
Macroeconomics and Jakarta Composite Index
Restu Hayati, Poppy Camenia Jamil and Azmansyah
Department of Management, Universitas Islam Riau, Pekanbaru, Indonesia
Keywords:
Jakarta Composite Index (JCI), Macroeconomics, Dow Jones Index, BI 7 Days Rate, The Fed Rate, Exchange
Rate, World Oil Prices
Abstract:
This study was conducted to determine the effect of macroeconomic variables on the Jakarta Composite Index
(JCI). By using time series data from 2016-2018, multiple regression analysis with the least square model
is used to prove the influence of dow jones index (DJIA), BI 7 days rate, fed rate, exchange rate, inflation
and world oil prices against the Jakarta Composite Index. After going through the data stationary test and
classic assumption test, the results of the study prove that there is no significant effect both simultaneously
and partially between macroeconomic variables on the Jakarta Composite Index (JCI) on the Indonesia Stock
Exchange (IDX).
1 INTRODUCTION
As a developing country, Indonesia has enormous
potential in the growth of investment, especially
in financial assets. This potential is evidenced by
the growth of the Jakarta Composite Index (JCI)
in the last 10 years which reached 200%. JCI
is the weighted average price of all shares of
companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange.
The increase in JCI will be an indicator of the
improving investment climate of Indonesia’s financial
securities. The JCI price increase also followed by
the growth of market capitalization originating from
foreign investment and domestic investment. At
the end of 2018, market capitalization in Indonesia
reached almost 7,000 trillion rupiah, an increase of
7 times compared to the previous 10 years. Even
though in 2019, domestic market capitalization in
Indonesia has reached 50% compared to foreign
market capitalization, but the composition of foreign
investment in the country continues to increase,
thereby reducing the composition of domestic
investment. The investment growth is an opportunity
that foreign and domestic investors can use in
investing in the indonesian capital market.
An increase in market capitalization will certainly
increase demand and supply of shares in Indonesia.
Although fundamental financial performance factors
play an important role in the investor’s consideration
of investment policies, macroeconomic factors and
competition in developing countries’ stock exchanges
can also influence the flow of funds and thus affect
JCI price levels. It cannot be denied that investors
are eagerly always trying to find information related
to macroeconomics which will be a consideration
of investment policies. (Barakat et al., 2016)
(Barakat, Elgazzar and Hanafy, 2016) explain that
macroeconomic variables can explain and have an
important role in market fluctuations. News about
the increase in the domestic interest rate (BI 7
days rate), the foreign interest rate (the fed rate),
the development of the Dow Jones index price, the
rupiah exchange rate against the USD, inflation, and
even the development of world oil prices has always
been highlights in financial media. And this is also
supported by the opinions of several experts from
securities companies (Paramitra Alfa Sekuritas, 2018)
(Artha Sekuritas, 2019) (OSO Securities, 2019) (Bina
Artha Sekuritas, 2019), and also by the Indonesian
Stock Exchange representatives (Wintoro, 2014).
Some studies that support the influence of the macro
economy on the stock index that are (Samadi et al.,
2012) (Vejzagic and Zarafat, 2013), (Sudarsana and
Candraningrat, 2014), and (Barakat et al., 2016).
Whereas some studies have found that
macroeconomics factors do not contribute to stock
index price. (Wijayaningsih et al., 2016) found that
the fed rate had no significant effect on JCI. (Salameh
and Alzubi, 2018). found that the Stock Exchange
in the United Arab Emirates was influenced by the
Stock Exchange in the UK, but not by the stock
exchange in the USA. (Ullah et al., 2014) found
Hayati, R., Jamil, P. and Azmansyah, .
Macroeconomics and Jakarta Composite Index.
DOI: 10.5220/0009060401170122
In Proceedings of the Second Inter national Conference on Social, Economy, Education and Humanity (ICoSEEH 2019) - Sustainable Development in Developing Country for Facing Industrial
Revolution 4.0, pages 117-122
ISBN: 978-989-758-464-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
117

that in the long run the exchange rate and interest
rate have a significant effect while inflation has no
effect on the stock market. Likewise with research
(Asmara and Asmara, 2018) which found that there
was no relationship between inflation and JCI. (Sir,
2012) found that there is a causality relationship
between macroeconomic variables on stock returns.
