
SATALex: Telecom Domain-specific Sentiment Lexicons for
Egyptian and Gulf Arabic Dialects
Amira Shoukry
and Ahmed Rafea
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, The American University in Cairo (AUC), Cairo, Egypt
Keywords: Arabic Sentiment Analysis, Arabic Sentiment Lexicons, Domain-specific, Egyptian Dialect, Gulf Dialect,
Arabic Opinion Mining.
Abstract: Given the sacristy of the Arabic sentiment lexicon especially for the Egyptian and Gulf dialects, together with
the fact that a word’s sentiment depends mostly on the domain in which it is used, we present SATALex
which is a two-part sentiment lexicon covering the telecom domain for the Egyptian and Gulf Arabic dialects.
The Egyptian sentiment lexicon contains close to 1.5 thousand Egyptian words and compound phrases, while
the Gulf sentiment lexicon contains close to 3.5 thousand Gulf words and compound phrases. The
development of the presented lexicons has taken place iteratively, in each iteration manual annotators
analyzed tweets for the corresponding dialect to try to extract as many domain specific words as possible and
measure their effect on the performance of the classification. The result are lexicons which are more focused
and related to the telecom domain more than any translated or general-purpose sentiment lexicon. To
demonstrate the effectiveness of these built lexicons and how directly they can impact the task of sentiment
analysis, we compared their performance to one of the biggest publicly available sentiment lexicon
(WeightedNileULex) using Semantic Orientation (SO) approach on telecom test datasets; one for each dialect.
The experiments show that using SATALex lexicons improved the results over the publicly available lexicon.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sentiment analysis or opinion mining received
considerable attention during the last decade caused
by the great opinionated web contents coming from
blogs and social network websites like Facebook,
Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, etc... which are among
the primary data generators of this opinionated data.
Sentiment analysis is the task of identifying whether
a piece of text holds a positive or negative opinion,
emotion, and evaluation. In general, sentiment
analysis aims to determine the attitude of a writer with
regards to the specified topic or the overall tonality of
a document (Abbasi et al, 2008). In this study, we are
interested in sentiment classification for the Arabic
language at the sentence level classifying a sentence
whether a blog, review, tweet, etc. as holding an
overall positive, negative or neutral sentiment.
One of the approaches for carrying out sentiment
analysis is the sematic orientation (SO) approach. The
SO approach is an unsupervised approach in which a
sentiment lexicon is created with each word having
its semantic intensity as a number indicating its class.
Then, this lexicon is used to extract all sentiment
words from the sentence and sum up their polarities
to determine if the sentence has an overall positive or
negative sentiment in addition to its intensity whether
they hold strong or weak intensity (Turney, 2002).
However, Arabic publicly available sentiment
lexicons are very limited with most of them focusing
on lexicons for Modern standard Arabic (Abdul-
Mageed and Diab, 2014) (Badaro et al., 2014)
(Mahyouba, Siddiquia, and Dahaba, 2014).
Nevertheless, trying to use any of these lexicons can
adversely affect the sentiment results as the dialectal
Arabic is the primary language commonly used in the
social media with many different variations of the
vocabulary used across dialects. Thus, building a
dialect independent Arabic sentiment lexicon is
considered a major challenge (El Beltagy, 2016).
On the other hand, domain-specific sentiment
lexicons are believed to be important for
computational social science (CSS) as lexical
sentiment is greatly affected by the context (Hamilton
et al, 2016). That is why, domain-specific lexicons
help in social sentiment analysis considering factors
such as demographic variation, community-specific
dialect, or genre (Deng et al., 2014; Hovy, 2015;
Shoukry, A. and Rafea, A.
SATALex: Telecom Domain-specific Sentiment Lexicons for Egyptian and Gulf Arabic Dialects.
DOI: 10.5220/0007950401690176
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2019), pages 169-176
ISBN: 978-989-758-386-5
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
169

Yang and Eisenstein, 2015), without being harmfully
biased towards domain-general contexts.
In this work, the main research objective was to
investigate to what extend using a domain specific
lexicon could improve the performance of a SO
approach classifier for both the Egyptian and the Gulf
dialects. This led to the following research questions:
1-What is the best way to develop the domain specific
lexicon?
2-Would using such lexicon improve the performance
with a statistically significant difference when
compared to using a general sentiment lexicon?
3-Would using such lexicon improve the performance
with a statistically significant difference when
compared to ML approach?
The remaining of the paper shows in more details
our achieved work in building and analyzing
sentiments from the Egyptian and Gulf Arabic
telecom tweets. Section 2 summaries the related work
done in this area, while section 3 explains the process
of developing the presented lexicons. Section 4
describes the experiments conducted to evaluate the
performance of the lexicons against a general
sentiment lexicon, and to compare the performance of
the lexicons with machine learning approaches.
Finally, Section 5 talks about the challenges,
conclusion and future work.
2 RELATED WORK
The SO is an unsupervised approach in which a
sentiment lexicon is created with the semantic
intensity of each word is represented by a number
indicating its class. The two main approaches for
building Arabic sentiment lexicons are: 1) linking an
Arabic sentiment lexicon with an English one, and 2)
applying semi-supervised or supervised learning
techniques on Arabic resources. In this section, we
will present some of the systems used these two
approaches.
