
Evaluation of Internal Control Design and Implementation of
Revenue Cycle: Case Study on Hotel ABC
Dafne Etty Melinda Malau and M. Malik
Master of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Indonesia, Jl. Salemba Raya 4 Salemba, Jakarta,
Indonesia 10430
Keywords: Internal Control, Revenue Cycle, Hotel.
Abstract: The hospitality industry in Indonesia continues to grow along with the increase popularity of tourism sector
in Indonesia. This caused the hospitality industry to become competitive. Therefore the hotel must be able to
manage the overall source of income to be able to create a stable profit stream. For this reason, supervision
of internal control is needed. With good internal control, the hotel can avoid threats in carrying out its
operational activities. This study aims to evaluate the design and implementation of the internal control system
in the revenue cycle. . The method in this research is descriptive analysis in the form of the case study. The
data obtained through observation, interview and analysis on the company internal documents. The results
show that there were weaknesses in Hotel ABC’s internal control design, where giving discounts, room
pricing, complimentary rooms are not monitored properly, and there are some sales recording procedures that
are done manually that had an impact on company's profits. Therefore this study provides recommendations
for improvements of internal control activities that will address those issues.
1 INTRODUCTION
Hospitality industry in Indonesia shows a significant
increase in the recent years. Based on data from the
Central Bureau of Statistics, the number of star-rated
hotel accommodations in Indonesia in 2016
increased 8.6% compared to 2015, while the number
of non-star hotel accommodations in 2016 also
increased 1.8% compared to 2015. The hospitality
industry continues to grow along with the increasing
popularity of tourism sector in Indonesia. e-tourism
created new phenomena related to hotel sales.
Among them is the creation of new distribution
channels to increase hotel room sales. These include
OTA sales, social media, events and conference
organizers, all of which aim to provide more options
in room sales (Stangl et al., 2016 in Xu et al., 2017).
This caused the hospitality industry to become
competitive. Therefore, hotels must be able to
manage their overall source of income better than
competitors, in order to create a stable profit stream
by investing in sources of income that provide the
greatest income and also maintain integrity in
carrying out pricing strategies to achieve business and
financial goals that established (Green & Lemono,
2012 in Dolasinski et al., 2018).
Hotel ABC has been actively running its
operations since 2011. The main source of income
including:
1. Room sales
2. Sales of F & B (restaurant and banquet)
3. Spa package sales
4. Playground ticket sales
Where the percentage of each sales unit against total
income is described as in table 1.
Table 1: Sales Percentage Table.
Room
F&B
Spa
Playground
2017
31%
60%
2%
7%
2016
30%
57%
3%
10%
2015
27%
64%
2%
7%
2014
27%
52%
1%
19%
According to the table above, it can be seen that
Hotel ABC's biggest income currently comes from
F & B sales, while the sales of rooms at ABC Hotels
which should be the main source of income for the
hospitality business has not yet given maximum
results.
Malau, D. and Malik, M.
Evaluation of Internal Control Design and Implementation of Revenue Cycle: Case Study on Hotel ABC.
DOI: 10.5220/0008431403730379
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World (ICIB 2019), pages 373-379
ISBN: 978-989-758-408-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
373
In a study conducted by Russo, 1991 in Morgan
(2018) it was found that hotel revenue was created
from (1) pricing for each room and type of room,
and (2) changes in room occupancy. There are two
indicators in measuring the performance of hotel
room sales. The first indicator is Average Room
Rate (ARR) = Total room income / Total rooms sold
and second indicator Revenue per Room Available
(RevPar) = Total room income / Total rooms
available, where ideally the number of ARRs =
RevPar which indicates that the occupancy rate
reaches 100% . Following are the ABC Hotel ARR
and RevPar calculations:
Table 2: ARR and RevPAR Calculation Tables.
ARR
RevPAR
2017
313.342,92
107.100,61
2016
337.841,50
106.926,84
2015
309.688,96
143.231,14
2014
333.301,26
123.754,76
2013
388.231,32
138.055,06
According to the table 2, it appears that RevPAR
Hotel ABC for the past 5 years is far below its ARR
which indicates that the sales performance of hotel
rooms is not good.
