Neuroevolution with CMA-ES for Real-time Gain Tuning of a Car-like
Robot Controller
Ashley Hill
1
, Eric Lucet
1
and Roland Lenain
2
1
CEA, LIST, Interactive Robotics Laboratory, Gif-sur-Yvette, F-91191, France
2
Universit
´
e Clermont Auvergne, Irstea, UR TSCF, Centre de Clermont-Ferrand, F-63178 Aubi
`
ere, France
Keywords:
Neuroevolution, Machine Learning, Neural Network, Evolution Strategies, Gradient-free Optimization,
Robotics, Mobile Robot, Control Theory, Gain Tuning, Adaptive Control.
Abstract:
This paper proposes a method for dynamically varying the gains of a mobile robot controller that takes into
account, not only errors to the reference trajectory but also the uncertainty in the localisation. To do this,
the covariance matrix of a state observer is used to indicate the precision of the perception. CMA-ES, an
evolutionary algorithm is used to train a neural network that is capable of adapting the robot’s behaviour in
real-time. Using a car-like vehicle model in simulation. Promising results show significant trajectory follow-
ing performances improvements thanks to control gains fluctuations by using this new method. Simulations
demonstrate the capability of the system to control the robot in complex environments, in which classical static
controllers could not guarantee a stable behaviour.
1 INTRODUCTION
Mobile robots are used to accomplish different mis-
sions, their sensors being used to correctly and ef-
ficiently understand the robot’s environment. Those
sensors have varying degrees of certainty in their mea-
surement depending on the environment and their
properties. This limits the efficiency of robots us-
ing static controllers, as the tuning of their parame-
ters takes into consideration the nominal behaviour of
the robot, which has a negative effect on the robot’s
efficiency when operating in sub-nominal states. The
purpose of tuning these controllers is also to guaran-
tee a higher level of margins, which has a negative ef-
fect on robot performance during nominal states. This
compromise reduces the overall performance of the
robot. In control theory, noise robustness is an es-
sential quality (Ghorbel et al., 1991); it is therefore
relevant to use the noise information directly to adjust
control parameters in real-time.
In the field of mobile robotics, finding an opti-
mal control policy is a challenging task. Especially in
complex environments where sensor precision varies
considerably and as so the level of noise in the system.
The aim of this paper is to integrate the noise into the
control policy in order to adjust the robot’s behaviour
to its complex environment. Different types of con-
trollers can be proposed (Jalali and Ghafarian, 2009;
Jiang et al., 2008; Doicin et al., 2016). However, tun-
ing controller gains relies on many parameters (Da-
ful, 2018). As a solution to the tuning problem, Neu-
ral networks have been used, with promising results
(Guo et al., 2009; Shu et al., 2015; Carlucho et al.,
2017); however such methods use small neural net-
works that are not capable of complex inference, and
are using the error or state vector as the basis for the
gradient which can cause instability if noisy.
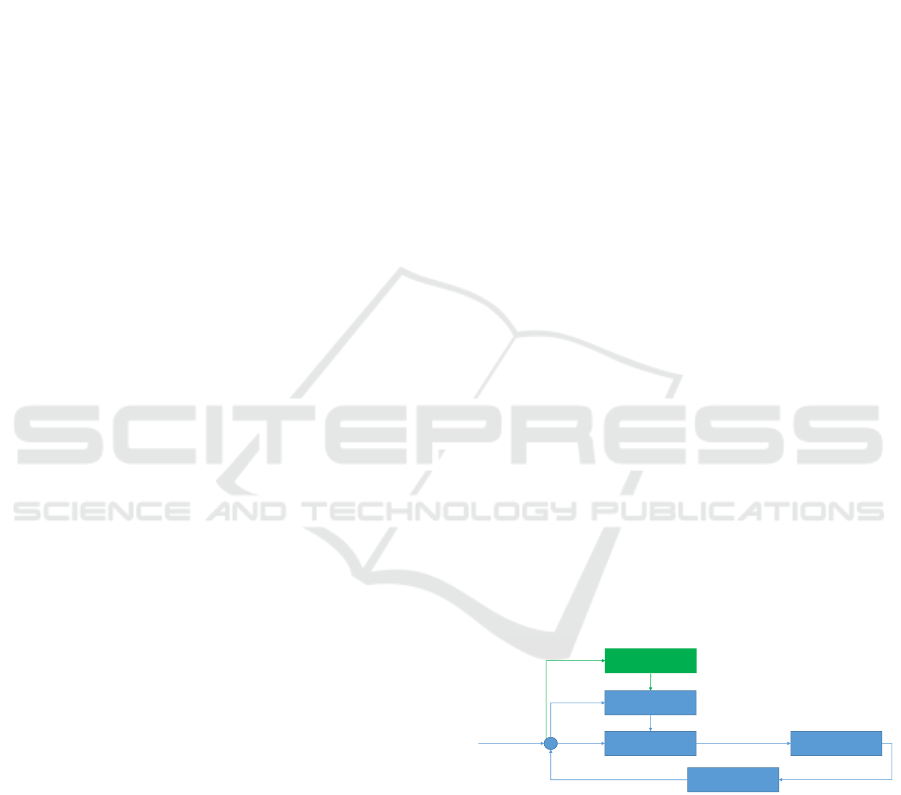
NN
CMA-ES
Controller
EKF
Robot
State
Measures
Control inputErrors
Setpoints
Errors, state
covariance,
curvature
Objective
function
Parameters
Gains
Figure 1: Control bloc diagram of the proposed method.
In green is the CMA-ES training method and in blue the
control loop with the neural network (NN).
In this paper, a new strategy for on-line gains
adaptation is propose and summarised in Figure 1.
CMA-ES (Hansen, 2016) is the optimisation algo-
rithm for the parameters of the neural network. The
neural network block takes parameters and environ-
mental information as inputs, and outputs the gains of
the controller. The controller uses the gains defined
by the neural network in order to effectively follow
Hill, A., Lucet, E. and Lenain, R.
Neuroevolution with CMA-ES for Real-time Gain Tuning of a Car-like Robot Controller.
DOI: 10.5220/0007927103110319
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2019), pages 311-319
ISBN: 978-989-758-380-3
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
311
the requested trajectory. The robot’s dynamics sim-
ulate the behaviour of the robot. The noise mimics
real world conditions, and so an extended Kalman fil-
ter (EKF) is used to observe the state of the robot. It
provides the estimated state ˆx and the corresponding
covariance matrix P.
