
The Instrument Development for Evaluating the School Budgeting
Planning Management at Yogyakarta Elementary School
Siti Maisaroh
1
, Dedek Andrian
2
1
Elementary School Teacher Education, Yogyakarta PGRI University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
2
Department of Mathematics Education, Universitas Islam Riau, Pekanbaru, Indonesia
Keywords:
Instrument, Development Research, Evaluating, School Budgeting Planning Management, Elementary School
Abstract:
The purpose of this research is to develop the instrument to evaluate the Budgeting Planning Management at
Yogyakarta Elementary Schools. Type of This research is a development research consisting of four phases: 1)
phase of the initial investigation, 2) phase of design and 3) phase of expert validation, and 4) phase of the trial.
From the phase of initial investigation obtained 6 components of the evaluation that is; 1) school program;
2) Financing; 3) fund source;4) Planning;5) organizing; 6) Implementation; 7) supervision; 8) evaluation.
The phase of design is done by studying from various the theory and making the instrument in the form
the questionnaire as many as 31 items. The phase of expert validation is done by 2 evaluation experts, the
school management expert and, and 6 management practitioners. The assessment results from expert and
practitioners were analyzed using the Aiken’s formula. The phase of the trial was analyzed using confirmatory
factor analysis (CFA) and construct reliability with the assistance Lisrel software 8.80. From the analysis
results of validity and reliability acquired 31 items of the questionnaire were valid and feasible to be used to
evaluate the Budgeting Planning Management at Yogyakarta Elementary Schools.
1 INTRODUCTION
Government Regulation No. 17 of 2010 concerning
Education Management and Implementation,
especially in articles 50 and 51 states that the unit of
education must plan and develop education policies
following schools regulation. One of the education
policies that are the obligation of the school is to
develop an annual work plan and prepare an annual
income and expenditure budget. The government
hopes that with the planned school activities, the
government will ease in monitoring and evaluating
school development. This school activity plan can
be a reference and working guide in submitting what
educational resources needed in developing schools’
program.
School expenditure budget management will
make it easier for schools to find out what activities
will be carried out by the school so that the expected
goals can be achieved and school obligations can
be fulfilled. In terms of participation, school
budget management can provide an overview of
what is needed and what support is needed by
school stakeholders both internally and externally.
This is in line with the regional autonomy policies
developed within the scope of formal education,
namely School-Based Management (SBM). SBM
makes the school’s education development better in
terms of school management, school funding, and
supervision. Schools become more independent and
have a responsibility for managing and developing
their schools. Schools will ease and flexible
in developing school programs have designed or
planned following the needs and the school resources
capabilities.
Budget planning is an activity of planning
activities for the future and how much funding
is needed to support the intended activities and
to explore sources of funds, collect, also describe
into activities that have been programmed for
the achievement of an educational goal. School
financing planning requires accurate and complete
data so that all future planning needs can be
anticipated in the draft budget. The position of the
Principal as a leader must be able to develop some
dimensions of administrative actions. The ability to
apply educational programs into cost equivalents is
important in preparing the budget. Activities to make
budgets are not routine or mechanical work, involve
consideration of the basic purposes of education and
Maisaroh, S. and Andrian, D.
The Instrument Development for Evaluating the School Budgeting Planning Management at Yogyakarta Elementary School.
DOI: 10.5220/0009038800130017
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education and Humanity (ICoSEEH 2019) - Sustainable Development in Developing Country for Facing Industrial
Revolution 4.0, pages 13-17
ISBN: 978-989-758-464-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
13

programs Based on these perspectives the planning
of school education costs must be able to open the
way for the development and explanation of concepts
about desired educational goals.
Harjanti’s (2010) research on budget planning
concluded that there were still important school
needs that had not been identified, budget planning
implemented in schools was still not accordance
to school needs, schools’ program targets, program
alternatives selection, and selection of effective
costs. If budget planning is not done well,
then budget implementation often appears important
but unplanned programs beforehand. activities to
evaluate the budget will be difficult because some
components of the budget are not recorded in
planning but implemented.
The school budgeting will be a success if
involve of all parties, namely the community, parent,
principal, teachers, schools committee and students.
The results of research conducted by Yuliastuti &
Prabowo (2014) state that the principals, teachers,
and school committees have involved in the budget
planning process of the school. the principals and
teachers in planning the school budget in the good
category but the school committee is still lacking in
planning and controlling the process of the school
budget planning. The school committee also signed
the ratification of the APBS but in the budget planning
process, the school committee didn’t get involved.
