglects sensor input and generates a nominal control
code only. In (Thomas and Wahl, 2010) an improved
version is presented that uses CAD data and other
models to compute assembly sequences that comply
with the desired goal configuration. The optimal plan
is chosen, mapped to the robot’s skills and executed
on the hardware. Due to the lack of a hierarchical de-
composition, this approach, however, suffers from the
curse of dimensionality.
3 FORMAL MODELS
The planning process requires models for declara-
tive and procedural knowledge. For our hierarchi-
cal planning approach, it is especially important that
both types are naturally hierarchically structured and
that these hierarchies match each other. We accom-
plish that with the following set-theoretic definitions,
which have been introduced in more detail in (Kast
et al., 2019).
3.1 Concepts
In this work we use the term concepts for elements of
the declarative knowledge. An example of such a con-
cept is a simple box. Each specific box is an instance
of the abstract concept ”box”, but the properties of
boxes differ in detail. For example, the shape might
be different, as one box is cubic and the other cylin-
drical. Thus, we have an abstract concept of a box and
two specializations capturing subsets. This notion of
concepts can be formally grounded by following set-
theoretic definitions:
• A concept base B
Γ
is the set of instances, not nec-
essarily finite.
• A concept C is a subset of B
Γ
, i.e., C ⊆ B
Γ
.
• A concept class Γ is the set of concepts C
i
that
have a common concept base B
Γ
, i.e.,
∀ C
i
∈ Γ, b ∈ C
i
: b ∈ B
Γ
.
• A partial order M , describing more detailed than,
can be defined on Γ: (C
i
,C
j
) ∈ M iff C
i
⊂ C
j
.
Extending the previous example: In most cases
you do not only want to know the shape of the box
but also the characteristics of the dimensions. Fur-
ther properties, like the weight or the current location,
might also be interesting. This directly leads to spe-
cial types of concepts, which we call composite con-
cepts.
The following definitions introduce composite
concepts formally:
• Given an ordered set R of identifiers, e.g. strings,
its elements r ∈ R are called roles. Thus, for each
subset R
i
⊆ R with n
R
i
:= |R
i
| there exists a bi-
jective mapping J to N
n
R
i
:= {1, . . . , n
R
i
}, i.e.,
J (r) ∈ N
n
R
i
∀r ∈ R
i
and J
−1
(n) ∈ R
i
∀n ∈ N
n
R
i
.
• A composite, recursively defined concept C =
Π
r∈R
C
C
r
with R
C
being the specific set of roles
for this composite concept
This definition of a composite concept corre-
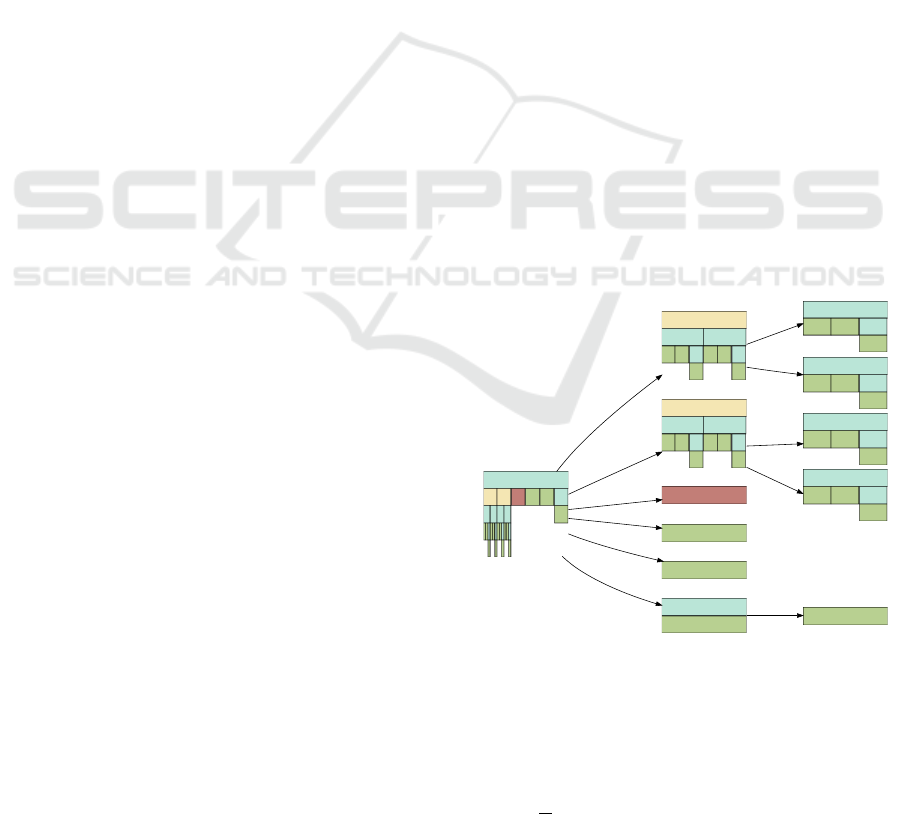
sponds to a (directed) graph, cf. Figure 2: the nodes
correspond to (sub-)concepts and the edges point
from the composites to their sub-concepts.
std_msgs__String
SceneObject
std_msgs__Float64
Connection
Connection
std_msgs__String
AssemblyLight
AssemblyLight
AssemblyLight
AssemblyLight
std_msgs__String
AssemblyLightScrew
object_type
a
b
a
b
object_type
objects[]
length
available_connections[]
current_connections[]
object_id
Figure 2: Example of a composite concept that describes
objects in the later examples. Here, only the composite
structure of the first level of sub-concepts is additionally de-
picted. Note that the small images for each node visualize
the composite structures. A common color is used for each
concept class. The edges are attributed with roles.
