
The Process of Mental Revolution Control with "Dewi SARTIKA"
Model Development Program for Accelerating Village Performance
in Indonesia's 122 Underdeveloped Regions: Case Study in Wersawe
Village, West Manggarai Regency, Flores
Lelo Yosep Laurentius
1
, Hendry Hartono
2
, Lim Sanny
2
and Adi Prasojo
3
1
Character Building Development Center, Computer Science Department, School of Computer Science, Bina Nusantara
University, Jakarta, 11480, Indonesia
2
Management Department, BINUS Business School Undergraduate Program, Bina Nusantara Universit, Jakarta, 11480,
Indonesia
3
Character Building Development Center, Industrial Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering,Bina Nusantara
University, Jakarta, 11480, Indonesia
Keywords: Control, Mental Revolution, Performance, Development, Program.
Abstract: This study aims to implement President Jokowi's mental revolution movement easily but comprehensively
at the village level through the "Dewi SARTIKA" model development program, which has an efficient and
effective framework to accelerate village performance in 122 underdeveloped regions. The program has a
transparency design of village performance assessment and stakeholder participation. The performance of
"Dewi SARTIKA" will be a regional innovation incubator, namely all forms of renewal in the
implementation of the regional government. The main actors of the program are the government,
researchers and local governments. The main stakeholders are village officials, NGOs, Civil Society
Organizations (CSOs), community groups, and business organizations. This research is an innovation from
the results of the CIPP model evaluation on the Wersawe Village-based ecotourism development program in
West Manggarai Regency, Flores in 2016-2018. Data was collected through FGDs, analysis of news
content, document studies, field surveys, observations, recordings, and in-depth interviews of three key
sources. Analysis and interpretation of data show that the acceleration of the development of 122
disadvantaged areas requires a "Dewi SARTIKA" development program as a role model that needs to be
implemented in each sub-district so that it becomes a benchmarking for other villages. This finding leads to
the need for regulatory innovations in the region through regent regulations regarding the implementation of
the "Dewi SARTIKA" model development program at the village level.
1 INTRODUCTION
President Indonesia, Mr. Joko Widodo (Jokowi)
offered a mental revolution movement to position
Indonesia as a superpower at the international level.
Its implementation requires a certain control system
at the village level so that it creates community
transformation. Because, mental revolution is a
movement of change in Indonesia so that citizens
always take the initiative to serve, clean, orderly,
independent, and united. Management engineering
development program "Dewi SARTIKA" model is
an intervention with a systems approach to
managing the movement of change. The intervention
also serves to bridge the government's initiative
through the third program Nawacita, namely to build
Indonesia from the periphery by strengthening
regions and villages within the framework of the
Unitary State of the Republic of Indonesia. This
intervention involves strategic partnerships between
stakeholders, namely the government, academics,
NGOs, local governments, Civil Society
Organizations (CSOs), community groups and
business organizations. The main actors of this
intervention are the government and local
governments because organizationally they play a
role in making strategic planning (goals, objectives,
strategies and plans) based on the law. Other
Laurentius, L., Hartono, H., Sanny, L. and Prasojo, A.
The Process of Mental Revolution Control with "Dewi SARTIKA" Model Development Program for Accelerating Village Performance in Indonesia’s 122 Underdeveloped Regions: Case Study
in Wersawe Village, West Manggarai Regency, Flores.
DOI: 10.5220/0008428701590164
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World (ICIB 2019), pages 159-164
ISBN: 978-989-758-408-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
159

stakeholders contributed to creating performance
appraisal standards for village development
programs with the "DewiSARTIKA" model based
on mapping the potential of the village, which of
course differed between regions. This intervention is
a very important management tool in two ways.
First, control strategies in the form of standards,
measurements, comparisons, and actions to
accelerate village performance. Second, the process
strategy between the input and output of the use of
village budget funds each year efficiently and
effectively. This control strategy and process
strategy will create a balance of flows of natural
resources and the environment. The balance of flows
of natural resources and the environment is a picture
of the flow of natural inputs from the environment
into the economy and the flow of waste from the
economy to the environment (PP 46, 2017).
