State Observability through Prior Knowledge:
A Conceptional Paradigm in Inertial Sensing
Tom L. Koller
a
, Tim Laue
b
and Udo Frese
c
Multi-Sensoric Systems, University of Bremen, Enrique-Schmidt-Str. 5, Bremen, Germany
Keywords:
State Estimation, Kalman Filter, Prior Knowledge, Inertial Navigation System (INS), State Observability.
Abstract:
Inertial Navigation Systems suffer from unbounded errors on the position and orientation estimate. Extero-
ceptive sensors may not always be available to correct the error. Applications in the literature overcome this
problem by fusing IMU data with prior knowledge in an ad-hoc fashion. In different applications, various
knowledge is available, which allows to correct the erroneous state estimate. In this position paper, we argue
that the fusion of knowledge and inertial sensor data should be viewed as a paradigm and that the observability
of systems with prior knowledge should be analysed theoretically. With a theoretical foundation, application
design will be simplified and verifiable. We show methods to start the analysis and give a first proof with
practical insight.
1 INTRODUCTION
Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) perform dead reck-
oning on the measurements of Inertial Measurement
Units (IMU). This way, the state of an object, consist-
ing of position, orientation and velocity, is estimated.
Dead reckoning has the major disadvantage that the
estimate’s error increases over time. This drift, e.g. a
position error of 1.5 m after only 5 s of dead reckon-
ing (Wenk, 2017, Figure 3.7), is caused by accumu-
lating the measurement errors of the IMU. To correct
the drift, IMU measurements are often fused with ex-
teroceptive position sensors, for example the GPS.
Given this drift, it seems necessary to have an ex-
teroceptive sensor. However, in fact drift-free esti-
mates can be obtained from IMU measurements alone
if appropriate scenario knowledge is exploited. This
surprising realisation motivates our position paper.
There already exist several works that success-
fully demonstrate the usefulness of prior knowledge
in state estimation. The pose (position and orienta-
tion) of humans walking in buildings can be tracked
using prior knowledge instead of exteroceptive sen-
sors (Harle, 2013; Beauregard et al., 2008; Woodman
and Harle, 2008). The estimate errors of the pose are
bounded, which means that the estimates are drift-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6629-1566
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2845-1300
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8325-6324
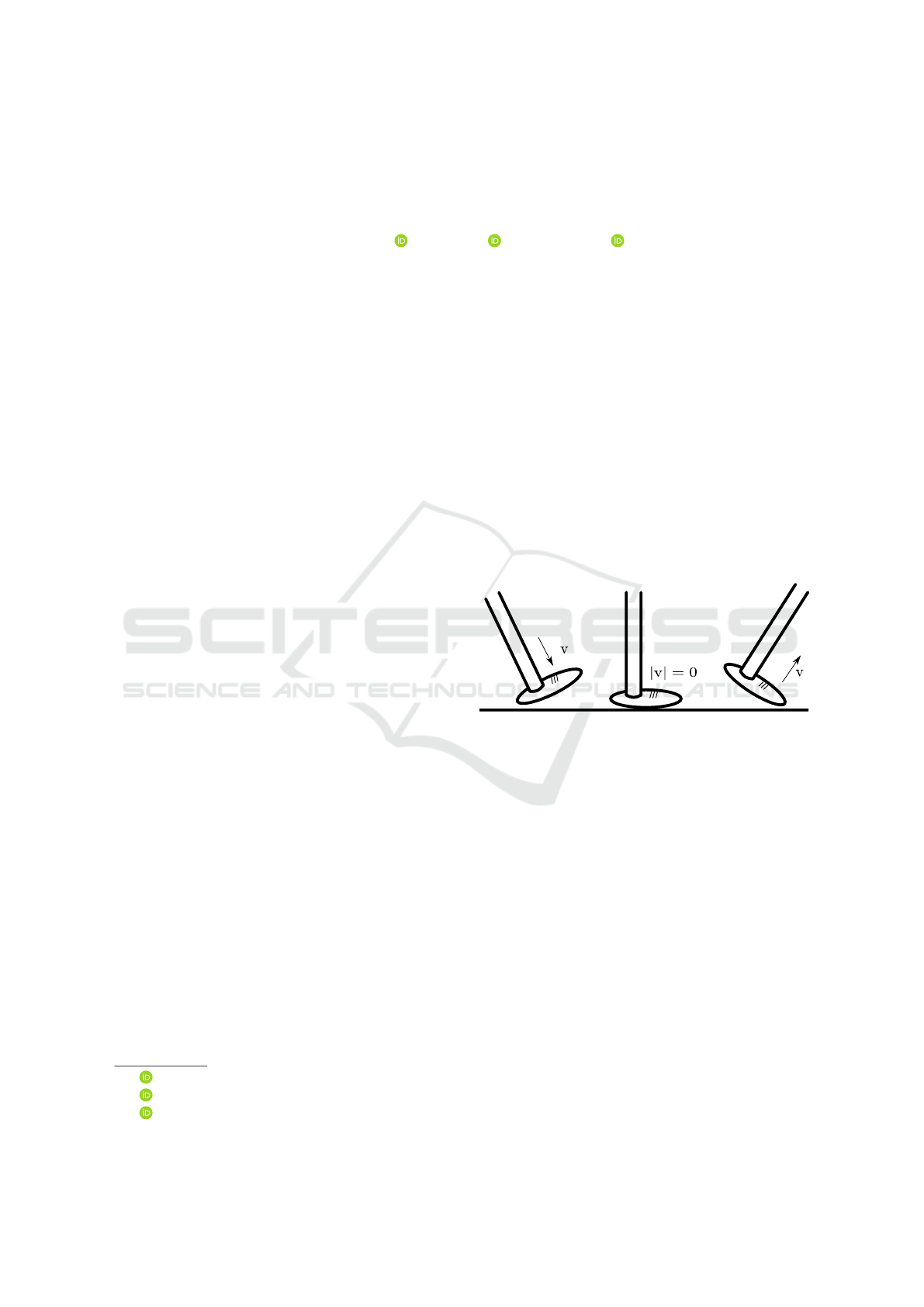
Figure 1: The foot has 0 velocity when it stands on ground.
