
Implementation of Weighted Product Method
in the Decision Support System
of University Selection in Australia
Ameliana, Windarto
Universitas Budi Luhur
Keywords: Decision support systems, Weighted products, University selection, Counseling
Abstract:
Choosing a university for high school students is the main thing for them to continue their study to
a higher level. Today there are many universities, both at domestic universities and overseas
universities. Each university began to offers based on prices, level of accreditation, the choice of
departments, up to the facilities at the University. With the increasing number of universities, more
students will find it difficult to determine the university they would choose. This is because there
are too many suggestions to determine certain university from other people, expensive tuition fees,
and there are still many students who do not have a mature plan to continue their study to a higher
level. Velocity International Inc. is a company engaged in the field of educational consulting. The
company has services to help students who want to continue their education abroad, by providing
consultations on universities abroad, especially in Australia. During the consultation period, the
counselor will provide many university choices to students and explain one by one about the
university that will be offered. After getting an explanation from the counselor, there are still many
students who have difficulty in choosing the university recommended by the counselor. This is
caused by information and recommendations given by the counselors to students are still not
appropriate. With this problem, the solution that might be needed is to make a decision support
system application that can help to provide conclusions in the form of recommendations so it can
be used as references for students to decide which university to choose. In this study, the method
which applied to a decision support system is the Weighted Product (WP) method. The criteria
used in this study are cost, accommodation, major, and IELTS score, whereas each non-
interdependent criterion will be evaluated to produce several alternative choices. The result of this
study is the realization of a decision support system that is able to produce recommendations for
university selection for students
.
1. BACKGROUND
Choosing a university for high school students is the
main thing for students to pursue higher education. At
present, there are many universities, both those in the
country and abroad. Many universities began to offer
prices, level of accreditation, and choice of majors
available to facilities at the University. In addition,
the more universities, the more students who have
difficulty in deciding which university they will
choose because there are too many suggestions about
the University to be addressed by others, expensive
tuition fees and many students who do not have a
mature plan to proceed to higher education level.
Velocity International Inc. is a company engaged
in the field of educational consulting. This company
helps students who want to continue their education
abroad by providing consultations on universities in
foreign countries, especially in Australia. During the
consultation period, the counselor provides many
Universities as choices to students and explains one
by one about the University offered. After being
explained by the counselor, there are still many
students who have difficulty in choosing a university
given by the counselor because the counselor is still
not right in providing information about the
University to students.
There are many ways that can be done as a
solution to solve these problems, one of them is by
Ameliana, . and Windarto, .
Implementation of Weighted Product Method in the Decision Support System of University Selection in Australia.
DOI: 10.5220/0008929400610070
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life (ICT4BL 2019), pages 61-70
ISBN: 978-989-758-429-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
61

developing a decision support system to determine
the best universities in order to help students choosing
the desired university. This system will help students
to choose the University according to the category
desired by students such as the range of tuition fees,
desired courses, and so on. With the existence of a
decision support system application is expected to
help provide conclusions or decisions that can be
taken as a reference for students to determine the
university to be addressed. With the existence of a
decision support system application is expected to
help provide conclusions or decisions that can be
taken as a reference for students to determine the
university to be addressed. One of the methods that
can be used in decision support systems is the
Weighted Product (WP) method. The reason for
choosing this method is because this method can be
used in each alternative against four criteria which are
cost, accommodation, major, and IELTS score that is
not interdependent. The data analysis technique used
in this method is by powering the values of each
criterion by the weight values which are then
multiplied (Ahmadi and Wiyanti, 2014).
2. THEORY
a. Decision Support System
The DSS or Decision Support System (DSS) was first
disclosed in the early 1970s by Michael S. Scott
Morton with the term Management Decision System.
The system is a computer-based system that is
intended to help make decisions by utilizing certain
data and models to solve various unstructured
problems (N.Syafitri, Sutradi and Dewi, 2007).
Decision Support System is a computer-based
information system that approaches to produce
various alternative decisions to assist certain parties
in handling problems using data and models.
