
Long Term Effect of Contralaterally Controlled EMG-Modulated
Electrical Stimulation Combined with Training and Botulinum
Toxin A (BONT-A) Motor Point Block on Hand Function in Patients
with Stroke
Ratna Darjanti Haryadi
1
, Lydia Arfianti
1
, Meisy Andriana
1
1
Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Department, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Airlangga,
Dr Soetomo Hospital Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Contralaterally Controlled Electrical Stimulation, EMG-Modulated, Stroke, Hand Function, Motor Point
Block
Abstract: Objective: This study describes the long term effect of contralaterally controlled EMG modulated electrical
stimulation combined with Botulinum Toxin A (BONT-A) motor point block and hand function training in
stroke. Methods: Three stroke patients, onset ≥ 6 months, with paresis of wrist and fingers extensors (MRC
2/5), flexor spasticity >3 (MAS), were given BONT-A injections before training. The training consisted of
40 minutes electrical stimulation on the affected side, proportional to the EMG signal picked-up from the
unaffected side, simultaneously doing hand function training, for 3-5 days/ week. Outcome measures were
Box and Block Test (BBT) and Nine Hole Peg Test (NHPT) scored before, after training, and at follow-up of
4 and 9 months. After 18 sessions, grasp function (BBT) improved in 3 patients, pinch grip (NHPT)
improved in 2 patients. One patient was lost to follow-up. At 4 and 9 months, BBT improved further in 1
patient, deteriorated in 1 patient, while NHPT deteriorated in both patients. Conclusion: Grasp function
improved at long term follow-up in 1 chronic stroke patient who consistently used the affected dominant-
hand. No improvement was seen in 1 patient affected at the non-dominant hand. Improvement in pinch grip
was lost at long term follow-up.
1 INTRODUCTION
A stroke is often causing long term severe motor
disability due to hemiplegia. In many patients the
upper extremity does not recover to a functional
level (Yavuzer et al, 2008). The synergy pattern that
develops usually consist of flexion of the wrist &
fingers, causing inability to open the fingers. Flexors
muscle spasticity that occur after stroke can worsen
the inability to extend the wrist and fingers. The
effort to elicit active movement in the affected arm
tend to increase spasticity, and is therefore less
successful in producing an effective functional hand
movement. The condition together has been shown
to be one of the motor impairments responsible for
disability (Hara, 2008). Botulinum Toxin A (BONT-
A) motor point block injections showed efficacy to
reduce spasticity and allow more voluntary grasping.
Another study reported the efficacy of phenol motor
point block to reduce spasticity in stroke patients
(Hara et al, 2006).
Chronic stroke-related motor problems that begin
in the first year after a stroke may lead to learned
nonuse as individuals stop trying to move the
affected upper extremity voluntarily (Inobe, 2013).
Recent knowledge in the field of neuroplasticity and
functional recovery in brain lesion has contributed in
the development of several combinations of
functional training with the application of physical
modalities to enhance activity. Electromyography
(EMG)-initiated electrical stimulation is one novel
method of Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES).
A surface electrode picks up the EMG signal and
stimulates the target muscle in proportion to the
integrated signal. This device induces greater muscle
contraction because electrical stimulation is
proportional to the EMG signal (Yamaguchi et al,
124
Haryadi, R., Arfianti, L. and Andriana, M.
Long Term Effect of Contralaterally Controlled EMG-Modulated Electrical Stimulation Combined with Training and Botulinum Toxin A (BONT-A) Motor Point Block on Hand Function in Patients
with Stroke.
DOI: 10.5220/0009064901240129
In Proceedings of the 11th National Congress and the 18th Annual Scientific Meeting of Indonesian Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Association (KONAS XI and PIT XVIII PERDOSRI
2019), pages 124-129
ISBN: 978-989-758-409-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2011). The efficacy of EMG-controlled electrical
stimulation was reported by Hara et al in a study of
combined Integrated Volitional Control Electrical
Stimulation (IVES) on the affected extensor
muscles, training, and motor point block using 5%
phenol for antagonist muscles in patients with
chronic stroke (Hara et al 2006).
