
Rhythmic Gymnastics Effectively Reduce Body Mass Index in Weight
Loss for Preschool
Atika Yulianti
1*
and Rahayu Kurniawati
2
1,2
Department of Physiotherapy, Faculty of Health Science, University of Muhammadiyah Malang
Jalan Bandung Nomor 1 Malang 65113, East Java, Indonesia
Keyword: Rhythmic gymnastics, Weight Loss, Preschool
Abstract: A child who experiences problems of excessive nutritional value when he is an adult will cause dangerous
diseases such as cardiovascular disorders and diabetes. Being overweight can also affect a child's intelligence.
In children with overweight status, intelligence can experience a decrease due to a decrease in creativity and
limitation when doing activities due to body conditions that are not free to move, so that makes children lazy
to do something. Rhythmic gymnastics (Rhythmic gymnastics) increases the ability of muscles to produce
energy aerobically and undergoes a metabolic process whose source of energy comes from burning fat. The
purpose of this study was to determine the effect of rhythmic gymnastics training on decreasing body mass
index of RA Muslimat Tarbiyatunnasi’in Paculgowang students in Jombang. The research design used was
the One Group Pre-test Post Test Design with a sample of 22 people, then BMI was measured using BMI / U,
and the nutritional status was obtained using the Z-score formula. This research was tested with the Wilcoxon
test and obtained a significance value smaller than 0.05 (0.00 <0.05) this means that H0 is rejected and H1 is
accepted. Conclusion: There is an effect of rhythmic gymnastics on the decrease in body mass index.
Keywords: Body Mass Index, Rhythmic gymnastics, RA Muslimat Tarbiyatunnasyi’in.
1 INTRODUCTION
Indonesia is a developing country that has a problem
with dual nutritional status. The problem of dual
nutrition that is being experienced by Indonesia
includes the problem of undernutrition and the
problem of over nutrition. The problem of obesity in
Indonesia based on data taken by Riskesdas in 2007
up to 2013, children aged 5-12 years tend to increase.
In 2007 the level of obesity at the age of 5 to 12 years
was 6.4%. Increase that number in 2010 as much as
9.2%. Riskesdas in 2013 obtained data in the form of
the prevalence of obesity aged 5 to 12 years, ages 13
to 15 years, and ages 16 to 18 years stated in
sequence, namely 8.8%, 2.5%, 1.6% (Riset
Kesehatan Dasar, 2018). From this data, the results
obtained in the form of obesity and obesity are more
common in pre-school children compared to
adolescents. The problem of over nutritional status in
Indonesia is still relatively serious, with a prevalence
of 18.8% with 10.8% with the nutritional value of fat
and 8.8% with the nutritional value of obesity.
National prevalence results in Indonesia show excess
weight for the age group of 6-14 years in men is 9.5%,
while for women, it is 6.4% (Ermona and Wirjatmadi,
2018).
Obesity can occur if there is an imbalance
between incoming energy intake with outgoing
energy intake so that it will accumulate into excessive
fat. The causes of obesity and obesity in children are
excessive food intake, such foods as fast food, sugary
drinks, high-calorie unhealthy snacks that exist in the
school environment, and are not matched by the habit
of consuming enough vegetables and fruit (Frutuoso
et al., 2016). Also, other causes of obesity in early
childhood are not given breast milk during infancy.
At the time of the baby, the child is given formula
milk with a dose that is not appropriate or exceeds that
required by the child. Children between 4 and 7 years
old are vulnerable to be affected by more nutrition
(Bobo-Arce and Méndez-Rial, 2013). Therefore,
children aged 4 to 7 years need to get more attention
related to eating patterns to form good eating habits
(Ayu and Sartika, 2011). In children who experience
more nutritional problems is a problem serious. The
problem of nutritional value in children can increase
the risk of various kinds of chronic diseases (Hecht,
2015).
240
Yulianti, A. and Kurniawati, R.
Rhythmic Gymnastics Effectively Reduce Body Mass Index in Weight Loss for Preschool.
