
Impact of Vibration of Piling Hammer on Soil Deformation: Study Case
in Highway Construction Section 5 Pekanbaru-Dumai
Firman Syarif
1
, Husnul Kausarian
2
and Dewandra Bagus Eka Putra
2
1
Civil Engineering Department, Universitas Islam Riau, Pekanbaru, Indonesia
2
Geological Engineering Department, Universitas Islam Riau, Pekanbaru, Indonesia
Keywords:
Vibration, Soil Deofrmation, Piling Hammer.
Abstract:
In the Pekanbaru-Dumai highway road construction in Section 5 will be built a bridge. The construction of
the bridge is in the area of PT TGI gas pipeline. The construction of this bridge uses a pile foundation whose
pile is carried out using a beating method using a hammer. The diameter of this pile is 60 cm with a hammer
weight of 5 tons and a height of fall of 2.5 meters. This work method will produce vibrations that affect the
condition of the gas pipe. One of the aspects that are affected by vibration is the deformation of the soil around
the gas pipe. This soil deformation will affect the position of the gas pipe which, if it forms a fairly large slope,
may cause gas pipelines to crack. The method used to determine the effect of vibration from the design of the
gas pipeline is to use a vibration meter tool. vibration meter is a sensor device that is placed on the stake and
on the ground above the gas pipe so that how much vibration and deformation of the soil can be seen. As a
result from the test using vibration meter, it was found that the greater the wave velocity due to the design, the
greater the deformation that occurs on the soil.
1 INTRODUCTION
Pile foundations are the part of a structure used to
carry and transfer the structure load of the building
to the bearing ground located at some depth below
ground surface. The main components of the foun-
dation are the pile cap and the piles. Wood, steel and
concrete are the main types of materials used for piles.
Piles made from these materials are driven, drilled or
jacked into the ground and connected to Pile caps
1
(Muhammad, 2008).
In past, theoretical and experimental studies were
undertaken by various investigators to evaluate the
vertical load and lateral load carrying capacity of sin-
gle and group piles embedded in different soil stra-
tum. On pile foundations, structures like Buildings,
towers, Bridges, Piers harbour and offshore structure
are invariably constructed (Muhammad, 2008).
In the erection process a vibration will occur with
the potential damage to infrastructure and disturb the
comfort of humans around him. Of course the greater
the vibration caused, the greater the potential dam-
age caused. This is compounded with the increasingly
1
API 1002 2013 “ Steel Pipeline Crossing Railroad and
Highway”
narrow land in urban areas and in certain areas, so the
potential damage that might be caused by the piling is
higher because of it the distance to the object is get-
ting closer. For this reason, an analysis will be con-
ducted related to propagation vibrations on the ground
as well as factors on the ground that affect it so that
vibrations are possible will occur due to predictable
pile erection (Fitriyah et al., 2019; HH, 2014).
Rayleigh waves (ground roll) are waves that are
known as surface waves that are generated by a mo-
mentary pressure at the ground surface that occurs as
a result impact and interference between compressive
waves and shear waves constructively. The movement
of particles on the face of the Rayleigh wave consists
of P waves and S waves in the horizontal plane. An-
other characteristic of the Rayleigh wave is that its
amplitude decreases exponentially with the depth it
goes through, whereas on the surface the amplitude
hardly affects its attenuation, it has a low frequency
with a not-so- sharp spectrum (Santoso, 2017; H., ;
Muhammad, 2014).
The vibration wave generated in vibrating com-
paction will quickly propagate from near to far on the
surface of ground. The incurred environmental vibra-
tion not only generates vibration damage to engineer-
ing structures, but also brings unfavorable influences
120
Syarif, F., Kausarian, H. and Eka Putra, D.
Impact of Vibration of Piling Hammer on Soil Deformation: Study Case in Highway Construction Section 5 Pekanbaru-Dumai.