Having two composite concepts of one concept
class C,C ∈ Γ, the partial order M can be deduced
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
252
recursively:
(C,C) ∈ M iff (C
r
,C
r
) ∈ M ∀r ∈ R
C
,
which requires that C has all the roles of C. This
means that (see Figure 3):
C
∼
=
Π
r∈R
C
∩R
C
C
r
× Π
r∈R
C
\R
C
C
r
⊆ C × Π
r∈R
C
\R
C
B
Γ(r)
.
SceneObject
AssemblyLight
sie_msgs__SceneObject
Assembly
AssemblyLightBox
AssemblyLightScrew
AssemblyScrew
AssemblyBoxLight
AssemblyScrewLight
RobotAssemblyCoarse
AssemblyBox
Figure 3: Example hierarchy of the concept class for objects
in the later examples. The graph is directed and acyclic, but
not necessarily a tree.
By definition the leaves of a concept are consid-
ered to be atomic at the modeling detail of the pro-
vided concept. Each element of a concept is called an
instance. For composite concepts this results in the
necessity to specify values for each leaf concept of a
composite concept.
In order to answer the question whether two in-
stances of the same concept represent the same thing,
we assume that for each concept C a relation, the so-
called compare relation F
C
, is defined. This means
two instances b
i
, b
j
are similar with respect to a con-
cept C if (b
i
, b
j
) ∈ F
C
. The product representation al-
lows to derive similarity of two composite concepts
when all their corresponding leaves are similar. Note,
that similarity does not mean that the instances are
identical, but rather that the information provided by
the second instance does not add any additional infor-
mation on a given level of abstraction of a domain.
This compare relation will help to introduce compact
domains, in which different results are mapped to the
same graph node if the corresponding instances are
similar.
3.2 Operators
Declarative knowledge is hardly useful if elements of
the procedural knowledge, so-called operators, do not
use them. We define operators as follows (see Fig-
ure 4):
• An operator π ∈ P is a mapping of given input
concepts I
r
i
to output concepts O
r
j
with given in-
put roles r
i
∈ R
π,I
and output roles r
j
∈ R
π,O
, i.e.,
π : Π
r
i
∈R
π,I
I
r
i
→ Π
r
j
∈R
π,O
O
r
j
.
• The output instances can be explicitly specified by
symbolically-representable mappings (mathemat-
ical formulas) or implicitly as the result of some
calculation or experiment in simulation or the real
world, operating on input instances
• Certain operators describe modifications of in-
stances, i.e., elements of knowledge are invali-
dated when such an operator is executed; such in-
puts are called consumed. The set of roles corre-
sponding to inputs that are consumed by the oper-
ator is denoted by R
c
π
⊆ R
π,I
.
• Operators are fully functional, i.e., they do not
have an internal state.
AssemblyLightBox
RobotAssemblyCoarse
AssemblyLightBox
RobotAssemblyCoarse
Assemble
obj_a
obj_b
result
result_b
Figure 4: Example of an operator with multiple concepts
as in- and outputs. A consumed input is depicted by a red
edge.
Since operators are elements of a functional space,
they can also be modeled as instances of an operator
concept on a higher level of abstraction that is often
called meta level. In addition to the input and out-
put structures and a reference to the executable code,
an instance of this operator-concept can contain meta
information like key performance indicators (kpi).
A hierarchy of operators is obtained from the hi-
erarchical structures of concepts. An operator π
1
is
more detailed than another π
2
in case the following
conditions hold true (see Figure 7):
• all input and output roles of operator π
2
are ele-
ments of the role set of operator π
1
: R
π
2
,I
⊂ R
π
1
,I
and R
π
2
,O
⊂ R
π
1
,O
,
• all (common) input concepts I
r,1
and outputs
O
r,1
of operator π
1
are more detailed than those
of operator π
2
: (I
r,1
, I
r,2
) ∈ M ∀r ∈ R
π
2
,I
and
(O
r,1
, O
r,2
) ∈ M ∀r ∈ R
π
2
,O
,
• the meta information, e.g. key performance indi-
cators, of operator π
1
are more detailed than those
of operator π
2
.
A Hierarchical Planner based on Set-theoretic Models: Towards Automating the Automation for Autonomous Systems
253

4 CONCEPTS AND GRAPHS FOR
PLANNING
In our context planning is based on the evaluation of
operators, working on the set of currently available in-
stances, to reach one or multiple goal instances. The
operators can use or consume available instances and
generate new ones. Many application domains pose
problems combining symbolic and sub-symbolic in-
stances. However, standard approaches run into the
curse of dimensionality. The approach of hierarchi-
cal planning is based on the hierarchies of concepts
and operators. It tries to solve the planning task on an
abstract level and to refine the plan step by step and
abstraction level by abstraction level until a plan on
the most detailed level is obtained.
To formalize the structures obtained during plan-
ning we first introduce formal models for a planning
task, a planner and a plan.
4.1 Planning Task
A planning task PT (X
init
, X
goal
, X
op
) specifies the com-
bination of three sets: the set of initial instances
X
init
:= {b
i
, i = 1, . . . , n
init
}, the set of goal instances
X
goal
= {b
j
, j = 1, . . . , n
goal
} and the set of available
operators X
op
:= {π
k
, k = 1, . . . ,n
op
} with n
init
∈ N
0
,
and n
goal
, n
op
∈ N. Consequently, a planning task is a
concept in the meta domain.
