
Improving Computer Support System for Drivers
with Multiport Memory Devices
Khasanov Rafael
1 a
, Shepelev Vladimir
2 b
, Almetova Zlata
2 c
, Shubenkova Ksenia
3 d
and Meruert Aristombayeva
4 e
1
Orenburg State University, Prospect Pobedy, Orenburg, Russia
2
South Ural State University, Chelyabinsk, Russia
3
Kazan Federal University, Naberezhnye Chelny, Russia
4
Kazakh-British Technical University, Tole Bi str. 59, 050000, Almaty, Kazakhstan
ksenia.shubenkova@gmail.com, mika.aristombaeva@gmail.com
Keywords: Lack of Visual Information, Positioning a Group of Vehicles, Digitized Borders of the Roadway.
Abstract: The deficiencies of existing methods and means of computer support in the positioning of vehicles have been
identified. The objective function for assessing the effectiveness of decision making when choosing the
positioning mode for a group of mobile objects on the roadway in the conditions of insufficient visual
information is defined, with the criteria for estimating the quality and effectiveness being established. A
stratified cellular model for roadways is developed, where the road is viewed as an extended object in the
space, the borders of which are digitized by the satellite navigation system “GLONASS/GPS” with the
required degree of discreteness and accuracy. The roadway model is realized as a multi-page dynamic array
and is used in the developed simulation model of vehicle traffic control, with navigation data errors being
taken into account. The platform prototype can be implemented on the basis of VRAM, WRAM, MDRAM,
ZigBee-modems “ETRX2-PA”, driver support systems based on mobile computers such as GLONASS/GPS-
modules of the “SIM68EVB KIT” type. The received results are recommended for creating computer support
systems for drivers, and for managing vehicles in the conditions of insufficient visual information.
1 INTRODUCTION
In computer support systems for drivers of vehicles,
special attention is paid to improving their
performance. The requirements for methods and high-
speed computer devices determine their
implementation in the form of specialized hardware
with the greatest possible extent of parallelism in their
performance (Gonzalez et al., 2014; Park et al., 2013;
Khasanov and Sarajkin, 2016). The number of
parameters for computer support systems for drivers
to be considered in case of positioning a group of
mobile objects significantly increasing, it is urgent to
provide control information to ensure a safe mode of
positioning the entire group of mobile objects on the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3024-7277
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1143-2031
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9304-8406
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9246-6232
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2609-5867
roadway (Khasanov, 2016). Quickly obtained control
information determines the effectiveness and safety of
operating vehicles.
Modern computer support systems for drivers are
being gradually involved in a wide range of complex
tasks in the process of operating vehicles. These
systems are indispensable in extreme and dangerous
conditions of insufficient visual information
(Gusarov, 2011; Turenko et al., 2013).
The lack of visual information occurs in the
process of moving vehicles because of insufficiency
of actual visual information (for example, marking
lines, road signs and landmarks) in bad weather
conditions (fog, snow or sand storms), in extreme
conditions of poor visibility caused by fogging or
Rafael, K., Vladimir, S., Zlata, A., Ksenia, S. and Aristombayeva, M.
Improving Computer Support System for Drivers with Multiport Memory Devices.
DOI: 10.5220/0007877906630670
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems (VEHITS 2019), pages 663-670
ISBN: 978-989-758-374-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
663
malfunctions of night lighting devices and (or)
ventilation of vehicle windows (Turenko et al., 2013;
Khasanov and Sarajkin, 2016).
The range of computer, navigation, optical, laser
methods and devices used in motor vehicles is
gradually reaching the level of aviation equipment
(Broggi et al., 2012; Cheng et al., 2011). The task of
highly precise positioning of vehicles has a special
urgency for countries with extended road networks,
with constantly changing relief, various weather and
climate zones, the existence of road sections with
missing or incorrectly done road markings, with
missing roadway markers and signs (Cheng et al.,
2015; Schätz et al., 2015).