free. Intuitively, we define that as observability, and
we will further refer to states that can be estimated
with bounded errors as observable.
The indoor tracking works achieve state observ-
ability through prior knowledge about human motion.
While walking, the feet periodically touch the ground,
wherefore they have 0 velocity at one moment (see
Fig 1). Updating the velocity with this information is
called a Zero-Velocity-Update (ZUPT) and makes the
velocity observable (Foxlin, 2005).
The ZUPTs are used to estimate step lengths,
which are fed to a Particle Filter (PF) as the dynamic
update. The PF models the knowledge that humans
can not pass through walls by removing particles that
cross walls. The used prior knowledge makes the
pose observable and even enables localization with-
out knowing the starting pose (Woodman and Harle,
2008). More surprisingly, the use of the prior knowl-
edge enables to map buildings, using an IMU as the
only sensor (Angermann and Robertson, 2012).
Koller, T., Laue, T. and Frese, U.
State Observability through Prior Knowledge: A Conceptional Paradigm in Inertial Sensing.
DOI: 10.5220/0007952307810788
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2019), pages 781-788
ISBN: 978-989-758-380-3
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
781
Several other works achieve state observability by
combining IMU data with knowledge. Dissanayake
et al. (2001) uses the knowledge, that a wheeled vehi-
cle only moves in forward direction. It is shown that
velocity and inclination are observable if the vehicle
drives a curve. In attitude estimation, several works
use the gravity vector to observe roll and pitch (Va-
ganay et al., 1993; Rehbinder and Hu, 2004; Sabatini,
2006). Wenk (2017, Sec. 3.9) shows that this is equiv-
alent to the prior that the acceleration is 0 in average.
The motion suit of Xsens fuses the measurements of
17 IMUs with the knowledge that they are linked
by the human body joints (Roetenberg et al., 2009).
This enables to observe the angles of all body joints
even without a magnetometer (Wenk, 2017, Sec. 4.4).
Applications with exteroceptive sensors incorporate
knowledge to improve the observability of the state
(L
´
opez-Araquistain et al., 2019; Xu et al., 2016; Bat-
tistello et al., 2012).
In most cases, the improvement of the estimate
is shown empirically. Instead, the state observability
can be analysed from a theoretical point of view. The
theoretical analysis has the advantage that it reveals
whether the knowledge reduces the state drift or elim-
inates it. This difference is critical, since a reduced
drift still causes an error on long term measurements.
It can be investigated which knowledge makes
which state observable. This may give further insight
about its use and benefits. More importantly, error
cases may be revealed before an application is tested.
The use of prior knowledge is highly beneficial,
but only understood on a per-case basis. It is mainly
evaluated application specific. Therefore, it misses
theoretical foundation for general applications. So
we argue that fusing prior knowledge with IMU data
should be viewed as a conceptional paradigm and in-
vestigated from a theoretical point of view.
The remainder of the paper is structured as fol-
lows. In Section 2, we explain the gain from under-
standing the paradigm of state observability through
prior knowledge. We will show the structure of prior
knowledge and algorithms to use it. In Section 3, we
will show a method to analyse state observability. We
give an example of its usage in form of a first proof
and show how to design an application in track cy-
cling based on the paradigm. At last, we state the
major research goals of our project in Section 4.
