
Partnership Valuation of Membership of Indonesia in Asia Pacific
Space Cooperation Organization (APSCO) with STPLEE
Intan Perwitasari
1,2
1
Magister of Economic and Development Studies, UNDIP, Semarang, Indonesia
2
Centre for Aerospace Policy Studies, LAPAN, Jalan Cisadane No. 25, Cikini, Jakarta Pusat, Indonesia
Keywords: Indonesia, APSCO, Benefit Cost Reviews, Multicriteria Analysis.
Abstract: Indonesian membership in Asia Pacific Space Cooperation Organization (APSCO) refers to the provisions of
Presidential Decree of the Republic of Indonesia Number 64 year 1999 on Indonesian Membership and
Contributions Government of The Republic of Indonesia at the international organizations, in article 3 that
first need to be assessed the benefits to be gained and the contribution to be paid. Indonesia's status as a state
signatory to the convention is urgency in this study. Indonesia signed the APSCO convention in 2005 and
actively involved in various activities of the organization forum. The purpose of this research is to identify
the costs and benefits of Indonesia membership in APSCO. The method used is a descriptive qualitative and
quantitative approach to the data sources both primary and secondary data. The results are (i) the membership
will have a high cost impact from economic aspect from annual fee, but high benefit from technical aspect if
Indonesia active on the programme (ii) the benefits and costs of this membership can be equal, or greater by
optimizing action in the organization, (iii) and based on the multicriteria valuation, the technical benefits be
the basis of the first priority, followed by sequential economic, legal, political, social and environmental in
determining Indonesia's membership in APSCO.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Asia-Pacific Space Cooperation Organization
(APSCO) is a collaborative organization outside the
United Nations system for the Asia-Pacific region
initiated by China. The establishment of APSCO aims
to collaborate between countries in the Asia-Pacific
Region in the field of application and development of
space technology, as well as establishing institutions
as a forum for cooperation. On October 27-29 2005 a
meeting was held in Beijing in the context of the
establishment of APSCO, and on October 28, 2005,
Indonesia along with seven other countries, namely:
Bangladesh, China, Iran, Mongolia, Pakistan, Peru,
and Thailand have signed the APSCO Convention.
The LAPAN study (2012, 2018) recommends that
Indonesia immediately ratify the convention which
has implications for the change of status of the
countries signing the convention into APSCO
member countries. Indonesia's participation in an
international organization including APSCO
according to Presidential Decree No. 61 of 1999 must
consider the following (Sekretariat Negara, 1999):
benefits that can be obtained from membership in the
relevant international organization;
1) contributions to be paid as agreed upon and
regulated in the provisions of the organization
concerned and the calculation formula; and
2) state financial capability and financial capacity of
Non Structural Institutions.
Therefore, it is necessary to study the costs and
benefits that Indonesia will get if it becomes a
member of APSCO, and the costs required with
benefit cost review (BCR) approach. Cost-benefit
analysis is a tool to aid to decision making or, and use
in space technology (Hein, Gerald et al., 1976 and
Hockley, Neal., 2014)
The benefits that need to be considered are the
benefits of ideology, politics, economy, socio-
culture, international peace and security, humanity
and other benefits (Sekretariat Negara RI, 1999).
FEM (2007) evaluates benefits and costs by involving
multicriteria namely social, technical, administrative,
political, legal, economic and environmental by
considering benefits and costs not only in monetary
terms but also non-monetary measures. The cost-
benefit analysis clearly embraces an enormous field.
240
Perwitasari, I.
Partnership Valuation of Membership of Indonesia in Asia Pasific Space Cooperation Organization (APSCO) with STPLEE.
DOI: 10.5220/0008429802400245
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World (ICIB 2019), pages 240-245
ISBN: 978-989-758-408-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

It offers clear guidelines for the evaluation of
government decisions in such varied fields (Dreze,
Jean., and Ster, Nicholas. 1987). The decision about
becoming or not becoming a full-member of APSCO,
will depend on many factors, and one of them is
financial performance (Diana, Shinta Rahma and
Syafriana, Maya., 2018). Based on the description,
the purpose of this research is counting and benefit
cost review analysis Indonesia membership on
APSCO from the multicriteria analysis.
