
Artistic Transformation of the Motion of the Shadow Puppet Scene
“Perang Kembang” into Digital Silhouette Animation
Arik Kurnianto
1
, Frans Santoso
1
1
Animation Program, Visual Communication Design Department, School of Design, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta,
Indonesia
Keywords: artistic, transformation, shadow play, wayang, digital, silhouette, animation.
Abstract: “Perang Kembang” is a battle scene between the knights against the giant in wayang performance. A knight
who has soft and gentle movement is in stark contrast to the giant who has a rugged and attractive
movement. The two contrasting characters can represent a very interesting and beautiful war scene, so this
war scene becomes a scene awaiting by the audience, as well as a scene capable of showing the skill of the
Puppeteer in the art of puppet movement. This study aims to transform the beauty of wayang movement in
the “Perang Kembang” scene into digital silhouette animation. The results of the artistic identification of
different movement patterns found in the wayang movement of the "Perang Kembang" scene became the
basis for digitally exploring the silhouette animation. The problem studied is how to transform the beauty of
the wayang movement in the “Perang Kembang” scene into the digital silhouette animation. This research
was conducted using art-based research methods, by experimenting with the motion of digital animation
based on the pattern of movement of the shadow of the “Perang Kembang” scenes. The results of motion
experiments show that the artistic transformation of the "Perang Kembang” scene can be digitally performed
with two-dimensional puppet-based animation techniques.
1 INTRODUCTION
Wayang kulit (shadow puppet) have long been an
inspiration in making animated films. Wayang itself
is included as one of the forerunners of animation
before the film era. This was confirmed by Dwi
Koendoro who looked at wayang as the precursor of
modern animation (Koendoro, 1998). Many figures
in the history of animation inspired by wayang,
including Walter Elias Disney, founder of Disney
Studio, were inspired by wayang kulit in their
animated careers (Khia K.K, 2009). Wayang
animation or better known as shadow or silhouette
animation has long developed and become one of
the important genres in animation.
Lotte Reiniger (1899-1981) was an animated
artist from Germany who became one of the
pioneers in silhouette animation. Lotte Reiniger is a
female animator who has made more than 38
animated silhouette films throughout her life
(Furniss, 2017). Like Walt Disney, an interesting
fact is that Lotte Reiniger was inspired to make a
silhouette animation as soon as she saw a puppet
show from China. But he was more fascinated by the
performances of Javanese shadow puppets which
were performed at the International Exhibition of
Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts in Paris in
the Dutch Pavilion in 1925 (Prakosa, 2004). One of
the famous animations made by Lotte Reiniger is an
animated silhouette titled "Adventures of Prince
Achmed" in 1926. In the present era, one of the
award-winning silhouette animation works is titled
"Invention of Love" by Andrey Shushkov of Russia
in 2010 (Shushkov, 2010). Like the wayang which a
shadow performance is, which is the power of this
type of animation is in the game of shadows or
silhouettes that give the impression of "mystical"
and "sacred". The difference is that in the shadow
puppet show, shadows are generated from behind
the screen (kelir) through the play of puppets
highlighted by lights (blencong). Whereas in
silhouette animation, the shadow impression is
captured by frame by frame through stop motion
techniques or made virtually if using digital
animation techniques. But in artistic principles, both
are classified as the art of shadow play.
In the puppet show, the scene of "Perang
Kembang" (Flower War) is a scene of war between
Kurnianto, A. and Santoso, F.
Artistic Transformation of the Motion of the Shadow Puppet Scene “Perang Kembang” into Digital Silhouette Animation.
DOI: 10.5220/0008764703510358
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Interdisciplinary Arts and Humanities (ICONARTIES 2019), pages 351-358
ISBN: 978-989-758-450-3
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
351

the knights (Bambangan) against the giant
(Buto/Cakil). The knight who has the character of
graceful soft movements that contrasts with the giant
character who has a character that is rough and very
attractive. However, the two contrasts of the
characters are actually able to display a very
interesting and beautiful war scene, so that this war
scene in the puppet show in the past became a
priceless scene and awaited by the puppet audience
as well as a scene that was able to show the
puppeteers expertise in wayang movements
(sabetan). Whereas in the human wayang show
(wayang wong), the scene of the "Perang Kembang"
in the wayang kulit was successfully transformed
into the form of the Bambangan-Cakil dance which
was also one of the headliners in wayang wong.