The problem of increasing the actual safety of
vehicles is primary importance in modern scientific
and technical, periodical, patent literature and in
Internet sources. Among the researches on this
subject, we should note the researches by T.Z.
Aralbaev, E.V. Balakina, S.V. Bakhmutov, V.O.
Volkov, S.V. Gaysin, A.P. Gusarov, A.S. Gurin, D.A.
Zatuschny, G.O. Kotiev, I.V. Lukashov, A.V.
Makarov, M.V. Nagaitsev, A.A. Revin, S.A.
Rynkevich, A.M. Saikin, V.P. Tarasik, A.N. Turenko,
A.V. Uzhva, I.V. Hodes, M. Bansal, L. Bombini, A.
Broggi, C. Caraffi, E. Cardarelli, J. Choi, A. Das, T.
Graf, D. Kim, G. Kreutzer, J. Lee, P. Medici, M.
Meinecke, C. Stefano.
The analysis of modern publications has shown the
existing methods and devices of computer support in
positioning vehicles to have disadvantages despite
significant advances in the methodology of
constructing active vehicle safety systems:
they are not informative and efficient for a
group of vehicles in the conditions of visual
information shortage;
they do not perform a coordinated exchange of
navigational data between the vehicles in a
group that use wireless technologies according
to “V2V” principles;
their hardware and software have a high cost
(more than 20 thousand euro) for one vehicle;
they have closed architectures due to foreign
defense orders and for this reason the results of
the printed researches are not often open.
Thus, the task of improving computer support
system for drivers based on the use of multiport
memory devices is relevant.
2 METHODS, THEORETICAL
APPROACHES AND
MATHEMATICAL MODELS
The effectiveness of a computer support system for
drivers is determined by its increased actual safety and
improved operating modes for mobile objects due to
reduced uncertainty for a driver in case of insufficient
visual information.
The “effect” in the study is understood as some
cumulative result, consisting of the sequence of the
following actions: the exact position determination
(orientation) of vehicles on the roadway, the choice of
a safe speed regime and the trajectory of the
movement of a motor vehicle at every moment of
time. In other words, it is the maintenance of adequate
positions (stable condition) of vehicles on the roadway
due to chosen safe modes of driving in the conditions
of insufficient visual information and, thus, ensuring
its active safety and safety of other road users.
The creation and further operation of computer
support systems for drivers to position the car on the
roadway in the conditions of insufficient visual
information is concerned with the development of
appropriate criteria and techniques for assessing their
quality and effectiveness.
According to the studies, the criterion was
established to meet the following basic requirements:
to account for the most significant and available
parameters in order to calculate both the
positioning mode of a vehicle and the hardware
and software of the computer support system for
a driver;
to provide the possibility of comparing different
types of computer support systems for a driver
and determining ways to improve their
technical and economic indicators;
to have a clear physical meaning and ease of
calculation when performing engineering
calculations with quantitative estimates.
In the researches (Shen and Neyens, 2014;
(Roessing et al., 2013; Meguro et al., 2005), the
number of criteria of monitoring systems and on-
board systems are noted. These criteria allow
assessing the quality of the organization of the system
that is being developed.
The analysis of the criteria shows that they are
useful for evaluating and comparative analysing for
on-board vehicle systems of various classes.
However, the attempt to apply them at the design
stage of computer support systems for drivers showed
that they do not include certain features of the
LogiTrans 4.0 2019 - Special Session on Logistics and Transport in the Industry 4.0
664
decision when choosing the mode of positioning for
vehicles, in particular:
the dynamics of occurring and developing the
errors of the satellite navigation system
“GLONASS/GPS” when a vehicle has “hot” or
“cold” starts;
the performance of each subsystem of the
computer support system for the driver,
depending on the time limits and the nature of
occurring errors;
the effect of the operation quality of one
subsystem of the driver's computer support
system on the operation results of the other
subsystems;
the considered criteria cannot determine the
qualitative contribution of each subsystem to
the overall result of the computer support
system for the driver.