DOI: 10.5220/0009141702400244
In Proceedings of the 2nd Health Science International Conference (HSIC 2019), pages 240-244
ISBN: 978-989-758-462-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Poor physical activity can result in the
occurrence of over nutrition, which, in principle, is
where more nutrition occurs due to an imbalance
between the incoming energy and the energy that is
released every day (Fernandez-Villarino, Bobo-Arce,
and Sierra-Palmeiro, 2013). The energy that will be
released by the body depends on one's daily activities
with advances in increasingly sophisticated
technology, creating a situation where lifestyle
changes become sedentary or less mobile. As a result,
food that will enter the body cannot be processed
properly by the body, and food intake is stored in the
form of fat tissue (Andini, 2016).
Characteristics of good physical activity given to
early childhood, namely by (1) giving a variety of
movements to get new experiences. Learning like
forms of games and competitions. (2) stimulates the
development of the five senses in children. (3)
developing imagination or fantasy, and (4) moves to
the rhythm/song or story (Paiman, 2009).
Research conducted (Prihatin, 2016) explains the
benefits of rhythmic gymnastics. According to
Mukhloid (2014), rhythmic gymnastics can reduce
and burn excess fat in the body, improve the
appearance of certain, such as the thighs of the arms,
abdomen, and legs, increase lung endurance, and
heart. Sean Cadence is a program for weight loss. If
you practice with a mild intensity will increase your
appetite, and if you practice with a heavy intensity
will suppress hunger because there is a lot of blood
circulating in the active muscle area and not in the
stomach area (Andini, 2016). Also, rhythmic
gymnastics can increase flexibility, balance,
coordination, agility, endurance, and able to do other
activities or sports (Kadi, Halida and Yuniarni, 2018).
2 METHODS
This study uses quasi-experimental with one group
pretest and posttest design approaches that aim to
determine the effect of rhythmic gymnastics on
decreasing body mass index of RA Tarbiyatunnasi’in
Jombang students who are overweight (Hilgers,
Heussen and Stanzel, 2018). The number of
respondents in this study was 22 people. The
sampling technique is purposive sampling with
