
Mechanical Properties and Morphology Biocomposites of
Polycaprolactone (PCL)/Modified using Trisodium
Trimetaphosphate
Marpongahtun
1*
, Cut Fatimah Zuhra
1
, Sovia Lenny
1
, Darwin Yunus Nasution
1
, Aulya M.
1
,
Suci A. Amaturrahim
1
, Mahmud
2
, Fitria Puspa Dewi
1
and Irmayani
1
1
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Bioteknologi
No. 1 Kampus USU Padang Bulan, Medan 20155, Indonesia
2
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Negeri Medan,
Sumatera Utara, Indonesia
fitriapuspadewi24@gmail.com, yirma1743@gmail.com
Keywords: Biocomposite, Breadfruit Strach Modified, Polycaprolactone, Mechanical Properties.
Abstract: The determination of the mechanical properties and morphology of polycaprolactone (PCL) / breadfruit
polytocyte biocomposites tied up with trisodium trimetaposphate was performed. The breadfruit starch is
tied with trisodium trimetaposphate to produce pospat starch. The highest degree of substitution was
obtained in variation of trisodium weight of trimetafosfat 3%, that is 0,0633. PCL / Starch Biocomposite
was prepared by mixing method between PCL in chloroform solvent with modified 3% sodium starch then
printed at 75˚C since 10 minutes. Mechanical properties, functional group, and morphological of
PCL/Modified breadfruit starch biocomposite was analyzed. The result of evaluation showed an optimal
tensile test value of 90%: 10% with tensile strenght of 7,4287 MPa and Modulus Young’s of 27,852 MPa.
The functional group analysis of phosphate starch showed asymmetric P-O-C group at wave number
1018,41 cm
-1
. Analysis with FT-IR from PCL/Modified Breadfruit Starch Biocomposite showed of physical
interaction occurred between PCL and modified breadfruit starch. Morphological analysis using SEM
showed smooth and homogeneous surface of biocomposite.
1 INTRODUCTION
Biocomposite is a type of composite that one of the
constituents, namely the padding or matrix derived
from natural materials (Xanthos, 2005). The matrix
used in this study is the polymer matrix.
Polymer matrixs that derived from nature were
start being selected by the community in the
manufacture of biocomposites because they were
considered more environmentally friendly. This
study uses matrix padding in the form of breadfruit
starch derived from breadfruit. Breadfruit is high in
carbohydrates and a valuable source of starch.
Breadfruit produced 18.5 grams/ 100 grams of starch
with 98.86% purity, 27.68% of amylose and 72.32%
of amylopectin (Rincon and Padilla, 2004).
Biocomposite in this study was made by mixing
breadfruit starch with polycaprolactone (PCL) with
the aim for improving the mechanical properties of
biocomposite. PCL is generally used as one of the
basic ingredients for making biomaterials. PCL has
good mechanical properties, that biocompatible with
many types of polymers. The use of PCL for tissue
regeneration is very limited due to its hydrophobic
nature which affect cell regeneration and
degradation rate. A simple way to increase its
hydrophilicity, by mixing PCL with natural
polymers (Wang et al., 2009).
Starch modification and processing techniques
have developed rapidly, natural starch can be
modified so it has better properties. Because the
starch industry wants a stable thickness of starch at
both high and low temperatures, good endurance to
mechanical treatment, and thickening power that
resistant to acidic and high temperature. (Koswara,
2009).
(Wang et al., 2005) conducted a study of thermal
and thermomechanical behavior of polycaprolactone
Marpongahtun, ., Fatimah Zuhra, C., Lenny, S., Yunus Nasution, D., M., A., Amaturrahim, S., Mahmud, ., Puspa Dewi, F. and Irmayani, .
Mechanical Properties and Morphology Biocomposites of Polycaprolactone (PCL)/Modified using Trisodium Trimetaphosphate.