Thus, in order to achieve this goal, it is necessary
to determine the objective function for assessing the
effectiveness of decision-making when choosing the
positioning mode of a group of vehicles on the
roadway in the conditions of visual information
shortage, and also to develop a prototype of a high-
performance computer support device for drivers
based on the use multiport memory devices.
To illustrate the definition of the objective
function and the generalized criterion for assessing
the effectiveness of the chosen mode of vehicle
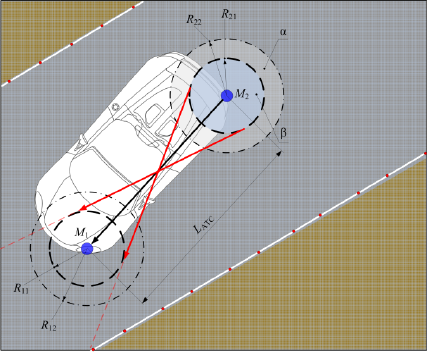
positioning, Figure 1 presents a topological scheme
for determining the effect of metrological errors of
the satellite navigation system, the magnitude of the
errors of the 1st and 2nd kind being considered.
The following conventions are adopted: points
M1 and M2 are the locations of the antennas the
satellite navigation system “GLONASS/GPS” on the
front and rear parts of the car; R11, R21 are the radii
of metrological errors of the “hot” start of navigation
equipment; R12, R22 are the radii of metrological
errors in the “cold” start of navigation equipment; α,
β are the distribution (spread) zone of probable errors
of the 1st and 2nd kind, respectively; LАТС is the
base of the car.
A black solid line indicates the direction of the car.
The red solid lines show the worst positions of
vehicles, with the magnitude of errors of the 2nd kind
being considered, and the red dotted lines indicate
possible directions (trajectories) of moving vehicles,
with the worst consequences of the errors of the 2nd
kind being taken into account. The red points along the
borders of the roadway indicate the coordinates of the
digitized borders of the roadway. Similarly, the worst
variants for vehicles and the worst possible directions
of their movement for errors of the 1st kind are
identified.
Figure 1: A topological scheme for determining the effect
of metrological errors of the satellite navigation system, the
magnitude of the errors of the 1st and 2nd kind being
considered.
Decision-making for choosing the mode of
positioning for vehicles is associated with the
corresponding errors of the first kind caused by the
“cold start” of navigation equipment, and of the
second kind caused by the “hot start” of navigation
equipment.
According to Gusarov (2011), the “hot start” is the
state of a navigation receiver, which occurs when its
power has been turned off for some time, while the
data on ephemerides, almanac and time are preserved.
This drastically shortens the time period necessary for
the first location determination. At the “cold start”
navigation signals are searched for unknown data on
ephemerides of satellites and the almanac of the
system.
When determining the objective function, the
navigation equipment, in addition to metrological
errors, is known to provide information with a certain
degree of discreteness, for example, the discreteness
of modern satellite navigation systems
“GLONASS/GPS” is 1 ÷ 500 Hz, with the range of
metrological errors being 2 ÷ 60 cm for modern
inertial satellite navigation systems, operating in the
differential correction mode, and the range of
metrological errors being 1 ÷ 15 m for widely
available 24-channel modern satellite navigation
systems “GLONASS/GPS” (Park et al., 2013;
Khasanov and Sarajkin, 2016; Khasanov, 2016;
Gusarov, 2011; Turenko et al., 2013).
