
DNN Based Cooperative Calibration for Master-Slave Multi-Camera
Network
Congcong Hua
1
, Shaozhuo Zhai
1
, and Yuehu Liu
1
1
Institute of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, Xi’an Jiaotong University, No.28 Xianning West Road,Xi’an,Shanxi,China
Keywords: Master-slave camera system, PTZ camera, Cooperative calibration, Deep neural network.
Abstract: Master-slave camera systems, consisting of wide-field and pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) camera, are widely applied
in surveillance. They can monitoring the wide scene, and the high-resolution details of interesting target can
be captured by PTZ camera. In order to achieve this function, the accurate cooperative calibration for these
system is a prerequisite. However, the nonlinear changing PTZ parameters (e.g. intrinsic and extrinsic) with
pan, tilt and zoom lead to inaccurate calibration by existing methods. What's more, the process of traditional
step-by-step calibration method makes accumulative error. In this paper, we provide a new end-to-end deep
neural network for cooperative calibration. This network establishes a mapping relationship between pix
coordinate in wide-field camera and control parameters of the PTZ camera. By this model, the control
parameters of the PTZ camera can be acquired without any complex camera calibration operation.
Experiments show that the proposed neural network has little calibration errors as compared to the ground
truth.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the field of large scene surveillance, there exists a
contradiction for a single camera between
monitoring the whole scene and the tiny interesting
object in the scene. These two requirements are
simultaneous needed for many situations, such as,
specific target monitoring in the park, the close-up
of a player in a football match, target monitoring of
military site. In order to cover the shortage of single
camera monitoring, the multi-camera system is
proposed. One of the famous camera system is
Master-Slave Network. This system consists of two
cameras: wide-field camera (wide camera) is static,
which aims to monitor the whole large scene and
detect the tiny interesting object; PTZ camera can
rotate and zoom, in order to tracking the detected
object (As is shown in Fig. 1), wide camera and
PTZ camera construct a master-slave camera
system).
In the master-slave network research, the most
basic issue is the calibration. Multi-camera
calibration is to establish a mapping relationship
between cameras and the world coordinate, though
estimating the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters.
After the pixel coordinate system and the world
coordinate system is converted, multiple cameras
can get the same target.
Figure 1: A Master-Slave Multi-Camera Network. The
wide camera monitors the entire scene and detects interest
targets, while the PTZ camera is controlled to dynamically
focus on the selected target and get its high-resolution
images. This paper is to calibration a Master-slave unit in
such multi-camera network system.
However, compared to establishing a mapping
relationship between camera pixel coordinate and a
world coordinate system, a PTZ camera is more
suitable to establish a mapping relationship between
Move
Pan
Tilt
Zoom
Fixedcamera1
PTZcamera1
Fixedcamera2
Fixedcamera3
Pan
Tilt
Zoom
PTZcamera2
Pan
Tilt
Zoom
PTZcamera3
Hua, C., Zhai, S. and Liu, Y.
DNN Based Cooperative Calibration for Master-Slave Multi-Camera Network.
DOI: 10.5220/0008096401710177
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computer Technology, Information Science and Communications (CTISC 2019), pages 171-177
ISBN: 978-989-758-357-5
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
171

pixel coordinates and camera movement
magnification.
At present, most scholars have the same
understanding of the goal to camera calibration for
such system. That is, after the fixed camera detects a
target, the target will displayed in the center of PTZ
camera image view by controlling the camera
parameters.Therefore, after the PTZ camera
calculated the target location in world coordinate
system, it need to use the intrinsic parameter to
compute the camera control parameters. When the
camera turning and zooming, the intrinsic
parameters will dynamically changing. So, the
calculated camera control parameters value cannot
let the target displayed in the center of PTZ camera
image view.
But, if we establish a mapping relationship
between pixel coordinates and camera movement
magnification, we can solve the problem and
calculate the control parameters more accurate. We
called this calibration as cooperative-calibration.
