
Evaluation of Teaching Material PPG SM3T Program in Civil
Engineering
Yose Fajar Pratama, M. Giatman, Rusnardi Rahmat Putra, and Nurhasan Syah
Faculity of Engineering, Padang State University, Jl. Prof. Dr. Hamka Air Tawar, Padang, Indonesia
Keywords: Evaluation, Teaching Material, PPG SM3T, Civil Engineering Education, Universitas Negeri Padang
Abstract: This research is a research evaluation of the teaching materials of PPG SM-3T Program in civil Engineering
education. The background of the evaluation is because only 11.7% of participants passed the competency
exam. The result of interview with several lectures in PPG SM3T program, was found the teaching material
has weakness, such as, the material no up to date, not source from trust sources and the print quality very
poor. The standard evaluation teaching material use standard from Kemenristekdiki, with 4 components such
as content feasibility, completeness feasibility, language feasibility, and graph feasibility. The evaluation
research model use discrepancy which compares standard and condition of teaching material PPG SM3T
Program. In research use instrument validation by expert and for evaluation teaching material use expert from
civil engineering and Indonesia language expert. The result of teaching material plumbing construction, on
content feasibility is less, completeness feasibility is less, language feasibility good and graphs feasibility is
less. The result evaluation teaching material concrete construction, on content feasibility is very little,
completeness feasibility is very little, language feasibility very little and graphs feasibility is very little.
1 INTRODUCTION
Education problems in Terdepan, Terluar and
Tertinggal (3T) by Adlim (2016:59), is the lack of
teachers, differences in the quality of education, very
poor educational facilities. Indonesian government
resolves the education problems in (3T) by
implementing the Sarjana Mendidik di daerah 3T
(SM3T). after participants implement the SM3T
program, participant can continue to Pendidikan
Profesi Guru SM3T (PPG SM3T) program for one
year.
Republic of Indonesia Law No. 14 of 2005
explains the importance of pedagogical, professional,
social and personality competencies for teachers and
PPG SM3T participants. Pedagogical competence is
the teacher's preparation before learning, and how to
evaluate learning. Professional competence is the
ability of teachers to master subject matter in their
field of study. Social competence is related to the
ability of teachers to communicate, interact and adapt.
Personality competence includes norms, law and
ethics that apply in society.
Universitas Ngeri Padang is one of the
universities implementing the PPG SM3T program.
Data from SM3T UNP and Belmawa Ristekdikt
website shows the number of participants is 206
people. The Result Ujian Kompetensi Nasional
Mahasiswa Pendidikan Profesi Guru (UKMPPG) in
Universitas Negeri Padang only 41.2% or 85 people
graduated. Table 1 show the number of participants
who graduated from PPG SM3T program.
Table 1: Number of participants and percentage of
graduates.
No
Study program
Number of
participants
Number of
participants
who pass the
exam
%
1
Pendidikan
Kimia
14
1
7.14
2
Pendidikan
Bahasa Inggris
22
4
18.1
3
Pendidikan
Geografi
18
0
0%
4
Pendidikan
Biologi
18
18
100
5
Pendidikan
Fisika
18
11
61.1
Pratama, Y., Giatman, M., Putra, R. and Syah, N.
Evaluation of Teaching Material PPG SM3T Program in Civil Engineering.
DOI: 10.5220/0009002705170523
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Education, Language and Society (ICELS 2019), pages 517-523
ISBN: 978-989-758-405-3
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
517
6
Pendidikan
Teknik
Bangunan
(PTB)
17
2
11.7
7
Pendidikan
Jasmani,
Kesehatan &
Rekreasi
20
17
85
8
Pendidikan
Anak Usia Dini
13
10
76.9
9
Pendidikan
Pancasila dan
Kewarganegara
an
17
0
0
10
Pendidikan
Matematika
17
4
23.5
11
Bimbingan dan
Konseling (BK)
15
1
6.66
12
Pendidikan
Guru Sekolah
Dasar (PGSD)*
0
2
-
13
Pendidikan
Bahasa
Indonesia
17
15
88.2
Jumlah
206
85
41.2
Table 1, show the number of participat PPG SM-3T
program in Padang State University in 2017. The
education study program whose participants
graduated 100% was only a biology education. While
the study program with the percentage of the least
number of graduation is the education study program
of Pancasila Citizenship and geography education.
Especially for the building engineering education
study program, the number of participants in the PPG
SM-3T building engineering education program that
was declared passed was only 2 out of 17 participants.
