
Standard Operational Procedures Development for Government
Building’s Care and Maintenance Work of Outer Spatial and
Housekeeping Component to Improve Work Effectiveness and Efficiency
using Risk-based Approach
Lasita Khaerani, Yusuf Latief and Rossy Armyn Machfudiyanto
Department of Civil Engineering, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords:
Standard operational procedures, care, maintenance, outer spatial, housekeeping, efficient, effective, duration
Abstract:
The damage phenomenon that occurs in a building is something that is certain to happen considering that the
older the building is, the damage is something that cannot be denied. Regarding the damage, care and mainte-
nance work is needed to maintain the condition of the building in order to remain feasible. Nevertheless, the
reality in the field shows that the implementation of care and maintenance is often carried out in accordance
with the target because there is no clear implementation procedure. The purpose of this research is to de-
velop procedures for care and maintenance work of outer spatial and housekeeping component in government
building. The risk in question is a risk that affects the duration of work activity. The objects in this study
are located in the DKI Jakarta Province, especially in the X’s Institution Government Building. The research
methods used in this study are archival analysis, surveys, and case studies. The products produced in this
study are standard operating procedures for the care and maintenance work of outer spatial and housekeeping
component in government buildings to improve work efficiency and effectiveness.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today, the development of construction has acceler-
ated rapidly and has encouraged various construction
of high-rise buildings, such as office buildings, hotels,
shopping centers, hospitals, and others. Investment
in the construction sector is considered profitable and
able to encourage economic growth that can be en-
joyed by all levels of society. Based on information
from the Central Statistics Agency of DKI Jakarta
Province, with an area of 661.5 km2 and a popula-
tion of 5,244,690 people, developments in the con-
struction sector were able to trigger economic growth
because of the thousands of workers that construction
services could absorb.
As a national capital city, in order to organize and
support the performance of state governments, DKI
Jakarta has provided various buildings that have been
equipped with facilities and what’s in them to realize
good governance marked by the construction of gov-
ernment buildings. According to Law Number 28 of
2002, building is a physical form of construction work
that is integrated with its place of domicile, partially
or wholly above and / or in land and / or water, which
functions as a place for humans to conduct their ac-
tivities, whether for residential or residence, religious
activities, business activities, social activities, culture,
and special activities.
If functional buildings can still be used, risks
in use can be minimized by care and maintenance.
Maintenance of building is an activity to maintain the
reliability of buildings and infrastructure and facilities
so that building buildings remain functionally feasi-
ble (Minister of Public Works of the Republic Indone-
sia, 2008). Maintenance of building buildings aims to
maintain the buildings to reach the calculated age of
the plan (Rosalina, 2011). Meanwhile, building main-
tenance is an activity to repair and / or replace parts
of buildings, components, building materials, infras-
tructure and facilities so that buildings remain func-
tionally feasible (Minister of Public Works of the Re-
public Indonesia, 2008).
Based on Minister of Public Works Regulation
No.24 of 2008, there are several components in the
building, namely: architectural, structural, mechani-
cal, electrical, outer space, and housekeeping. The
scope of maintenance work on the components of
outer space is the maintenance of conditions from
274
Khaerani, L., Latief, Y. and Machfudiyanto, R.
Standard Operational Procedures Development for Government Building’s Care and Maintenance Work of Outer Spatial and Housekeeping Component to Improve Work Effectiveness and
Efficiency using Risk-based Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0009187202740284
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Science, Engineering and Technology (ICoSET 2019), pages 274-284
ISBN: 978-989-758-463-3
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

the surface of the land and / or the outer courtyard
of buildings, maintenance of elements of landscaping
outside and inside the building, maintaining cleanli-
ness outside buildings, gardens and the environment,
as well as carrying out garden maintenance efforts
correctly by officers who are experts and competent
in that field (Minister of Public Works of the Repub-
lic Indonesia, 2008). In the housekeeping component,
the scope of work covered are all housekeeping activ-
ities such as cleaning service, landscape, pest control,
and general cleaning, starting from preparatory, op-
erational work, to the final work result (Minister of
Public Works of the Republic Indonesia, 2008).