Wayang kulit (shadow puppet) and wayang wong
are two different types of performing arts, in which
wayang kulit uses wayang puppets with the
puppeteer (dalang) as the driver and director, at the
wayang wong, it is precisely the people who become
"puppets" and no puppeteer or dalang who controls
the puppets. If viewed from the aspect of motion,
puppet dolls made of leather certainly have
differences in movement when compared to wayang
wong by real people. But the movement of
Bambangan-Cakil dance can transform the beauty of
motion or "sabet" in the scene of "Perang Kembang"
which is the reference. Of course, the process of
transformation of this movement requires the
sensitivity and expertise of the artists to be able to
produce a transformation of puppet movements into
the movements of wayang wong dance who are
different medium but still artistic and beautiful. The
successful transformation of the wayang kulit
movement in the "Perang Kembang" scene into the
Bambangan-Cakil dance inspired the writer to carry
out the artistic transformation of the wayang scene
"Perang Kembang" movement to a more cinematic
animation medium.
With the background above, this study focuses
on how the shadow motion of the puppet scene
"Perang Kembang" is transformed into an animated
silhouette motion. The results of this study were in
the form of experimentation on the motion of
animation based on shadow motion of wayang in the
scene of "Perang Kembang" in the form of animated
two-dimensional silhouettes with digital techniques.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Wayang Motion Scene "Perang
Kembang"
One of the attractions in shadow puppet shows is the
movement or "sabet" wayang. What is meant by
puppet motion includes, among others: worship,
walking, running, dancing, flying, and war. The
wayang movement is principled on social status,
age, classification, and "wanda" puppet characters
(Darmoko, 2004). Among the various forms of
wayang movement, the most popular of wayang
movement is a war scene. And among various types
of war, the most popular is the "sabet" wayang scene
"Perang Kembang". Because of its popularity, this
scene was used as a reference in the Bambangan-
Cakil dance in wayang wong performances. Almost
all of the movements in the Bambangan-Cakil dance
were developed or created based on the scene of the
"Perang Kembang".
"Perang Kembang" is one scene as part of a
puppet show (pakeliran). In the eyes of past
Javanese people, puppet shows are loaded with
cultural symbols. As one of the spectacles, the scene
of "Perang Kembang" has extraordinary charm.
Because, in this scene there has been a physical
conflict between two very contrasting camps,
namely a fight between subtle, graceful figures
against dynamic and attractive figures. (Isharyanto,
2016). The "Perang Kembang" scene is usually
presented in the middle of an all-night show, when
the audience has begun to get bored, tired and
sleepy. In the past, this war scene could be said to be
a flagship scene, which was almost always awaited
by most shadow puppet viewers. Perhaps because
this war scene is very interesting, where in the
tradition of the performance of the Surakarta style is
then called the scene of "Perang Kembang". In the
context of spectacle, the term "Perang Kembang"
can be interpreted as a "èdèn-èdèn" (decoration)
war, superior war, or prima donna war from an intact
puppet show (Isharyanto, 2016).
Wayang movements in war scenes require "big
space" (walking, running, kicking, rolling, hitting,
entering the earth and into the water, and flying).
Puppet movements at the time of war are based on
wewaton (norm). There are several types of war,
namely: "ampyak war", a war of a group of soldiers
or ampyak (together) jointly clearing obstacles or
damaged roads; Perang gagal or "Failed war", war
of two groups of soldiers, one of them strayed;
"Perang Kembang", a war between bambangan or
ksatria with Butho Cakil or giant which requires
ICONARTIES 2019 - 1st International Conference on Interdisciplinary Arts and Humanities
352

developmental techniques or variations in motion;
and "brubuh war", a battle between two groups that
went berserk. The norms of motion used in each war
are different (Darmoko, 2004). The composition of
the war is based on the sequence of events, namely
the beginning (“Perang Ampyak” and “Perang
gagal”), middle (Perang Kembang) and the end
(brubuh war).