Interview result with lecture in PPG SM3T, found a
few things. first, teaching material have never
evaluated. Second, content teaching material have
never updated. Result of observation in PPG SM3T
program found the teaching material is less appealing
to users, it is evidenced by the design of the cover,
and the placement of images that do not support the
explanation of the material.
A teaching material according to Prastowo
(2012:17) is a systematic set of information or
materials that contains competencies that must be
mastered by users of the teaching materials. M.
Muhammadi (2014:1149) teaching materials is an
element of universal teaching and there is no learning
situation without teaching materials. The Division of
Teaching Materials Asep Herry (2012:5) divides
printed materials in several types, such as handouts,
textbooks and modules.
Opinion of Kelik Purwanto (2017:193) The
Handout is a compact, clear and easy to understand
printed teaching material that contains the learning
points. While the textbook according to Sitepu
(2012:21) is a teaching material that must be learned
by learners according to the level of education. The
definition of a module according to Depdiknas
(2008:3) is a learning goal that aims to help the users
to learn independently, with the principles of goal
oriented, Self-instruction, continuous programs, self-
contained, cross referencing, selt evaluation.
Kemenristekdi (2017) and Masnur Muslich
(2014:200), teaching material must have four aspect.
First content feasibility, completeness, language
feasibility, and graph feasibility. Masnur Muslich
(2014:201), content feasibility is the suitability of the
description of the material with the standards
competence must be mastered by the user, the
accuracy and depth of the material and supporting
material of teaching material. The component of
material suitability is a match between the
competency standard that must be mastered with the
material of teaching materials. The accuracy and
depth of the material is directed at the accuracy of the
principles, concepts, and illustrations contained in the
teaching material, while the supporting material of
teaching material covers the suitability of the material
with technological developments, the recency of
features and fostering creativity of the users of
teaching materials
Completeness feasibility consists of three
components that must be have, the first, teaching
materials must be systematic, and have a balance
between chapters. Both teaching materials are
equipped with examples of questions and exercises
that strengthen understanding of concepts or
principles. The completeness aspect of the teaching
material presentation has a summary that is presented
at the end of each chapter.
The feasibility of the language of teaching
materials is reviewed from three indicators namely
suitability to the level of education of the users of
teaching materials, communicativeness and
wrangling or integration of the flow of thought. The
graph feasibility of teaching material graphic consists
of a leather design consisting of layout, typography
and use of letters. The design of the contents of the
book consists of the use of colors, layout of images,
and completeness of the layout.
Based on these conditions, the researchers have
evaluated the teaching material PPG SM3T Program
to be reviewed from content, completeness, graphic,
and language feasibility.
ICELS 2019 - International Conference on Education, Language, and Society
518
2 RESEARCH METHOD
This type of research is mixed methods with an
unbalanced mixture. The Quantitive method is more
dominant than qualitative method. Quantitive data is
the result of the evaluation of teaching material used
as primary data and collected by questionnaire.
Qualitative Data is collected through interviews and
observations. The instrument has been validated by
expert. The formula to calculate the validity uses
Aiken`s V coefficient.
V =
∑
S/[n
(
c − 1
)
] (1)
S = r-lo.
r = The number given by the judge.
lo = Lowest validity assessment numbers.
n = Number of votes.
C = Highest validity assessment figures.