Recently a device of EMG-modulated electrical
stimulation enables to pick up EMG signal from
active voluntary contraction of the contralateral non-
affected arm, and send it as a trigger electrical
stimuli to the muscle at the affected arm. The trigger
delivered to the affected arm then should be
followed by voluntary effort to increase the activity
of the recipient muscle. This method requires active
participation from patients to perform bilateral
symmetrical movement on both arms or wrists.
Several studies have reported the effectiveness of
contralaterally controlled electrical stimulation alone
in patients with early-phase stroke (< 15 days post
stroke), subacute, and chronic stroke (> 6 months,
but less than 2 years) (Zheng et al, 2019). None of
these studies used combined electrical stimulation
with motor point block injections. This study,
therefore, aims to demonstrate the long term effect
of contralaterally controlled EMG-modulated
electrical stimulation combined with training, and
Botulinum Toxin A (BONT-A) motor point block,
to improve functional hand movement in stroke
patients.
2 METHODS
The study participants were 3 patients with first
episode unilateral stroke, onset ≥ 6 months. Two
patients had chronic stroke (> 6 months), and one
patient had a stroke 6 months before intervention.
All 3 patients had hemiparesis of wrist and fingers,
difficulty in extension movements (MRC scale 2/5),
with flexor spasticity graded ≥ 3 (Modified
Ashworth Scale). Patient 1 was a 40-year-old male
with left hemiparesis after a hemorrhagic stroke 4
years ago. Patient 2 was a 50-year-old male with left
hemiparesis after a thrombotic stroke 6 months ago.
Patient 3 was 50-year-old female with right
hemiparesis after a thrombotic stroke 3 years ago.
Botulinum toxin A (BONT-A) motor point block
injections were given by an-experienced physiatrist
to the flexor wrist and fingers muscles 7-10 days
before start of training. All 3 patients received
training that consisted of 40 minutes integrated
volitional control electrical stimulation of extensor
wrist and fingers on the affected side, in proportion
to the voluntary EMG signal picked-up at the non-
affected side, while doing therapist-supervised
activities with the affected hand. Electrodes
placement were on extensor carpi radialis longus and
brevis, and extensor digitorum communis. The
equipment Integrated Volitional Control Electrical
Stimulation (IVES) GD-611 by OG Wellness
Technologies Co, Ltd. was used in this study.
The combined contralaterally controlled EMG-
modulated electrical stimulation with training is
depicted in Figure 1. Treatment frequency was 3-5
days a week, up to 18 sessions. Subjects were
dropped out from this study if they missed
consecutively 2 therapy session in 1 week, or if they
wished to stop the therapy.
The outcome measures were Box and Block Test
(BBT) and Nine Hole Peg Test (NHPT) scored
before training, after training, and at follow-up of 4
and 9 months. All patients were given detailed
information about the procedure, and informed
consent was obtained.
3 RESULTS
All 3 patients were successfully completed 18
sessions of training. Baseline scores of BBT were <
4, and NHPT were 0. All 3 patients showed
improvement in grasp function starting from session
6 and achieved peak performance at session 12, as
shown by the BBT results. Compared to session 12,
session 18 did not show further improvement. Pinch
performance as shown by the NHPT showed peak
performance in session 18 in Patient 1 and Patient 3.
Patient 2 was never able to perform the NHPT.
Table 1 summarizes the changes in outcome
measurement scores over the sessions, and at long
term follow-up of 4 and 9 months.