In the "Perang Kembang", a knight figure who
bowed his head (a bambangan figure), refined to
fight against Cakil, he was calm when he did
"gendiran" (beating). Before the knight carried out
the beating, did "prapatan", "jeblos" and "ngantem".
On the motion "prapatan", finally Cakil held his
head and hair and slammed it to the ground.
Gendiran is the knocking of a knight against Cakil
using a hood, a handle to move the hand made of
horn or bamboo). The Cakil movement is "nggero"
(scary, frightening), "nyawur" (throwing sand) and
turning upside down (rolling). Whereas the position
of knight when facing Cakil is on standby
(Isharyanto, 2016).
2.2 Aesthetics of Puppet Motion and
the Principles of Motion in
Animation
The art of motion or aesthetic motion in a puppet
show is often referred to as "sabetan". In the art of
wayang movement there are rules, norms or
“wewaton” which are conventions that are adopted
and referred to by mastermind artists when moving
puppets. One of the conventions of the art of motion
in puppet shows is "Udanagara". Udanegara is a
way of speaking, behaving, and behaving in a
character in a puppet show, which contains ethics and
aesthetics. What is meant by puppet motion includes,
among others: worship, walking, running, dancing,
flying, and war. Wayang movements are principled
or guided by social status, young people (age),
classification, and the character of puppet figures. In
the art of wayang motion also pay attention to the
principle "wiraga" (true and precisely action in
motion), "wirasa" (true and precisely appreciation in
motion), and "wirama" (true and precisely rhythm in
motion) (Darmoko, 2004).
Ismurdyahwati (2007) has carried out research
specifically related to "sabet" or motion in purwa
shadow puppets using the visual language approach.
He divided the motion into three different types of
motion. Where the various types of puppet
movements determine the character type and
personality of the puppet characters. Grouped in
three important parts: gesture (body language),
transition (one movement to the next movement) and
war (war scene). Furthermore, specifically for the
war scene, based on the scenario made by the
pedhalangan Habirandha school, there were thirty-
two Yogyakarta puppet-style war movements. Body
movements include movements, attacks, throws,
stabbing, killing and falling movements, which are
common in wars. Movements are grouped in general
groupings, namely attacking movements, dodging
movements and falling movements, and this applies
to all characters or all individuals (Ismurdyahwati,
2007). Her research comprehensively also succeeded
in finding 40 types of 'motion language' of shadow
puppets, namely the wayang kulit visual language in
a 'silent' position or embedded in 'the universe of
wayang' and found the visual language of wayang
kulit in a moving position or in the form of “sabetan".
Whereas in the research conducted by Darmoko
(2004) concluded that puppet motion consists of two
senses, "broad" (totality of movement of characters)
and "narrow" (war); puppet movements are limited
by conventions (norms) agreed upon by puppeteer
(udanegara); the principle of puppet motion refers to
social status, age (young-old), classification, and
wanda of puppet figures; the movement of puppets
today has a lot of cultivation, dynamic. The
development of the puppet motion is in line with the
mindset of an increasingly advanced, critical and
dynamic society.
More specifically, the so-called "sabetan" (puppet
motion) comes from the word "sabet", which means a
messenger, sebat; disabet means embellished,
insulated, framed; ‘Disabeti’ means to be broken;
"Nyabet" means dropping a card, "doing" shadow
puppets; and "sabet" in krama inggil means sword.
Understanding "sabetan", nyabet that is referred to is
"doing" the shadow puppets moving, running,
playing the puppet puppets. Puppet movements
involve how characters speak, behave, and act in
their relationships with other characters. In a puppet
movement there is a change or change in the body or
a small part of the body of puppets.