In the following, the paper is structured into three
main sections before conclusions. The second sec-
tion presents all the localisation, modelling, and con-
trol algorithms applied to the robot. The third section
is dedicated to the presentation of gains adaptation.
Finally, results are detailed and discussed along with
perspectives.
2 LOCALISATION PROCESS AND
CONTROL
2.1 Modelling
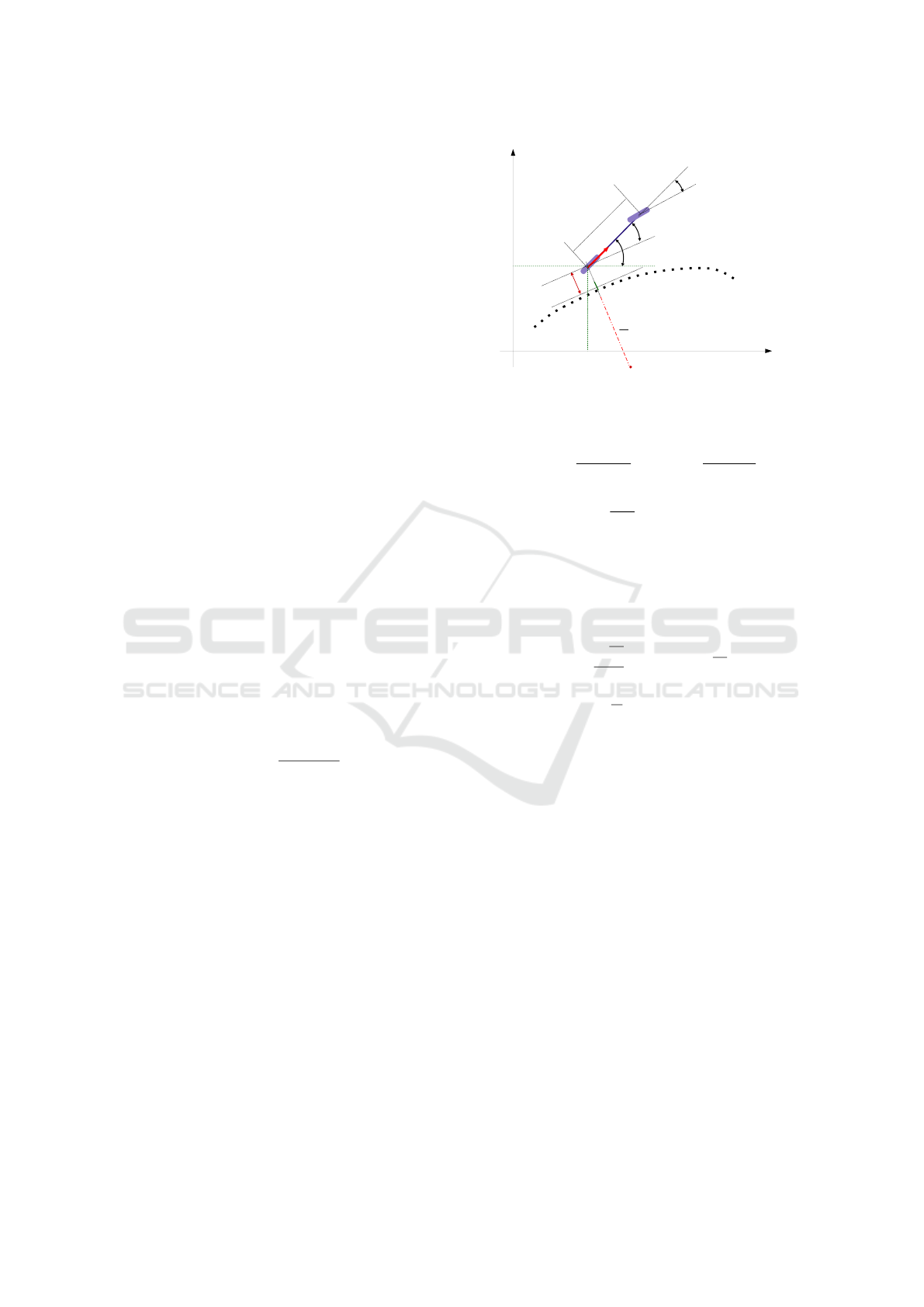
The focus of this study is to adapt the control policy of
a car-like mobile robot to the precision of the percep-
tion, the lateral error, the angular error, and the current
curvature of the trajectory; using a neuroevolution al-
gorithm. In order to train the system and test it, a
model of the robot was used to simulate its behaviour.
The model is fairly representative of the task and had
been used in previous works (Jaulin, 2015). The robot
is described by the following kinematic model:
˙
X =
˙x
˙y
˙
θ
˙v
=
v cos(θ) +α
x
v sin(θ) + α
y
v
tan(u
2
+α
u
2
)
L
+ α
θ
u
1
+ α
u
1
(1)
The state variables are: x,y the coordinates of the
robot in the world frame, θ its heading, L its wheel-
base, and v its rear velocity. u
1
and u
2
are the acceler-
ation and steering inputs respectively. α
i
is the white
Gaussian noise of the i state variable.
In Figure 2, u
2
is the steering angle of the robot
(Ackermann angle) and constitutes the control input,
ε
l
is the distance from the robot to the path, ψ is the
robot heading, (D) is the trajectory, κ is the curvature
of the trajectory, L is the wheelbase of the robot. The
angular deviation ε
θ
is representative of the difference
between the robot heading and the orientation of the
trajectory.
