
Students’ Acceptance of Mobile Application based-Office English
Learning Material for University Students
Sri Wahyuni and Fauzul Etfita
English Language Education, Universitas Islam Riau, Pekanbaru, Indonesia
Keywords:
Acceptance, Office English, Learning Material, ENFORCE, Mobile Application
Abstract:
Learning material is one of the strategic tools that can be used to achieve the learning goal. However, the
conventional learning material is still employed such as a book, printed module, etc. Responding to this issue,
the researchers have developed mobile application-based office English learning material. The application was
named ENFORCE. Hence, this research aimed to analyse the correlation among factors and to figure out the
best factor that influenced students’ acceptance of the mobile application as a learning material for university
students. In this research, 105 students had been asked to use a supportive mobile application-based learning
material during the learning process. Further, at the end of the semester, online questionnaires were distributed
to obtain the data. In analysing the data, the correlation and regression analysis were carried out through SPSS.
The results revealed that the correlation among the factor was correlated significantly. It was emphasized by
the significant value which was greater than 0.01. Additionally, the result of regression analysis showed that
significant value which was .000 that greater than 0.005. It can be declared that the best factor that influenced
students’ acceptance of mobile application-based office English learning material for university students was
ease of use.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of the mobile application has
been utilized for educational issues (Domingo and
Gargant
´
e, 2016). Specifically for language learning,
there are many mobile applications designed for
supporting language learning and providing learning
material (Hao et al., 2019). The movement of mobile
objectives has opened opportunities an alternative
media in providing an interactive learning material
(Akpan, 2017; Al-Hunaiyyan et al., 2018). Besides,
it also becomes challenges for lecturers and students
to maximize the mobile application-based learning
(Chavoshi and Hamidi, 2019).
As confirmed by several studies that have
announced the advantages of language learning
through mobile applications (Pilar et al., 2013;
Shanmugapriya and Tamilarasi, 2013; Wu, 2015). In
term of the students’ acceptance of learning mobile
also showed positive attitude (Al-Emran et al., 2018;
Bozdo
˘
gan, 2015; Dashti and Aldashti, 2015). In this
research, the students’ acceptance was determined
based on the internal factors that influenced the
students’ behavioural intention of use mobile-based
learning material such as usefulness perception and
ease of use perception (Davis, 1989).
Additionally, external factors were also
considered as affected aspect in acceptance namely
self-efficacy and compatibility (Venkatesh and Davis,
2000). In consequence, the current research aimed
to reveal the correlation and the best-affecting factor
on students’ acceptance of mobile application-based
office English learning material at the end of the
semester after using the application.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
The respondents of this research were 105 private
university students who had learned English for office
through mobile application namely ENFORCE. The
students were asked to use ENFORCE as a supportive
learning material during 14 weeks of the effective
learning time allocation. To have the app, the
installation through play store was required for every
student at the first week. In its implementation, the
semester learning plan was modified for applying this
application. Further, the quantitative method was
used through the survey to achieve the purpose of this
study. The 20 statements of the questionnaire were
52
Wahyuni, S. and Etfita, F.