This study will prove whether these macroeconomics
number really affect investor behavior that will
significantly change JCI prices.
2 RESEARCH PROBLEM
The problem in this study is the value of JCI which
continues to increase with a significant increase over
the past 10 years reaching 200%. By ignoring
the fundamental factors, this study focuses more on
macroeconomic variables that have been trusted and
have been proven by various studies to affect stock
indexes.
In Indonesia in the last 2 years (2016-2018), the
pattern of JCI change is very much in accordance with
the changing pattern of macroeconomic variables.
JCI in the last two years has increased by 30%
where there has been a decline in interest rates by
17%, a decrease in inflation by 24%, a decline in
the exchange rate by 4.5%, an increase in DJIA by
42%, an increase in world oil prices by 81%, and an
increase The Fed’s interest is 995%.
So, the research problem that we want to prove
in this research is “Are there significant influences
between macroeconomic factors on the Jakarta
Composite Index (JCI)?”
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
3.1 Macroeconomic Variables
Research that links macroeconomic variables to stock
returns begins to be enlivened by (Fama and Schwert,
1977) and (Fama, 1981). By using inflation as the
main macroeconomic variable that is most influential
so that it causes a stock anomalous return. After that,
more and more studies using other macroeconomic
variables are used in predicting stock prices, stock
returns, and also stock index prices.
Macroeconomic variables used in this study are:
• Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) The DJIA
is the index used to determine the weighted
average of the 30 largest companies in the United
States which was founded by The Wall Street
Journal. This index is used as a measure of the
performance of the largest companies in America
that will determine the condition of the USA
economy.
• BI & Days Rate The 7 days BI rate is the reference
interest rate of banks in Indonesia, which has been
determined by Bank Indonesia as the central bank.
7 days showing a period of 7 days used Bank
Indonesia s to evaluate monetary policy in setting
the benchmark interest rate.
• The Federal Reserve Rate (The Fed Rate)
The Fed Rate is the interest rate at which
depository institutions (banks and credit unions)
lend reserve balances to other depository
institutions overnight, on an uncollateralized
basis (wikipedia).
• The exchange rate of the rupiah against the dollar
An exchange rate is an agreement known as a
currency exchange rate for payments now or later,
between two currencies of each country or region
(wikipedia).
• Inflation Inflation is an increase in the prices of
goods in general and continously. Inflation data
in Indonesia is obtained from the publication of
Bank Indonesia as the central bank in Indonesia.
• Oil Prices oil price is the price of petroleum that
uses the West Texas Intermediate (WTI) standard.
WTI is a world standard of petroleum produced
from North America which is in great demand,
especially in the USA and China.
3.2 Jakarta Composite Index
The Jakarta Composite Index is the average daily
stock of all shares listed on the Indonesia Stock
Exchange. JCI is seen as the most commonly used
general index in Indonesia as a measurement of the
average performance of all shares.
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Population and Sample
The population and sample in this research are Jakarta
Composite Index (JCI) in Indonesia Stock Exchange.
Secondary data used is from 2016 - 2018 so the
overall data is 36 (n = 36).
