
A Comparative Study among Asean and Asia Countries Community to
the Realization and Application of English, Culture, Science and
Technology
Seno H. Putra
Universitas Islam Riau, Pekanbaru, Indonesia
Keywords:
English, Culture, Economy, Education, Science and Technology
Abstract:
The Problem of this study was to find out the realization and the application of English, Culture heritage,
Human sources, Economy, Science and Technology among ASEAN, Asia Countries Community. The
Research Methodology used in this study was Qualiquantitative approach, where the obtained data were
explained and analyzed throughout sentences and also added by the percentage. The results of this study
explained as follows: The Results of this study showed that Hongkong, Singapore, Malaysia, Philippines, and
Brunei were accustomed to using English in formal and non formal settings, on Culture, Japan, Indonesia,
Malaysia, Brunei still maintained their own Cultures in Economy in addition to, Japan, Singapore, Hongkong,
Malaysia, and Brunei were dominant among other ASEAN , Asia countries, human sources, science,
technology, Singapore, Hongkong, South Korea, and Japan were the Top Ranks if it was compared to other
Asian Countries. Therefore, other ASEAN countries, such as Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, Cambodia, and
Philippines were beyond in Economy, Education, science and technology rather than Singapore, Hongkong,
Japan, Korea, Malaysia, and Brunei were also expected to be able to quickly run in the future, so that the
beyond ASEAN Countries as cited in this study will be the same level not only in ASEAN and Asia Countries,
but also in the world.
1 INTRODUCTION
There are some Asian and Asia Countries which
have potential issues on the use and application of
English, culture, and science and technology. Most
of the ASEAN Countries are developing Countries
which start to increase all devices on their lives in
their own Countries to be developed Countries after
these Countries had been colonized by the Colonized
by many years. After their own Independence,
they realized that they must exist again to build
their Nations and Countries all aspects of their
lives, such as to increase human sources, to dig the
potential natural sources, to maintain and promote
their languages own cultures heritage, to increase
economy, science and technology, etc.
The Majority of the ASEAN and Asia Countries
were colonized by the Colonizations (Putnam et al.,
1976). During the colonizatios, their people to be
slaves and hard workers to assist the Colonizations
and their own natural sources digged and taken to be
the Colonizatios, even the whole devices of their lifes
to be limited and not allowed to develop their own
potential issues, including to increase human sources
of each level of schools. The Nations became stupid,
slaves, trauma, etc.
The ASEAN and Asia Countries which were
Colonized by the Colonizations are Indonesia,
Malaysia, Vietnam, Cambodia, Philippines,
Singapore, Hongkong, Maccau, etc., excluding
Thailand. From these cases and phenomena the
questions raises:
• Do they realize to exist to increase their own
human resources?
• Do they realize to increase their own Economy?
• Do they realize to maintain their own Languages
and Cultures Heritage?
• Do They realize to create and develop their own
Science and Technology?
• How are the comparative devices used and
Applied by among Asian and Asia Countries?
Therefore, based on the Cases and the Questions
Raises above, I would like to carry out this Study
which is also accordace with the the Title above.
Putra, S.
A Comparative Study among Asean and Asia Countries Community to the Realization and Application of English, Culture, Science and Technology.
DOI: 10.5220/0009128602950301
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education and Humanity (ICoSEEH 2019) - Sustainable Development in Developing Country for Facing Industrial
Revolution 4.0, pages 295-301
ISBN: 978-989-758-464-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
295

1.1 Context of the Problem
The context of the problem of this study is only to find
out some devices which have been explained above on
the realization and the application each ASEAN and
Asia Countries Community to increase all aspects of
life (Wilken, 1979).
1.2 Limitation of the Problem
The Limitations of the Problem of this Study are
focused on as follows:
• Language and Culture Heritage
• Economy
• Education
• Science and Technology.
1.3 The Problem of This Study
The Problem of this Study is as follows: How are
the Realization and the Application of Languages
and Cultures Heritage, Human Sources, Economy,
Science and Technology among ASEAN and Asia
Countries Community?
1.4 The Purpose of the Study
The Purpose of this Study is to find out and set
up the ASEAN and Asia Countries Community on
the Realization and the Application of Languages
and Cultures Heritage, Human Sources, Economy,
Science and Technology.
1.5 Key of Terms
• Comparative Study is a study to compare two or
more variables which are focused on the main
problems of the research, then from these can
be distributed to become several indicators in a
research (Seno Putra,2007). Therefore, in this
study, it is only focused on, or to compare a few of
variables and indicators as stated on the limitation
and the formulation of the problems of this study.