2 LITERATURE REVIEWS
2.1 APSCO
The APSCO organization was established with the
initiation of the establishment of the Asia-Pacific
Multilateral Cooperation in Space Technology and
Applications (AP-MCSTA) forum by China, Pakistan
and Thailand in Beijing in 1992. At the signing
meeting, Beijing, October 27-29, 2005, Indonesia co-
signed the APSCO Convention on October 28, 2005
along with seven other countries namely Bangladesh,
Iran, Mongolia, Pakistan, Peru, Thailand and China.
The seven countries have ratified the APSCO
Convention and have become members. Indonesia is
still on progress ratification. The aim of this
organization according to the convention (Article 4)
is (APSCO, 2005):
1) Enhance and strengthen the development of space
programs among its Member States by forming
the basics of peaceful cooperation in the
application of space science and technology;
2) Take effective actions in these areas such as
research and development of space technology,
implementation and training, elaborating and
implementing space development policies.
3) Enhancing cooperation, joint development and
sharing of results among the Member States in the
field of space technology and its application and
space science research by bringing together the
potential of regional cooperation;
4) Encourage cooperation between relevant
companies and institutions of Member States and
improve the industrialization of space technology
and its application;
5) Contribute to the peaceful use of space in
activities of international cooperation in the field
of space technology and its application.
2.1.1 Consequences of Indonesian
Membership at APSCO and Programs
In accordance with the provisions of the Convention,
the APSCO provides equal opportunities for all of its
member countries in utilizing basic activities. Some
of the APSCO activities offered and APSCO member
countries obtain the same benefits as percentage-
based contributions are (LAPAN, 2018):
a) Space Technology Applications, which includes 5
sub-fields namely Earth Observation
Applications, Navigation and Positioning
Applications, Weather Forecast Applications,
Communication Applications, Experimental
Technologies and Applications;
b) Space Technology Development, which includes
8 sub-fields namely Earth Observation Satellite
Systems, Communication Satellite Systems,
Navigation Satellite Systems, Metrological
Satellite Systems, Scientific experimental
satellites, Space Ports, Space Launch, Deep Space
Missions;
c) Space Science which includes 3 subfields namely
Space and solar physics, Study on an exploration
of deep space, Study on space life and
microgravity,
d) Education and Training, which includes 6 sub-
fields namely Short training, Degree education,
Distance education, Space education, Education
resources, cross-country platform development,
International cooperation for education.
e) Space Policies, Law and Regulations, which
include 4 subfields namely Space policies, Space
law, Space regulations, Space Law Research
Center,
f) Capacity Building which includes 5 sub-fields,
namely Data and information sharing and service
capacity, Mission planning and implementation
capacity, Infrastructure construction and
management capacity, Standardization and policy
coordination capacity, Space education and
training capacity.
2.2 Benefit and Cost Analysis
Cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is the method used by
economists to evaluate public policies (Belfield,
Clive., 2012). CBA is a policy assessment method
that quantifies the value to a given agency of public
policy impacts and consequences in monetary terms
with the goal being to help effective social decision
Partnership Valuation of Membership of Indonesia in Asia Pasific Space Cooperation Organization (APSCO) with STPLEE
241

making through efficient allocation of society’s
resources when markets fail (Boardman et al., 2006;
Adler & Posner, 2006). BCA method is in principle
almost the same as the CBA, which is relatively
simpler. Cost Reviews (BCR) benefits are not
complex and more comprehensive so they can cover
the lack of costs and benefits from a monetary
perspective (FEMA, 2007).
3 METHODS
The methode in this paper was descriptive qualitative
and quantitative analysis with benefit cost review.
Loeb, Susanna, et al. (2017) said that descriptive
analysis characterizes the world or a phenomenon to
answering questions about who, what, where, when,
and to what extent, and the goal is to identify and
describe trends, aimed at identifying causal effects,
description plays a critical role in the scientific
process in general.
