
The Connectivity as Value Strategic: The Development the Digital
Media in Bolivia
Kruzkaya Ordóñez
a
, Abel Suing
b
, María Isabel Punín
c
and Mishell Jaramillo
Department of Communication, Universidad Técnica Particular de Loja, San Cayetano Alto, Loja, Ecuador
Keywords: Digital Convergence, Digital Media, Conecctivity, Internet, Bolivia.
Abstract: Access to the Internet is accepted by the United Nations as a human right. This declaration states that all
countries must guarantee Internet access and freedom of expression for all people. In this sense, Bolivia has
experienced remarkable progress, so, between 2015 and 2017 Internet access covered 45%, with more
incidence in the urban area, but there is still a need to provide a higher coverage of this service, to more than
half of its habitants. A pending issue is the enlargement of connectivity coverage. This scenario and conditions
allow the performance analysis of Bolivian digital media. The research study is focused on eight native and
traditional media that have been uploaded to the web. The methodology used is mixed (qualitative and
quantitative) through an extended file. The file includes indicators such as: media morphology, accessibility,
interactivity, hypertextuality, multimedia, constant updating, usability, new trends in journalism, presence in
social networks and digital platforms as content support.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital convergence has meant that more than 55% of
the world's population have access to the web
(Internet World Stats, 2018) and is involved in a
digitalization process in several ambits. According to
Mayer (2011), "Internet has gradually and
unstoppably gained ground in all spheres of our lives,
from leisure and entertainment activities to the way in
which social relations are established, constituting a
source of information"
Variations in the digital field are different in each
nation, some present greater obstacles to their
development, richer countries tend to be globally
connected in terms of depth and breadth, while
countries with geographical locations that do not have
access to the sea have a negative association of
connectivity (Ghemawat and Altman, 2016).
The deployment of the Internet allows people to
be connected and access information of all kinds. This
has led to the massive use of smart devices that help
improve the quality of life in the population in
personal and professional environments. Among the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2360-8188
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4234-5926
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2117-6991
business models that have emerged from connectivity
is Crowdfunding, social solutions, digital
entrepreneurship and digital applications (Ortiz and
Rojas, 2014).
In the digital context the connectivity according to
the Report 2018, Mapping your transformation into a
digital economy, published by Global Connectivity
Index (GCI), Bolivia reached a score of 25 that is to
say, it was placed in the classification between 20 -24
of the nations that are in the stage of development of
the TIC infrastructure and pending to expand
connectivity coverage so that more people can access
and be an active part of the ecosystem and the digital
economy.
Bolivia this evaluation in spite of has remarkable
progress, so, between 2015 and 2017 the enlargement
of Internet in this nation covered 45%, with more
incidence in the urban area, but there is still a need to
provide and favour this service to more than half of
its in habitants.
In addition, Bolivia, among the countries of the
Andean Community, the lowest score in terms of
connectivity compared to Colombia, which registers
39 points, followed by Peru with 37 and Ecuador with
Ordóñez, K., Suing, A., Punín, M. and Jaramillo, M.
The Connectivity as Value Strategic: The Development the Digital Media in Bolivia.
DOI: 10.5220/0008506405170524
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2019), pages 517-524
ISBN: 978-989-758-386-5
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
517

31 (GCI, 2018). These three countries have the
highest GDP growth in terms of investment in the TIC
infrastructure. In this approach, Bolivia must attend
the growing demand for high-speed connectivity to
facilitate the digitalization of the industry and
economic growth.
In this way, the selection of the Bolivian territory
is justified to raise the study on the performance of
the cybermedia. It also looks at the limitations it has
for the deployment of the Internet added to the lower
levels of connectivity, caused by the lack of
infrastructure because that the country is surrounded
by land, that has been situation that has been
occurring since 1879 (Los Tiempos, 2018).
Having no access to the sea reduces the ability to
connect submarine fiber optic cables. Therefore,
Bolivia requires alliances with other countries in
order to act as intermediaries to facilitate connection
to its citizens, however, this generates a high cost in
Internet rates (Salaverría, 2016).
This is the scenario, at the technological level, that
is presented for evaluate the digital media in Bolivia,
and the study itself sets out the objectives: 1) to
observe the architecture of information, 2) to know
how digital media are developed in the framework of
transformation digital and its adaptation to the
process with its web information services and the
lacks that are detected.
2 METHODOLOGY
The study of digital media in Bolivia use as a
reference the studies carried out by Said and Arcila
(2011) "Cybermedia in Latin America and Web 2.0".