DOI: 10.5220/0008925802870292
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Chemical Science and Technology Innovation (ICOCSTI 2019), pages 287-292
ISBN: 978-989-758-415-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
287

and starch/ polycaprolactone compound for
biomedical applications, corn starch was used where
a compound of corn starch with 30/70% weight of
PCL (SPCL), and used a commercial PCL. After
conducting thermal analysis, the melting peak
temperature and melting enthalpy for PCL is higher
than SPCL which is equal to 58.40
0
C and 59.80
0
C
at SPCL crystallization rate is much higher than
PCL which is equal to 47.60
0
C, this indicates that
starch acts as an agent for PCL .
(Sujito, Munawaroh and Purwandari, 2013)
conducted a study of the mechanical properties and
ability of biodegradation of poly lactic acid
biocomposite with amplifier of thin bamboo sheets
and sengon wood, biodegradation test of
biocomposite was carried out using the land fill
method where the materials was buried in the soil
for 4 weeks and watered with ± 150 cc / day.
Observation of the test material was carried out
every week by calculating the percentage changes in
relative mass and physical changes from the material
using a microscope. The results showed a decrease
in the quality of biocomposite synthesized materials
due to burial.
(Zuhra and Marpongahtun, 2016) conducted a
study of breadfruit starch modification by
crosslinking method using trisodium
trimetaphosphate with various weight of sodium
trimethaphosphate 1%, 2%, 3% and 30, 60, and 90
minutes of reaction times. Results from the research
using IR spectroscopy phosphate starch was formed
asymmetric P-O-C vibrations at wave numbers
1050-995 cm
-1
and 1643 cm
-1
. The effect of
increasing Trisodium trimetaphosphate
concentration increases the value of substitution
degree and decreases the swelling power value. The
highest degree of substitution was 0.003 gram at 3%
concentration and 60 minutes of reaction time.
Starch can be divided into 2 types, native starch
which has not been modified and modified starch.
Modifications made to improve the properties of
native starch, including producing higher brightness
starch, lower viscosity and gel formed, starch
granules break more easily and higher gelatinization
time and temperature (Koswara, 2009).
Cross-linking is a method that can be used to
modify starch by replacing -OH groups with groups
of added crosslinking agents such as esters, ethers or
phosphates (Siswanto, Manurung and Budiyati,
2012). The advantage of using the crosslinking
method is to produce starch with little swelling
power. This will strengthen starch granules so that it
is not easily broken during heating and make the
starch more resistant to acidic and heat media. In
addition, it strengthens hydrogen bonds in granules
with chemical bonds that act as bridges between
starch molecules. As a result, when starch is heated
in water, the granules will expand that make the
hydrogen bonds weaken (Koswara, 2009).
In this study, a combination of polycaprolactone
and modified starch was mixed homogeneously
through perfect stirring. That is produce a thin
membrane formed by pouring and evaporating the
solvent at room temperature. Characterization
carried out is the mechanical strength test, functional
group analysis and surface morphology analysis.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Equipment
Tools used in this research are analytical scale,
measuring cup, hotplate, stirrer, glass funnel, beaker
glass, oven thermometer, desiccator, aquadest bottle,
measuring flask, aluminum foil, hot press, magnetic
stirrer, pH meter, spectrophotometer FT-IR, tensile
testing equipment, Scanning Electron Microscopy
(SEM), and whatman filter paper No.1.
2.2 Materials
Materials used in this study include: breadfruit,
trisodium trimetafosfat (TMP), vanadate-molybdate
reagent, Na
2
CO
3
, KH
2
PO
4
, 0.5 N NaOH, 0.5 N HCl,
polycaprolactone (PCL), chloroform, aquadest and
water.used in this study include: breadfruit,
trisodium trimetafosfat (TMP), vanadate-molybdate
reagent, Na
2
CO
3
, KH
2
PO
4
, 0.5 N NaOH, 0.5 N HCl,
polycaprolactone (PCL), chloroform, aquadest and
water.
2.3 Methods
2.3.1 Isolation Starch from Breadfruit
Breadfruit that has yellowed peeled and removed the
stalks of fruit, then washed from dirt and sap. Then
cut into small pieces and mashed with blender.
Furthermore, filtered the mashed breadfruit using
gauze and left until precipitate. Washed the
precipitate repeatedly with water until the top layer
is clean. The obtained starch is dried in the oven at
45 °C for 24 hours. Ground and sifted the crude
starch. Then, analyzed breadfruit starch using FT-IR.