In the preparation of the school budget, a budgeting
team has been formed, but the school does not
yet understand how to estimate the ideal budget,
so many school programs are not carried out by
school, and there was a lack of commitment to the
budget prepared. Reports made by schools were less
accountable because the administration wasn’t neatly
arranged. Budgeting management transparency is
still lacking because the APBS is not disseminated to
school residents.
The elementary school in Yogyakarta also faces
a big dilemma between the strong desire to provide
quality-assured education on the one hand and the
fact that there is a lack of funds from the government
on the other side. Of the 93 Elementary Schools
in the city of Yogyakarta, the sources of funds in
the School Expenditure and Revenue Budget Plan
(SERBP) that come from School Operational Costs
(SOC) funds are on average 55 percent, from the
State School Operational Costs (SSOC) an average
of 24 percent, and those that come from school
committee contributions are on average 23 percent.
The use of financial resources for the construction and
procurement of school facilities and infrastructure
averages 22 percent, for school needs as much as 20
percent, for teaching and learning activities as much
as 19 percent, for honorariums as much as 16 percent,
for student activities as many as 16 percent, and for
other purposes as much as 3 percent (Setyaningrum,
2010).
Thus, the quality of education can be guaranteed
by program synchronization with the budget planning
at each year. Planning is the first and foremost
thing to do. If in carrying out activities there is no
planning, then the goal will not be achieved so that
waste occurs and activities are not as expected. based
on the problems that have found, the development of
instruments to evaluate budget planning needs to be
carried out so that weaknesses or shortcomings can be
identified that need to be improved in improving the
quality of learning through the management of good
school budgets.
The purpose of budget planning is to facilitate
future work, so decisions can be made with careful
planning. According to Robbins & Coulter (2012:
204), ”planning involves determining the objectives
of the organization, strategies for achieving goals,
and developing networks to achieve goals. Poston,
(2011: 5), states that school budget planning is part
of prediction, communication, and decision making,
(Lipham, 1985: 237) ”School budgets are systematic
planning for income and expenditure related to
educational programs and supported by data that
reflects the needs, goals, and results that the school
wants to achieve.
Anthony & Govindarajan (2005: 373) states that
budgeting planning is one of important activity for
effectively developing, controlling, and planning an
institution like schools. Budget planning is one
strategy to help the program made by schools in
achieving institutional goals have planned . Budget
planning is affected by the length of management
carried out by schools stakeholders (Sato, 2012).
Based on the expert statement above, it can conclude
that budgeting planning management of schools is an
important thing have to consider in implementing an
education program.
(Sisk, 1969) states that school management is a
unity of all resources through a process of planning,
organizing, directing and controlling. Education
management is activities that related to education
management at school (Sun, 2014). Management
made by stakeholders aims to check standards or
criteria with their implementation, which can increase
the attitude of the value of the individual in the
workgroup (Berggren and S
¨
oderlund, 2008). School
management is various roles in education were
made by schools to give education and training to
schools community who are carried out teaching and
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
14

learning process (Pant and Baroudi, 2008). School
management is a system needed to handle student
diversity so that the school can get the goal of the
school program was the transferring knowledge to
the student (Passailaigue and Estrada, 2018; Oplatka
and Arar, 2017) stated that school management is
an important part to implement good atmosphere for
school staff in getting a good quality of teaching and
learning in the classroom.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
Research on instrument development to evaluate The
Instrument Development for evaluating the School
Budgeting Planning Management at Yogyakarta
Elementary Schools using research and development.
The purpose of this research is to develop a valid and
reliable instrument of a questionnaire for evaluating
the budgeting planning management at Yogyakarta
elementary schools.(Borg, 1983) model was an
appropriate model for carrying out this research. This
model consisting of 10 steps which are simplified into
four steps:
• phase of initial investigation
• phase of design
• phase of expert validation
• phase of trials
Initial investigations were done by studying
the theory from a variety of sources and FGD
with 10 Participants consisting of 6 expert and 4
practitioners. The purpose of the FGD is to get
what is component can be used to evaluate budgeting
planning management of Elementary Schools of
Yogyakarta Province. The instrument design
phase was conducted by developing a questionnaire.