Only Patient 1 and Patient 3 were assessed for
long term follow-up at 4 and 9 months. Patient 2
was lost to follow-up because he worked in a
different city. Hand function at follow-up of 4 and 9
months improved further as shown by the BBT score
in Patient 3, while it deteriorated in Patient 1. The
NHPT score deteriorated in both Patient 1 and
Patient 3 at follow-up of 4 and 9 months. Figure 2
shows the progress in the NHPT and BBT scores of
all 3 patients after 18 sessions, and at long-term
follow-up of 4 and 9 months.
Long Term Effect of Contralaterally Controlled EMG-Modulated Electrical Stimulation Combined with Training and Botulinum Toxin A
(BONT-A) Motor Point Block on Hand Function in Patients with Stroke
125
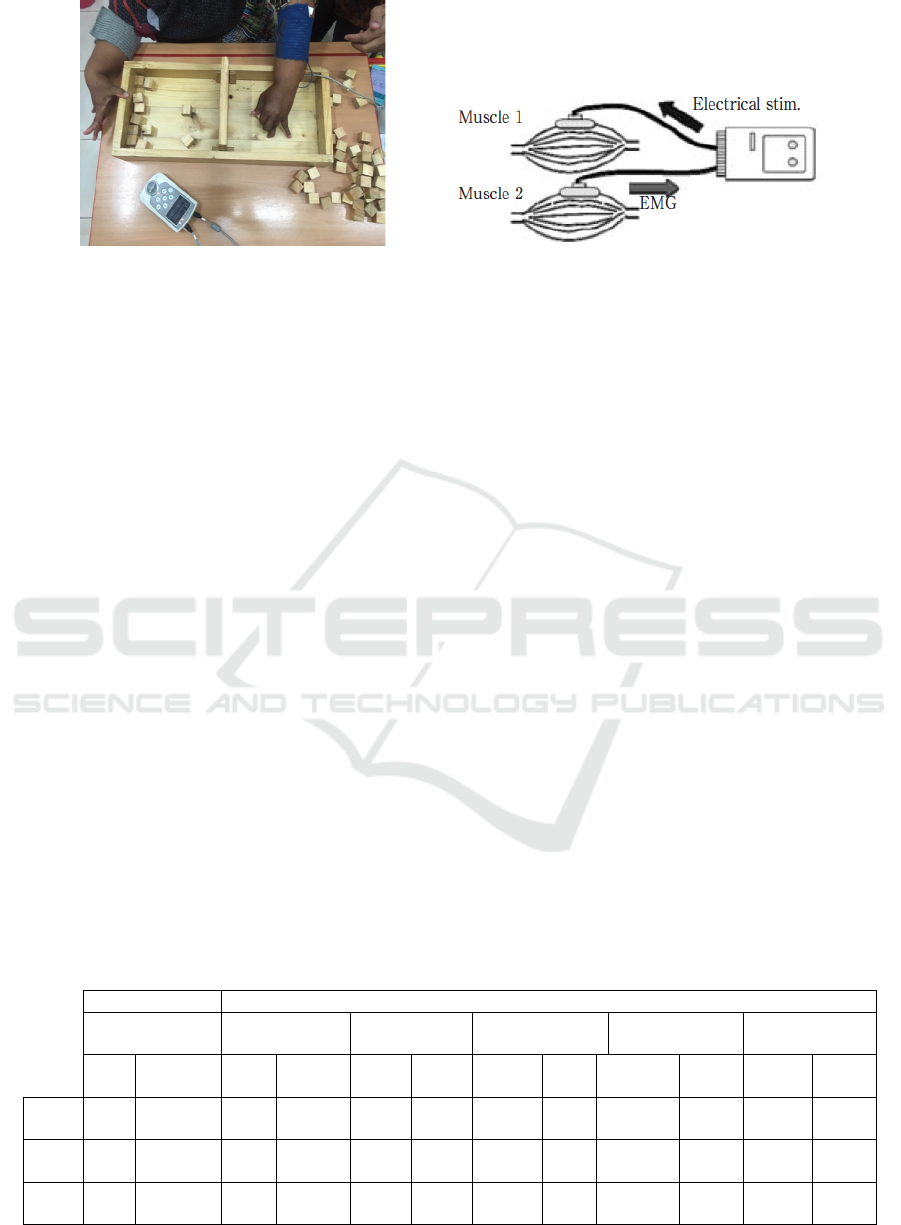
Figure 1: The EMG signal was picked up from active voluntary contraction of the contralateral non-affected arm (muscle 2)
and delivered to the muscle in the affected arm (muscle 1). Integrated volitional control electrical stimulation on the
affected side was in proportion to the voluntary EMG signal picked up on the non-affected side. The trigger delivered to the
affected arm should then be followed by voluntary effort to increase the activity of the recipient muscle (Hara, 2008).