Improving Computer Support System for Drivers with Multiport Memory Devices
665
The objective function when choosing the mode
for positioning a group of vehicles can be presented
in the following way:
Δ≤Δ
3
, D≥D
3
, H≥H
3
, Z≤Z
3
(1)
where: Z
PM
(positioning mode) is the cost of
maintenance and repair of vehicles, determined by the
positioning mode; M is the number of vehicles in a
group; λ is the discreteness of obtaining navigation
information; T is the time necessary to obtain
navigation information; N is the number of categories
(gradations) of the conditions for insufficient visual
information (for example, the visibility being up to 50
m, 50 ÷ 100 m, 100 ÷ 200 m, 200 ÷ 300, 300 ÷ 400
m, > 400 m); Z
V,TR
is the total costs caused by an
incorrectly chosen positioning mode and determined
by the speed and trajectory of vehicles; E
V,TR
is the
overall economic effect of a correctly chosen
positioning mode for a vehicle; P
d
(i) is the probability
of a driver’s mistake occurring while driving the
vehicle in the i-th category of insufficient visual
conditions that led to slipping or driving the vehicles
from the existing roadway borders; Δ, Δ
З
are the actual
and required metrological error of navigation
equipment; D, D
З
are the actual and required
reliability of results; H, H
З
are the performance of the
computer support system for a driver, with the actual
and specified ones being considered, respectively; Z,
Z
З
are the costs for the hardware and software of the
computer support system for a driver, with the actual
and specified ones being considered, respectively.
Z
V
,
TR
=[( z
Vα
+ z
TRα
)·α+( z
Vβ
+ z
TRβ
)·β ]
(2)
where z
Vα
, z
Vβ
are the costs (negative effects) caused
by an incorrectly chosen speed mode, with the errors
of the 1st and 2nd kind
,
respectively, being made;
z
TRα
, z
TRβ
are the costs caused by the incorrect
determined current location (orientation) of vehicles
on the roadway and (or) caused by the incorrect
choice of the vehicle trajectory in conditions of
insufficient visual information, with the errors of the
1st and 2nd kind, respectively, being considered.
E
V,TR
=[( e
Vα
+ e
TRα
)·(1-α)]+
+[( e
Vβ
+ e
TRβ
)·(1-β)]
(3)
P
d
(i)=δ·(1-P
FNE
)·(1-P
CSSD
)·(1-P
U
)+
+P
FNE
·(1-δ)·(1-P
CSSD
)·(1-P
U
)+
+P
CSSD
·(1-δ)·(1-P
FNE
)·(1-P
U
)+
+P
U
·(1-δ)·(1-P
FNE
)· (1-P
CSSD
)+
+δ·P
FNE
·P
CSSD
·P
U
(4)
P
d
(i) is determined by the value of the insufficient
visual information parameter δ
IVI
, probable failures of
navigation equipment P
FNE
and computer support
system devices P
CSSD
, and the value of the relative
accident rate on the investigated part of the roadway
P
U.
The relative accident rate P
U
shows the number of
road accidents in relation to the mileage of vehicles
or to the number of vehicle passages.
The value of insufficient visual information δ
IVI
is
determined by the ratio of the visible roadway part to
the total area of the roadway that the transport process
subject must see from the observation point (h=1.2
m).
According to Cheng et al. (2015), the relative
accident rate is used to assess the degree of accident
rate within some sections of the roadway or road
network.
The relative accident rate P
U
shows the number of
road accidents in relation to the mileage of vehicles
or to the number of vehicle passages.
In the first case, the coefficient P
U
characterizes
the degree of accidents on long and homogeneous
parts of roads along geometric elements (Cheng et al.,
2015):
P
U
=z/(T·λ
TI
·L)
(5)
where z is the number of accidents for a period of time
T; λ
TI
is the average annual traffic intensity (the
average one for the period of time T), aut./day; L is
the length of the roadway section, km.