Decision making is the result of a selection process of
various alternative actions that may be selected with
certain mechanisms, with the aim of producing the
best decisions. A DSS only provides alternative
decisions and the final decision is then left to the user
(Nurjannah, Arifin and Khairina, 2015).
b. Basic of Decision Making
Decision making is a form of the selection process of
many alternatives through a certain method that will
produce a decision at the end. The model that
describes the decision-making process consists of
four phases that are: (Nurjannah, Arifin and Khairina,
2015):
a. Intelligence
This stage is the stage of defining the problem and
identifying the information needed that is related to
the problems faced and the decisions that will be
made.
b. Design
This stage is a process to represent the system
model that will be built based on the assumptions
that have been set. In this stage, a model of the
problem is created, tested, and validated.
c. Choice
This stage is a process of testing and choosing the
best decision based on certain criteria that have been
determined and leads to the objectives to be
achieved.
d. Implementation
This stage is the implementation stage of the
decisions that have been taken. At this stage, a series
of planned actions need to be developed so that the
results of the decisions can be monitored and adjusted
if improvements are needed.
c. Objectives, Strengths, and
Disadvantages of Decision Support
System
The objectives of a Decision Support System (DSS)
is to increase the ability of decision-makers by
providing more or better decision alternatives and to
help formulate problems and conditions faced. Thus,
DSS can save time, effort, and cost. So simple it can
be said that the objective of DSS is to increase
effectiveness and efficiency in decision making.
Nevertheless, the emphasis of a DSS is on increasing
the effectiveness of decision making rather than
efficiency (Abadi, 2015).
The Decision Support System (DSS) can provide
several benefits for the user. According to Turban
(Turban, E. Aronson and Liang, 2007) these benefits
include:
a. Extending the ability of decision-makers in
processing data or information for decision
making.
b. Save time needed to solve problems, especially
various problems that are very complex and
unstructured.
c. Produce solutions faster and the results are
reliable.
d. Able to provide various alternatives in decision
making, even if the DSS is not able to solve
problems faced by decision-makers, but can be
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
62

used as a stimulant in understanding the
problem.
e. Strengthen the confidence of decision makers
in the decisions they make.
f. Providing competitive advantages for the
organization as a whole with saving time,
effort, and cost.
Although it was designed very carefully and
considered all the factors, according to Turban
(Turban, E. Aronson and Liang, 2007) DSS has
weaknesses or limitations, that is:
g. There are several management abilities and
human talents that cannot be modeled so that
the models that exist in the system do not all
reflect the real problem.
h. DSS is limited to providing an alternative to the
knowledge given to it at the time of designing
the program.
i. The processes that can be carried out by DSS
usually also depend also on the capabilities of
the software used.
j. Continuous changes must always be made to
adapting the environmental conditions
changing so that the system is up to date.
k. However, it must be remembered that DSS is
designed to assist or support decision making
by processing information and data needed, and
not to take over decision making.
d. Decision Support System
Architecture
Things that must be considered to make DSS
architecture that is:
a. Strategic, tactical, and operational decisions.
b. Unstructured, semi-structured, and structured
decisions.
c. All levels of management and staffs who have
knowledge in the company.
d. All major functional positions, products, and
business lines, and geographical positions of a
company.
e. Multi Attribute Decision Making
(MADM)
Multi Attribute Decision Making (MADM) is a
method used to find the most optimal alternative from
a number of optimal alternatives with certain criteria
(N.Syafitri, Sutradi and Dewi, 2007). The essence of
MADM is to determine the weight value for each
attribute, then proceed with a ranking process that
will select alternatives that have been given
(N.Syafitri, Sutradi and Dewi, 2007). The approach
that can be done in the Multi Attribute Decision
Making (MADM) method is in two stages, that is:
a. Grouping decisions on each alternative.
b. Ranking of alternative decisions based on
decisions that have been grouped before.
f. Weighted Product Method (WP)
Weighted Product (WP) is one of the methods used to
solve MADM problems. WP is a method that uses
multiplication to link the rating of an attribute, where
the rating of each attribute should be pre-populated
with the corresponding weights. This process is
similar to the normalization process. The WP method
can be helpful in taking a laptop selection decision,
but the calculations using this WP method only
produce the largest value that will be voted as the best
alternative. The calculation will correspond to this
method if the selected alternative meets the
predefined criteria. This WP method is more efficient
because of the time required in shorter calculations.