2 EXPLAINING THE NEED FOR
A PARADIGM
In application design regarding sensor fusion, we
want to know whether we can estimate the states we
require. The estimate error of unobservable states
increases over time, whereas the error of observable
states is bounded. Hence, we want to achieve observ-
ability of relevant states.
2.1 State Observability
Position:“If we understand the state observability
through prior knowledge, we can predict the error be-
haviour of the estimate.”
For many applications, prior knowledge that may
lead to observability of the relevant states is avail-
able. State observability analysis reveals whether the
knowledge is sufficient to observe the state.
An example of observability analysis can be seen
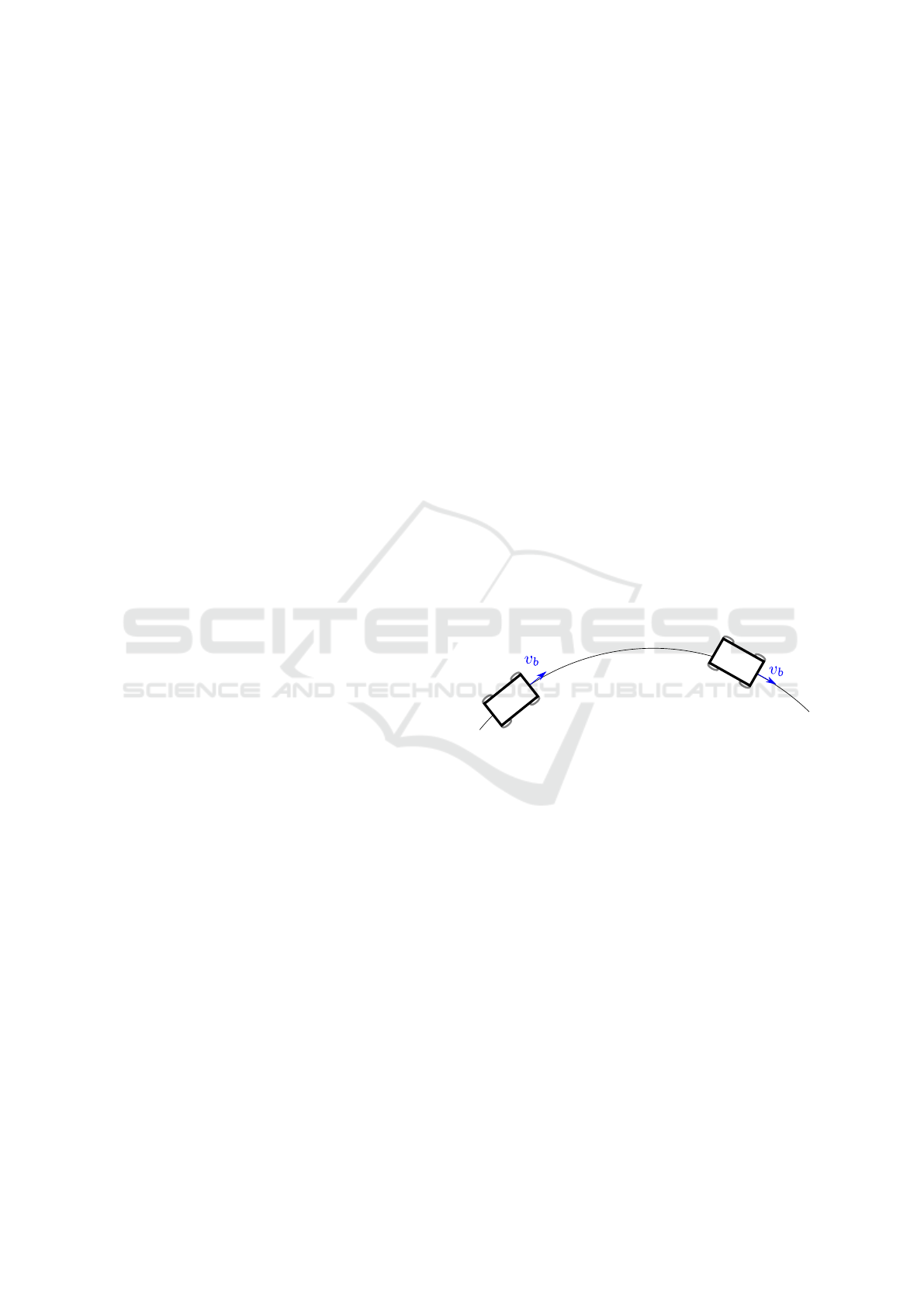
in (Dissanayake et al., 2001). They use the forward
velocity prior (see Figure 2). It states that the wheeled
vehicle only drives forward with no side slip. This can
be modelled by:
~v
b
=
|~v
w
| 0 0
T
(1)
where ~v
b
is the velocity in body coordinates and ~v
w
the velocity in world coordinates. Whenever the vehi-
cle drives a curve around the y or z axis, the forward
velocity is observable. Additionally, the sensor biases
are observable (Rothman et al., 2014).