In the 2nd case the coefficient P
U
characterizes the
degree of accidents on long and homogeneous parts
of roads within short sections (intersections and
junctions, small bridges, overpasses) (Cheng et al.,
2015):
P
U
=z/(T·λ
TI
)
(6)
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
The studies established that the effectiveness of the
chosen mode of positioning vehicles in the conditions
of insufficient visual information largely depends on
the reliability of the navigation methods and means
LogiTrans 4.0 2019 - Special Session on Logistics and Transport in the Industry 4.0
666
used. Thus, the use of the criterion in (1) – (6) made
it possible to take into account:
the specific character of operating means the
satellite navigation system “GLONASS/GPS”,
with their discreteness and inaccuracy being
taken into account;
the efficiency of each subsystem of the
computer support system for the driver,
depending on the time limits and the nature of
the violations of the rules for the safe operation
of vehicles in the conditions of insufficient
visual information;
the influence of the operation quality of one
subsystem on the results of the other operating
subsystems, with their contribution to the
overall result of the computer support system
for the driver.
As sources of information about the Driver-Car-
Road system, the following types of data are taken
into account: the prior data received as a result of
registration, collection and processing the
information from mobile road laboratories; the
posterior data obtained as a result of exchanging the
information between road users and road
infrastructure elements via wireless communication
channels in the operation of motor vehicles; the
operational data obtained as a result of registration,
collection and processing of the data from sensors and
devices located directly in the vehicle.
The analysed factors influencing the efficiency of
solving the problem of choosing a high-speed mode,
with (1) – (6) being taken into account, proved that to
cope with it a complex information support system is
necessary, including subsystems for collecting and
recording data on the state of road situations,
identifying the surface condition of the roadway, the
choice of optimal values for the Driver-Car-Road
system operational parameters, visualizing and
exchanging the information received between road
users. To solve this problem, an integrated simulation
model is developed as a complex ergatic system
Driver-Car-Road, supplemented with modern
hardware and software means for selecting and
optimizing high-speed modes for vehicles.
As the choice of the trajectory and speed of the car
is significantly influenced by the characteristics of the
roadway, some field studies (Khasanov and Sarajkin,
2016; Khasanov, 2016; Gusarov, 2011; Turenko et
al., 2013) of the quality of roadways of the route
“Orenburg-Isyangulovo” and “Orenburg-Orsk” along
two routes P-314 and P-336 were carried out. 30 % of
road sections are found to be unsatisfactory; 15 % of
the road length have no road signs regulating high-
speed modes for vehicles.
The second variant is characterized by: the
condition of 55 % of road sections is excellent; 10 %
of the road have no road signs regulating high-speed
modes for vehicles; 2 especially dangerous areas are
identified, as they have no any warning information
for road users.
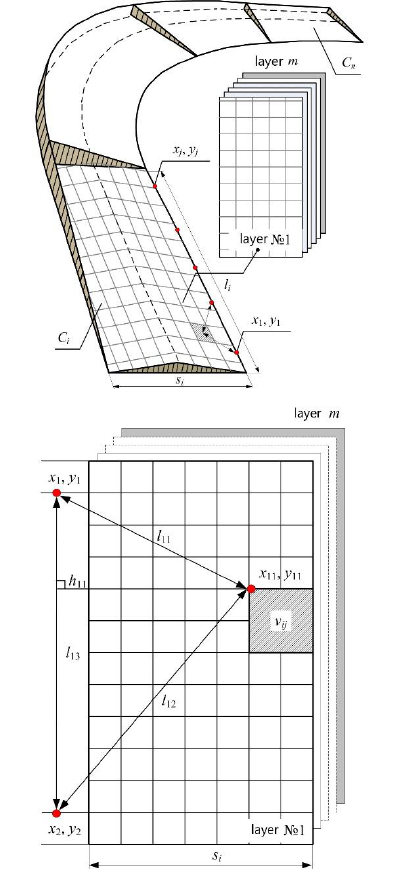
Figure 2 presents a block diagram of a stratified
cellular model for a roadway, as an extended object
in space, with the values of cells (facets) determining
some specific category and level of road safety.
In this case, the road is viewed as an extended
object in the space, the boundaries of which are
digitized by the satellite navigation system
“GLONASS/GPS” with the required degree of
discreteness and accuracy.