The weight for the benefit attribute serves as a
positive rank in the multiplication process, while the
cost weight serves as a negative rank. (N. Syafitri,
Sutradi and Goddess, 2007)
Weight fixes for Σ
1 using equation (1)
…………………….……………… (1)
Variable W is the positive value power for profit
attribute and negative value for cost attribute. The
preference for
alternatives is given by equation (2).
Π
…………………….…………… (2)
by 1,2, … , and 1,2, … , as an attribute
Whereas:
Π : Product
: Score of each alternative
: The i-th alternative value towards the j-th
attribute
: Weight of each attribute or criterion
: Number of criteria
To find the best alternative done with equation (3)
∏
∗
……………………….. (3)
Whereas:
: Alternative preference is analogous as
vector V
: Scores of criterion
: Weight of criterion/ sub criterion
: Alternative
: Criterion
: Number of criteria
∗ : The number of criteria that have been assessed
in vector S
Implementation of Weighted Product Method in the Decision Support System of University Selection in Australia
63
The biggest
value states that
alternative is
chosen. The steps in the calculation of the WP method
are as follows.
1) Switches all attributes for the entire alternatives
with W (weight) as a positive power for the
profit attribute and negative value for the cost
attribute.
2) The results of the multiplication are aggregated
to generate value on each alternative.
3) Divides the V values for each alternative with
the total value of all alternatives.
4) Found the best alternative in order to be a
decision.
(a) 6.0, having a weighted value of = 2
(b) 6.5, having a weighted value of = 1
3. DESIGN
a. Program Flow
In this program, there are several pages that will be
created, namely the Start Page, menu page, weight
input page, university page, consultation page, report
page, and help page. On the Start page, the user can
select the "GO!" button to go to the menu page. On
the menu page, there is weight input, university page,
consultation page, report page, and help page. First,
the user can select the weight input page. On this
page, the user can fill in the criteria's name and
weight. Once completed, the user can choose the
University page to input the university data according
to the available weights and criteria. If any student
wants to consult, the user can choose a consultation
page. User can select the criteria that the student
wants and then press the "Result" button to see the
university name that will be the university
recommendation that has been selected according to
user needs. If the user wants to view the student's
personal data and the selected university results, the
user can select the report page. Weighted Product
