
Cocoa Pod (Teobroma cacao L.) Utilization as Material for CMC
Yeni Afriani, Zanira Urfa Harahap, Era Fazira Matondang and Cut Fatimah Zuhra*
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: CMC, Alkalization, Carboxymethylation, Cacao Pod.
Abstract: Cacao pod contain 31.25% cellulose. It can be used for CMC (carboxymethyl cellulose) with four phases
involving alkalization, carboxymethylation, neutralization and drainage were used to making of CMC. The
first proses using NaOH. Media such as methanol, propanol, sodium monochloroacetate, and water. The
neutralization process, acetic acid was added. And for the last step it was heating in the oven. The result
showed that contents of CMC of NaCl 87-91%, viscosity 5.5 cP, pH 8, and DS value is 0.872. On the other
hand, acetic acid did not give significant effect for colors of CMC.
1 INTRODUCTION
Indonesia is the third largest producer of cacao
(Theobroma cacao L.) in the world. The large number
of processing cocoa fruit in Indonesia are mostly only
used the seeds and pulp to be produced while the
cocoa pod husks were being a waste unused. S hile it,
in the pod husks containing crude fiber composed of
cellulose (31.25%), hemicellulose (48.64%) and
lignin (20.11%) (Ashadi, 1988).
Cellulose is a polysaccharide which if hydrolysed
will produce glucose monomers and some cellobiose.
Cellulose can swell if reacted with alkali metal, salts
in strong base solutions and amine compounds. The
amine compound that is commonly used to develop
cellulose bonds is NaOH (Irawadi, 1990). Cellulose
is also insoluble in water and is very easy to absorb
water. It’s really support to make the pod husks as raw
material for the manufacture of carboxymethyl
cellulose or carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC).
CMC is derivative from cellulose used in industry
food for get good texture. There are several the most
important CMC function that is as thickener,
stabilizer, gelling agent, as emulsifier, and in some
could levelling spread antibiotics. CMC has group
carboxyl, then viscosity CMC solution is affected by
the pH of the solution (Winarno, 1995). CMC is
capable tie water so water molecules are trapped in
gel structure formed by CMC. CMC is an ingredients
stabilizer that has power strong tie and play a role for
improve viscosity and texture product food, like jelly,
salad and produkes (Belitz and Grosch, 1987).
Rahman et al. (2016) conducted a study on the use
of cellulose to CMC produced from rice straw cellulose
resulting in optimum purity conditions of CMC, which
were added to 4 grams of NaMCA (sodium
monochloroacetic) and 5 grams of cellulose. The
amount of sodium monochloroacetate used will affect
it substitution of anhydrous unit glucose in cellulose.
Increasing the amount of alkali used will result in an
increase in the amount of monocloroacetate. This
carboxymethylation process is actually an
etherification process. At this stage is the process of
attaching the carboxylic group to the cellulose
structure. This is very important to control when
making CMC (Personal, 1985).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials
The materials used in this study include: Cocoa pod,
NaOH 30%, NaOH 2%, H
2
O
2
10%, methanol,
propanol, acetate acid 90%, aquadest, Fehling A,
Fehling B, Na-MCA, K
2
CrO
4
, AgNO
3
, Nitric acid.
2.2 Preparation PVA 10%
Waste of cocoa fruit peel is broken and cleaned with
water. Then dried in the sun. Mashed using a blender.
Sifted using 80 mesh sieves. Furthermore, the water
content is determined by weighing 2 grams of cocoa
pod powder into a weighing bottle, put in the oven for
Afriani, Y., Harahap, Z., Matondang, E. and Zuhra, C.
Cocoa Pod (Teobroma cacao L.) Utilization as Material for CMC.
DOI: 10.5220/0008857201210123
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Chemical Science and Technology Innovation (ICOCSTI 2019), pages 121-123
ISBN: 978-989-758-415-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
121
4 hours at 105°C and then put into the desiccator and
weighed until the weight remains.