In this paper, a 11-layer deep neural network
based cooperative-calibration method is proposed.
The mapping between the object coordinate in the
wide camera and PTZ control parameters can be
fitted by the neural network.
This method has the following contributions:
The traditional calibration method based on
accurate mathematical model is cumbersome,
and there are many nonlinear disturbance
factors that affect the accuracy of 3D
reconstruction. Our method can solve the
nonlinear problem well.
The benefits of neural network for camera
calibration is that it can quickly establish a
mapping between the pixel coordinate in wide-
field camera and PTZ control parameters.
There is no need for the pre-established model.
Compared to establishing a map between
camera pixel coordinate and a world coordinate
system, our method can decreased the
calibration error.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows:
Sect. 2 introduces the current research status of the
camera cooperative-calibration. Sect. 3 defines our
research problems, and Sect. 4 describes the design
of the network structure. Experiment will be
conducted and analyzed in Sect. 5. We give our
conclusion in Sect. 6.
2 RELATED WORK
There exist many research works about the
parametric calibration method (Senior et al. 2005;
Jie et al. 2010; Kumar et al. 2009) and non-
parametric calibration method (Robinson 1994;
Turton et al. 1994; Cui and Yuan 2009; Jin and Zhou
2015) on master-slave system that consists of PTZ
and the wide-field camera.
The parametric calibration method: It is assumed
that there is a relationship between the camera
coordinate and the word coordinate system, which
can be expressed by intrinsic parameters and
extrinsic parameters. The PTZ camera mainly has
two imaging models: the pinhole imaging model and
the complex camera imaging model.
Pinhole model is a linear model, that means it
simplifies the camera kinematic model, and does not
solve the lens distortion.
Some simplifications can make the calibration
problems easier, but at the expense of accurate.
This simplifications are (1) collocation of the
optical center on the axes of pan and tilt, (2)
parallelism of the pan and tilt axes with the height (y)
and width (x) dimensions of the CCD, and (3) the
requested and realized angles of rotation match, or
the angle of rotation does not require calibration. Xu
(Xu, 2010) uses SIFT feature match method to
calibrate the two camera. Marchesotti(Marchesotti et
al., 2005) uses geometry-based pixel offset matching
based on the position of the two cameras. Hampapur
(Hampapur et al., 2003) uses shape-based head
detection to achieve target matching.
The advantage of complex model is that the
accuracy is much better, and it considered the
kinematic model. Jain (Jain et al.,2006) adopt a
general formulation that declared does not make
above simplifications. Horaud(Horaud et al., 2006)
solve for a general pan–tilt kinematic model and
develop a close-form solution for a simplified pan–
tilt model. They establish the link between the
epipolar geometry constraint and the kinematic
model constrains. Both the Pinhole model and the
complex model were affected when the camera
change zoom.
The non-parametric method: The main idea of
non-parametric calibration method is to obtain the
corresponding relationship between the
corresponding point in space and fitting image point
(such as the genetic algorithm or neural network).
As an intelligent optimization algorithm, neural
network has been successfully applied on camera
cooperative-calibration. The camera calibration
method based on neural network can effectively
CTISC 2019 - International Conference on Advances in Computer Technology, Information Science and Communications
172
overcome the measurement error (including
mathematical model error, image acquisition error,
optical system adjustment error and Camera
photosensitive element nonuniformity error).
A large number of scholars at home and abroad
carried out a camera calibration method based on
neural network. Among them, Jin(Jin et al., 2017)
used the 2D coordinates of the center of the circles
as the input sample set for training, and required the
3D position of the materials. Their system used two
High-speed camera to calibrated. Khosravi and Fazl-
Ersi (Khosravi and Fazl-Ersi, 2017) researched the
neural network function in a feed-forward network.
Their system was consist of a central PTZ camera
and two wide camera, they used the wide angle
cameras as its input, and computed the desired pan
and tilt values.