method runs on the consultation page, where the user
pressing the "result" button came to the calculation of
the Weighted Product method which will generate
university name as a recommendation chosen by the
student previously.
b. Design
The screen design is an important aspect for the user
to give the idea of a program so that users feel
comfortable and have no trouble using the program.
Here are some of the screen designs to be created:
a. Weight Input Page Design
On the input criteria page, the user can enter the
criteria data and weights to be saved into the database.
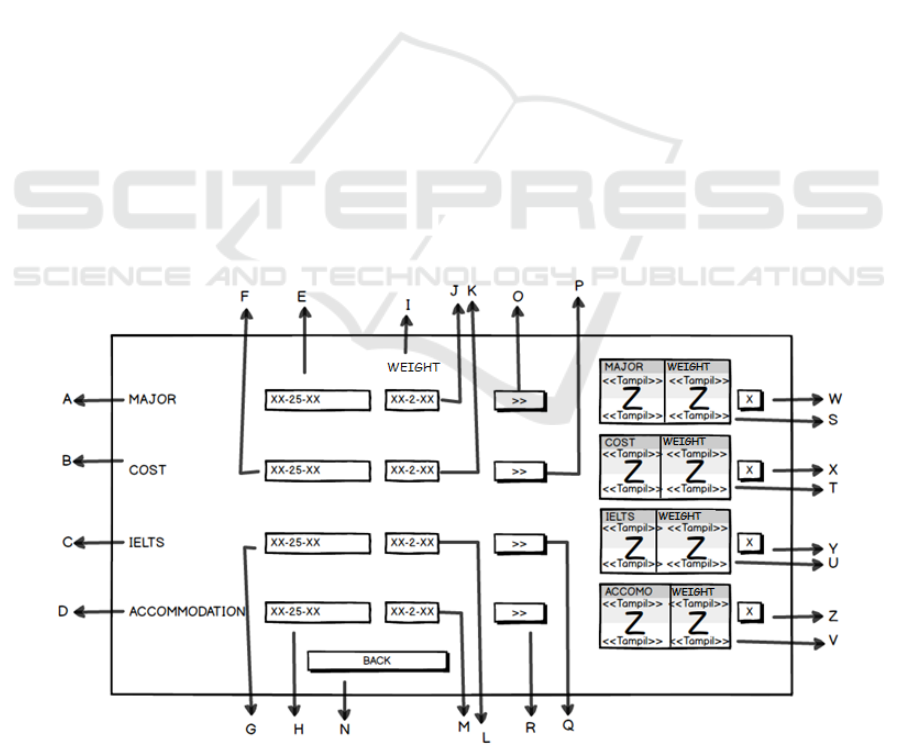
Figure 1. Weight Input Page Screen Design
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
64
Detail for figure 1:
A. Label “MAJOR”
B. Label “COST”
C. Label “IELTS”
D. Label “ACCOMMODATION”
E. Text Field to input Major
F. Text Field to input Cost
G. Text Field to input IELTS
H. Text Field to input Accommodation
I. Label “WEIGHT”
J. Text Field to input weight of Major
K. Text Field to input weight of Cost
L. Text Field to input weight of IELTS
M. Text Field to input weight of Accommodation
N. Button Back to return to menu page
O. Button “>>” to input into the list of Major
P. Button “>>” to input into the list of Cost
Q. Button “>>” to input into the list of IELTS
R. Button “>>” to input into the list of
Accommodation
S. List of criteria and weight of Major
T. List of criteria and weight of Cost
U. List of criteria and weight of IELTS
V. List of criteria and weight of Accommodation
W. Button “X” to delete data from the list of Major
X. Button “X” to delete data from the list of Cost
Y. Button “X” to delete data from the list of IELTS
Z. Button “X” to delete data from the list of
Accommodation
b. University Page Screen Design
In this page, user can input universities data and put
weights to each university to be saved into the
database.
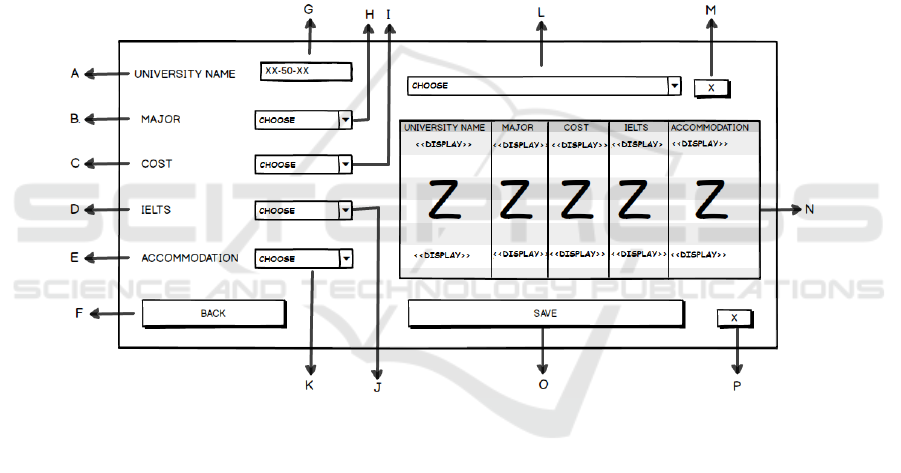
Figure 2. University Page Screen Design
Detail for figure 2:
A. Label “UNIVERSITY NAME”
B. Label “MAJOR”
C. Label “COST”
D. Label “IELTS”
E. Label “ACCOMMODATION”
F. Button back to return to menu
G. Text Field to input name of university
H. Combo box to choose name of Major
I. Combo box to choose name of Cost
J. Combo box to choose name of IELTS
K. Combo box to choose name of Accommodation
L. Combo box to choose name of University
M. Button X to delete name of University from the
Combo Box
N. List to show name of university and its criteria
O. Button Save to save data
P. Button X to delete data from the list
c. Consultation Page Screen Design
In this page, students who assisted by the
counselor can input the weight of criteria based
on the existing criteria
.