Hotel ABC continues to make various efforts to
increase the potential of room sales, including by
cooperating with OTA, providing monthly promos,
and giving discounts for group stays. In its
implementation, problems arise, especially in terms
of price discounting and the provision of
complimentary rooms carried out by the marketing
department that are not according to the rules created
by management.
Barry, Yayla, Papastathis in Yemer (2017)
explained that poor income performance is a result of
the low quality of service, absence of a system that
creates long-term relationships with customers, and
results from weak internal controls. Therefore there is
a management tool that can control and supervise the
income from each hotel source of income.
The quality of internal controls can be assessed by
reviewing the design and implementation through the
COSO Integrated Framework. COSO Integrated
Framework. Therefore, the components of the COSO
framework must be implemented and enabled so that
the internal control system can run optimally. This is
the background of the author to raise the title
"Evaluation of Design and Implementation of Internal
Control in the Revenue Cycle (Case Study on ABC
Hotels)"
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Internal Control
According to the Institute of Internal Auditors (2016)
internal control is a process that is influenced by the
board of directors, management and other personnel
of the company designed to provide reasonable trust
regarding the achievement of objectives of
operational activities, reporting and compliance.
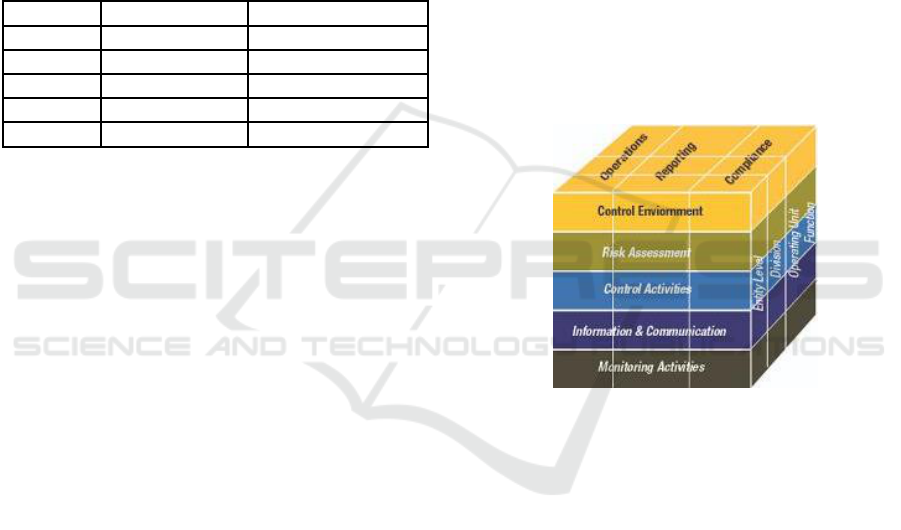
2.1.1 Internal Control According to COSO
Internal control according to COSO Internal Control
- Integrated Framework 2013 has three categories of
objectives: operations, reporting and compliance and
consists of five components of internal control:
Control Environment, Risk Assessment, Control
Activities, Information and Communication, and
Monitoring Activities.
Figure 1: COSO's Internal Control.
This integrated COSO 2013 internal control
framework, as in figure 1, views each component of
internal control as appropriate and relevant for the
entire company, therefore stipulating that all
components must be present and functioning
simultaneously in an integrated system.
2.2 Accounting Information Systems
Romney and Steinbart (2017) explain that accounting
information systems are systems that collect, record,
store and process data to produce information for
decision making. This includes people, procedures,
instructions, data, software, information technology
infrastructure and internal controls and system
security.
Romney and Steinbart (2017) added that a well-
designed accounting information system could create
values for companies by improving quality and
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
374

reducing production costs due to increased efficiency
and effectiveness in conducting operational activities.
2.2.1 System Documentation Technique
The design of a system needs to be documented to
explain how the system works. In his book, Romney
and Steinbart (2017) explain there are several
methods for documenting a system:
1. Data flow diagram (DFD) that displays
graphically the origin of the data, data flow, data
transformation process, data storage and final
destination data.