We proposed a 11-layer depth neural network
based cooperative-calibration method. This method
obtains the corresponding relation between pixel
coordinates and PTZ control parameters by
measuring the coordinates of the calibration objects
of the Self-identifying marker, and completes the
calibration of the camera.
3 PROBLEM FORMULATION
As is mentioned in Sect.1, the master-slave multi-
camera system consists of one wide-field camera
and PTZ camera. It means that, when the network
wants to capture a target, the two camera have to
cooperate. In a task, the wide-field camera monitors
the entire scene and detects interest targets, while the
PTZ camera is controlled to dynamically focus on
the selected target and get its high-resolution images.
After the object is detected in the wide-field camera,
the PTZ camera is controlled to point to the target.
Thus, in these systems, the cooperative calibration
is to find the mapping between image coordinate
point () and the control parameters (i.e. pan, tilt,
and zoom ratio). Since a target can be seen in the
PTZ camera with multiply group of control
parameters, the pixel coordinate of wide-field
camera corresponds to many control parameters of
PTZ cameras. Therefore, the deep neural network
fails to estimate this one-to-most relationship. This
paper adds two constraints to solve this problem,
Concretely, the pixel of wide-field camera
corresponds to one group of control parameter,
which can
make the object locate in the centre of image.
make the region of object occupy the whole
image.
Through this way, the deep neural network can
estimate this mapping. In addition, given the image
captured by wide-field camera,
by PTZ, the
object
in
, the object
in
and the current
status
of the PTZ camera, the control
parameters
of PTZ camera can be estimated
by the neural network to make the object in PTZ
camera and satisfy the two constraints. Therefore,
the problem can be formulated by
(1)
4 DNN BASED COOPERATIVE
CALIBRATION METHOD
As it is mentioned in Sect.3, requiring the mapping
relation can control PTZ camera accuracy. Thus it
can using the neural network to fit the mapping .
This section introduces from the network structure
and the training strategy, and analyse its rationality.
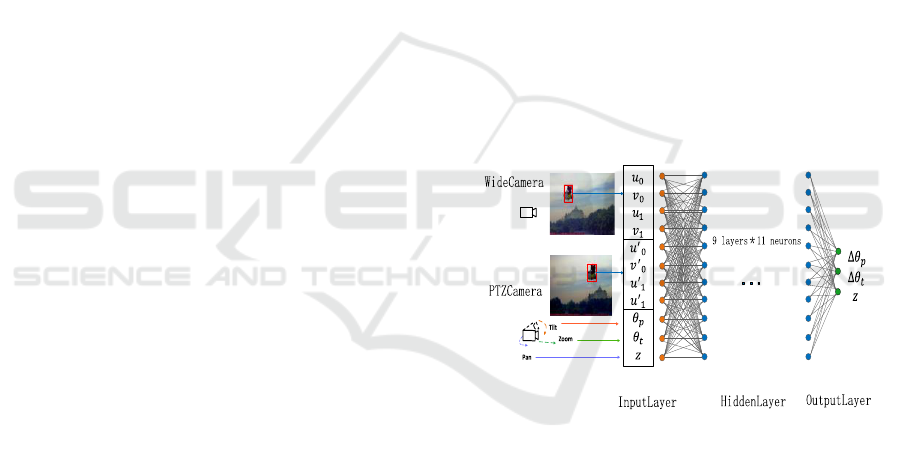
Fig.2 is the structure of the network.
Figure 2: The structure of the neural network. The Input
layer have 11 neurons, and the hidden layer have 9 layers
with 11 neurons in each layer. The parameters of output
layer is 3.
4.1 The Design of Neural Network
4.1.1 Input Layer
This layer is to input the parameters to training the
model.
From the Eq.1 in Sect.3, when calculate , we
need to know the object point location from the two
camera image and the current status of PTZ camera.