2.2 Control Law
The robot has to complete a task, which is in our case
following a trajectory. To accomplish this, the follow-
ϵ
θ
u
2
L
v
ϵ
l
1
κ
(D)
x
y
ψ
Figure 2: The mobile robot studied.
ing controller is used:
u
2
= arctan
L cos
3
ε
θ
α
k
θ
(e
θ
) +
κ
cos
2
(ε
θ
)
(2)
with e
θ
= tanε
θ
−
k
l
ε
l
α
is the relative orientation
error of the robot to reach its trajectory (i.e. ensur-
ing the convergence of ε
l
to 0). This control detailed
in (Lenain et al., 2017) guaranties the stabilisation of
the robot to its reference trajectory, providing a rele-
vant choice for the gains k
θ
and k
l
. Theoretically, a
relevant choice for these gains may be:
k
l
=
p
k
p
2L
and k
θ
= 2
p
k
p
it implies k
θ
× k
l
=
k
p
L
and guaranties that the con-
straint k
θ
> k
l
is respected, we then get our final con-
troller with k
p
the controller gain. As a result, the
control law (2) has only one parameter k
p
, defining
the theoretical distance of convergence of the robot to
the trajectory (as it has been proven in (Lenain et al.,
2017)). As a result, the higher the gain is, the more
reactive the robot is. However the sensor noise as well
as delays in the low level may lead to instability. The
choice of this gain has to then be made with respect
to localisation properties.
2.3 Robot Localisation
In order to feed the control law (2) with lateral and
angular error, the state vector defined by (1) has to be
known. For estimating the state of the robot, an EKF
is proposed. It assists in determining the linear speed,
the x, y position, and the heading. It is widely used
due to its simplicity and robustness.
In the proposed system, P is the covariance matri-
ces of the estimation and it is used to determine the
level of precision of the perception. A novelty of this
paper is that both the estimate and the corresponding
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
312

covariance matrix are integrated in the tuning of the
Controller. The observed variables are used to control
the robot along a path. Even though the controller is
easy to implement, the tuning of its parameters is not
a simple task and is a large research area (Ho et al.,
1996; Tyreus and Luyben, 1992; Hang et al., 2002).
3 CONTROL GAINS
ADAPTATION
The nature of the environment forces the mobile
robot’s perception to vary in precision. These changes
in precision will be given by the changes in the co-
variance matrix of the EKF. Therefore, the controller
gains must adjust periodically. In order to adapt the
controller’s parameters to the level of precision in the
perception, but also to the properties of the trajectory,
a neural network is used. The network will tune the
controller in real-time, based on the tracking errors,
the path curvature and the covariance matrix of the
EKF.
3.1 The Neural Network Model
Hidden layer
100
Hidden layer
40
Hidden layer
10
Input layer
7
Output layer
1
Figure 3: Graphical representation of the used neural net-
work. With 7 neurons in the input layer, 3 hidden layers of
40, 100, and 10 neurons respectively, and 1 neuron for the
output layer. all the layers except the output layer go though
a hyperbolic tangent function as the activation function.
Neural networks (NN) are highly connected systems
which are used to model complex non-linear func-
tions. In neural networks the inputs are transformed
through matrix multiplications and non-linear activa-
tion functions, in order to obtain a universal function
estimator through the tuning of the weights (Hornik
et al., 1990). The used neural network (see Figure 3)
has as input the vector of concatenated values for: the
lateral error ε
l
, the angular error ε
θ
, the curvature of
the trajectory κ, and the diagonal of the EKF covari-
ance matrix P. As output, this neural network returns
a vector corresponding to each controller gain respec-
tively. The training of the neural network is the pro-
posed neuroevolution algorithm, which means that an
evolution strategy will be used to optimise the neural
network. Evolution strategies are stochastic optimi-
sation algorithms (Beyer and Schwefel, 2002). The
great advantage of this family of algorithms is that
they do not need to calculate any gradient when opti-
mising a neural network. This allows to reduce com-
putation when training and it is robust to noisy re-
turn signals (e.g. reward, objective function, etc ...)
unlike reinforcement learning for example (Salimans
et al., 2017). All evolutionary algorithms go through
the same steps: mutation, evaluation, selection, repro-
duction and repeat until a termination criterion is met.
There exists multiple algorithms in the family of evo-
lution strategies, a few of them were considered, es-
pecially genetic algorithms. However, the CMA-ES
(Hansen, 2016) optimisation algorithm has shown its
superiority in highly modal, non-convex, noisy func-
tions (Hansen et al., 2010); such as the highly non-
convex search spaces of neural networks with a noisy
objective function (Salimans et al., 2017; Risi and To-
gelius, 2014; Such et al., 2017).
3.2 CMA-ES Neuroevolution
To adjust the behaviour of the robot, a neural net-
work was chosen to adjust the parameters of the con-
troller. This neural network’s architecture was chosen
based on previous work and experimentation, in or-
der to be able to infer a complex enough non linear
outputs from the given inputs. Neural network pa-
rameters, such as weights and biases, are optimised
by the CMA-ES method during the offline training
phase. The CMA-ES optimisation algorithm starts by
generating an initial population of parameters for the
neural network, by drawing samples from the follow-
ing distribution:
x
g+1
k
∼ m
g
+ σ
g
N (0,C
g
) f or k = 1, ..., λ (3)
with m
g
the mean vector of the current generation, σ
g
the step size vector of the generation, C
g
the covari-
ance matrix of the generation which differs from the
covariance matrix of the Kalman filter, and λ the size
of the population. CMA-ES uses the covariance ma-
trix to chose the optimal direction of the search and
the step size over every parameter to know the op-
timal length of the step to take between consecutive
generations. Here both phases are presented. The first
one is the training phase where the neural network is
optimised to learn the behaviour which robot is in-
tended to have. After this, the neural network and the
controller are deployed into the robot to work online.
Neuroevolution with CMA-ES for Real-time Gain Tuning of a Car-like Robot Controller
313

During the online training phase, a simulation of the
robot’s kinematics is used to simulate its behaviour,
and a controller is used to follow the requested path.
The robot’s state is measured by adding noise to the
simulated state, and an EKF is then used to observe
the state of the robot. Once the online training is
completed and the objective function is calculated, the
CMA-ES method then optimises the neural network
parameters based on the objective function.
The CMA-ES generates a population of neural
networks based on the architecture. Each neural net-
work is used by the simulation to generate controller
gains for each timestep using the current errors, cur-
vature, and EKF covariance matrix. These parameters
are then used to control the robot. For each neural
network, a series of simulated trajectories are used in
order to calculate the objective function of the neural
network using the robot over many examples to avoid
overfitting; this objective function is the criterion for
comparing the performance of each neural network.