Implementation of Weighted Product Method in the Decision Support System of University Selection in Australia
65
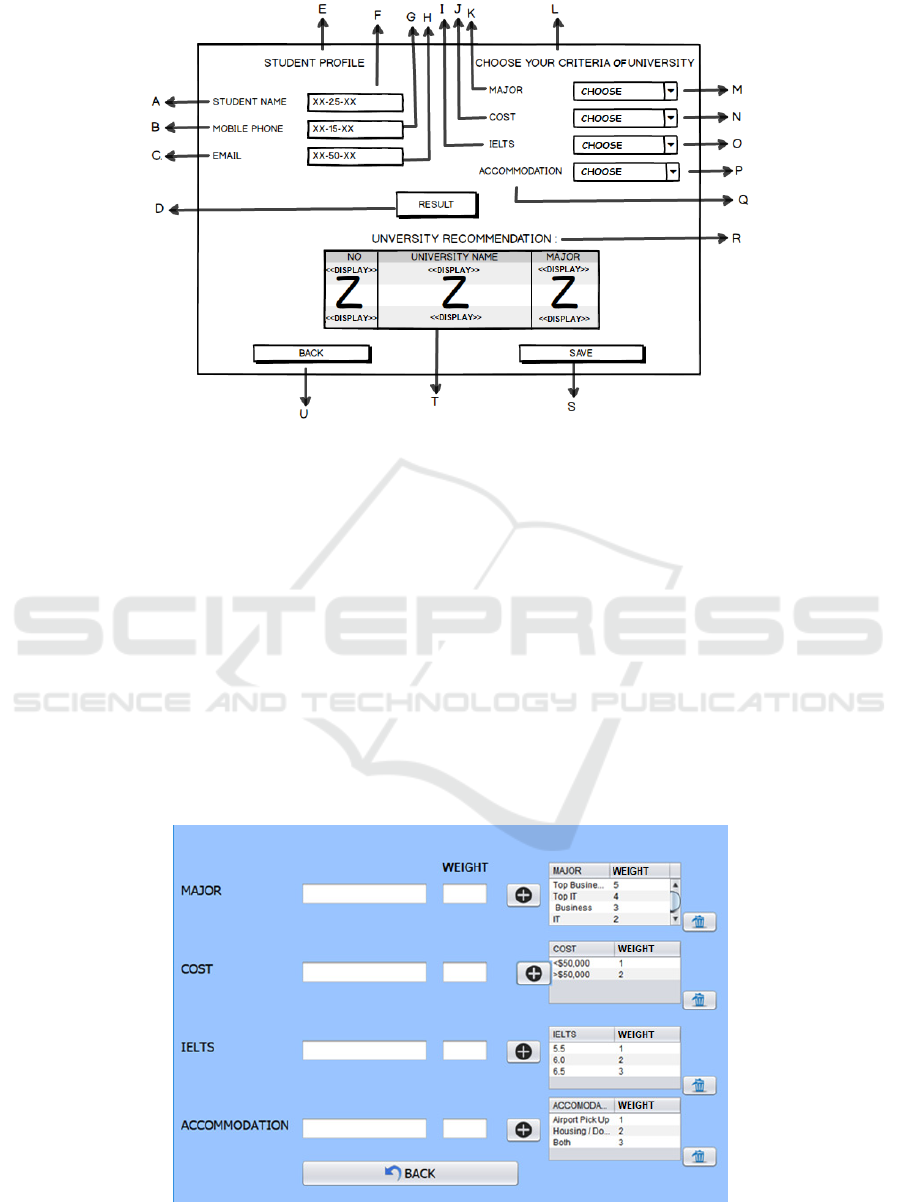
Figure 3. Consultation Page Screen Design
Detail for figure 3:
A. Label “STUDENT NAME”
B. Label “MOBILE PHONE”
C. Label “EMAIL”
D. Button Result to show recommendation results
E. Label “STUDENT PROFILE”
F. Text Field to input student’s name
G. Text Field to input student’s cellphone number
H. Text Field to input student’s email
I. Label “IELTS”
J. Label “COST”
K. Label “MAJOR”
L. Label “CHOOSE YOUR CRITERIA
UNIVERSITY”
M. Combo box to choose Major
N. Combo box to choose Cost
O. Combo box to choose IELTS
P. Combo box to choose Accommodation
Q. Label “ACCOMMODATION”
