
The Relationship between Fatigue and Work
Productivity of Nurses in the Inpatient Room of the
Regional General Hospital Deli Serdang in 2018
Selamat Tuahta
1
, Gerry Silaban
1
and Siti Saidah Nasution
2
1
Departement of Occupational Safety and Health, Faculty of Public Health, Universitas Sumatra Utara. Jl. Universitas
No.21 Kampus USU, Medan, Indonesia
2
Departemen of Nursing, Nursing Faculty, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Prof. Maas Road No. 03 Kampus USU, Medan,
Indonesia
Keywords: Fatigue, Nurse, Productivity.
Abstract: Nurses are medical personnel who have the most direct contact with patient, making them vulnurable to
fatigue. Work fatigue is a condition where the body’s resistance becomes decreasaed due to doing work
continuously and resulting in a decrease in work productivity. The type of this research is observational
analytic with cross sectional research design. The pupose of this study was to analyze the relationship
between work fatigue dan nurse productivity in Deli Serdang Hospital in 2018. The research sample was 59
nurses who worked in the inpatient ward of Deli Serdang Hospital. The results showed that of 59 nurses
there were 36 people (61%) who experienced work fatigue and of 59 nurses there were 31 people (52,5%)
who experienced low work productivity (p=0,000 <α =0,05) with a values of RP = 2,817,95% CI = 1,595-
4,977. The conclusion of this study shows that there is a relationship between work fatigue and nurses work
productivity.
1 INTRODUCTION
Work productivity is some result between output and
input in a certain period of time. Work productivity
involves the final problem, namely how much the
end result is produced in the work process
(Hasibuan, 2013)
Productivity is one benchmark for the progress
and success of an organization, including health
organizations (Malik et.al, 2014). Many reports on
productivity problems are closely related to the
health problems of human resources, so that efforts
to improve health are a priority (Sehat, 2010).
Health is one of the most important factors for
increasing nurse work productivity. Good health
conditions are the potential to achieve good work
productivity. High work productivity can only be
obtained if the nurse is in good health (Muizzudin,
2013). One of the factors that can cause a decrease
in nurse work productivity is work fatigue.
Fatigue is often considered a symptom, not a
sign because it is a subjective feeling that is felt by
someone, which can be seen by others (Kuswana,
2014). Fatigue is a mechanism to protect the body
from further damage so that recovery occurs after
resting (Tarwaka, 2014). Fatigue usually shows
different conditions in each individual, but all result
in loss of efficiency and decreased work capacity
and endurance.
Fatigue can lead to raises some of conditions,
such as a decrease in energy, a slower reaction time,
reduced motivation, not being able to think quickly
and a reduced morale (Heitman et. al, 2013).
According to the Canadian Nurse Association
research report cited by Angouw (2016) shows that
almost 80% of nurses in Canada experience fatigue.
According to Lippincott Williams and Wilkins,
data from a national study on the relationship
between health and productivity in the workplace, it
was found that out of the 29,000 workers
interviewed, 38% said they had decreased cognitive
function, lack of sleep, or feeling tired (Fatona,
2015).
The American Association of Nurse Anesthesist
(2015) states that work fatigue is one of the causes
of an increase in accidents in the workplace. Nurses
Tuahta, S., Silaban, G. and Nasution, S.
The Relationship between Fatigue and Work Productivity of Nurses in the Inpatient Room of the Regional General Hospital Deli Serdang in 2018.
DOI: 10.5220/0008553102750278
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Resources and Technology (ICONART 2019), pages 275-278
ISBN: 978-989-758-404-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
275

who work for 12 hours a day are more at risk of
workplace accidents (as many as 37% of workplace
accidents occur. Of the 37% of cases of workplace
accidents that occur to nurses, needle puncture cases
are the most reported cases. This happens due to a
lack of focus when working due to work fatigue,
especially for nurses working on the night shift.
Other errors that occur due to fatigue experienced
are errors in using personal protective equipment.