2. A flowchart that displays graphically a system,
where there are 2 (two) types of flowcharts, including
document flowchart to describe a system graphically
related to the flow of documents and information
between divisions or departments responsible and
flowchart programs to show logical operational
sequences when the computer runs a program.
3. Business process diagrams that will make
graphical descriptions related to the business
processes of an entity. Some of the symbols used to
make DFD and flowcharts are as follows:
2.3 Revenue
According to IAI in PSAK 23 Paragraph 7: Revenue,
revenue is defined as gross inflows of economic
benefits arising from the entity's normal activities
during a period if the inflows result in an increase in
equity that does not originate from the contribution
of investors. In this case, recognized revenue does
not include amounts that are billed for the benefit of
third parties, such as value added tax or sales tax. In
the hospitality industry, the revenue received is
mostly related to the sale of services. Paragraph 20 of
PSAK 23 states that the requirement for recognition
of service sales revenue is if the transaction results
related to the sale of such services can be estimated
reliably with reference to the level of transaction
settlement at the end of the reporting period.
2.4 Definition of Revenue Cycle
Romney and Steinbart (2017) define the revenue
cycle as a series of business activities and repetitive
data processing operations related to the supply of
goods and services to customers and collect
payments for those sales.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Methods
This research is a case study research that uses an
evaluation method with a descriptive qualitative
approach. Denzin and Lincoln, 2004 in Sri Wahyuni
(2015) say qualitative research is a multi-focus
method, involving an interpretive, naturalistic
approach to the subject matter. This method was
chosen with the consideration that the purpose of this
study is to explore a process and phenomena that
occur in the field and then draw conclusions from the
phenomena that occur.
3.2 Case Selection
This study selects cases originating from the income
cycle. This is based on the consideration that the
income post always receives special attention from
the management because it affects the business
continuity of an entity. Therefore, the authors assess
that this study can have a positive impact on the
object of research, Hotel ABC.
3.3 Unit Analysis
This research will be conducted with a case study
approach on one object of research. The object of
research chosen was Hotel ABC, an entity engaged
in hospitality. The selection of ABC Hotels as a place
to conduct research because, in general, there is
limited access to hotel financial information. This
study will conduct observations on Hotel ABC, with
the consideration that Hotel ABC has problems in its
internal control which affect the overall revenue of
the hotel.
3.3.1 Overview of Hotel ABC
ABC Hotel stands on 4.3 hectares of land consisting
of 47 villas with 4 room types, spa, restaurant,
multifunctional room and playground. The ABC
hotel carries the concept of a private villa with a
touch of traditional furniture with a wooden stage
house feel that describes the authentic characteristics
of West Kalimantan.
Hotel ABC's revenue comes from 4 (four) main
activities,including revenues from hotel sales,
revenues from food and beverages sales, spa sales,
and playground ticket sales. Below will be described
the business processes of the four activities listed
below:
Evaluation of Internal Control Design and Implementation of Revenue Cycle: Case Study on Hotel ABC
375

a. Hotel room sales
Guests make hotel room reservations through a
variety of booking options (walk in, online travel
agents, marketing). The reservation will
automatically enter the ABC Hotel reservation
system and guests will get proof of reservation in
the form reservation form. At check in Front
Office (FO) will request proof of reservation to be
matched with Reservation Form. After the check-
in process is complete, the FO will provide the
room key, access card, and breakfast coupons to
guests.
At check out, the room key is handed over to the
front office and housekeeping will check the room
to check the furniture condition again. if
everything is safe, then the check-out process can
continue.
b. Food and beverages sales
Visitors make orders, which will be inputted to
the system, at the time of payment, the cashier
will print bills and visitors will make payments.
c. Spa sales
Visitors do maintenance with a spa package that
has been selected, which will be inputted to the
system, at the time of payment, the cashier will
print the bill and the visitor will make a payment.
d. Playground ticket sales
Visitors make a purchase for a playground ticket,
the number of tickets sold will be input to the
system, at the time of payment, the cashier will
print the bill and the visitor will make a payment.
3.4 Data Collection Techniques
The data used in this study consisted of primary data
and secondary data.