Figure 2: Forward velocity prior on a wheeled vehicle.
The collected insight enables us to predict the er-
ror behaviour, instead of measuring it. We can predict
that the velocity error is low while driving curves and
high otherwise. The observations of (Dissanayake
et al., 2001) match this prediction.
As shown, the analysis allows to predict the error
behaviour of the state estimate. Hence, we could vali-
date the quality of the state estimate before we test it.
Therefore, we need the analysis of state observability
through prior knowledge.
Position:“Predicting the error behaviour of a state es-
timator is a powerful tool, which points out knowl-
edge that yields state observability.”
The effect of prior knowledge is dependent on the
state configuration. For example, the forward velocity
prior yields observability of the velocity for a vehicle
driving on a curved line (see Figure 2), but not on a
straight line (see Figure 3). Hence, fusing IMU data
with prior knowledge may not yield state observabil-
ity in all state configurations.
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
782

Figure 3: Vehcile driving a straight line. The velocity is not
observable with the forward velocity prior.
The observability analysis reveals the observable
and unobservable state space configurations. A do-
main expert can evaluate how likely the unobservable
configurations occur. The unobservable configura-
tions may be isolated points in the state space, which
are surrounded by observable configurations. Con-
sider a smooth transition between a left and a right
curve. The transition point itself is straight, wherefore
the velocity is unobservable with the forward velocity
prior. However, the velocity can be dead reckoned at
that single point. The accumulated error is negligible.
If the vehicle drives on a straight line during the
whole application, the velocity is unobservable. In
other words, the application takes place in unobserv-
able configurations only. This is the other extreme,
which makes the prior knowledge useless.
When we evaluate how likely unobservable con-
figurations occur in the application, we use additional
prior knowledge about the application. The evalu-
ation reveals which additional prior renders the un-
observable configurations impossible. This prior ei-
ther has to be modelled explicitly, or already makes
the state observable implicitly. In both cases, the ob-
servability analysis points out which assumptions are
needed for state observability.
Overall, the analysis of the observability shows,
whether the application can work. Hence, it can be
used for verification of the system design. This is the
most important part of the paradigm of state observ-
ability through prior knowledge. We have to under-
stand how using knowledge corrects the drift or only
improves the state estimate and when it is useless or
even disruptive. In the end, the better the knowledge
is understood, the greater the benefit is.
2.2 Types of Knowledge
Position:“Prior knowledge is structured in several
groups with different observability characteristics.”
In the literature, we find various types of prior knowl-
edge. Different knowledge constrains different states
of the state vector. Building plans (Beauregard et al.,
2008), vessel routes (Battistello et al., 2012), flight
corridors (Xu et al., 2016) and road maps (L
´
opez-
Araquistain et al., 2019) constrain the position of the
object. ZUPTs (Foxlin, 2005) and the forward veloc-
ity prior (Dissanayake et al., 2001) constrain the ve-
locity. The low acceleration prior (Wenk, 2017) con-
Figure 4: Upper and lower y-position bounds (red). Left is
almost an equality constraint. Right has a minor effect.
strains the acceleration.
In many cases, the knowledge can be modelled as
equality or inequality constraint. Equality constraints
reduce the dimension of the state space and occur
if the state is overparametrized. An example is the
quaternion parametrization of rotations. It uses four
states that are constrained to have norm one, instead
of the three rotation angles.
Inequality constraints reduce the state space, but
not its dimension. They often occur in the form of up-
per or lower bounds on a state. Building maps, as they
are used in PFs (Harle, 2013), are a representation of
complex inequality constraints. They model that the
object’s position does not equal the position of a wall.
Particles that violate the constraint are deleted.
In contrast to equality constraints, inequality con-
straints can have different strength (see Figure 4). The
strength of the constraint affects the observability of
the state. Close bounds are almost an equality con-
straint. However, if the bounds are far apart from each
other, the constraint has a minor effect.
In general, constraints are modelled imperfectly.
They are either simplified or known inexactly. The
imperfection can be grouped into inaccuracy, incom-
pleteness or inconsistency (Podt et al., 2014). An im-
perfect constraint can be modelled as a probability
distribution. However, constraints are often assumed
to model the reality perfectly.
The imperfection of a constraint affects the obser-
vability of the system. Consider the perfect constraint
˙x = 0. x stays at its starting value and is observable.
A similar imperfect constraint ˙x = N (0,σ
2
) allows
accumulating changes of the state. Hence, it does not
yield observability.
Position:“The structure of prior knowledge may be
exploited to proof observability for general systems.”
Knowledge may be grouped by the type of constraint
it imposes on the system. This allows to investigate
the state observability in a general fashion. Differ-
ent equality constraints reduce the dimension of the
state space in a similar manner. Hence, the observ-
ability can be investigated for general state space de-
scriptions, such as 2D- or 3D-systems.