Astuti (2016) cites data from the Ministry of
Health and University of Indonesia which states that
there are around 78.8% of nurses carrying out
cleaning tasks, 63.6% carried out administrative
duties and more than 90% performed non-nursing
assignments.
Only about 50% do nursing care according to
their function. The higher the task demands of a
nurse, the greater the chance that the nurse will
experience fatigue while working.
According to the results of a study conducted by
Ali (2017) at Monompia Kotamobagu General
Hospital, results showed that of 69 nurses studied,
there were 11 people who experienced mild work
fatigue and 58 people who experienced severe work
fatigue. From 11 people who experienced mild work
fatigue, there were 4 people with good work
productivity and 7 people with fairly good work
productivity. From 58 people who experienced
severe work fatigue, there were 11 people with good
work productivity and 47 people with fairly good
work productivity.
Deli Serdang Regional General Hospital is one
of the hospitals engaged in the health service that
operates 24 hours a day. Based on interviews
conducted by researchers during the initial survey at
Deli Serdang Regional General Hospital, out of 10
nurses interviewed there were 6 nurses who
experienced fatigue at work and as many as 4 people
who did not experience fatigue while working.From
6 nurses who experienced fatigue while working, all
experienced a decrease in work productivity. Based
on the description of the background above, the
researcher is interested in conducting research
whether there is a relationship between work fatigue
and work productivity of nurses in the inpatient
ward of Deli Serdang Hospital.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The type of this research is observational analytic
with cross sectional research design. This study uses
a simple random sampling method in sampling.The
study was conducted on 59 nurses who served in the
inpatient room.
To measure the work productivity of nurses,
using a work productivity questionnaire with a score
of 46-60 is a high work productivity category and a
score of 30-45 is a low work productivity category.
As for measuring work fatigue, a tool called the
reaction timer is used. The results of the fatigue
measurements are categorized into 2 parts. Normal
category (not experiencing fatigue) with
measurement results of 150-240 milli seconds.
While the category experiences fatigue with a
measurement of> 240 milli seconds.
Data analysis was carried out in 2 stages, namely
univariate analysis and bivariate analysis. Univariate
analysis explains the results of the study in the form
of frequency distributions of each variable, while
bivariate analysis explains the relationship between
two different variables using the chi-suare test with a
significance level of p < 0.05.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Nurse Work Fatigue
Table 1 : Distribution of Frequency of Nurse Work
Fatigue.
Work Fatigue
F
%
Normal
23
39
Fatigue
36
61
Total
59
100
Based on Table 1, it can be seen that there were
36 (61%) nurses who experienced fatigue at work,
and 23 (39%) who did not experience work fatigue
(normal).
3.2 Work Productivity of Nurses
Table 2: Distribution of Frequency Work Productivity of
Nurses.
Work Productivity of Nurse
F
%
High
28
47,5
Low
31
52,5
Total
59
100
Based on Tabel 2 it can be seen that nurses with
low work productivity were 31 people (52.5%), and
nurses with high work productivity were 28 people
(47.5%).