DOI: 10.5220/0009129901200124
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Science, Engineering and Technology (ICoSET 2019), pages 120-124
ISBN: 978-989-758-463-3
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

on production and the lives of residents around the
construction site. If enough safety protection mea-
sures fail to be taken, the vibrating compaction con-
struction may lead to cracking of subgrade retain-
ing wall, culvert and bridge abutment, disturb normal
life of surrounding residents, affect safe production of
the neighboring industrial and mining enterprises, and
damage normal use and safety of surrounding build-
ings (Chen et al., 2019; Maizir, 2015; Muhammad,
2008).
The structural work of the Pekanbaru-Dumai
highway road is designed crossing with the PT TGI
pipeline position, the highway road works are con-
structed with pile foundations. The vibration caused
by the erection felt quite large, so PT TGI was worried
that there would be an impact on their gas pipeline due
to the work of the pile. Therefore testing was carried
out to determine how big of the impact of the vibra-
tion on the PT TGI gas pipeline.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Vibration Test
Ground vibration is seismic movement on the ground
caused by rock blasting, pole erection, traffic, excava-
tion, vibration due to compaction etc., which is a form
of energy transport through the soil, can damage adja-
cent structures when vibrations reach a certain level.
Some types of energy released from blasting prop-
agate in all directions from explosive holes as seis-
mic waves with different frequencies. Energy from
seismic waves is dampened by distance and waves
with the highest frequency being muffled faster. This
means that the propagation of the dominant frequency
from an explosion is a high frequency in a short dis-
tance and a lower frequency at a greater distance
2
.
Ground vibration measurements are usually car-
ried out at one or several points on the ground. For
total analysis, the practice is to measure in three di-
rections: vertical, longitudinal and transverse. Usu-
ally the vertical component is dominant at shorter dis-
tances. Therefore it is usually sufficient to measure in
the vertical direction. For vibration analysis of mea-
sured values, vibration phenomena can be recorded as
a function of history over time. Then displacement,
particle velocity and acceleration can be recorded.
The basic rule is that vibration velocity is measured
2
Ground Vibration Dalam Kegiatan Blasting Batuan.
Viewed in 04 April 2019. http://studi- kelayakan-
tambang.blogspot.com/2017/03/ground- vibration-dalam-
kegiatan.html
on building structures etc. by geophone and accel-
eration on computer installations etc (Syahidi, 2017;
Sukiman and Yakin, 2017). with an accelerometer.
If vibration velocity is measured, acceleration can be
calculated and vice versa. The most interesting pa-
rameter to pay attention to is the damage structure cri-
teria that need to be protected from vibration (HA., ;
Santoso, 2017; Sukiman and Yakin, 2017).
2.2 Effect of Ground Vibration on
Geological Factors
Soil and rock are porous material with a relatively
rigid base mass. The pores are filled with water or air.
Soil is a mass consisting of mineral grains that have
friction and cohesiveness between materials. In ce-
mented mineral granular sedimentary rocks together
with magma rocks and metamorphous mineral rocks
it has crystallized in rock masses which usually con-
tain water gaps and joints. In practice it may be diffi-
cult to assess accurate propagation velocity of seismic
waves in different soils and rocks seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Propagation velocity of seismic waves in different
soils and rocks
3
Each geological environment has the characteris-
tics of each ground vibration that influences the prop-
agation of vibration waves. The characteristics of
ground vibration depend on the following properties:
• Elastic soil constants (elastic and shearing mod-
uli) which determine the wave propagation speed
• The type and depth of the soil that determines the
dominant range of frequencies and types of waves
• Soil moisture and groundwater level
• Topography and morphology, which can focus on
seismic waves
• Damping characteristics from the soil
Impact of Vibration of Piling Hammer on Soil Deformation: Study Case in Highway Construction Section 5 Pekanbaru-Dumai
121

2.3 Potential Damage Caused By
Vibration
When planning a project, where driven piles or sheet
piles are to be used, the design engineer must iden-
tify potentially vulnerable structures and installations
in the vicinity of the project site and propose limiting
values of ground vibrations. As part of this task, the
risks must be assessed of vibration damage to struc-
tures and vibration-susceptible installations or envi-
ronmental aspects affecting occupants of buildings.