4 DISCUSSION
This study showed that after 18 sessions of
combined contralaterally controlled EMG-
modulated electrical stimulation, therapist-guided
training, and Botulinum toxin A (BONT-A) motor
point block, the grasp function represented by BBT
score, optimally improved after 12 sessions in all 3
patients. No further improvement was seen after 12
sessions in Patient 1 and Patient 2, while Patient 3
showed further improvement at long-term follow up
of 4 and 9 months. Improvement of the pinch started
to emerge later than the grasp. Pinch grip
performance, assessed by NHPT score, showed
improvement after 18 sessions in two patients
(Patient 1 and Patient 3), both who had chronic
stroke (> 6 months). One patient who had stroke 6
months before intervention (Patient 2) did not show
any improvement. These findings indicated that to
improve the pinch grip more sessions are necessary
compared to the grasp function. This can be
explained because the pinch grip is a more selective
and precise movement than the grasp. At long-term
follow up of 4 and 9 months, the NHPT deteriorated
in two patients, while one patient was lost to follow-
up.
Patients who had chronic stroke still have a
chance of recovery. A study by Hara et al in 16
chronic (more than 1 year) stroke patients showed
improvement in motor performances of upper
extremity with combined of power-assisted FES,
training, and phenol motor point block injections
(Hara et al, 2006). Lewinsky et al reported in a study
of 9 chronic stroke patients, that BBT result at the
time of inception (before training) has predictive
value potential. There was no significant gain if the
BBT score was below 4, even after 8 weeks of
combined training and EMG-triggered electrical
stimulation (Lewinsky et al, 2009).
Table 1: The Nine Hole Peg Test (NHPT) and the Box and Block Test (BBT) scored before treatment, after treatment, and at
follow-up of 4 months and 9 months.
Sessions
Baseline 6 12 18
4 months
follow-up
9 months
follow-up
NH
PT
BBT
NH
PT
BBT
NHP
T
BBT NHPT
BB
T
NHPT BBT NHPT BBT
Patie
nt 1
0 1 0 1 0 10 3 10 0 0 0 0
Patie
nt 2
0 0 0 0 0 3 0 2 - - - -
Patie
nt 3
0 2 0 5 4 6 5 5 2 10 0 16
KONAS XI and PIT XVIII PERDOSRI 2019 - The 11th National Congress and The 18th Annual Scientific Meeting of Indonesian Physical
Medicine and Rehabilitation Association
126

A B
Figure 2: (a) The Nine Hole Peg Test (NHPT) and (b) the Box and Block Test (BBT) scored before treatment, after
treatment, and at follow-up of 4 and 9 months.
In this study, all 3 patients had BBT scores <4 at
baseline measurement. Only one patient who had
chronic stroke, with an initial BBT score 2, gained
significant improvement (BBT score 16) after 18
sessions, and improved further at long term follow-
up of 4 and 9 months. The other two patients, who
had chronic stroke and stroke at 6 months before
intervention, with initial BBT score 1 and 0, showed
improvement (BBT score 10 and 2) after 18
sessions, and then deteriorated at long term follow-
up of 4 and 9 months.