State Observability through Prior Knowledge: A Conceptional Paradigm in Inertial Sensing
783

In the case of INS, the dynamic equations make
the observability of the states dependent. If the po-
sition is observable, the velocity can be derived by
differentiation. There may be other observability re-
lations between the states.
A general view on the types of knowledge enables
a fast observability analysis without proofs for appli-
cations. With rules and proofs for general systems and
types of knowledge, only the structure of the available
knowledge has to be determined. The observability
characteristics can be derived intuitively by analysing
the observability for each knowledge followed by de-
riving the implied observability. This allows to use
concepts based on the paradigm of state observability
through prior knowledge without proofing the observ-
ability mathematically.
Position:“Structural similarities in prior knowledge
may reveal new possible applications.”
Many assumptions can be transferred on other appli-
cations. For example, the forward velocity prior for
vehicles is valid for bikers as well. If observability
of a prior knowledge has been proofed for one appli-
cation, other suitable applications are likely to exist.
The observability proof can be generalized for simi-
lar applications. Hence, the discovery of a prior that
yields observability reveals that similar applications
are possible, which were previously thought to be im-
possible.
2.3 Algorithms for Prior Knowledge
Position:“A better comprehension of the structure of
prior knowledge may enable new algorithms.”
Using constraints algorithmically in state estimation
is already a topic of research and reviewed in (Simon,
2010; Rasool, 2018). Several methods project either
the state estimate, the Kalman gain or the whole sys-
tem on a constrained subspace. On the subspace, the
constraint is guaranteed to hold.
A common approach is the use of constraints as
pseudo measurements (Tahk and Speyer, 1990). The
constraint is handled as a measurement with a con-
stant measurement observation. This allows an easy
integration in all variants of Kalman filters. The ap-
proach can be used with perfect and imperfect con-
straints.
In principle, the algorithms search the most proba-
ble solution. This can be formulated as a least squares
minimization problem. The Moving Horizon Estima-
tor solves the least squares problem for a moving win-
dow on the measurements. It can deal with highly
non-linear systems and constraints.
The algorithms solve the state estimation problem
for different assumptions about the system description
and constraints. The performance of each algorithm
depends on the (non-)linearity of the system and the
constraints, and the type of the constraints. Simon
(2010) proposes a decision chart to choose the algo-
rithm based on these parameters. If we understand
the structure of prior knowledge in greater detail, we
can evaluate the algorithm’s performance with regard
to other parameters. Hence, we may choose a better
algorithm or develop a new one that exploits the pe-
culiarities of the knowledge.
3 OBSERVABILITY ANALYSIS
OF PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
In the Introduction, we defined an observable state as
a state that can be estimated with bounded errors. The
estimate of an observable state, does not drift away
from the true value. This definition is relevant for ap-
plications, because we generally need estimates of the
pose that are always close to the object’s real pose.
For theoretical analysis of prior knowledge, we
will make use of the more formal observability defi-
nitions in (Adamy, 2018) and (Kou et al., 1973) taken
from control theory. Both works assume a system def-
inition as follows:
The system has an unknown state x. The deriva-
tive of the state depends on the known input u and can
be calculated by:
˙x = f (x,u) (2)
with the known function f . The system has an mea-
surable output z defined by:
z = h(x) (3)
with the known function h. State, input and output are
vectors with arbitrary dimension.
Adamy (2018) defines two forms of observability.
The state is strongly observable if it can be derived
from the in- and outputs of one time point, i.e. without
any data from previous or following time points. In
contrast, the state is weakly observable if it can be
derived from the in- and outputs of a time interval. We
will mainly use weak observability, since the strong
one can not be applied on most non-linear systems.
Kou et al. (1973) defines observability similar to
uniqueness. The state is observable if there is only
one trajectory, which starts at the known start state
x
0
= x(t
0
) and fits the out- and inputs since the time
point t
0
. Any ambiguity yields the state unobservable.
We will use this definition to further analyse why a
state is unobservable and to give advice which prior
knowledge would make the state observable.
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
784

The strength of observability can not be expressed
by the notation of observable or unobservable. An-
other notation is shown in (Han and Wang, 2008),
where a Degree of Observability (DoO) is computed
based on the covariance of the state. The continu-
ous DoO takes sensor noise into account. Consider
a wheeled vehicle with the forward velocity prior. If
the gyrometer error is considerably higher than the
rotation axis change of a curve, it dominates the mea-
surement. Hence, a system can be analytically ob-
servable, whereas the real application is not. In that
case, the DoO would show poor observability for the
velocity. It has to be investigated, how the DoO can
be predicted from the system parameters.