1. Primary data
Primary data is obtained directly from Hotel ABC
during the data collection process. This primary
data includes:
a. Data from interviews
Interviews were conducted with the ABC
division of finance and sales division.
b. Internal documentation obtained from Hotel
ABC is as follows:
• Hotel ABC sales report
• Organizational structure
• SOP
2. Secondary Data
Secondary data obtained from publicly published
data, including legislation and other data related
to the company's operations.
3.5 Analysis Methods
This study uses data obtained to analyze accounting
information systems and internal control practices in
the income cycle at ABC Hotels. The analysis will
produce information on the comparison of internal
control practices with existing formal procedures.
The results of interviews, observation and analysis of
the company's internal documents will produce an
overview of current operational activities and the
design of system development which can be the basis
for the preparation of a framework for accounting
information systems and internal controls.
4 RESEARCH RESULTS
4.1 Analysis of Control Activities
In the Hotel ABC revenue cycle, there are several
external parties that interact with the system,
including guests, banks, management and accounting
information systems owned by Hotel ABC. Each type
of sales will be discussed in the revenue cycle at ABC
Hotels, including hotel room sales, food and
beverages sales, spa sales and playground ticket
sales.
4.1.1 Hotel Room Sales
These internal control activities are grouped based on
the business processes found in the Hotel ABC
learning cycle, namely the order process, service
delivery process, billing process, and the process of
receiving money.
This study finds weaknesses include:
1. Pricing, discounts and complementary rooms
are still done manually. This causes the risk of
the billed value not to be in accordance with the
value that should be billed in accordance with
the room price set by the company and causes
the risk of rising occupancy without an increase
in revenue which will further reduce RevPAR.
Based on the results of interviews with senior
marketing, this is because there are no rules that
explicitly determine the maximum discount and
complementary rooms so that the marketing
division provides a large discount and a number
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
376

of complementary rooms so that group guests
want to hold an event at the ABC Hotel.
2. Lack of control activities in the billing process.
Especially for guests from government
agencies. Based on the results of interviews
with financial staff, this was due to government
agencies contributing large margins to ABC
hotel sales as a whole, so Hotel ABC decided
not to be too aggressive in billing.
Based on the analysis above, this study will re-
describe the business activities of selling hotel rooms
with the addition of internal control activities. This is
done to facilitate Hotel ABC in implementing the
proposed improvements from this research that are
related to business processes and operational
activities of ABC Hotels. The following are proposed
hotel room sales flowcharts, as in figure 2 and figure
3, which are divided into 2 main activities:
Check In Process
Figure 2: Proposed Flowchart for check in process.
Check Out Process
Figure 3: Proposed Flowchart for check out process.
Based on the analysis above, this study will re-
describe the business activities of food and beverages
sales with the addition of internal control activities
referring to the weaknesses above. This was done to
facilitate Hotel ABC in implementing the proposed
improvements from this research that were linked to
the business processes and operational activities of
the ABC Hotel. The proposed flowchart is described
as follows:
Figure 4: Proposed Flowchart for Food and Beverages
Sales.
4.1.2 Food and Beverages Sales
These internal control activities are grouped based on
the business processes found in the Hotel ABC: the
order process, service delivery process, the billing
process, and the process of receiving money.
It is known that the control activities in food and
beverages sales are running quite well, but there are
still some control activities that have not been
implemented which have resulted in weaknesses:
1. Non-strict supervision related to existing raw
material inventories.
2. Recording of visitor payment methods is still
done manually, so there is a possibility of
recording errors that may result in possible
billing errors.
4.1.3 Spa Sales
These internal control activities are grouped based on
business processes found in the Hotel ABC revenue
cycle: the order process, service delivery process,
billing process, and the process of receiving money.