The methodology used is mixed (qualitative and
quantitative) through an extended file. The file
includes indicators such as: media morphology,
accessibility, interactivity, hypertextuality,
multimedia, constant updating, usability, new trends
in journalism, presence in social networks and digital
platforms as content support.
The selection the sample is established on the
basis of the ranking "Top sites by country" (Alexa
2018). "To determine the ranking [...] Alexa estimates
the average number of visits and impressions per day"
(Digital Guide,2017), and for obtain the registration
of the domain of the pages digital tool was used Who
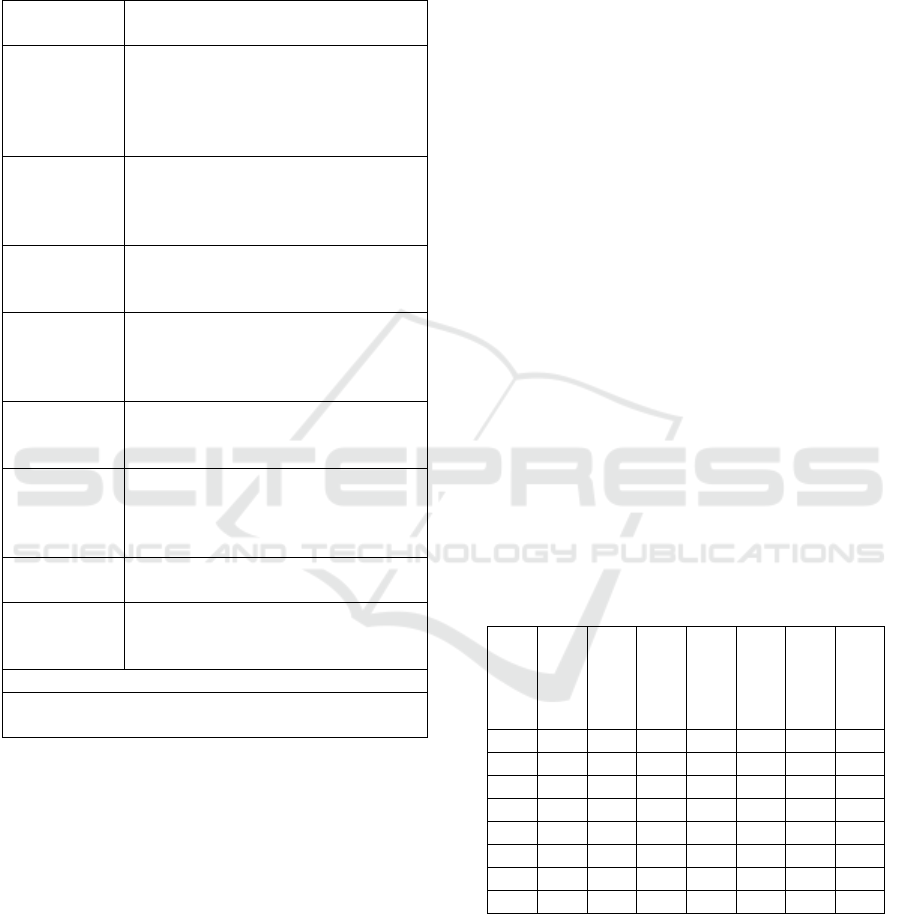
is Lookup (table 1). The digital media for study are:
El Deber (Santa Cruz), Los Tiempos and El Diario
(Cochabamba), and to Bolivia TV, La Razón digital,
El Erbol Digital, Red Bolivisión and Radio
Panamericana (La Paz).
Table 1: Sample of Bolivian digital media and its
technological convergence.
Media URL
Creation
on line
Sector
M1- El Deber http://eldeber.com.bo 1998 P
M2- Los
Tiempos
http://lostiempos.com 1996 P
M3- Bolivia
Tv
http://www.boliviatv.bo/sitio/ 2009 PDTV
M4- La Razón http://la-razon.com
/
1997 P
M5- El Erbol
Digital
http://www.erbol.com.bo/ 2002 PND
M6- Red
Bolivisión
http://www.redbolivision.tv.bo/ 2012 PDTV
M7- El Diario http://www.eldiario.net 1997 G
M8- Radio
Panameriacna
http://panamericana.bo 2004 PDR
Identification code of digital media: M1,M2, M3…
Sector Code: P- Prensa, PDTV- Portal Digital de Tv., ND Nativo Digital, G
-General, PDR- Portal Digital Radio.
In the extraction of the information was used the
method of the single week in the period understood
from September 3 to September 7, 2018. And a week
composed from September 3 to September 28, 2018.