4.2 Data Analysis
Data were analyzed using multiple regression
analysis using software EViews. The multiple
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
118
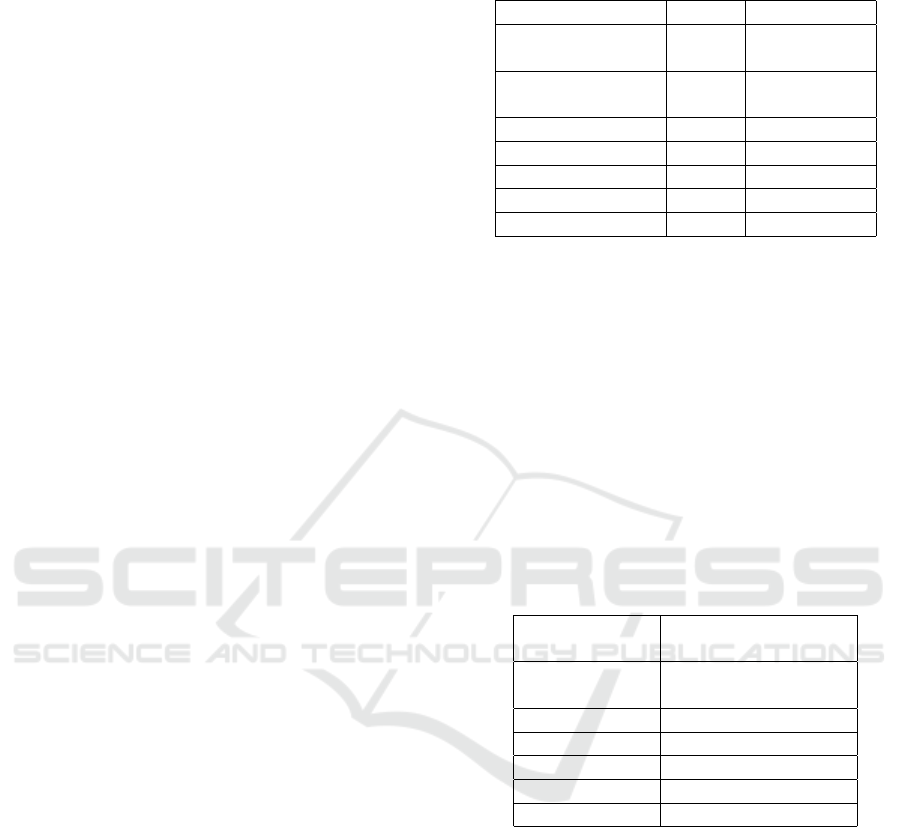
regression equation from the study is as follows:
Y = a + b
1
X
1
+ b
2
X
2
+ b
3
X
3
+ b
4
X
4
+ b
5
X
5
+b
6
X
6
+ e
(1)
Where,
• Y = Jakarta Composite Index
• X
1
= Dow Jones Index (DJIA)
• X
2
= BI 7 Days Rate
• X
3
= The Federal Reserve Rate
• X
4
= Exchange Rate (IDR to USD)
• X
5
= Inflation
• X
6
= Oil Price
• a = constanta
• b
1
, b
2
, b
3
, b
4
, b
5
, b
6
= The Federal Reserve Rate
• e = error
Before the multiple regression testing is carried
out, each variable is subjected to data stationarity
testing to determine whether or not there is a trend
pattern on time series data. This is done to avoid
spurious regression in research.
After that, classical assumptions were tested on
the data, namely multicollinearity and normality
so that best linear unbiased estimator (BLUE)
requirements were fulfilled in the regression with the
least squares model.
Furthermore, the F test is used to determine
the simultaneous effect between all macroeconomic
variables on JCI. Likewise, with the t test, it is used to
determine the partial effect of each macroeconomic
variable on JCI. The hypothesis is accepted if the
significance value < 0.05.
5 RESULTS
5.1 Data Stationarity
Data stationarity is tested using a unit root test
at various levels until it reaches stationary. The
probability of the unit root test can be seen in the table
below:
At level 0, all time series data on each variable
forms a trend pattern with a probability value > 0.05.
Therefore, stationary testing is carried out at level 1st
difference. Based on the table above the data at the 1st
difference is stationary with all probability values in
each variable ¡ 0.05. Furthermore, multiple regression
analysis is done using the 1st difference data.
Table 1: Unit Root Test
Variable Level 1
st
difference
Jakarta Composite
Index (JCI)
0.4476 0.0004
Dow Jones
Index (DJIA)
0.4490 0.0004
BI 7 Days Rate 0.0609 0.0008
The Fed Rate 0.9997 0.0002
Exchange Rate 0.7247 0.0000
Inflation 0.1724 0.0000
Oil Price 0.2295 0.0023
5.2 Classical Assumption Test
Classical assumption test is done so that the multiple
regression equation model satisfies the best linear
unbiased estimator (BLUE).
5.2.1 Multicollinearity
Multicollinearity is used to determine the correlation
between independent variables.
Table 2: Multicollinearity Test
Variable
Centered Variance
Inflation Factor (VIF)
Dow Jones
Index (DJIA)
1.310733
BI 7 Days Rate 1.250585
The Fed Rate 1.133625
Exchange Rate 1.308130
Inflation 1.180933
Oil Price 1.457788
Based on the table above, there is no correlation
between the independent variables with the centered
VIF value <10. This means that each independent
variable in the study has no resemblance so that it is
suitable to be used as an economic macro variable that
can affect Jakarta Composite Index (JCI).