Firstly, A Sentiment Lexicon for Standard Arabic
(SLSA) (Eskander and Rambow, 2015) is constructed
by developing an algorithm that links the lexicon of a
Standard Arabic morphological analyzer (AraMorph)
to entries in SentiWordNet with the corresponding
scores in SentiWordNet are propagated to the entries
of the lexicon of the AraMorph to build SLSA. Their
weighted-average F1-score was 68.6%.
Furthermore, (Ibrahim, Abdou and Gheith, 2015)
introduced a large-scale sentiment lexical resource
for MSA and Egyptian dialects called ArSeLEX. The
lexicon is built in two steps: 1) manual step; and 2)
automatic step. The manual step started by
constructing their basic lexicon through collecting
and annotating 5244 sentiment words that have
semantic meaning that is either positive or negative.
For the automatic step, they developed a mechanism
to determine the sentiment polarity of new sentiment
words automatically using some lexical information
such as part-of-speech (POS) tags and synset
aggregation techniques from online Arabic
dictionaries, thesauruses and lexicons like Google
translation API to get Arabic synonyms and
antonyms.
Moreover, (Shoukry and Rafea, 2015) presented a
hybrid approach which combines both the machine
learning approach using support vector machines and
the semantic orientation approach. The authors used
a manually built sentiment lexicon containing 390
negative entries and 262 positive entries. The
proposed approach was applied on Egyptian tweets.
The feature vector of each tweet was of a count vector
of unigrams, bigrams, and trigrams. Features which
are members in the sentiment features list their
frequencies are multiplied by a factor (1/Net_Weight)
to boost up their importance, together with adding a
new feature for the SO score which sums the weights
of all the sentiment words and smiley faces present in
the tweet. They tested their system by annotating
4800 tweets (1600 positive, 1600 negative, 1600
neutral); and their best classification accuracy and
FScore were 80.9% and 80.6%.
On the other hand, (Mahyouba, Siddiquia, and
Dahaba, 2014) developed an Arabic sentiment
lexicon with 7.5K terms exploiting the semantic
relations found in the Arabic WordNet. They started
with a small seed list of positive and negative entries
in the Arabic WordNet, then they adopted a semi-
supervised algorithm to propagate the sentiment
scores. The algorithm’s main task is to search the
words in the seed list to identify the nodes in the
Arabic WordNet, then it iteratively spread the scores
of these words to the neighboring nodes until the
entire network was reached. Each term has a triplet
score containing a positive, negative and neutral
score. They conducted different experiments on
several Arabic sentiment corpora, and they were able
to achieve a 97% classification accuracy.
Moreover, (Abdul-Mageed, and Diab, 2014)
proposed a large-scale multi-genre, multidialectal and
multi-lingual lexical resource consisting of 224,564
entries for subjectivity and sentiment analysis of the
Arabic dialects (SANA). This lexicon is developed
both manually and automatically. For the manual
step, native Arabic speakers have labeled two-word
records from both Penn Arabic Treebank (Maamouri
et al., 2004) and Yahoo Maktoob. For the automatic
WEBIST 2019 - 15th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
170

step, they have adopted two main methods: 1) a
statistical method based on pointwise mutual
information (PMI); and 2) a machine translation
method. For the PMI method, they have calculated
the co-occurrence between a word and its polarity
using two datasets one from the Twitter and another
from the chat genre. While for the machine translation
method, they have used the Google’s translation APIs
to translate all entries from different lexica like
Youtube Lexicon (YT), SentiWordNet (SWN), etc.…
into Arabic, which were then expanded using a
Standard Arabic Morphological Analyzer (SAMA).
Additionally, (ElSahar and El-Beltagy, 2015)
tried to build a multi-domain lexicon for sentiment
analysis in Arabic using large multi-domain datasets
collected from several reviewing Arabic websites
consisting of annotated reviews for products,
restaurants, hotels and movies. The approach they
followed was a semi-supervised approach. They
started by using the feature selection capabilities of
Support Vector Machines to select the set of most
significant unigram and bigram features from the
collected documents that contribute to accuracy of
sentiment classification. For each collected dataset,
the same process was applied to produce the
necessary unigram and bigrams features, which were
then manually reviewed by two Arabic native
speakers to filter any irrelevant or incorrectly labeled
entries. They tested using different test datasets and
their best accuracy was 60.6%
Likewise, NileULex (El-Beltagy, 2016) is a
manually built Arabic sentiment lexicon mostly in
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) and Egyptian, with
a few entries from other dialects, together with some
terms that are transliterations of English words like
(cute) and (like). The lexicon is made up of
different types of entries; single terms, common
idioms, or compound phrases, adding up to 6287
entries which are assigned either positive or negative
polarity with few entries assigned a neutral polarity.
They tested it using two test datasets: 1) Egyptian
dataset of size 683 tweets and their best classification
accuracy and FScore were 73.56% and 73.3%; 2)
Saudi dataset of size 1414 tweets and their best
classification accuracy and FScore were 79.02% and
79.0%.