ICOCSTI 2019 - International Conference on Chemical Science and Technology Innovation
288
2.3.2 Phosphate Starch Manufacture
Dissolved 30 grams of breadfruit starch with 45 mL
aquadest until a suspension was formed and then
added 1% trisodium trimetaphosphate while stirring
to pH 10 by dripping 1 M NaOH. Then heated the
compound at 45 °C while stirring for 60 minutes.
Furthermore, neutralized the obtained starch
porridge to pH 6.5 with 1 M HCl then washed
thoroughly using distilled water. Phosphate starch
then dried at 40° for 24 hours. Ground and sifted the
coarse phosphate starch. Used the same procedure
for trisodium trimetaphosphate 2 and 3% weight.
Furthermore, the obtained phosphate starch was
characterized by FT-IR and calculated the degree of
substitution (DS).
2.3.3 Determination of Degree of
Substitution for Crosslink Starch
(Phosphate Starch)
Determination of phosphate substitution degrees was
carried out according to (Deetae et al., 2008) as 1.5
grams of sodium carbonate were dissolved in 5 mL
aquadest. Then added 2.5 grams of starch phosphate
to the sodium carbonate solution and put into the
kiln at 550 °C for 6 hours to be ignited. Dissolved
the sample that has been ignited with 2 mL of 25%
HCl and stirred until it dissolves. Then added
aquadest until it reach 50 mL volume of solution.
Piped 10 mL from the solution and added vanadate-
molybdate reagent, then left at room temperature for
± 45 minutes. After that, observed the samples using
a UV-Visible spectrophotometer at a 435nm
wavelength should be aligned to the center with
linespace exactly at 13-point. The text must be set to
11-point.
2.3.4 Manufacture of Modified Starch
Biocomposite with PCL
Dissolved 9 grams of PCL with chloroform at 60 °C.
Then added with 1 gram of starch phosphate while
being distirer until homogeneous for 30 minutes,
then cooled and dried. Next, put it into the mold and
pressed with a Hot Press tool at 75 °C for 10
minutes. Use the same procedure on the manufacture
of biocomposite according to predetermined
variations. Then carried out biocomposite
characterization of tensile test analysis, FT-IR and
SEM.should appear aligned to the center including
organisation, address and e-mail.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Phosphate Starch Manufacture
Phosphate starch is starch obtained from cross-
linking reaction between starch and trisodium
trimetaphosphate in the presence of sodium
hydroxide which acts as a catalyst.
The reaction between starch and sodium
hydroxide starts with the attack of Na atom from
sodium hydroxide on C2 starch atom. Sodium
hydroxide will break the C2-C3 bond which has a
secondary alcohol group to form the phosphate