Wersawe Village has Cunca Wulang (Moon
Waterfall) as a favorite destination for domestic and
foreign tourists. However, the facilities and
infrastructure are very limited and very unorganized.
The problem lies in the performance of the local
government and the village administration which
does not give an example of how citizens should
adapt quickly from simple farming habits to small
and medium-sized entrepreneurs in the tourism
sector who are growing very rapidly. As a result,
local communities have not optimally utilized the
environment as an economic instrument to increase
their income which directly impacts on improving
the level of welfare of their daily lives. This is
clearly seen in the low level of public hygiene in
homes and public spaces. 90% of people's homes do
not have bathrooms and toilets. Residents do not
build clean public toilet facilities for tourists. Local
people are accustomed to disposing of their
household waste directly into the Cunca Wulang
river flow because residents do not have trash cans
in their homes. Local government also has not made
a water management system to provide clean water
to people's homes, which will usually be occupied
by foreign tourists to stay on average 2-3 days. The
National Electricity Company (PT-Perusahaan
Listrik Negara- PT PLN) has not yet provided an
electricity network to Wersawe Village. Even so,
residents tried to use solar panels for household
lighting at night. Tourist Information Center to serve
tourist retribution registration is also like a shack in
figure 1. This office does not have a laptop or PC.
This office only has stationery, tables, chairs and
registration books. Residents also do not have kiosks
for the daily needs of tourists. The existing kiosk
only provides the basic needs of the local
community.
Figure 1: Tourism Information Center in Warsawe
Village.
Wersawe Village is a research sample because it
has a Cunca Wulang destination as support for
ecotourism in Labuan Bajo and is only about 30 km
from Labuan Bajo. The ecotourism of Labuan Bajo
and the coastal areas of West Manggarai Regency
has the character of marine, forest, mountain and
karst ecotourism ecosystems.
The researchers used the Stufflebeam CIPP
evaluation model (Context, Input, Process, Product)
which aims at continuous improvement in
organizational development. The CIPP Evaluation
Model is a continuous effort to help leaders and
members of their organizations to obtain, regulate,
and use feedback systematically to validate program
objectives, meet the needs of planning goals,
program beneficiaries, and pass accountability tests
(Stufflebeam, 2014). Management engineering
development program model "Dewi SARTIKA" is
an innovation from the evaluation results of the
CIPP model on ecotourism-based regional
development programs in West Manggarai Regency.
Then, the management engineering model "Dewi
SARTIKA" has a framework to measure the process
of accelerating village performance. In the context
of the position of Labuan Bajo, this intervention
focuses on developing ecotourism into the leading
sectors of the village and/or region.
The main problem found in the evaluation results
is the results of general data analysis at each CIPP
stage and the results of questionnaire data analysis
of 83.00% of respondents, have illustrated that the
West Manggarai Regency Government and
Wersawe Village Apparatus do not have a
mechanism that acts as a control measure and
organizing actions to develop the ecosystem of
Wersawe Village, especially at the Cunca Wulang
destination. Therefore, management engineering
development program "Dewi SARTIKA" model
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
160

uses the theoretical framework of the control process
(Robbins & Coulter, 2016) as shown in figure 2. The
control process is a three-step process for measuring
actual performance, comparing actual performance
with standards, and taking managerial actions to
correct deviations or inadequate standards. Step 123
of this theoretical framework must be implemented
in each of the "SARTIKA" indicators as a system
that controls the process of change in the village.
Building awareness of these issues is often a first
step to fostering active and effective citizenship and
encouraging citizens to engage (Gaventa & Barrett,
2010).
Figure 2: The Control Process. (Source: Robbins &
Coulter (2016)).