The data sources were primary and secondary
data. This study modifies FEMA (2007) in benefit
and cost reviews method. The perspective of the
benefit cost from the multicriteria analysis in this
study was from sosial, technichal, political, legal,
economic and enviromental (STPLEE) factors
approach. The steps to conducting BCR are as
follows:
a) list identification;
b) identification benefits and cost reviews; and
c) action priority- qualitative and quantitative
approach.
At this stage a list of identified actions, identify
benefits and cost and assign priorities is carried out
by providing high, medium, and low ratings and
performance associated with the cooperation scheme.
Figure 1: Steps Benefit- Cost Reviews.
4 RESULT
Indonesia's membership in the APSCO organization
will provide benefits and costs that are tangible and
intangible.
4.1 Benefit
Membership in an organization will have an impact
on both the positive and negative rights and
obligations of member countries, including Indonesia
if it becomes ratified by the APSCO convention.
Some benefits if Indonesia becomes an APSCO
member country, as follows:
rights obtained Indonesia to participate in
programs related to the development of space
technology,
Indonesia's membership in APSCO will certainly
enhance bilateral relations between APSCO
member countries in terms of space transfer of
technology. The joining of Indonesia in APSCO
can facilitate the realization of bilateral
cooperation among APSCO member countries,
such as cooperation between Indonesia and China
through LAPAN and the China National Space
Agency (CNSA) which aims to improve the
development of national space research &
development (LAPAN, 2018), and
the right as a member country is also having the
same voting rights, participation in the program
and proposing Indonesian representatives in the
administrative position of the organization.
(LAPAN, 2018; and Nasution, Husni., et al.
2018),
income in salary (LAPAN, 2018, and Nasution,
Husni et. All, 2018), or other benefit likes health
insurance, or fasilities for Indonesian staff
working at APSCO,
participating in promotions and exhibitions
related to space technology in the APSCO
program as part of share and management
marketing, and
extending the organization to improve efficiency
and bargain position, and other.
4.2 Cost
As a member state, the obligations related to the
funding contribution of the APSCO program are
regulated in the provisions of Article 18 (APSCO,
2005). Membership at APSCO has an impact on the
financial consequences of annual fees. APSCO's
annual fee uses to calculate the scale of contribution
by member countries using GDP and population data
issued / published by the World Bank. The results of
the calculation of the contribution (%) of each
member country by using the basis of data taken from
the World Bank are as follows:
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
242
According Table 1, there is a deviation from the
percentage of Indonesia's contribution if it is a
member state of 0.07 percent, where the value will
change every 3 years or other conditions such as (i)
the existence of new member countries, (ii)
macroeconomic conditions of each country
(exchange rates against the US dollar, gross domestic
product, total population), and (iii) increasing
activity. The contribution of each member state,
including Indonesia, will be changed annually
according to the scale of APSCO's annual fee for
basic activities and if additional for optional
activities. Differences in the calculation of the scale
of contributions from the previous 2 studies indicate
the possibility of misdata, so for the initial analysis
for the LAPAN report (2018a) use a version of
APSCO.
Table 1: Percentage of State Contributions of APSCO and
Indonesia Members 2015-2017 (USD).