4.2 Plan Family
We introduce the concept (in the meta domain) of a
plan family that contains the following information:
the initial instances, the executed operators, the input
instances of executed operators with their roles, and
the output instances of executed operators.
To represent this plan family, we use an anno-
tated bi-partite graph G
PF
(V, E, E
con
), in which all an-
notated edges in E
con
⊆ E correspond to consumed
operator inputs. The one node set V
B
only contains
nodes representing instances and the other V
π
consists
of operators only. The bi-partite property ensures that
V = V
B
∪V
π
, V
π
∩V
B
=
/
0 and ∀e ∈ E : e = (v
1
, v
2
) with
{v
1
, v
2
} 6⊆ V
π
and {v
1
, v
2
} 6⊆ V
B
. The representation
mapping f
v
: V → B ∪ P of nodes in G
PF
to instances
and operators is assumed to be bijective.
Adding an Executed Operator to a Plan Family.
For every operator that is executed during planning,
all new nodes are added to the graph as long as the
graph does not already contain the information. The
result is the bi-partite graph (
V , E, E
con
) with V ⊆ V
and E ⊆ E. In more detail, this means that, with the
given operator π : Π
r
i
∈R
π,I
I
r
i
→ Π
r
j
∈R
π,O
O
r
j
, the ex-
ecution results in the following mapping between in-
stances:
{b
r
| r ∈ R
π,I
} 7→ {b
r
| r ∈ R
π,O
}.
The graph is only modified if the entropy (number of
different results for a given input set) of the operator,
is not yet exhausted by former executions. Thus, a
node v
π
is added to V
π
and all inputs are connected via
a directed edge to this new node. Edges correspond-
ing to consumed inputs are marked by adding them
to E
con
. Additionally, nodes for all output instances,
i.e., {v
f
−1
v
(b
r
)
| r ∈ R
π,O
}, are added to V
B
and v
π
is
connected to all these outputs via directed edges.
We introduce a so-called compact domain, in
which new nodes are only added for instances that
carry new information, i.e., node v ∈ V is added
if ∀v
i
∈ V
B
with v
i
6= v : ( f
v
(v
i
), f
v
(v)) 6∈ M or
( f
v
(v), f
v
(v
i
)) 6∈ M . If the plan family already con-
tains a node related to an instance with the same infor-
mation as the output instance, the mapping f
v
points
to that node instead. Thus, compact domains have a
considerably smaller number of nodes enabling better
scaling. In particular, the number of considered oper-
ators during planning can exceed the number of nodes
in the corresponding plan family (see Table 1 for the
graph sizes in the robotic example). Note that in con-
sequence a plan family in a compact domain can have
cycles, since the operator outputs can be mapped to
ancestor nodes of the operator node v
π
.
Thus, the following equations hold for the sets of
the plan family:
V
π
= V
π
∪ {v
π
},
V
B
= V
B
∪
n
v
f
−1
v
(b
r
)
r ∈ R
π,O
o
,
E = E ∪
n
v
f
−1
v
(b
r
)
, v
π
r ∈ R
π,I
o
∪
n
v
π
, v
f
−1
v
(b
r
)
r ∈ R
π,O
o
,
E
con
= E
con
∪
n
v
f
−1
v
(b
r
)
, v
π
r ∈ R
c
π,I
o
.
4.3 Planner State Graph
Planning considers sets of instances X
i
, i ∈ N. The
initial set is X
init
. A plan is available if, by applying
operators, a set X
m
is generated that fulfills the goal
set X
goal
, i.e.,
∀b
i
∈ X
goal
∃b
j
∈ X
m
: (b
j
, b
i
) ∈ F
C
i
,
in which b
i
∈ C
i
. Each set of instances X
i
is obtained
by executing one operator π
k
∈ X
op
, k ∈ N, on one
selection of instances (b
1
, . . . , b
n
π
k
) with n
π
k
:= |R
π
k
|
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
254

from a previous set of instances X
j
, j ∈ {0, . . . , j − 1}
(with X
0
:= X
init
):
X
i
= (X
j
∪ π
k
(b
1
, . . . , b
n
π
k
)) \ {b
ˆn
| J
−1
π
k
( ˆn) ∈ R
c
π
k
},
in which the instances have to be an element of the
correct concept type b
J (r
l
)
∈ C
r
l
∩ X
j
.
Figure 5: Part of the planner state graph for the later exam-
ple of a hat-rail assembly.
Therefore, we introduce a directed graph
G
PS
(V, E) to describe the planner state as shown in
Figure 5. Each node v
i
∈ V corresponds to a set of
instances X
i
(and a subgraph of the plan family).
There exists a directed edge e = (v
i
, v
j
) ∈ E iff X
j
was
obtained from X
i
by applying an operator. We assume
a compact graph structure similar to a compact
domain, i.e., ∀v
i
, v
j
∈ V, v
i
6= v
j
: X
i
\ X
j
∪ X
j
\ X
i
6=
/
0.
This property reduces the size of the planning space
considerably, because plan duplication is avoided for
similar paths leading to the same intermediate planner
state X
i
. Additionally, this structure allows to detect
dead ends, which is later used by the backtracking
techniques for hierarchical planning.
5 SINGLE-LEVEL PLANNING
The classical planning problem is named single-
level planning (SLP) as it doesn’t consider hierar-
chies of concepts or operators. A planning task
PT (X
init
, X
goal
, X
op
) is solved in a constructive manner
by applying operators from X
op
to available instances.