In the processing of data was applied a model
validated in the study to the web pages of local
channels in Ecuador, entitled "Local television and
the strategic use of the Internet: Analysis of the sites
of the channels of Zone 7 of Ecuador" Ordóñez,
Rodríguez, Campos and Ramón published in 2017,
which establishes, for each indicator, a score of 0 in
case of non-compliance and 1 to 10 if it complies.
2.1 Morphological Aspects of
Evaluation
A set of indicators (table 2) were used to know the
structure of the information and the organization of
the digital media. The morphology, accessibility, was
observed, which raises "the possibility that a web
product or service can be accessed and used, for as
many people as possible, [independent] from the
limitations of the individual or the derivatives of the
context of use” (Hassan Montero and Martín
Fernández, 2003).
For the digital media the access and use of
information is a key aspect to gain audience therefore
usability, "must be centred on the user to making to a
software to perform a task from orders and input data
and valid output, performance that should be
satisfactory for the user; what is equivalent to saying,
simple, easy to learn and efficient" (Serrano
Mascaraque, 2009).
The hypertextuality that is measured by the
existence "of hyperlinks embedded in the
conventional text entries of the site, which
communicate the user to other websites or multimedia
2ETI 2019 - Special Session on E-Learning and Educational Technological Innovation
518
languages". By multimedia is conceived to the forms,
that is, text, sound, fixed and animated image, in the
same environment, and in a juxtaposed or integrated
manner" (Abadal and Guallar, 2010).
Table 2: Cybermedia evaluation indicators.
Macro
indicators
Specific indicators
Morphology of
the medium
Headboard, logo, horizontal, vertical or
mixed menu, sections, cover news,
headlines, number of news, photographs,
videos, advertising banners, icons and
microsites.
Accessibility
Simple search, advanced, newspaper
library, site map, multi-language,
description of photos, listen to option, font
size, high contrast, adaptable content.
Usability
RSS, Newsletter, registration, download
option (with free or paid application), free
subscription or payment.
Hypertextuality
Author of the news, specific author, printed
version, internal link to related news,
external link, images or others, tags (tag or
categories), sponsored content.
Multimediality
Illustrations, photographs, infographics,
audio, video, narrative duplicity, live
coverage.
Interactivity
Blogs, blog users, comments, share, contact
author, forums, chat, news, most read
content, social bookmarking, surveys,
services, letters to the director.
Constantly
updated
Current time, last minute section.
New trends in
journalism
Immersive journalism, data journalism,
open data, mojo journalism, drone
journalism, mashup.
External indicators
Presence in social networks and digital platforms as content
support
This digital structure is completed with the
interactivity that becomes a key indicator of
evaluation, due to the feedback that is established
with the user and between the same audience "is the
ability of action of the user on the multimedia product
that is presented" (López, Gago and Pereira, 2002).
To conclude with the observation of digital media,
it was considered aspects such as constant updating,
due to the fact that the "renewal or update of the
contents of the cybermedia converts them into means
free of any periodicity or regularity [...], [facilitating]
the cumulative information flow” (Salaverría, 2009).
Finally, aspects related to the new journalistic
tendencies are evaluated with which the media have
the possibility of presenting immersive research
works, data processing and visualization of findings
through infographics or graphics; journalistic
coverages made with technologies such as
smartphones, drones and use of other digital sources
through links or web resources used to complete
information. All this in addition to external indicators,
to measure presence in social networks and digital
platforms.
3 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
The Bolivian cybermedia, despite the connectivity
problems that the country has landlocked, and high
Internet service costs, have expanded and use
technology as an effective information mechanism
inside and outside their territory.
The benefits of the Internet for traditional media
such as digital natives are an opportunity. The results
in terms of the morphology of the media, with the
basic indicators (0 to 6) which shows a complete
compliance by the number of values is Bolivia Tv.
The means that report 4 compliance values and 1 of
no compliance are: Los Tiempos (M2), La Razón
(M4), El Erbol Digital (M5), Red Bolivisión (M6), El
Diario (M7), Radio Panamericana (M8) and El Deber
(M1). These media present a classic design, the
distribution of the information they provide is
expanded in horizontal menus and leave aside the use
of vertical or mixed menus to display the information
hosted on the website.
Table 3: Morphology of the digital media.
Headboard
Logo
Horizontal
menu
Vertical
menu
Mixed
menu
Sections
Total
M1 1 1 1 0 0 1 4
M2 1 1 1 1 1 1 6
M3 1 1 1 0 0 1 4
M4 1 1 1 0 0 1 4
M5 1 1 1 0 0 1 4
M6 1 1 1 0 0 1 4
M7 1 1 1 0 0 1 4
M8 1 1 1 0 0 1 4
Likewise, the media morphology indicator
included information regarding cover news, featured
headlines, number of news, photographs, audios,
videos, advertising banners, number of icons,
microsites.