Printing a boudingbox in the image can position
the target, and the boudingbox can be expressed by
four coordinates of coner points. If the boudingbox
DNN Based Cooperative Calibration for Master-Slave Multi-Camera Network
173

is a rule rectangle, it can be expressed by only two
points, top-left and lower-right corner. There will
have four points to express the target location in
wide camera and PTZ
camera:
,
.
The PTZ camera is controlled by these three
parameters: pan field (
), tilt field(
) and zoom
ratio ( ). The first two parameters control the
orientation of PTZ camera, while zoom ratio
changes the focal length of the PTZ camera to adjust
its monitoring range. Thus these parameters can
describe the current state of the camera.
The neural numbers of input layer are determined
by the above parameters. So the neurons number of
input layer is 11.
4.1.2 Output Layer
This layer used to output the parameter that need to
required.
This model is designed to calculate the PTZ
control parameter when the camera controlled to
point to the target. Thus the output layer should have
3 neurons to output the PTZ control parameters (
,
, ) .
4.2 The Training Strategy
4.2.1 Training Function
This paper used TRAINBR function and mean
square error function performance function to
train.
TRAINLM function is a Levenberg-marquardt
learning rule, which is used to compute the
derivative of network output error to the network
weight value. This algorithm has the fastest
convergence speed for the medium sized neural
network. Because it avoids the direct calculation of
the Hesse matrix, it reduces the amount of
calculation in training, but requires a large amount
of memory.
4.2.2 Learning Rate
The learning rate determines the amount of weight
changes in each iteration. Large learning rate may
lead to the instability of the system. And small
learning rate will lead to a long training time and a
slow convergence speed, but it can ensure that the
network error value does not jump out of the error
surface of the trough, and lead to a minimum error
value.
In general, we tendency to choose a small learning
rate to ensure the stability of the system. And the
learning rate is generally selected between 0.01 to
0.8. We selected 0.01.
4.2.3 Expected Error
When designing the network, the expected error
value should be determined by comparing the
performance of different values.
After a number of different expected error values
be trained in the network, we select 1e-5.
5 EXPERIMENTAL
EVALUATION
We describe the data collection methods and
experimental methods in this section.
5.1 Data Set
The process of camera cooperative-calibration
process in neural network is the process of collecting
samples.
In the data acquisition of large scene, we mainly
consider the collection method of the cooperative-
calibration target.
5.1.1 Target Calibration
We select a self-identifying marker as the
calibration target. Self-identifying marker array not
only has the checkerboard, but also contains the
unique identification code. So it is possible to
automatically establish the correspondence between
the points to the 3D coordinates on the cooperative-
calibration target and the 2D projection points on the
image. The cooperative-calibration can be done
simply, by photographing the Self-identifying
marker patterns of different angles, and without any
human intervention at all. The calibration efficiency
is very high that can deal with occlusion, large tilt
field, lens distortion and other circumstances.
By painting the marker as a red mark, it can
increase the color contrast of the markers in the
scene, and enlarge the recognition range of the tags.
Since we only need one target in the scene, we use a
single red self-identifying marker as target.
5.1.2 Target Distribution
An important problem of camera cooperative-
calibration is the calibration of depth. The target at
CTISC 2019 - International Conference on Advances in Computer Technology, Information Science and Communications
174
different distances on the same ray will be projected
in the same position on the camera. As a result, the
monocular camera cannot know whether the
imaging points belong to a distant point or a nearer
point. But they are projected on another camera in
different locations. The depth of the point can be
determined by observing the imaging points on the
two cameras. If we put the large size tag farther than
the small size marker, while adjustment the distance
appropriately. The two marks will show the same
pixel size on the two cameras.
Data sets of different depths can be collected on
the same ray by placing a number of different sizes
of markers. At different depths, the markers should
be evenly covered by the entire lens for data
collection. The distortion model must be considered
when the lens distortion is obvious. Camera
distortion in the edge of the camera is more obvious,
the target in the edge of the camera needs to be fully
collected. So we collect each position on the lens to
make the marker evenly covered on the lens.