As the prediction of building damage can be com-
plex, theoretical methods have low reliability. How-
ever, it is possible to assess the potential damage to
buildings based on statistical observations. This ap-
proach is used in codes and standards but is limited
to the specific conditions in the region where the ob-
servations were made. Therefore, local building stan-
dards should be applied with caution in other regions,
where pile driving methods, geological conditions,
and building standards may be different.
The damage potential of pile-driving vibrations
depends on the displacement and the frequency of the
vibration. Neither of these two characteristics alone
will damage a structure. Concerning displacement,
it is common knowledge that a structure can be uni-
formly jacked through several feet without causing
damage. Likewise, with regard to frequency, normal
sound, in pa ssing through a wall, can vibrate the wall
at high frequencies (several thousand cycles per sec-
ond) without causing damage. It is a combination
of displacement (amount of motion) and frequency
which causes damage. The particle velocity of earth-
borne vibration is the best measure of damage poten-
tial because it combines displacement and frequency
in the most significant manner. The relation between
Velocity and Frequency seen in figure 2.
Several investigators have found that particle ve-
locities in excess of 4. 0 in. I sec are required to
cause plaster cracks in dwellings. Figure 3 shows a
comparison of the results of several of the investiga-
tions. With appropriate conservatism, the investiga-
tors agree that a vibration level of 2. 0 in. /sec (par-
ticle velocity) is safe with regard to plaster cracks in
residential-type structures
The effect of ground motion on an engineered
structure can be computed by commonly used meth-
ods in the earthquake engineering field. The structure
is considered a lumped mass-spring dashpot system,
and its response to a series of impacts can be calcu-
lated. Based on observation and experience, it can be
stated that ground motion particle velocities below 4.
0 in. /sec are well within the safe range for engineer
structures.
Figure 2: Propagation velocity of seismic waves in different
soils and rocks
4
Figure 3: A comparison of the results of several of the in-
vestigations about the effect of particle velocity to structural
damaged
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research was conducted with the aim of know-
ing how much the vibrational impact on soil defor-
mation at the PT TGI gas pipeline location. The re-
search locations are STA 78 + 448 Titian Antui Vil-
lage, Madau District, Bengkalis Regency - Riau and
Pipeline: Grissik - Duri Section.
This research was conducted in 3 stages:
1. Initial Investigation
the initial investigation was carried out to look
back on the problems that occurred in the field
based on information from the informants. From
ICoSET 2019 - The Second International Conference on Science, Engineering and Technology
122

Figure 4: Research Location on STA 78 + 448 Titian Antui
Village, Madau District, Bengkalis Regency - Riau
the initials of this investigation, the data is ob-
tained in the form of data and current conditions
with visualization of photos and other supporting
data.
2. Soil Investigation
soil investigation is a model of general investiga-
tion that must be done in looking at the problems
that occur in a structure above the ground. From
this soil investigation, soil data was obtained re-
lated to the physical and mechanical properties of
the soil.
3. Vibration Test With Vibration Meter
This vibration test equipment consists of three
sensors that read vibrations produced by piles of
3 directions as seen in figure 4, namely:
(a) 1V vibration is in vertical direction
(b) 2L vibration is in longitudinal direction
(c) 3T vibration is in transversal direction
This sensor is installed on the stake and on the gas
pipe. with the aim when the pile works vibration that
occurs due to erection will be read on the sensor that
works and is read on a computer device as shown in
the figure 5.