The media that presented an acceptable
performance according to the accounting of more
The Connectivity as Value Strategic: The Development the Digital Media in Bolivia
519

than one thousand records (in the month of
observation) are: La Razón (M4), Los Tiempos (M2),
El Erbol Digital (M5) and El Deber (M1), while those
that obtained less resources are: Bolivia Tv, El Diario,
Red Bolivisión (M6) and Radio Panamericana (M8).
In the monitoring it was evident that, each journalistic
note includes photographs that support the
information, however, there is little use of audios as a
multimedia resource, except Radio Panamericana
(M8), which by its nature works with this format.
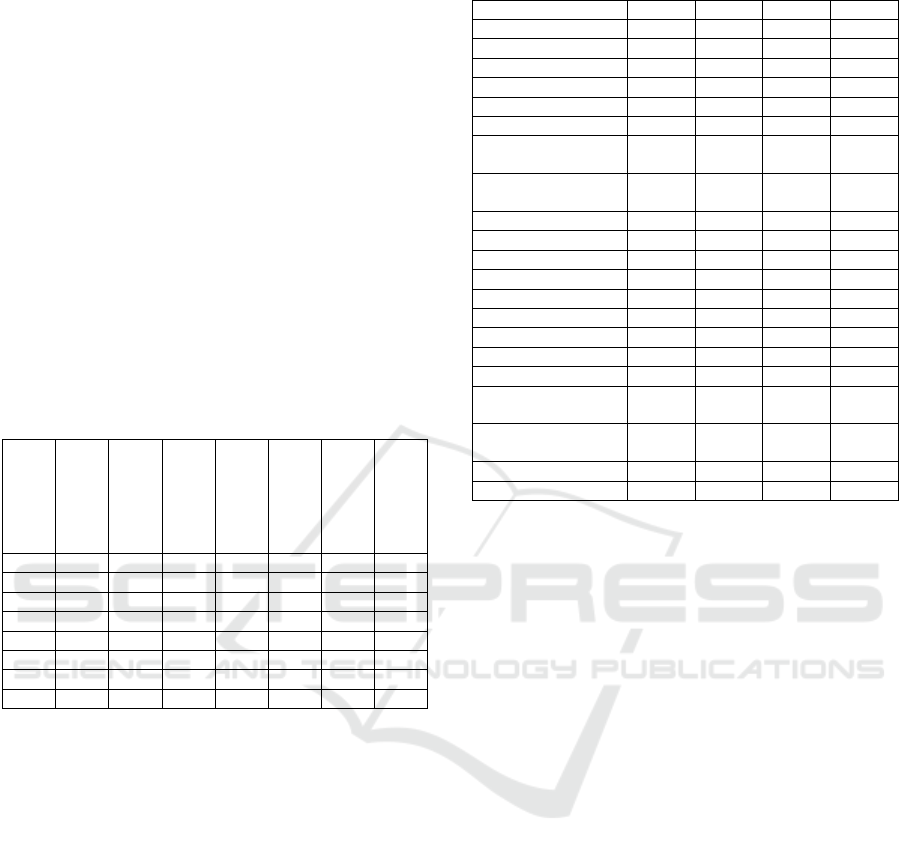
Table 4: Morphology of the information indicators.
M1 M2 M3 M4
Cover News 7 7 7 7
Featured
headlines
6 0 7 3
News 525 160 493 380
Photographs 672 198 670 622
Audios 0 0 0 6
Videos 54 160 102 11
Advertising
banners
13 0 0 48
Icons 56 32 64 0
Microsites 0 0 7 7
Total 1337 562 1354 1088
M5 M6 M7 M8
Cover News 0 7 7 7
Featured
headlines
0 2 0 7
News 144 272 143 496
Photographs 216 262 159 532
Audios 0 0 8 0
Videos 133 0 24 123
Advertising
banners
0 0 0 18
Icons 0 0 6 72
Microsites 0 15 22 30
Total 497 562 373 1288
On the other hand, the presence of advertising
banners was recorded in three media outlets: El Erbol
Digital (M5), El Deber (M1) and Los Tiempos (M2
13, which allows us to deduce that Bolivian
cybermedia do not yet consider websites as models of
advertising sustainable business.