Table 2: Result of validation by experts
Indicators
V Value
V Index
Category
Content
0.833
0.79
Valid
Presentation
0.875
0.79
Valid
Language
0.875
0.79
Valid
Graphs
0875
0.79
Valid
2.1. Qualitative Analysis
Analysis of qualitative data using the Miles and
Huberman whit interactive model, whit 4 aspect such
as data collection, data display, data reduction and
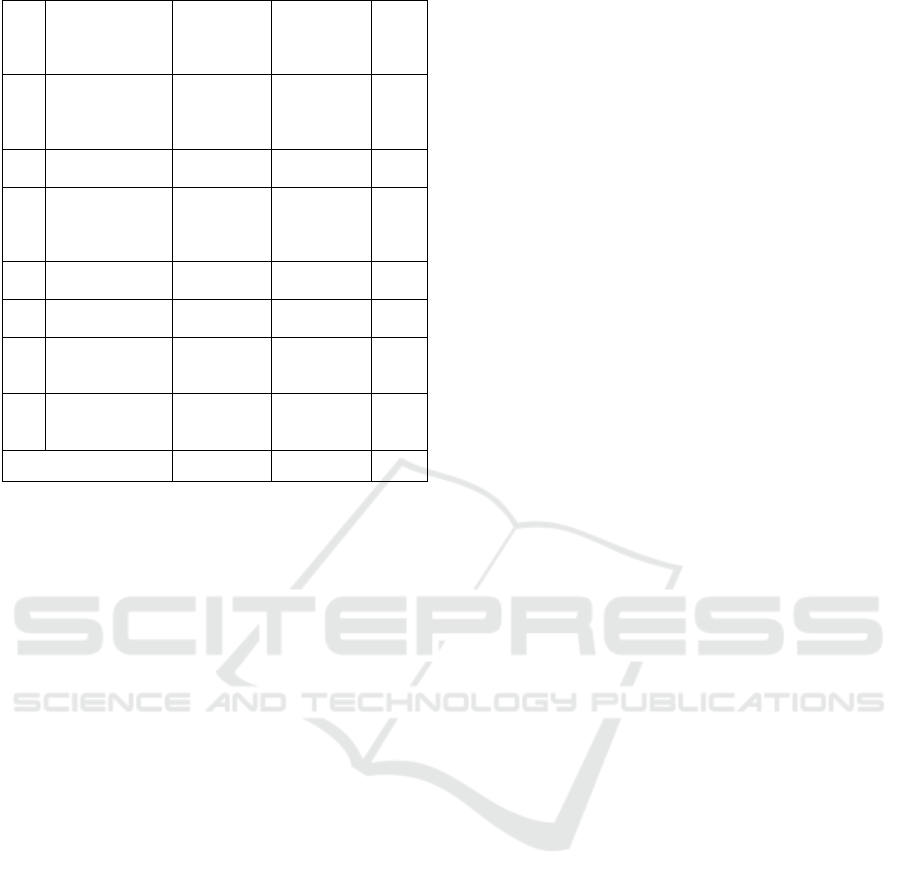
conclusion. For more details seep figure 1.
Figure 1: Qualitative Data analysis (interactive model)
Source: Sugiyono, 2012
Figure 1 we can see the interactive model have
four components, first data collection, obtained form
interview and observation. Second data reduction is
collecting data from interviews and observation in to
several groups. Third data display is result from data
reduction interview and observation. Fourth
conclusion are the essence of the results of interviews
and observations.
2.2. Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative data analysis uses the formula of
Riduwan (2009:102) to determine the level of
achievement of the teaching materials.
Achievement level =
𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒
𝐼𝑑𝑒𝑎𝑙 𝑆𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒
𝑋100% (2)
Category the achievement teaching material use Nana
Sudjana (2009:29), achievement level category.
Table 3: Achievement level Category
Percentage
Category
90%-100%
Excellent
80%-89%
Good
65%-79%
Enough
55%-64%
Less
0%-54%
Very little
3 RESULT & DISCUSSION
3.1 Qualitative
Result the interview with 10 lectures in PPG SM3T
program, found several things, First, lecture used
teaching material to achieve the competency of PPG
SM3T. Second he quality of the contents and graphics
of teaching materials need to be improved, especially
on information updates and good print quality. Fourth
the teaching material is accordance with the lattice
exam.
3.2 Quantitative
The result of the evaluation of teaching material PPG
SM-3T program in building Engineering education
for plumbing construction, wood construction and
concreate construction is are as follows.
3.2.1 Plumbing Construction
The results of the evaluation of the teaching materials
of plumbing construction by experts can be seen in
table 4.