Goals and objectives nationally and regionally
are accelerated regional performance. The
acceleration of the performance of Wersawe Village
requires engineering management development
program model "Dewi SARTIKA". Because, this
engineering is a management tool that formulates
control strategies and process strategies between
input and output of the use of village budget funds in
five priority matters. Those five things are
(Permendes 19, 2017) : a) Priority in the use of
village funds to finance the implementation of
programs and activities in the field of village
development and empowerment of rural
communities; b) Priority in the use of village funds
to finance the implementation of programs and
activities that are cross-sectoral in nature; c)
Programs and activities that are cross-sector in
nature include areas of superior product activities in
the village or rural areas, Village-Owned Enterprises
(Badan Usaha Milik Desa-BUM Desa) or BUM
Desa together, embung, and village sports facilities
in accordance with the authority of the village; d)
The construction of village sports facilities in
accordance with village authority is a business unit
managed by BUM Desa or BUM Desa together; e)
Priority in the use of village funds to finance the
implementation of programs and activities in the
field of village development and empowerment of
rural communities must be published by the village
government to village communities in public spaces
that can be accessed by village communities.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The method used in this study is content analysis.
Content analysis is an analytical technique that
assesses and analyzes objectively to assess research
factors (Kerlinger, 1973). This content analysis was
used to analyze the results of the research factors
from the evaluation of the CIPP model that had been
carried out on an ecotourism-based regional
development program in West Manggarai Regency.
Determination of the source of the interview was
conducted purposively, namely the Head of the
Regional Development Planning Agency, Head of
the Culture and Tourism Office, and the Village
Head of Wersawe. Researchers conducted
observations, interviews and distributed
questionnaires to collect primary data. There were
86 respondents who filled out a questionnaire
designed for the component Context, Input, Process,
Product. The respondents' backgrounds are spread as
follows: business organizations (6.7%), local
government apparatus (10.12%), village apparatus
(10.12%), foreign tourists (20.23%), domestic
tourists (10.12 %), community groups (15.17%), and
local travel operators (15.17%).
3 COPYRIGHT FORM
All national regulations encourage the optimization
of the potential of the region to become a superior
product and service product through a cross-sectoral
strategic partnership. The main problem related to
the inability of the community to create regional
superior products lies in the lack of competency of
the regional government and village government to
design a program that can encourage the process of
regional superior product innovation. Management
engineering development program model "Dewi
SARTIKA" at the same time is a system of
organizational development and human resources.
Because, the process of implementing the "Dewi
SARTIKA" model adopts strategic planning
processes, utilization strategies, institutional
strengthening strategies, and community
empowerment strategies in every aspect of
"SARTIKA". However, the implementation of the
"Dewi SARTIKA" development program in the
village depends on the regulations of the village
The Process of Mental Revolution Control with "Dewi SARTIKA" Model Development Program for Accelerating Village Performance in
Indonesia’s 122 Underdeveloped Regions: Case Study in Wersawe Village, West Manggarai Regency, Flores
161
administration and the regent's regulatory support.
Because, the results of data analysis showed that
79% of respondents doubted the District Head of
West Manggarai Regency and the Wersawe Village
Head to manage their agency to regularly provide
guidance, supervision, consultation, monitoring,
evaluation, education and training in developing
entrepreneurship to the community.
Transformation is the adoption of new
technology, massive strategic shifts, the re-
establishment of processes, mergers and
acquisitions, restructuring into different business
units, and various efforts to significantly improve
innovation and changes in organizational culture
(Kotter & Cohen, 2002). The development
management engineering model of "Dewi
SARTIKA" requires strategic thinking, innovative
thinking and situation management skills from the
regents and village heads to create partnerships with
ecotourism actors and stakeholders. However, data
analysis showed 77% of respondents thought that
regents and village heads ignored the participation of
stakeholders in ecotourism development, namely
community members, community institutions,
village consultative bodies, community
empowerment cadres, religious leaders, community
leaders, and NGOs. In addition, 83% of respondents
agreed that the regent and village head had not
allocated funds for skills training and
entrepreneurship development for the community.
Because the regents and village heads do not
involve stakeholders and do not allocate funds for
skills training and development of citizen
entrepreneurship, currently the residents of Wersawe
Village have a number of crucial issues, namely: a)
Tourist visits to the Cunca Wulang destination
always increase every day, but there are potential
conflicts among community groups because there is
no business system that regulates equitable
distribution of income among the local community;
b) The weak process of control and supervision of
local governments towards the Cunca Wulang
destination has caused some criminal acts against
tourists in the Wersawe Village; c) Lack of
coordination of partnerships between government,
NGOs, local government, Civil Society
Organizations (CSO), community groups and
business organizations has led to the lack of a
standard data management system in the Tourist
Information Center office, especially data on tourist
character; d) Tourist visits to the Cunca Wulang
location are only limited to enjoying the natural
panorama, other economic activities according to the
needs of tourists do not yet exist because the
community members have not received training and
entrepreneurship development that supports tourism
activities. Accelerating underdeveloped areas into
developed regions requires a system approach.