More recently, (El-Beltagy, 2017) introduced a
WeightedNileULex lexicon which builds on
NileULex. The scoring mechanism they have
followed to assign strength scores for each positive
and negative lexicon entry in the constructed lexicon
consisted mainly of three steps: 1) Data collection; 2)
Collecting term statistics; and 3) Term Scoring. The
scoring mechanism they have adopted used a lot of
equations with the aim of indicating that “the stronger
a polar term is, the less likely it is to co-occur with
terms of an opposite polarity or in a context that does
not have the same polarity” (El-Beltagy, 2017). They
tested using different test datasets of different sizes,
but their best accuracy and FScore measures were
80.3% and 80.4%.
Finally, (Mohab and El-Beltagy, 2018) introduced
MoArLex lexicon with the aim of building a large-
scale Arabic lexicon for use in social media. They
used the NileULex lexicon as a seed or a base for
generating new sentiment terms. For the automatic
step, they used word embeddings to generate
candidate terms to be added to the lexicon, which are
then filtered, and the polarity of the remaining terms
was determined by sharing the same polarity as the
seed that generated that term. They tested it using a
test data of size 1824 tweets, and their classification
accuracy was 58%.
3 METHODOLOGY
The main goal of this work is to build a rich Arabic;
Egyptian and Gulf domain-specific sentiment
lexicons for use in the sentiment analysis tasks of the
telecom community. To accomplish this goal, our
research work has been targeting three main areas: 1)
generation of the lexicons; 2) comparison with a
general sentiment lexicon; and 3) comparison with
ML approaches. Each of these areas is detailed in the
following subsections.
3.1 Domain Specific Lexicons
The process of building the lexicons has taken place
over the past year. The process was mainly iterative,
where in each iteration manual annotators try to
extract as many sentiment words as possible, then
measure the effect of these extracted words on the
performance of the test dataset classification. Also,
re-validations and revisions usually take place to
ensure that terms in the lexicons are of high quality,
more domain- specific with no ambiguity. For
example, the term “” (best) was indicated as a
positive term.
However, it is sometimes used by
people to complain that they remained on hold for
long time (negative), to express that something is
super amazing (positive), or that they prefer
something (neutral). So, to eliminate this
ambiguity in the
current version of the lexicon, this
term has been removed.
Whereas, some compound
terms and phrases that uses this term like “”
SATALex: Telecom Domain-specific Sentiment Lexicons for Egyptian and Gulf Arabic Dialects
171

(best company), were
collected and added, each with
its corresponding polarity.
After each iteration, we conducted an experiment
to measure the performance of the lexicons for
classifying the tweets. Then, we checked the tweets
that were erroneously classified in the training and the
development dataset. It turned out that there were two
major reasons for misclassification: 1) there were
some sentiment words still not recognized in the
tweets; 2) some of the sentiment words in the list
implied wrong sentiment as they are more of a
domain specific words, not sentiment general words.
We worked on capturing as many of these missed
sentiment words in order to make our lexicon as
comprehensive as possible. Also, we tried to identify
as many of the sentiment words that caused
misclassification of the tweets to improve the
performance of each classifier. An example from
these words is (), it usually implies ungrateful
(negative), but in the telecom-domain it is used more
to express that something is super amazing (positive),
so it resulted in many of the positive tweets being
classified as negative.
Following (El-Beltagy, 2017) approach for
assigning scores to the lexicon terms, we adopted its
equations for scoring our built Egyptian and Gulf
sentiment lists. The main hypothesis behind the
presented scoring method is that the stronger a polar
term is, the more likely it is to co-occur with terms of
the same polarity or in a context that does have the
same polarity. Three steps were carried out for
assigning strength scores to lexicon terms. In the first
step, an initial score was calculated for each term
indicating the likelihood of this term being positive or
negative based on its polarity contexts. In the second
step, the weights are re-adjusted, taking the initial
calculations into consideration. In the third step,
terms that have not occurred at all in the corpus or
have score less than 0.2 are assigned a default value
based on their given polarity.
3.2 Comparison against a General
Sentiment Lexicon
We have been searching for a general lexicon that is
publicly available, as comprehensive as possible, and
from the same date range as our lexicon. These
constraints directed us to work with the
WeightedNileULex general sentiment lexicon.
Besides, as mentioned by the authors, 45% of the
terms in the lexicon are in the Egyptian dialect and
55% of the terms are in the Modern Standard Arabic.
So, we believed this lexicon will help in minimizing
the dialect effect in the sentiment terms extraction
process. Also, the lexicon terms’ distribution is so
close to our lexicons’ terms’ distribution with the
negative terms and negative compound terms being
more dominant than the positive terms and positive
compound terms. Finally, we have followed their
scoring approach when it comes to assigning scores
to our lexicons’ terms, so the sentiment terms’ scores
are on the same scale.
