
The Influence of Customer Relationship Management, Website
Quality and Service Quality on Student Satisfaction
Randy Eryll Endarwan and Dewi Murtiningsih
Universitas Budi Luhur
Keyword: Customer Relationship Management, Website Quality, Service Quality.
Abstract: This research aims to determine the influence of customer relationship management on student satisfaction,
website quality on student satisfaction and service quality on student satisfaction. This research is
explanatory research. The population in this research were bachelor degree student (S1) in five Faculties of
Budi Luhur University Jakarta who had taken 4th semester of education. Data was collected using a
questionnaire that was tested for reliability and validity. The study sample used proportional random
sampling with the number of respondents are 110 students. Data were analyzed by SEM-PLS. The results of
this study are customer relationship management influences student satisfaction; website quality influences
student satisfaction; service quality influences student satisfaction.
1. INTRODUCTION
To produce graduates who are ready for
globalization competition, Budi Luhur University
must compete with other universities, especially
private universities. The growth of new universities
has made the existing universities try their best to
maintain their current customers by applicating
customer relationship management (CRM).
Maintaining customer is easier than gaining new
customer. According to research, it needs five times
standard cost to gain one new customer than to
maintain one existing customer (Ratnasari and aksa,
2011).
Website quality can be considered as an attribute
of a website which contributes to its usefulness for
consumer (Gregg and Walczak, 2010). Effective
Website must also displays 7 elements which usually
called 7C. Those 7 elements are context (layout and
design), content (text, picture, sound and video in
the website), community (how the site enables
communication between users), customization (the
ability of the site to present itself to various users or
enable user to personalized the site), communication
(how the site enables site communication with users,
users with site or two way communication),
connection (connection level of the site with other
sites), and commercial (the ability of the site to
support commercial transaction). The website of
Budi Luhur University nowadays is already
displaying those 7C criteria well.
The inconsistency result of the research
conducted by Kurniawan and Lubis (2013) states
that customer relationship management does not
influence customer satisfaction. Furthermore, the
result of the research conducted by Nugroho and
Sari (2016) states that website quality in information
dimension does not positively and significantly
influence user satisfaction; and the research result of
Kurniawan and Susanto (2017) states that service
quality positively but insignificantly influences
patient satisfaction.
Based on the inconsistence of the above research
results, therefore the research gap of this research is
the existence of insignificant previous research
results. Based on this, the researchers are interested
to redo the research by adding other variable
entitled: “The influence of customer relationship
management, website quality and service quality on
student satisfaction (A Study at Budi Luhur
University Jakarta)”.
Endarwan, R. and Murtiningsih, D.
The Influence of Customer Relationship Management, Website Quality and Service Quality on Student Satisfaction.
DOI: 10.5220/0008931001530159
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life (ICT4BL 2019), pages 153-159
ISBN: 978-989-758-429-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
153

2. THEORITICAL REVIEW
2.1 Customer Relationship
Management (CRM)
According to Kotler and Armstrong (2006) customer
relationship management (CRM) is the whole
process to build and maintain relationship with
customer by giving superior customer value and
customer satisfaction. Customer relationship
management (CRM) is an activity involving all
human resources to maintain the existing customer,
a strategy to process and maintain relationship with
customer, an effort to find out the expectation and
needs of customer (Lukas, 2001). According to
Laudon and Traver (2002) customer relationship
management (CRM) keeps information of
customers, stores and records all contacts happened
between customers and company, and also creates
customer profile for company staff who needs
information about the related customer. Lukas
(2001) divided customer relationship management
(CRM) into three main components, they are (1)
Human resources, in this case, employees as the
applicator of customer relationship management
(CRM). In human resource dimension, the important
key factor is organizational structure, role, and
responsibility, company culture, procedure and
change management program. Overall, (2) process
includes system and procedure that help people to
know more and establish close relationship with
customer. Organizational structure, operational
policy, and reward-punishment system must be able
to reflect what was achieved by customer
relationship management (CRM). The
implementation of customer relationship
management (CRM) will change the existing
business process, both process which involves
customer directly and indirectly. In customer
relationship management (CRM), the whole existing
business functions must focus on customer, (3)
technology is introduced to help to accelerate and
optimizing human factor and process in daily
customer relationship management activity.
