
The Effect of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn to Decrease
Blood Glucose Level on Diabetes Type II Patients
Zaqqi Ubaidillah
*
and Yessy Witantry
Department of Nursing, Faculty of Health Science, University of Muhammadiyah Malang
Jalan Bendungan Sutami No. 188A Malang, East Java, Indonesia 65145
Keywords: Type II Diabetes, Blood Glucose, Caesalpinia Sappan Linn Wood
Abstract: The prevalence of blood glucose control problems is higher in Indonesia. Orally administered
antihyperglycemic agents (OHAs) have various side effects, and it can’t control blood glucose level by single
doses. Diabetes management used complementary therapies as support the administration of OHAs can help
to control blood glucose levels. Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood has substances high antioxidant and anti-
hyperglycemic that can be used as support therapy in stabilizing blood glucose levels. The aim of this study
was This study used the pretest-posttest control group design. Thirty-two subjects were recruited using a
purposive sampling method. T-Independent test analysis was employed (p <0,05). The result showed the
provision of stew Caesalpiniasappan Linn wood as support of OHAs therapy gave a significant effect of
54.51% compared with control (p = 0,010). Caesalpinia sappan Linn has a brazilin content as a transporter
that helps the pancreas work in insulin secretion. People with diabetes with uncontrolled blood sugar can take
of drinks Caesalpinia Sappan Linn as a supporting the consumption of OHAs.
1 INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a metabolic disorder that
is characterized by hyperglycemia and disturbance of
carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism because
inadequate of insulin production, the resistance of
insulin action, or both (Holt et al., 2016)
.
The
prevalence of DM type 2 accounts for 90% of all of
the diabetes cases worldwide (WHO, 2017). The
largest increases in the prevalence of diabetes in the
world will take place in the regions where economies
are moving from low-income to middle-income
levels, such as Indonesia (IDF, 2015). The prevalence
of diabetes in Indonesia is in sixth place worldwide
and the largest number in Southeast Asia (IDF, 2017).
Lifestyle modification can improve glycemic
control significantly in diabetes type 2 or prediabetes
people (West-Pollak et al., 2014) and treatment with
oral antihyperglycemic or insulin (Yki-Järvinen et al.,
2014; Ishii et al., 2017). Unfortunately, it so many
reports that those regimens had a fatal side effect.
Based on meta-analysis and various studies show that
many oral antihyperglycemics, i.e. metformin,
sulfonylurea, and thiazolidinediones or in
combination with other oral agents could increase
cardiovascular and mortality risk in individual with
diabetes type 2 (Kahler et al., 2007; Rao et al., 2008;
Shimoda and Kaku, 2016) and either insulin could
increase risk of severing hypoglycemia (Ghosh et al.,
2017).
Supporting treatment is needed to improve the
glycemic control of diabetes patients. One of them is
a complementary therapy, for example, traditional
treatment. Based on study by Chinnala, Elsani, and
Nalla (2015) in India found that traditional medicine,
the Caesalpinia Sappan Linn plant used for the
treatment of diabetes mellitus, can reduce the
development of complications and more significantly
reduce blood glucose levels, cholesterol, and total
triglyceride levels and total protein serum levels than
Glibenclamide 10 mg/kg body weight (Chinnala,
Elsani, and Nalla, 2015). This study was conducted to
know the effect of Caesalpinia Sappan L on blood
glucose level on diabetes patients type 2.
2 METHOD
This research used Quasi-Experimental Design and
pretest-postest control group design approach. The
sampling method used a non-probability sampling
technique i.e. purposive sampling. The total of
Ubaidillah, Z. and Witantry, Y.
The Effect of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn to Decrease Blood Glucose Level on Diabetes Type II Patients.