The advertising is displayed in sections
independently of the main information, the user can
observe the publicity when he needs it. Classified ads,
sale of motorcycles, cars, real estate, among others,
are presented. As additional services, information
related to the weather, peak day and license plate
when vehicles can be mobilized, monetary
quotations, among other aspects, are incorporated.
3.1 Accessibility
With respect to accessibility (table 5) taking into
account the evaluation criteria of this indicator from
0 to 12, the medium that obtains 8 compliance values,
with simple search, newspaper library, site map,
description of photos, size option of letter, content
adaptable, operability on the web and link to the main
page, is the digital medium La Razón (M4); to this
medium, as to the remaining seven, they still need to
implement an advanced search, an option to listen and
high contrast elements that help improve accessibility
for anyone, including those with some kind of visual
or auditory disability. In addition, the criteria
evaluated and existing in the pages allow these to be
perceived and be operable by the user.
The media that present 7 compliance indicators
and 5 non-compliance indicators are: Los Tiempos
(M2), Bolivia Tv (M3), El Diario (M7) and El Deber
(M1). And those that are less accessible, that is to say
they present 6, 5 and 4 values of fulfillment are El
Erbol Digital (M5), Red Bolivisión (M6) and Radio
Panamericana (M8).
Table 5: Accessibility of digital media.
Simple search
Advanced
search
Newspaper
library
Site Map
Multi language
Description of
photos
M1 1011 0 1
M2 1011 1 1
M3 1011 0 1
M4 1001 0 1
M5 1001 1 0
M6 1010 0 1
M7 1000 0 0
M8 1001 0 1
Option to listen
Letter size
High contrast
Content
adaptable
Operability of
the web
Link home
Page
M1 0 0 0 1 1 1
M2 0 0 0 0 1 1
M3 0 1 0 1 1 1
M4 0 0 0 1 1 1
M5 0 0 0 0 1 1
M6 0 1 0 1 1 1
M7 0 0 0 1 1 1
M8 0 1 0 1 1 1
It is highlighted that, all the cybermedia evaluated
have private ownership, except Bolivia Tv (M3)
public medium is operates under the economic model
of subsidies with state contribution and self-financing
2ETI 2019 - Special Session on E-Learning and Educational Technological Innovation
520
and in order to meet its objective of public good,
investment the digital must be greater, and with that,
achieve compliance with the 12 indicators.
3.2 Usability
In the evaluation the medium that registers 3 values
of compliance and 4 they do not comply, considered
the highest rank of the observation (0 to 7) is Los
Tiempos (M2), it needs to incorporate newsletter, a
user record, APP for free download and payment,
subscription and payment service.
In that average, the register presented by the
bolivians cybermedia is between 0 and 3 less the half
of the 7 proposed values. Only 4 media have an RSS
channel and a newsletter that they send to their
subscribers free, of charge through their email or in a
link to their web pages (Tabla 6).
Table 6: Usability of digital media.
RSS Channel
Newsletter
Registry
Free download
App
Payment
download APP
Free
subscription
Payment
subscription
M1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0
M2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
M3 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
M4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
M5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
M6 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
M7 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
M8 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
The only digital medium, which has a free
subscription is Los Tiempos (M2), as observed,
classifies the most relevant and interesting
information according to the user's profile.
In regard to download APPs, only Radio
Panamericana (M8) has incorporated this service for
free, but requires changes in its functions.
3.3 Hypertextuality, Interactivity and
Multimedia
Hypertextuality in the digital environment is defined
as the action of linking (hyperlinks) and combining
texts. In the observation made to the Bolivians
cybermedia, its use is evidenced in a modest way, the
editorial structure is based on sections and headlines,
and therefore, they do not make use of innovative
resources to enlarge or present the news. The eight
media place information combined with text and
images, or texts and audios.
Table 7: Hypertextuality of digital media.
M1 M2 M3 M4
Author of the news 1 1 1 0
Specific autho
r
10 0 0
Printed version 0 0 0 0
Internal lin
k
00 2 0
Link to related news 6 0 3 8
External lin
k
00 1 0
Broken link or
image
0 0 0 0
Tags (labels or
categories)
6 0 0 0
Sponsored conten
t
10 0 0
Total 15 1 7 8
M5 M6 M7 M8
Author of the news 0 0 0 1
Specific autho
r
00 0 0
Printed version 0 0 0 0
Internal lin
k
01 0 3
Link to related news 0 8 0 4
External lin
k
00 0 0
Broken link or
image
5 0 2 0
Tags (labels or
categories)
7 0 0 8
Sponsored conten
t
00 0 0
Total 12 9 2 16
On the other hand, the media that use links to
related news is: El Erbol (M5) Digital and El Diario
(M7), the information they generate is complemented
by external sources related to the subject they publish.