However, we must first see the business structure,
consumer behavior, employee and work culture,
because technology cannot just solve problems. We
must realize that technology is a supporting tool to
complete the added value of customer relationship
management. Lovelock and Wirtz (2011) explain
that an effective customer relationship management
(CRM) strategy consists of 5 processes, they are: (1)
Strategy development, determination of gradual
service, determination of target in every segment
and design of loyalty rewards, (2) Value creation,
company (bank) must relays what consumer needs to
consumer through gradual service and loyalty
programs, (3) Multichannel integration, giving
service to worldwide consumer directly through
every existing service channel, (4) Information
management, gradual and accurate data processing
and also the usage of analysis tools related to
company and consumer effectively, (5) Performance
assessment, successfully applying customer
relationship management (CRM) process, company
must be able to create value between consumer and
company, target and goal achievement of marketing
sector, and also control of customer relationship
management (CRM) program so that other programs
related to CRM can run as expected.
2.2 Website Quality
Website quality is one of the methods or website
quality measurement technique based on end-user
perception. Website quality can be considered as an
attribute of website which contributes its usage to
consumer (Gregg and Walczak, 2010). According to
Zeithaml, Parasuraman and Berry (1990) website
quality is one of the methods or website quality
measurement technique based on end-user
perception. While according to other experts like
Barnes and Vidgen (2002), website quality is an
instrument developed to measure usage, information
and service interaction quality of website internet.
Website quality has been developing starting from
webqual version 1.0, webqual version 2.0, webqual
version 3.0 and the latest is webqual version 4.0.
Website quality first version is webqual version 1.0
which was developed in a website domain of a
business school in Great Britain. It was done in a
workshop with 6 master students as delegation. The
purpose of this development was to compile criteria
of website quality which is appropriate with the
studied object. The issue raised was “What is
website quality of an excellent business school?”.
From the workshop, 24 indicators are found to
emphasize on information quality. Website quality
second version is webqual version 2.0 which was
applied on business to customer (B2C) website. This
version emphasizes more on interaction quality
aspect. At this time, the version was tested on a
domain of an online bookstore such as Amazon,
Blackwells and Internet Bookshop, and it shows that
interactive level of website influences internet
purchase. Website quality third version is webqual
version 3.0 which was implemented on online
auction website. In this version, based on review
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
154

result of Barnes and Vidgen (2002) of the previous
two versions, indicators on website quality are
summarized into three categoriees, they are:
usability quality, information quality and interaction
quality. The newest version of website quality is
webqual version 4.0. In this version, it uses three
measurement categories which includes 23 questions
about usability, information quality and service
interaction quality. In this version, the dimension for
website quality has been replaced with usability.
Kim and Niehm (2009) mentioned that the previous
researchers divide website quality dimension into
five, they are:(1) Information that includes content
quality, usability, completeness, accurate and
relevance, (2) Security that includes trust, privacy
and security guarantee, (3) Convenience that
includes easy to be operated, understandable and
speed, (4) Comfort that includes visual attraction,
emotional attraction, creative and attractive design,
(5) service quality that includes online completeness
and customer service.