R. Label “UNIVERSITY RECOMMENDATION”
S. Button Save to save data
T. List to show recommendation result
U. Button Back to return to menu page
4. SCREEN DISPLAY
a. Screen display of weight input page
Figure 4. Weight input page screen display
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
66
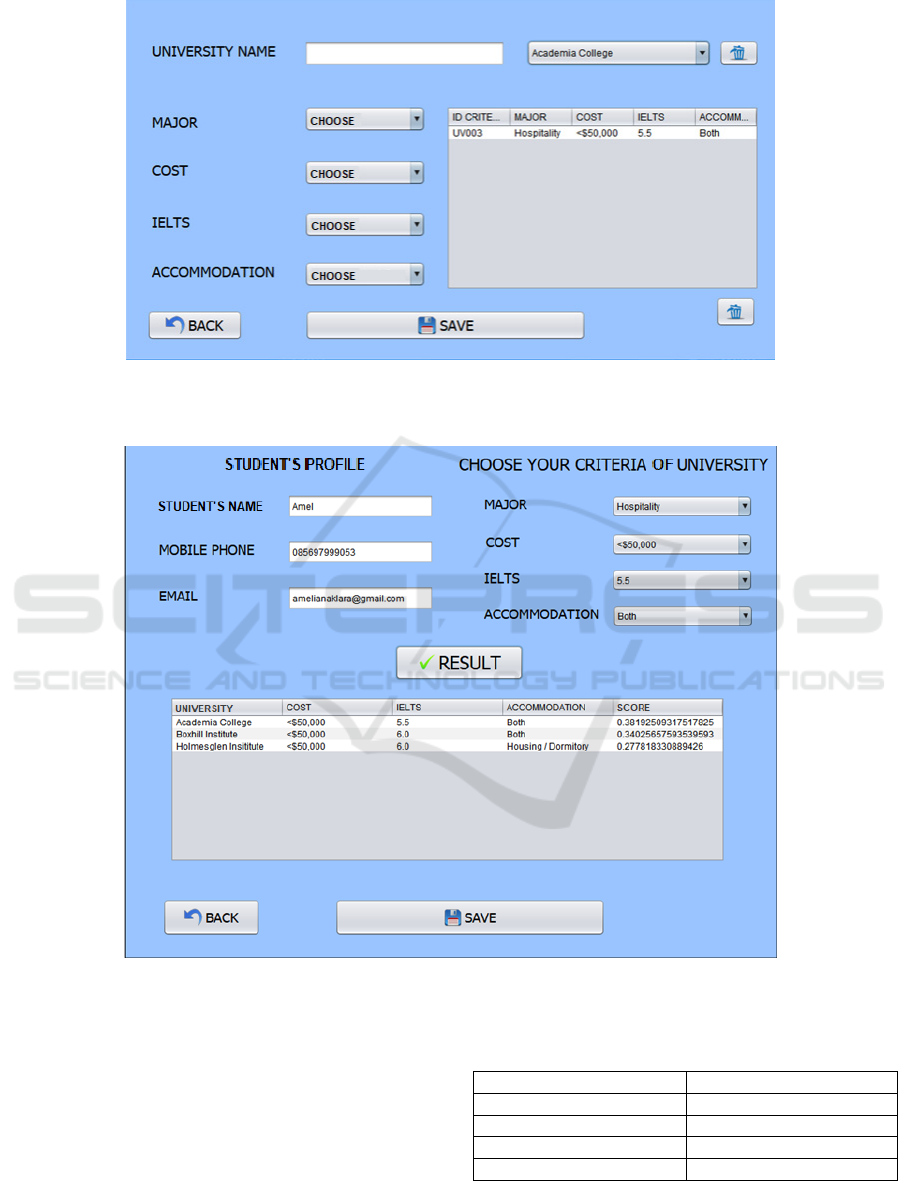
b. Screen display of university page
Figure 5. University page screen display
c. Consultation Page Screen Display
Figure 6. Consultation page screen display
5. PROGRAM EVALUATION
Program evaluation aims to know the results and
determine both shortcomings and advantages of the
system that has been created. Therefore, an
experiment was conducted to evaluate successful
access or failed access based on several conditions.