several inclusion and exclusion criteria. Respondents
measured body weight and height then calculated
using BMI / U and using a Z-score to classify the
nutritional value in children. The training program
provided five meetings a week. The time duration is
30 minutes. This research conducted from February
to March 2019. Analysis of the data used to test the
hypothesis in this study was to use the Shapiro Wilk
test (Warner et al., 2018).
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Sample characteristics can be seen in the following
graphic image:
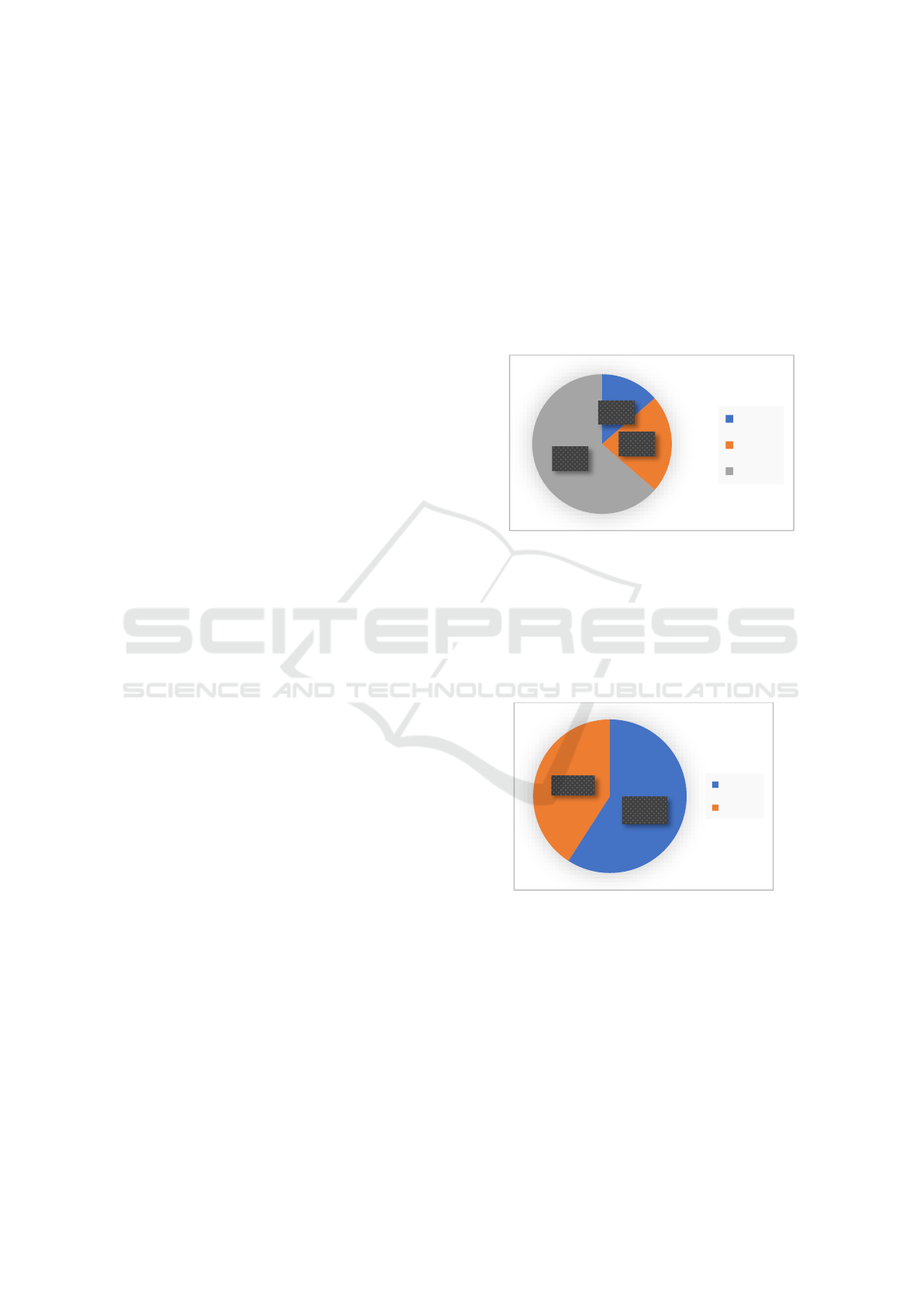
3.1 Characteristic based on Age
Figure 1: Characteristics by Age
Characteristics of respondents by age who
experienced the most nutritional value in the age
range of 6 years with a number of 14 people with a
percentage of 63.6%.
3.2 Characteristics Based On Gender
Figure 2: Characteristics Based on Gender
Characteristics of respondents by sex who
experienced more nutritional value there was male
sex amounted to 13 people with a percentage of 9.1%.
13%
23%
64%
4 Years
5 Years
6 Years
13,6%
40,9%
Male
Female
Rhythmic Gymnastics Effectively Reduce Body Mass Index in Weight Loss for Preschool
241

3.3 Identification of Body Mass Index
Values Before and After Giving
Gymnastic Exercise
Table 1: IMT Values Before and After Treatment
Body Mass
Index
Before
Intervention
“Rhythmic
gymnastics”
After
Intervention
“Rhythmic
gymnastics”
Normal
0 %
40,9 %
Overweight
90,9 %
50,0 %
Obesitas
9,1 %
9,1 %
Result
100 %
100 %
Based on the above table, the characteristics of
respondents based on nutritional value after rhythmic
gymnastics given the results in the form of
respondents with grades normal nutrition as many as
9 people (40.9%), respondents with overweight
nutritional value as many as 11 people (50%),
respondents with nutritional value of obesity as much
as 2 people (9.1%).
3.4 Normality Test
Table 2: Normality Test
Group
Shapiro - Wilk
Statistic
Df
Sig(2-
tailed)
Pre-Test
0,86
22
0,00
Post Test
0,91
22
0,07
The normality test is done using the Shapiro-
Wilk test with a significance value of the pre-test
intervention group that is 0.00 P <0.05) and post-test
0.07 (P <0.05), it can be concluded that the normality
test uses Shapiro- Wilk shows the data distribution is
not normal.