CMA-ES puts the neural networks found in order,
based on their score. A set of the best preforming
individuals are then used to produce the next genera-
tion and the cycle continues until a stopping criterion
is met. By the end of the training, the resulting neu-
ral network is the one with the lowest score. For a
neural network to have the best score, it must adapt
the behaviour of the robot so as to decrease the er-
ror by considering the real state and not the observed
one. For this to happen, the neural network has to
choose high gains on the controller to force the robot
to follow the reference, especially when cornering or
correcting any lateral errors. However, when the level
of noise is high, it must lower the mean values of the
gains to not have an oscillatory behaviour which com-
promises both the mechanical structure of the robot
and the comfort of the passengers in the case of occu-
pied vehicles.
For the deployment phase, the trained neural net-
work and the controller are deployed into the robot.
The neural network does not consume too much re-
source as it is only used for inference of the controller
gains and not for training.
3.3 The Objective Function
The objective function is an essential part of evolution
strategies, it is what the algorithm tries to minimise in
order to find the best local optimum for the search
space. To minimise the objective function, CMA-ES
tweaks the parameters of the neural network in order
to have the lowest possible value; this tweaking of
the parameters is what is called learning, because the
model is in fact a system that has the capacity to learn
certain behaviours, and is adapting to reach said be-
haviours. Since the objective function determines the
behaviour of the neural networks, we have tested the
following objective functions formulated as:
ob
1
=
T
∑
τ=0
|ε
l
(τ)| + |ε
θ
(τ)L| (4)
ob
2
=
T
∑
τ=0
|ε
l
(τ)| + |ε
θ
(τ)L| + |u
2
(τ)L| (5)
ob
3
=
T
∑
τ=0
|ε
l
(τ)| + |ε
θ
(τ)L| + k
steer
|u
2
(τ)L| (6)
with ε
l
the lateral error, ε
θ
the angular error, u
2
the
steering input, L the wheelbase of the robot, k
steer
the
weight of the steering input in the objective function,
and T the total timesteps of the simulation. The abso-
lute value of the errors and steering input are used as
we are measuring the accumulated amplitude of these
values. Since the objective functions takes into ac-
count both the lateral and the angular errors, using
the accumulation of them at the end of the simulations
guarantees a coherent objective function that will per-
form a similar trade off as the controller, meaning it
wont degrade the overall performance in order to op-
timise one of the errors.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Here are presented the results of the developed sys-
tem. Since evolution strategies are comparable to re-
inforcement learning methods (Salimans et al., 2017),
we will compare this method to reinforcement learn-
ing methods using the negative amplitude of lateral
and angular errors as its rewards, and a constant gain
method trained using CMA-ES on the same objective
function as the proposed method, similarly to existing
methods (Wakasa et al., 2010; Sivananaithaperumal
and Baskar, 2014; Marova, 2016). Tests are focused
on the trained system and not on the training phase.
This section is divided into two main parts. In the
first part: The experimental environment is presented.
Then, the limitations of using a constant gain method
are shown qualitatively. Then, the qualitative results
from the training phase are presented. Finally, the
system performance is compared to results in same
conditions with a fix gain controller and with a rein-
forcement learning algorithm. And in the second part,
the results are discussed in a general context and im-
provements are suggested.
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
314
4.1 Results
4.1.1 Simulated Environment
The training setup for all the methods were on a sim-
ulated robotic environment, with a cinematic model,
without wheel slipping, and without control latency,
written in Python and C, where the robot must follow
a series of trajectories, with noisy position measure-
ments distributed randomly in zones along the trajec-
tories to simulated GPS-like perturbations, and with
a randomly placed change lane along the trajectories
to simulated abrupt changes in the setpoints. This al-
lows rather realistic types of noises that a robot can
encounter that will cause instability and higher over-
all errors to occurs. The trajectories are: a line, a sine
wave, a parabola, a Bezier spline in an sigmoid shape
called spline1, and a Bezier spline in a u-turn shape
called spline2. With the perturbations and trajecto-
ries, this setup helps prevent CMA-ES or reinforce-
ment learning methods from falling into bad local op-
timums and overfitting, due to the high randomness of
the perturbations and the variations in the trajectories.
4.1.2 Limitations of the Constant Gain Model
An ideal gain model must allow the controller asso-
ciated to the gains, to simultaneously minimise the
errors and not be too reactive to noise present in said
error. In our case study this means finding the gains
that are able to follow a line as closely as possible,
whilst avoiding undesirable reactions to noise that can
induce unstable behaviours.
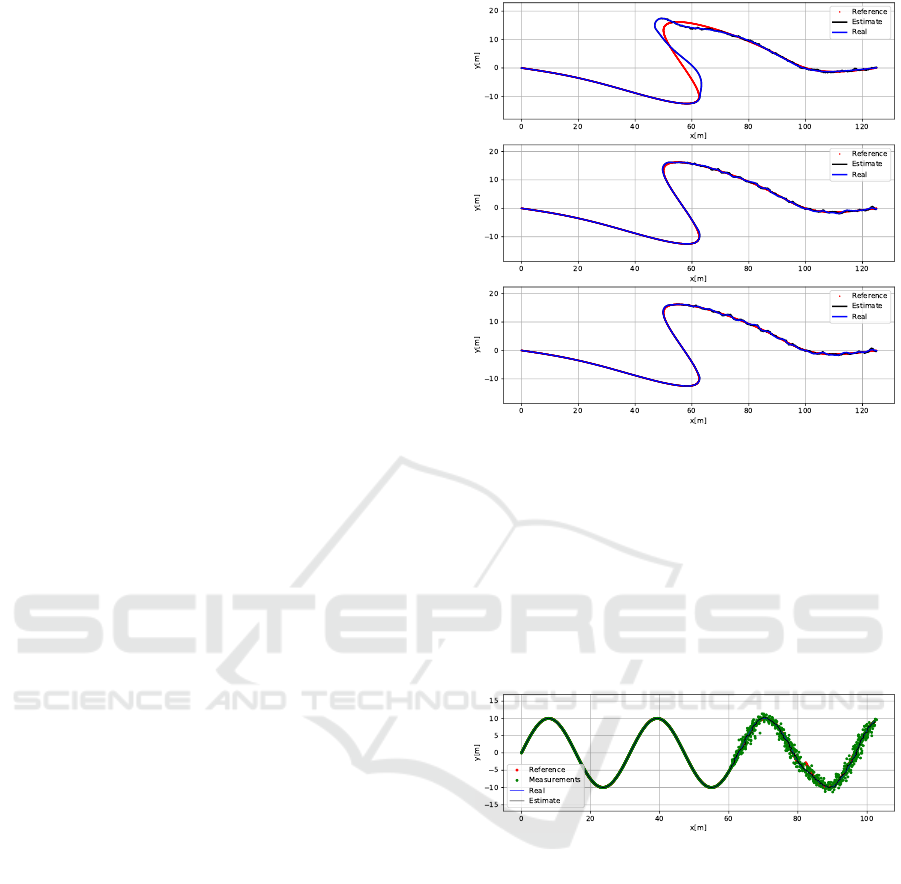
Looking at figure 4, we can see the compromise
a constant gain model must achieve. In the first plot
with a small gain, we can see the robot having trouble
following the line when the corners occur; however
it is quite steady and stable in the noisy region of the
trajectory. In the third plot with the very high gain, we
see the complete opposite of this, the robot becomes
completely unstable in the perturbed region; however
it was very close to the curve in the high accuracy
region. And in the second plot with a gain that is mid-
way of the first and third plot, we can see some dif-
ficulties following the lines in the stable region, and
some instability and oscillation in the noisy region.