Stroke affecting dominant or non-dominant hand
also plays a role in recovery. If the dominant hand is
affected, the patient can be motivated to actively use
the hand for daily activities. In this study, two
patient (Patient 2 and Patient 3) were affected in the
dominant hand. Patient 2, who had subacute stroke
showed improvement in grasp function showed by
BBT score, after 12 sessions of combined treatment.
He consciously used his right (dominant) hand in
activities of daily living, such as holding a cup and
picking up objects. Patient 3, who had chronic
stroke, showed further improvement in grasp
function after 12 sessions and even at long-term
follow-up of 4 and 9 months after BONT-A
injections. This is because the patient actively used
her right hand for daily household activities. She
could use her right hand for cooking, such as cutting
tofu and vegetables, holding saucepan and frying
tofu. While Patient 1, who had chronic stroke, did
not show improvement in grasp function. This can
be explained because he did not actively use his left
(non-dominant) hand for daily activities. He only
used the left hand to open the door. This will worsen
or deteriorate the learned nonuse as individuals stop
trying to move the affected extremity voluntarily
(Inobe, 2013).
The current study used contralaterally controlled
(from the non-affected side) EMG-modulated
electrical stimulation in chronic stroke patients. It is
considered as novel method of FES, that requires
active participation from patients to perform
bilateral symmetrical movement, and not only
electrical stimulation of the affected side (Zheng et
al, 2019). Because this technique uses a control
signal from the non-affected side, EMG signal will
still be picked-up even when the target-affected
muscles display no muscle contraction at all. With
the non-contralaterally EMG-controlled electrical
stimulation, the stimulator will not work when there
was no contraction at all on the target-affected
muscles (Chuang et al, 2017). The mechanism of
contralaterally controlled EMG-modulated electrical
stimulation on motor recovery after stroke remains
unclear. The possible explanation may be that
movement of the non-affected side can increase the
corticospinal excitability of the stimulated muscles
by interhemispheric disinhibition and intracortical
facilitation (Zheng et al, 2019). Zhou et al reported
that because patients could control the timing and
degree of movements during training with EMG
bridge detects surface electromyographic signals
from the non paretic limb, may induce synaptic
remodelling and cortical reorganization. In addition,
because patients were more willing and more able to
use their affected hand actively, it might enhance
further the treatment effects (Zhou et al, 2017).
In stroke patients, good balance of movement
between flexion and extension in the wrist and
fingers should be obtained to achieve effective hand
Long Term Effect of Contralaterally Controlled EMG-Modulated Electrical Stimulation Combined with Training and Botulinum Toxin A
(BONT-A) Motor Point Block on Hand Function in Patients with Stroke
127

function. For patients who had stroke with
significant flexor muscles spasticity in upper
extremity, NMES or FES alone does not produce
satisfactory improvement (Hara et al, 2006). Some
authors have reported the efficacy of a phenol motor
point block which is more cost-effective than
Botulinum toxin A (BONT-A) (Hara et al 2006). We
use motor point block with BONT-A to reduce
spasticity in this study, because of technical
constraints to obtain phenol for injection. Studies
have shown the efficacy of BONT-A to reduce
spasticity, thus allowing more voluntary grasping.
For the long term follow-up assessment 4 and 9
months were the time points chosen because the
average duration of the BONT-A effect is said to
wear off within 3-6 months (Ambrose et al, 2018).
Longer duration of training seemed to have
better results in chronic stroke. Hara et al evaluated
the hand function after 4 months (2 times per week,
total of 32 sessions) of combined treatment in
chronic stroke. In this study, we have difficulty in
maintaining patients’ compliance for more than 18
sessions. The number of visits as well as frequency
in an outpatient-based treatment plan is often limited
by several technical factors, such as transportation
and availability of family members to bring the
patient to a rehabilitation facility. This condition is
quite common in developing countries such as
Indonesia.