Students’ Acceptance of Mobile Application based-Office English Learning Material for University Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0009058700520056
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education and Humanity (ICoSEEH 2019) - Sustainable Development in Developing Country for Facing Industrial
Revolution 4.0, pages 52-56
ISBN: 978-989-758-464-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
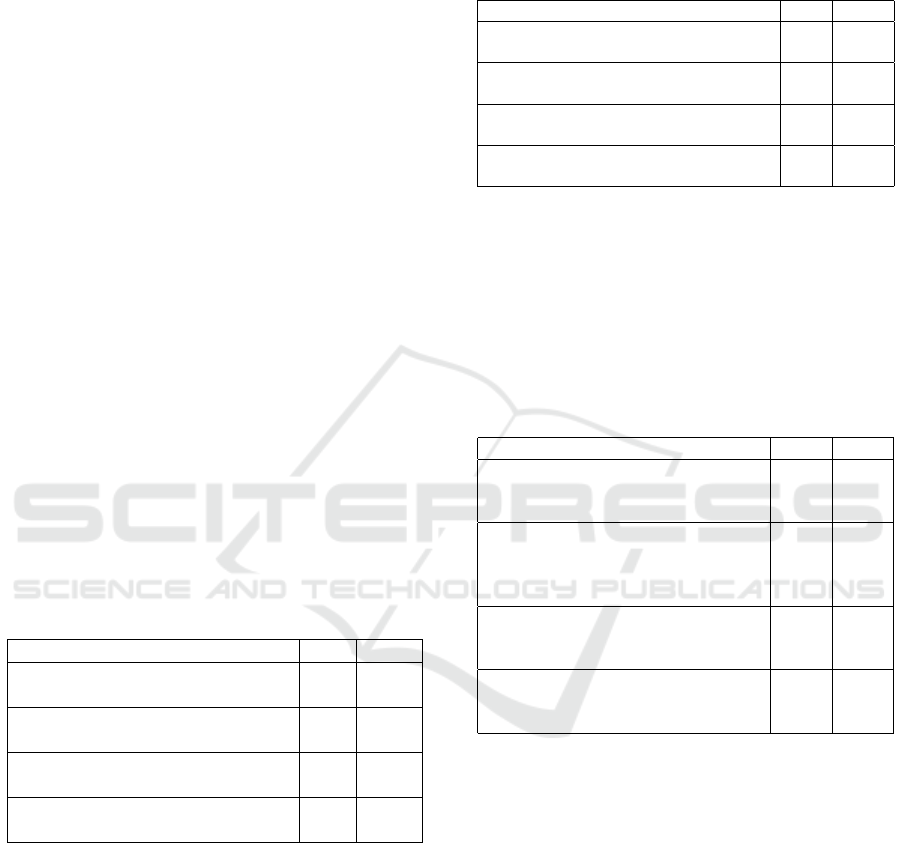
adapted from (Davis, 1989); (Venkatesh and Davis,
2000); and (Chung et al., 2015) employed to collect
the data at the end of semester. The google form was
utilized to address the questionnaire to the students.
After collecting the data, SPSS was used to compute
and analyse quantitatively the data. Additionally, the
correlation analysis was carried out to figure out the
correlation among factors and regression analysis was
conducted to know the best-affecting factor.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this part, the researchers discussed the results and
discussion in some sub-section. To elaborate on the
research results obviously, the researcher divided the
sub-section into descriptive statistics, the result of
correlation among factors, and the result of regression
analysis.
3.1 Descriptive Statistics of Each Factor
The descriptive statistics revealed that ease of use
showed the greatest mean score which was 16.45. The
behavioural intention of use, usefulness, self-efficacy,
and compatibility were 15.96, 15.84, 14.75, and 14.4
respectively. The criteria for each factor are based on
the range of average scores with levels from very high
to very low. The descriptive statistics of each factor
can be seen in table 1-5.
Table 1: Descriptive statistics of ease of use
Items SD Mean
studying English for office through
ENFORCE App is easy for me
.994 4.05
studying English for office through
ENFORCE App saves time
.814 4.17
studying English for office through
ENFORCE App is convenient
.872 3.99
studying English for office through
ENFORCE App is easy to use
.861 4.24
In term of ease of use perception, students trusted
that studying office English class by using ENFORCE
application was easy to operate it. The evidence
of students’ perceived of ease of use can be seen
from the means score which were 4.24 and 4.05.
As well, it can save their time learning through
that application. Besides, mobile application-based
office learning material was appropriate to use in
learning English for office. The evidence of students’
perceived of convenience and saving the time can be
seen from the means score which were 4.17 and 3.99.
It was evidenced from the mean score that was at a
high level and the students’ perceived of ease of use
was positive (see table 1).
Table 2: Descriptive statistics of behavioural intention of
use
Items SD Mean
I am ready using ENFORCE
App to learn office English
.898 4.10
I will continue using ENFORCE
App to learn office English in the future
.950 3.96
Overall, I will learn office English
through ENFORCE App
.946 3.90
I will recommend others learning office
English through ENFORCE App
935 3.99
In term of behavioural intention of use, students
intended to use ENFORCE application to learn office
English. It was evidenced by mean score which was
4.10. As well, they would like to promote that app for
other office learners. It was also evidenced by mean
score which was 3.99. Overall, It can be proven from
means scores that were at a high level and students’
intention were positive (see table 2).
Table 3: Descriptive statistics of usefulness
Items SD mean
studying English for office
through ENFORCE App is
not limited by time and place
1.182 3.67
studying English for office
through ENFORCE App can
assist me to access the
information I need
.895 4.08
studying English for office through
ENFORCE App improve my
learning effective
.866 3.98
studying English for office through
ENFORCE App provides serviceable
guidance in running tasks
.870 4.11
In term of usefulness, students perceived that
using learning office English through ENFORCE
Application can be done anywhere and anytime.