Validation Phase conducted by 2 evaluation experts
or 1 measurement expert and 4 practitioners. The
validation phase aims to see the validity of the
contents of the developed questionnaire. Content
validity affects the accuracy of data to be obtained
in the field. The trial used to see the validity and
reliability of component or indicators have got from
studying the theory.
2.1 Population and Sample
The population in this study were all elementary
schools from 5 districts in Yogyakarta Province,
namely; 289 schools from Kolun Progo Regency,
280 from Bantul Regency, 431 from Gunung Kidul
Regency, 379 from Sleman Regency, and 99 from
Yogyakarta City. The sampling technique in this
study is the Proportional Random Sampling Cluster
technique, which is school sampling in each region.
Sampling is based on the school from a defined
area using the Krejcie & Morgan table developed
from Isaac and Michael, if the population is 1,464
Elementary Schools with an error rate of 5%, the total
sample is 284 Primary Schools.
2.2 Population and Sample
The instruments in this study were expert validation
sheets and instrument effectiveness sheets.
Instrument validation sheet is used to assess the
content of the instrument being analyzed. the
instrument effectiveness sheet is used to test whether
the instrument is effective in gathering information.
The instrument to be developed in this study is
a questionnaire consisting of 8 components or
indicators, namely; school programs, financing,
Fund Source, Planning, Organizing, Implementation,
Supervision, and Evaluation.
2.3 Analysis Data Technique
Analysis data in this development research used
Content Validity uses Aiken’s Validity, Construct
Validity uses CFA, Cronbach’s Alpha, and Construct
Reliability. Aiken’s Validity used to see the content
quality of the instrument. CFA used to check the
construct validity of the instrument has developed.
Cronbach’ Alpha used to analysis the reliability of
items of instrument. The construct reliability used to
analysis the construct reliability of each indicator or
components.
3 RESULT & DISCUSSION
3.1 Content Validity
Content Validity analyzed with the help excel
program based on Aiken’s Formula. The assessment
of experts and practitioners analyzed from the score
have given through the assessment sheet. the result
shows that 31 items of the instrument has a high
category and middle category. 19 items with the
high category and 12 items with the middle category.
these results show that all items have developed by
researcher have a good category and can use to get
good data from the field.
The Instrument Development for Evaluating the School Budgeting Planning Management at Yogyakarta Elementary School
15
3.2 Reliability of Instrument
Reliability of instrument based on all items or items
total was analyzed with Cronbach’s Alpha. For
getting the reliability coefficient, the researcher gives
the instrument to the respondent as many as 30
respondents and analyzed using Cronbach’s Alpha
Formula with the help SPSS software. From the
analysis, the result was got the coefficient Cronbach’s
Alpha about 0.87. Based on this result can make a
conclusion that the instrument was developed by the
researcher was reliable.
3.3 Validity and Reliability of Construct
3.3.1 Confirmatory Factors Analysis (CFA)
CFA used to check so far model measurement has
developed by studying theory from various sources
is fit with data to have acquired from the field.