ICONART 2019 - International Conference on Natural Resources and Technology
276
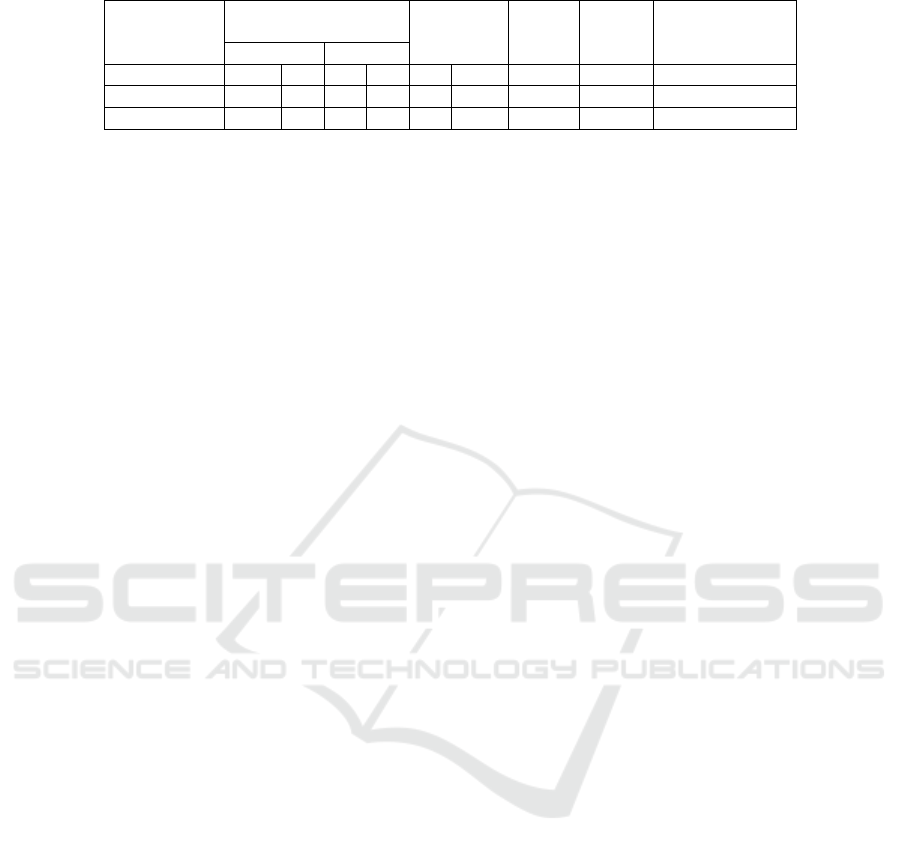
Table 3 : Relationship between Fatigue and Work Productivity of Nurses.
Work Fatigue
Work Productivity
of Nurses
Total
p
value
RP
95% CI
High
Low
N
%
N
%
N
%
Normal
18
78
5
22
23
100
0,000
2,817
1,595 – 4,977
Fatigue
10
28
26
72
36
100
3.3 Relationship between Fatigue and
Work Productivity of Nurse
Based on Table 3, out of 36 nurses who experienced
work fatigue, there were 10 people (28%) with high
work productivity and as many as 26 people (72%)
with low work productivity. Then from 23 nurses
who did not experience work fatigue (normal), there
were 18 people (78%) with high work productivity
and 5 people (22%) with low work productivity. The
chi-square test results show that the value of p =
0,000 <0,05, which means there is a relationship
between work fatigue and work productivity. RP
value = 2,817, 95% CI = 1,595 - 4,977.
4 DISCUSSION
Based on the results of the study, it was found that
more nurses in the inpatient room of Deli Serdang
Hospital experienced fatigue in the workplace. This
is caused by the number of tasks carried out based
on the main tasks, additional assignments, the
number of patients being treated in the nurse's work
capacity and the time needed to carry out nursing
actions. In addition, nurses are also often faced with
other workloads such as administrative duties. This
causes the workload of nurses to be higher, causing
fatigue to nurses while on duty.
Judging from the demands or workload given to
nurses, it is certain that a nurse can experience
fatigue while working. work fatigue experienced by
a nurse will cause the nurse to no longer be able to
work, so the nurse must pause to restore her
condition. If a nurse who is experiencing fatigue still
forces herself to keep working, then the fatigue she
experiences will increasingly get worse and affect
the smooth running of her work (Suma'mur, 2014).
According to Nurmianto quoted by Nurul (2017),
work fatigue experienced by a person can cause
work productivity to decrease and increase the level
of errors at work. Decrease in work productivity that
occurs in nurses can be seen from the findings of
researchers that not all nurses in charge can carry out
nursing care properly. Most of the nurses who have
not been able to carry out nursing care properly are
due to experiencing fatigue while working.