Phenomenon in the field shows that the many in-
accessibility of the objectives of the care and main-
tenance work of government buildings is a result of
lack of efficiency and effectiveness in carrying out
these two things. According to the Indonesian Dic-
tionary, one of the meanings of effective is to be use-
ful. The purpose of success is to bring a result after
doing a business. Meanwhile, some of the meanings
of the word efficient are precise and accurate, effi-
cient, and effective (KBBI). This means that all ef-
forts have been carried out correctly and accurately
without wasting time, energy, costs, and others.
Related to the previous explanation, to create a
proper building maintenance work, a building mainte-
nance work program is needed to achieve the planned
age of the building. However, the maintenance work
program will not run well if it is not accompanied
by implementation procedures. Standard operational
procedure of building’s care and maintenance work is
an important matter to be prepared so that the imple-
mentation of maintenance and maintenance activities
are done according to procedures, well scheduled, and
facilitates workers in carrying out maintenance and
maintenance activities (Mohammad et al., 2014).
2 OBJECTIVE RESEARCH
The objective of study is:
• Identifying the state of existing organizations in
government buildings in carrying out care and
maintenance work on government buildings (RQ
1).
• Identify tasks, responsibilities, and roles of re-
sources for implementing government building
care and maintenance work (RQ 2).
• Develop business processes related to the care and
maintenance work of the outer spatial and house-
keeping component of government buildings (RQ
3).
• Determine the length of duration needed for care
and maintenance work of the outer spatial and
housekeeping component of government build-
ings (RQ 4).
• Establish input and output from each activity of
maintenance work and care of components of the
outer spatial plan and governance of government
buildings (RQ 5).
• Identify the risks that may occur from each care
and maintenance activity of the outer spatial and
housekeeping component of government build-
ings (RQ 6)
• Develop communication flow in the process of
carrying out care and maintenance work of the
outer spatial and housekeeping component of gov-
ernment buildings (RQ 7).
• Develop standard operating procedures for the
care and maintenance work of the outer spa-
tial and housekeeping component in government
buildings using risk-based approach (RQ 8).
3 LITERATURE STUDIES
3.1 SOP for Building Care and
Maintenance of Government
Building
Standard operational procedure is a series of written
instructions standardized on various processes for or-
ganizing organizational activities, how and when to
do, where and by whom is carried out (Minister of
Administrative Reform and Bureaucratic Reform of
the Republic Indonesia, 2012). Based on the Guide-
lines for the Preparation of Operational Standards
in Government Administration Procedures within the
Secretariat General and the Expertise Board of the
People’s Representative Council of the Republic of
Indonesia (Representative Council of The Republic of
Indonesia, 2016), the standard operating procedure is
a standardized written instruction on the implementa-
tion of the tasks and functions of the General Secre-
tariat and DPR RI BK.
According to the Regulation of the Minister of
Administrative Reform and Bureaucratic Reform of
the Republic of Indonesia No. 35 of 2012 (Minister
of Administrative Reform and Bureaucratic Reform
of the Republic Indonesia, 2012), there are 2 elements
of standard operating procedures, namely:
• Identity Section This section contains logos, SOP
numbers, manufacturing dates, revision dates, ef-
fective dates from the entry into force of SOPs,
Standard Operational Procedures Development for Government Building’s Care and Maintenance Work of Outer Spatial and Housekeeping
Component to Improve Work Effectiveness and Efficiency using Risk-based Approach
275
endorsement by competent officials, titles, legal
basis, linkages, warnings, implementing qualifi-
cations, equipment and equipment, and recording
and data collection.