starch. And the secondary -OH group on C2 starch
atom attacks H atoms of C3 starch atoms to produce
water. Then the C2-C3 bond is cut off and the
electron is displaced to produce phosphate starch.
3.2 FT-IR Spectrum Analysis of
Breadfruit Starch and Modified
Starch
Function group analysis using FT-IR for starch and
modified starch from the breadfruit isolation can be
seen from FT-IR spectroscopic data. The FT-IR
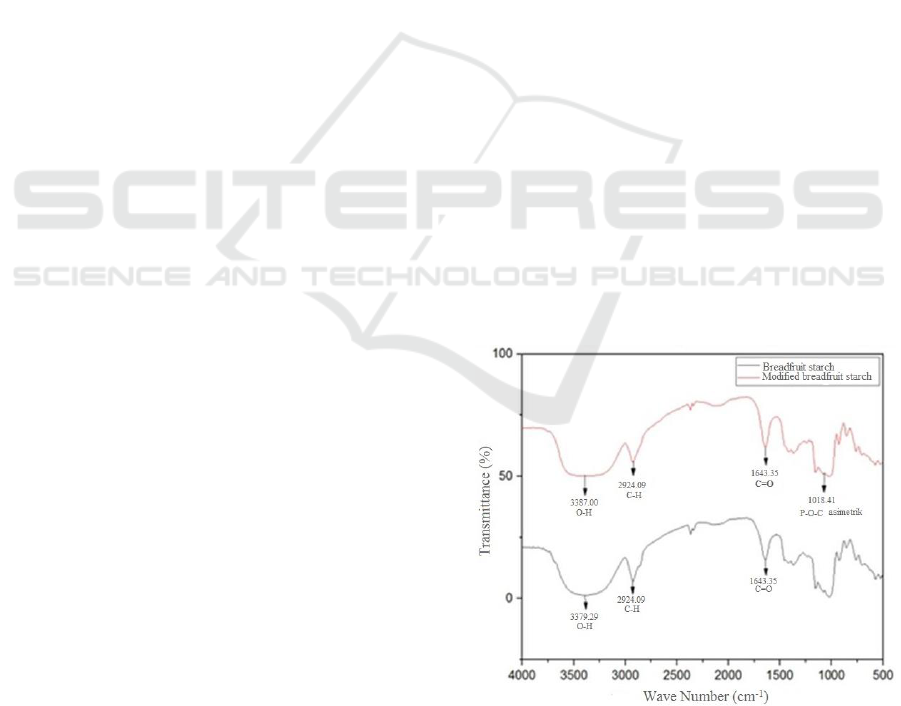
spectrum of breadfruit starch (Figure 1) shows the
group contained in starch, where the wave number
3379.29 cm
-1
shows the –OH group; 2924.09 cm
-1
shows the –CH group; 1643.35 cm
-1
shows the C =
O group. The results of FT-IR spectrum analysis
showed that starch isolation was successfully carried
out can be seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1: FT-IR Spectrum Breadfruit Starch and Modified
Breadfruit Starch.
The FT-IR spectrum phosphate starch supports
the emergence of a vibration peak in the wave
Mechanical Properties and Morphology Biocomposites of Polycaprolactone (PCL)/Modified using Trisodium Trimetaphosphate
289
number 1149 cm
-1
– 1018,41 cm
-1
indicating the
presence of a P=O aliphatic group that supported by
band absorption which indicate the presence of
asymmetric P-O-C groups in the wave number
1080,14 cm
-1
. The vibration peak at the wave
number 1643 cm
-1
shows the hydrogen
intramolecular bond and the break-off of the
hydrogen bond so that the -OH group is converted
into phosphate ester (Li and Yeh, 2001). This
absorption comes from an added crosslinking agent,
namely trisodium trimetaphosphate which replaces
the -OH group in starch molecules. This shows the
addition of new groups to the modified starch.
3.3 Determination of Phosphate
Percentage and Degree of
Substitution (DS)
Determination degree of substitution was carried out
using UV-visible spectrophotometry. The results of
determining the degree of substitution can be seen in
Table 1.
Table 1: Results of determination degree of substitution of
variations in the trisodium trimetaphosphate weight.
Treatment
Phosphate
Percentage
Degree of
Substitution (DS)
0,3 g TMP
0,9592
0,0520
0,6 g TMP
1,1585
0,0633
0,9 g TMP
1,2426
0,0681
Results of the substitution degrees obtained
ranged from 0,0520 – 0,0681. The highest value of
0,0681 was obtained from phosphate starch with a
variation weight of 0,9 gram trisodium
trimetaphosphate with 60 minutes reaction time. The
more crosslinking agents were added and the longer
the reaction time, the more phosphate groups can
substitute the -OH group. This is because the longer
the contact time between trisodium trimetaphosphate
and starch, the weakens the hydrogen bonds found in
starch molecules.