A planning step is comprised by three actions:
1. choose the planning node v
i
with the correspond-
ing instances X
i
to proceed from,
2. select an operator π
j
∈ X
op
with its input concepts
I
r
for r ∈ R
π
j
,I
,
3. single out instances from X
i
and map them to the
inputs of π
j
such that b
r
∈ I
r
∀r ∈ R
π
j
,I
.
This general structure is valid for all kinds of
planners ranging from PDDL to motion planning.
Even classical graph algorithms like depth-first and
breadth-first search can be used to realize such a
single-level planner. In our implementation we let
the search algorithm determine the next node v
i
and
iterate over all operators and all possible combina-
tions of corresponding input instances for that state.
More evolved planners have either better heuristics
and sampling strategies or use suitable problem re-
formulations for specific sub-problems. Nevertheless,
the core elements of forward planners correspond to
the three steps described above.
Since each node v
i
corresponds both to a set of
instances X
i
and a subgraph of the plan family, this
subgraph captures the respective plan if the goal in-
stances X
goal
are met by the instances of X
i
.
6 GRAPHS FOR HIERARCHICAL
PLANNING
The computational complexity of the planning prob-
lem, which results from the mixture of symbolic and
sub-symbolic properties, can be handled if hierarchies
of suitable concepts and operators are considered.
The core idea is to generate a plan on an abstract
level where only a few instances and operators exist.
Then each step of this plan has to be recursively re-
fined until the maximal level of detail is reached for
all operators. In case a plan step cannot be refined on
a more-detailed level, a back-tracking procedure is re-
quired that is described in subsection 7.2. This hierar-
chical divide and conquer approach ideally scales log-
arithmically with the number of required plan steps.
Nevertheless, it is only beneficial with the right num-
ber of layers, if abstract plans sort out steps that are
less promising on a more detailed level and if the
downward refinement property holds often, thus most
steps can be refined later on. In turn this requires the
models of the concepts and operators to be suitably
structured. Determining such models is a hard task
on its own. However, the set-theoretic approach of the
introduced formal models for concepts and operators
helps to manually or automatically define them.
6.1 Parent Child Mapping
A central aspect of hierarchical planning is to refine
an operator by posing a new planning task on a more-
detailed level. This mainly corresponds to a selec-
A Hierarchical Planner based on Set-theoretic Models: Towards Automating the Automation for Autonomous Systems
255

tion of suitable operators. Thus, we introduce the set-
valued parent child mapping F
PC
: P ⇒ P such that
F
PC
(π
i
) := F
PC
({π
i
}) = X
op
.
Currently, we assume that such a mapping is pro-
vided and engineered during modeling of operators.
For some domains an algorithmic extraction of that
mapping just from the sets of concepts and operators
was successfully tested. For general domains, how-
ever, this is a problem to be addressed in future re-
search.
In the following we introduce two graphs for a
formal description of dependencies between plans on
different levels of abstraction: the layer graph G
LG
addresses the hierarchical dependencies between plan
steps and planning tasks, and the extended planner
state graph G
EPS
represents temporal dependencies.
These two combined with the previously described
plan family, which captures the causal dependencies
between instances and operators, could be represented
in a single multi-layer graph. In this paper we stick to
a presentation with separate graphs though as it is eas-
ier to understand.
6.2 Layer Graph
Since our planning approach does not assume a fixed
number of hierarchy levels, each planning task PT de-
fines some layer. Note that consequently the number
of layers can vary during the planning process.
We introduce the (directed) bi-partite layer graph
G
LG
(V, E) to capture dependencies between planning
states and layers, cf. Figure 6. Each node within the
first set V
l
corresponds to a planning task. As de-
scribed in subsection 4.3, several planner states re-
sult during (single-level) planning for a given plan-
ning task. Each of these states is represented in the
layer graph by a node in the set V
p
. Note that the two
sets V
l
and V
p
are disjoint.
Figure 6: Part of the layer graph for the box-lid-example
(subsection 8.2). The node colors match the temporal order
during planning, compare Figure 8.
The set of vertices E represents dependencies of
two kinds, which are discriminated by the direction
relative to layer nodes. The first type connects plan-
ner state nodes obtained during planning with their re-
spective layer nodes which represent planning tasks,
i.e., ∀e = (v
1
, v
2
) ∈ E, v
1
∈ V
l
: v
2
∈ V
p
. The second
type connects a planner state to exactly one layer node
if the layer node specifies the planning task to refine
the operator that led to the planner state (cf. subsec-
tion 4.3), i.e., ∀e = (v
1
, v
2
) ∈ E, v
1
∈ V
p
: v
2
∈ V
l
and
∀v
1
∈ V
p
: |{e | e = (v
1
, v
2
) ∈ E}| ≤ 1.
Consequently, the layer graph G
LG
is tree-
structured and captures the hierarchical refinements
of plans. For later references, the mapping of each
planning state to its corresponding layer is given by:
F
PS, L
: V
p
→ V
l
with F
PS, L
(p) := l such that (l, p) ∈ E.
6.3 Blacklist
The planning task that refines a plan step, has a re-
duced set of instances for two reasons. First, the com-
putational complexity is reduced, as less combina-
tions are possible with fewer instances. Second, this
assures that the plan is in accordance with the higher-
level plan. This is particularly important for domains
that are persistent and thus can’t be set to an arbitrary
state (e.g. real-world execution).
For example, assume that one out of two boxes
has to be moved to a different working surface. In the
coarse plan the smaller box is picked and then trans-
ported. If this pick is refined, only the smaller box is
available. Otherwise, the more detailed planner could
choose the bigger box for this task and an inconsis-
tency between the plans on the different levels of ab-
straction would result.