The weak observability after (Adamy, 2018) can
be investigated for prior knowledge that can be mod-
elled as an equality constraint. The main approach
is to observe the states by the time derivatives of the
system’s output equation z = h(x). This results in an
observation vector Z(x) of dimension n, where n is
the state’s dimension.
Z(x) =
h(x)
˙
h(x)
.
.
.
(4)
The state is observable if x can be derived from Z(x),
which is possible when Z is left invertible:
x = Z
−1
(Z(x)) (5)
Z is left invertible at x if its Jacobian is full ranked at
x
0
which yields the weak observability criteria:
rank
dZ
dx
(x
0
)
= n (6)
Evaluating the Jacobian at a state configuration x
0
, re-
sults in a local form of the observability. If the system
has an equal form at multiple configurations (see Fig-
ure 5), the correct state can not be determined.
x?
Figure 5: A system with repeating slopes. With the weak
observability criteria only, the correct state is unknown.
3.1 ”Rollercoaster” Observability Proof
We show the application of the observability analysis
in a simple theoretical example. We will proof that
a one dimensional system is weakly observable if the
rotation axis changes. The proof is a first step towards
observability analysis for complex systems.
Consider a rollercoaster. It can only ride on the
track, which defines position and orientation. In other
words, its pose x is a function of the variable λ:
x = f (λ) (7)
All derivatives of the pose, such as the cartesian and
angular velocities, depend on λ and its derivatives:
˙x =
˙
λ · f
0
(λ) (8)
¨x = (
˙
λ)
2
· f
00
(λ) +
¨
λ · f
0
(λ) (9)
˙
λ is the velocity on the track and
¨
λ the acceleration.
Theorem 1: A system which pose x only depends
on the variable λ is weakly observable from gyrome-
ter measurements if the rotation axis of the orientation
is changing.
Proof: We parametrize the orientation q as a quater-
nion. The orientation quaternion only depends on λ.
q = q(λ) (10)
˙q(λ) =
˙
λ
dq
dλ
(11)
dq
dλ
=
1
2
q(λ) ∗ ω(λ) (12)
Where ω(λ) is the angular velocity as a quaternion
with 0 real part
˙q(λ) =
˙
λ ·
1
2
q(λ) ∗ ω(λ) (13)
With the gyrometer we measure z =
˙
λω(λ)
z =
˙
λω(λ) = 2q(λ)
−1
∗
˙
q(λ) (14)
dZ
dx
(λ) =
dz
dλ
dz
d
˙
λ
(15)
Now we proof the full rank of the matrix via linear
independency of the columns:
0
!
= k
1
dz
dλ
+ k
2
dz
d
˙
λ
(16)
= k
1
˙
λ · ω
0
(λ) + k
2
· ω(λ) (17)
Equation 17 shows that if
˙
λ is 0, the Jacobian is
singular. This is the trivial case, where the object does
not move. In this case, no system can be observed
from the gyrometer. The other case is when ω
0
(λ) and
ω(λ) are collinear, meaning that the rotation axis does
not change its direction. Hence, the angular velocity
and acceleration rotating around the same axis is the
only non-trivial unobservable case. This only occurs
at state configurations where there is either no rotation
State Observability through Prior Knowledge: A Conceptional Paradigm in Inertial Sensing
785

or the rotation axis is constant. Therefore, the system
is observable if the rotation axis changes.
The gathered insight supports the intuitive ob-
servability analysis. Observability can be analysed
for the rollercoaster in Figure 6 without any cal-
culations. Between the red lines, the rotation axis
changes, wherefore the segment is observable. The
other segments are unobservable, because the roller-
coaster turns around a constant axis only. One would
expect to observe a transition from a straight part to
a curved part due to the angular velocity change. But
the transition would result in a similar angular rate
signal as starting at 0 velocity on a curve. Thus, it can
not be observed if the velocity can be 0.
Figure 6: Side view (top) and top-down view (bottom) of a
rollercoaster. The dashed red lines mark the segment with
weak observability after Theorem 1.
Theorem 1 reveals local observability conditions
for general 1D systems. Based on this, we assume
that observability analysis can be performed on more
complex general systems. For example, a general-
isation of Theorem 1 for systems of higher dimen-
sion, where the prior knowledge can be modelled as
an equality constraint of the form:
z = f (x, y) (18)
could be applied in sports like track cycling or For-
mula 1. In these sports, the position can be expressed
with two parameters and the orientation with one.
3.2 Track Cycling Design Example
The focus of our research project are theoretical
proofs as in Theorem 1, which give insight about ob-
servability conditions for prior knowledge. Neverthe-
less, we want to show how the gathered insight can
be used in real world scenarios. The forward velocity
prior (Dissanayake et al., 2001) directed us to track
cycling (see Figure 7), which has similar conditions
as the wheeled vehicle. We will argue that the pose
of a track cycler is likely to be observable if available
prior knowledge is fused with IMU data, due to the
track’s shape.