• Languages and Cultures Heritage language
language is media created by the God, the
developed by human depends on societies used
both spoken and written, formal and non formal,
verbal and non verbal which can communicate to
have mutual understanding one another close and
long distance. While culture heritage is creativity
of individual, a group, local, nation, and global
which are created by human beings to be used by
them and show them to other societies, as well
as maintain and developing so that not escaping
from values, norms, ethics, habits and customs
from their own societies .
• Human Sources is human or person who has
competence or quality in skills and sciences
after he/she joins each level of education, then
from that he/she is able to create, develop, and
contribute his/her skills and sciences to local,
national, and global societies.
• Economy is the system by which country’s money
and goods are produced and used . In this study, it
means that the systems of state economy produced
by industry which can give the welfare of nation
and state (Klein, 1967).
• Science and Technology is Knowledge is obtained
by observation and testing of the facts, and
systematic application of knowledge to practical
tasks in industry (Oxford). In this study
means that the education, science and technology
founded and created by the scholars and scientists
which can be sale to the market, as well as
developing and getting ranks to compete among
Universities through out institutions survey (Yang
and Pedersen, 1997).
2 A GLANCE RELATED
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
Under the ASEAN Economic Community (AEA), a
single regional common market of ASEAN Countries
will be created by 2015. The regional integration’s
objective is to create a competitive market of over
600 million people ASEAN Countries: Brunei,
Combodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar,
the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
There will be free flow of good, services, investment,
capital and skilled labour following the liberalization.
These will include tariff reductions and streaming of
certain administrative procedures. Many businesses
have begun preparing themselves three years ahead
of time to the most challenges and opportunities of
the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC).
ASEAN Member 2016 GDP Growth Forecast
For ASEAN member countries 2016 promises
a mixed bag with the World bank forecasting
Thailand’s economy to remain on the intensive care
list, constrating by 20 per cent from a 2015 Thailand
GDP of 2.5 per cent to just 2.0 percent this year
primarily due to domestic consumption constricted
by high household debt and subdued export growth.
Also, forcast to see a continued contraction is the
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
296

Malaysia economy with 2016 Malaysia GDP forecast
to contract by 4.26 per cent from 4.7 percent GDP
growth last year to 4.5 per cent growth in 2016.
At the opposite end of the economic performance
chart for 2016 is Myanmar, Lao PDR, Vietnam, the
Philippines, and Indonesia, all of who are forecast
to continue experiencing strong growth (Shavit et al.,
2007). Moreover, Leading the field for pure 2016
GDP growth is Myanmar which the World bank
forecasts will see 2016 Myanmar GDP growth of 7.8
per cent, a 20 per cent increase in the 2015 Myanmar
GDP growth of 5.8 per cent followed by Lao PDR
where 2016 Lao GDP is forecast to reach 7.0 per cent,
an increase of 9.37 per cent over 2015 Lao GDP of
6.4 per cent. Bringing up third place in the growth
stakes is Cambodia where 2016 Cambodia GDP is
expected to continue at the same 6.9 per cent the
country recorded in 2015.
For Vietnam the World Bank said rapid
investment, consumption, and export growth
should see 2016 Vietnam GDP to increase by 6.6
per cent, a 1.54 per cent increase over 2015 Vietnam
GDP growth of 6.5 per cent, while public private
partnerships (PPP) and government spending are
expected to be the chief drivers of the Philippines
GDP growth is forecast to come in at 6.4 per cent,
a 10.34 per cent increase over the 2015 Philippines
GDP of 5.8 per cent. Tempering its outlook for
the region the World Bank warns that economic
growth in the region remains at risk from a faster
than expected slowdown in China; The possibility
of greater financial market vitality and restricted
credit; A steep appreciation of the value of the US
dollar; and a slower than expected acceleration of
high income economies.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Design
The Design of this Study is Qualiquantitative
Approach, where the data of this Study are obtained
from the Informants are analyzed through out detailed
explanations based on cited above problems. The
kind of this Study is focused on A Comparative
Study, in which this Study is only to compare
some devices mentioned on point (1.3) among
ASEAN and Asia Countries Community. In short
word, Comparative Study is a study used by the
Researcher to compare one variable and Indicator to
other Variables and Indicators in one Research or
Study, as well as to compare the required results
of the study, then to decide the argumentations,
Conclusions, and Recommendations in the forms of
Scientific Academics; while Quantitative approach,
where the obtained data were analyzed through out
the percentage (%) only (Putra, a).