Based on bivariate test between work fatigue and
work productivity on nurses showed the results of 36
nurses who experienced fatigue at work, there were
10 people (28%) with high work productivity and as
many as 26 people (72%) with low work
productivity. Then from 23 nurses who did not
experience work fatigue (normal), there were 18
people (78%) with high work productivity and 5
people (22%) with low work productivity. The chi-
square test results showed that the value of p = 0,000
<0,05, which means that there is a relationship
between work fatigue and work productivity of
nurses in the inpatient ward of Deli Serdang
Hospital. The value of Rp. 2.817 means that nurses
who experience fatigue while working have the
potential to 2,817 experience low work productivity.
This research is in line with the research
conducted by Ali (2017) which states that there is a
relationship between work fatigue and nurse
productivity.
This research is also in line with research
conducted by Majore (2018), which states that there
is a relationship between work fatigue and nurse
productivity (performance).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Fatigue in 59 nurses showed that there were 36
nurses (61%) experiencing work fatigue and 23
nurses (39%) not experiencing work fatigue. While
work productivity in 59 nurses showed that there
were 31 nurses (52.5%) experiencing low work
productivity and 28 nurses (47.5%) experiencing
high work productivity. So that there is a
relationship between work fatigue and work
productivity of nurses in the inpatient ward of
RSUD Deli Serdang Hospital.
REFERENCES
Ali, R. F. 2017. The Relationship between Work Shift and
Fatigue Work with Work Productivity at Nurses in the
The Relationship between Fatigue and Work Productivity of Nurses in the Inpatient Room of the Regional General Hospital Deli Serdang in
2018
277

Inpatient Room of Monompia General Hospital
Kotamobagu
Angouw, T. A. 2016. Differences in Occupational Fatigue
Levels in Morning Shift Nurses, Evening Work Shifts
and Night Shift Work in the Inpatient Room of
Bethesda Tomohon GMIM Hospital. Pharmacon,
5(2).
American Association of Nurse Anesthesist (ANNA).
2015. Patient Safety: Fatigue, Sleep and Work
Schedule Effeects.
Astuti, L. Y. 2016. The Relationship Work Fatigue and
Length of Work with Nurses’ Workloads in the
Inpatient Room of Internal Medicine at Ambarawa
Hospital. STIKes Karya Husada Semarang.
Fatona, L. 2015. Differences in Fatigue Levels between
Morning, Afternoon and Night Shifts in Inpatients at
PKU Aisyah Boyolali Hospital. Universitas
Muhammadiah Surakarta.
Hasibuan, M. S. P. 2013. Human Resource Management.
Bumi Aksara. Jakarta.
Heitmann, A., Moore-Ede, A. 2013. Fatigue Nurses:
Assessing the Risk, Implementing the Defences.
Kuswana, W. S. 2014. Ergonomics, Occupational Health
and Safety. PT. Remaja Rosdakarya Offset. Bandung.
Majore, C. E. 2018. The Relationship Fatigue Work with
Nurse Performance in Inpatient Installation Pancaran
Kasih Hospital GMIM Manado. Universitas Sam
Ratulangi.
Malik M, Hussain S, Mahmood A. Examining a
ChainRelationship of Layoff Survivors' Role
Overload, Work Life Balance and their Productivity.
Interdiscip J. Contemp, 3(6), 402-9
Muizzudin, A. 2013. The Relationship between Work
Fatigue and Work Productivity in Weaving Parts at
PT. Alkatex Tegal. Universitas Negeri Semarang.
Nurul, 2017. Analysis of Nurse Work Fatigue Levels in
the ER Room at UNHAS Hospital and Dr. Wahidin
Sudirohusodo Makassar. Universitas Islam Negeri
Alauddin Makssar. Sehat, A. 2010. The relationship
between principals’ creativity and personnel’s
productivity in technical vocational colleges. Procedia
Soc Behav Sci, 5, 2277-81
Suma’mur, P. K. 2014. Coorporate Hygiene and
Occupational Health. Jakarta: Sagung Seto.
Tarwaka, 2014. Industrial Ergonomics: Basics of
Ergonomics and Implementation at Work. Surakarta.
Harapan Press.
ICONART 2019 - International Conference on Natural Resources and Technology
278