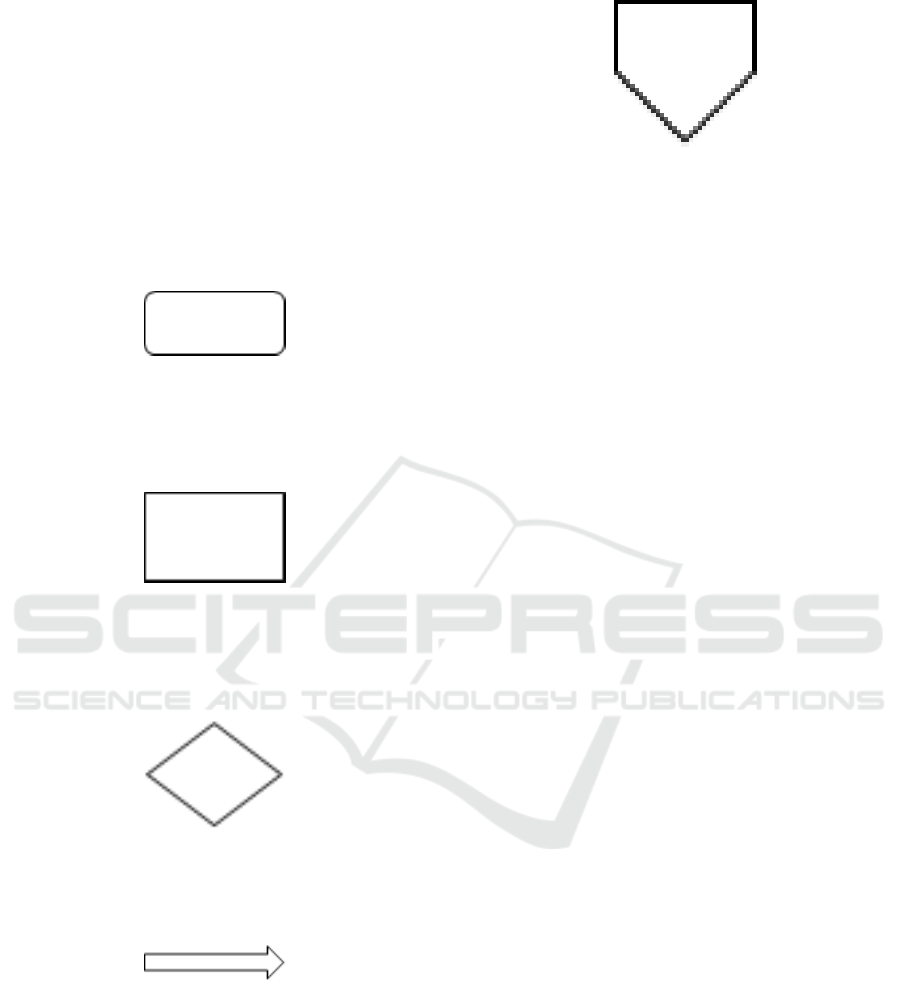
• Flowchart Flowchart is a description of the
steps in sequence of the standardized procedure.
Flowchart contained in the SOP document com-
munication flow is described with 5 symbols that
have different function which is illustrated in fig-
ure 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, they are:
– Capsule / Terminator Symbol
Figure 1: Capsule Symbol
Function: describes the start and completion of
activities
– Box Symbol / Process
Figure 2: Box Symbol
Function: describes the execution process or
activity
– Rhombus Symbol / Decision
Figure 3: Rhombus Symbol
Function: describes decision making activities
– Arrow Symbol / Arrow
Figure 4: Arrow Symbol
Function: describe the direction of the activity
process
– Pentagon Symbol / Off-Page Connector
Function: describes the relationship between
different symbol pages
3.2 Business Process
According to the Minister of Research, Technology
and Education Regulation of the Republic of Indone-
Figure 5: Arrow Symbol
sia No. 71 of 2017 (Minister of Research, Technol-
ogy, and Education of the Republic Indonesia, 2017),
business processes or governance is a set of structured
and interrelated work activities that produce output
according to user needs. In addition, (Paul, 2003) de-
fines business processes as a series of activities car-
ried out by a business from the initiation of input to
produce a number of output. Business process is a
key element in ensuring that activities are executed
in line with specified requirements (Machfudiyanto
et al., 2018).
The purpose of mapping and management (busi-
ness process) analysis is to see in full the whole set
of processes that affect the work and achievements
of the organization in serving key external and inter-
nal stakeholders (Minister of Administrative Reform
and Bureaucratic Reform of the Republic Indonesia,
2011).