3.4 FT-IR Spectrum Analysis of PCL
Biocomposite/Modified Breadfruit
Starch
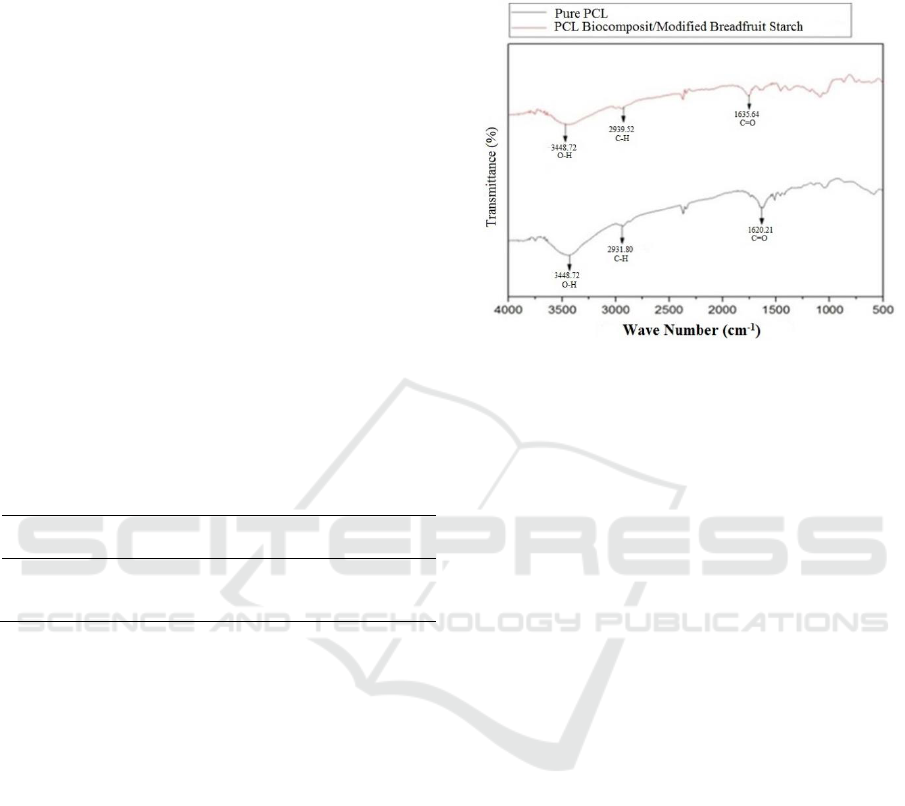
FT-IR spectroscopy was used to determine the
characteristics of composite membranes functional
groups. The FT-IR spectrum of polycaprolactone
(PCL) and PCL biocomposite/modified breadfruit
starch can be seen in Figure 2.
The FT-IR spectrum of polycapolactone shows the
-OH, -CH, C=O group at wave numbers respectively
3448,72 cm
-1
, 2931,80 cm
-1
, 1620,21 cm
-1
.
Figure 2: FT-IR Spectrum of Pure PCL and Biocomposite
PCL/ Modified Breadfruit Starch.
The FT-IR spectrum of biocomposite PCL/
breadfruit starch showed –OH, C–H, and C=O
groups at wave numbers of 3448,72 cm
-1
, 2939,52
cm
-1
, and 1635,64 cm
-1
, respectively.
Based on FT-IR analysis, it can be seen that the
functional groups formed are a combination of
specific functional groups found in their constituent
components. The functional group reappeared on the
spectrum compound between polycaprolactone and
breadfruit starch where the intensity was almost
same and new functional group was not found. This
proves that the compound of PCL/ breadfruit starch
produced is a physical mixing process.
3.5 Mechanical Properties Analysis of
Biocomposite PCL/Modified
Breadfruit Starch
Tensile strength is the ability of a material to hold a
load without breaking the material. Mechanical
properties are carried out to determine the tensile
strength and biocomposite elasticity produced.
Composites with good mechanical properties can
be obtained if the padding material is well dispersed
in the matrix. Fillers and matrixs must be
compatible, that is, they are suitable when mixing. In
this study, the fillers used were starch and the matrix
was polycaprolactone. The results of the mixture
between PCL / breadfruit starch and the results of
tensile strength analysis can be seen in Figures 3 and
Figure 4 and in Table 2.