The road is represented as a set of roadway
sections, the number of which is k. The section of the
road prototype C
i
with the length l
i
and the width s
i
is
a collection of two-dimensional matrices in the form
of independent layers, the number of which is z.
In each of the 7 layers of C
i
, the information is
kept about the specific form of the transport and
operational condition (TOC) of the roadway: the
longitudinal α and transverse slope β, the flatness r,
wheel tracking ρ, the roughness γ and the adhesion
coefficient φ, the location K
δ
, the area S
δ
and the depth
of potholes h
δ
.
The points x
1
,y
1
– x
j
,y
j
denote the navigation
coordinates of the digitized boundaries of the
roadway; l
11
– l
13
indicate distances between the
navigation coordinates and up to the described the
TOC of the roadway with a specific value of v
ij
; h
11
is
the height of the triangle to the described TOC and
(or) the damage of the roadway.
Each cell from a two-dimensional matrix (layer)
is associated according to its address with certain
values of the TOC of the roadway: α, β, r, ρ, γ, φ, K
δ
,
S
δ
and h
δ
. The values of the cells (facets) of the TOC
of the roadway determine the specific category and
level of road safety. On the totality of the TOC values
of the roadway, the computer support system for the
driver determines the safe high-speed mode V
safe
and
recommends the trajectory TR
rec
for the vehicle.
The input of the choosing (determinating)
subsystem model V
safe
is the set S = {α, β, r, ρ, γ, φ,
K
δ
, S
δ
, h
δ
} of the registered values of the parameters
of the DVRE (driver-vehicle-road-environment)
system, the output of the model is the critical v
cr
and
safe v
safe
speeds of the car to be calculated on the basis
of the mathematical model by I.V.Hodes. In this case,
the computer support system of the driver is
considered as a hardware-software converter of the
parameters S in the speed parameter V
safe
.
Improving Computer Support System for Drivers with Multiport Memory Devices
667
a)
b)
Figure 2: Block diagram of a stratified cellular model for a
roadway а) a set of sections of the roadway and layers of
TOC roadway; b) the addressing scheme of cells of the
matrix fragment.
Addressing of cells in the matrix is carried out in
the following way:
1. The digitized section of the roadway is divided
into sectors. The discreteness of the subdivision of the
road section into sectors is determined by the error
value of the satellite navigation system
“GLONASS/GPS”. For example, if the distance
between the neighboring coordinates x
1
y
1
и x
2
y
2
of the
digitized roadway border is l
1
=540 cm, and the
navigation equipment error Δ
SNS
= 60 cm, then the
number of rows m in the matrix will correspond to
]l
1
/Δ
SNS
[ = 9. For the width of segment of the road
cover s
1
=700 cm, the number of columns n in the
matrix will be equal to ]s
1
/Δ
SNS
[ = 11, where the
functional in the reverse brackets means the whole
part of the ratio.
2. To have access to an arbitrary cell of the matrix,
it is necessary to specify the coordinates of the two
nearest points x
i
y
i
and x
i+1
y
i+1
, as well as the distances
l
11
and l
12
. The developed simulation model in the
automatic mode according to Heron formula
determines the address (index) of the row and column
for the corresponding layer. In situations, if any of the
layers does not require such a detailed subdivision
into sectors, any other necessary dimension is
specified.
Thus, it is possible to store and match with
cartograms the defects and values of the TOC of the
roadway when using dynamic arrays. The use of
dynamic arrays as an approach when developing a
software design. firstly. makes it possible to change
automatically their dimensionality for accumulating
the information in the process of collecting. recording
and processing data on the geometric and operational
parameters of the roadway. Secondly, the use of
dynamic arrays can reduce the amount of memory
resources consumed in the computer support system
of the driver. since unused address ranges and pages
(layers) can be automatically freed from the system’s
RAM.
Thus this program approach makes the work with
information more flexible. since it does not require a
preliminary determining the dimensions of the stored
arrays, the roadway data and the route of movement
of the mobile object.