5.2.2 Normality
The normality test aims to test whether in the
regression model, the residual confounding variable
has a normal distribution.
The data in this study are normal with a Jarque
Beta> 0.05 probability value, which is 0.643257.
Macroeconomics and Jakarta Composite Index
119
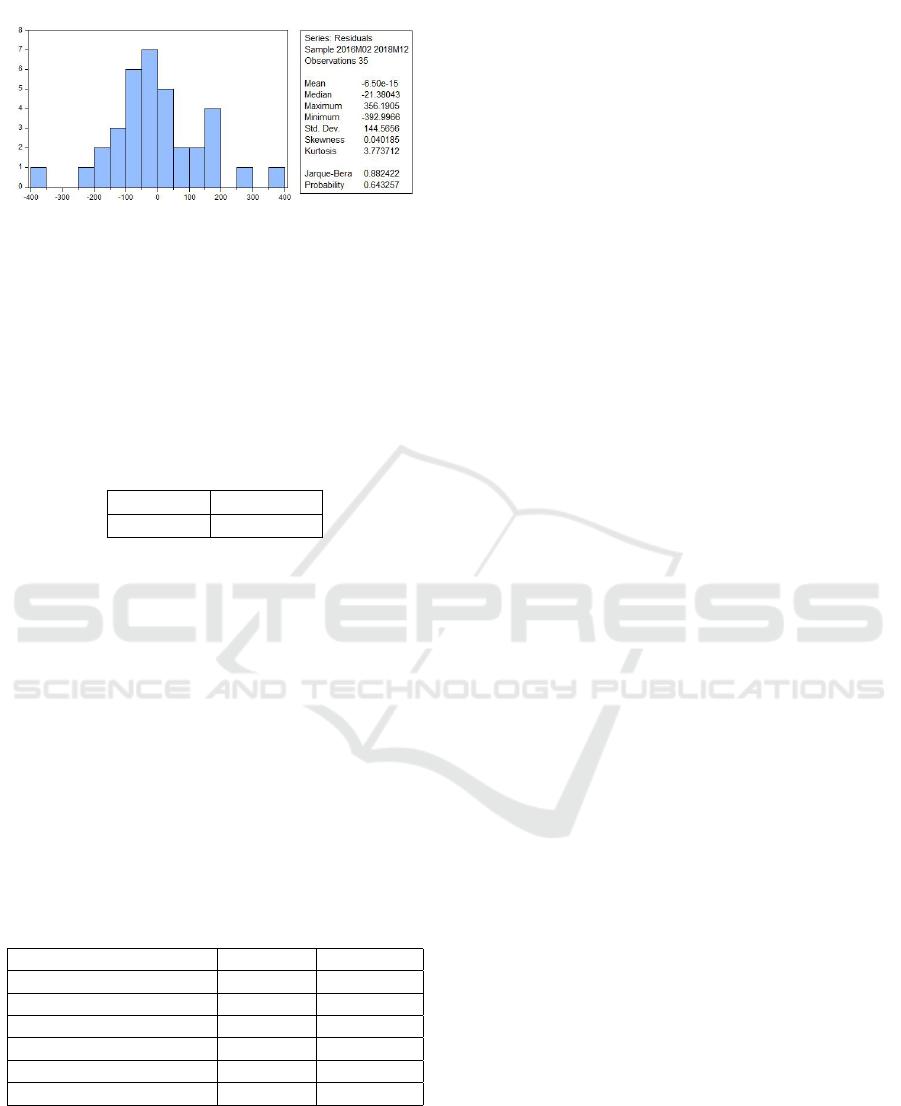
Figure 1: Jarque Beta Normality Test
5.3 Hypothesis Test
5.3.1 Simultaneous Effect
The value of F and its probability that determines the
influence all macroeconomic variable on the Jakarta
Composite Index can be seen in the table below:
Table 3: Simultaneous Effect
F-statistic Probability
0.79 0.585318
The calculated H
456
F value is 0.79, smaller than
the F table value of 2.42. In addition, the probability
F value > 0.05, which is 0.58. Based on the statistical
analysis, the decision was that there was no significant
simultaneous effect between the DJIA, the BI 7 days
rate, the Fed rate, the rupiah exchange rate, inflation
and world oil prices against the Jakarta Composite
Index (JCI).