2.3 Service Quality
According to Kotler (2008), service quality is the
performance offered by a person to another. This
performance can be intangible and does not affect
the ownership of any item and to anybody. The main
point is service, which is an action done by a seller
to its buyer or consumer to fulfill consumer’s needs
and expectation. Tjiptono and Chandra (2012)
mention that to create customer satisfaction, product
offered by organization must be qualified. The term
quality itself contains various interpretation because
it has several universal level (common anywhere),
cultural (depends on culture value system), social
(formed by social economy class, ethnic group,
family, friends), and personal (depends on each
individual’s preferences or taste). In simple way,
quality can be considered as invalid free product. In
other words, product which is made according to
standard (target, goal or requirement that can be
defined, observed and measured). Tjiptono and
Chandra (2012) in the case of service marketing,
state that quality dimensions that are frequently used
as reference are: (1) Reliability, the ability to give
promised service immediately, accurately and
satisfying, (2) Responsiveness, employee’s desire
and willingness to help customers and give
responsive service, (3) Guarantee that covers
knowledge, competence, courtesy and trustworthy
nature of employees, free of physical harm, risk or
doubt, (4) Empathy covers the convenience in
starting relationship, effective communication,
personal attention and understanding of individual
needs of customers, (5) Physical proofs that cover
physical facility, equipment, employees and
communication means. The concept of service
quality according to Mudrick, Render and Russell
(2007) are as follow: (1) Consumer’s perception of
service quality which is generated from the
comparison of their expectation before they receive
service and the experience of the service, (2) Quality
perception comes from service process and service
result, (3) There are two kinds of service quality,
normal and exception. Normal is the level of quality
in which service should be given. The exception is
the level of quality in which there is exception of a
handled problem.
2.4 Consumer Satisfaction
Tjiptono (2012) mentioned that consumer
satisfaction is a person’s feeling level after
comparing the perceived performances or results
with expectation. According to Kotler and
Armstrong (2003), consumer satisfaction is a
person’s happiness or disappointment which appears
after comparing his perception or impression of a
certain product’s performance or result with his
expectations. While Lupiyoadi (2001) mentioned
that consumer satisfaction is someone’s feeling level
where that person is stating the comparison result of
a product or service performance he received, and he
expected. According to Kotler and Keller (2007), the
characteristic of satisfied customer is more loyal or
becoming a loyal customer, buying more product
when company launches new product, perfecting the
existing product, giving comment that is beneficial
for the product and company, paying less attention
on competitor’s product and advertisement, less
sensitive of prices, giving opinions or ideas to
company, and requiring less service cost then new
customer, because the transaction is becoming
regular. According to Tjiptono (2002), there is two
models of consumer satisfaction: (1) Kognitif
Model; it is consumer’s judgment based on the
difference between a set of combination which is
considered to be ideal for individual and his
perception of the real combination and attribute. In
other words, the judgment based on the difference
between the ideal and the actual, (2) Affective
Model which states that individual consumer’s
judgement of a product or service is not only based
on rational calculation but also subjective needs.
According to Tjiptono and Chandra (2005) six
factors influence consumer satisfaction: (1) Service
product that includes product which is good and
The Influence of Customer Relationship Management, Website Quality and Service Quality on Student Satisfaction
155
fulfilling consumer’s taste and expectation. (2) Price
which is attached to a product reflects the quality of
the product, (3) Promotion, the basic of promotion
research related to company product and service
information in their effort to communicate the
benefits of the product and service to targeted
consumer, (4) Location is a place which is part of
company attribute in the form of company and
consumer location, (5) employee’s service which is
service given by employees in their effort to fulfill
consumer’s needs and expectation to satisfy them,
(6) Facility is a part of company attribute in the form
of mediator to support the operational running of the
company which is related to consumer, (7)
Atmosphere is a supporting factor because if a
company is impressive then the consumer will
experience their satisfaction.
2.5 Research Hypothesis
2.5.1 Customer Relationship Management
Influences Customer Satisfaction.
According to the research conducted by Sirait
(2018), it is stated that customer relationship
management influences customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, the idea stated by Victor, Jorie, and
Sumawauw (2015) also proved that customer
relationship management affects customer
satisfaction.
H1: Customer relationship management influences
customer satisfaction
2.5.2 Website Quality Influences Customer
Satisfaction.
Research conducted by Kurniawati, Kusyanti, and
Mursityo (2018) stated that website quality
influences customer satisfaction. The idea of
Risyandi and Zuliestiana (2017) also proved that
website quality influences customer satisfaction.
H2: Website quality influences customer
satisfaction.
2.5.3 Service Quality Influences Customer
Satisfaction.
The research conducted by Lubis and Andayani
(2017) stated that service quality influences
customer satisfaction. The idea of Fadli (2017) also
proved that service quality influences customer
satisfaction.