Moreover, based on the approach proposed by
(El-Beltagy et al, 2018) for lexicon extension by word
embedding, we have adopted the AraVec model to get
the most similar term to the ones in the lexicons. So,
for the 1322 terms in the Egyptian lexicon, only 769
terms were found in the model, and after manually
cleaning and checking the uniqueness of these terms,
only 522 terms (444 negative and 78 positive) were
remained, thus the resulting Egyptian lexicon
contained 1844 (1322 + 522) terms. As for the 3369
terms in the Gulf lexicon, only 1859 terms were found
in the model, and after cleaning and checking the
uniqueness of these terms, only 996 terms (788
negative and 208 positive) were remained, thus the
resulting Gulf lexicon contained 4365 (3369 + 996)
terms.
3.3 Comparison against ML
It was important to compare the performance of the
different machine learning approaches to our built
lexicons. Based on the literature, Support Vector
Machines (SVM), Naïve Bayes (NB) and Random
Forest Trees (RFT) are the ones used mostly in
sentiment analysis. Since we are dealing with a multi-
class text classification problem, usually there are
some decisions need to be made for each of the ML
classifier. Firstly, for the SVM classifier, we studied
the different kernels, and we chose to work with RBF
kernel since it is relatively easy to calibrate, as
opposed to other. Moreover, for the NB classifier, we
tried the different models like Gaussian, Multinomial,
Bernoulli, etc.… and the Multinomial model
produced the best result. Finally, for the RFT, we
tried different numbers of forest trees and number
1000 trees produced the highest results.
Three sets of experiments were carried out for
each chosen ML approach with different set of
features used for tweets’ representation. In, the first
set of experiments, test tweets are represented using
the bag of words model, with unigram presence is
used in representing the tweet vector. So, the feature
vector for each tweet is represented as shown:
(word1:0, word2: 1, word3: 0 …, “polarity”)
While, in the second set of experiments, we
proposed a hybrid approach combining both the ML
WEBIST 2019 - 15th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
172

approaches and our built semantic lexicons. This
approach involves building a classifier using the
sentiment words in the lexicon as features to represent
each tweet in the data set. If any of the sentiment
words are present in the tweet, it is marked as present
(1) otherwise it is set to be absent (0). So, the feature
vector for each tweet is represented as shown:
(senti_word1:0, senti_word2: 1, …, “polarity”)
The third set of experiments, we added negation
words to our proposed hybrid approach. In case the
tweet has sentiment words, negation words are
considered, otherwise negation words are ignored.
So, the feature vector for each tweet is represented as
shown: (neg_word1:1, senti_word2: 1, …, “polarity”)
4 EVALUATION
Following our proposed methodologies, we have
carried out different experiments to compare the
performance of both methodologies and discuss the
results obtained in each methodology. In this section,
we present the details of the built domain specific
lexicons for each dialect; the datasets used and their
distributions; and finally, the experiments conducted
with their results.
4.1 The Built Domain Specific Lexicons
The resulting lexicons are: 1) Egyptian lexicon
consists of a total of 1322 unique terms (94 positive
single terms, 24 compound positives, 940 negative
single terms, 264 compound negative) ; 2 ) Gulf
lexicon consists of a total of 3369 unique terms (291
positive single terms, 115 compound positives, 2286
negative single terms, 677 compound negative) .
Some terms that are English transliterations are also
included in the lexicon, like (over) and
(down). These have been included since they are
commonly used in social media telecom domains. It
is obvious that the negative terms and negative
compound terms are more dominant in the two
lexicons than the positive terms and positive
compound terms, this results from the nature of the
telecom community itself in which people usually
complain or criticize on social media more than they
praise or compliment.
4.2 The Used Datasets
All the datasets used were collected by an Egyptian
Company named RDI
1
who thankfully gave us these
1
http://www.rdi-eg.com/
datasets for research purposes, and they are all on the
telecom domain. These datasets were annotated by
the same company where rules for the annotation
were set, and we revisited some of their annotations
to check and fix any mis-annotation took place. The
Egyptian train dataset consists of 8101 labeled
tweets: 183 positive, 2597 negative, and 5321 neutral,
while the Gulf train dataset consists of 21320 labeled
tweets: 437 positive, 6754 negative, and 14129
neutral. The Egyptian test dataset consist of 2692
labeled tweets: 77 positive, 943 negative, and 1672
neutral, while the Gulf test dataset consists of 7098
labeled tweets: 223 positive, 2262 negative, and 4613
neutral. Given the unstructured and the noisy nature
of the used datasets, we have followed the approach
proposed in (Shoukry and Rafea, 2012) for
preprocessing, except that we didn’t apply the
stemmer, since its rules and built lists need to be
revised and updated. So, only normalization and stop
words removal were applied for preprocessing.
4.3 Experiments and Results
The built lexicons were used in two main
experiments. The first experiment was to compare
against a general sentiment lexicon. While, the
second experiment was to compare against the
machine learning approaches using the same datasets
for training and testing.
4.3.1 SATALex vs. Sentiment Lexicon
Based on the methodology discussed in section 3.2,
we wanted to evaluate the performance of the built
SATALex lexicons in contrast to WeightedNileULex
lexicon. We started by assessing the two lexicons
against the same test datasets, then we combined the
two lexicons to examine how an aggregate of both
would affect the results, and finally we applied the
word embedding technique on SATALex lexicons to
expand the lexicons and evaluated the quality of these
added terms on the performance of the SO classifier.
