
The Quick Design Method for the Big and Complex Products based
on Function Disassembling
Xianying Yang
1, a
, Weizhan Li
1, b
1
Chongqing Jiaotong University, Art Design Collage, Chongqing 400074,China
Keywords:
Modularity, Disassembling, Concept Design, Industrial Design.
Abstract: This paper gave out an analyst the condition, disassembling and unfold principle of module concept with the
function planning and relationship, developed the process with the sample of leveling machine. It got the
idea plan of the product, put forward the action of function disassembling and transit into the design by the
quick industrial design sketch and rendering method, improved the efficiency of concept design. It get
conclusion the modularity and disassembling method will guiding the designer and give a reference on the
large and complex product function defining and design.
1 BACKGROUND
Simplified conceptual design is usually adopted to
start the creative process first in the early stage of
product development, because of massive
components of big and complex products. These
products are characterized by large size, complex
design, high technical standard, and strict
requirements for the adaptability in actual working
environment (Jungmin Yoo, Minjung Park, 2016). In
simplified methods, the modular design concept is
universal in this kind of products design, and it is the
study object of traditional design. Previously, the
team of foreign scholars Browning. T.R and Wei XP
proposed multi-level evolutionary design theories
and methods for complex products to improve the
intelligence of complex product design, aiming at
the multidisciplinary coupling integration of
complex product design. Liu FY studied the key
technologies of complex customized products
development and design. Lin ZQ studied the digital
design of complex equipment. Zhang SY studied the
theory and method of engineering semantic
expression, transmission and driving in product
design based on fuzzy interaction modeling
technology for product design information of
engineering semantics. Feng YX researched the
principles, methods and applications of complex
mechanical product design intent (Lei Zhang,
Xuening Chu, Deyi Xue, 2019; CHEN Mengyue,
et.al, 2016). Based on the above methods, this paper
put forward research on the product form design
from further function disassembling and unfolding
process of modularity, to obtain a creative method
that is easier for designers to control.
2 DEFINING MODULES BY
PRODUCT FUNCTION
Module is a relatively independent and replaceable
component in a product system or service system,
which is also a function unit of modular system. In
mechanical products system, module is a group of
combined elements with the same function. Modular
design is a way of disassembling and reorganization.
It is a method of integrating and innovating based on
product system design by exchanging and
transplanting innovative ideas. The purpose is to
improve the demand of system diversity, plurality,
economy and standardization. According to the
relevant demand information of the product system,
considering the correlation between the product
modules, the product function re-design module can
be identified according to the output efficiency of
product core function, after determining the
importance of each module by using QFD (Quality
Function Deployment) matrix and fuzzy evaluation
method (CHEN Mengyue, et.al, 2016, Chen, L., A.
Macwan, and S. Li, 2007). In the module
construction and combination of ideas, the module is
Yang, X. and Li, W.
The Quick Design Method for the Big and Complex Products based on Function Disassembling.
DOI: 10.5220/0008849501870191
In Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Vehicle, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering (ICVMEE 2019), pages 187-191
ISBN: 978-989-758-412-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
187

a bit fuzzy, which needs to be sorted and determined
according to the design goals and research methods.
Taking automotive products as an example, the
body structure is a large and complex system. Soon
after the birth of the first production line, Ford
Motor faced consumer demand to cars
diversification, and thus produced a variety of
models by determining the core modules. Toyota
launched a global framework to improve the
common use of component layers whose versatile
rate increased from around 20% to 80%. In addition,
domestic and foreign automobile enterprise
introduced different types of modular platforms such
as MLB, MMB, UKL, MFA and MRA to improve
the common use of design and increase differential
controllability. At the same time, the platforms
number of cars were reduced by modular design. For
example, the number of Ford Motor car platforms
was reduced from 27 to 8, and its utilization rate of
core modules was greatly increased. In today's
highly competitive marketplace, the development
team of automotive manufacture enterprises
introduce modular design ideas in automotive
construction system, to reduce production risks and
costs, increase production flexibility, and improve
production acumen. The car body is divided into
several modules according to the specific function,
and the module is disassembled hierarchically from
the model, the body, the units, the components, the
parts, etc. And then the modules are combined
according to the produced models. The production
adaptability and R&D production efficiency are
greatly improved by this form of production
organization. As shown in Figure. 1, from left to
right is the module layer subdivision of automobiles.