3.2 Location of the Study
Locations of the Study are Japan, Hongkong, Brunei,
Malaysia, Vietnam, Cambodia, Singapore, Thailand,
Philippines and Indonesia.
3.3 Population and Informants
Since the Population is too broad, this Study only
uses in formants. The reasons to use Informants
on Qualitative Approach are (1) Informant can be
used one person or more people; (2) the Informants
must be indigenous People; (3) Comprehension of
Problems of Study to be asked; and (3) Gendre, Age,
Background of the Education, Experience, Duration
of Stay, etc. (Read Seno Putra,1997-2004). Total
Informants of this Study is 45 People who are
different Social Status.
3.4 Instruments of the Study
The Instruments of the Study are Talk active with the
Infrormants, Introduction to Informants and asking
something with them; relaxing and interviewing non
formal setting with them, Handphone for recording
and taking photos,etc.
3.5 Data Collection Technique and
Collection Procedure of the Study
Procedure of this Study is to visit each Country,
then find out the Informants at certain Locations,
then Talk Active with them, such as in the Markets,
Academics, Offices, Trains, Bus, Cafeteria, Air Ports,
Mall,Tourism Places, Hotels, Street Markets,and also
provided by the Documents,etc.
3.6 Data Analysis Technique
The Data Collection Techniques of this Study are
• After asking and interviewing nonformal setting
with the Informants, the obtained data are
classified into descriptions.
• The descriptions of the data are also divided into
5 components of the Study as cited (1.3).
• All required data are analyzed to be clear
descriptions based on the main Problems.
A Comparative Study among Asean and Asia Countries Community to the Realization and Application of English, Culture, Science and
Technology
297

• Clear Descriptions and Transcripts of data are
check and recheck over and over before becoming
permanent Scripts.
• The Descriptions and Scripts of Data are coded
with numbers based on the questions of the Study
of each Country.
4 RESULTS OF THE STUDY
4.1 The Use and the Application of
English
ProductMajority of people in Indonesia, Vietnam,
Thailand, Cambodia, and Japan are not able to use
and Apply English in their daily life and activities.
Only 10 to 15 percent of each were able to use
English, especially those who worked at Hotel,
Tourism Places, Airport, Souvernir Markets, Taxi,
Bajai, Bus Station, Trains, Certain Offices. The
People of these Countries still Maintained their own
Languages both mother tongues and Their National
Languages. Moreover, English was also used by them
in certain Academics, such as International Seminar,
Conference,etc.
4.2 Culture Heritage
Most of the ASEAN and Asia still maintain their
own Cultural Heritage, in which they still used and
applied their own Culture in daily life activities, such
as in family, wedding party, ceremony, any states’
activities in their home countries. The rest of each
was only 25% that Communities used and applied
modern culture, especially in Towns (Dahlgren et al.,
1982).
4.3 Economy
The Most Increasing Economy Micro and Macro
in ASEAN Countries were Singapore, Malaysia,
Vietnam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Thailand. The
micro economy, Vietnam, Indonesia, Cambodia,
and Thailand were mostly similar activities to
have merchants, traditional markerts products, home
industries to sell the local buyers and to the foreigners
(Tourists). The ways of sale of 5 ASEAN countries
were most the same one another, except Singapore.
ASEAN Founded in 1967, where the members
are Singapore, Malaysia, Malaysia, Philippines,
Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, and
Myanmar. Economically, these Countries are
different stages of development but all sharing
immense growth potential. ASEAN is also major
global hub of manufacturing and trade, as well as one
of the fastest growing consumer markets in the World.
Singapore ranks number two in the world
for competitiveness as a result of consistently
world in the area of ‘basic requirements’, which
covers the quality of institutions, infrastructure
for macroeconomic factors. Singapore also comes
second area of ‘efficiency enhancers’ covers labour
market flexibility access to finance and regulation
and business sophistication. Malaysia, moreover,
is the highest placed developing Asian Economy.
It ranks 4th in financial markets become the
leading center of global Islamic finance. Thailand
continues to advance up the world competitiveness
rankings macroeconomics, but market competition
remains limited by high barriers to entry, especially
those affect to remain in other areas, particularly
governance. Indonesia has benefited from
infrastructure and connectivity improvements,
strengthen for government efficiency.Philippines is
one of the most digitally connected developing Asian
Nation that can be said of Infrastructure. Vietname
ranks 68th with its labour markets ranking 49
th
, its
best showing among the 12 market size (34
th
).The
macroeconomic environment (75
th
) is improving
and public institution back of better property rights
protections.Cambodia is the country faces major
property rights and corruption, and in the area of
innovation where scientific research (118
th
) and
patent applications (124
th
) are towards the bottom of
the tables (Barendt and Barendt, 1993).