Whereas in animation, motion aesthetics in many
animations refer to twelve principles of animation
developed by Walt Disney Studios in the 1930s. The
principles were outlined in detail in the book The
Illusion of Life: Disney Animation (1981). The
twelve principles also helped to transform animation
from a novelty into an art form and become the
artictis standart for traditional animation. By
applying them to their work, these pioneering
animators produced many of the earliest animated
feature films that are now considered timeless
classics such as Snow White (1937), Pinocchio and
Artistic Transformation of the Motion of the Shadow Puppet Scene “Perang Kembang” into Digital Silhouette Animation
353

Fantasia (1940), Dumbo (1941) and Bambi (Ghani &
Ishak, 2012). Although the principles were developed
for traditional hand-drawn animation, they also apply
to both two-dimensional (2D) and three dimensional
(3D) computer-based animation. John Lasseter
(1995) still uses twelve traditional Disney animation
principles when making the first feature length 3D
computer animation "Toy Story" in 1995 (Lasseter,
1987).
In conjunction with wayang, Ghani and Ishak
(2012) in their study concluded that there was a very
close relationship between the 12 animated principles
of Disney and wayang kulit. Even stated that "it is
strongly believed that Walt Disney studied and
adapted the 12 principles of animation from wayang
kulit” (Ghani & Ishak, 2012). The twelve principles
of animation are: squash and stretch, anticipation,
staging, straight ahead action and pose to pose,
follow through and overlapping action, Slow in and
slow out, arc, secondary action, timing, exaggeration,
solid drawing, and appeal (Frank Thomas, 1981).
3 RESEARCH METHODS
This study will use an experimental art approach or
art-based research. In the context of art research, art-
based research or practice-based research requires
the involvement of researchers directly with the
object under study (the researcher is involved
intensely with the artwork that he is about to create).
Intense involvement in the process of creating
artwork requires artistic ability and experience as the
creator of the work. This position in the view of
Carole Gray and Julian Malins (2004) places artists /
designers as reflective researchers. (Gray & Malins,
2004). The stages to be carried out in this study
include: puppet motion observation of the "Perang
Kembang" scene to classify the pattern of puppet
motion, followed by exploration and
experimentation of digitally animated puppet
movements, then applying the results of
experimental motion into 2D digital animation.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Classification of Character
Movements and Puppet Motion
Scenes "Perang Kembang"
The character of the puppet figure (body shape)
greatly determines the main movement and character
of the character. Apart from body shape also: eye
gaze, how to stand, nose shape, hair style, and
equipment attributes that are worn. The types of
puppet characters are classified into seven main
characters that determine the personal identity of
each character (Heru S Sudjarwo, 2010).
Alus or alusan (refined, courteous, courteous),
who has a whole character (has a personality
with a careful and polite attitude) with a
marked on the body shape of a standing
position with a downward gaze. Examples of
these characters are Arjuna, Pandu, Rama, etc.
Lanyap, having a person like loneliness is only
more aggressive, with a marked on the body
shape of the standing position with the eyes
gazing forward. Examples of these characters
are Krishna and Karna.
Gagah, or Stout, has a muscular body shape
with round eyes (thelengan) Examples of such
characters include Bima, Gatotkaca, Baladewa,
etc.
Gusen, has a muscular body shape and visible
gums on its molars. This character is more
aggressive and inconsistent. Examples of these
characters include Cakil, Durmogati, etc.
Danawa, giants with large and fat bodies, for
example Dasamuka, Rahwana, etc.
Wanara, monkeys like Hanoman, Subali,
Anila, etc.
Dhagelan or comedian, including Semar,
Gareng, Petruk, Bagong, Cangik, Limbuk, etc.
In the wayang both wayang kulit and wayang
wong, the embodiment of the figure of the mosaic is
usually "luruh" meaning that it is bent (not looking
up) with a slim and small body (mbambang).