The idea is to set all instances on a black list X
Black
that belong to a concept corresponding to an operator
input on the more abstract level. Let the coarse plan-
ning task PT(X
c
init
, X
c
goal
, X
c
op
) and a corresponding plan
be given as a plan family (V, E, E
con
):
∀v
1
∈ V
B
, v
2
∈ V
π
, (v
1
, v
2
) ∈ E : v
1
∈ X
Black
and
∀v
1
∈ V
B
, v
2
∈ X
Black
, v
1
, v
2
∈ C : v
1
∈ X
Black
.
Let v
2
∈ V
π
be one operator in the plan that has no
preceding operators, i.e., ∀v
1
∈ V
B
with (v
1
, v
2
) ∈ E
holds v
1
∈ X
c
init
, then the corresponding planning task
for refinement is:
PT
v
2
( X
c
init
\ X
Black
∪ {v
1
| (v
1
, v
2
) ∈ E},
{v
3
| (v
2
, v
3
) ∈ E},
F
PC
(π
v
2
)).
If the operator has predecessors, the set of initial
instances has to be replaced by resulting instances of
the refinement of that preceding operator. In order
to formally capture these dependencies, we have to
extend the planner state graph G
PS
of the single-level
planning.
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
256

6.4 Extended Planner State Graph
Hierarchical planning requires encoding of temporal
relations between instances of different layers. There-
fore, we extend the planner state graph G
PS
and dis-
cuss the related blacklists.
A single-level plan that resulted from a refinement
step, is defined by the sequence of planning states in
the G
PS
and a blacklist X
c
Black
. The planning task corre-
sponds to the first planning state p
0
in that sequence
as it maps to the layer node in the layer graph. Solv-
ing this task results again in a separate planner state
graph. However, the goal is to combine all planner
state graphs in one large graph, the extended planner
state graph G
EPS
, for unified data handling during hier-
archical planning. Thus, we extend the node informa-
tion of the (one-layer) planner state graphs by their
layer information given by F
PS, L
to avoid mixing of
layers.
Assuming that a refining plan for the planner state
p
i
is found, the definition of the planning task corre-
sponding to the layer l
i+1
= F
PS, L
(p
i+1
) has to use
the resulting instances of that plan. Therefore, we
add one additional node to G
EPS
(V, E) for each plan-
ner state that reached the goal set X
goal
. Let p
j
be
such a planning state and v be the corresponding addi-
tional node, then a matching edge is added (p
j
, v) ∈ E.
The set of instances corresponding to the node v con-
tains the union of instances from the preceding node
X(p
j
) and the blacklisted instances in the correspond-
ing layer X
Black
(l): X(v) := X(p
j
) ∪ X
Black
(l).
In order to refine the next planner state of the
coarse plan, one of the plans refining the preceding
node has to be selected, leading to the node with
blacklisted instances v. Let the planner state p
i+1
cor-
respond to the operator π in the plan family G
PF
. Now,
the set of blacklisted instances for the next layer can
be specified:
X
Black
(l
i+1
) := (X(v) ∩ X
c
Black
)
\{v
k
| (v
l
, π) ∈ E
G
PF
, (v
k
, v
l
) ∈ F}.
Then the set of initial instances for the next layer l
i+1
results: X
init
(l
i+1
) := X(v)\ X
Black
(l
i+1
).
This means that for each plan refining the previ-
ous planner state p
i
a new set of initial instances re-
sults and a corresponding new layer is generated. To
also keep track of these dependencies, we add fur-
ther edges to the extended planner state G
EPS
linking
the node v with the added blacklist elements to the
planner state p corresponding to the initial instances
X
init
(l
i+1
).
7 HIERARCHICAL PLANNING
The goal of hierarchical planning is to find a sequence
of planner states in G
EPS
such that no corresponding
operator has a further refinement. For this task, the
graphs of the plan family G
PF
, the extended planner
state G
EPS
and the layers G
LG
are used.
The basic idea to reduce the fanout and thus
counter the curse of dimensionality, is to use prior
knowledge that is encoded by abstractions, like visu-
alized in Figure 7. Once a plan was found on an ab-
stract level, each step in this plan defines a new plan-
ning task that can either be refined by a single, more
detailed operator or poses a new planning task on its
own.
However, there is freedom in choosing the order
of refining planning states on different levels of ab-
straction. The performance of such a refinement strat-
egy depends highly on the domain at hand. If, for in-
stance, the downward refinement property holds, one
can always refine all operators to the most detailed
level before proceeding to the next step. On the other
hand, if some refinements repeatedly fail even on a
rather coarse level, it is suboptimal to refine the first
steps to maximal detail before checking the refine-
ments of later steps on coarser levels.
If a refinement fails previous planning steps need
to be adapted accordingly. Such backtracking meth-
ods are the key to real-world scenarios in which the
coarser level cannot consider all details.