ASEAN, moreover, is the fourth-largest exporting
region in the Wo. It Accounts for 7 percent of global
exports and as its member states have developed more
sophiscated manufacturing capabilities, their exports
have diversified. Vietnam specializes in textiles
and apparel, while Singapore and Malaysia are
leading exporters of electronics. Thailand has joined
the ranks of leading vehicle and automotive-parts
exporters.Indonesia is the World’s largest producer
and exporter of palm oil, the largest exporter of
coal, and the second largest producer of cocoa and
tin.Philippines has established a thriving business
process outsourcing Industry, and Malaysia and
Singapore are the most important export market.
ASEAN Economic Community integration plan,
which aims to allow the freer movement of goods,
services, skilled labour, and capital. While tariffs on
goods are now close to zero in many sectors among
the original six member states (Brunei, Indonesia,
Malaysia, The Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand.
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
298
4.4 Education and Science Technology
The systems of Education of each ASEAN and Asia
Countries are very different one another, since starting
from the election of the new students, processes,
and until the outcomes, of course are not the same
systems, strategies, and others. For examples, most
of Universities In Singapore, Hongkong, Japan, and
Malaysia are very strict to elect the new students
to study at those Universities, and so does in the
processes of Teaching and learning, as well as the
outcomes to be the scholars (?). The systems do
not give tolerance for those who are not able to
complete their study to become Scholars, because
all the students who are studying there must have
highest competiveness to maintain themselves to be
very good and excellent scholars, and they also must
maintain their Universities as alumni to compete other
Scholars in the World. The right Veto (Authority)
of each Lecturers have very strong which are given
by the systems of Universities, except if any big
problems both must be over come together whether
pass or not. Therefore, the quality Universities had
applied drop out for the students are not able to
complete their studies based on they year entry and
finish study. In short words, no excuses for them to
play in the back screen.
Moreover, the systems and the Quata of subject
matters and the guidance of Scriptions, Theses, and
Disertations of the students must be equal to the
Lecturers with suitable ranks, Academics, and their
experiences of Teaching and Research (Putra, c). No
Research and Scientific Writings of the Lecturers, no
given to become guidance or supervisors for students
in scientific writings. These are only among criteria
explained in here, but still have a lot of requirements
which had been applied by those Universities both
Lecturers and Students.
In order to see the ranks of Universities in ASEAN
and Asia, the following tables are attached below.
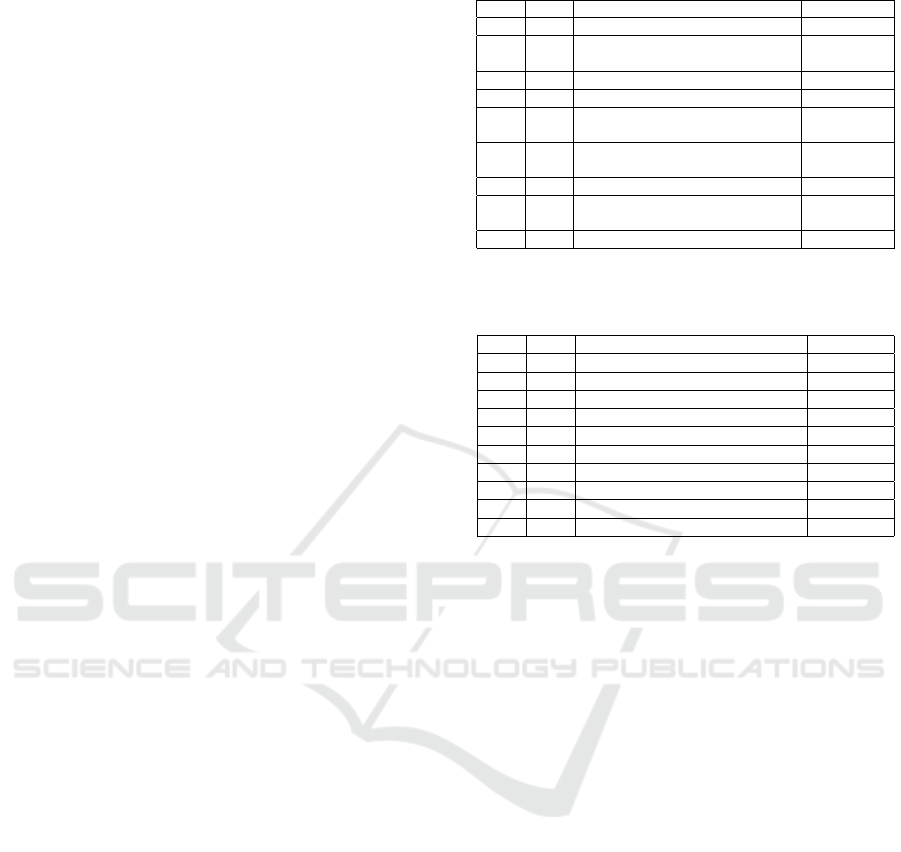
4.5 A Total of 47 Schools (Universities)
from 7 ASEAN Countries Made it to
the Top 300 of the Annual
Rangkings
• Brunei
118. Universiti Brunei Darussalam
• Vietnam
191-200. Vietnam National University