One can then see the limitations of a constant gain
model that must reach a paradoxical compromise be-
tween contradicting gains. In this case, the clear solu-
tion is an adaptive model, such as the proposed con-
tribution.
Figure 4: The x,y view of the simulation using the spline1
trajectory and a constant gain model. Midway through the
trajectory noise is applied to the position measurements.
Above: The first plot with a low gain of 0.1. Middle: The
second plot with a high gain of 3.0. Below: The third plot
with a very high gain of 7.0.
4.1.3 Qualitative Results
In order to help visualise the gain adaptation to the
perturbations, the trajectory in figure 5 is used in the
following results:
Figure 5: The x,y view of the simulation using the sine tra-
jectory. Midway through the trajectory noise is applied to
the position measurements, and then a change lane occurs
just before the last corner.
After training, (see Figure 6), the real vehicle han-
dles the EKF covariance matrix’s errors, the curvature
of the trajectory, and even the lateral error due to a
change lane.
It can be seen that, as expected, a higher gain is
computed when cornering, when an unexpected per-
turbation occurs, and when the position accuracy is
high. In contrast, the gain is reduced when the posi-
tion accuracy is too low, in order to avoid a possibly
unstable behaviour.
Furthermore, when using objective functions ob
2
and ob
3
, the neural network is able to lower signif-
icantly the oscillatory behaviour of the steering, as
shown in Figure 7.
Neuroevolution with CMA-ES for Real-time Gain Tuning of a Car-like Robot Controller
315
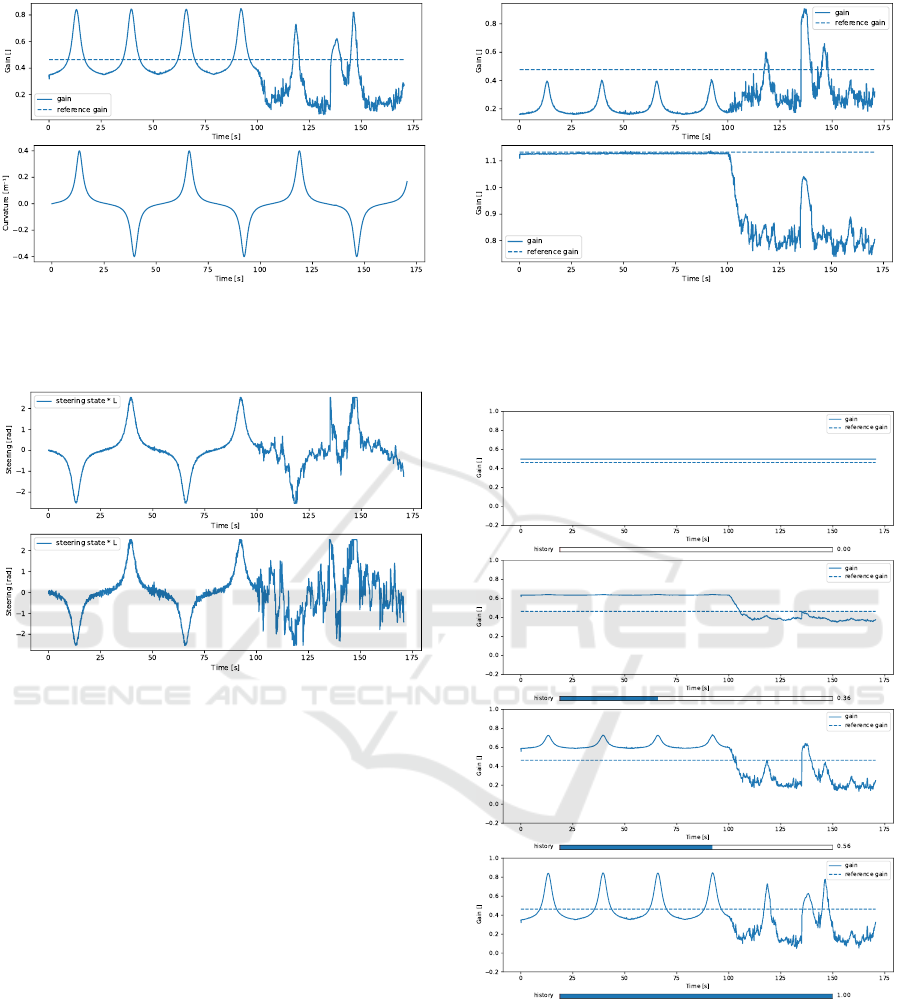
Figure 6: Above: the gain outputed by the neural network
in the solid line, and the chosen constant gain value in the
dashed line. Below: the curvature of the trajectory over
time.
Figure 7: Steering input u
2
over time by using the proposed
method. Above: when trained with the objective function
ob
2
. Below: when trained with the objective function ob
1
.
Additional experiments such as ablation over the
given inputs to the neural network were done. The
EKF covariance matrix seems to be an invaluable in-
formation for predicting a useful gain, as when trained
without it causes a much lower gain overall, as it can-
not know the regions where instability occurs (see
Figure 8). Also the curvature is helping to obtain a
lower objective function overall when the trajectory
is not curved, allowing for smoother control.