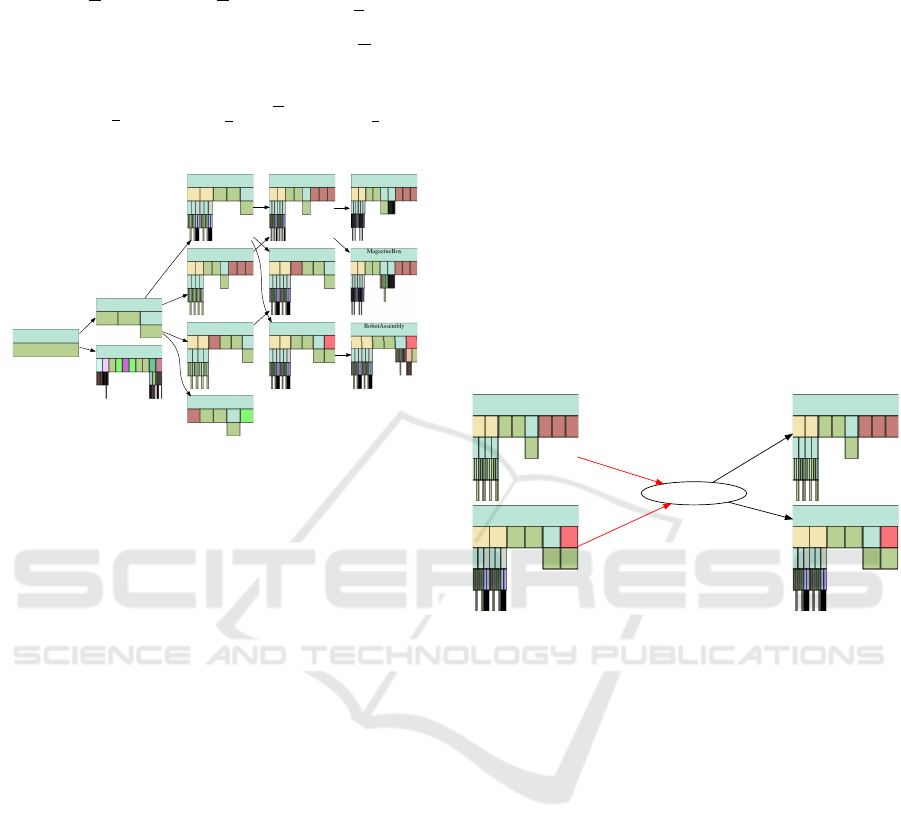
Assemble
obj_a
obj_b
result
More detailed Assemble
obj_b
obj_a
result
result_b
Figure 7: Visualization of the basic planning idea to reduce
the fanout. An abstracted planning task is obtained based on
the original instances and goals (arrows pointing upwards).
New tasks in the refined level are posed by each step in the
coarse plan. Either a primitive, single operator plan exists
(white ellipse) or a planner has to be used to find a suitable
plan (gray ellipses). The compare function is used to ensure
that the abstractions of available instances and goals comply
with the instances of the course plan.
A Hierarchical Planner based on Set-theoretic Models: Towards Automating the Automation for Autonomous Systems
257

7.1 Hierarchical Strategies
The two most basic strategies follow the spirit of
depth- and breadth-first search and define the ex-
trema of possible approaches. Naturally, interme-
diate strategies, possibly including heuristics, could
increase planning performance for specific domains,
however this is a topic for further research.
The breadth-first strategy refines all operators of
one level once.
7.2 Backtracking
Only the downward refinement property could assure
that all plan steps can be refined until the finest level is
reached. However, this property cannot be guaranteed
for all real-world problems. Therefore, the hierarchi-
cal strategies have to be complemented by backtrack-
ing procedures.
Such a backtracking method triggers re-planning
on former layers. Since the overall problem is as-
sumed to be solvable, there exists a set of layers and
some selection of corresponding plans such that all
operators are fully refined.
In most cases it is reasonable to choose the back-
tracking procedure that inverts the hierarchical (for-
ward) search strategy. In the case of a breath-first
search, tasks that are predecessors within the ex-
tended planner state G
EPS
of the failing step are con-
sidered first. Only, if there exist no alternative plans
in these layers that lead to a succeeding refinement,
the more abstract layer, i.e., an ancestor in G
LG
of the
node given by F
PS, L
, is addressed.
Re-planning means that the original goals are
blacklisted and the (single-level) planner continues its
search then.
8 EXAMPLE: AUTONOMOUS
ASSEMBLY CELL
Our example setup consists of two robot arms with
seven degrees of freedom each, cf. Figure 1. The
workspaces of the arms have considerable overlap
to enable cooperation and wrist-mounted cameras to
perceive the environment. To demonstrate the capa-
bilities of our approach, two different use-cases are
analyzed. The first one considers a setup for the as-
sembly of control cabinets: circuit breakers and other
components have to be automatically assembled on a
hat-rail. The focus of this example is the scalability
with an increasing number of necessary steps. The
second use-case is simpler, thus we can discuss the
backtracking algorithm on the real graph structures.
The difficulty for both scenarios is the combina-
tion of high dimensional continuous properties (14
degrees of freedom for the robotic arms and up to
five times three dimensions for the objects) and a
even higher number of discrete options. Those dis-
crete options not only result from the actions directly
visible on the robot, such as perception, grasping,
clicking, pushing or releasing, but also from differ-
ent sequences of varying operators that calculate pa-
rameterizations such as grasp configurations, view
poses or initialize the hardware. The operators in
our models are kept rather atomic, to ensure flexibil-
ity, easy extension and composability as demanded
for autonomous manufacturing systems. Addition-
ally, these requirements result in subsection 4.3 in the
definition of planner states being the combinations of
available instances. In consequence, inhomogeneous
planner states have to be considered during planning
in opposition to most motion planner that assume a
homogeneous state for performance reasons.
8.1 Hat-rail Assembly
For the hat-rail example four components and the hat-
rail are initially placed in the working area of the
robot arm. The precise configuration of the parts is
not known in the beginning, thus a perception step is
required. The goal of the task is specified on an ab-
stract level, which only states the final position of the
components on the rail.
To actually control the robotic system the se-
quence of the four assembly operations of the coars-
est plan have to be refined three times. The first re-
finement adds further symbolic properties to the first
domain. Then, the second refinement actually simu-
lates all necessary robot motions assuring collision-
free paths and reachability. Finally, the actual control
of the robotic hardware is the most-detailed layer.