3.5 Hypothesis Test Results
Table 3: Wilcoxon Test Results.
n
α
p
the effect of rhythmic
gymnastics on the decrease in
body mass index
22
0,05
0,00
Hypothesis test results using the Wilcoxon test
showed that there were significant differences after
doing rhythmic gymnastics exercises to decrease the
value of body mass index with a value of Sig = 0.00
(P <0.05), which means it can be concluded that H0
is rejected and H1 is accepted. So, there is the effect
of rhythmic gymnastics exercises on students' body
mass index decline
Overweight and obesity in children occur due
to poor diet and also low levels of physical activity
(Cyrilla et al., 2017). Diet is one of the triggers of
obesity, which is to consume food in large quantities
and exceeds the body's daily nutritional needs
(KEMENKES RI, 2012). These foods have
characteristics such as high calories, high glucose,
high carbohydrates, high fat but low in fiber. From
the results of research conducted by (Warhamny,
Laenggeng and Moonti, 2018), children with more
nutritional status have a poor diet due to the number
of types and amount of food consumed is not healthy
and the mother's lack of understanding about
balanced nutrition. Mothers are more likely to
provide fast food, fatty foods and also foods that are
high in carbohydrates. Not only food, but the high
consumption of formula milk also cause obesity in
children.
Children with less physical activity can also
result in the occurrence of more nutritional value. If a
poor eating pattern is not matched by physical
activity, there will be an imbalance between the
energy that enters and the energy that goes out. So
that energy will be stored in the body in the form of
fat. (Warhamny, Laenggeng and Moonti, 2018). The
impact of increasingly sophisticated technology
makes children reluctant to do physical activities such
as exercise, playing in the park with friends. Children
tend to prefer not to do many activities such as
watching television, playing video games where for
hours. These habits are sometimes also offset by the
availability of snacks, so children enjoy it for hours
(Era, 2012).
Overweight occurs as a result of the disruption
of the homeostatic mechanism that controls the
energy balance in the body. Fat tissue is the biggest
place to store energy. The storage energy of
triglycerides is through the process of lipogenesis.
Regulation of energy balance requires a sensor of
energy storage in adipose tissue. The control
mechanism originating from the hypothalamus
carries out further integrase. Where, the process will
determine the body's intake and energy expenditure
need (Utami, 2017).
Lipogenesis is a process of fat deposition and
includes the process of fatty acid synthesis, and then
the triglyceride synthesis will occur in the liver in the
mitochondrial region, cytoplasm, and also in adipose
tissue. The process of lipogenesis is partly mediated
by hormones that can inhibit (for example, growth
hormone, Leptin) or stimulate (such as insulin)
lipogenesis. Insulin stimulates lipogenesis by
HSIC 2019 - The Health Science International Conference
242

increasing glucose uptake in adipose tissue through
glucose transporters to the plasma membrane,
activating lipogenic and glycolytic enzymes, and
causing SREBP-1 (Sterol Regulatory Element
Binding Protein-1) increases expression and action of
glucokinase enzymes that result in increased
metabolic concentrations, and causes SREBP -1
(Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein-1)
increases expression and action of glucokinase
enzymes that result in increased metabolic
concentrations. Glucose. Leptin, by the contrary,
works, limiting fat storage by reducing food input
(increasing expression of the Corticotropin-Releasing
Factor gene in the hypothalamus resulting in
decreased food requirements) and influencing
specific metabolic pathways in adipose and other
tissues. Leptin sends signals to the brain about the
amount of fat storage. This hormone stimulates the
release of glycerol from adipocytes by stimulating
fatty acid oxidation and inhibiting lipogenesis
(Utami, 2017).
Lipolysis is the process of chemical
decomposition and release of fat from fat tissue.
Hormone Sensitive Lipase (HSL) enzyme causes the
hydrolysis of triglycerides into free fatty acids and
glycerol. Fatty acids then undergo a process of re-
esterification, then released into the blood circulation,
formed into ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), and then
brought into the circulation of blood, which will then
become a source of energy for tissues in need. The
hormone insulin inhibits the mobilization of fatty
acids from fatty tissue. Energy expenditure is
determined by physical activity, metabolic rate, and
thermogenesis. The metabolic part of energy
expenditure includes the work of the individual
cardio-respiratory. Physical activity increases energy
expenditure by activating skeletal muscle work
(Utami, 2017).
The results of research on the benefits of
rhythmic gymnastics, according to Mukhloid (2014)
in (Prihatin, 2016) is rhythmic gymnastics can burn
excess fat in the body so that it is good as a program
for weight loss. Rhythmic gymnastics is also able to
improve the appearance of several parts of the body,
such as hips, thighs, waist, abdomen, arms, and legs.