Figure 7: Tracking a biker with an IMU as the only sensor
may be possible with prior knowledge.
At track cycling, bikers run a race on a track. It
is desired to track their velocity and when they drive
in the slipstream of other bikers. To detect whether
a biker drives in the slipstream, the positions of all
bikers are required. The values should be retrieved by
using an IMU at each bike and prior knowledge.
Following the paradigm, we gather knowledge
about the dynamics and constraints of the motion. At
track cycling, both wheels stay on the symmetrical
track. A typical track is shown in Figure 8. The track
is taken counter clockwise. The bikes drive forward
with almost no side slippage, similar to wheeled ve-
hicles. A biker’s speed is limited. Bikers lean into the
curve. We measure the local gravity vector with the
IMU. The starting position of the bikers is known.
With this still incomplete list of knowledge, we try
to analyse the observability of the state. We already
know from (Dissanayake et al., 2001) that the velocity
is observable when we drive a curve with the forward
velocity prior. The bikers follow the track, which con-
tains 2 curves and 2 straight segments. Hence, the
velocity is observable periodically.
Since the wheels of the bike have to be on the
track, the position is constrained and has only 2 DOF.
The height can be calculated from the x and y posi-
tion. We try to use Theorem 1 to make assumptions
about the observability. The theorem states that a 1D
system is observable from gyrometer measurements
alone if the rotation axis changes. At a single round
of track cycling, the biker roughly follows a 1D path
on the track’s 2D surface. In the curves of this path,
the rotation axis changes, which yields observability
after Theorem 1.
At the straight track parts, dead reckoning has to
be performed. In principle, the velocity and position
error will grow unbounded, but only until the biker
drives a curve. Hence, the error growth is practically
bounded, depending on the time the biker drives on
the straight part.
The change of rotation axis can be surely detected,
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
786

Figure 8: The track of the Sixdays Bremen.
but the biker can be in either curve. Thus, if the start-
ing position is unknown, the biker can not be local-
ized uniquely. This ambiguity can be resolved since
the starting position is known. However, the state es-
timator can not recover if it looses the position once.
At long term, roll and pitch are observable due to
the known gravity vector. Since the bikers drive only
counter-clockwise, the yaw can be constrained to fol-
low the path of the track.
The analysis of the state observability shows that
the relevant states, the position and the velocity, can
be expected to have bounded errors if the IMU data is
fused with the knowledge. Therefore, we expect that
the application is possible, which will be evaluated in
a future publication.
The theoretical insight on the prior given by The-
orem 1 and (Dissanayake et al., 2001) revealed the
behaviour of the estimate error. It has to be investi-
gated whether Theorem 1 can be generalized to the
2D case, as it was used in this example, to back up
the approximate argument in this example.
4 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
The concept of fusing IMU data with prior knowledge
is already used in the literature. Surprisingly, various
works report bounded errors on normally unobserv-
able states. Their success shows that prior knowledge
has the potential to make states observable. However,
only a few works provide a theoretical foundation for
the observability.
By analysing the observability of states in appli-
cations with prior knowledge, we can predict the er-
ror behaviour of the state estimate. Thus, applications
can be verified before testing. Possible failure cases
can be predicted from the observability conditions re-
vealed by the analysis.
We have shown suitable methods, taken from the
field of control theory, to analyse the state observ-
ability in applications with equality constraints. We
started to investigate the observability conditions for
simple systems. At a first shot, we found Theorem 1,
which states that a 1D system is observable if its rota-
tion axis changes. The method can be used to validate
the design of applications before testing it.
Prior knowledge is structured into groups with
different observability characteristics. Analysing the
groups will result in a better comprehension of prior
knowledge. The comprehension can point out appli-
cations that were thought to be impossible with IMUs
alone, such as the tracking of bikers at track cycling.
The utility of prior knowledge depends on the re-
quired estimation accuracy, modelling errors and the
sensor noise. This results in different grades of state
observability through prior knowledge. Theoretical
observability alone, can only guarantee bounded er-
rors for precise models of the real world applications.
It has to be investigated how the utility of prior knowl-
edge can be estimated for imperfect conditions.
The paradigm of state observability through prior
knowledge aims at understanding the influence of
prior knowledge on the observability of the state es-
timate. With the investigation of the paradigm, we
expect to simplify the analysis of the state observabil-
ity by proofing observability for structural groups of
prior knowledge. The gained theoretical insight will
result in faster application development and enables
verification of state estimation systems.
In our research project, we focus on the theoretical
foundation of prior knowledge. We will further anal-
yse general system descriptions, such as 2D systems.