Automobile companies form a variety of models
through multi-layer module combination, which
meets the needs of consumers' meticulousness and
greatly improves the efficiency of supporting
production.
Figure 1. The Module Layer of Car Body.
3 PRODUCTS MODULARITY
FUNCTION DEPARTING
3.1 The Condition and Demand
Modular design is a special design idea and the
designers need to consider factors such as using
conditions, economy, and necessity of demand. The
design team analyzes the system factors such as the
conditions and requirements of the design object,
and understands the modular advantages of the
design object function. Through the analysis and
evaluation, the modular design method is
determined.
The design conditions and requirements of the
modular design are often the requirement of multi-
function, multi-purpose, and variable function, such
as the space variability requirements of product
combination, requirements for high frequency
switching of storage and placement functions, multi-
function requirements for both home and outing.
To determine the use time and condition of modular
product design, we can observe the product's
operating conditions, core functional components,
and maintenance needs, it can be observed in terms
of product use conditions, core function
components, and maintenance requirements.
3.2 Function Layer Disassembling
The modular concept facilitates the complex product
functions disassembling. The function output of the
product system can be disassembled into constituent
units to determine the core modules and non-core
modules of the modular layout. Module functions
can be disassembled from the following layers:
3.2.1 The Whole Product
This layer mainly focuses on products serialization
and product group differentiation. The serialization
of products is targeted at the function disassembling
of modules. Take construction machinery - leveling
machine as an example, product group and system
composition layers can be classified from the
function requirements. The core function module
can be divided into four basic modules: power unit,
operation unit, cockpit and frame platform (Chen,
L., A. Macwan, and S. Li, 2007). By product
modules disassembling, the multiple combinations
of product serialization extension are provided, as
shown in Figure. 2 below.
ICVMEE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Vehicle, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering
188

Figure 2. The Product Model of Leveling Machine.
3.2.2 Parts Layer
Components are independent modules that make up
a product, which is also the layer of the most
common modular design applications. Different
configurations can be obtained by modularizing the
components, with obvious modular design traces and
visual elements. The structural connection between
the component modules affects the basic direction of
the exterior form design. According to the algorithm
of module division under design structure matrix
(DSM) architectural constraints, Wei et al. adopted
the modularity
Q
function as the optimization
target of module division (Wang, Y., Cho, H, 2012).
3.2.3 Components Layer
Part modularization is the basic module element
layer division in product design category. The
modules are combined from the basic functions, and
then the overall form is designed, based on the
consideration of product serialization. According to
the modular design idea of the leveling machine
structure described above, the chassis components
are further subdivided into basic component module
elements (Smith, S., G. Smith, and Y. T. Shen,
2012), such as transmission, frame and suspension,
to form a new combination scheme. Then, the
holistic design of the new combination is made.
The module elements are divided from the
perspective of function flow disassembling of the
components level. The form of function flow is
divided into material flow, energy flow and
information flow. The disassembling or aggregation
of product functions is made by the module division
based on function flow, through materials, energy
and information flow. And then, the product module
is qualitatively divided. Through the static and
dynamic relation between components, the
correlation between function input and output is
established, such as the input-output relation matrix
of a certain parameter. Where, each matrix element
(, )
ki j
s
IO
is the correlation degree of the j function
input to the i function output when the k parameter
is considered. If the input and output functions are
listed separately,
1
()
k
sI
is the input function and
1
()
k
sO
is the output function. When observing the
correlation degree, it is assumed that there are
correlation degree indexes of M categories of
indicators and parameters for analyzing functions.
Among them, the influence coefficient of the
correlation degree of category k parameter on the
total correlation degree is
k
W
. Since the sum of
product functions is set by the goal, the sum of the
influence coefficients of various parameters is equal
to 1, as shown in equation (1).