Besides, they believed that application was a very
effective learning resource during having to learn
English for office. These statements can be proven by
the means score which were 3.67 and 4.08. Besides,
students perceived that this app was effective to
employ as a supportive learning material especially
for running the tasks. It can be proven by the means
score which were 3.98 and 4.11. Additionally, the
mean score was at a moderate level and the students’
perceived of usefulness was positive (see table 3).
In term of self-efficacy, students believed that
they can solve the obstacles faced during the learning
process by using ENFORCE application. It can be
seen from the means score which were 3.60, 3.63,
Students’ Acceptance of Mobile Application based-Office English Learning Material for University Students
53

Table 4: Descriptive statistics of self-efficacy
Items SD mean
I can finish learning office English
tasks through ENFORCE App if
there is no information I got from
people around me
.957 3.67
I can finish learning office English
tasks through ENFORCE App if
someone had helped me get started
1.025 3.60
I can solve the obstacles faced when
I used ENFORCE App to study office
English
1.058 3.63
I can finish learning office English
assignments through ENFORCE
App, no matter what the difficulties
.903 3.86
3.67, and 3.86 respectively. Overall, it can be said that
in term of perceived of self-efficacy was responded
positively (see table 4).
Table 5: Descriptive statistics of compatibility
Items SD mean
studying English for office
through ENFORCE App, I
don’t have to substitute
anything I recently do
1.090 3.34
studying English for office
through ENFORCE App
does not need changes
significantly in my existing
work custom
1.010 3.48
studying English for office
through ENFORCE App is
similar to using other
application that I have
applied in the past
1.027 3.57
studying English for office
through ENFORCE App
can strengthen from computer
.976 3.72
In term of compatibility, students perceived that
using ENFORCE application was related to their
previous impression while using another application.
It also confirmed by the means score which were
3.57 and 3.48. They also believed that using that
application was useful as same as another application
that they used before. It also strengthened by the
mean score which was 3.34. As well, students
perceived that this app was easy because it can be
used through computer. This statement was supported
by the mean score which was 3.72 (see table 5). It
can be said that in term of compatibility that students
positively responded.
3.2 The Correlation among the Factors
To see the correlation among the students’ acceptance
factors of ENFORCE application as a learning
resource, correlation analysis was conducted (see
table 6).
Table 6: The correlation among the factors
factors
Useful
ness
Ease
of use
Self-
Efficacy
Compati
bility
Intention
Useful
ness
1
.778**
.000
.569**
.000
.550**
.000
.666**
.000
Ease
of use
.778**
.000
1
.514**
.000
.416**
.000
.704**
.000
Self-
Efficacy
.569**
.000
.514**
.000
1
.704**
.000
.591**
.000
Compati
bility
550**
.000
.416**
.000
.704**
.000
1
.538**
.000
Intention
.666**
.000
.704**
.000
.591**
.000
.538**
.000
1
**. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
As could be seen in table 6, all of the factors
were correlated to each other significantly. In term
of the perception of usefulness, this factor had a
significant correlation with ease of use perception
(r
calculated
=.778**> r
table
=.176), behavioural
intention of use (r
calculated
=.666**> r
table
=.176),
self-efficacy r
calculated
=.569**> r
table
=.176), and
compatibility (r
calculated
=.550**> r
table
= .176)
respectively.
In term of perceived ease of use, it also had
correlated significantly with perceived usefulness
(r
calculated
=.778**> r
table
=.176), behavioural
intention of use (r
calculated
=.704**> r
table
=.176),
self-efficacy (r
calculated
=.514**> r
table
= .176),
and compatibility (r
calculated
=.416**> r
table
=
.176) sequentially. Further, self-efficacy
had significant correlation with compatibility
(r
calculated
=.704**> r
table
=.176), behavioural
intention of use (r
calculated
=.591**> r
table
= .176),
usefulness (r
calculated
=.569**> r
table
= .176), and
ease of use (r
calculated
=.514**> r
table
= .176). Next
factor, compatibility had significant correlation with
others factor as well.
The most positive correlation was compatibility
with self-efficacy (r
calculated
=.704**> r
table
=.176)
and followed by perceived usefulness
(r
calculated
=.550**> r
table
=.176), behavioural
intention of use (r
calculated
=.538**> r
table
= .176),
and ease of use (r
calculated
=.418**> r
table
=.176).