Evaluation of Teaching Material PPG SM3T Program in Civil Engineering
519
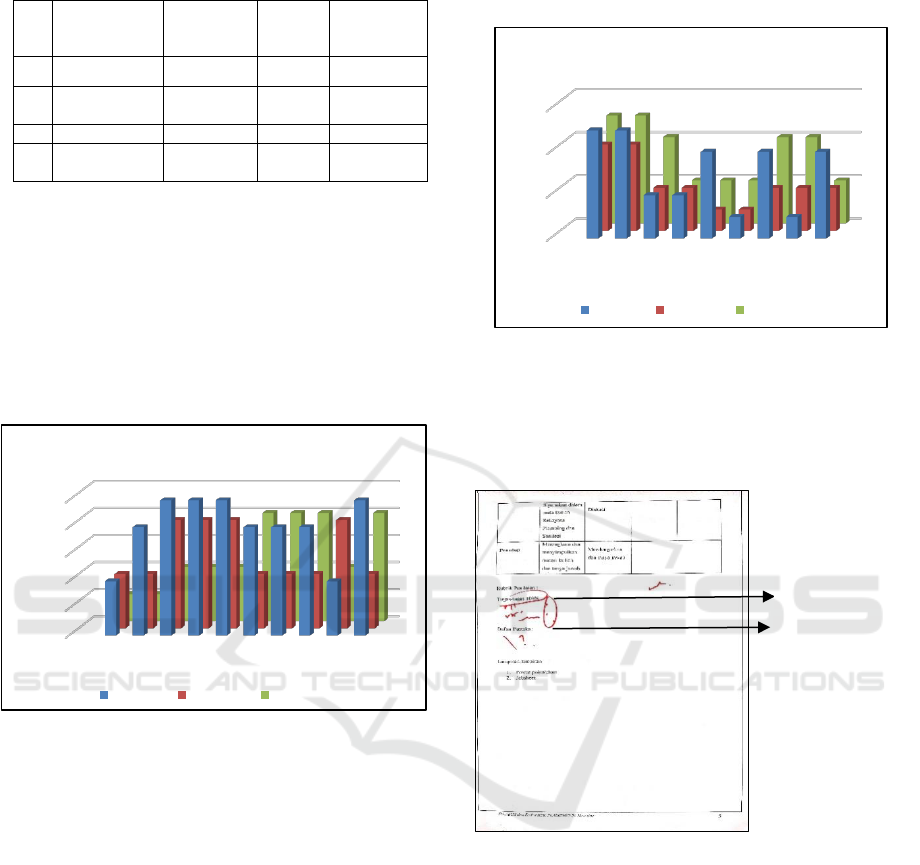
Table 4: Evaluation result by experts
N
o
Feasibility
Achievemen
t (%)
Categor
y
Discrepanc
y
(%)
1
Content
63.0
Less
37
2
Completenes
s
57.8
Less
42.2
3
Language
83.0
Good
17
4
Graphs
51.9
Very
little
48.1
From the table 4 can be see the plumbing
construction material from the content feasibility in
category less with discrepancy 37%. The
completeness feasibility is less category with
discrepancy 42,2%. Language feasibility in category
good, with discrepancy 17%. Graphic feasibility in
very little category, with discrepancy 48.1%. To more
clearly evaluate the result of the evaluation plumbing
construction can see in figure 2.
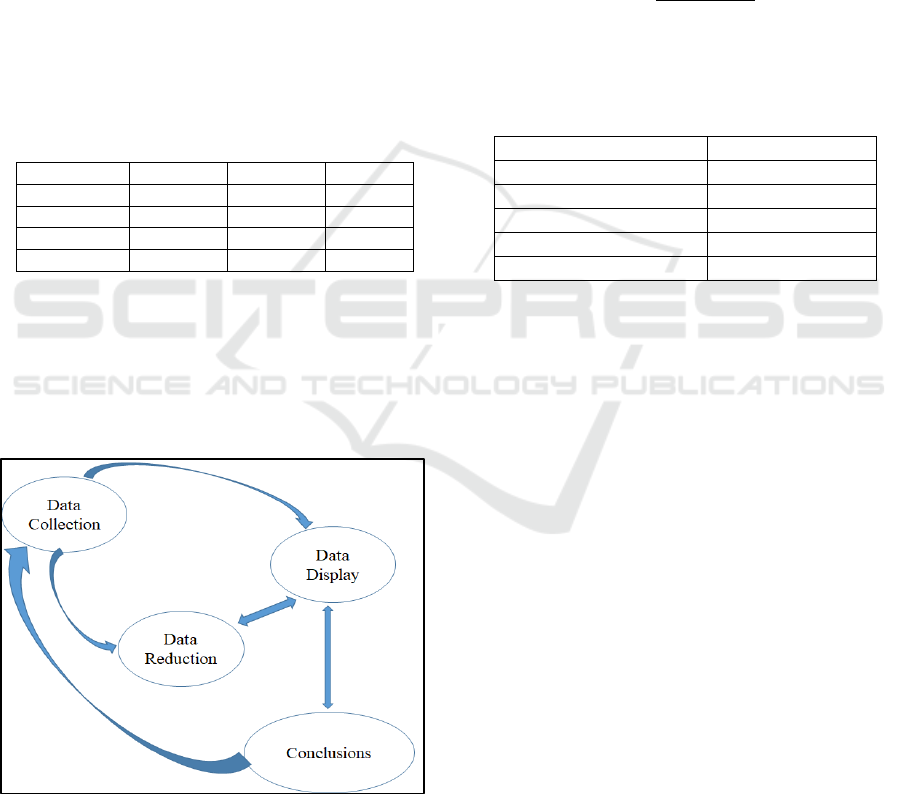
Figure 2: Content Feasibility
In Figure 2, it can be seen item number 1, 2 and 9
got the lowest from the experts. The item measures
the basic competencies contained in the teaching
materials as well as the clarity of concepts, formulas
and procedures that the teaching materials are used
for, while other items are in sufficient categories.