Bambangan is a symbol of a handsome-looking
knight figure who is all-smooth in everything,
including: behaviour, ways of speaking, content of
speech, and mindfulness of his character. Knight
figures that included mining included Sumantri,
Rama, Laksmana, Palasara, Pandu, Arjuna,
Abimanyu, Irawan, and Priyambada. Gagah
(gagahan) puppet figures such as: Gandamana,
Salya, Bima, Gathutkaca, Antareja, Kakrasana, and
the like are not commonly referred to as bambangan,
even though they are classified as knights. Apart
from gagahan figures, related to the "Perang
Kembang" or Bambangan-Cakil, handsome figures
who are small and slim but look up (lanyapan) are
also not commonly referred to as bambangan. So
that the warrior figures such as: Karna, Nakula,
Sadewa, Truthajumena, Narasoma, Kresna,
Wisanggeni, and Samba, for example, are not
included in the figures of Bambangan because their
face features look up.
ICONARTIES 2019 - 1st International Conference on Interdisciplinary Arts and Humanities
354
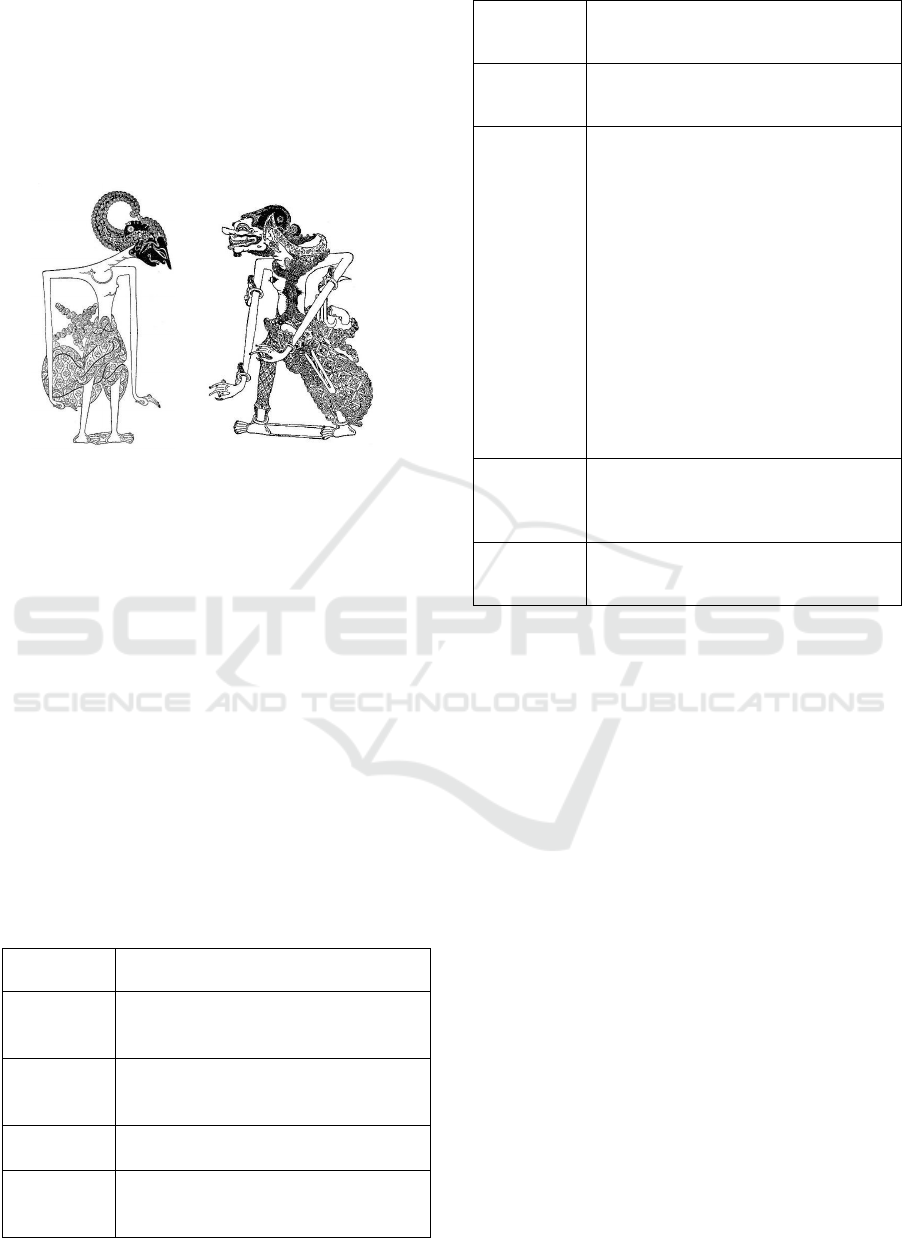
The figure of bambangan in the "Perang
Kembang" in this study is Arjuna who has the
character "alusan" or "luruh" who opposes Cakil
who is classified as a "gusen" character whose
behavior is very attractive. The contrast between the
two characters eventually became an attraction in the
"Perang Kembang" scene which was adopted into
the Bambangan-Cakil dance.