In lesser proportion, Los Tiempos, El Deber and La
Razón are registers.
In the integral evaluation of the specific
parameters, the one that presents an outstanding
performance is the hypertextuality indicator for the
sum of the resources employed, El Deber (M1) is
highlighted, this means uses more tags (labels or
categories) to link the information generated and
hosted on the web, however, this does not guarantee
better results when the user performs a specific
search.
Likewise, Los Tiempos registers a number of
acceptable resources (15 in total) followed by the Red
Bolivisión (M6) that presents 12 resources, the latter
concentrates its results in broken links, which can
become a negative aspect when evaluating
performance and usefulness of the page.
Another aspect of observation is related to the
identification of the author in the news, this practice
is not continuous, they avoid at least on sensitive
issues, include the name of the journalist who
generated the information.
Regarding the Interactivity indicator (evaluation
from 0 to 12), the medium that obtained 6 compliance
values and 6 non-compliance means is Los Tiempos
(M2). This medium is highlighted by the
The Connectivity as Value Strategic: The Development the Digital Media in Bolivia
521

incorporation of comments, the action of sharing
information to reach more people; it offers the
resource of classification of the most read news or
content, social markers, surveys and social services.
The aspects that need to be incorporated are: general
blog and of users for direct interaction, forum, chat
and letters to the director.
Table 8: Interactivity of digital media.
M1 M2 M3 M4
Blogs 0 0 0 0
Blog users 0 0 0 0
Comments 1 0 1 0
Share 1 1 1 1
Contact autho
r
0 0 1 0
Forums 0 0 0 0
Cha
t
0 0 0 0
News / content +
read
1 0 1 1
Social bookmarks 1 0 0 1
Surveys 1 0 0 1
Services 1 0 1 0
Letters to the edito
r
0 0 0 0
Total 6 1 5 4
M5 M6 M7 M8
Blogs 0 0 1 1
Blog users 0 0 0 0
Comments 1 0 0 0
Share 1 1 1 1
Contact autho
r
0 0 0 0
Forums 0 0 0 0
Cha
t
0 0 0 0
News / content +
read
1 0 1 1
Social bookmarks 0 0 0 0
Surveys 0 0 0 1
Services 0 1 0 1
Letters to the edito
r
0 0 0 0
Total 3 2 3 5
They follow with 5 compliance values and 7 non-
compliance La Razón (M4) and El Deber (M1).
Finally, with values less than 5, that is, with little
interactivity on the site, there are El Erbol Digital
(M5), Red Bolivisión (M6), El Diario (M7) and
Bolivia Tv (M3). With these results it is deduced that
the generality the of digital media grants a passive
consumption of information, because the user does
not have the possibility to choose the content.
There is no personalization, the reader is subjected
to a predefined itinerary, there are few resources that
offer the user to become an interlocutor – issuer.
Regarding the indicator multimediality, it was
evaluated with the numerical record of the integrated
resources, used by the cybermedia and the
combination of at least two resources in the same
publication. In the observation of the bolivians media
it is determined that they combine, according to the
capacity granted by the digital support, illustrations,
infographics and videos.
Table 9: Multimedia of digital media.
Illustrations
Photography
Infographics
Audio
Video
Narrative
Duplicity
Live Coverage
M1 8407 0 0
M2 8000 0 2
M3 8817 0 0
M4 8100 0 1
M5 3108 0 1
M6 8100 0 0
M7 8007 0 1
M8 8308 0 4
In this sense, the medium that uses a greater
amount of resources is La Razón (8 illustrations,
infographics, 1 audio and 7 videos), followed by El
Deber, which counted 23, unlike La Razón (M4),
which includes live coverages. The media remaining,
register for between 16 and 9 multimedia resources.
We must highlight the juxtaposition of
multimedia resources, since they are placed one
followed by another, without connectors. The
cybermedia of Bolivia does not achieve the
simultaneous integration of the integrated
multimedial narrative, an aspect that is worked by
digital media with more trajectory and media
positioning, such as the New York Times and The
Guardian.
3.4 Constantly Updated and New
Trends in Journalism
In this indicator, two specific aspects were noted: the
current time and the last-minute section. The medium
that incorporates these two elements is La Razón
(M4), which means that it updates its contents in a
constant way (characteristic of digital journalism).