ICOCSTI 2019 - International Conference on Chemical Science and Technology Innovation
290
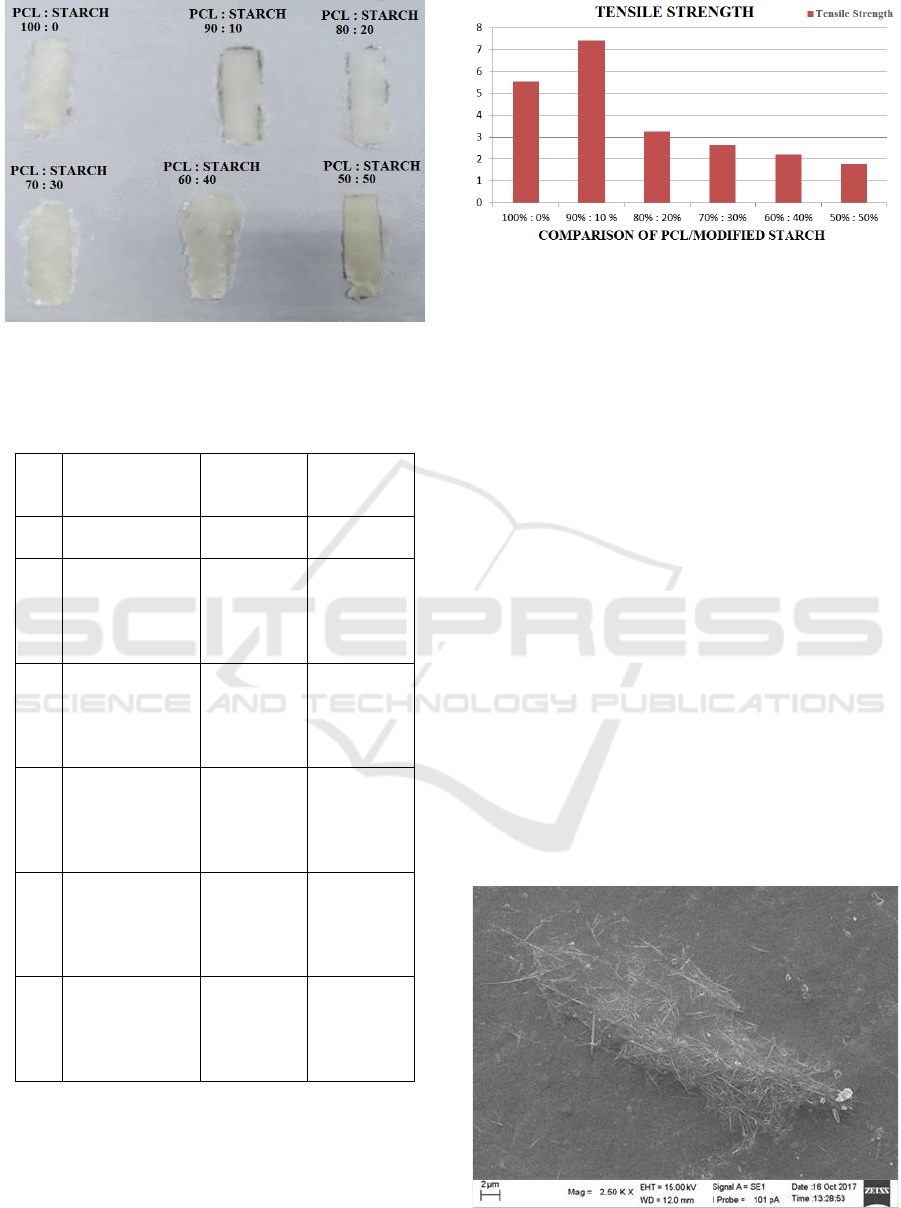
Figure 3: PCL Biocomposite/ Modified Breadfruit Starch.
Table 2: Result of Tensile Strength and Modulus Young’s
from Pure PCL Pure and Biocomposite PCL / Modified
Breadfruit Starch.
NO
Material Type
Tensile
Strenght
(MPa)
Modulus
Young
(MPa)
1
Pure PCL
(100% : 0%)
5.5473
4.9771
2
Biocomposite
PCL/Modified
Breadfruit
Starch
(90% : 10%)
7.4287
27.852
3
Biocomposite
PCL/Modified
Breadfruit
Starch
(80% : 20%)
3.2615
58.126
4
Biocomposite
PCL/Modified
Breadfruit
Starch
(70% : 30%)
2.6466
13.309
5
Biocomposite
PCL/Modified
Breadfruit
Starch
(60% : 40%)
2.2155
4.732
6
Biocomposite
PCL/Modified
Breadfruit
Starch
(50% : 50%)
1.7954
42.968
The comparison of the tensile strength result and
Modulus Young's can be concluded that
biocomposite with a ratio of 90%: 10% has the most
optimum value, with 7.4287 Mpa of tensile strength
and 27.852 Mpa of Modulus Young’s.