• Singapore
1. National University of Singapore
Table 1: ASEAN Universities in Top 10
2014 2013 Institution Country
1 2 National University of Singapore Singapore
2 6
Korea Advanced Institute if
Science and Technology
South Korea
3 2 University of Hong kong Hong kong
4 4 Seoul National South Korea
5 1
The Hong kong University of
Science and Technology
Hong kong
6 7
The Chiness University of Hong
Kong
Hong Kong
7 10 Nanyang Technological University Singapore
9 7
Pohang University of Science and
Technology
South Korea
10 9 The University of Tokyo Japan
Source (Southeast
Asia:http:/www.rappler.com/nation/95860
Table 2: ASEAN Universities in Top 10
2015 2014 Institution Country
1 1 National University of Singapore Singapore
4 7 Nanyang Technological University Singapore
29 32 University Malaya Malaysia
44 40 Mahidol University Thailand
49 57 Universiti Sains Malaysia Malaysia
56 56 Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Malaysia
61 66 Universiti Putra Malaysia Malaysia
70 63 University of the Philippines Philippines
79 71 University of Indonesia Indonesia
99 92 Chiang Mai University Thailand
Source
(http:/www.rappler.com/world/southeast-asia/95897
4. Nanyang Technology University
• Philippines
70.University of the Philippines
114.Ateneo de Manila University
143.University of Santo Tomas
• Indonesia
79.University of Indonesia
122.Bandung Institute of Technology (ITB)
137.Universitas Gajah Mada
147.Airlangga University
161-170.Padjadjaran University
201-250.Bogor Agricultural University
251-300.Diponegoro University
• Thailand
44.Mahidol University
53.Chulalongkorn University
99.Chiang Mai University
143.Thammasat University
171-180.Kasetsart University
171-180.Khon Kaen University
A Comparative Study among Asean and Asia Countries Community to the Realization and Application of English, Culture, Science and
Technology
299

171-180.King Mongkut’s University of
Technology Thonburi
191-200.Prince of Songkla University
251-300.Burapha University
251-300.Naresuan University
251-300.Srinakharinwirot University
• Malaysia
29.Universiti Malaya
49.Universiti Sains Malaysia
56.Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
61.Universiti Technologi Malaysia
66.Universiti Putra Malaysia
151-160.International Islamic University
Malaysia
151-160.Universiti Teknologi Petronas
191-200.Universiti Utara Malaysia
201-250.Universiti Malaysia Serawak
201-250.Universiti Teknologi MARA
201-250.Universiti Malaysia Perlis
201-250.University of Malaysia Sabah
251-300.Limkokwing University of Creative
Technology
251-300.UCSI University
251-300.Universiti Malaysia Pahang
251-300.Universiti Malaysia Terengganu
251-300.Universiti Tenaga Nasional
251-300.Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman.
Source (http:/www.rappler.com/world/southeast-asia/
95897
From the above tables, we know that among
Universities in ASEAN and Asia Countries which are
the Top ranks whether 10 Top ranks, 100 Top ranks
or 300 Top ranks, where Singapore is still the most
top among others,the second top is Malaysia, the third
top is Thailand, the fourth top is Philippines, and the
fifth top is Indonesia, the sixth top is Brunei, and the
seventh top is Vietnam in ASEAN Countries.While
in Asia Countries are Hongkong, Korea, and Japan.