Table 1. Weight Input by Student
Criterion Weight
C1 5
C2 2
C3 3
C4 3
Implementation of Weighted Product Method in the Decision Support System of University Selection in Australia
67

Afterwards, the weight of each criterion needs to
be fixed first before being used for normalizing
calculations using formula
∑
.
Wfirst = 5+2+3+3 = 13
W1 =
= 0.38461538461538464
W2 =
= 0.15384615384615385
W3 =
= 0.23076923076923078
W4 =
= 0.23076923076923078
After obtaining the latest Wi value, it will be
normalized to get Si value by rounding up the latest
Wi value.
University Alternative A1
S1 = (5
0.38461538461538464
)*(2
-0.15384615384615385
)*(2
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(3
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.832984339228869
University Alternative A2
S2 = (2
0.38461538461538464
)*(2
-0.15384615384615385
)*(2
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(3
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.2885607692309613
University Alternative B1
S3 = (3
0.38461538461538464
)*(1
-0.15384615384615385
)*(2
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(2
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.5258371159564497
University Alternative B2
S4 = (2
0.38461538461538464
)*(1
-0.15384615384615385
)*(2
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(2
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.3055116977098093
University Alternative B3
S5 = (1
0.38461538461538464
)*(1
-0.15384615384615385
)*(2
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(2
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1
University Alternative C1
S6 = (3
0.38461538461538464
)*(1
-0.15384615384615385
)*(1
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(3
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.9661338478579946
University Alternative C2
S7 = (1
0.38461538461538464
)*(1
-0.15384615384615385
)*(1
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(3
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.2885607692309613
University Alternative D1
S8 = (4
0.38461538461538464
)*(2
-0.15384615384615385
)*(3
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(2
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.3951239160136684
University Alternative D2
S9 = (3
0.38461538461538464
)*(2
-0.15384615384615385
)*(3
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(2
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.2489913293790396
University Alternative E1
S10 = (3
0.38461538461538464
)*(2
-0.15384615384615385
)*(3
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(2
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.2489913293790396
University Alternative F1
S11 = (5
0.38461538461538464
)*(2
-0.15384615384615385
)*(2
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(3
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.832984339228869
University Alternative F2
S12 = (4
0.38461538461538464
)*(2
-0.15384615384615385
)*(2
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(3
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.6822311574409705
University Alternative G1
S13 = (1
0.38461538461538464
)*(1
-0.15384615384615385
)*(2
-
0.23076923076923078
)*(3
0.23076923076923078
)
= 1.0980862271455496
∑S = 1.832984339228869 + 1.2885607692309613+
1.5258371159564497 + 1.3055116977098093+ 1 +
1.9661338478579946+ 1.2885607692309613+
1.3951239160136684+ 1.2489913293790396+
1.2489913293790396+ 1.832984339228869+
1.6822311574409705+1.0980862271455496
∑S = 18.71399683780218
After obtaining the Si value, the next stage is to
calculate Vi to get the best employees ranking using
formula
∑
.
University Alternative A1
V1 =
.
.
= 0.09794723997848763
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
68
University Alternative A2
V2 =
.
.
= 0.06885545511197666
University Alternative B1
V3 =
.
.
= 0.08153453958452457
University Alternative B2
V4 =
.
.
= 0.06976124389807965
University Alternative B3
V5 =
.
= 0.05343593934888377
University Alternative C1
V6 =
.
.
= 0.10506220904592727
University Alternative C2
V7 =
.
.
= 0.06885545511197666
University Alternative D1
V8 =
.
.
= 0.0745497569602836
University Alternative D2
V9 =
.
.
= 0.06674102492398007
University Alternative E1
V10 =
.
.
= 0.06674102492398007
University Alternative F1
V11 =
.
.
= 0.09794723997848763
University Alternative F2
V12 =
.
.
= 0.08989160209981824
University Alternative G1
V13 =
.
.