H3: Service quality influences customer
satisfaction.
3. RESEARCH METHOD
This research is explanatory. The research objects
are customer relationship management, website
quality, and service quality. The subjects are
bachelor degree students (S1) of five faculties of
Budi Luhur University who are at least already on
their 4th semester. The sample of the research is 100
plus 10%, therefore, the total sample (n) becomes
110 respondents. This is determined based on
consideration that if there are invalid questionnaire
data, the rest can still fulfill the minimum principle
of sample measurement. The analysis model is using
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) with Partial
Least Square (PLS) application.
4. DISCUSSION
4.1 Structural Test
Structural model in PLS is evaluated using R2 for
the dependent variable and path coefficient value for
independent variable, and then the significance level
is measured based on t-statistic value of each path.
The structural model of this research can be seen in
Picture 1 .
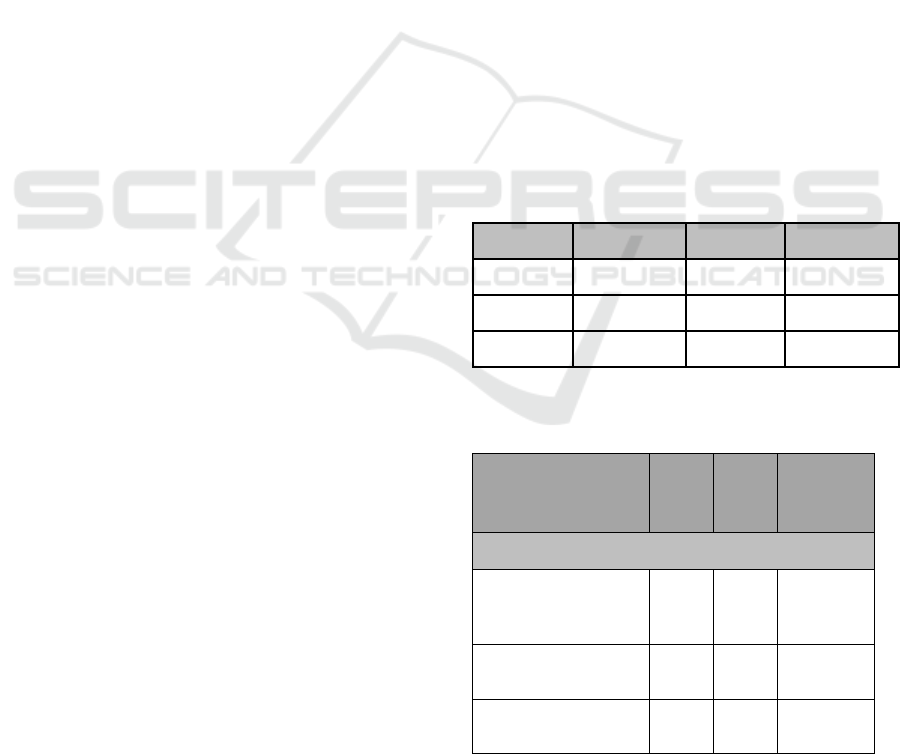
Table 1: Model Fit Test (Model Fit)
Size
Result
Criteria
Remarks
SRMR
0,0718996
< 0.08a
Model Fit
NFI
0,9174420
> 0.90b
Model Fit
rms Theta
0,1124196
< 0.12a
Model Fit
a) Henseler, J. et al., (2014), b) Lohmöller (1989)
Source: Data processed, 2019
Table 2: Path Coefficients (t-Value)
Path
T
Statistic
(>1.96)
P
Values
(<0.05)
Remarks
From Variable to Variable
Customer Relationship
Management ->
Student Satisfaction
1,97145
0,04959
Significant
Website Quality ->
Student Satisfaction
1,20378
0,22962
Insignificant
Service Quality ->
Student Satisfaction
4,56790
0,00001
Significant
Source: Data Processed in 2019