Management engineering development program
model "Dewi SARTIKA" is an accelerated
intervention with a focus on a systems approach to
redesigning organizational structures and human
resource strategies . This intervention focuses more
on the control strategy and the strategy of the
ecotourism development process involving
stakeholders. The role of stakeholders focuses on
how to make detailed performance appraisals on
every aspect of "SARTIKA" so that the process of
implementing the "Dewi SARTIKA" model creates
multiple impacts on various aspects of people's lives.
So, this "Dewi SARTIKA" model development
program serves as a mental revolution control
system at the village level with a focus on improving
ways of thinking, behavior patterns, and improving
motivation that drives village performance. Because,
a village is a legal community unit that has territorial
limits that are authorized to regulate and manage
government affairs, the interests of the local
community based on community initiatives, origin
rights, and/or traditional rights that are recognized
and respected in the system of government of the
Unitary Republic of Indonesia (UU 6, 2014).
Meanwhile, the village government is the
administration of government affairs and the
interests of the local community in the system of
government of the Unitary State of the Republic of
Indonesia.
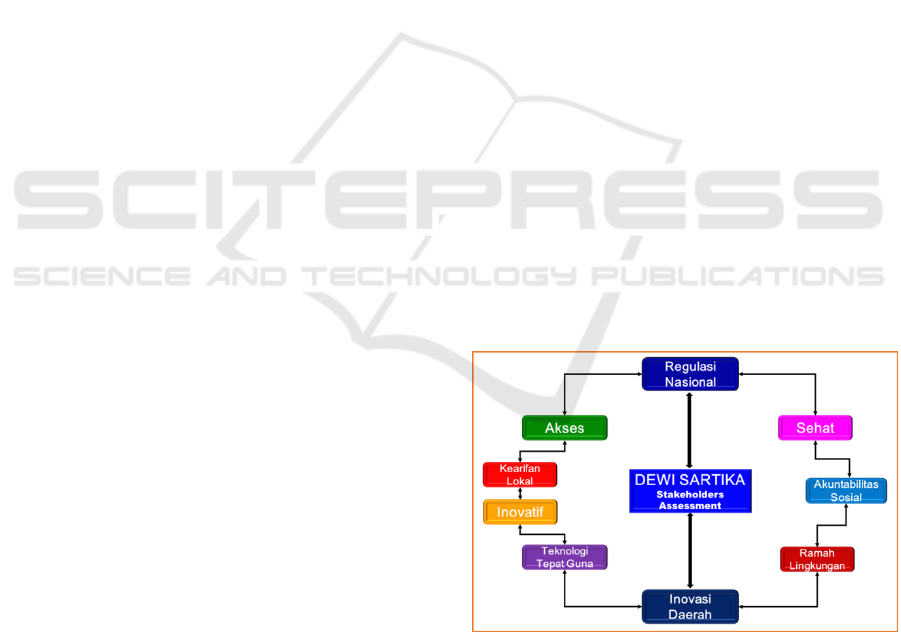
Figure 3: Management Engineering Model Development
Program.
The management model of the Dewi SARTIKA
model development program is shown in figure 3.
The output of the "Dewi SARTIKA" model is
regional innovation with a number of fundamental
principles (PP 38, 2017), namely: increased
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
162

efficiency; improvement in effectiveness; improving
service quality; does not cause a conflict of interest;
oriented to the public interest; done openly; fulfill
propriety value; and can be accounted for the results
are not for self-interest.
Healthy is a state of well-being from the body,
soul, and social which allows every person to live
productively socially and economically (UU 23.