2.3 Isolation of Cellulose
Cocoa pod husk was weighed as much as 250 grams
then mixed with NaOH 2% and then heated at 80°C
for 4 hours while stirring. Then is filtered, the
sediment will be washed with aquadest until pH 7 and
then bleached with H2O2 10% as much as 250 ml
after that it was heated at 60°C for 15 minutes then
left for 1 night. Ovened cellulose for 1 night at 75°C
then characterized by FT-IR and tested qualitatively.
Cellulose is prepared in the form of pulp. Porridge is
examined in a thin film placed between flat salt
plates. The test is done by clamping the mixed film
on the sample site. Then the film is placed on the plate
in the direction of infrared light. The result will be
recorded periodic paper in the form of a 4000-200 cm
-
1
wave number curve flow to intensity.
2.4 Antimicrobial Activity
About 10 gram cocoa pot husk put into 3 neck flask
placed on waterbath then added 400mL propanol p.a,
50 ml methanol, 50 mL aquadest and stirred for 10
minutes. Then added 30% NaOH solution (22 grams
of NaOH) drop by drop and the alkalization process
continues for 1hour at 24°C. After completed
followed carboxymethylation process by adding as
much as 20 grams of sodium monochloroacetate for
3.5 hours at a temperature of 55°C.
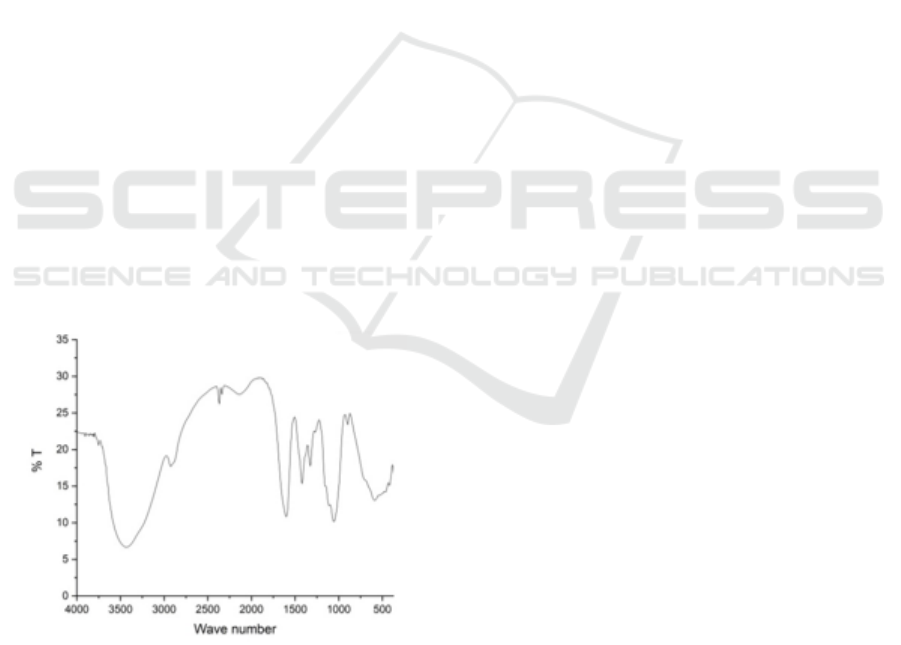
Figure 1: FTIR spectra of CMC.
After the carboxymethylation process is complete,
the stirrer is turned off then the mixture is transferred
to the beaker glass and the pH is measured. Next, 90%
acetic acid was added until the pH was neutral and
decanted. The residue obtained was added with 200
mL of methanol and stirred and then filtered using a
vacuum pump. Finally wrapped in aluminum foil
dried in the oven for 4 hours at 60°C. The dried CMC
is then mashed with a blender and stored in a closed
place. The CMC obtained will be analyzed by FT-IR.
CMC is prepared in the form of pulp. Porridge is
examined in a thin film placed between flat salt
plates. The test is done by clamping the mixed film
on the sample site. Then the film is placed on the plate
in the direction of infrared light. The result will be
recorded periodic paper in the form of a 4000-200 cm
-
1
wave number curve flow to intensity.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Characterization of Cellulose
The FT-IR spectrophotometric test results also
showed positive results by comparing wave number
of bagasse cellulose and commercial cellulose. Figure
1 is the result of FT-IR spectroscopic test which
shown spectrum with vibration peak in area of
3448.72 cm
-1
for –OH group, supported by
emergence of vibrational peaks at wave number
2900.94 cm
-1
which shows C–H stretching groups,
1064, 71 cm
-1
which shows the ether group, and the
glycoside bond in α-cellulose structure is found at
wave number 1635.64 cm
-1
(Epriadi, 2017).