5.3.2 Partial Effect
The value of t and its probability that determines
the influence of each macroeconomic variable on the
Jakarta Composite Index can be seen in the table
below:
Table 4: Partial Effect.
t-statistic Probability
Dow Jones Index (DJIA) 1.122180 0.2713
BI 7 Days Rate -0.882821 0.3848
The Fed Rate 1.648327 0.1105
Exchange Rate 0.508940 0.6148
Inflation 0.426376 0.6731
Oil Price -0.898726 0.3765
The t value of statistics for each variable does
not exceed t table, which is 2.03. Likewise, the
probability value of each variable is more than
0.05. This means that none of the macroeconomics
variables have a partial effect on JCI.
5.3.3 Contribution of Macroeconomic Variables
to JCI
The contribution of Dow Jones Index (DJIA), BI 7
days rate, fed rate, exchange rate, inflation and world
oil prices against the JCI are 0.1447 or 14.47%. With
no significant influence between all macroeconomic
variables on JCI it is reasonable that macroeconomic
contributions are 14.47%. The rest, 85.53% is
influenced by other variables outside of this study.
Following are the multiple regression equations
that explain the effect of macroeconomics on JCI:
JCI = 4.64 + 0.07DJIA − 94.53BI7DaysRate+
495.03T heFedRate + 0.06ExchangeRate+
41.54In f lation − 6.9OilPrice
(2)
Based on the regression equation above it is
known that the variable domestic interest rate (BI 7
Days Rate) and oil prices, have a negative relationship
while other macroeconomic variables have a positive
relationship. If the Indonesian government increases
the benchmark interest rate, JCI will decline even
though the decline is not significant. Likewise, with
world oil prices. The increase in world oil will add to
the average operational burden of public companies
in Indonesia, especially manufacturing companies so
that it will reduce the company’s stock price even
though the decline is not significant.
6 DISCUSSION
The results prove that suprisingly macroeconomic
factors do not have a significant influence on
JCI. During this time, every financial media and
even investment managers from securities companies
always make a fuss if macroeconomic changes occur
that could affect investors’ decisions. This research
proves the opposite.
The Down Jones Index is often seen as a
baromater of world market performance consisting
of 30 companies. When market experts say the
market is going up or down, it illustrates that DJIA
is experiencing fluctuations. The stock price of
the 30 best companies in America is a reference
to the state of the world economy. The rising
price of Dow Jones provides information that the
world economy is improving which should affect the
economies of other countries including Indonesia.
The rising price of DJIA has often been responded
positively by domestic investors related to the
hope of future economic conditions. If economic
conditions improve, stock prices will also experience
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
120

an increase. But, in fact, DJIA did not significantly
influence JCI. This might be due to the lack of
direct connection between these 30 companies and
companies in Indonesia. Dow Jones has also been
criticized as no longer a reflection of market prices
in the world economy.
BI 7-days rate does not contribute to JCI because
the offered interest rate is not too competitive so
investors tend not to mind the fluctuation in the BI
7 Day Rate. The 7 days BI rate in Indonesia, which
were around 4-6% in the past two years, did not
provide an incentive for investors to moved their
funds to financial institutions that provide less risk.
The Federal Reserve Rate has no effect on the
JCI, this can be caused by the average company
incorporated in the Indonesia Stock Exchange which
is represented through the JCI is a company that
operates almost entirely in Indonesian territory and
is not directly related to The Federal Reserve Rate.
From the investor side, it might be preferable to
invest in Indonesia despite the opportunity to increase
profits with promising interest rates in America.
Exchange rate risk will be an additional consideration
for investors in transferring funds from Indonesia.