1992). ‘Social accountability’ refers to a form of
civic engagement that builds accountability through
the collective efforts of citizens and civil society
organizations to hold public officials, service
providers, and governments to account for their
obligations with responsive efforts (Houtzager and
Joshi, 2008). At the same time as strengthening civic
engagement and amplifying ‘citizen voice’, social
accountability initiatives aim to increase the
transparency of governance in many areas, ranging
from local service delivery to national processes of
development policy formulation (UNDP, 2013).
Environmental friendly criteria cover all aspects of
the environment throughout the product life cycle,
including among others the selection of raw
materials, the selection of types of energy for
production, manufacturing, utilization and post-
utilization (PP43, 2017). Local wisdom is the noble
values that apply in the order of life of the
community to protect and manage the environment
sustainably (UU 32, 2009). Local wisdom is usually
directly related to customary law communities,
namely community groups who have traditionally
settled in certain geographical areas because of ties
to ancestral origins, strong relationships with the
environment, and a value system that determines
economic, political, social institutions, and law (UU
32, 2009). Appropriate technology is a technology
that fits the needs of the community, can answer
community problems, does not damage the
environment, can be utilized and maintained by the
community easily, and produces added value from
economic aspects and environmental aspects
(Permendagri 10, 2010). Infrastructure is technical,
physical, system, hardware, and soft facilities
needed to service the community and support the
network structure so that the community's economic
and social growth can run well (Perpres 38, 2010). A
beautiful and sustainable Indonesia is one of the
missions of the eight national development missions
for 2005-2025. The realization of a beautiful and
sustainable Indonesia is characterized by the
following (UU 17, 2007): a) Improvement of
management and utilization of natural resources and
preservation of environmental functions reflected by
the continued functioning of its functions, carrying
capacity and recovery capacity in supporting the
quality of social and economic life harmonious,
balanced and sustainable; b) The maintenance of a
wealth of diversity and distinctiveness of natural
resources to realize added value, national
competitiveness, and national development capital;
c) Increased awareness, mental attitude, and
behavior of the community in natural resource
management and preservation of environmental
functions to maintain comfort and quality of life.
Management engineering model development
program "Dewi SARTIKA" is a change management
strategy, which is specifically for regional
government and village government. This
engineering will accelerate regional innovation
competencies based on village capabilities in aspects
of "SARTIKA". Because, this engineering focuses
on redesigning the organizational structure and
human resource strategy by taking into account the
internal environment and the external environment
comprehensively on the aspects of "SARTIKA".
Therefore, we propose a number of steps for change
management for the initiative to form Dewi
SARTIKA in villages in various regions, namely: a)
Regents and village heads cooperate with
stakeholders across sectors to organize education
and communication programs; b) Regents and
village heads work together with cross-sector
stakeholders to build commitment to change through
participation and involvement in implementation
"Dewi SARTIKA; c) Regents and village heads
work together with stakeholders across sectors to
support and provide training needed by the
community; and d) Regents and village heads
collaborate with cross-sector stakeholders to
negotiate an agreement on mutual awards and
incentives from the success of Dewi SARTIKA.
Starting from the President initiating a mental
revolution movement, then all regions, especially
122 disadvantaged regions, need to develop a
comprehensive framework and partnership, which
supports the Indonesian change movement that is
more serving, clean, orderly, independent, and
united in various villages in 122 underdeveloped
regions . This can only be achieved if the regional
government and village government dare to take
total responsibility and determine moral choices to
carry out the mental revolution movement by
practicing the "Dewi SARTIKA" model
development program.