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
156
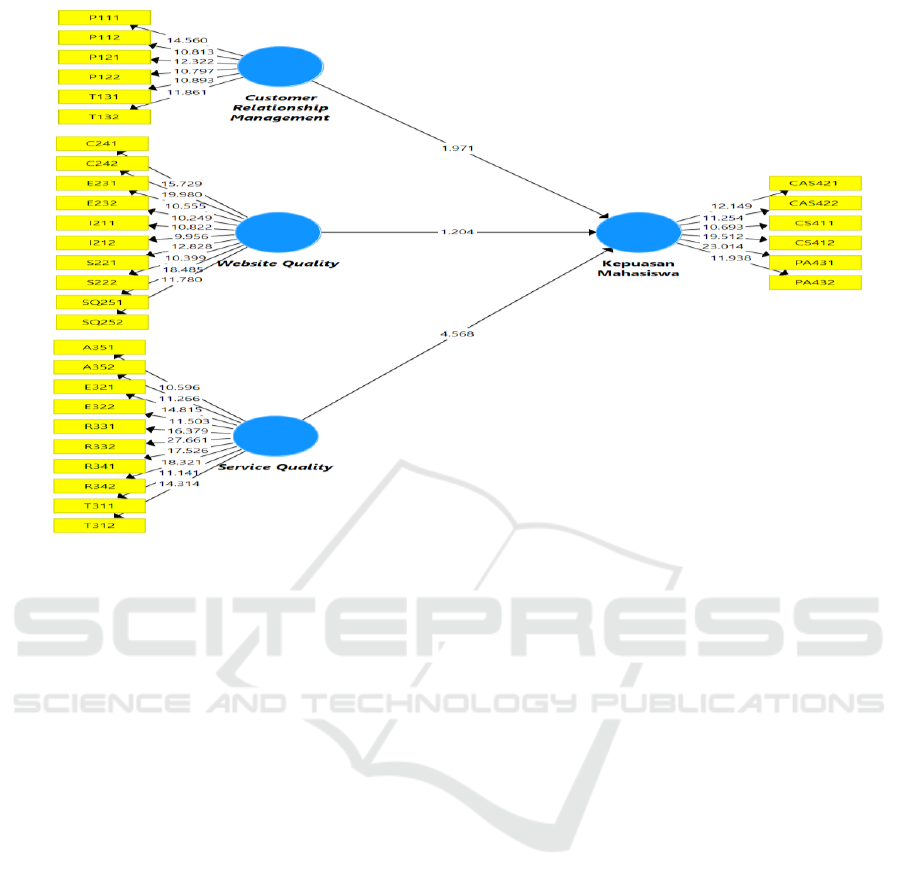
Figure 1: Display of PLS Algorithm Bootstrap Result
Source: Output Model Structural, Data Processed in 2019
To measure the significance of the prediction
model in the model structural test, it can be seen
from t-statistic value from independent variable to
dependent variable on Path Coefficient table on
output PLS on table 2.
4.2 Hypothesis Test
Hypothesis H1 Test: From Table 4.10 above, it can
be seen that the p-value customer relationship
management (CRM) is 0,04959 with
significance below 5% shown by t statistic
value>t-table value or 197145>1,96. The
positive p-value shows that customer
relationship management positively influences
student satisfaction.
Hypothesis H2 Test: The second test is conducted
to see whether website quality (WQ)
positively influences student satisfaction. The
test result on table 4.10 above shows that WQ
p-value is 0,22962 by t-statistic value < t-table
value or 1,20378 < 1,96, which means the
significance level of website quality is below
5% (insignificant).
Hypothesis H3 Test: The test on hypothesis three
is to see the influence of service quality (SQ)
on student satisfaction. The test shows that p-
value of SQ is 0,00001 by t-statistic value > t-
table value or 4,56790 > 1,96, which means
that SQ variable positively influences student
satisfaction with significance below 5%
(significant).
4.3 Research Results
4.3.1 The Influence of Customer
Relationship Management on
Student Satisfaction
Based on the test result of hypothesis one, it can be
concluded that customer relationship management
variable positively influences customer satisfaction.