Some tools were developed in order to understand
the training process in further details. On the history
of the trained network displayed in Figure 9, we can
see that the CMA-ES method first optimises the gain
using the covariance of the Kalman filter, then using
the lateral error, and then using the curvature. This
order makes sense, as it is from the most to the least
impactful to the objective function through the gain,
and as such, it should be optimised in this order.
Figure 8: The gain outputed by the neural network in the
solid line, and the optimal constant gain value in the dashed
line. Above: when trained without using the EKF covari-
ance matrix as input. Below: when trained without using
the curvature of the trajectory as input.
Figure 9: Gain values over the training generations. The
gain outputed by the neural network in the solid line, and
the optimal constant gain value in the dashed line.
4.1.4 Quantitative Results
In order to help verify quantitatively the relevance of
our results, we used the Welch t-test (Welch, 1947)
over the distribution of the values of the objective
functions, with the null hypothesis being that our
method produces the same results as the constant gain
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
316

method. The resulting test returns p-values, that are
the probability of obtaining these results if the null
hypothesis is true; as such, if the p-value is lower than
1.00e
−2
we can consider the null hypothesis being re-
jected, and show the significance of our results.
We used two methods to compare our results
quantitatively. The first is to see the improvement
relative to a static gain controller using the objective
function with a Welch t-test over multiple trajectories
and seeds. The second is to see the improvement rel-
ative to a gain tuned by reinforcement learning meth-
ods using the objective function with over multiple
trajectories and seeds. These two methods should al-
low us to see how the suggested method improves the
quality of the control over the traditional constant gain
method and over reinforcement learning based meth-
ods.
Table 1: Welch test p-values between fixed gain and the
suggested method, for every trajectory over the objective
functions. With k
steer
= 0.5.
trajectory ob
1
ob
2
ob
3
line 3.22e−2 1.80e−8 7.01e−5
sine 1.61e−4 4.07e−9 6.06e−7
parabola 6.53e−12 4.20e−21 1.49e−17
spline1 2.09e−28 3.63e−21 5.08e−19
spline2 3.48e−1 8.42e−16 1.49e−9
We can see from the table 2 that across all the
objective functions and the trajectories, that the
proposed method obtained between 3% to 20%
improvement with an average of 10% improvement
over the constant gain method. Furthermore, with the
table 1 we can see that the p-values associated with
these improvements, are for the most part significant,
except for the line and spline2 trajectories, which
are both hard to improve upon as the first is a very
easy trajectory for the constant gain, and the second
is quite hard for the robot model to follow with its
given design. Nevertheless, the other results are quite
significant and do indeed show the benefit of this
method when compared to the constant gain method.
As discussed earlier, CMA-ES based neuroevolu-
tion can obtain similar if not better performance when
compared to reinforcement learning (RL) based meth-
ods. The trade-off is that neuroevolution is more sta-
ble to noise, but requires more time to train than rein-
forcement learning. Here four commonly used mod-
els where tested on the training environment: Soft ac-
tor critic (labeled SAC) (Haarnoja et al., 2018), Prox-
imal policy optimization (labeled PPO) (Schulman
et al., 2017), Deep deterministic policy gradient (la-
beled DDPG) (Lillicrap et al., 2015), and Advantage
actor critic (labeled A2C) (Mnih et al., 2016); using
the RL library stable-baselines (Hill et al., 2018).
We can see from the table 3 that none of the reinforce-
ment learning models where capable of reaching even
the baseline constant gain model; with most of the
models between 19% and 3870% with an average of
588% of degradation in performance when compared
to the constant gain model. Considering the scale of
the amplitude and variance of the performance loss,
no t-test was performed on this dataset.
4.2 Discussion
Neuroevolution is used to tune controller gains in
real-time after a training phase. As mentioned before,
the CMA-ES optimises a neural network, then the
said neural network tunes the controller gains. The
proposed controller was used due to its simplicity and
ease of use. The objective was to develop an adapt-
able system that works with different types of con-
trollers whose parameters must be tuned.
As demonstrated in the results section, the pro-
posed method outperforms the traditional constant
gain method by a significant amount; as it is capable
of adapting the robot behaviour to the environment
using the information present in the control loop. It is
able to achieve such performance by minimising the
wanted objective function through the CMA-ES train-
ing.
We also showed that modern reinforcement learn-
ing methods are not capable of learning a beneficial
behaviour in the same environment. This is probably
due to the fact that the reward signal depends on the
information in the control loop, such as lateral and an-
gular errors; as in our experiments, they become very
noisy due to the position noise. This noise on the re-
ward signal prevents the critic of actor critic models
from correctly converging, causing erratic learning.
This flaw does not occurs when using CMA-ES, as
it is inherently resilient to noisy objective functions
(Hansen, 2016; Salimans et al., 2017).
It is important to note that the selection of the ob-
jective function is very important to the quality of
the gain tuning, as the optimisation can compromise
the performance of other features. For example dur-
ing experimentation, the objective function ob
2
had
higher lateral error when compared to ob
1
, however
this is a trade off as ob
2
is more stable with respect to
the steering.