Country
Persentage
(A)
APSCO
Versi
(B)
Deviation
(A-B)
Bangladesh 8 8 0
China 18 18 0
Iran, Islamic Rep. 10,11 9,08 1,03
Mongolia 4,61 4,19 0,42
Pakistan 8 8 0
Peru 7,63 7,99 -0,36
Thailand 7,52 7,87 -0,35
Turkey 15,12 15,75 -0,63
Indonesia 7,88 7,81 0,07
TOTAL 76,87 76,63 0,24
Source: LAPAN (2018), data processed
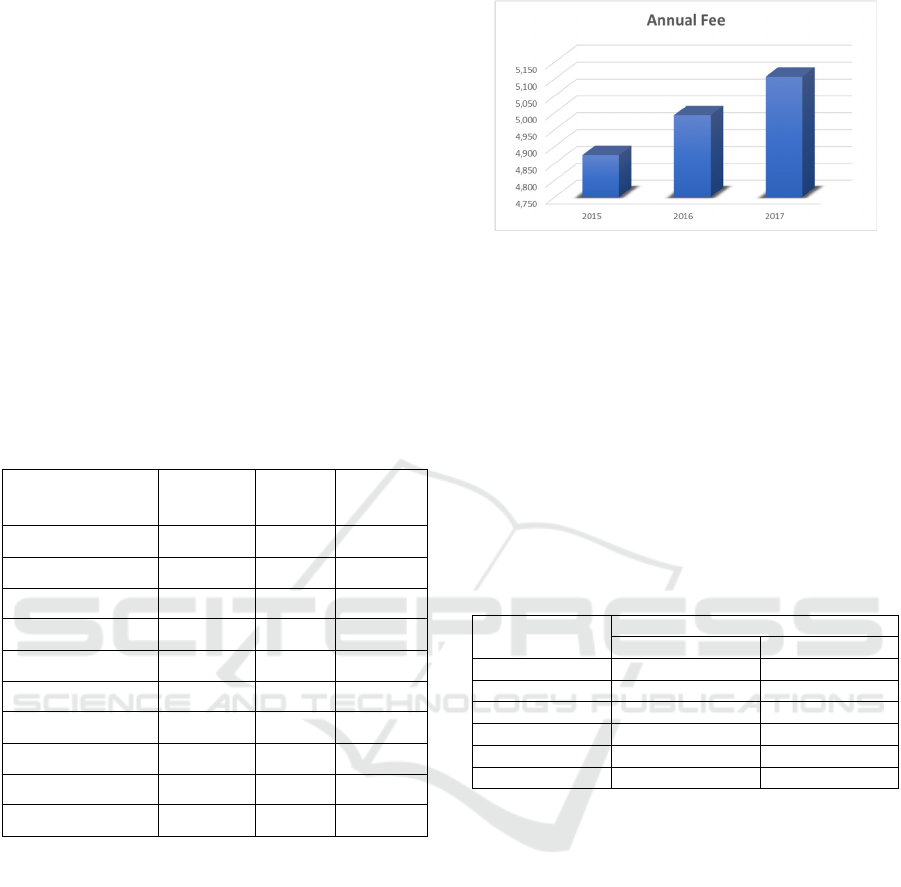
If we are assuming the amount and data are same
with planed expenditure in 2015, 2016, and 2017, that
if Indonesia becomes a member state it will have an
increasing annual fee (See Fig 1). The trend of
annulling fee slope is positif (increase), for staff,
basic activity and administrative expenditure.
LAPAN (2018a) has calculated Indonesia's annual
fee estimates in 2015-2017. From these calculations,
if 2015 is the base year, it will show how much
progress, the trend is increasing each year. This value
increases by 2.42 percent in 2016, and increase by
4.75 percent in 2017. Thus, if Indonesia will become
a member in 2019, then what needs to be anticipated
is an annual fee increase every year. This is based on
the provisions of member contributions that have
been arranged in the organization.
Source: LAPAN (2018a), data processed
Figure 2: Estimated Indonesian Annual Contribution to
APSCO (in IDR Million).
4.3 Benefit-cost Reviews
From Fig 2, the obligation of annual fees in the
calculation of 2017 is equal to 5,106 billion Rupiah.
Based on the assumption that if 2019 is the same
value that is paid to APSCO, then the need to see the
priority of how important benefits can be taken from
the membership. In Table 2, the priority of benefits
and costs can be seen from the social, technical,
political, legal, economic and environmental aspects.
Table 2: Prioritization using STPLEE.