So, the management engineering of Dewi
SARTIKA's model development program in this
study has a strategic contribution, namely: 1)
Creating synchronization of central-regional
The Process of Mental Revolution Control with "Dewi SARTIKA" Model Development Program for Accelerating Village Performance in
Indonesia’s 122 Underdeveloped Regions: Case Study in Wersawe Village, West Manggarai Regency, Flores
163

development regulations through intervention in
village organizational and human resource
development systems in each region; 2) Enhancing
the capability of the regent and village head
leadership in strategic thinking, innovative thinking,
and situation management skills in various aspects
of community empowerment; 3) Improving the
quality of human resources in regional government
and village government, especially the management
function control skills; 4) Improve the quality of
strategic planning through a process of collaboration
and cross-sector partnerships with stakeholders; and
5) Improve the quality of innovation of goods and
services; and 6) Increase regional superior products
that are sustainable.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Management engineering development program
"Dewi SARTIKA" model, which focuses on assessing
village performance by partnerships between regents,
village heads and stakeholders across sectors is a
diagnostic tool to examine the correlation between the
design of regional or village development
organizations through the empowerment of human
resources. The diagnosis aims to make the process of
change in the system and culture of work in regional
government and village government have a dual
impact on the citizens of the community. Therefore,
the implementation of a system-based intervention
approach such as the "Dewi SARTIKA" model
focuses on systematizing stakeholder evaluations
that create accountability in all aspects of
SARTIKA. So, the successful implementation of
this model relies on regent regulations and village
head regulations and accountability of stakeholders'
assessment processes. Regulation on regional or
village innovation incubator models through the
"Dewi SARTIKA" model development program will
illustrate the capabilities of the leadership of the
regents and village heads in strategic thinking,
innovative thinking, and situation management
skills. Whereas, the accountability of the assessment
process will describe the process of accelerating
performance in the context, inputs, processes and
products.
REFERENCES
Houtzager, P. & Joshi, A., 2008. Introduction: Contours of
Research Project and Early Findings. IDS Bulletin 38
(6).
Gaventa, J. & McGee, T., 2010. Citizen Action and
National Policy Reform: Making Change Happen.
London: Zed Books.
Kerlinger, F. N., 1973. Foundation of Behavioral
Research. New York: Holl, Rinehart and Winston Inc.
Kotter, J. P., & Cohen, D. S., 2002. The Heart of Change:
Kisah Nyata Keberhasilan Orang Mengubah
Organisasi Mereka. Jakarta: Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Peraturan Presiden Nomor 131 Tahun 2015 tentang
Penetapan Daerah Tertinggal Tahun 2015–2019.
Peraturan Presiden Republik Indonesia Nomor 38 Tahun
2015 tentang Kerjasama Pemerintah Dengan Badan
Usaha Dalam Penyediaan Infrastruktur.
Peraturan Pemerintah Republik Indonesia Nomor 38
Tahun 2017 tentang Inovasi Daerah.
Peraturan Pemerintah Republik Indonesia Nomor 46
Tahun 2017 tentang Instrumen Ekonomi Lingkungan
Hidup.
Peraturan Menteri Dalam Negeri Nomor 33 Tahun tentang
2009 Pedoman Pengembangan Ekowisata di Daerah.
Peraturan Menteri Dalam Negeri Nomor 9 Tahun 2014
tentang Pedoman Pengembangan Produk Unggulan
Daerah.
Peraturan Menteri Dalam Negeri Nomor 10 Tahun 2010
tentang Pemberdayaan Masyarakat Melalui
Pengelolaan Teknologi Tepat Guna.
Peraturan Menteri Kemendesa Nomor 19 Tahun 2017
tentang Alokasi Prioritas Penggunaan Dana Desa
untuk Tahun 2018.
Robbins, S. P., & Coulter, M., 2016. Management.
England and Associated Companies: Pearson
Education Limited.
Stufflebeam, D., 2014. CIPP Model for Evaluation: An
Improvement-and Accountability-Oriented Approach
dalam Evaluation Theory, Models, & Applications.
USA: Jossey-Bass.
Undang-Undang Nomor 23 Tahun 1992 tentang
Kesehatan.
Undang-Undang Nomor 32 Tahun 2009 tentang tentang
Perlindungan dan Pengelolaan Lingkungan Hidup
Undang-Undang Nomor 17 Tahun 2007 tentang Rencana
Pembangunan Jangka Panjang Nasional Tahun 2005-
2025.
Undang-Undang Nomor 6 Tahun 2014 tentang Desa.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), 2013.
REFLECTIONS ON SOCIAL ACCOUNTABILITY :
Catalyzing democratic governance to accelerate
progress towards the Millennium Development Goals.
New York.
Wilkins, D., & Carolin, G., 2013. Leadership Pure and
Simple: How Transformative Leaders Create Winning
Organizations. New York: The McGraw-Hill
Companies.
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
164