Figure 1. The Arjuna figure (left) which is classified as an
alus/luruh and Cakil character (right) is classified as a
"gusen" character.
Motion analysis in this study was carried out
based on the category or classification of motion
carried out by Ismoerdijahwati based on the results
of his dissertation entitled "The shadow performance
of wayang kulit purwa in the study of "motion"
visual language (Yogyakarta Style Parta Krama)" in
2007. Ismurdyahwati (2007) classifies the types of
puppets in three important parts: gesture (body
language), transition (one movement to the next) and
war (war scene). Ismoerdijahwati describes the
classification of puppet movements in descriptive
form. In order to facilitate the analysis of the motion
of the "Perang Kembang" scene and the Cambangan
Bambangan dance, the classification of motion is
shown in the table below.
Table 1: Classification of shadow puppet movements.
Movement
t
yp
e
Name of movement
Silence is
stuck
(Gesture)
Angapurancang, Methenteng, Malang
kadhak, Malangkerik, Makidhupuh,
Kinkin
Sembah or
worship
(Gesture)
Sembah ratu, Sembah karna, Sembah
jaya, Sembah suwunan, Sembah biasa
Dialogue
(Gesture)
Hands moving slowly, hands moving
medium, hands moving high and fast
Walk
(transition
movement)
Lampahan dhodokh, walk
slowly/smoothly, walk medium, walk
fast/rough
Dancing
(Transition
Movement)
Turn around, up and down
Flying
(transition
movement)
Fly high, fly low
Attack and
resist
attacks
(War)
Nyepeng (hold hand), Hold the head, or
hands, body (nyikep), Njunjung (lift
your opponent into the air), Mbanting
(drop hard on the ground), Mbucal
(throwing), Mbanting binanting
(charging many times), Cangklet
cengkah (loud jolt), Nglarak (smashing
face into the ground / knee), Ngantem
(hitting up hard), Nyaut (freeing the
forearm), Clapping (freeing both arms),
Nubruk (bumping into opponents),
Jeblosan (storming together), Binten
(kick with knees), Nendhang (kick
melee), Ndugang (kicking high),
Accusation war, Nempiling (slapping
face),
N
apu
k
(slapping face for woman)
Evade
(War)
Nangkis (parrying), Endho aside
(dodging sideways), Endho backing
(dodging backwards), Endho advancing
(
dod
g
in
g
forward
)
,
Ny
olot
(j
um
p
in
g)
Fall (War) Jungkir (forward salto), Koprol (back to
back), Jlungup (fall to face), Nggeblag
(falling backwards)
4.2 Wayang Motion Scene "Perang
Kembang"
The analysis of the puppet motion in the war scene
begins with analysing the puppet motion, which is
divided into three main parts, among others;
1) The meeting between Arjuna and the Cakil in
the middle of the forest or road, where the
Cakil intends to block the road or the goal of
the knight, followed by a scene of dialogue
mutually challenging between the two.
2) The occurrence of a war that began with
scenes of gendiran or dance to attack each
other. This round of war can be divided into
three main parts, namely; early war, tuding
war, and weapons war.