Figure 5: The Direction of The Sensor
Figure 6: The Instalation of The Vibration Meter Sensor
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Soil Investigations Result
From the results of soil investigation, it was found
that the type of soil at the position of the gas pipe
was soft clay with high plasticity.Fine-grained soils
are cohesive soils (Sukiman and Yakin, 2017). One
of the problems in the geotechnical field is cohesive
soil which is usually soft soil. Soft soil can expand or
shrink due to the entry or discharge of water. Giving
a load on soft soil, will cause an increase in the volt-
age acting on the soil. Additional stress that works on
soft soil will initially be bear by pore water due to the
Impact of Vibration of Piling Hammer on Soil Deformation: Study Case in Highway Construction Section 5 Pekanbaru-Dumai
123
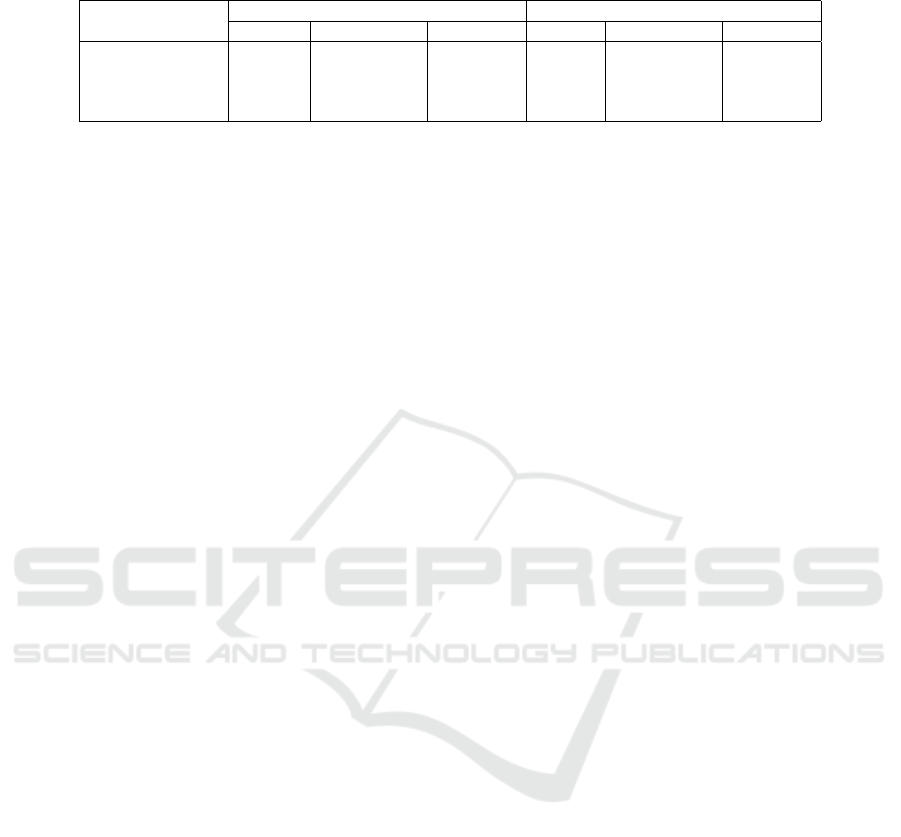
Table 1: Result of Vibration Test
Lokasi Pengujian
Velocity (mm/s) Displacement/Amplitude (mm)
Vertical Longitudinal Tranversal Vertical Longitudinal Tranversal
test 1 4.9017 0.9328 2.6744 0.0869 0.0135 0.0422
test 2 2.7704 1.3061 1.6897 0.0374 0.018 0.0229
test 3 12.7969 3.6527 12.5259 0.1535 0.02 0.1518
test4 14.202 3.8665 15.2374 0.1653 0.0384 0.1759
incompressible nature of water. This will cause ex-
cess pore water to arise. This excess pore water will
be dissipated by the release of soil pore water through
the soil pores, while the additional stress is
Initially the pore is gradually transferred to solid
soil particles. This will result in a reduction in the
volume of the land, resulting in increasing of the de-
formation of the soil.