In line with research conducted by Faridah (2012)
that rhythmic gymnastics can reduce weight and also
increase muscle flexibility. Rhythmic gymnastics can
lose weight because it is aerobic exercise.
Copra (1996), in Silalahi (2017), rhythmic
gymnastics is one of the aerobic exercises. Aerobic
exercise is an exercise that requires oxygen as a form
of energy that is done continuously, rhythmically, by
involving large muscle groups. Sharkey in (Andini,
2016) aerobic exercise can increase the function and
capacity of the respiratory and cardiovascular
systems and blood volume, but the most significant
changes occur in the muscle fibers used during
exercise. Aerobic exercise increases the ability of
muscles to produce energy aerobically and changes
the metabolic process from carbohydrates to fat.
Aerobic exercise can overcome excess
cholesterol as well as achieve a good level of physical
fitness and can improve functional abilities
(Richmond, 2012). When exercising, movements in
the body can occur because of the muscles contract.
Muscle contractions require ATP (Adenosine Tri
Phosphate). Energy obtained from potential energy is
in the form of energy stored in food in the form of
chemical energy. The energy will be released after the
metabolism of food is processed in the body. The
process of aerobic energy metabolism is a metabolic
process that occurs within the mitochondria and
requires the presence of oxygen (O2) so that the
process can run perfectly to produce ATP (Joyner and
Coyle, 2008). When exercising, both of the body's
energy stores, namely carbohydrate (blood glucose,
glycogen) deposits, as well as fat deposits in the form
of triglycerides, will contribute to the rate of aerobic
energy production in the body. Kusumaningtyas
(2011) explained that energy stores would be used by
the body, namely carbohydrate storage (glucose,
glycogen), fat, and protein. Among the three, savings
carbohydrates and fats are the main energy sources
during the aerobic process. The aerobic system
requires oxygen to break down glycogen/glucose into
CO and H2O through the Tricarboxylic acid cycle
(TCA) and electron transport systems (Awaliyah,
2014).
The aerobic system is used for sports that
require more than 3 minutes of energy, such as
marathon running and 1500-meter freestyle
swimming. There are three stages of chemical
reactions that always occur in the aerobic system,
namely aerobic glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the
electron transport system (Hecht, 2015). The aerobic
system can be used for the breakdown of glycogen
and fat which can be used for large ATP resynthesis
without the formation of side effects, which can cause
muscle fatigue, as in the lactate system (Frutuoso et
al., 2016). The production of body heat that is
produced during the breakdown of glycogen or fat,
half of it is used for ATP resynthesis to become ATP
energy. Some are released as heat stored in the body,
and others are lost out (Adiwinanto, 2008). If the
intensity of the activity rises, carbohydrates are used,
whereas if the duration (length of time) of the activity
increases, then fat is used, and when carbohydrates
Rhythmic Gymnastics Effectively Reduce Body Mass Index in Weight Loss for Preschool
243

and fats are used up, the protein will be used (Sari,
2016).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The use of body fat in activities will cause a
reduction in stored fat. The demolition of stored fat
requires far more oxygen when compared to
unloading carbohydrates. In aerobic exercise, the
intensity of energy needed by the body is at a mild
level, and due to sufficient time, the cardiovascular
system is still able to meet the oxygen needs of the
working muscles, so fat oxidation is the main energy
source for muscle contraction. The use of body fat in
aerobic activity will cause a reduction in stored fat so
that it automatically reduces overall body weight.
REFERENCES
Adiwinanto, W. (2008) Effect Of School Exercise
Intervention On Body Mass Index And Physical Fitness
Of Obese, Program Pascasarjana Magister Ilmu
Biomedik Dan. Universitas Diponegoro Semarang.
Andini, E. A. (2016) ‘Perbedaan Pengaruh Frekuensi
Latihan Senam Aerobik Badan Pada Members Wanita
Di Cakra Sport Club Yogyakarta’, V(1), pp. 3–9.
Awaliyah, H. (2014) ‘Pengaruh Senam Zumba Terhadap
Perubahan Berat Badan Pada Mahasiswa Keperawatan
Yang Melakukan Senam Zumba Di Fakultas Ilmu
Kesehatan Uin Alauddin Makassar’.