Figure 4: Tensile Strength Graph of Pure PCL and
Biocomposite PCL / Modified Breadfruit Starch.
The mixing process is more stable and the
mixture of starch added is less so that it increases the
value of the tensile strength produced. The value of
the tensile strength mixture is decreases with
increasing starch. This is consistent with (Sabo et
al., 2013) which states that the more starch mixtures
werw added, the lower the tensile strength value,
because starch molecules will interact with the
polymer chain structure which causes the polymer
chain to be difficult to move because of the
intermolecular forces between starch molecules.
3.6 Morphological Analysis with SEM
Surface morphology analysis with SEM was carried
out to provide information about the shape and
change of surface from pure PCL and modified
biocomposite PCL /breadfruit starch. Figures 5 and
6 are SEM results of pure PCL and modified PCL /
modified breadfruit starch with a ratio of 90%: 10%
that obtained from the most optimum tensile test
analysis result. Morphological analysis was carried
out using a ZEISS device with a magnification of
2500 times with a power of 15,0 kV.
Figure 5: SEM Analysis of Pure PCL.
Mechanical Properties and Morphology Biocomposites of Polycaprolactone (PCL)/Modified using Trisodium Trimetaphosphate
291
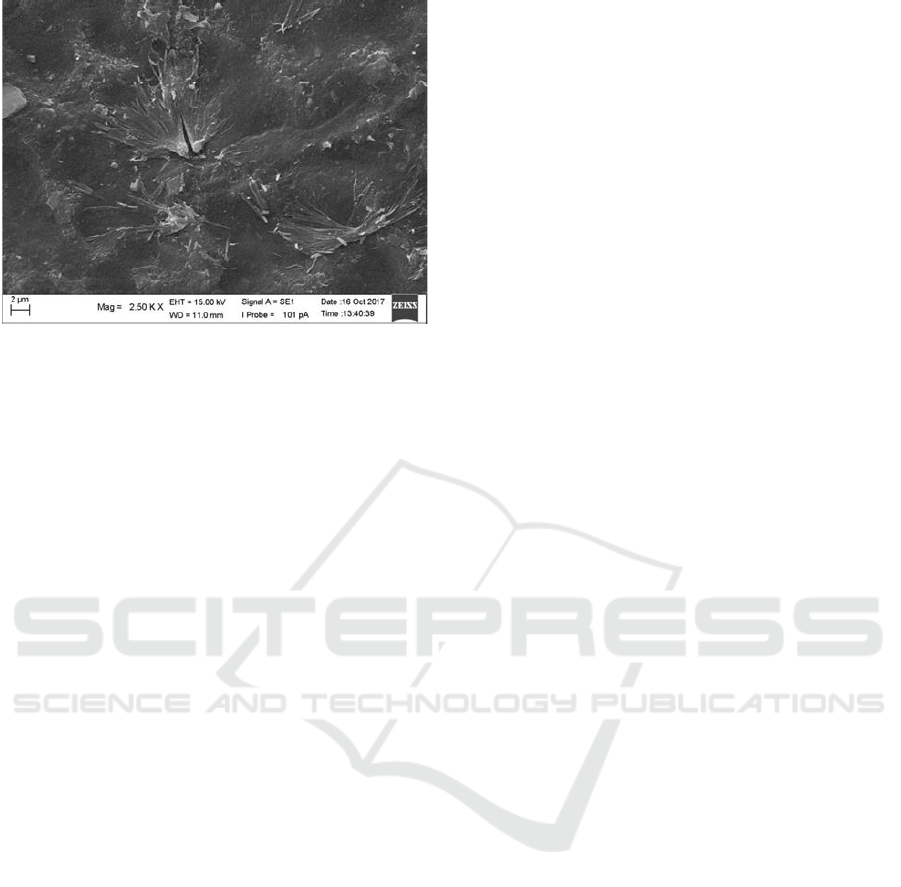
Figure 6: Biocomposite PCL/Modified Breadfruit Starch
(90%: 10%).