5 STUDY LIMITATION
A limitation of this study is that we only had 3
patients as study participants, and the study was
ended after 18 sessions.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Improved grasp function was seen as long-term
effect of contralaterally controlled EMG-modulated
electrical stimulation combined with training and
Botulinum Toxin A (BONT-A) motor point block
injections, in 1 chronic stroke patient who
consistently use the affected dominant-hand. No
improvement was seen in 1 chronic stroke patient
affected at the non-dominant hand. Improvement in
pinch grip performance was lost at long term follow-
up.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Equipment Integrated Volitional Control Electrical
Stimulation (IVES) GD-611 was provided on loan
during this study by OG Wellness Technologies Co,
Ltd. This study was funded by a grant from OG
Wellness Technologies Co, Ltd.
REFERENCES
Ambrose AF, Verghese T, Dohle C, Russo J. 2018.
Muscle Overactivity in the Upper Motor Neuron
Syndrome. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 29: 483-
500
Hara Y. 2008. Neurorehabilitation with New Functional
Electrical Stimulation for Hemiparetic Upper
Extremity in Stroke. J Nippon Med Sch. 75: 4-14
Hara Y, Ogawa S, Muraoka Y. 2006. Hybrid Power-
Assisted Functional Electrical Stimulation to Improve
Hemiparetic Upper-Extremity Function: Am J Phys
Med Rehabil. 85: 977–985.
Hara Y, Ogawa S, Tsujiuchi K, Muraoka Y. 2008. A
Home-Based Rehabilitation Program for The
Hemiplegic Upper Extremity by Power-Assisted
Functional Electrical Stimulation: Disability and
Rehabilitation. 30(4): 296-304
Inobe J, Kato T. 2013. Effectiveness of Finger-equipped
Electrode (FEE)-triggered Electrical Stimulation
Improving Chronic Stroke Patients with Severe
Hemiplegia. Brain Injury. 27(1): 114-119
Lewinsky F, Hofer S, Kaus J, Merboldt KD, Rothkegel H,
Schweizer R, et al. 2009. Efficacy of EMG-triggered
Electrical Arm Stimulation in Chronic Hemiparetic
Stroke Patients. Restorative Neurology and
Neuroscience 27: 189-197
Shindo K, Fujiwara T, Hara J, et al. 2011. Effectiveness of
Hybrid Assistive Neuromuscular Dynamic Stimulation
Therapy in Patients with Subacute Stroke: A
Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Neurorehabil
Neural Repair. 20(10): 1-8
Yamaguchi T, Tanabe S, Yoshihiro M, et al. 2011. Effects
of Integrated Volitional Control Electrial Stimulation
(IVES) on Upper Extremity Function in Chronic
Stroke: Keio J Med. 60(3): 90-95
Yavuzer G, Selles R, Sezer N, Sutbeyas S. 2008. Mirror
Therapy Improves Hand Function in Subacute Stroke:
A Randomized Controlled Trial. Archives of Physical
Medicine and Rehabilitation.89:393-98
Zheng Y, Mao M, Cao Y, Lu X. 2019. Contralaterally
Controlled Functional Electrical Stimulation Improves
Wrist Dorsiflexion and Upper Limb Function in
Patients with Early-Phase Stroke: A Randomized
Controlled Trial. J Rehabil Med. 51: 103-108
Zhou YX, Xia Y, Huang J, Wang HP, Bao XL, Yang Z, et
al. 2017. Electromyographic Bridge for Promoting the
Recovery of Hand Movements in Subacute Stroke
KONAS XI and PIT XVIII PERDOSRI 2019 - The 11th National Congress and The 18th Annual Scientific Meeting of Indonesian Physical
Medicine and Rehabilitation Association
128

Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Rehabil
Med.49: 629-636
Long Term Effect of Contralaterally Controlled EMG-Modulated Electrical Stimulation Combined with Training and Botulinum Toxin A
(BONT-A) Motor Point Block on Hand Function in Patients with Stroke
129