1
1
M
k
k
W
(1)
4 FUNCTION PLANING
After the decomposition of modularization, a
preliminary layout plan can be obtained through the
graphic arrangement of functional layout, that is, the
function modules are simplified into blocks to show
the basic construction system of modular design and
the basic logic relationship of the product is
expanded. For example, the function modules of a
product are divided into four parts: P1, P2, P3 and
P4, among which P1 is determined to be the core
module and cannot be replaced, while the other three
modules can be replaced according to the
application. The basic combination scheme of P1+
P2+ P3+ P4. It can also be divided into P1+( P2+
P3)+ P4 combination scheme according to the
function application frequency. In addition, it can be
divided into P1+( P2+ P3+ P4) combination scheme,
that is, P1 is the core module, P2, P3, P4 is the
component or part module, can be replaced, as
shown in the lower part of Figure. 3. By dividing in
this way, different combinations are formed. After
the basic plan is determined, differential exploration
of the detailed modeling for the certain plan is
obtained, such as the differential combination of the
basic combination scheme. Then the detailed
decomposition form is obtained, thereby forming
different structure prototypes and appearances.
The Quick Design Method for the Big and Complex Products based on Function Disassembling
189
5 QUICK CREATIVE DESIGN
PROCESS
In this paper, a large-scale engineering equipment -
leveling machine is taken as a design object for
modular design process analysis and industrial
design process study (Minjung Park, Jungmin Yoo,
2018; Daie P, Li S, 2016).
5.1 Function Decomposition and
Developing
According to the previous function division
principle, the following main function modules are
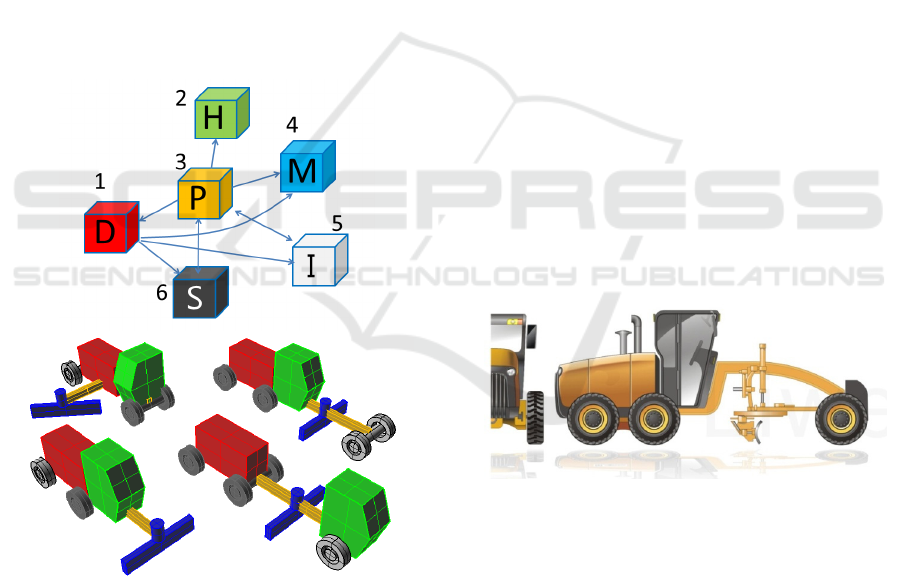
determined: ① D engine cabin (Driving, red); ② H
cockpit (Human, green); ③ P chassis and frame
(Planning, orange); ④ M flat shovel module
(Moving, blue); ⑤ I guide wheel set (Index, gray);
⑥ S supporting wheel set (Supporting, black),as the
Figure3.
Figure 3. The Image of Function Relationship.
It can be seen that the chassis and frame are the
main body supporting the engineering vehicle, and
its shape is variable, according to the principle of
function decomposition and interrelation. P supports
and links each of the other modules, from the
function input and output relationship. H cockpit is
supported by the chassis and is not directly related to
other modules. In the design process of it, care must
be taken to maintain the open view of the cockpit. In
the design process, it is necessary to ensure the wide
operation vision of the cockpit. D engine cabin
module is supported by P, outputting power to M, S,
I and other modules, and the product function
expansion is shown in Figure. 3. There are 8
unidirectional or mutual output - input relationships
among the 6 basic modules of the leveling machine.
At the same time, the M, S, and I modules must
touch the ground at the same time, according to the
body supporting and operation requirements.
Through logical relationship analysis, creatives
compile function relationship and use system
software to rationally combine ideas.
5.2 Quick Creative and Rendering
According to the above combinations, the paper
created a preliminary creative plan by divergent
thinking and discussion. We evaluated and filtered
the design schemes, according to the requirements of
the engineering machinery products in the practical
application, such as the operating range, the stability
of the car, the steering stability, the passivity, the
work efficiency, etc. Then, they obtained the more
specific design schemes and drew detailed sketches.