Based on analysis it is known that the weakness
of control activities in sales is caused by the existing
control activities that have not been adequately
designed through adjusting the internal procedures of
the ABC Hotel. These disadvantages include:
Evaluation of Internal Control Design and Implementation of Revenue Cycle: Case Study on Hotel ABC
377
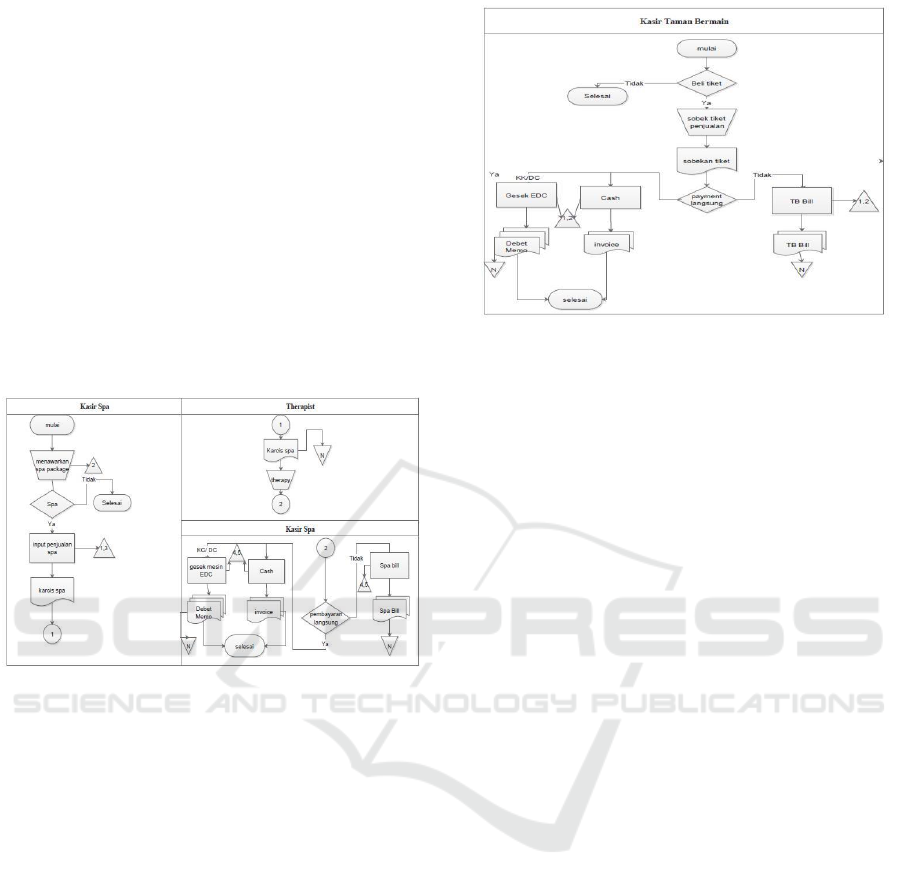
1. Lack of supervision on spa package booking
activities and supervision of spa supplies so as to
enable potential fraud committed by therapists.
2. Recording of visitor payment methods is still
done manually, so there is a possibility of
recording errors that may result in possible billing
errors.
Based on the analysis above, this study will
describe the spa sales business activities with the
addition of internal control activities. This was done
to facilitate Hotel ABC in implementing the proposed
improvements from this research that were linked to
the business processes and operational activities of
the ABC Hotel. The following figure 5 is the
proposed flowchart described as follows:
Figure 5: Proposed Flowchart Spa Package Sales.
4.1.4 Playground Ticket Sales
These internal control activities are grouped based on
the business processes found in the Hotel ABC: the
order process, service delivery process, the billing
process, and the process of receiving money.
Based on the results of observations in the field
and interviews with informants during the study, it
was found that not all internal control activities were
implemented. There are still a number of control
activities that have not been implemented which have
resulted in weaknesses, including recording the
method of selling a playground ticket and recording
payments is still done manually, so that the error of
recording and fraud is possible.
Based on the analysis above, this study will
describe the playground sales business activities with
the addition of internal control This was done to
facilitate Hotel ABC in implementing the proposed
improvements from this research that were linked to
the business processes and operational activities of
the ABC Hotel. The proposed flowchart is as follows:
Figure 6: Proposed Flowchart Playground Ticket Sales.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Conclusions
This research was conducted to analyze internal
control activities in the ABC Hotel revenue cycle.
When viewed from the analysis of control
activities carried out, it can be concluded that:
a. At current hotel room sales pricing, discounting
and complementary rooms made by marketing
are carried out with minimum supervision from
the General Manager, this causes a difference
between occupancy and revenue levels. This
can be seen from the calculation of ARR and
RevPar for the past 5 years.
b. At the sales of food and beverages, spa and
playground recording the sales transaction
method and payment method are still done
manually.