In this experimental setup we use the breadth-first
strategy to hierarchically refine the coarse plan. Our
numerical result (cf. Table 1) shows that the hierar-
chical approach scales almost linearly in the number
of pieces to be assembled, which is the best we can
expect without (automatically generated) additional
abstraction levels for longer tasks. Note, that those
planning times include all execution times of called
operations. This includes computation and simula-
tion of controllers for both robot arms considering the
full nonlinear robot dynamics (∼ 0.3 [s] per motion
task). A considerable offset for the planning times is
caused by the loading and construction of the geomet-
ric scene (∼ 1.2 [s] once). For comparison we used a
simple breadth first search on the same problem. For
a single piece that is assembled, this algorithm is one
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
258

order of magnitude slower than our hierarchical ap-
proach. For two pieces it took at least three orders of
magnitude longer than the hierarchical algorithm and
did not find any solution before we ran out of mem-
ory. Arguably a faster algorithm can be found to solve
this problem, which will be faster at least for the sin-
gle piece assembly. However, the interesting point is
how the solution will scale with increasing numbers
of pieces. One can expect, that non hierarchical ap-
proaches run into the curse of dimensionality.
Table 1: Planning times t, and number of nodes in the plan
family and planner state over the number of pieces to as-
semble. The first block states the results of the hierarchical
planner and the second block a single-level approach which
highlights the complexity of the task.
1 pc. 2 pcs. 3 pcs. 4 pcs.
t [s] 3.7 5.5 7.9 10.5
|G
EPS
| 159 330 502 688
|G
PF
| 89 200 314 439
t [s] 79.2 > 7 · 10
3
* *
|G
EPS
| 32,203 > 2 · 10
6
* *
|G
PF
| 981 > 4 · 10
3
* *
|Plan| 16 36 56 76
These results demonstrate that the hierarchy suc-
cessfully handles the curse of dimensionality. Note
that the models for this example fulfill the downward
refinement property, thus no backtracking is needed,
which explains the almost perfect results.
8.2 Box Lid Assembly
In order to show the backtracking features of our plan-
ning approach, we consider a simple assembly pro-
cess, in which a lid has to be placed on top of a box.
The coarse level has to choose which robot arm
should pick the lid and assemble it on the box. How-
ever, the box is only reachable by one of the arms, as
it is placed outside of the workspace overlap of the
two robots. If the coarse level now chooses the wrong
arm to do this task, there exists no valid refinement
on the sub-symbolic level. Therefore, backtracking is
needed. Note that only the second step of the coarse
plan cannot be refined, since both arms can pick the
lid, but only one can put it on the box.
Consequently, the backtracking procedure tries to
find an alternative plan in the temporal preceding step
first and then chooses a new plan on the coarser layer.
See Figure 8 for a visualization of the planner state of
this example.
The orange area shows the part where no plan that
refines the second step in the coarse plan is found.
The backtracking approach then tries to find an alter-
Figure 8: The planner state G
PS
with backtracking. No re-
fined plan is found (orange area), therefore backtracking
considers the preceding layer (red area) first. A second plan
on the coarser level (dark green area) can then be success-
fully refined (green and petrol area).
native plan in the preceding layer (red area). How-
ever, there exists no plan to pick the lid in a way that
allows assembly, with the left arm, as the box is out
of reach. Thus, the backtracking goes to the more ab-
stract level (dark green area) and selects an alternative
plan that uses the right arm instead of the left one.
Here, the backtracking stops, and the breadth-first
search is restarted. In this second coarse plan both
actions, i.e., picking and assembling, can be refined
successfully (green and petrol area, respectively).
9 CONCLUSIONS
The approach to ground the declarative and procedu-
ral knowledge on set theory enables to flexibly reason
about hierarchies. Based on these structures we intro-
duce a hierarchical planner that allows to seamlessly
traverse different abstraction levels and obliterate the
differences between symbolic and sub-symbolic do-
mains. This approach additionally allows for mod-
eling robot and task description independently. This
leads to highly flexible and composable systems. We
discussed examples of autonomous production sys-
tems with real hardware that is controlled with this
hierarchical approach. Our examples show that hier-
archy can help to avoid the curse of dimensionality
and backtracking allows to handle cases that do not
have the downward refinement property.
REFERENCES
Bacchus, F. and Yang, Q. (1994). Downward refinement
and the efficiency of hierarchical problem solving. Ar-
The presented research is financed by the TransFit
project which is funded by the German Federal Ministry of
Economics and Technology (BMWi), grant no. 50RA1701,
50RA1702, and 50RA1703.
A Hierarchical Planner based on Set-theoretic Models: Towards Automating the Automation for Autonomous Systems
259

tificial Intelligence, 71(1):43–100.
Bechon, P., Barbier, M., Infantes, G., Lesire, C., and Vidal,
V. (2014). Hipop: Hierarchical partial-order planning.
In STAIRS, pages 51–60.
Bercher, P., H
¨
oller, D., Behnke, G., and Biundo, S. (2016).
More than a name? on implications of preconditions
and effects of compound htn planning tasks. In ECAI,
pages 225–233.
Bryan, A., Ko, J., Hu, S., and Koren, Y. (2007). Co-
evolution of product families and assembly systems.
CIRP Annals, 56(1):41–44.
Cashmore, M., Fox, M., Long, D., and Magazzeni, D.
(2016). A compilation of the full PDDL+ language
into SMT. In AAAI Workshop: Planning for Hybrid
Systems.