Regard to the intention of use, ease of use perception
was the most positive correlated factor. It can be seen
from the r
calculated
=.704**. Perceived usefulness
(r
calculated
=.666**), self-efficacy (r
calculated
=.591**),
and compatibility (r
calculated
=.538**) were correlated
with the intensive attitude of use. Overall, Correlation
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
54

analysis revealed that the intensive attitude to use
the application as a learning resource had a positive
correlation with the acceptance factors (p < 0.01).
This result was confirmed by previous studies
that mentioned usefulness perception and ease of use
perception had correlation to behavioural intention to
use an application in learning as a resource during
the learning process. Wahyuni & Etfita (2019) dan
(Weng et al., 2018) stated that perceived usefulness
and perceived ease of use influenced the attitude in
using an application as a material. (Van De Bogart
and Wichadee, 2015); (Elkaseh et al., 2016); and
(Wahyuni, 2018a) also revealed that the intention of
using an application mobile learning was the effect of
two internal factors such as ease of use perception and
usefulness perception of mobile application-based
learning material. The effectiveness of its mobile
application-based learning material was in the context
of usefulness and ease of use perception affected the
attitude use it intensively (Kitchakarn, 2016). To sum
up the research finding based on the analysis and
supported by other studies, perceived usefulness and
perceived ease of use had a correlation in influencing
the intensive behaviour on using an additional mobile
application-based learning material.
Further, the external factor namely self-efficacy
and compatibly that also had a correlation to
intention of use a mobile application in learning also
emphasized by several related researchers. (Chen,
2014); (Chung et al., 2015); (Alshammari et al.,
2016) strengthened that these external factors had a
significant correlation in effecting the intention of
using the mobile application in learning. It can be
inferred that self-efficacy and compatibility should
be considered in designing mobile application-based
learning material.
3.3 The Analysis Regression Result
In figuring out the best-affected factor of students’
acceptance, regression analysis was carried out. The
result was presented in table 7.
Table 7: The result of regression analysis
Factors t Sig.
Compatibility 1.644 .103 not significant
Usefulness 1.205 .231 not significant
Self-efficacy 1.852 .067 not significant
Ease of use 4.270 .000 significant
The result revealed that the best factor that
influenced intention in using ENFORCE application
as a supportive learning resource was ease of use
intentionally. It can be proven from the significant
value which was .000<0.005. Additionally, the result
was confirmed that the value of t
calculated
was greater
that t
table
which was 1.6602 < 4.270 (see table 7).
As emphasized by (Abu-Al-Aish and Love, 2013);
(Davis, 1989); and (Wahyuni, 2018b), the perception
of ease of use can give positive impression on using
the learning based mobile application intentionally.
Additionally, mobile language learning meets the
students’ needs, following the digital era, and creating
autonomous learning (Shroff and Keyes, 2017).
On contrary to the research finding conducted by
(Alqahtani and Mohammad, 2015), they stated that
the most affecting factor was perceived usefulness to
behavioural intention in using the mobile application.
It could be inferred that the most considerable factor
of students in using ENFORCE application as an
additional learning material for university students
was the ease of use.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study analysed the correlation among students’
acceptance factors and which one the best factor that
affected students’ acceptance of behavioural intention
in using ENFORCE application. The result showed
that each factor had a positive correlation to the
behavioural intention of use the mobile application.
Furthermore, the most affected factor to intention of
use was the sense of ease of use. Specifically, it
could be inferred that students believed that utilizing
ENFORCE application was easy and useful as an
alternative media for providing learning material.
It is very crucial for lecturer to design
implementation plan mobile assisted language
learning model. As well, the lecturers should
cooperate with practitioners or designer’s mobile
application to develop learning material based mobile
to provide interactive learning.
In conclusion, the research findings indicated
that the university should expand the strategic plan
and offer guideline reflecting in students’ acceptance
of mobile learning in order to accommodate all
on reflecting factors for sustainable development of
mobile language learning. The result and findings of
this study can contribute which factors can be offered
for modelling to run plan of mobile assisted language
learning in the university.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The researchers would like to deliver thank to the
willingness and participating of the students in this
Students’ Acceptance of Mobile Application based-Office English Learning Material for University Students
55

study.
REFERENCES
Abu-Al-Aish, A. and Love, S. (2013). Factors influencing
students’ acceptance of m-learning: An investigation
in higher education. The International Review of
Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 14(5).