3) Climax scene where the Cakil is killed by his
own weapon. By using the puppet motion
classification as described previously, an
analysis of the puppet motion from the
beginning to the end is carried out. To clarify
the analysis of the motion of the "Perang
Kembang", the data from the analysis are
tabulated based on the table in the following.
Artistic Transformation of the Motion of the Shadow Puppet Scene “Perang Kembang” into Digital Silhouette Animation
355
Table 2: Tabulation of puppet movements "Perang
Kembang"
Motion of Arjuna Motion of Cakil
- Plugged in, hands
danced slowly.
- Hands move slowly
- Dance, move right and left,
up and down with medium
to fast tempo movements.
- Silence is stuck with
an honest hand
position.
- Fend off by hitting
(ngantem) with one
hand.
- Arjuna shot off the
screen chasing
Cakil.
- The body turns back
in an unfortunate
position of the
pebble.
- Holds Cakil's head,
turns back and is
knocked into
gunungan (njeblos).
- Catch the head from
behind and bang it
on the ground
(
n
j
eblos
)
.
- Shot off the screen.
- Return to the screen with
the sad position of Kadhak
and attack Arjuna with a
crash.
- After that fall backward
(nggeblag) at Arjuna.
- Move to attack by biting
Arjuna's head, kicking
(ndugang) hard and
ngantem.
- Biting Arjuna's neck and
back.
- Back to bite Arjuna's head
and thighs.
- Attack with a prophecy
- The head fell and the body
fell down
- Shot off the screen.
- Hit with a cover
from the front and
back with the body
position like
floating.
- Njeblos with
accusations
- Mbanting right and
left
- Ndugang hard
- Attacking from the front and
back with variations of
nubruk, ngantem, nendang
and ndugang.
- Falling Salto because at
Arjuna.
- Crawl fast after falling and
return to the poor position
of the kadhak.
- Attacking from the front and
back with variations of
nubruk, ngantem, nendang
and ndugang.
- Fallin
g
and crawlin
g
in
p
ain
- Standing with the
poor position of the
kadhak.
- Avoiding aside from
the attack of the
Cakil keris.
- Hold the dagger by
hand and push it
forward.
- Silence is stuck
- Pulling the keris and
swiping it in your hand
- Turn the keris around
- Throw the keris up and be
held with the head.
- Dancing while walking
away from the screen.
- Enter the screen quickly
while stabbing Arjuna with
the keris in the hand.
- Repeatedly attack with a
dagger with fast
movements.
- Falling behind (nggeblag)
because of Arjuna's
encouragement.
- Detain and hold - Do a final stab or attack.
Cakil's hand.
- Stab the keris to the
Cakil body.
- Silence is stuck with
an honest position
- Fall with the keris piercing
the stomach / chest.
- Dying to embrace Arjuna's
body
- Slowly backward.
- Cakil was kille
d
4.3 Puppet Motion Experimentation
The experimentation of motion was carried out using
adobe animate 2018 software. The step of the
motion experiment began with:
1)
Create a silhouette model of Arjuna's character
and Cakil character. To get detailed silhouette
character modelling is done in Adobe
Illustrator. In Adobe Illustrator the parts of the
model are also separated.
2)
Gives bone to character. This process is quite
complex, and the researcher must make several
attempts to determine the appropriate
connection so that when the character is moved
it is easy to control while being based on the
motion of the puppet which is more dependent
on hand movements. However, in this study
bone or armature/rigging vector is not only in
the hands of puppets. To produce more
animatic motion, joints are also carried out on
the head, waist and legs.
3)
Conduct experiments on various puppet scenes
in the "Perang Kembang". This stage is based
on observing the video of the scene of the
"Perang Kembang" puppeteer by Ki Bayu Aji
Pamungkas.
4)
Make an animation per scene "Perang
Kembang" based on a predetermined
classification of motion.
The following are pictures that explain the
experimental process of transforming the shadow
motion of the "Perang Kembang" scene into
silhouette animation.