Table 1: Test Results on the Egyptian Dialect.
Test Data
Acc
(%)
Pre
(%)
Rec
(%)
FScore
(%)
SATALex
87.3
72.6
82.3
75.8
WeightedNileULex
74.6
50.0
59.0
47.8
Combined
80.7
58.4
77.9
60.1
ExpSATALex
86.6
70.5
81.4
74.3
SATALex: Telecom Domain-specific Sentiment Lexicons for Egyptian and Gulf Arabic Dialects
173
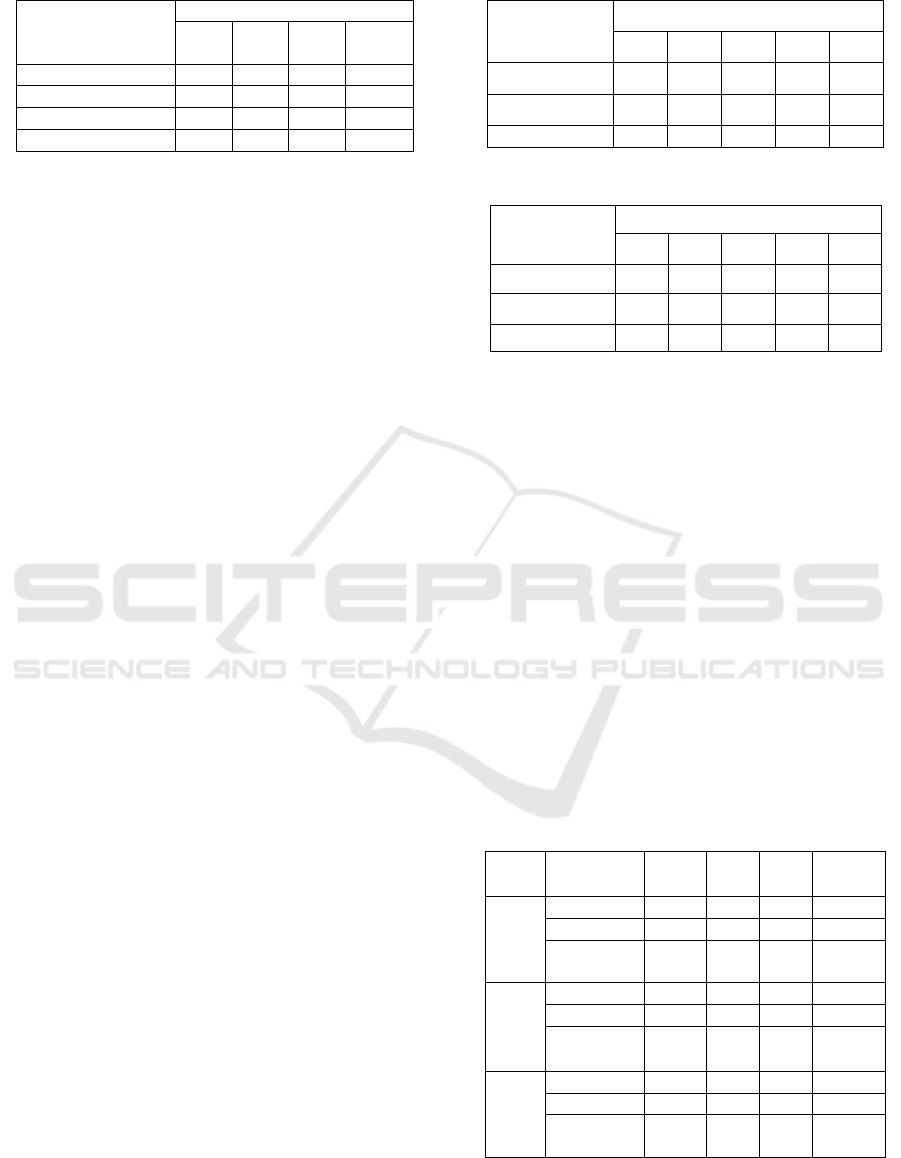
Table 2: Test Results on the Gulf Dialect.
Test Data
Acc
(%)
Pre
(%)
Rec
(%)
FScore
(%)
SATALex
86.8
69.6
80.3
73.5
WeightedNileULex
72.0
49.6
55.5
44.5
Combined
77.2
56.3
74.6
55.6
ExpSATALex
85.0
64.4
79.6
68.6
Tables 1 and 2 show the results obtained after running
the SO classifier using SATALex,
WeightedNileULex, combining both lexicons, and
finally after expanding SATALex lexicons.
From the results, using SATALex for both dialects
has the highest classification accuracy, precision, recall
and FScore with a notable increase when compared to
WeightedNileULex or even when combining them
together. SATALex was able to capture most of the
domain related sentiment words with their
corresponding correct polarity, whereas
WeightedNileULex’s result shows that there are some
sentiment words were not recognized and from the
recognized sentiment words they could have opposite
polarities.