Castillo, L., Fern
´
andez-Olivares, J., Garcia-Perez, O., and
Palao, F. (2006). Efficiently handling temporal knowl-
edge in an htn planner. In ICAPS, pages 63–72.
Castillo, L., Fern
´
andez-Olivares, J., and Gonzalez, A.
(2003). Integrating hierarchical and conditional plan-
ning techniques into a software design process for au-
tomated manufacturing. In ICAPS.
Dornhege, C., Eyerich, P., Keller, T., Tr
¨
ug, S., Brenner,
M., and Nebel, B. (2009). Semantic attachments for
domain-independent planning systems. In Conf. on
Automated Planning and Scheduling.
Erol, K., Hendler, J., and Nau, D. (1994). Htn planning:
Complexity and expressivity. In AAAI, volume 94,
pages 1123–1128.
Fernandez-Gonzalez, E., Williams, B., and Karpas, E.
(2018). Scottyactivity: Mixed discrete-continuous
planning with convex optimization. Artificial Intel-
ligence Research, 62:579–664.
Fox, M. and Long, D. (2002). Pddl+: Modeling continuous
time dependent effects. In Int. NASA Workshop on
Planning and Scheduling for Space, volume 4.
Garrett, C., Lozano-P
´
erez, T., and Kaelbling, L. (2015).
Ffrob: An efficient heuristic for task and motion plan-
ning. In Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics XI,
pages 179–195. Springer.
Gateau, T., Lesire, C., and Barbier, M. (2013). Hidden:
Cooperative plan execution and repair for heteroge-
neous robots in dynamic environments. In IROS,
pages 4790–4795. IEEE.
Georgievski, I. and Aiello, M. (2015). Htn planning:
Overview, comparison, and beyond. Artificial Intel-
ligence, 222:124–156.
Goldman, R. (2006). Durative planning in htns. In ICAPS,
pages 382–385.
Helmert, M. (2006). The fast downward planning system.
Artificial Intelligence Research, 26:191–246.
Hitomi, K. (2017). Manufacturing Systems Engineering:
A Unified Approach to Manufacturing Technology,
Production Management and Industrial Economics.
Routledge.
Hu, S., Ko, J., Weyand, L., ElMaraghy, H., Lien, T., Koren,
Y., Bley, H., Chryssolouris, G., Nasr, N., and Shpi-
talni, M. (2011). Assembly system design and oper-
ations for product variety. CIRP Annals, 60(2):715–
733.
Kambhampati, S., Mali, A., and Srivastava, B. (1998). Hy-
brid planning for partially hierarchical domains. In
AAAI/IAAI, pages 882–888.
Kast, B., Albrecht, S., Feiten, W., and Zhang, J. (2019).
Bridging the gap between semantics and control for
industry 4.0 and autonomous production. In CASE.
IEEE.
Kaufman, S., Wilson, R., Jones, R., Calton, T., and Ames,
A. (1996). The archimedes 2 mechanical assembly
planning system. In ICRA, volume 4, pages 3361–
3368. IEEE.
Lozano-P
´
erez, T. and Kaelbling, L. (2014). A constraint-
based method for solving sequential manipulation
planning problems. In IROS, pages 3684–3691. IEEE.
Marthi, B., Russell, S., and Wolfe, J. (2008). Angelic hier-
archical planning: Optimal and online algorithms. In
ICAPS, pages 222–231.
McDermott, D., Ghallab, M., Howe, A., Knoblock, C.,
Ram, A., Veloso, M., Weld, D., and Wilkins, D.
(1998). Pddl - the planning domain definition lan-
guage. The AIPS-98 Planning Competition Comitee.
Molineaux, M., Klenk, M., and Aha, D. (2010). Planning in
dynamic environments: extending htns with nonlinear
continuous effects. In Conf. on Artificial Intelligence,
pages 1115–1120. AAAI Press.
Nau, D., Au, T.-C., Ilghami, O., Kuter, U., Murdock, J., Wu,
D., and Yaman, F. (2003). Shop2: An htn planning
system. Artificial Intelligence Research, 20:379–404.
Piotrowski, W., Fox, M., Long, D., Magazzeni, D., and
Mercorio, F. (2016). Heuristic planning for hybrid
systems. In Conf. on Artificial Intelligence, pages
4254–4255. AAAI Press.
Schattenberg, B. (2009). Hybrid planning and scheduling.
PhD thesis, University of Ulm, Germany.
Schmitt, P., Neubauer, W., Feiten, W., Wurm, K.,
v. Wichert, G., and Burgard, W. (2017). Optimal,
sampling-based manipulation planning. In ICRA,
pages 3426–3432. IEEE.
Schmitz, S., Schluetter, M., and Epple, U. (2009). Au-
tomation of automation — definition, components and
challenges. In Conf. on Emerging Technologies &
Factory Automation. IEEE.
Srivastava, S., Fang, E., Riano, L., Chitnis, R., Russell, S.,
and Abbeel, P. (2014). Combined task and motion
planning through an extensible planner-independent
interface layer. In ICRA, pages 639–646. IEEE.
Thomas, U. and Wahl, F. (2010). Assembly planning and
task planning—two prerequisites for automated robot
programming. In Robotic Systems for Handling and
Assembly, pages 333–354. Springer.
Toussaint, M. (2015). Logic-geometric programming: An
optimization-based approach to combined task and
motion planning. In IJCAI, pages 1930–1936.
Young, R. M., Pollack, M., and Moore, J. (1994). Decom-
position and causality in partial-order planning. In
AIPS, pages 188–194.
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
260