The training time for the method was about 5
hours wall time using 8 CPU cores, and can be scaled
extremely well with more CPUs thanks to the CMA-
ES method (Salimans et al., 2017). This training is
only feasible in simulation however, as the 5 hours of
training time is the equivalent of 1 simulated year. To
Neuroevolution with CMA-ES for Real-time Gain Tuning of a Car-like Robot Controller
317
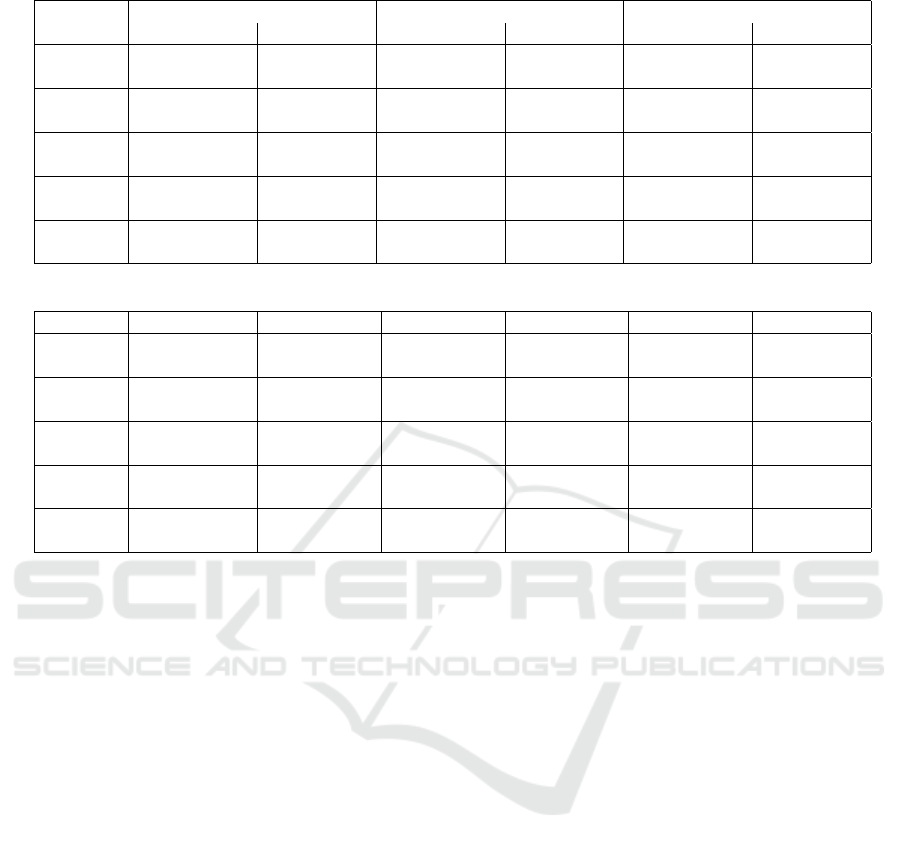
Table 2: The values of the objective functions for every trajectory. With k
steer
= 0.5.
ob
1
ob
2
ob
3
trajectory CMA-ES NN fixed gain CMA-ES NN fixed gain CMA-ES NN fixed gain
line 27.41
(±1.98)
28.30
(±2.08)
41.60
(±2.34)
48.20
(±2.45)
36.63
(±2.63)
40.46
(±4.65)
sine 39.81
(±2.18)
41.54
(±2.18)
144.76
(±2.86)
151.70
(±2.83)
94.11
(±2.32)
98.66
(±2.37)
parabola 64.41
(±2.90)
69.10
(±3.04)
98.73
(±3.39)
125.29
(±4.02)
83.38
(±3.27)
101.62
(±4.00)
spline1 52.34
(±2.14)
59.79
(±2.52)
117.66
(±3.04)
142.04
(±3.45)
87.30
(±3.07)
105.43
(±3.54)
spline2 68.33
(±2.59)
71.76
(±25.26)
147.32
(±3.18)
164.94
(±4.45)
110.03
(±3.12)
119.04
(±3.79)
Table 3: The values of the objective function ob
2
for every trajectory with RL methods.
trajectory CMA-ES NN SAC PPO DDPG A2C fixed gain
line 41.60
(±2.34)
60.99
(±22.21)
115.11
(±57.10)
158.14
(±4.09)
57.52
(±15.12)
48.20
(±2.45)
sine 144.76
(±2.86)
1140.52
(±3004.65)
2403.93
(±2824.32)
309.18
(±5.79)
280.51
(±175.61)
151.70
(±2.83)
parabola 98.73
(±3.39)
191.48
(±2.43)
389.65
(±6.34)
417.99
(±6.23)
208.80
(±26.57)
125.29
(±4.02)
spline1 117.66
(±3.04)
508.24
(±152.24)
2864.41
(±14.31)
272.20
(±5.27)
542.85
(±4.47)
142.04
(±3.45)
spline2 147.32
(±3.18)
6563.63
(±3310.81)
3169.80
(±23.61)
258.85
(±26.39)
437.22
(±736.97)
164.94
(±4.45)
address the simulation issue, transfer learning could
be used to bridge the difference between simulated
and real world robotics. For example using domain
randomisation (OpenAI et al., 2018; Tan et al., 2018),
or by learning the gap between the simulation and the
real world (Golemo et al., 2018).
Further care should be taken should this method
be used in the real world, as even though the p-
values and objective functions values are favourable,
the method can have unexpected behaviour because
it is not currently possible to prove the stability of
method due to neural networks being black boxes and
CMA-ES not having a proof of convergence; this can
be mitigated with a supervisor that can replace the
method with a constant gain in unseen states, or by
clipping gain between certain bounds.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents a method of neuroevolution,
which is used to train a neural network to then tune
a controller in real time in order to adapt a robot’s
behaviour to a varying level of precision in the per-
ception. The proposed method has been shown to im-
prove the overall performance in the context of mo-
bile robotics when compared with constant gain mod-
els or reinforcement learning methods. Furthermore,
the proposed method can be used with varying con-
trollers in many different applications, such as nav-
igation in urban landscapes, agricultural application,
or even drones. Many possible variants exist of this
method that could be put in application, such as vari-
ants of the CMA-ES algorithm could be used, or even
the possible variants of the objective function for dif-
ferent tasks. In this paper, first simulation tests have
been achieved to prove the theoretical validity of the
proposed approach, accounting for sensors noises and
low level settling times. Further experimentation with
existing adaptive control algorithms, and experimen-
tation with real world robots are required for future
works, especially with respect to grip conditions.
REFERENCES
Beyer, H.-G. and Schwefel, H.-P. (2002). Evolution
strategies–a comprehensive introduction. Natural
computing, 1(1):3–52.
Carlucho, I., Paula, M. D., Villar, S. A., and Acosta, G. G.
(2017). Incremental q-learning strategy for adaptive
pid control of mobile robots. Expert Systems with Ap-
plications, 80:183 – 199.
Daful, A. G. (2018). Comparative study of pid tuning meth-
ods for processes with large small delay times. In 2018
Advances in Science and Engineering Technology In-
ternational Conferences (ASET), pages 1–7.
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
318

Doicin, B., Popescu, M., and Patrascioiu, C. (2016). Pid
controller optimal tuning. In 2016 8th International
Conference on Electronics, Computers and Artificial
Intelligence (ECAI), pages 1–4.
Ghorbel, F., Fitzmorris, A., and Spong, M. W. (1991). Ro-
bustness of adaptive control of robots: theory and ex-
periment. In Advanced Robot Control, pages 1–29.