The stratified cellular model of the roadway is
implemented in the programming environment
“Borland Delphi 7” in the form of a multi-page
(multi-layered) dynamic array and is used in the
developed simulation model of vehicle controlling,
with the errors in navigational data being taken into
account.
The effectiveness of the chosen mode of
positioning vehicles in the conditions of insufficient
visual information depends largely on the reliability
of navigation methods and means used. The use of the
criterion in (1) – (6) makes it possible to consider the
specific character of operating satellite navigation
systems “GLONASS/GPS”, with their discreteness
and inaccuracy being considered (Khasanov, 2016;
Cheng et al., 2015).
In determining the objective function navigation
equipment is considered to provide information with
certain discreteness in addition to metrological errors,
LogiTrans 4.0 2019 - Special Session on Logistics and Transport in the Industry 4.0
668
for example, the discreteness of modern means of
satellite navigation “GLONASS/GPS” is 1÷500 Hz,
while the range of metrological error is 2÷60 cm for
modern inertial satellite navigation systems operating
in the differential correction mode, and in the range
1÷15 m for widely available 24-channel satellite
navigation devices.
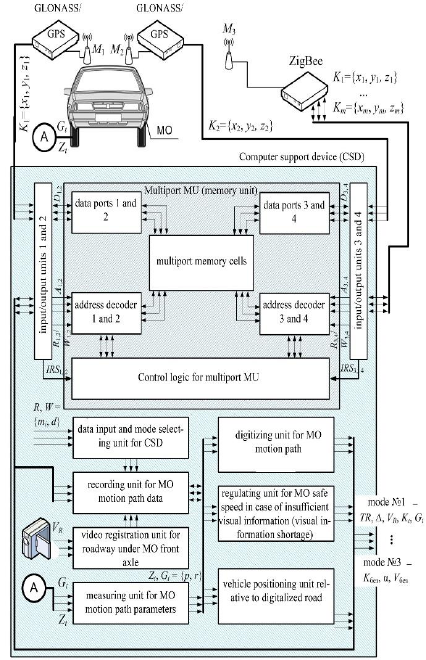
In Figure 3 the functional diagram for the device is
presented.
Figure 3: Functional diagram of a device for computer
support system for drivers for positioning a group of
vehicles.
The requirements for high-speed performance of
computer support systems for drivers to position a
group of vehicles caused the development of this
system in the form of a specialized hardware platform
that uses the principles of organization and
architecture of multi-port memory devices, modern
relational database management systems, “V2V” and
EIIP approaches (Turenko et al., 2013) to the group
members.
Due to the use of multiport memory devices, the
design principles for database management systems,
multi-page (n-dimensional) organization of dynamic
arrays, wireless ZigBee-modems for data exchange
between vehicles (“V2V”) a single virtual information
space for group members is organized. When the
computer support system for drivers functions inside
multi-port memory devices, the same copies of the
dynamic arrays (images) Q
t
are stored. When the
structure or content changes at the time moments t, the
modified image Q
t'
becomes equally updated for all
members of the complex group (Shen and Neyens,
2014).
The presented prototype of the platform can be
realized on the basis of the following elements and
means of computer technology: multiport memory
devices based on VRAM, WRAM and MDRAM
technologies, ZigBee-modems “ETRX2-PA”,
computer driver support systems based on mobile
computers of the type (Khasanov and Sarajkin, 2016),
(Broggi et al., 2012), (Cheng et al., 2011), (Chen et
al., 2015), (Schätz et al., 2015) GLONASS/GPS-
modules of the “SIM68EVB KIT” type.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The purpose of the research was to increase the
efficiency of the information provided to the subjects
of the transport process to ensure a safe mode of
positioning a group of vehicles on the roadway. Thus,
we have suggested the approach to ensuring vehicles’
active safety and safety of other road users by the
maintenance of adequate positions (stable condition)
of vehicles on the roadway due to chosen safe modes
of driving in the conditions of insufficient visual
information.