Akpan, V. I. (2017). Cell phones as effective learning
resource. Journal of Education, Society and
Behavioural Science, pages 1–8.
Al-Emran, M., Mezhuyev, V., and Kamaludin, A. (2018).
Technology acceptance model in m-learning context:
A systematic review. Computers & Education,
125:389–412.
Al-Hunaiyyan, A., Alhajri, R. A., and Al-Sharhan, S.
(2018). Perceptions and challenges of mobile learning
in kuwait. Journal of King Saud University-Computer
and Information Sciences, 30(2):279–289.
Alqahtani, M. and Mohammad, H. (2015). Mobile
applications’ impact on student performance and
satisfaction. Turkish Online Journal of Educational
Technology-TOJET, 14(4):102–112.
Alshammari, S. H., Ali, M. B., and Rosli, M. S. (2016).
The influences of technical support, self efficacy and
instructional design on the usage and acceptance of
lms: A comprehensive review. Turkish Online Journal
of Educational Technology-TOJET, 15(2):116–125.
Bozdo
˘
gan, D. (2015). Mall revisited: Current trends
and pedagogical implications. Procedia-Social and
Behavioral Sciences, 195:932–939.
Chavoshi, A. and Hamidi, H. (2019). Social, individual,
technological and pedagogical factors influencing
mobile learning acceptance in higher education:
A case from iran. Telematics and Informatics,
38:133–165.
Chen, Y.-L. (2014). A study on student self-efficacy
and technology acceptance model within an online
task-based learning environment. Journal of
Computers, 9(1):34–43.
Chung, H.-H., Chen, S.-C., and Kuo, M.-H. (2015). A
study of efl college students’ acceptance of mobile
learning. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences,
176:333–339.
Dashti, F. A. and Aldashti, A. A. (2015). Efl
college students’ attitudes towards mobile learning.
International Education Studies, 8(8):13–20.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of
use, and user acceptance of information technology.
MIS quarterly, pages 319–340.
Domingo, M. G. and Gargant
´
e, A. B. (2016). Exploring the
use of educational technology in primary education:
Teachers’ perception of mobile technology learning
impacts and applications’ use in the classroom.
Computers in Human Behavior, 56:21–28.
Elkaseh, A. M., Wong, K. W., and Fung, C. C. (2016).
Perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness of
social media for e-learning in libyan higher education:
A structural equation modeling analysis. International
Journal of Information and Education Technology,
6(3):192.
Hao, Y., Lee, K. S., Chen, S.-T., and Sim, S. C.
(2019). An evaluative study of a mobile application
for middle school students struggling with english
vocabulary learning. Computers in Human Behavior,
95:208–216.
Kitchakarn, O. (2016). How students perceived social
media as a learning tool in enhancing their language
learning performance. Turkish Online Journal of
Educational Technology-TOJET, 15(4):53–60.
Pilar, R.-A., Jorge, A., and Cristina, C. (2013). The
use of current mobile learning applications in
efl. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences,
103:1189–1196.
Shanmugapriya, M. and Tamilarasi, A. (2013). Design
and development of mobile-assisted language learning
(mall) application for english language using android
push notification services. International Journal
of Research in Computer and Communication
Technology, 2(6):329–338.
Shroff, R. H. and Keyes, C. J. (2017). A proposed
framework to understand the intrinsic motivation
factors on university students’ behavioral intention
to use a mobile application for learning. Journal
of Information Technology Education: Research,
16:143–168.
Van De Bogart, W. and Wichadee, S. (2015). Exploring
students’ intention to use line for academic purposes
based on technology acceptance model. The
International Review of Research in Open and
Distributed Learning, 16(3).
Venkatesh, V. and Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical
extension of the technology acceptance model: Four
longitudinal field studies. Management science,
46(2):186–204.
Wahyuni, S. (2018a). Students’ perception of using an
android smartphone application as a supplementary
learning resource. Asia Proceedings of Social
Sciences, 2(4):115–119.
Wahyuni, S. (2018b). Students’perspectives on using
telegram messenger as a learning media. ELT-Lectura,
5(1):31–37.
Weng, F., Yang, R.-J., Ho, H.-J., and Su, H.-M. (2018). A
tam-based study of the attitude towards use intention
of multimedia among school teachers. Applied System
Innovation, 1(3):36.
Wu, Q. (2015). Designing a smartphone app to teach
english (l2) vocabulary. Computers & Education,
85:170–179.
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
56