Springer.
Golemo, F., Taiga, A. A., Courville, A., and Oudeyer, P.-Y.
(2018). Sim-to-real transfer with neural-augmented
robot simulation. In Billard, A., Dragan, A., Peters,
J., and Morimoto, J., editors, Proceedings of The 2nd
Conference on Robot Learning, volume 87 of Pro-
ceedings of Machine Learning Research, pages 817–
828. PMLR.
Guo, B., Liu, H., Luo, Z., and Chen, W. (2009). Adaptive
pid controller based on bp neural network. 2009 In-
ternational Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
pages 148–150.
Haarnoja, T., Zhou, A., Abbeel, P., and Levine, S. (2018).
Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep
reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor. CoRR,
abs/1801.01290.
Hang, C., Astrom, K., and Wang, Q. (2002). Relay feedback
auto-tuning of process controllers—a tutorial review.
Journal of process control, 12(1):143–162.
Hansen, N. (2016). The CMA evolution strategy: A tutorial.
CoRR, abs/1604.00772.
Hansen, N., Auger, A., Ros, R., Finck, S., and Po
ˇ
s
´
ık, P.
(2010). Comparing results of 31 algorithms from
the black-box optimization benchmarking bbob-2009.
In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference Com-
panion on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation,
GECCO ’10, pages 1689–1696, New York, NY, USA.
ACM.
Hill, A., Raffin, A., Ernestus, M., Traore, R., Dhariwal,
P., Hesse, C., Klimov, O., Nichol, A., Plappert, M.,
Radford, A., Schulman, J., Sidor, S., and Wu, Y.
(2018). Stable baselines. https://github.com/hill-a/
stable-baselines.
Ho, W. K., Gan, O., Tay, E. B., and Ang, E. (1996). Per-
formance and gain and phase margins of well-known
pid tuning formulas. IEEE Transactions on Control
Systems Technology, 4(4):473–477.
Hornik, K., Stinchcombe, M., and White, H. (1990). Uni-
versal approximation of an unknown mapping and
its derivatives using multilayer feedforward networks.
Neural Networks, 3(5):551 – 560.
Jalali, L. and Ghafarian, H. (2009). Maintenance of robot’s
equilibrium in a noisy environment with fuzzy con-
troller. In 2009 IEEE International Conference on
Intelligent Computing and Intelligent Systems, vol-
ume 2, pages 761–766.
Jaulin, L. (2015). Mobile Robotics. Mobile Robotics.
Jiang, L., Deng, M., and Inoue, A. (2008). Support vec-
tor machine-based two-wheeled mobile robot motion
control in a noisy environment. Proceedings of the In-
stitution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I: Journal of
Systems and Control Engineering, 222(7):733–743.
Lenain, R., Deremetz, M., Braconnier, J.-B., Thuilot, B.,
and Rousseau, V. (2017). Robust sideslip angles ob-
server for accurate off-road path tracking control. Ad-
vanced Robotics, 31(9):453–467.
Lillicrap, T. P., Hunt, J. J., Pritzel, A., Heess, N., Erez, T.,
Tassa, Y., Silver, D., and Wierstra, D. (2015). Contin-
uous control with deep reinforcement learning. CoRR,
abs/1509.02971.
Marova, K. (2016). Using CMA-ES for tuning coupled
PID controllers within models of combustion engines.
CoRR, abs/1609.06741.
Mnih, V., Badia, A. P., Mirza, M., Graves, A., Lillicrap,
T. P., Harley, T., Silver, D., and Kavukcuoglu, K.
(2016). Asynchronous methods for deep reinforce-
ment learning. CoRR, abs/1602.01783.
OpenAI, Andrychowicz, M., Baker, B., Chociej, M.,
J
´
ozefowicz, R., McGrew, B., Pachocki, J. W., Pa-
chocki, J., Petron, A., Plappert, M., Powell, G., Ray,
A., Schneider, J., Sidor, S., Tobin, J., Welinder, P.,
Weng, L., and Zaremba, W. (2018). Learning dexter-
ous in-hand manipulation. CoRR, abs/1808.00177.
Risi, S. and Togelius, J. (2014). Neuroevolution in
games: State of the art and open challenges. CoRR,
abs/1410.7326.
Salimans, T., Ho, J., Chen, X., Sidor, S., and Sutskever, I.
(2017). Evolution Strategies as a Scalable Alternative
to Reinforcement Learning. ArXiv e-prints.
Schulman, J., Wolski, F., Dhariwal, P., Radford, A., and
Klimov, O. (2017). Proximal policy optimization al-
gorithms. CoRR, abs/1707.06347.
Shu, H., Wang, X., and Huang, Z. (2015). Identification
of multivariate system based on pid neural network.
In 2015 Sixth International Conference on Intelligent
Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), pages
199–202.
Sivananaithaperumal, S. and Baskar, S. (2014). Design
of multivariable fractional order pid controller us-
ing covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy.
Archives of Control Sciences, 24(2):235–251.
Such, F. P., Madhavan, V., Conti, E., Lehman, J., Stanley,
K. O., and Clune, J. (2017). Deep neuroevolution: Ge-
netic algorithms are a competitive alternative for train-
ing deep neural networks for reinforcement learning.
CoRR, abs/1712.06567.
Tan, J., Zhang, T., Coumans, E., Iscen, A., Bai, Y., Hafner,
D., Bohez, S., and Vanhoucke, V. (2018). Sim-to-
real: Learning agile locomotion for quadruped robots.
CoRR, abs/1804.10332.
Tyreus, B. D. and Luyben, W. L. (1992). Tuning pi con-
trollers for integrator/dead time processes. Industrial
& Engineering Chemistry Research, 31(11):2625–
2628.
Wakasa, Y., Kanagawa, S., Tanaka, K., and Nishimura,
Y. (2010). PID Controller Tuning Based on the Co-
variance Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategy. IEEJ
Transactions on Electronics, Information and Sys-
tems, 130:737–742.
Welch, B. L. (1947). The generalization of ‘student’s’ prob-
lem when several different population varlances are
involved. Biometrika, 34(1-2):28–35.
Neuroevolution with CMA-ES for Real-time Gain Tuning of a Car-like Robot Controller
319