Plumbing teaching material still use SNI 03-7565-
2005, while there is now SNI 8153-2015. One of
difference SNI 03-7565-2005 whit SNI-8153-2015 is,
in SNI 8153-2015 not explain type of equipment use
in plumbing work, whereas at SNI-8153-2015 it is
explained.
The completeness feasibility teaching material
plumbing construction can see in figure 3.
Figure 3. Completeness Feasibility
Based on Figure 3, educational evaluation
teaching materials are very well-served and very
good. It can be seen in items 1 and 2. The three
experts give scores 5 and 4. But in items No 3, 4, 5,
and 8 feasibility of the presentation is in the category
of less once. The cause of this is that the teaching
material does not come with photographs or images
and has no examples of questions, exercises, answers
keys, and conclusions in each chapter. In figure 4
show the plumbing teaching material not have task
list and bibliography.
Figure 4. Plumbing teaching material completeness
feasibility.
0
2
4
6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
skor
item
Expert I Expert II Expert III
COMPLETENESS FEASIBILITY
No Task List
No Blibliography
0
1
2
3
4
5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Score
item
Expert I Expert II Expert III
CONTENT FEASIBILTY
ICELS 2019 - International Conference on Education, Language, and Society
520

Result evaluation language feasibility teaching
material plumbing construction can see in figure 4.
Figure 5. language Feasibility
Base figure 5, can see the plumbing construction
in general is in good category, but on items 5 and 6
gets enough categories. At that number the teaching
materials do not use a consistent symbol and the
language used is less encouraging thinking skills.
Graphic feasibility can see in figure 6.
Figure 6: Graphic Feasibility
The feasibility teaching material the plumbing
construction is categorized as less. This is because
the picture not clear, not have maps, and the picture
too small. In picture 7, give example the picture
plumbing construction is not clear.
Figure 7.: The example the picture plumbing construction
Recommendations given to educational
evaluation teaching materials are the teaching
materials can be used with revisions.
3.2.2 Concreate Construction
The results of the evaluation teaching material
competency evaluation of pedagogic materials of
educational media conducted by the three experts can
be seen in table 5.
Table 5: Educational Media Materials Evaluation results
No
Feasibility
Achievement
(%)
Category
Discrepancy
(%)
1
Content
60
Less
40
2
Completeness
44.4
Very
Little
55.6
3
Language
71.9
Enough
28.1
4
Graphs
54.8
Less
45.2
In table 5, based on the results of evaluation
conducted by the experts, the aspect of content
feasibility and the discrepancy of the teaching
materials are in the category less with the percentage
of gaps 40% and 45.2%. The aspect of the
completeness is in the category very little, with
discrepancy 55.6%, while the language aspect is in
the category enough with the discrepancy of 28.1%.
To clarify the results of educational media teaching
materials, picture 7 depicts the feasibility of the
content of the concreate construction.
0
1
2
3
4
5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Score
Item
Expert I Expert II Expert III
LANGUAGE FEASIBILITY
0
2
4
6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Score
Item
Expert I Expert II Expert III
GRAPHIC FEASIBILITY
Not clear
picture
Evaluation of Teaching Material PPG SM3T Program in Civil Engineering
521

Figure 7. Content Feasibility
The feasibility of concreate construction content
in general is less category. In items number 1, 2, 9 and
10, the experts give a low score. It is caused, first the
teaching materials do not include basic competencies
and the explanations of the contents of the teaching
materials are difficult to understand. Second, the
concrete construction teaching materials still use
concrete SNI 2847-2002.
When compared with the SNI used currently using
SNI 2847-2013, one of the differences in SNI for
concrete and steel in 2002 with 2013 is that the
effective height of beams that exceed 0.9m must be
paired with longitudinal reinforcement, whereas in
SNI 2847-2013 the high beam more than 0.4m must
be paired with longitudinal reinforcement.