Measurement model can be said fit with the data
from the field if this model already fulfills criteria
or standard from statistics expert or consensus of
statistics expert based on statistics theory that is
Goodness of Fit Index. The result of analysis CFA
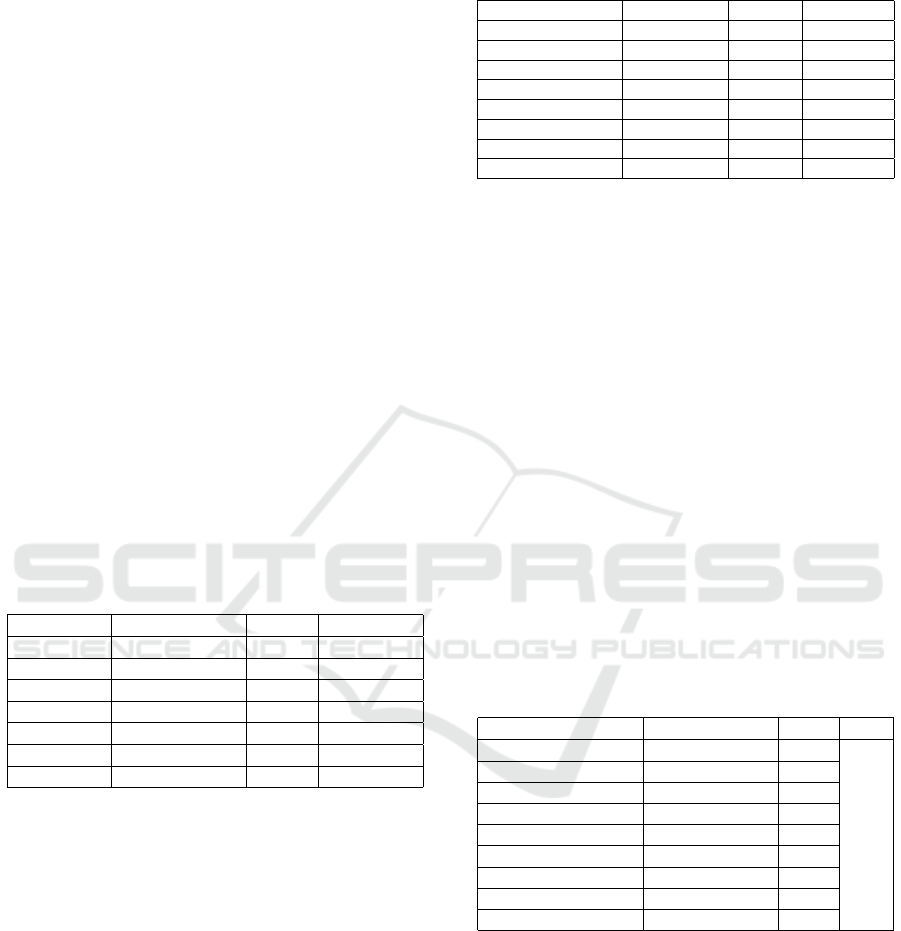
in this model can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1: Standard and Result of Goodness of Fit Model
Budgeting Planning Management.
GOF Standard Result Conclusion
Chi-Square P >0,05 0,4421 Fit
RMSEA RMSEA <0.08 0,000 Fit
GFI GFI ≥ 0.90 0.96 Fit
NFI NFI ≥ 0.90 0.95 Fit
CFI CFI ≥ 0.90 0.96 Fit
IFI IFI >0.80 0.96 Fit
RFI RFI 0-1 0.91 Fit
From table 1 acquired that seven criteria of GOF
show the data was fit with the measurement model
was built by the researcher. From this result can be
concluded that the measurement model has built from
studying theory from various sources was fit with data
were acquired at the field
CFA is the measurement model that shows one
latent variable can be measured by one or more
observed variables. CFA will see so far the observed
variables or indicators were got from studying the
theory are the variable builder. CFA will be helped by
Lisrel Software. At this analysis, observed variables
or indicators must meet established standard with
loading factor at standardized>0.3 or T-value>1.96.
The analysis result can be seen clearly in table 2
From Table above can be concluded that planning,
organizing, implementation, supervision, evaluation,
Table 2: Summary of Measurement Model of Manifest
Variables
Manifest Variables Standardized T–value Decision
Planning 0,48 12,28 Significant
Organizing 0,26 8,41 Significant
Implementation 0,65 15,1 Significant
Supervision 0,51 12,86 Significant
Evaluation 0,55 13,45 Significant
School program 0,63 13,98 Significant
Financing 0,73 15,08 Significant
Fund Sources 0,43 11,41 Significant
school program, financing, and fund sources are
significant so that eight indicators have found from
studying the theory were indicators as variables
builder of budgeting planning management variable.
indicators of budgeting management variable have
T-value score more 1.96 so that indicators have found
from studying the theory has fulfilled the good of
measurement standard.
3.3.2 Construct Reliability
Construct reliability used to the analysis level of
construct reliability from various indicators from
studying the theory both the references book
or journals have published at various publishers.
Good indicators are indicators have high construct
reliability coefficient is more 0.70. this reliability
was calculated with error and loading factor have
found from analysis uses CFA. the summary of CFA
analysis can be seen in Table 3 below.
Table 3: Construct Reliability
Observed Variables Loading Factor Error CR
Planning 0,70 0,51
0,82
Organizing 0,55 0,70
Implementation 0,84 0,20
Supervision 0,68 0,54
Evaluation 0,69 0,33
School program 0,80 0,37
Financing 0,85 0,27
Fund Sources 0,66 0,56
Total 2,31 1,20
Based on Table 3, it was got construct reliability
coefficient about 0.82. This value or coefficient more
good standard of measurement theory that is more
0.70. from this table can make a conclusion that all
of the indicators have found from studying the theory
were valid and reliable based on construct so that
this instrument can be used to get information or data
about the school budgeting planning management.