Action
Criteria
Basic Activit
y
BENEFIT COST
Sosial L M
Technical H L
Political M L
Le
g
al M H
Economic L H
Enviromental L L
Definition: H-High, M-Medium, L-Low
Source: data processed
The finding in these studies, Indonesia has created
high benefits from technical aspects, medium benefits
from political and legal aspects and low benefits from
social, economic and environment aspect. From this
membership will have an impact to cost, that high
cost from legal and economic aspects, medium cost
from the social aspect, and low cost from the
environment, technical, and politic aspects (see Table
2). The high priority of technical factor is based on
the benefits that can be obtained, from the basic
activity program can support in terms of collaborative
research collaboration and increase capacity building
for mastering space technology. So, it can be
concluded that utilization that has technical benefits
must be optimized from the organization. This is
because on a cost basis, it has high consequences
from economic and political aspects.
Partnership Valuation of Membership of Indonesia in Asia Pasific Space Cooperation Organization (APSCO) with STPLEE
243

From a cost and benefit perspective it can be
assumed to have an equal score (costs (-3) = benefits
(3)), and this benefit can be greater. LAPAN reports
(2018) shows that the benefits of Indonesia's
membership to APSCO are greater than the costs
incurred. However, there are other costs and benefits
that are not measurable, intangible, where the value
will be greater. Table 3, it can be seen that technically
the benefits from APSCO are highest, followed by
legal benefits, while in terms of costs they have
consequences on costs from technical, legal and
economic aspects (see Tabel 3).
Table 3: Valuation Benefits and Cost.
Action
Criteria
Basic Activity
BENEFIT COST
Sosial 0 0
Technical 2 1
Political 0 0
Legal 1 1
Economic 0 1
Enviromental 0 0
Sub Total Of
Cost/ Benefi
t
3 3
Definition: 2=Very beneficial, 1=Favorable, 0=None/Not
applicable, -1=Not Favorable
Source: data processed
Table 4: Priority Action from Benefit and Cost Reviews.
No
Action
Criteria
Basic Activity
Benefi
t
Cos
t
Priority
1
Sosial
Increase the
bargaining
position as
member states
and organization
Improving data
sharing to
mitigation
none
5
2
Technic
al
Use of research in
the fields of
regulation, space
law, the science
between
examinations,
space
technology,
space
applications
Capacity building
(short training
course, degree
education
program, etc)
Admini
strative
to
support
progra
m
Resear
ch in
domest
ic to
transfer
knowle
dge
1
3
Political
APSCO as a
forum to
establish
connectivity with
member states
and open bilateral
cooperation
b
etween partners
politic
cost
(no
data
availab
le yet)
4
No
Action
Criteria
Basic Activity
Benefi
t
Cos
t
Priority
to obtain the
transfer of
technology
increasing
national pride
4
Legal
Indonesia has
the right to
determine
policies and make
decisions about
APSCO
admini
strative
(additi
onal
regulat
ory
require
ments
related
to
nationa
l
legislat
ion)
3
5
Econom
ic
Salary if
occupying a
strategic position
in the
administration
Savings budget
space savings in
b
asic activity
annual
fee
2
6
Envirom
ental
Encouraging
stability in the
Asia Pacific
Region
(no data
available
yet)
6
Source: data processed
In Table 4, it shows the priority scale, so to
optimize the benefits of Indonesian membership at
APSCO it is necessary to actively participate in the
use of the forum for technical needs, and support
national space programs. This is because annual fees
that have to be spent are very large compared to other
international organizations. To optimize the benefits
and cost reviews of this membership, the strategies
that must be taken are:
a) national coordination related to involving
academics, industry and government for
opportunities for participation and collaboration
from the cooperation offered,
b) active participation in APSCO;
c) utilize rights in organizations in accordance with
national interests; and
d) sets a national roadmap related to the APSCO
program.