Singapore University can loose other Universities in
Asia, such as Hong kong, Korea, and Japan. In short
words, Singapore is the most top Universities both
ASEAN and Asia Countries (Putra, b).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the Research Problems and the Results of
the Study above, it states that
• The use of English in formal and non formal
activities were dominant is Singapore, mostly
(90%) of people in here communicated in English;
• Malaysia is only (60%), and the rest is Malay
as a mother tongue and National Language, as
well as (5%) of the Community in here used India
Language.
• Hongkong was also used English as a formal
and non formal daily activities, mostly (60%)
of the people used it, and the rest is Mandarin,
Hongkian, etc.
• Japan was (30%) of the people in here is also used
English, especially in formal setting, and the rest
was Japanese as a mother tongue and National
Language;
• Cambodia was (25%) of the people used it as
Formal setting, and the rest is non formal setting;
• Vietnam (25%) for formal setting, and the rest is
its mother tongue and National Language;
• Indonesia was (20%) only for formal setting,
while others is mother tongue and Indonesian as
National Language; and
• Thailand only for (20%) for formal setting, and
the rest is their own mother tongue and National
Language;
• Brunei, (70%) of the people there can use English
both formal and non-formal setting, since English
in that Country is also as a second Language,
while Malay is used by most people there in daily
activities.
While in Culture Maintenance is
• Japan (90%), in which people in here still
maintained their own traditional Culture both
family and other ceremonies;
• Indonesia was (80%) still maintained their own
traditional culture, and the rest is influenced by
other cultures;
• Malaysia, where people in here used Malay
Culture, only (30%) of the People there used
Chiness and India Cultures;
• Singapore, where most of the People use Chiness
Culture, (15%) of the People was Malay, and the
rest was India ones;
• Hongkong, in which most of the People there
used Chiness, and only (3%-5%) was from ouside
Cultures;
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
300

• Thailand also maintained its own Cultures, and a
little bit out of other Cultures;
• Vietnam also maintained its own Culture, and
only (3%) was outsiders;
• Cambodia, where most of the People there used
their own Cultures, and only a little bit out of
others; and
• Brunei, in which most of the People there used
Malay Cultures (90%), and the rest was only
(3%-5%).
In Economy, the trade and industry, Japan is the
third rank in the world after America and China.
Therefore, while in ASEAN, of course, Singapore is
the rank number one, the third is Malaysia, the fourth
is Brunei, the fifth is Thailand, the sixth is Indonesia,
the seventh is Philippines, the eight is Cambodia,
the ninth is Vietnam.However, Hongkong is number
three in Asia after Singapore. Furthermore, related
to Education, Science and Technology, for examples;
ASEAN and Asia Universities in top ten is as
follows: The rank number one is National University
of Singapore, the second rank is Korea Aadvanced
Institute of Science and Technology of Korea, the
third rank is National University of Hongkong, the
fourth is Soul National University of South Korea,
the fifth is the Hongkong University of Science and
Technology of Hongkong, the sixth is the Chiness
University of Hongkong, the seventh rank is Nanyang
Technological University of Singapore, the Ninth is
the University of Science and Technology of South
Korea, and the Tenth rank is the University of Tokyo,
Japan.
REFERENCES
Barendt, E. M. and Barendt, E. (1993). Broadcasting law:
A comparative study. Clarendon press Oxford.
Dahlgren, R. M., Clifford, H. T., et al. (1982). The
monocotyledons: a comparative study. Academic
Press.
Klein, H. S. (1967). Slavery in the Americas: a comparative
study of Virginia and Cuba. Oxford University Press
London.
Putnam, R. D. et al. (1976). The comparative study of
political elites. Prentice-Hall Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Putra, S. 2014. Karya Ilmiah Populer dan Karya Ilmiah
Akademik. Pekanbaru.
Putra, S. 2015. Linguistics, Science and Technology.
Conferences Abstract.IEDRC.Tokyo, Japan, 28.
Putra, S. H. 2016. Contribution Language (Englsih)
and Culture to Market Integration in ASEAN. The
13th Insyama International annual symposium on
Management. Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
Shavit, Y. et al. (2007). Stratification in higher education:
A comparative study. Stanford University Press.
Wilken, P. H. (1979). Entrepreneurship: A comparative and
historical study. Ablex Norwood, NJ.
Yang, Y. and Pedersen, J. O. (1997). A comparative study
on feature selection in text categorization. In Icml,
volume 97, page 35.
A Comparative Study among Asean and Asia Countries Community to the Realization and Application of English, Culture, Science and
Technology
301