This research is in line with the research conducted
by Sirait (2018) which stated that customer
relationship management influences customer
satisfaction, and also the research of Victor, Jorie
and Sumarauw (2015) which proved that customer
relationship management influences customer
satisfaction.
4.3.2 The Influence of Website Quality
on Student Satisfaction
Based on the test result of hypothesis two, it shows
that website quality insignificantly influences
student satisfaction. This research contradicts with
the research conducted by Kurniawati, Kusyanti and
The Influence of Customer Relationship Management, Website Quality and Service Quality on Student Satisfaction
157

Mursityo (2018) which stated that website quality
influences customer satisfaction, and also research
by Risyandi and Zuliestiana (2017) which proved
that website quality influences customer satisfaction.
4.3.3 The Influence of Service Quality
on Student Satisfaction
The test result of hypothesis three shows a
significant influence of service quality on student
satisfaction. This research is in line with the research
conducted by Lubis and Andayani (2017) which
stated that service quality influences customer
satisfaction, and also the research by Fadli (2017)
which proved that service quality influences
customer satisfaction.
5. CONCLUSION
Based on the discussion, contribution and research
findings, configuration of conceptual framework
such as research model, therefore specifically the
research conclusion is customer relationship
management can influence student satisfaction;
website quality does not significantly influence
student satisfaction; service quality can influence
student satisfaction.
A recommended suggestion based on the
research for Budi Luhur University is to focus more
on paying attention to customer relationship
management through a more friendly service from
the lecturers to students. To pay more attention to
the infrastructure that supports website and its
display because respondents mention easiness as
dominant contribution in reflecting website quality
variable which is still lacking. In example, the
website of Budi Luhur University is not fast enough
to be accessed and less user friendly. And to more
attentive on suggestion and complaints relay by the
students since service quality has important
contribution in reflecting and it needs to be
improved.
Suggestion for further research is to add the
number of sample, expand the research object, and
add relevant topic. Furthermore, future research is
suggested to analyze data using different tools such
as SPSS, GeSCA, and SEM_Amos.
REFERENCES
Barnes, S. J., and Vidgen, R. T., 2002. An Integrative
Approach To The Assessment Of ECommerce
Quality. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, 3
(3), 114127.
Fadli, Uus MD. 2017. Pengaruh Kualitas Pelayanan
Terhadap Kepuasan Pelanggan di Rumah Makan
Saung Endah Karawang. Karawang. Journal of
Management and Business, Universitas Buana
Perjuangan. Vol. 2 No. 1.
Gregg, D.G., and Walczak, S. 2010. The Relationship
between Website Quality, Trust, and Price Premiums
at Online Auctions. Journal of Electronic Commerce
Research.
Henseler, J. et al., 2014. Common Beliefs and Reality
about Partial Least Squares: Comments on Rönkkö &
Evermann (2013). Organizational Research Methods,
17(2): 182-209.
Kim, Hyejeong and Niehm, L.S. 2009. “The Impact Of
Website Quality On Information Quality, Value, And
Loyalty Intentions In Apparel Retailing”. Journal Of
Interactive Marketing.
Kotler, Philip. 2008. Principle Of Marketing 12th Edition.
Prinsip-prinsip Pemasaran (12th Ed). Ahli Bahasa:
Sabran, Bob. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Kotler, Philip dan Gary Armstrong. 2003. Manajemen
Pemasaran. Jakarta: Salemba empat.
Kotler, Philip dan Gary Armstrong. 2006. Principles of
Marketing. 11th Edition. New Jersey: Prentice Hall
International Inc.
Kotler, Philip dan Kevin Lane Keller. 2007. Manajemen
Pemasaran. Alih bahasa: Benyamin. Jakarta: PT
Indeks.
Kurniawati, Rizka Amalia, Ari Kusyanti dan Yusi Tyroni
Mursityo. 2018. Analisis Pengaruh Kualitas Website
Terhadap Kepuasan Pelanggan MisterAladin Dengan
Menggunakan Webqual 4.0. Jurnal Pengembangan
Teknologi Informasi dan Ilmu Komputer. Vol. 2, No.