As for the expanded SATALex lexicons after
applying word embedding for Egyptian and Gulf
dialects, the results show that there is a drop in the
accuracy measure by 0.7% for the Egyptian dialect,
and 1.8% for the Gulf dialect. Same for the other
performance measures which decreased by 1-2% for
the Egyptian dialect, while for the Gulf dialect they
decreased by 1-5% in all three measures. By checking
the new terms, we found that some of the added
sentiment words in the list are not necessary domain
specific sentiment words, but general sentiment words.
This resulted in many tweets being wrongly classified.
For example, the negative sentiment word “”
(fake), should have been considered as positive
sentiment word as in telecom domain it usually means
super nice. Also, we found that some sentiment terms
like “” (problem) were added to the list, however
these words are mostly used in neutral tweets for
general questions or commercial tweets, so they need
to be removed.
Moreover, we calculated the statistical significance
of the proposed lexicons. So, for each dialect, we
divided the test datasets into 5 sets and calculated the
FScore for each set. The results are shown in tables 3
and 4.
Table 3: FScores for Egyptian Test Set.
FScore (%)
Set 1
Set 2
Set 3
Set 4
Set 5
SATALex
82.6
72.8
77.1
72.8
72.7
Combined
68.2
59.5
58.4
59.0
55.2
ExpSATALex
79.3
72.2
76.6
70.2
72.0
Table 4: FScores for Gulf Test Set.
FScore (%)
Set 1
Set 2
Set 3
Set 4
Set 5
SATALex
76.6
70.0
63.4
81.8
77.4
Combined
59.5
54.4
53.6
55.4
55.0
ExpSATALex
71.9
66.1
58.9
75.2
72.0
Then, we applied the T-Test between SATALex and
Combined Lexicon; and between SATALex and
Extended SATALex for each dialect using these
FScore values. The value of alpha was set to 0.05. For
the Egyptian dialect, the p-values were 0.001 and
0.572. while for the Gulf dialect, the p-values were
0.001 and 0.282. For both dialects, the difference is
significant between SATALex and combined lexicon
since the results are less than value of alpha.
However, the difference is not significant between
SATALex and Extended SATALex as the results are
more than value of alpha.
4.3.2 SATALex vs. ML Approaches
According to the methodology discussed in section
3.3, we have carried out three experiments for each
ML classifier. Each experiment utilizes different set
of features for tweets’ representation.
Table 5: ML Test Results for the Egyptian Dialect.
ML
Features
Acc
(%)
Pre
(%)
Rec
(%)
FScore
(%)
SVM
Unigrams
62.11
20.7
33.3
25.7
Sentiment
79.83
82.7
55.0
57.3
Sentiment
+Negation
79.64
75.7
52.7
54.0
NB
Unigrams
56.20
34.3
35.7
13.0
Sentiment
64.00
54.3
41.7
35.3
Sentiment
+Negation
64.15
52.7
41.3
35.7
RFT
Unigrams
61.78
47.3
35.0
30.7
Sentiment
78.08
78.0
56.7
61.3
Sentiment
+Negation
77.97
73.0
56.7
60.3
WEBIST 2019 - 15th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
174
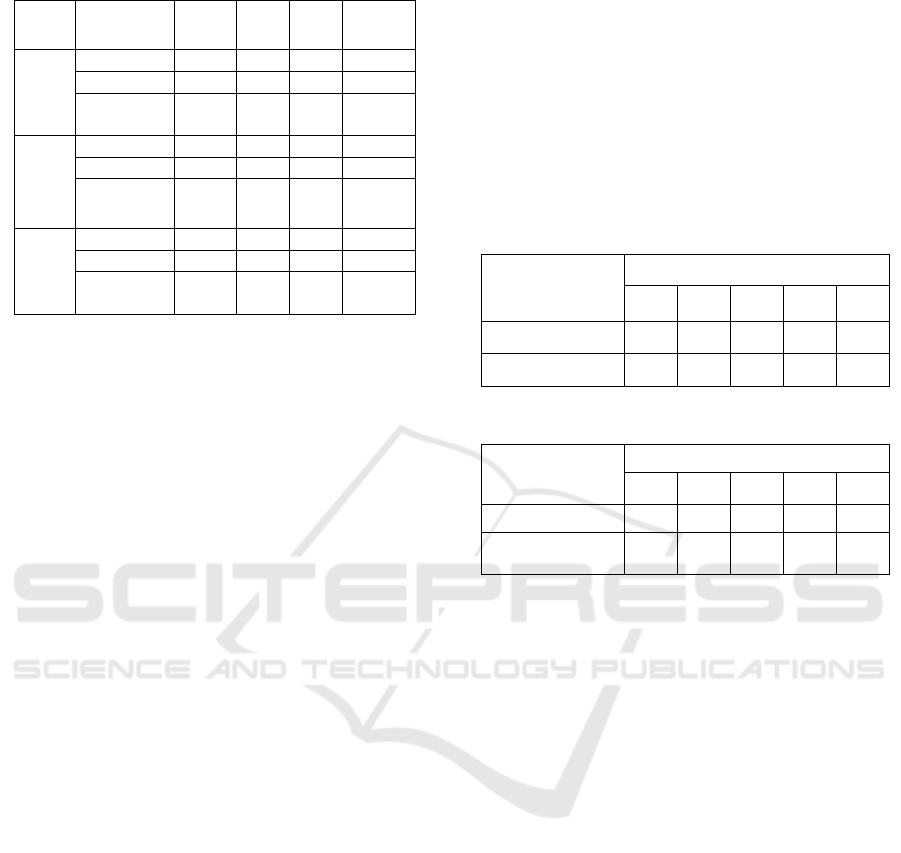
Table 6: ML Test Results for the Gulf Dialect.