When the wide-field camera collect a position, the
position of the marker in the PTZ lens should be
evenly distributed. One pixel coordinate on a wide-
field camera with different PTZ camera lens location
will corresponding to different PTZ control
parameters. These datas need to be training.
To sum up, we use a single red self-identification
mark as a target, and at different depths placing a
number of different sizes of tags. Collecting datas on
all parts of the camera lens evenly. At the same time,
when we collecting each location of the fixed
camera, we should collecting the different fields of
PTZ lens.
5.2 Experiment Setup
5.2.1 Hardware Equipment
In order to verify the feasibility and validity of the
method, a binocular stereo vision camera
cooperative-calibration experiment was carried out.
We construct a binocular stereo vision system: the
PTZ camera is EVI-D70P camera, its image is 768
*576, 18x (optical) *12x (digital), and focal length is
4.1-73.8mm. Another type is Microvision, fixed
camera used mv-em200c, the image resolution is
1600*1200.
5.2.2 Data Set
The dataset have 6260 groups, and the target used a
single red self-identification marker. 7 markers of
different sizes appeared in this dataset. And the
target Distribution on the camera lens evenly.
5.2.3 Evaluation Metrics
In the experiments, the evaluation metrics are mean
absolute error () of the pan and tilt parameters
value and mean relative error () of the zoom
parameters value, which are defined as follows:
(2)
(3)
Where
denotes the groundtruth of PTZ
control parameters precalculated by triangulation. M
is the number of test points in a specific range. The
and is the evaluation metric to evaluate
the accuracy of experimental result.
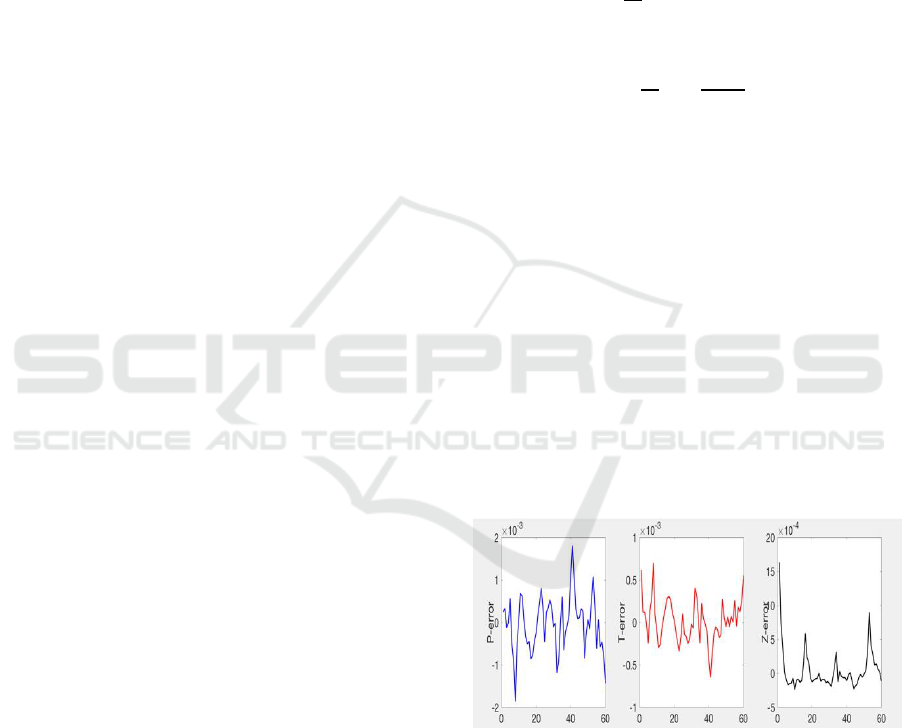
5.3 Training Performance
Using the iterative network, 60 sets of data to test
the model and Fig.3 shows the predicted results of
the test data. We trained the network with 6200 sets
of data in the dataset as a training sample, and 60
sets of data as test samples to test the network. When
testing the network, compare the predicted results
with the actual data to adjust the network structure.