Figure 2. Arjuna and Cakil puppet modeling (source:
personal document)
ICONARTIES 2019 - 1st International Conference on Interdisciplinary Arts and Humanities
356

Figure 3. Cutting for puppet joints (source: personal
document)
Figure 4. Arjuna and Cakil puppet armature processes
(source: personal document)
The following is an example of silhouette
animated sequence images based on the shadow
motion of the puppet scene "Perang Kembang".
Figure 5. Pre-war dialogue scene (source: personal
document)
Figure 6. War scene, Arjuna "Njeblos" head of Cakil
(source: personal document)
Figure 7. Animated wayang scenes using weapons
(source: personal document)
Figure 8. The climax scene, Cakil was killed by his own
weapon (source: personal document)
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the experimentation of the animated
motion of the "Perang Kembang" scene, it can be
concluded that the transformation of motion is very
possible in animation even though it is different in
medium. The aesthetics of puppet motion must be
understood by animators before carrying out motion
transformation so that the beauty of puppet motion
can be transformed into animation. But animators
must also be sensitive to artistic language in
animation (12 principles of animation) which is also
different from the language of puppet movements
even though they are interconnected. Thus the
possibility of more animatic movements can be done
in animation because of wider and unlimited motion
control on the animation medium. The silhouette
animation is one of the best choices to be able to
carry out the artistic transformation of the shadow
puppet scene of the "Perang Kembang".
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research can be realized due to research grant
support from the Ministry of Research, Technology,
and Higher Education, Bina Nusantara University in
2018.
REFERENCES
Darmoko. (2004). Seni Gerak dalam Pertunjukan
Wayang. Makara: Sosial Humaniora, 83-
89.
Frank Thomas, O. J. (1981). The Illusion of Life
Disney Animation. New York: Walt Disney
Production.
Furniss, M. (2017). Animation the Global History.
London: Thames & Hudson.
Ghani, D. A., & Ishak, S. B. (2012). Relationship
Between The Art of Wayang Kulit and
Disney’s Twelve Principles of Animation.
Artistic Transformation of the Motion of the Shadow Puppet Scene “Perang Kembang” into Digital Silhouette Animation
357

Revista de cercetare si interventie social,
vol. 37, pp. 162-179.
Gray, C., & Malins, j. (2004). Visualizing Research
A Guide to the Research Process in Art and
Design . England.: Ashgate Publishing
Limited.
Heru S Sudjarwo, S. U. (2010). Rupa dan Karakter
Wayang Purwa. Jakarta: Kaki langit
Kencana.
Isharyanto. (2016, Desember 1). Perang kembang
primadona pagelaran wayang. Retrieved
from http:/isharyanto.worpress.com:
http:/isharyanto.worpress.com/2015/06/28/
perang-kembang-primadonapagelaran-
wayang/
Ismurdyahwati. (2007). Kajian Bahasa Rupa
Berdasar Rekaman Video Pergelaran
Wayang Kulit Purwa dalam Lakon ‘Parta
Krama’. , Vol 1D, Bandung: ITB. Jurnal
Wimba, Vol 1D.
Khia K.K, C. Y. (2009). A Study on the Visual
Styles of Wayang Kulit Kelantan and Its
Capturing Method. Sixth International
Conference on Computer Graphics,
Imaging and Visualization. IEEE Journal.
Koendoro, D. (1998, February 6 - 12). Menghimpun
Karya Animasi Indonesia. Pekan Komik
dan Animasi Nasional 98, p. 27.
Lasseter, J. (1987). Principles of Traditional
Animation Applied to 3D Computer
Animation. SIGGRAPH Computer
Graphics, (pp. 35- 44).
Prakosa, G. (2004). Film Animasi Indonesia pada
Masa Reformasi. Yogyakarta: Fakultas
Sastra UGM.
Shushkov, A. (Director). (2010). Invention of Love
[Motion Picture].
ICONARTIES 2019 - 1st International Conference on Interdisciplinary Arts and Humanities
358