The stages of mapping business processes accord-
ing to the Regulation of the Minister of Administra-
tive Reform and Bureaucratic Reform of the Republic
of Indonesia No. 12 of 2011, are:
• Understanding the organization’s strategic direc-
tion (vision, mission, tasks, and organizational
functions).
• Identifying management (business processes) to
be mapped based on needs analysis.
• Identifying the name and type of management
(business process) in question.
• Determining who are the main users or users of
the management (business process) in question.
• Describing the sequence of activities that form the
management chain (business process) in question.
• Determining the main input of management (busi-
ness process) in question.
• Determining the main management (business pro-
cess) output in question.
• Specifying the owner (owner) the management
(business process) in question.
ICoSET 2019 - The Second International Conference on Science, Engineering and Technology
276
3.3 Assignment Matrix (RAM / RACI)
RAM is a matrix that serves to show the resources
assigned to each work package. RAM describes the
responsibilities of the project team, group, or unit of
each component of work that exists (Institute, 2016).
One example of RAM is RACI which is shown in
table 1. RACI means responsible (executor), assign
(person in charge), consult (advisor), and inform (in-
formed).
Table 1: Example of RAM / RACI Matrix
Activities
Responsible Agency
Cisa Lisa Fisa Risa Tisa
1 R C I I I
2 A R C I I
3 I A R C I
4 I C A R I
The sample matrix above shows the work that
must be done in the left column and who is respon-
sible for the work in the column to the right of the
activity column using RACI.
3.4 Risk Management
Risk is a potential event that can be avoided or re-
duced as small as possible to minimize the impact ac-
cording to planning or permissible tolerance limits to
the intended target (Asiyanto, 2009). According to
(Institute, 2016), one method for analyzing risk is to
use qualitative risk analysis. Qualitative analysis is
a step to prioritize risk based on the possibility and
impact of risk. This study uses qualitative risk analy-
sis that refers to PMBOK to make a risk-related study.
The risk management process carried out in this study
is risk identification, qualitative risk analysis, and risk