Figure 3: The error of three parameters. The horizontal
axis to be test data set number, and the error is parallel to
the vertical axis. Left: the absolute error of pan. Middle:
the error of tilt. Right: the relative error of zoom.
DNN Based Cooperative Calibration for Master-Slave Multi-Camera Network
175
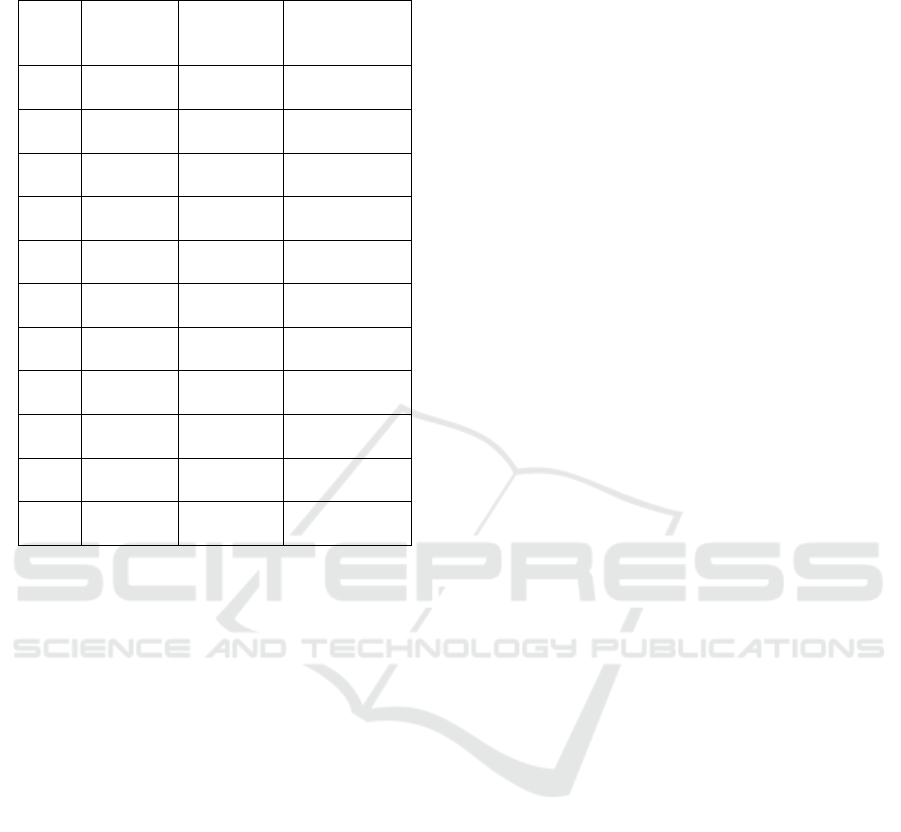
Table 1: Cooprative-calibration test error of three
parameters.
No.
Absolute
pan
error()
Absolute
tilt error()
Relative zoom
error (%)
1
0.0002
0.6175
0.16
2
0.0003
0.1203
0.07
3
-0.0001
0.1207
0.04
4
-0.0000
0.0138
0.00
5
0.0006
0.2433
-0.01
6
-0.0005
0.1468
-0.02
7
-0.0009
0.2858
-0.01
8
-0.0019
0.6984
-0.01
9
-0.0005
0.0968
-0.01
10
0.0000
0.0761
-0.02
Mean
Error
0.0005
0.2440
0.035
Table1 shows the detailed error values of the first
10 groups. The pan and tilt used absolute error, and
the zoom value used relative error. From the test
results can be seen: in the P, T two directions, the
error is less than . In the Z direction, the error
is less than . The MAE is close to 0.0005 in
pan,
in tilt and MRE is 0.035% in
zoom. This precision can meet the general
measurement needs.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, a camera cooperative-calibration
method of the system that consist of a PTZ camera
and a wide camera was discussed. This method
based on depth neural network, and established a
mapping relationship between the marker
coordinates and the PTZ control parameters. Firstly,
the cooperative-calibration plane with a self-
identifying marker were placed in multiple positions
within the effective field of view. The images of the
cooperative-calibration plane in each position can be
captured by the system. Then, after image
processing, the 2D coordinates of the bounding-box
were used as the input sample set for training, and
with the PTZ camera control parameters to input.