ML
Features
Acc
(%)
Pre
(%)
Rec
(%)
FScore
(%)
SVM
Unigrams
65.02
59.3
33.3
26.0
Sentiment
77.80
77.7
54.3
57.3
Sentiment
+Negation
77.71
78.7
54.7
58.0
NB
Unigrams
54.66
35.7
36.7
35.3
Sentiment
68.89
51.7
41.7
40.0
Sentiment
+Negation
69.23
49.0
42.0
38.3
RFT
Unigrams
63.27
44.7
36.7
35.7
Sentiment
77.11
71.0
55.7
59.7
Sentiment
+Negation
77.64
72.3
56.3
60.3
Tables 5 and 6 show the results of running the
different ML classifiers using unigrams, sentiment
words, and mix of negation and sentiment words as
features. The same training and test datasets were
used, together with the decisions taken in section 3.3.
The results show that both SVM and RFT
produced the best results. However, if we compared
the results of all ML classifiers to the results obtained
by SO using SATALex lexicons, it is obvious that
SATALex improves over the ML experiments in all
the performance measures. So, for example in the
unigrams experiments, accuracy improved by around
20% for both dialects, while for the other
performance measures it improved by 40-50% for
both dialects. Also, for the sentiment words and the
mix of sentiment words and negation words
experiments, accuracy improved by around 7-9% for
both dialects, while for the other measures it
improved by around 15% for both dialects.
Comparing the ML results obtained, we can see
that using sentiment words in tweets’ representation
showed significant improvements compared to the
unigrams experiment in terms of the accuracy,
precision, recall and FScore. That is mainly due to the
benefits taken from each approach: 1) the ML
approach associates the combination of specific
sentiment words to specific class; and 2) the SO
approach helps to identify these sentiment words. For
example, in the tweet:
Orange_Egypt
The negative sentiment words present like “”,
and “ were used to represent the tweet. Therefore,
the combination of these features will be interpreted
to correspond to negative class.
On the other hand, if we checked the results of
using negation words combined with sentiment
words, it doesn’t necessary improve the results as in
the case of the Egyptian dialect we can see that the
performance measures decreased.
Moreover, we calculated the statistical
significance of the proposed lexicons against the ML
approach that produced the best results for each
dialect. For the Egyptian dialect, we chose the ML
using only sentiment words, while for the Gulf
dialect, we chose the ML using sentiment and
negation words. Then, we used the same 5 test
datasets and calculated the FScore for each test set
using RFT classifiers. The results are shown in tables
7 and 8.
Table 7: FScores of ML for the Egyptian Dialect.
FScore (%)
Set 1
Set 2
Set 3
Set 4
Set 5
SATALex
82.6
72.8
77.1
72.8
72.7
SentimentWords
72.7
54.3
57.7
65.0
56.0
Table 8: FScores of ML for the Gulf Dialect.
FScore (%)
Set 1
Set 2
Set 3
Set 4
Set 5
SATALex
76.6
70.0
63.4
81.8
77.4
SentimentWords
+ Negation
62.3
63.3
52.0
68.7
61.3
Then for each dialect, we applied the T-Test between
SATALex results and their corresponding results of
RFT approach. The value of alpha was set to 0.05. For
the Egyptian dialect, the p-value was found to be
6.21E-03 when SATALex was compared against ML.
While for the Gulf dialect, the p-value was found to
be 1.93E-02 when SATALex was compared against
ML. For both dialects, the p-values are less than value
of alpha, which means that the difference is
significant.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has presented SATALex, a phrase and
word level sentiment lexicon for Egyptian and Gulf
Arabic Dialects. Through a series of experiments, the
presented work has shown the potential of SATALex
in enhancing the results of sentiment analysis.
Although the generated lexicons are not very large,
when compared to other general sentiment lexicon,
SATALex has proven to produce the best accuracy of
87.3% and FScore of 75.8% for the Egyptian dialect;
whereas accuracy of 86.8% and FScore of 73.5% for
the Gulf dialect. These percentages are also among
the top ones in the literature, reflecting the importance
of having a domain-specific lexicon for each domain.
SATALex: Telecom Domain-specific Sentiment Lexicons for Egyptian and Gulf Arabic Dialects
175

For future work, we will continue in this line of
research to improve our SATALex lexicons. One of
the directions will be building word vectors
representation from a domain specific corpus to
enhance our lexicons and get more domain-related
sentiment words. Integrate the SO approach with ML
approach by engineering the features used by ML
approaches and measure the effect of these features
on sentiment analysis performance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank ITIDA for
sponsoring the project entitled "Sentiment Analysis
Tool for Arabic", and the Egyptian industrial
company RDI for collecting and annotating tweets.