3.
Kurniawan, Arif dan Susanto. 2017. Pengaruh Kualitas
Layanan Terhadap Kepuasan dan Kepercayaan Pasien
Rawat Jalan di Rumah Sakit Paru dr. Ario Wirawan
Salatiga. Proceeding Health Architecture, 1(1) 17 Mei
2017 ISBN: 978-602-19568-6-1.
Kurniawan, Ferri dan Nawazirul Lubis. 2013. Pengaruh
Relationship Marketing dan Layanan Purna Jual
Terhadap Kepuasan Pelanggan PT. Astra Internasional
Isuzu Semarang. Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis, 2 (1).
Laudon, Kenneth C. and Carol Guercio Traver. 2002. E-
Commerce: Business, Technology, Society, Pearson
Education, p.374.
Lovelock, Christopher, and Jochen Wirtz. 2011. Services
Marketing. Peoples, Technology, Strategy. 7th edition.
England: Pearson Education Limited.
Lubis, Alfi Syahri dan Nur Rahmah Andayani. 2017.
Pengaruh Kualitas Pelayanan (Service Quality)
Terhadap Kepuasan Pelanggan PT. Sucofindo Batam.
Journal of Business Administration. Vol. 1, No. 2.
Lukas, Ade Paul. 2001. Customer Relationship
Management, CRM Slide Presentation. Jakarta:
Ciptamaya.
Lupiyoadi, Rambat. 2001. Manajemen Pemasaran.
Jakarta: Salemba empat.
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
158

Lohmöller, J.B., 1989. Latent Variable Path Modeling
with Partial Least Squares. Heidelberg: Physica-
Verlag.
Mudrick, Render dan, Russel. 2007. A Review of Kualitas
Layanan in Corporate and Recreational Sport/Fitness
Programs. Journal of retailing, 20(1), 75 -85.
Nugroho, Anif Kurniawan dan Puspita Kencana Sari.
2016. Analisis Pengaruh Kualitas Website Tokopedia
Terhadap Kepuasan Pengguna Menggunakan Metode
Webqual 4.0. e-Proceeding of Management, 2930.
Ratnasari, Ririn Tri dan Mastuti H. Aksa. 2011. Teori dan
Kasus Manajemen Pemasaran Jasa. Bogor: Ghalia
Indonesia.
Risyandi, Okki dan Dinda Amanda Zuliestiana. 2017.
Pengaruh Kualitas Website Traveloka Terhadap
Kepuasan Pengguna. e-Proceeding of Management,
2244.
Sirait, Dodi Putra. 2018. Pengaruh Customer Relationship
Management dan Kualitas Pelayanan Terhadap
Kepuasan Pelanggan (Studi pada PT. Matahari
Department Store Jambi City). Jurnal Digest
Marketing. Vol. 3 No.1.
Tjiptono, Fandy. 2002. Manajemen Pemasaran.
Yogyakarta: Andi.
Tjiptono, Fandy. 2012. Service Management:
Mewujudkan Layanan, Prima Edisi II. Yogyakarta:
Andi.
Tjiptono, Fandy dan Gregorius Chandra. 2005. Service
Quality and Satisfaction. Yogyakarta: Andi.
Tjiptono, Fandy dan Gregorius Chandra. 2012. Pemasaran
Strategik. Edisi Kedua. Yogyakarta: Andi.
Victor, Christian, Rotinsulu Jopie Jorie dan Jacky S.B.
Sumarauw. 2015. Pengaruh Customer Relationship
Management dan Kepercayaan Terhadap Kepuasan
Serta Dampaknya Terhadap Loyalitas Konsumen PT.
Bank BCA TBK. di Manado. Jurnal EMBA. Vol.3
No.2 Juni 2015.
Zeithaml, Valarie A., A Parsu Parasuraman and Leonard L
Berry. 1990. Delivery Quality Service: Balancing
Customer Perceptions and Expextations. New York:
The Free Press.
The Influence of Customer Relationship Management, Website Quality and Service Quality on Student Satisfaction
159