response preparation.
4 METHODOLOGY
The object of this research is the buildings inside The
House of Representatives of the Republic of Indone-
sia (DPR RI) Complex. There are six buildings there
with Nusantara as the main building. Nusantara build-
ing consists of a plenary meeting hall with 1700 seat-
ing. The other five buildings are used as the office and
meetings rooms.
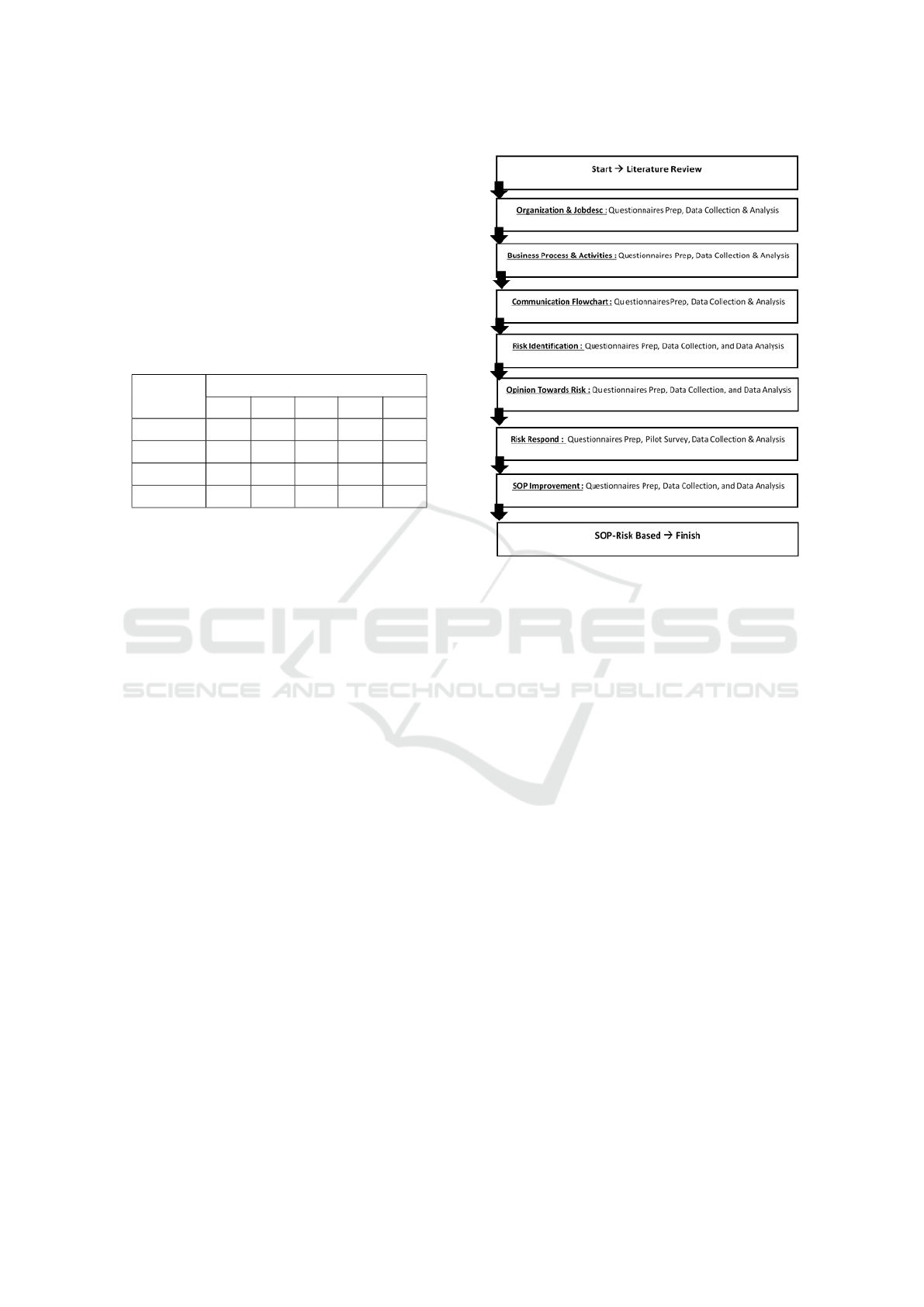
This research was conducted to answer the re-
search objectives by using 3 research strategies,
Figure 6: Research Process Flowchart
namely: survey, archive analysis, and case study. The
flow of research conducted is illustrated in figure 6.
At the end of this study, the products are stan-
dard operating procedures for the care and mainte-
nance work of the outer spatial and housekeeping
component in government buildings using risk-based
approach. Risks reviewed are occupational risks that
affect the duration because of the duration of the rela-
tion to efficiency and effectiveness of work. With the
development of standard operating procedures for the
care and maintenance work of the outer spatial and
housekeeping component, it is expected that care and
maintenance work can be carried out well.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
5.1 For Answering RQ 1 and RQ 2
5.1.1 Form of Organization Structure and Job
Description There Is Institution X
Government Building
In the first stage of data collection process, the au-
thor gave questionnaires to the three experts to be ver-
ified, clarified and validated. Experts validate the or-
ganizational structure and the distribution of job de-
scriptions by referring to the applicable regulations in
Standard Operational Procedures Development for Government Building’s Care and Maintenance Work of Outer Spatial and Housekeeping
Component to Improve Work Effectiveness and Efficiency using Risk-based Approach
277
the Secretariat General and the The House of Repre-
sentatives of the Republic of Indonesia (DPR RI) Ex-
pertise Agency. Those experts are the Head of State
Property Management Bureau of Institution X, the
Head of Building and Garden Division of Institution
X, and the Project Manager of Procedure from a na-
tion owned company. These three experts are the ones
who did all the validation needed for this research.