Changes in the exchange rate of the rupiah against
the dollar also did not contribute to fluctuations in
the value of the JCI. Investors who invest in the
Indonesia Stock Exchange usually have their own
preferences on the choice of industrial sectors that
are of interest so that even if there are significant
changes to the exchange rate it will not affect
investor interest in investing. In addition, in terms of
companies in general, they have carried out exchange
rate risk management so that it does not affect the
company’s financial performance. Likewise, inflation
is not the main focus of investors in investing which
is supported by research (Ullah et al., 2014) and
(Asmara and Asmara, 2018) and (Geetha et al., 2011).
Oil Price should be a consideration because it can
affect production costs but not the entire company is
in the manufacturing production sector. Of the 600
companies listed on Indonesia Stock Exchange, only
about 23% are manufacturing companies. JCI is a
combination of all sectors in the Exchange, because
on the average there is no effect of oil price on the
value of the JCI.
Based on the results it is known that overall macro
factors do not affect the JCI, assuming that the round
of funds that occur in the capital market already has
its own investment preferences by each investor.
7 RESEARCH DEFICIENCY
Due to limitations in data collection, this study uses
short-term time frames, from 2016 to 2018. Future
research is expected to use a span of 10 years so that it
can see changes in macroeconomic strength towards
JCI from year to year.and add a comparison of the
influence of fundamental and macroeconomic factors
on JCI.
8 CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study prove that although the
JCI change pattern follows the changing pattern
of macroeconomic variables, but after it has been
proven by a series of statistical tests, none of the
macroeconomic variables affect JCI in the short run.
This might be caused by investors in Indonesia pay
more attention to the fundamental factors which are
the company’s financial performance. In addition,
stock indices in a country do have a tendency to
increase due to developments in a country’s Stock
Exchange.
REFERENCES
Asmara, W. P. and Asmara, I. P. W. P. (2018). Pengaruh
variabel makro ekonomi terhadap indeks harga saham
gabungan. None, 7(3).
Barakat, M. R., Elgazzar, S. H., and Hanafy, K. M. (2016).
Impact of macroeconomic variables on stock markets:
Evidence from emerging markets. International
journal of economics and finance, 8(1):195–207.
Fama, E. F. (1981). Stock returns, real activity,
inflation, and money. The American economic review,
71(4):545–565.
Fama, E. F. and Schwert, G. W. (1977). Asset returns
and inflation. Journal of financial economics,
5(2):115–146.
Geetha, C., Mohidin, R., Chandran, V. V., and Chong,
V. (2011). The relationship between inflation and
stock market: Evidence from malaysia, united states
and china. International journal of economics and
management sciences, 1(2):1–16.
Salameh, H. M. and Alzubi, B. (2018). An investigation of
stock market volatility: evidence from dubai financial
market. Journal of Economic and Administrative
Sciences, 34(1):21–35.
Samadi, S., Bayani, O., and Ghalandari, M. (2012).
The relationship between macroeconomic variables
and stock returns in the tehran stock exchange.
International Journal of Academic Research in
Business and Social Sciences, 2(6):559.
Macroeconomics and Jakarta Composite Index
121

Sir, M. M. (2012). Impact of the macroeconomic variables
on the stock market returns: The case of germany and
the united kingdom. Global Journal of Management
and Business Research, 12(16).
Sudarsana, N. M. A. D. and Candraningrat, I. R. (2014).
Pengaruh suku bunga sbi, nilai tukar, inflasi dan
indeks dow jones terhadap indeks harga saham
gabungan di bei. Jurnal Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis
Universitas Udayana (Unud), Bali, Indonesia, hlm.
3291, 3308.
Ullah, F., Hussain, I., Rauf, A., et al. (2014). Impacts
of macroeconomy on stock market: Evidence from
pakistan. International journal of management and
sustainability, 3(3):140–146.
Vejzagic, M. and Zarafat, H. (2013). Relationship between
macroeconomic variables and stock market index:
Cointegration evidence from ftse bursa malaysia
hijrah shariah index. Asian journal of management
sciences & education, 2(4).
Wijayaningsih, R., Rahayu, S. M., and Saifi, M. (2016).
Pengaruh bi rate, fed rate, dan kurs rupiah terhadap
indeks harga saham gabungan (ihsg)(studi pada
bursa efek indonesia periode 2008-2015). Jurnal
Administrasi Bisnis, 33(2):69–75.
Wintoro, D. (2014). Structural model of the idx credibility.
Indonesian Capital Market Review.
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
122