Results infrared spectra from cellulose to show
absorption on number wave 3332,66 cm
-1
which is is
a OH area on number wave 1321,54 cm
-1
to show
area peak for CH groups, and on number wave
1040,31 cm
-1
which is is a C-O-C group.
3.2 Characterization of CMC
The CMC samples were analyzed by FTIR, which can
be depicted in the two spectra in Fig. 1. The x-axis
represents the wavelength (cm
-1
) and y-axis whos the
light transmittance through the sample. The FTIR
spectrum of the sample shows that the carboxyl,
methyl and hydroxyl functional groups are found at
wavelength of 1617.60, 1454.44 and 1195.72 cm
-1
(for CMC-55-10), 1613.57, 1426.01 and 1214.54 cm
-
1
(for CMC-28-10), respectively. However, for
sample CMC-82-10 only carboxyl and methyl
functional groups are shown in the peak at 1654.16
and 1458.13 cm
-1
. Consequently, for all CMC
samples synthesized the IR spectra indicates the
typical absorptions of the cellulose backbone as wel
as the presence of the carboxymethyl ether group at
1654.16, 1617.60 and 1613.57 cm
-1
consecutively for
each sample. The additional peak at wavelength of
ICOCSTI 2019 - International Conference on Chemical Science and Technology Innovation
122

2357.27 cm
-1
at sample CMC-55-10 might be due to
the existence of the contamination from impurities or
combination band with water. Subsequently the bands
around 1458.15 – 1420.05 cm
-1
are assigned to CH2
scissoring. It is obvious that those in the broad
absorption band of approximately above 3500 cm
-1
is
due to the stretching frequency of the hydroxyl group
(-OH) (Saputra, 2014). Based on Table 1, the
viscosity of CMC is 5.5 cP. The purity of CMC based
on NaCl contents is 94,15%. The substitution degree
during carboxymethylation was 0.872.
Table 1: Result of viscosity test.
CMC (g)
Viscosity (cP)
0.01
5.5
0.02
5.3
0.03
5.6
0.04
5.5
0.05
5.6
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research it can be
concluded that CMC from cacao pod husk can be
used. But CMC were obtained to show less result s
well from facet viscosity. Expected next researcher
more pay attention composition in making CMC.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to send gratitude to Risekti
dikti for the financial support towards this research in
the PKM-PE Project 2019 and also for Universitas
Sumatera Utara which facilitated this research.
REFERENCES
Adinugraha M. P, Marseno, D. W., Haryadi., 2005.
Synthesis and Characterizationof Sodium
Carboxymethyl Cellulose from Cavendish Banana
PseudoStem (Musa cavendishii LAMBERT).
Carbohydrate Polymers, 62: 164-169.
Figueira A, Janick J., 1993. New products from Theobroma
cacao: Seed pulp andpod gum.New York: New crops.
475- 478
Hong, K. M., 2013.Preparation and Characterization of
Carboxymethyl Cellulose from Sugarcane Bagasse.
Malaysia: Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman. 1:21-84.
Mandal, A, Chakrabarty D. 2011.Isolation of Nanocellulose
from Sugarcane
Bagasse (SCB) and Its Characterization Carbohydrate
Polymers. 86(1): 1292 –1299.
McKee T, McKee J. R., 2003 .Biochemistry: The
Molecular Basis of Life.New York:McGrawHill
Companies, Inc. 3: 219-220.
Ott, Spurlin., 1995. Cellulose and Cellulose Derevative,
Vol 5 Part 2. New York: Inter Science Publisher Inc.
Preparation, Proximate Composition and Culinary
Properties, Journal of food research 18: 1283-1287.
Susanto, F. X., 1994. Tanaman Kakao: Budidaya dan
Pengolahan Hasil. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Kanisius. 43-
54
Cocoa Pod (Teobroma cacao L.) Utilization as Material for CMC
123