We continued to optimize the creative plans, and
used CAR (Computer Aided Rendering) to elaborate
the 2D plan design scheme and 3D data construction
(Computer Aided Design, CAD) , as shown in
Figure 4.
Figure 4. The CAD Picture of Leveling Machine.
5.3 Concept Evaluation
According to the 2D and 3D concept schemes
completed by designers, explicit visual evaluation
was made from the aspects of man-machine
interaction measure, function range, assembly
relation, maintainability and overall form. If detailed
evaluation is needed, in-depth evaluation can be
carried out based on 3D data, by methods of
computer-aided simulation, dynamic analysis,
structural performance, ergonomics, color survey
ICVMEE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Vehicle, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering
190

(Wei Wei, Xu Shaopeng, Liang He, 2016; Stone R
B, Wood K L, Crawford R H, 2000), etc.
6 DESIGN EVALUATION
The industrial design method needs to be quickly
evaluated in the conceptual design stage. Generally,
the design evaluation is carried out from several
aspects: the function realization effect, realizability,
maintainability, sustainability, and overall
appearance effect, which provides direction for later
optimization. The corresponding evaluation
mechanism and content should be established for
each index. For example, Minjung Park has
calculated the results of each evaluation index in the
modular design by FAHP (fuzzy analytic hierarchy
process). The design of color image has been studied
by Daie P et al. based on mathematical evaluation
for the evaluation of engineering machinery
products color.
7 CONCLUSION
The big and complex device products design is
meticulous, which is systemic and the link between
the steps will affect the progress and efficiency of
the next stage. Following the idea of modularity
disassembling and function unfolding principle with
a leveling machine as an example, this paper
explored and found out the intuitive results in
concept design stage by using the methods of
function disassembling, function relationship and
industrial design. The results would provide a
reference for industrial design and research on the
big and complex products. Due to the difference in
production level and innovation, the role of
industrial design in big and complex products needs
to be improved, and further exploration of it is
needed.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper was financially supported by Chongqing
Education Commission (KJ1500525) and
Chongqing Science and Technology Commission
(cstc2016jcyjA0467, cstc2017jcyjAX0248) in China
fund.
REFERENCES
Chen, L., A. Macwan, and S. Li. Model-based Rapid
Redesign Using Decomposition Patterns [J]. Journal
of Mechanical Design, 2007. 129 (3): 283–294.
CHEN Mengyue CHEN Dongping CHU Xuening. CHEN
Mengyue CHEN Dongping CHU Xuening [J].
Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2016,
11: 2522-2529.
Daie P, Li S. Matrix-based hierarchical clustering for
developing product architecture [J]. Concurrent
Engineering Research and Applications, 2016, 24(2):
139-152.
Lei Zhang, Xuening Chu, Deyi Xue. Identification of the
to-be-improved product features based on online
reviews for product redesign [J]. Taylor journal, 2019:
2464-2479.
Minjung Park a, Jungmin Yoo. Benefits of mass
customized products: moderating role of product
involvement and fashion innovativeness [J]. Heliyon,
2018, 4(2):1-25.
Smith, S., G. Smith, and Y. T. Shen. Redesign for Product
Innovation [J]. Design Studies, 2012, 33 (2):160–184.
Stone R B, Wood K L, Crawford R H. A heuristic method
for identifying modules for product architectures [J].
Design Studies, 2000, 21(1): 5-31.
The design structure system: A method for managing the
design of complex systems. Steward DV. IEEE
Transactions on Engineering Management. 1981
The effects of e-mass customization on consumer
perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty toward
luxury brands [J]. Jungmin Yoo, Minjung Park.
Journal of Business Research. 2016 (12)
Wang, Y., Cho, H. The effect of fashion innovativeness on
consumer’s online apparel customization [J]. Int. J.
Ogan. Implant, 2012, 5 (2), 263e283.
Wei Wei, Xu Shaopeng, Liang He. A module partition
method of product platform based on environmental
resource factors [J]. Journal of Computer-Aided
Design & Computer Graphics, 2016, 28(2): 335-
344(in Chinese).
The Quick Design Method for the Big and Complex Products based on Function Disassembling
191