Today the speed of information requires immediacy
and constant updating is what guarantees that a
cybermedia is visited frequently and that each visit
generates one and another. On the other hand, the
media Los Tiempos (M2) and El Deber (M1) register
one compliance value (last minute section), while
Bolivia Tv (M3), El Erbol Digital (M5), Red
Bolivisión (M6), El Diario (M7) and Radio
Panamericana (M8), must evaluate their activity of
constant updating, due to register negative the values
and determine their function in the digital space.
In the digital field, the journalist has at his
disposal a series of tools and resources to tell stories
2ETI 2019 - Special Session on E-Learning and Educational Technological Innovation
522

and get the user involved. These expressions of
journalism have their own characteristics, starting
with immersion, through virtual reality. Regarding
this indicator, the bolivian cybermedia, mostly have a
value of 0 compliance, pending task for the
incorporation of these innovations in their websites.
With the same rating of 0 is assigned to mojo,
drone and mashup journalism, the absence of these
informative trends reflects that the media, although
they use mobiles for journalistic coverage, they have
not managed to complete the filming process,
production and edition, more they use small video
impressions for complete the stories broadcast on the
networks. The use of drones for hard-to-access
coverage is scarce and neither does it offer an
integrated information service from several sources,
characteristic of mashup journalism.
Along with the above, the presence of data
journalism in two cybermedia stands out: Los
Tiempos (M2) and El Deber (M1), in spaces called El
Deber Data and LT-Data. The works published in
these sections, with visualization and interpretation of
data, are eventual.
3.5 Social Networks and Digital
Platforms as Content Support
Social networks are, for the media, spaces of
interaction with the digital audience, the boom of
these "together with the participation of users and
technology have led to a paradigm shift in the
information models" (Ferreras Rodríguez, 2011). On
the other hand, it is undeniable the development and
positioning digital media without these networks of
connection that, in parallel, contribute to the
formation of communities and loyalty.
In the observation made to social networks and
digital platforms as content support, it is possible to
determine that the eight media evaluated have active
Twitter and Facebook accounts. Similarly, Google
Pus social network (closed in December 2018 by
decision of the Google team) present in the 8 media
evaluated, lacks updating, thus, the final closure did
not affect these media companies.
On the other hand, the use of Instagram is
highlighted, mainly with the publication of photos
and short videos, in 6 digital media: Los Tiempos
(M2), Bolivia TV(M3), La Razón (M4), El Erbol
Digital (M5), Red Bolivisión (M6) and El Deber
(M1). The media that have a value of 0, that is, do not
have Instagram are: El Diario (M7) and Radio
Panamericana (M8). As regards, Snapchat, Pinterest
and Flickr networks, these have not been considered
for the dissemination of information and approach to
users.
Among the digital platforms we can distinguish
the preferential use of YouTube in seven media: Los
Tiempos, Bolivia TV, La Razón (M4), El Erbol
Digital (M5), Red Bolivisión (M6), Radio
Panamericana (M8) and El Deber (M1) of the eight
evaluated. In compared to the Soundcluod that use 5
media Bolivia TV (M3), La Razón (M4), El Erbol
Digital (M5), Radio Panamericana M8), El Deber
(M1), and Vimeo that has a rating of 0, this last one
is a digital platform that allows sharing and storing
videos with momentary free and payment
membership, a factor that It is evaluated by bolivians
cybermedia, when sharing content.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In Bolivia, a pending issue is the enlargement of
connectivity the Internet that reaches a 45% coverage
with more incidence in the urban area. With this
scenario the country accomplishes develop and
maintain themselves in the digital space.
The pending task is connectivity, so that more
people can access the information provided by these
information platforms and be an active part of the
digital ecosystem. Actions that undoubtedly the
contribute for the development of TIC infrastructure.
The digital media represent information structures
that originate in the traditional systems that made the
leap to the web, and others digital natives. In both
cases, the Internet is an opportunity for the
deployment of business models and, above all, the
expansion of their coverage.
In this context, the level of Bolivian cybermedia,
according to the information architecture is positive
due to the number of compliance indicators. In the
specific evaluation, of media morphology, in of the
Bolivian digital media a scarce use of multimedia
resources is detected and the advertising aspect is not
exploited. The webs not sustainable models’
business.
The medium that accounts for the greatest number
and recurrent use of resources: cover news,
highlights, photographs, audios, videos, advertising
banners, icons and microsites is La Razón. The 6
remaining digital media, they need to incorporate
strategies so that their sites leave aside classic and
static web designs.
On the other hand, the distribution of information
in Bolivian digital media is limited to the presentation
of front-page news. The distribution of sections and
headlines is modest, strategy that does not guarantee
The Connectivity as Value Strategic: The Development the Digital Media in Bolivia
523

adequate performance of cybermedia. In addition,
resources hypertextuality, interactivity and constant
updating, they are not fully exploited.