We will derive and investigate common structures in
prior knowledge from existing applications to proof
observability in generalized cases. Our results will be
interpreted from an intuitive point of view. This will
allow a wide audience to use our results without exe-
State Observability through Prior Knowledge: A Conceptional Paradigm in Inertial Sensing
787

cuting the analysis themselves.
The theoretical results will be accompanied by ap-
plication examples from the field of sports science.
Since most sports follow a rulebook, various kinds of
prior knowledge can be applied. Player policies can
be used to investigate vague prior knowledge.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This project (ZaVI FR 2620/3-1) is funded by the
German Research Foundation.
REFERENCES
Adamy, J. (2018). Nichtlineare Systeme und Regelungen.
Springer.
Angermann, M. and Robertson, P. (2012). FootSLAM:
Pedestrian simultaneous localization and mapping
without exteroceptive sensors;hitchhiking on human
perception and cognition. Proceedings of the IEEE,
100(Special Centennial Issue):1840–1848.
Battistello, G., Ulmke, M., Papi, F., Podt, M., and Boers,
Y. (2012). Assessment of vessel route information use
in bayesian non-linear filtering. In 2012 15th Interna-
tional Conference on Information Fusion, pages 447–
454.
Beauregard, S., Widyawan, and Klepal, M. (2008). Indoor
PDR performance enhancement using minimal map
information and particle filters. In 2008 IEEE/ION
Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, pages
141–147.
Dissanayake, G., Sukkarieh, S., Nebot, E., and Durrant-
Whyte, H. (2001). The aiding of a low-cost strap-
down inertial measurement unit using vehicle model
constraints for land vehicle applications. IEEE trans-
actions on robotics and automation, 17(5):731–747.
Foxlin, E. (2005). Pedestrian tracking with shoe-mounted
inertial sensors. IEEE Computer Graphics and Appli-
cations, 25(6):38–46.
Han, S. and Wang, J. (2008). Monitoring degree of ob-
servability in GPS/INS integration. In International
Symposium on GPS/GNSS.
Harle, R. (2013). A survey of indoor inertial positioning
systems for pedestrians. IEEE Communications Sur-
veys and Tutorials, 15(3):1281–1293.
Kou, S. R., Elliott, D. L., and Tarn, T. J. (1973). Observ-
ability of nonlinear systems. Information and Control,
22(1):89–99.
L
´
opez-Araquistain, J.,
´
Angel J. Jarama, Besada, J. A.,
de Miguel, G., and Casar, J. R. (2019). A new ap-
proach to map-assisted bayesian tracking filtering. In-
formation Fusion, 45:79 – 95.
Podt, M., Bootsveld, M., Boers, Y., and Papi, F. (2014).
Exploiting imprecise constraints in particle filtering
based target tracking. In Information Fusion (FU-
SION), 2014 17th International Conference on, pages
1–8. IEEE.
Rasool, G. (2018). Constrained state estimation-a review.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.03463.
Rehbinder, H. and Hu, X. (2004). Drift-free attitude es-
timation for accelerated rigid bodies. Automatica,
40(4):653 – 659.
Roetenberg, D., Luinge, H., and Slycke, P. (2009). Xsens
MVN: Full 6DOF human motion tracking using
miniature inertial sensors. Xsens Motion Technol. BV
Tech. Rep., 3.
Rothman, Y., Klein, I., and Filin, S. (2014). Analytical ob-
servability analysis of INS with vehicle constraints.
Navigation: Journal of The Institute of Navigation,
61(3):227–236.
Sabatini, A. M. (2006). Quaternion-based extended kalman
filter for determining orientation by inertial and mag-
netic sensing. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical En-
gineering, 53(7):1346–1356.
Simon, D. (2010). Kalman filtering with state constraints: a
survey of linear and nonlinear algorithms. IET Control
Theory & Applications, 4(8):1303–1318.
Tahk, M. and Speyer, J. L. (1990). Target tracking problems
subject to kinematic constraints. IEEE transactions on
automatic control, 35(3):324–326.
Vaganay, J., Aldon, M. J., and Fournier, A. (1993). Mobile
robot attitude estimation by fusion of inertial data. In
[1993] Proceedings IEEE International Conference
on Robotics and Automation, pages 277–282 vol.1.
Wenk, F. (2017). Inertial Motion Capturing Rigid Body
Pose and Posture Estimation with Inertial Sensors.
PhD thesis, University of Bremen.
Woodman, O. and Harle, R. (2008). Pedestrian localisation
for indoor environments. In Proceedings of the 10th
International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing,
UbiComp ’08, pages 114–123, New York, NY, USA.
ACM.
Xu, L., Liang, Y., Pan, Q., Duan, Z., and Zhou, G. (2016).
A kinematic model of route-based target tracking: Di-
rect discrete-time form. In 2016 19th International
Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), pages
225–231.
ICINCO 2019 - 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
788