The completeness feasibility teaching material
concreate construction get very little category, it can
bee seen in figure 8.
Figure 8. Completeness Feasibility
The completeness feasibility teaching material
concreate construction in item 4, 5, 6, and 8 the
teaching material not have examples of questions,
exercises, key answers, and conclusions. The
language feasibility the teaching materials concreate
construction can be seen in figure 9.
Figure 9: Language feasibility
The language feasibility of the concreate
construction teaching materials in general is in good
category, but items no. 1, 3 and 9, teaching materials
are less effective, and less appropriate to the level of
teaching materials users.
The graphic feasibility of teaching material
concreate construction can see in figure 10.
Figure 10: Graphic Feasibility
Items 3, 4, and 6 graphic feasibility teaching
material concreate construction are less categorize,
this is due to the use of color and placement of photos,
images, graphics that are inappropriate. In figure 11,
example the image in concreate construction not
clear.
0
2
4
6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Score
Item
Expert I Expert II Expert III
CONTENT FEASIBILITY
0
1
2
3
4
5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Score
item
Expert I Expert II Expert III
COMPLETENESS FEASIBILITY
0
1
2
3
4
5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Score
Item
Expert I Expert II Expert III
LANGUAGE FEASIBILITY
0
1
2
3
4
5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Score
Item
Expert I Expert II Expert III
GRAPHIC FEASIBILIY
ICELS 2019 - International Conference on Education, Language, and Society
522

Figure 11: Example Image in Teaching Material Concreate
Construction
Based on the results of the Teaching material
concreate construction recommended to be used with
revisions.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Teaching materials plumbing construction are
declared suitable to be used with revisions. Revisions
that need to be done are to update the teaching
material information, and to reprint teaching
materials.
Teaching materials concrete construction are
suitable for use with revisions. Concrete construction
teaching materials need to use the latest SNI such as
SNI 2847-2013. The print quality of concrete
construction teaching materials needs to be improved
and printed with the best quality.
REFERENCES
Adlim, H. G. (2016). Permasalahan dan Solusi Pendidikan
di Daerah Kepualauan (Studi kasus di SMA Negeri
Pulau Aceh, Kabupaten Aceh Besar). Jurnal
Pencerahan, 48-61.
Asep Harry, Permasih, Laksmi. (2012). Pengembangan
Bahan Ajar . Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, 1-13.
Kelik Puwanto and Aulia Rahmawati. (2017).
Pengembangan Handout untuk Siswa Kelas V SDN 14
Koto Baru Pada Materi Bermain Drama. Jurnal
Tarbiyah.
Kementerian Riset, Teknologi, dan Pendidikan Tinggi RI.
(2017, March 4). Ristekdikti. Retrieved from
http://seleksi.dikti.go.id/
sm3t/?tf=7zi5@MliYLK1hfu2Z@RF/VEwc2Q0FAo0
9WlZsiRHtlU=
Kementrian Riset Teknologi dan Pendidikan Tinggi.
(2017). Panduan PGG Program Profesi Guru 2017.
2017: Ristekdikti.
Mansur Muslich. (2014). Text Book Writing . Jogjakarta:
AR-Ruzz Media.
Mohammad Mohammadi, Heidar Abdi. (2014). Texbook
Evaluation A Case Study. Procedia Social and
Behavioral Sciences , 1148-1155.
Muhammad Giatman. (2017). Building School
Organization Work Culture Through The
Implementation Of Quality Management System ISO
9001: 2008. International Jornal of Geomate.
Persada.
Prastowo, Andi. (2011). Panduan Kreatif Membuat Bahan
Ajar Inovatif. Yogyakarta: Diva Press.
Ristekdikti. (2018, Desember 24). Sistem Rekrutmen
Peserta PPG. Retrieved from Sistem Rekrutmen
Peserta PPG Web Site: http://seleksi.dikti.go.id/sm3t/
Saifudin Azwar. (2013). Reliabilitas dan Validitas.
Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Sugiyono. (2013). Metode Penelitian Kombinasi (mixed
methode). Bandung: Alfabeta.
Undang-Undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 14 Tahun .
(2005). Tentang Guru dan Dosen.
Wirawan. (2011). Evaluasi Teori, Model, Standar, Aplikasi
dan Profesi. Jakarta: Rajagrafindo
Not clear
picture
Evaluation of Teaching Material PPG SM3T Program in Civil Engineering
523