The neural network was used to establish an implicit
vision model. By this model, PTZ adjustment
parameters can be acquired without any complex
camera calibration operation. Experiments showed
that the proposed scheme is feasible, which will
provide a good basis for further research.
REFERENCES
SENIOR, A. W., HAMPAPUR, A. & LU, M. Acquiring
Multi-Scale Images by Pan-Tilt-Zoom Control and
Automatic Multi-Camera Calibration. Application of
Computer Vision, Wacv/motions 051 Seventh IEEE
Workshops on, 2005.
JIE, Z., WAN, D. & YING, W. 2010. The Chameleon-
Like Vision System. Signal Processing Magazine
IEEE, 27, 91-101.
KUMAR, S., MICHELONI, C. & PICIARELLI, C. Stereo
Localization Using Dual PTZ Cameras. Computer
Analysis of Images & Patterns, International
Conference, Caip, Münster, Germany, September,
2009.
ROBINSON, M. A genetic algorithm approach to camera
calibration in 3D machine vision. IEEE Colloquium
on Genetic Algorithms in Image Processing & Vision,
1994.
TURTON, B. C. H., ARSLAN, T. & HORROCKS, D. H.
A hardware architecture for a parallel genetic
algorithm for image registration. IEEE Colloquium on
Genetic Algorithms in Image Processing & Vision,
1994.
CUI, A. & YUAN, Z. 2009. Self-adaptive neural network
for binocular camera calibration. Computer
Engineering & Applications, 45, 55-56.
JIN, W. & ZHOU, M. 2015. Study on calibration of
binocular stereovision based on BP neural network
with different layers. Optical Technique, 41, 72-75.
XU, Y. & SONG, D. 2010. Systems and algorithms for
autonomous and scalable crowd surveillance using
robotic PTZ cameras assisted by a wide-angle camera.
Autonomous Robots, 29, 53-66.
MARCHESOTTI, L., PIVA, S., TUROLLA, A.,
MINETTI, D. & REGAZZONI, C. S. Cooperative
multisensor system for real-time face detection and
tracking in uncontrolled conditions. Proc Spie 5685,
Image & Video Communications & Processing, 2005.
HAMPAPUR, A., PANKANTI, S., SENIOR, A., TIAN,
Y. L., BROWN, L. & BOLLE, R. Face cataloger:
multi-scale imaging for relating identity to location.
IEEE Conference on Advanced Video & Signal Based
Surveillance, 2003.
JAIN, A., KOPELL, D., KAKLIGIAN, K. & WANG, Y.
F. Using Stationary-Dynamic Camera Assemblies for
Wide-area Video Surveillance and Selective Attention.
IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer
Vision & Pattern Recognition, 2006.
HORAUD, RADU, KNOSSOW, DAVID, MICHAELIS
& MARKUS 2006. Camera cooperation for achieving
CTISC 2019 - International Conference on Advances in Computer Technology, Information Science and Communications
176

visual attention. Machine Vision & Applications, 16,
1-2.
JIN, S., MA, Y., HAN, Y. & ZHU, X. Camera calibration
and its application of binocular stereo vision based on
artificial neural network. International Congress on
Image & Signal Processing, 2017.
KHOSRAVI, H. & FAZL-ERSI, E. Trackerbot: A robotic
surveillance system based on stereo-vision and
artificial neural networks. International Conference on
Robotics & Mechatronics, 2017.
DNN Based Cooperative Calibration for Master-Slave Multi-Camera Network
177