REFERENCES
Abbasi, A., Chen, H. and Salem, A., “Sentiment Analysis in
Multiple Languages: Feature selection for opinion
classification in Web forums,” ACM Transactions on
Information Systems (TOIS), v. 26, no. 3, pp. 12, 2008.
Abdul-Mageed, Muhammad, and Mona T. Diab. "SANA: A
Large Scale Multi-Genre, Multi-Dialect Lexicon for
Arabic Subjectivity and Sentiment Analysis."
Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on
Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’14). pp.
1162–1169 (2014).
Badaro, G., R. Baly, H. Hajj, N. Habash, and W. El-Hajj.
2014. “A Large Scale Arabic Sentiment Lexicon for
Arabic Opinion Mining.” Pp. 165–73 in Proceedings of
the EMNLP Workshop on Arabic Natural Language
Processing (ANLP). Association for Computational
Linguistics.
El-Beltagy, Samhaa R. 2016. “NileULex: A Phrase and
Word Level Sentiment Lexicon for Egyptian and Modern
Standard Arabic.” to appear in proceedings of LREC
2016. Portorož , Slovenia.
El-Beltagy, Samhaa R. 2017. “WeightedNileULex: A Scored
Arabic Sentiment Lexicon for Improved Sentiment
Analysis.” Book Series on Language Processing, Pattern
Recognition and Intelligent Systems: Special Issue on
Computational Linguistics, Speech & Image Processing
for Arabic Language, Publisher: World Scientific
Publishing Co, Editors: Neamat El Gayar, Ching Suen.
El-Beltagy, Samhaa R., Khalil, Talaat, Halaby, Amal, and
Hammad, Muhammad. 2018 “Combining Lexical
Features and a Supervised Learning Approach for Arabic
Sentiment Analysis:. In: Gelbukh A. (eds) Computational
Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing. CICLing.
Deng, Lingjia, and Janyce Wiebe. “Sentiment Propagation
via Implicature Constraints.” Proceedings of the 14th
Conference of the European Chapter of the Association
for Computational Linguistics, 2014,
doi:10.3115/v1/e14-1040.
ElSahar, Hady, and El-Beltagy, Samhaa R.. 2015. "Building
Large Arabic Multi-domain Resources for Sentiment
Analysis." CICLing (2).
Eskander, Ramy, and Owen Rambow. 2015. “SLSA: A
Sentiment Lexicon for Standard Arabic.” Proceedings of
the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural
Language Processing (September):2545–50.
Hamilton, William L., et al. “Inducing Domain-Specific
Sentiment Lexicons from Unlabeled Corpora.”
Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical
Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2016,
doi:10.18653/v1/d16-1057.
Hovy, Dirk. “Demographic Factors Improve Classification
Performance.” Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting
of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the
7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language
Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), 2015,
doi:10.3115/v1/p15-1073.
Ibrahim, Hossam S., Sherif M. Abdou, and Mervat Gheith.
2015. “Automatic expandable large-scale sentiment
lexicon of Modern Standard Arabic and Colloquial.” Pp.
94-99 in Proceedings of the 16th International
Conference on Intelligent Text Processing and
Computational Linguistics (CICLING). Cairo-Egypt
Maamouri, Mohamed, Bies, Ann, Buckwalter, Tim, and
Mekki, Wigdan. (2004). “The penn arabic treebank:
Building a largescale annotated arabic corpus”. In
NEMLAR Conference on Arabic Language Resources
and Tools, pages 102–109.
Mahyouba, Fawaz H. H., Muazzam A. Siddiquia, and
Mohamed Y. Dahaba. 2014. “Building an Arabic
Sentiment Lexicon Using Semi-Supervised Learning.”
Journal of King Saud University - Computer and
Information Sciences 26(4):417–24.
Shoukry, Amira, Rafea, Ahmed. 2015. “A Hybrid Approach
for Sentiment Classification of Egyptian Dialect
Tweets”. In First International Conference on Arabic
Computational Linguistics (ACLing). pp. 78–85, Cairo,
Egypt.
Shoukry, Amira, Rafea, Ahmed. 2012. “Preprocessing
Egyptian Dialect Tweets for Sentiment Mining”. In
Proceedings of the fourth workshop on Computational
Approaches to Arabic Script-Based Languages. pp. 47–
56, San Diego, California, USA.
Turney, P. “Thumbs up or thumbs down?: semantic
orientation applied to unsupervised classification of
reviews”. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on
Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL ’02,
pages 417–424, Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2002.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Yang, Yi and Jacob Eisenstein. “Putting Things in Context:
Community-specific Embedding Projections for
Sentiment Analysis.” CoRR abs/1511.06052 (2015)
Youssef, Mohab, and Samhaa R. El-Beltagy. “MoArLex: An
Arabic Sentiment Lexicon Built Through Automatic
Lexicon Expansion.” Procedia Computer Science, vol.
142, 2018, pp. 94–103.,
doi:10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.464.
WEBIST 2019 - 15th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
176