The methods and principles of the theories of
active vehicle safety, control and optimization, the
theory of pattern recognition and the theory of
designing computer systems were used.
The objective function is to assess the
effectiveness of decision-making when choosing the
positioning mode for a group of vehicles on the
roadway in the conditions of visual information
shortage, with an experimental model (a prototype) of
a high-performance computer support device for
drivers based on the use of multiport memory units
being also developed.
We have developed an emulator program that,
using navigation stands, simulates the operation of a
multiport memory device.
The results obtained can be recommended for
creation of computer support systems for drivers, as
well as in the management of vehicles in the
conditions of insufficient visual information.
Improving Computer Support System for Drivers with Multiport Memory Devices
669
REFERENCES
Broggi, A., Cerri, P., Felisa, M. et al., 2012. The VisLab
Intercontinental Autonomous Challenge: an Extensive
Test for a Platoon of Intelligent Vehicles. Intl. Journal
of Vehicle Autonomous Systems, 10(3), pp. 147–164.
Chen, Z., Shi, Q., Huang, X., 2015. Automatic detection of
traffic lights using support vector machine. In: Proc.
IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 37–40.
Cheng, Y., Lin, J., Yi, C. et al., 2011. AR-based positioning
for mobile devices. In: Proc. Int. Conf. Parallel
Processing Workshops, 63–70.
Gonzalez, A., Bergasa, L. M., Yebes, J. J., 2014. Text
Detection and Recognition on Traffic Panels from
Street-Level Imagery Using Visual Appearance. In:
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation
Systems 15(1), 228–238.
Gusarov, A. P., 2011. Regulation tendencies for requirements
for on-board intellectual transport systems in UNECE
Inland Transport Committee. The Journal of Automotive
Engineers 3, 4-8.
Khasanov, R. I., 2016. The positioning of vehicle with
given location of defects on roadway. The Journal of
Automotive Engineers 5, 14–18.
Khasanov, R. I., Sarajkin, A. I., 2016. ADAS in the problem
of vehicle positioning in the conditions of visual field
information gap, The International Technical-Economic
Journal 3, 36–42.
Khasanov, R. I., Saraykin, A. I., 2016. Mobile object outfit
based on the integrated infosphere positioning. The
International Technical-Economic Journal 4, 86–93.
Meguro, J., Hashizume, T., Takiguchi, J. et al., 2005.
Development of an autonomous mobile surveillance
system using a network-based RTK-GP. In: Proc. Int.
Conf. IEEE Robotics and Automation, 3096–3101.
Park, H. S., Park, M. W., Won, K. H. et al., 2013. In-vehicle
AR-HUD system to provide driving-safety information.
ETRI Journal 35(6), 1038–1047.
Roessing, C., Reker, A., Gabb, M., et al., 2013. Intuitive
visualization of vehicle distance, velocity and risk
potential in rear-view camera applications. In: Proc. Int.
Conf. IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 579–585.
Schätz, B., Voss, S., Zverlov, S., 2015. Automating design-
space exploration: Optimal deployment of automotive
SW-components in an ISO26262 context. In: Proc. Int.
Conf. Design Automation Conference, July, 2015.
Shen, S., Neyens, D. M., 2014. Assessing drivers’
performance when automated driver support systems fail
with different levels of automation. In: Proc. Int. Conf.
Human Factors and Ergonomics Society, January, 2014,
pp. 2068–2072.
Turenko, A. N., Uzhva, A. V., Lukashov. I. V. et al., 2013.
Development of a global positioning device for
reproducing the trajectory of a racing car’s movement.
Automobile transport 32, pp. 7–11.
Turenko, A. N., Uzhva, A. V., Lukashov, I. V. et al., 2013.
Using GPS navigation satellite system to reproduce the
trajectory of a racing car’s movement. Automobile
transport 60, pp. 83–89.
LogiTrans 4.0 2019 - Special Session on Logistics and Transport in the Industry 4.0
670