5.2 Suggestions
Based on the results of the analysis of internal control
on Hotel ABC and identification of
existing weaknesses, this study provides
suggestions:
For Hotel ABC:
1. Improvement of control activities starting from
the improvement of sales recording procedures,
especially for recording procedures that are still
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
378

running manually, pricing procedures, giving
discounts, complementary rooms and billing
procedures.
2. In the long term, considering the expected
volume of transactions that will increase, it is
necessary to consider improving or developing
the accounting information system that
currently implemented.
For Academics and Future Research:
Future research is expected to broaden the scope of
research not only for the revenue cycle but also
expand the scope of the entire business cycle of the
company.
REFERENCES
Addey, Josephine Nana Ama. (2012). An assessment of
internal control system on the image of the hospitality
industry in Royal Mac-Dic Hotel and Capital View
Hotel: http://hdl.handle.net/123456789/4833
Badan Pusat Statistik (2017), (online), (https://bps.go.id )
Cheng, Qiang and Goh, Beng Wee and Kim (January 16,
2017). Internal Control and Operational Efficiency.
Contemporary Accounting Research
Chris Guilding (2014). Accounting Essentials
forHospitality Managers. New York: Routledge
COSO Internal Audit Integrated Framework. (2013).
(www.coso.org)
Creswell W. John (2013). Research Design Pendekatan
Kualitatif, Kuantitatif, dan Mixed. Yogyakarta: Pustaka
Pelajar.
Hall, J.A. (2011). Accounting Information System Seventh
Edition. Ohio: South-Western
Ikatan Akuntan Indonesia. (2015). Standar Akuntansi
Keuangan per efektif 1 Januari 2015. Jakarta: Ikatan
Akuntansi Indonesia
Jo Dolasinski, Mary & Roberts, Chris & Zheng, Tianshu.
(2018). Measuring hotel channel mix: A Dea-Bsc
Model. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism.
Karagiorgos, Theofanis and Drogalas, George and
Giovanis, Nikolaos. (2011). Effectiveness of Internal
Audit in Greek Hotel Business. International Journal of
Economic Sciences and Apllied Research, Vol. 4, No.
1, pp. 19-34: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1806943
Kementerian Pariwisata. (2017). Jumlah Kunjungan
Wisatawan Mancanegara Menurut Pintu Masuk dan
Kebangsaan, (online), (http://kemenpar.go.od/asp/detil.
asp?c=110&id=350
Romney, M. B., & Steinhart, P. J (2015). Accounting
Information Systems (13th Edition). Kendallville:
Pearson
Romney, M. B., & Steinhart, P. J (2017). Accounting
Information Systems (14th Edition). Kendallville:
Pearson
Moeller, R. R. (2014). Executive Guide to COSO Internal
Control: Understanding and Implementing the New
Framework. John Wiley and Sons,
Morgan, Kevin. (2018). An Empiral Study in the U.S Hotel
Industry: How Quality Assurance, Customer
Satisfaction, Brand Signaling, And Guest Loyalty
Impact Revenue. Dissertation, Georgia State University
(https://scholarworks.gsu.edu/bus_admin_diss/94 )
Wahyuni, S. (2015). Qualitative Research Method: Theory
and Practice 2nd Edition. Jakarta: Salemba Empat
Yemer Maefin, Chekol Firew. (2018). The effect of internal
controls systems on hotel revenue. A case ofhotels in
Bahir Dar and Gondar Cities. Oman. Chapter of
Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review
2017 Vol.6 Issue 6, pp. 19-37
Xu, X. and Li, Y. (2017). Maximising hotel profits with
pricing and room allocation strategies. Int J. Services
and Operations Management, Vol. 28, No.1, pp.46-63.
Zekeriya Yetis, Huseyin Cetin. (2017). Evaluation of the
Effectiveness of the Internal Control System in Hotel
Businesses. ISBN: 978-1-943579-61-7
Evaluation of Internal Control Design and Implementation of Revenue Cycle: Case Study on Hotel ABC
379