From the SEM results, it can be seen that PCL has
more evenly surface, because PCL is not filled with
padding so that it produces a more evenly and smooth
surface (Panindia, 2015) .Meanwhile, biocomposite
PCL/breadfruit starch shows that starch can be
distributed evenly on the PCL surface with the
presence of physical interactions that produce a more
evenly and smoothly surface. PCL and starch have the
ability to mix with each other because both have good
properties and characteristics so that they have
compatibility when mixing to produce a smooth and
more evenly surface morphology.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The results from the research conducted can be
concluded that phosphate starch in the variation of
the weight of trisodium trimetaphosphate 3% is the
most optimum condition with the highest value of
Substitution Degrees which is 0,0681. Mechanical
biocomposite analysis of PCL/Starch Breadfruit with
90%: 10% showed an optimum conditions with
tensile strength values of 7,4287 MPa and 27.852
Mpa of Modulus Young's. FT-IR analysis on
optimum biocomposite showed the occurrence of
physical interactions between starch molecules and
PCL. Morphological analysis shows the formation of
a homogeneous surface and evenly distributed on the
surface of the biocomposite.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Author would like to thank to Rector of University of
Sumatera Utara for the funding from the project of
PD-TALENTA 2018 Number: 122/UN/5.2.3.1/PPM/
KP-TALENTA USU/2017
REFERENCES
Deetae, P. et al. (2008) ‘Preparation, pasting properties
and freeze-thaw stability of dual modified crosslink-
phosphorylated rice starch’, Carbohydrate Polymers.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.12.004.
Koswara, S. (2009) Starch Modifications Technology.
Li, J. Y. and Yeh, A. I. (2001) ‘Relationships between
thermal, rheological characteristics and swelling
power for various starches’, Journal of Food
Engineering. doi: 10.1016/S0260-8774(00)00236-3.
Panindia, N. (2015) Preparation of
Polycaprolacton/nanocrystal cellulose of sweet
corncobs (Zea mays saccarata) nanocomposites.
University of Sumatera Utara.
Rincon, A. and Padilla, F. (2004) ‘Physicochemical
properties of Venezuelan breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis)
starch’, Arch Latinoam Nutr., 54(4), pp. 449–56.
Sabo, R. et al. (2013) ‘Effect of environmental conditions
on the mechanical properties and fungal degradation
of polycaprolactone/ microcrystalline cellulose/wood
flour composites’, BioResources. doi:
10.15376/biores.8.3.3322-3335.
Siswanto, S., Manurung, T. and Budiyati, S. (2012)
‘Modification Of Flour From Umbi Gadung Using
Ginger Raw Extract As Functional Food Ingredients’,
Journal of Chemistry Technology and Industry, 1(1),
pp. 109–117.
Sujito, Munawaroh, H. and Purwandari, E. (2013)
‘Mechanical Properties and Biodegradation Capability
of Poly Lactic Acid Composites with Strengthening of
Bamboo and Sengon Thin Sheets’, Kimia Dasar,
14(2), pp. 67–72.
Wang, T. et al. (2009) ‘Bone marrow stem cells
implantation with α-cyclodextrin/MPEG-PCL-MPEG
hydrogel improves cardiac function after myocardial
infarction’, Acta Biomaterialia. doi:
10.1016/j.actbio.2009.04.040.
Wang, Y. et al. (2005) ‘Thermal and thermomechanical
behaviour of polycaprolactone and
starch/polycaprolactone blends for biomedical
applications’, Macromolecular Materials and
Engineering. doi: 10.1002/mame.200500003.
Xanthos, M. (2005) Modification of Polymer Mechanical
and Rheological Properties with Functional Fillers.
Zuhra, C. and Marpongahtun (2016) ‘Physical-Mechanical
Properties And Microstructure Of Breadfruit Starch
Edible Films With Various Plasticizer’, Eksakta, 13,
pp. 56–62. doi: https://doi.org/10.20885/eksakta.
vol13.iss1-2.art7.
ICOCSTI 2019 - International Conference on Chemical Science and Technology Innovation
292