= 0.058677269033594194
Table 2. University Ranking Process
Name of University Calculation Results Ranking
Academia College, major: Business 0.10506220904592727 1
Victoria University, major: Top Business 0.09794723997848763 2
Deakin University, major: Top Business 0.09794723997848763 3
Deakin University, major: Top IT 0.08989160209981824 4
Holmesglen Institute, major: Business 0.08153453958452457 5
RMIT University, major: Top IT 0.0745497569602836 6
Holmesglen Institute, major: IT 0.06976124389807965 7
Victoria University, major: IT 0.06885545511197666 8
Academia College, major: Hospitality 0.06885545511197666 9
Swinburne University, major: Business 0.06674102492398007 10
RMIT University, major: Business 0.06674102492398007 11
Boxhill Institute, major: Hospitality 0.058677269033594194 12
Holmesglen Institute, major: Hospitality 0.05343593934888377 13
Implementation of Weighted Product Method in the Decision Support System of University Selection in Australia
69

From the calculation above, the university
recommendation for Top Business major according
to user input (student) is Deakin University or
Victoria University with a value of
0.09794723997848763.
a. Advantages
1. Facilitate the counselor of Velocity
International Inc. in providing university
recommendations according to the student's
criteria.
2. Calculation results are 100% accurately using
the Weighted Product method.
3. Provide the university recommendation
according to the student's selected major.
4. This app helps counselors if there is a better
university than the previous counselor's
recommendation.
b. Disadvantages
1. This application is desktop based so it can not
be accessed using the Internet network.
2. There is a similar calculation result based on
weight value inputted
3. This application has predefined criteria and
cannot be changed.
4. The calculation results are always in the form
of rank despite there is a similar calculation
result of more than one university.
6. RESULT
a. Summary
Based on the analysis that has been done during a
series of processes from design to implementation
of the University Recommendation Decision
Support System, it can be concluded that:
a. This decision support system can generate
several university recommendations
according to the student's selected criteria.
b. By implementing the Weighted Product (WP)
method in this decision support system can
provide the results of the University
recommendation, which is the highest
calculation results of Weighted Product (WP)
method.
b. Suggestion
As for the suggestions needed to make this
system running better:
a. This application can be developed using other
methods.
b. This application can be developed for the
addition of other criteria according to the
system user’s needs, so it can improve system
performances.
c. This application can be developed into online
based application or other display based (not
only desktop-based).
d. Can be added add criteria feature for
subsequent needs.
REFERENCES
Abadi, R. S. (2015) ‘Makalah Sistem Penunjang
Keputusan’.
Ahmadi, A. and Wiyanti, D. T. (2014) ‘Implementasi
Weighted Product (WP) dalam Penentuan Penerima
Bantuan Langsung Masyarakat PNPM Mandiri
Perdesaan’, Seminar Nasional Aplikasi Teknologi
Informasi, pp. 19–22.
Lestari, S. (2013) ‘Penerapan Metode Weighted Product
Model To Seleksi Calon Karyawan’, Jurnal Sistem
Informasi (JSI), 5(1), pp. 540–545. Available at:
http://ejournal.unsri.ac.id/index.php/jsi/article/viewFi
le/873/435.
N.Syafitri, Sutradi and Dewi, A. (2007) ‘Penerapan
metode WEIGHTED PRODUCT DALAM SISTEM
PENDUKUNG KEPUTUSAN PEMILIHAN
LAPTOP BERBASIS WEB’, semanTIK, Vol.2, No.1,
Jan-Jun 2016, pp. 169-176 ISSN: 2502-8928 (Online),
2(1), pp. 169–176.
Nurjannah, N., Arifin, Z. and Khairina, D. M. (2015)
‘Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Pembelian Sepeda
Motor Dengan Metode Weighted Product’, Jurnal
Informatika Mulawarman, 10(2), pp. 2–6.
Supriyono, H. and Sari, C. P. (2015) ‘Pemilihan Rumah
Tinggal Menggunakan Metode Weighted Product’,
Jurnal Ilmu Komputer dan Informatika, 1(1), pp. 23–
28.
Turban, E., E. Aronson, J. and Liang, T.-P. (2007)
‘Decision Support Systems and Business
Intelligence’, Decision Support and Business
Intelligence Systems, 7/E, pp. 1–35. doi:
10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004.
Yoni, D. C. and Mustafidah, H. (2016) ‘Penerapan
Metode WP (Weighted Product) To Pemilihan
Mahasiswa Lulusan Terbaik di Fakultas Teknik
Universitas Muhammadiyah Purwokerto’, Juita,
IV(1), pp. 22–27.
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
70