The digital media insert information, texts,
images and audios with scarce innovative resources
(video or 360 images with first-person narrative that
allows the reader to become the main actor in the
story) and of integration and direct interaction with
the user (forum, chat, letters to the editor) on the web.
The reader is subjected to a predefined itinerary, the
resources offered to the user to be interlocutors and
senders are scarce. That is, they do not get with the
information a narrative multimedia integrated.
Accessibility allows a site to be perceived and
operated by the user. In the evaluation, La Razón led
compliance (8/12), however, the eight Bolivian
cybermedia should work with content that provides
options to listen to texts, regulate font sizes, work
with high contrast and adaptive content. Additionally,
invest in free and paid download applications, and
subscription mechanisms, to comply with the
usability indicator.
Is determined the null presence of journalistic
works that apply the new trends immersive
journalism, data, mojo, drone, mashup. Nor do they
present stories that highlights the use of drones in the
coverage the issues dangerous, as well as information
integrated coming from other sources.
Most cybermedia have a section dedicated to
journalistic work with visualization and interpretation
of data, but the publication of journalistic research
with data based is sporadic.
The study of the digital media allows to affirm
that, to these means they need to take advantage "the
potential that the Internet offers in all its context, the
audiences every time more they are associated with
technologies changing the forms of reception, [...].
They must restructure their "business models digital,
as a business instrument of economic retribution and
sustainability in the market" (Ordóñez et al., 2017).
REFERENCES
Abadal, E. and Guallar, J. 2010. Prensa digital y
bibliotecas. Gijón: Trea.
Alexa: Top sites in Bolivia. 2018. Homepage:
https://www.alexa.com/topsites/countries/BO
Digital Guide: El ranking de Alexa: qué es y cómo puedes
mejorarlo. (Publicación del 18 de mayo de 2017).
https://www.ionos.es/digitalguide/online-marketing/
marketing-para-motores-de-busqueda/ranking-de-alex
a-que-es-y-como-mejorarlo/
Ferreras Rodríguez, E. 2011. La estrategía de la
corporación EITB (Euskal Irratia Telebista) en Face-
Facebook y Twitter.
Ghemawat, P., Altman, S. 2016. DHL GLOBAL
CONNECTEDNESS INDEX 2016. The State of
Globalization in an Age of Ambiguity.
Global Connectivity Index. 2018. Tap New Growth with
Intelligent Connectivity. Mapping your transformation
into digital economy with GCI 2018.
https://www.huawei.com/minisite/gci/assets/files/gci_
2018_whitepaper_en.pdf?v=20180914
Hassan Montero, Y. and Martín Fernández, F. 2003. Qué es
la accesibilidad Web. Revista digital no solo
usubilidad: revista sobre personas, diseño y tecnología.
Internet World Stats. 2018. Internet usage statistics. The
Internet Big Picture. World Internet Users and 2018
Population Stats. Homepage,
https://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm
López, X., Gago, M., and Pereira, X. 2002. Novas
tendencias do xornalismo electrónico. Santiago,
Edicións Lea.
Los tiempos online: Bolivia está más conectada pero aún se
reclama internet de calidad y mejor costo (Publicación:
17 de mayo de 2017) https://goo.gl/RPHa1o
Mayer, M., 2011. La utilización de Internet entre los
adolescentes, riesgos y beneficios. Atención Primaria,
Vol. 43, 287-288. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.aprim.2010.12.004
Ordóñez, K., Rodríguez, A., Campos, F. and Ramon, M.
2017. La televisión local y el uso estratégico de
Internet. Análisis de los sites de los canales de la zona
7 de Ecuador. Revista Prisma Social. Investigar lo
local: reflexiones, métodos y casos de estudio. 19, 388-
418.
Ortíz, A., Rojas, I. 2016. Las TIC como dinamizador de los
nuevos negocios económicos y sociales. Ploutos, 4(2),
4-13.
Said, E. and Arcila, C. (2011). Los cibermedios en América
Latina y la Web 2.0. Revista Comunicar, 37, 125-131.
Salaverría, R. 2009. Cibermedios. El impacto de internet en
los medios de comunicación de España. Sevilla:
España.
Salaverría, R. coord. (2016). Ciberperiodismo en
Iberoamérica. https://goo.gl/8XFfDK
Serrano, E. 2009. Accesibilidad vs usabilidad web:
evaluación y correlación. Investigación
Bibliotecnológica, 23 (48), 61-103.
2ETI 2019 - Special Session on E-Learning and Educational Technological Innovation
524