DOI: 10.5220/0009126601810186
In Proceedings of the 2nd Health Science International Conference (HSIC 2019), pages 181-186
ISBN: 978-989-758-462-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
181

subjects were 32 and divided into two groups, 16
intervention group, and 16 control group,
respectively. The intervention group was given
decoction of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood
(Caesalpinia Sappan Linn), which has been boiled
with 5 cc/kg BB of water. The boiling process needed
20 minutes with temperature 70
0
C, whereas the
control group was given standard treatment following
the therapeutic regimen given by the doctor. Dosis of
treatment was once a day for 7 days. Data analysis
used Independent T-test.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Respondents Characteristics
Table 1: Results of Analysis of Body Weight, Age, Genetic
Factors and Diabetes duration in Intervention Group
Intervention Group
Sample Weight
(Kg)
Age
(year)
Duration
(year)
Genetic
1 46 52 3 Yes
2 57 64 3 No
3 60 70 5 Yes
4 76 49 8 No
5 65 47 5 No
6 52 63 7 No
7 61 55 5 No
8 49 60 7 Yes
9 51 70 9 Yes
10 49 70 6 No
11 54 51 5 No
12 53 57 4 No
13 51 63 3 Yes
14 50 60 3 Yes
15 55 57 8 No
16 62 57 2 No
Mean 55,68 59,06 5,18
Table 2: Results of Analysis of Body Weight, Age, Genetic
Factors and Diabetes duration in Control Group
Sample Weight
(Kg)
Age
(year)
Duration
(year)
Genetic
1 51 60 3 No
2 61 59 5 No
3 69 62 8 Yes
4 62 52 8 Yes
5 76 55 3 Yes
6 58 53 3 No
7 60 61 3 No
8 66 60 7 Yes
9 50 55 5 No
10 60 65 5 Yes
11 58 66 4 No
12 85 65 6 No
13 56 56 3 No
14 64 62 5 Yes
15 59 63 3 No
16 62 59 6 No
Mean 62,31 59,56 4,81
Based on Table 1 and 2 shows that the
demographic data in the two groups were no
significant difference. The sample in the intervention
group and the control group had an average age that
was not much different from the average age of 59.06
in the intervention group and 59, 56 in the control
group. The average sample weight data in both groups
also did not show much difference; in group A the
average body weight was 55.68 kg, while in group B,
it was 62.31 kg. Data on the length of time for
diabetes in both groups were also not much different,
which is approximately 5 years with an average of no
genetic offspring who had type II diabetes before.
3.2 Overview of the Effect of
Caesalpinia Sappan Linn Decoction
on Decreasing Blood Glucose
Table 3 shows that the decrease in blood glucose
values was not only in group A (intervention) but also
in group B (control) decreased blood glucose values
with OHO therapy despite fluctuations in each
individual. Samples have decreased blood glucose
values, but each group has a different average value
of decline. The average decrease in blood sugar (GD)
in group A (intervention) for 7 days was 47.13 mg/dl,
and the average decrease in blood sugar (GD) in
group B (control) was 17.94 mg/dl, the difference in
the value of the decrease in blood glucose levels
between intervention group and control group
showed a decrease in blood glucose levels in group A
(intervention) better than group B (control).
HSIC 2019 - The Health Science International Conference
182
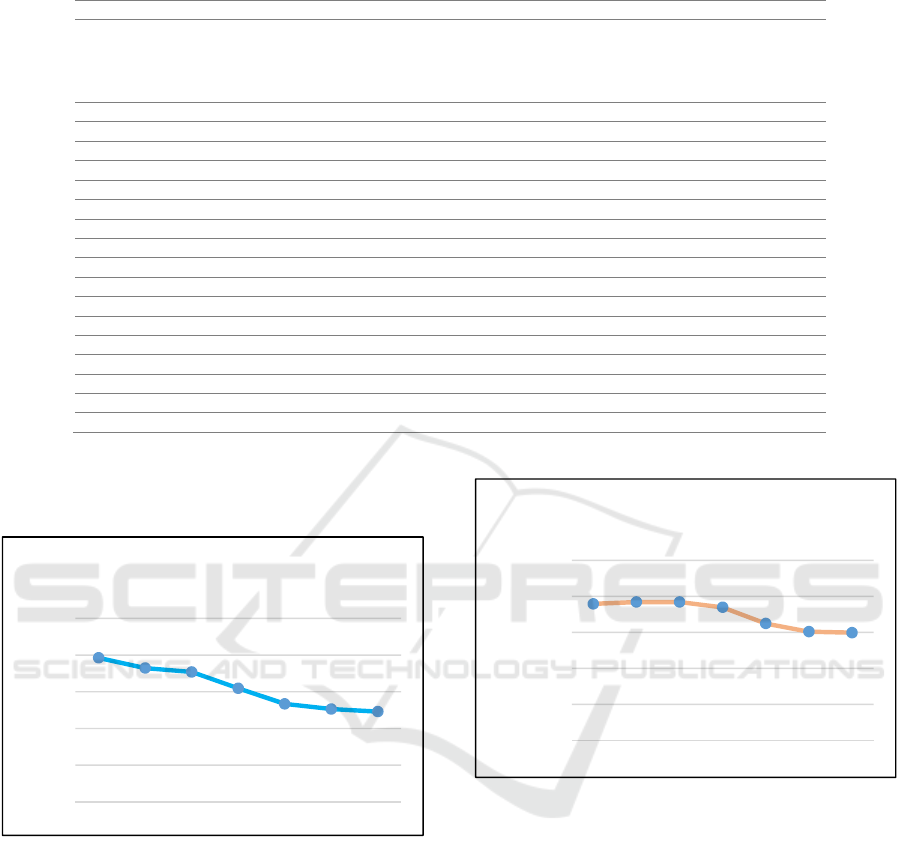