Evaluating an education program needs an
instrument valid and reliable based on content and
construct. the content validity shows how far
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
16

items have developed from indicators are fulfilled or
appropriate indicators definition or items represent
indicators have found from studying the theory of
various references sources, while construct explains
how far indicators are valid and reliable which marked
have good loading factor is more 0.30 (Andrian
et al., 2018) Feasibility of an instrument to evaluate
an education program is very important in the
measurement theory. This thing shows for getting
good data from field needed a good instrument. The
instrument becomes the main key in getting good
information or data in the field.
The instrument for evaluating the school
budgeting planning management already valid and
reliable in content and constructively (Wynd et al.,
2003). This instrument is expected to provide
convenience in evaluating the school budgeting
planning management at elementary school fo
Yogyakarta Province. The instrument has a good
validity of content and construct can give valid
information and the right conclusion (Setiawan and
Mardapi, ). The valid and reliable instrument will
describe what happened in the education program
evaluated. The valid and reliable instrument will give
accurate information about weakness and strengthen
of educational programs have created or designed
the government or private (Wright and Craig, 2011).
If an instrument was good in content and construct,
it will give a good conclusion in making a policy
(HADI et al., 2019).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the analysis result can be made the
conclusion that the instrument was developed by the
researcher as many as 31 items were valid and reliable
in content and construct. Analysis of Aiken’s formula
shows all items have assessed by experts have score
or coefficient with middle and high category, while
the reliability of instrument based on total items
show coefficient from Cronbach’s Alpha is more 0.70.
Construct reliability was analyzed with CFA shows
all indicators have loading factor is more 0.3 or has
fulfilled the good standard of measurement theory,
while construct reliability has coefficient more 0.70.
The Instrument for evaluating the school budgeting
planning management is feasible to get good or valid
data in the field.
REFERENCES
Andrian, D., Kartowagiran, B., and Hadi, S. (2018). The
instrument development to evaluate local curriculum
in indonesia. International Journal of Instruction,
11(4):921–934.
Berggren, C. and S
¨
oderlund, J. (2008). Rethinking project
management education: Social twists and knowledge
co-production. International Journal of Project
Management, 26(3):286–296.
Borg, W. (1983). Gall. m. d. Educational research (4th ed.).
New York: Longman.
HADI, S., ANDRIAN, D., and KARTOWAGIRAN, B.
(2019). Evaluation model for evaluating vocational
skills programs on local content curriculum in
indonesia: Impact of educational system in indonesia.
Eurasian Journal of Educational Research (EJER),
(82).
Oplatka, I. and Arar, K. (2017). The research on educational
leadership and management in the arab world since
the 1990s: A systematic review. Review of Education,
5(3):267–307.
Pant, I. and Baroudi, B. (2008). Project management
education: The human skills imperative. International
journal of project management, 26(2):124–128.
Passailaigue, R. M. and Estrada, V. (2018). Educational
management with technology support. International
Journal of Applied Engineering Research,
13(12):10647–10650.
Sato, Y. (2012). Optimal budget planning for investment in
safety measures of a chemical company. International
Journal of Production Economics, 140(2):579–585.
Setiawan, A. and Mardapi, D. Supriyoko, & andrian,
d.(2019). the development of instrument for
assessing students’ affective domain using self-and
peer-assessment models. International Journal of
Instruction, 12(3):425–438.
Setyaningrum, T. (2010). The education budget
commitment in the education city of Yogyakarta still
hasn’t reached 20 percent. Jurnal Populasi.
Sisk, H. L. (1969). Principles of management: A systems
approach to the management process. South-western
Publishing Company.
Sun, M. (2014). 30 years of chinese educational
management: achievements, characteristics and
problems. International Journal of Educational
Management, 28(3):340–348.
Wright, P. M. and Craig, M. W. (2011). Tool for assessing
responsibility-based education (tare): Instrument
development, content validity, and inter-rater
reliability. Measurement in Physical Education and
Exercise Science, 15(3):204–219.
Wynd, C. A., Schmidt, B., and Schaefer, M. A. (2003).
Two quantitative approaches for estimating content
validity. Western Journal of Nursing Research,
25(5):508–518.
The Instrument Development for Evaluating the School Budgeting Planning Management at Yogyakarta Elementary School
17