4.2 Vibration Test Result
From the vibration test the results are obtained as
shown in Table 1. From the results we can conclude
if the velocity of the vibration from piling is high the
deformation of the soil also high, like in the test 1
in vertical wave the velocity is 4,9017 mm/s and de-
formation is 0,0869mm, in the test 2 the velocity is
lower than test 1 2.7704 mm/s and the deformation
also lower than test 1 0.0374 mm. this situation hap-
pen because the velocity of vibration can produce en-
ergy and also force, so the force from the velocity can
affect the soil like a load. If the velocity become high
the deformation of soil also high.
5 CONCLUSIONS
From this research we can conclude : Cohesive soil
(clay) has a high deformation because of the mechan-
ical aspect of this soil that have pore, initially the pore
is gradually transferred to solid soil particles. This
will result in a reduction in the volume of the land,
resulting in increasing of the deformation of the soil.
The higher wave velocity due to the design, the higher
deformation that occurs on the soil.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to gratitude to my parent whose always
motivate me, also to my wife and children my inspi-
ration. Secondly I would like to say thanks to all
the team that help me in this research, PT HKI, PT
TONAMA and PT TGI.
REFERENCES
Chen, A., Cheng, F., Wu, D., and Tang, X. (2019). Ground
vibration propagation and attenuation of vibrating
compaction. Journal of Vibroengineering, 21(5).
Fitriyah, D., Propika, J., Lestari, L., Istiono, H., Pertiwi,
D., and Sekartadji, R. (2019). Pile foundation anal-
ysis on high–rise building using finite element-spring
method on sandy clay soil. In IOP Conference Series:
Materials Science and Engineering, volume 462, page
012045. IOP Publishing.
H., G. et al (2017). Pengaruh Tinggi, Kedalaman Pon-
dasi Mesin Jenis Blok Dan Parameter Tanah Berbu-
tir Halus Terhadap Amplitudo. e-Jurnal MATRIKS
TEKNIK SIPIL/September, 2017/777.
HA., S. (2013), Kajian Analitik Pengaruh Rambatan Energi
Gempa Terhadap Perilaku Benturan Gedung, Konfer-
ensi Nasional Teknik Sipil 7 (KoNTekS 7) Universitas
Sebelas Maret (UNS) - Surakarta.
HH, S. (2014). Measurement of mechanical vibrations in
residential areas due to the construction of the sabo-
magelang dam with standard bs 6472-2:2008. Journal
Instrumentasi, 38(2).
Maizir (2015). Evaluasi Daya Dukung Tiang Pancang
Berdasarkan Metode Dinamik. Annual Civil Engi-
neering Seminar 2015, Pekanbaru ISBN: 978-979-
792-636-6.
Muhammad, H. (2014). et al. Studi Pengaruh Diameter Dan
Panjang Tiang Pancang Terhadap Amplitudo Getaran
Pada Perencanaan Pondasi Alternatif Turbin Gas, Jur-
nal Teknik POMITS.
Muhammad, R. (2008). Pengaruh getaran pemasangan pon-
dasi tiang pancang terhadap lingkungan permukiman.
Jurnal Permukiman, 3(1).
Santoso, H. H. (2017). Pengukuran getaran mekanik pada
daerah permukiman akibat konstruksi pembangunan
bendungan sabo-magelang dengan standard bs6472-
2: 2008. Instrumentasi, 38(2):43–52.
Sukiman, N. A. and Yakin, Y. A. (2017). Analisis deformasi
dan tekanan air pori ekses pada tanah lempung lunak
akibat beban timbunan (hal. 1-12). RekaRacana: Jur-
nal Teknil Sipil, 3(2):1.
Syahidi (2017). Pengaruh Luas Penampang Pondasi Mesin
Jenis Blok Dan Parameter Tanah Berbutir Halus
Terhadap Amplitudo. e-Jurnal MATRIKS TEKNIK
SIPIL/Juni 2017/491.
ICoSET 2019 - The Second International Conference on Science, Engineering and Technology
124