Table 3: Effect of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn Decoction on Decrease in Blood Glucose
Intervention group Control Group
Sample Blood
Glucose at
first day
(mg/dl)
Mean blood
glucose
during 7
th
day
Mean of
decline
blood
glucose
Sample Blood
Glucose at
first day
(mg/dl)
Mean blood
glucose
during 7
th
day
Mean of decline
blood glucose
1 244 195 49 1 162 145 17
2 162 116 46 2 159 150 9
3 189 140 49 3 207 192 15
4 155 124 31 4 137 138 1
5 273 180 93 5 187 179 8
6 131 115 16 6 165 165 0
7 196 156 40 7 236 203 33
8 137 120 17 8 193 186 7
9 127 110 17 9 226 201 25
10 224 177 47 10 277 229 48
11 280 191 89 11 165 168 -3
12 238 182 56 12 126 120 6
13 233 188 45 13 130 122 8
14 191 111 80 14 230 204 26
15 155 125 30 15 225 175 50
16 203 154 49 16 206 167 39
Mean 196,12 149,00 47,13 Mean 189,47 171,50 17,94
Graphical in the below showed of changes in blood
glucose from each group:
Figure 1: Changes in Blood Glucose on Intervention Group
Figure 2: Changes in Blood Glucose on Control Group
196.125
182.1875
176.875
154.625
133.375
126.375
122.875
0
50
100
150
200
250
Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7
Mean blood glucose
Changes in Blood Glucose on Intervention
Group
189.4375
192 192
184.6875
162.1875
150.875
149.5
0
50
100
150
200
250
Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7
Mean blood glucose
Changes in Blood Glucose on Control
Group
The Effect of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn to Decrease Blood Glucose Level on Diabetes Type II Patients
183

Table 4: Respondent’s Life Style
Intervention Group Control Group
Sample Diet Physical Activity Drug Sample Diet Physical Activity Drug
1 Fair Good Good 1 Fair Good Fair
2 Good Good Fair 2 Poor Good Fair
3 Fair Good Good 3 Good Good Fair
4 Good Fair Fair 4 Fair Fair Poor
5 Fair Good Fair 5 Good Poor Good
6 Good Good Poor 6 Poor Fair Good
7 Fair Good Fair 7 Poor Good Good
8 Good Fair Poor 8 Fair Fair Poor
9 Fair Fair Poor 9 Fair Good Fair
10 Fair Good Good 10 Good Good Good
11 Good Good Good 11 Poor Fair Good
12 Fair Good Fair 12 Fair Fair Fair
13 Fair Good Fair 13 Fair Fair Fair
14 Fair Good Good 14 Fair Good Fair
15 Good Fair Fair 15 Good Good Fair
16 Poor Fair Good 16 Fair Good Fair
Analysis of respondents' life habits which are
considered to affect the results of the study so that the
sample is given an observation sheet that will be used
as a process of observing various other factors besides
the administration of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood
(Caesalpinia Sappan Linn) which can affect blood
sugar levels. The assessment summary of the
observation sheet is by Gardner & Shoback, 2017.
Table 3 shows that the living habits in both groups
cannot be categorized as good, because there are still
many samples found that do not consume drugs
regularly and correctly, excessive consumption of
food and still consume food or drinks with artificial
sweeteners or added sugar.
Based on the Independent T-Test, a significance
value of 0.010 was obtained. These results indicate
there was a difference significantly on blood glucose
level decline between the intervention group and the
control group. Various factors cause the difference,
those factors are as follows.