5 CONCLUSSION
From this study, Indonesia's membership in APSCO
can conclude that the benefits and costs obtained are
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
244

both tangible and intangible thats not come from only
one aspect but many aspects such as social, technical,
legal, political, economic and environmental. From a
qualitative valuation, technical benefits are the
highest priority, followed by legal and political
aspects as a medium priority. From weigthing score,
the benefits and costs of this membership can be
equal, or greater by optimizing action in the
organization. Then from benefit and cost reviews
based on the multicriteria valuation, the technical
benefits are the basis of the first priority, followed by
sequential economic, legal, political, social and
environmental in determining Indonesia membership
in APSCO.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thank You for Dr. Mardianis, and my partner at
POKLIT 1 for supporting data and information in this
paper.
REFERENCES
Adler M. & Posner, E. 2006. New Foundations of Cost-
Benefit Analysis. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University
Press.
APSCO. 2005. Convention of APSCO
Belfield, Clive. 2012. How Does Cost-Benefit Analysis
Help Determine Public Value?. Conference on
Creating Public Value in a Multi-Sector, Shared-Power
World at the University of Minnesota, September 20-
22, 2012. Download: https://appam.confex.com/
appam/2012/webprogram/Paper4039.html
Boardman, A. E., Greenberg, D. H., Vining, A. R. and
Weimer, D. L. 2006. Cost-benefit Analysis: Concepts
and Practice (3rd edition). New York, NY: Prentice
Hall
Diana, Shinta Rahma and Syafriana, Maya., 2018.
Indonesias Membership of Asia-Pacific Space
Cooperation Organization (APSCO): Organizational
Performance with Stochastic Analysis. Global and
Stocastic Analysis. Vol 5, Number 5, Spesial Issues
2018: MUK Publication
Dreze, Jean., and Ster, Nicholas. 1987. Chapter 14 The
Theory of Cost-Benefit Analysis. Handbook of Public
Economics, Volume 2. Page 909. Download:
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1573-4420(87)80009-5
FEMA. 2007. Using Benefit-Cost Reviews in Mitigation
Planning. State and Local Mitigation Planning How-
To Guide Number Five. FEMA 386, 5 May 2007. US:
Washington. Download: https://www2.illinois.gov/
iema/Mitigation/Documents/Plan_FEMA_HTG5.pdf
Hein, Gerald et.all, 1976. Cost Benefit Analysis of Space
Technology. NASA. November 1976. Download:
https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19
770004965.pdf
Hockley, Neal., 2014. Cost–Benefit Analysis: A Decision-
Support Tool or a Venue for Contesting Ecosystem
Knowledge?. SAGE Journals. download:
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1068/c1384j
LAPAN. 2015. Pengkajian Kebijakan Keantariksaan
nasional pada Asia-Pacific Space Coopertaion
(APSCO). Laporan DIPA. Pusat Kajian Kebijakan
Penerbangan dan Antariksa. Desember 2015: Jakarta.
LAPAN, 2018. Draft Naskah Urgensi Ratifikasi Konvensi
Organisasi Kerjasama Keantariksaan Asia Pacific
(Asia-Pacific Space Cooperation Organization –
APSCO). Pusat Kajian Kebijakan Penerbangan dan
Antariksa: Jakarta
LAPAN. 2018a. Biaya dan Manfaat Keanggotaan
Indonesia pada Asia-Pacific Space Coopertaion
(APSCO). Ringkasan Eksekutif. Pusat Kajian
Kebijakan Penerbangan dan Antariksa
Loeb, Susanna, et.all, 2017. Descriptive analysis in
education: A guide for researchers. Download:
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED573325.pdf
Nasution, Husni., et.all. 2018. Indonesia Membership on
Asia Pacific Space Cooperation Organization
(APSCO): Cost and Benefit Analysis. Jurnal
Hubungan Internasional, Tahun XI, No. 1, Januari-Juni
2018
Sekretariat Negara RI. 1999. Keputusan Presiden RI Nomor
64 Tahun 1999 Tentang Keanggotaan Indonesia dan
Kontribusi Pemerintah Republik Indonesia pada
Organisasi-Organisasi Internasional: Jakarta.
Partnership Valuation of Membership of Indonesia in Asia Pasific Space Cooperation Organization (APSCO) with STPLEE
245