Ayu, R. and Sartika, D. (2011) ‘Faktor Risiko Obesitas
Pada Anak 5-15 Tahun Di Indonesia’, 15(1), pp. 37–43.
Bobo-Arce, M. and Méndez-Rial, B. (2013) ‘Determinants
of competitive performance in rhythmic gymnastics. a
review’, Journal of Human Sport and Exercise. doi:
10.4100/jhse.2013.8.Proc3.18.
Cyrilla, V. et al. (2017) ‘Artikel Penelitian Hubungan
Kebiasaan Mengonsumsi Makanan Cepat Saji dengan
Indeks Massa Tubuh pada Mahasiswa Fakultas
Kedokteran Ukrida Angkatan 2016 Periode September
2017 Relationship Between Habit of Fast Food
Consumption Against Body Mass Index in St’,
(September).
Ermona, N. D. N. and Wirjatmadi, B. (2018) ‘Hubungan
Aktivitas Fisik Dan Asupan Gizi Dengan Status Gizi
Lebih Pada Anak Usia Sekolah Dasar Di Sdn Ketabang
1 Kota Surabaya Tahun 2017 Relationship between
Physical Activity , Nutrition Intake and Overweight
Status among Elementary School Student in SD’, pp.
97–105. doi: 10.20473/amnt.v2.i1.2018.97-105.
Fernandez-Villarino, M. A., Bobo-Arce, M. and Sierra-
Palmeiro, E. (2013) ‘Practical skills of rhythmic
gymnastics judges’, Journal of Human Kinetics. doi:
10.2478/hukin-2013-0087.
Frutuoso, A. S. et al. (2016) ‘Lower Limb Asymmetries In
Rhythmic Gymnastics Athletes’, International journal
of sports physical therapy.
Hecht, S. (2015) ‘Handbook of Sports Medicine and
Science, Gymnastics’, Clinical Journal of Sport
Medicine. doi: 10.1097/jsm.0000000000000171.
Hilgers, R.-D., Heussen, N. and Stanzel, S. (2018)
‘Statistik, deskriptive’, in Lexikon der Medizinischen
Laboratoriumsdiagnostik. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-
49054-9_2900-1.
Joyner, M. J. and Coyle, E. F. (2008) ‘Endurance exercise
performance : The physiology of champions Endurance
exercise performance : the physiology of champions’, J
Physiol, 586 (Pt 1)(January 1), pp. 35–44. doi:
10.1113/jphysiol.2007.143834.
Kadi, K., Halida, H. and Yuniarni, D. (2018) ‘Senam Irama
Dalam Mengembangkan Kecerdasan Kinestetik Anak
Usia 5-6 Tahun Di TK Karya Yosef’, Jurnal
Pendidikan dan Pembelajaran.
Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia (2012) Profil
Kesehatan Indonesia. Jakarta.
Paiman (2009) Olahraga Dan Kebugaran Jasmani (
Physical Fitness ) Pada Anak Usia Dini Paiman SMPN
5 Wates Kulon Progo Yogyakarta.
Prihatin, R. (2016) ‘Pengaruh Kegiatan Senam Terhadap
Kecerdasan Konestetik Anak Kelmpok A di TK Pertiwi
II Metuk’.
Riset Kesehatan Dasar (2018). Jakarta.
Sari, S. P. (2016) ‘Upaya Meningkatkan Keterampilan
Motorik Kasar Melalui Senam Irama Pada Anak
Kelompok A TK Pertiwi Setda Kabupaten Sragen’,
(September).
Utami, N. A. (2017) Hubungan Pola Makan Dan Aktivitas
Fisik Terhadap Kejadian Overweight Dan Obesitas
Pada Remaja. Universitas Diponegoro.
Warhamny, W., Laenggeng, A. H. and Moonti, S. W.
(2018) ‘Hubungan Pola Makan Dan Aktivitas Fisik
Dengan Kejadian Obesitas Pada Anak Balita Di
Kelurahan Lolu Selatan Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas
Birobuli Kota Palu’, Jurnal Kolaboratif Sains, 1(1), pp.
736–744.
Warner, R. M. et al. (2018) ‘Health services research’,
Journal of Clinical Urology. doi:
10.1177/2051415818754578.
HSIC 2019 - The Health Science International Conference
244