3.3 The Active Ingredient in the
Decoction of Caesalpinia Sappan
Linn Wood
Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood has substances that
help the body to help stabilize blood glucose levels so
that group A has a more stable blood sugar value
compared to group B. Screening results show that
Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood contains flavonoids,
saponins, and Brazilians. Flavonoids function as
natural biological response modifiers because their
ability to modify the body responds to inflammatory
activity due to oxidative stress in people with diabetes
to stop the chain of cell damage and cell death more
quickly which can worsen the condition of sufferers
(Kusmiati, Dameria, and Priadi, 2014). Saponin is
used as a treatment for patients with
hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, antioxidants,
anticancer, anti-inflammatory and antifungal. The
decoction of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn saponin wood
functions as an antioxidant and anti-hyperglycemic
which can activate an increase in hydrodynamic
activity, which helps to decrease blood glucose levels
quickly (Kusmiati, Dameria, and Priadi, 2014).
Other studies have concluded that the Brazilian
content of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood
(Caesalpinia Sappan Linn) is very useful in the
treatment of vascular inflammatory processes or
hyperglycemia through inhibition of oxidative stress
and activation of NF-kB (Nuclear Factor kB). Further
studies on the determination of the Brazilian
mechanism in Indonesia, the transport of glucose
from adipocytes reported that Brazil caused increased
transport of glucose with the help of glucose
transporter (GLUT4) from intracellular to plasma
membrane through activation of phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase (PI3-kinase), not by affecting protein
synthesis, including GLUT4 synthesis (Nirmal et al.,
2015). Various contents in Caesalpinia Sappan Linn
wood, flavonoids, saponins, and brazil are proven to
control glucose levels in the blood of people with
diabetes.
3.4 Age and Genetic
The results of the observation showed that the
administration of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood
stew was effective at an average age of approximately
59 years. Age above the vulnerable limit is more than
HSIC 2019 - The Health Science International Conference
184

45 years (PERKENI, 2015). This result shows that
supporting therapy using wood stew has a success on
the body of a person with an age of approximately 59
years. A decoction of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood
as support therapy can still tolerate well with
someone of that age. The results of the observation
showed that the administration of Caesalpinia Sappan
Linn wood was effective at an average bodyweight of
60 kg. According to the Indonesian Endocrinology
Association, a bodyweight of more than 60 kg can
cause a person to have a slower tolerance to drug
therapy, as well as providing supportive therapies
such as herbs and Simplicia (PERKENI, 2015)
3.5 Duration of Diabetes
Respondents who experienced a significant decrease
in blood sugar values were respondents who had
diabetes on average for the last 2-5 years.
Respondents who had diabetes more than 6 years
showed a fairly good response, but have not been able
to show a significant decrease in blood sugar values.
This is in accordance with the theory and survey
according to the Indonesian Endocrinology
Association (2015), the length of time to have
diabetes that is more than 10 years requires more
therapy than drug administration and supporting
therapy. This is because body tolerance is different
compared to people who have long had diabetes
(PERKENI, 2015)
3.6 Life Style
Other results showed that respondents who
experienced a significant decrease in blood glucose
values were respondents with good daily activity
patterns, good sleep rest patterns, and food
consumption patterns were at a fairly good level,
although in terms of pharmacological therapy, require
compliance was still considered poor. This is in line
with the statement of the Indonesian Endocrinology
Association in (2015) stating that food and beverage
consumption factors, daily activities, sleep rest are the
main factors in influencing blood glucose values,
followed by the importance of adherence to taking
medication or therapy that contributes on the stability
of the condition of blood sugar levels of type II
diabetics, and can prevent or delay diabetes
complications continue (PERKENI, 2015)
3.7 Drug Choice
The results of the study found that most of the
samples that experienced a significant decrease in
blood glucose values were the samples that consumed
secretagogue drug class, while the samples taking
combination drugs remained significantly less. This
is due to the content of Brazilian, flavonoid, and
saponin in the decoction of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn
wood in general functions as a substance that helps
the activity of glucose transporters to optimize the
stability of blood glucose levels, which works to
support the function of secretagogue drug class which
functions to help and optimize insulin secretion. This
is supported by research by Chinnala, Elsani, and
Nalla (2015) in India who have tested the use of
glibenclamide along with the administration of
Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood without being
affected by the number of doses consumed, the results
showed significant effectiveness in various doses
(Chinnala, Elsani, and Nalla, 2015). This shows that
the type of drug consumed can affect the reaction of
the decoction of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood, and
the number of doses does not affect the reaction
results of the Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood stew.
Based on the data and several things that have
been explained, it can be concluded that the pattern of
daily activities, sleep rest patterns, consumption
patterns, types of medication, age factors, genetic
factors, long-term diabetes, and body weight can
influence the results of research and the effect of
Caesalpinia Sappan Linn decoction. Against
decreasing blood glucose levels.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the analysis of research data and discussion,
it can be concluded that the decoction of Caesalpinia
Sappan Linn wood in accordance with the dose of
each respondent in the intervention group was
considered sufficient to have a significant effect on
reducing blood glucose levels in the respondents
during the 7 days of research that was obtained with
sig values (0.010 ) <0.05, whereas in the control
group the results were no better than the intervention
group, by analyzing the data before and after the
administration of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn wood
stew, the intervention group experienced improved
blood sugar levels better than the control group.
REFERENCES
Chinnala, K. M., Elsani, M. M. and Nalla, M. K. (2015)
‘Anti Diabetic Activity of Methanolic Extract of
Caesalpinia Sappan Linn. on Alloxan Induced Diabetes
Mellitus in Rats’, International Journal of
The Effect of Caesalpinia Sappan Linn to Decrease Blood Glucose Level on Diabetes Type II Patients
185

Experimental Pharmacology, 5(2), pp. 65–69.
Gardner, D. G., and Shoback, D. M. (2017) Greenspan’s
Basic and Clinical Endocrinology, Tenth Edition.
McGraw-Hill Education.
Ghosh, S. et al. (2017) ‘Diabetes and driving.’,
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing
Countries, 37(4), pp. 400–406.
Holt, R. I. G. et al. (2016) Textbook of Diabetes. Wiley.
IDF (2015) IDF Diabetes Atlas - 8TH Edition.
IDF (2017) IDF Diabetes Atlas estimates for the global
diabetes prevalence of adults aged 18 to 99 years.
Ishii, H. et al. (2017) ‘Improvement of quality of life
through glycemic control by liraglutide, a GLP-1
analog, in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus: the PAGE1 study.’, Diabetology & Metabolic
Syndrome, 9, pp. 1–10.
Kahler, K. H. et al. (2007) ‘Impact of Oral
Antihyperglycemic Therapy on All-Cause Mortality
Among Patients With Diabetes in the Veterans Health
Administration.’, Diabetes Care, 30(7), pp. 1689–
1693.
Kusmiati, Dameria and Priadi, D. (2014) Analisa Senyawa
Aktif Ekstrak Kayu Secang (Caesalpinia sappan L.)
yang Berpotensi Sebagai Antimikroba [Analysis on
Compound Extract Secang Wood (Caesalpinia sappan
L.) as Potential Antimicrobial].
Nirmal, N. P. et al. (2015) ‘Brazilin from Caesalpinia
sappan heartwood and its pharmacological activities: A
review.’, Asian Pacific journal of tropical medicine.
India, 8(6), pp. 421–430. doi:
10.1016/j.apjtm.2015.05.014.
PERKENI (2015) Konsensus Pengelolaan Dan
Pencegahan Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 Di Indonesia
2015, PERKENI.
Rao, A. D. et al. (2008) ‘Is the Combination of
Sulfonylureas and Metformin Associated With an
Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease or All-Cause
Mortality?’, Diabetes Care, 31(8), pp. 1672–1678.
Shimoda, M. and Kaku, K. (2016) ‘Controversy about the
relationship between sulfonylurea use and
cardiovascular events and mortality.’, Journal of
Diabetes Investigation, 7(5), pp. 674–676.
West-Pollak, A. et al. (2014) ‘Impact of a novel
community-based lifestyle intervention program on
type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk in a resource-
poor setting in the Dominican Republic.’, International
Health (1876-3413), 6(2), pp. 118–124.
WHO (2017) Diabetes Mellitus.
Yki-Järvinen, H. et al. (2014) ‘New Insulin Glargine 300
Units/mL Versus Glargine 100 Units/mL in People
With Type 2 Diabetes Using Oral Agents and Basal
Insulin: Glucose Control and Hypoglycemia in a 6-
Month Randomized Controlled Trial (EDITION 2).’,
Diabetes Care, 37(12), pp. 3235–3243.
HSIC 2019 - The Health Science International Conference
186