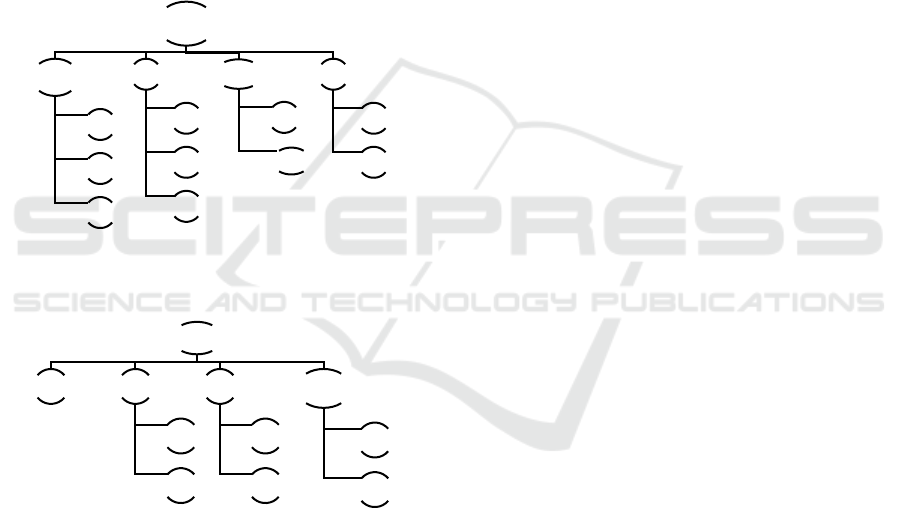
Based on the results of processing the first stage
of data collection taking into account the recommen-
dations of experts, the authors made several adjust-
ments to the existing form of organizational structure
because of the inequality of responsibilities between
one position and another. The previous organizational
structure and the results of developing a new organi-
zational structure are illustrated in figure 7 and 8:
State Property Management
Bureau
Administration
Division
Planning &
Utilization
Administration
Reporting
Building and
Installation
Building and
Garden
Mechanical
Electrical
Houses Management
Division
Kalibata
Houses
BoD & Ulujami
Hoses
Guest House
Management
Guest House
Maintenance
Guest House
Service
Figure 7: Organizational Chart Before Development
State Property
Management Bureau
Administration
Division
Building and
Installation
Building
Garden
Installation
Division
Mechanical
Electrical
Housing & Guest House
Management
Housing
Maintenance
Guest House
Service
Figure 8: Organizational Chart After Development
5.2 For Answering RQ 3, 4 and 5
5.2.1 Business Processes, Duration, and Inputs
and Outputs Activities for Maintenance
and Maintenance of Outer Spatial
Components and Governance of
Government Buildings
The second stage of the data collection process is to
determine the technical procedures for the care and
maintenance work of government buildings. This
stage begins with the collection of business pro-
cesses, activities, output, input, and the duration of the
care and maintenance work on government buildings
through literature studies and followed by validation
on experts.
Based on the literature study, 12 components of
building space and 26 components of building struc-
ture in the building were found. After being verified,
clarified, and validated by experts, we found a reduc-
tion of 7 outer spatial components and the addition of
4 components of housekeeping component, so that the
final total components produced by this study were
7 components of outer spatial and 30 components of
housekeeping.
There are several activities in each component of
care and maintenance work. The activity is then sup-
plemented with input, output, and duration of imple-
mentation in the form of documents. The example of
the details of each component that includes the activ-
ity, input, output, and the duration will be given at the
same time as the SOP product discussed in the next
discussion.
5.3 For Answering RQ 7
5.3.1 Communication Flow
The third stage of the data collection process is to
map the communication flow by defining the person
in charge and executor of each activity in each busi-
ness process.
After getting the organizational form, business
process, duration, input and output from the activities
in the work and maintenance of the outer spatial and
housekeeping component of government buildings,
the author makes communication flows that show the
relationship between activities that need to be done by
parties involved with the activity.
In the outer spatial component, there are seven
care communication flow charts and nine mainte-
nance communication flow charts. Whereas in the
housekeeping component, there are thirty mainte-
nance communication flowcharts and no care commu-
nication flowcharts.
The communication flow chart is made by refer-
ring to the results of data analysis in stage three which
is collected using the RAM / RACI method. The
RAM / RACI method is used to define the person
in charge of each activity. The communication flow
chart serves as an instrument that is useful for show-
ing those responsible (responsible) for an activity in
each business process.
Figure 9 is an example of the development of a
communication flowchart in one of the care and main-
ICoSET 2019 - The Second International Conference on Science, Engineering and Technology
278
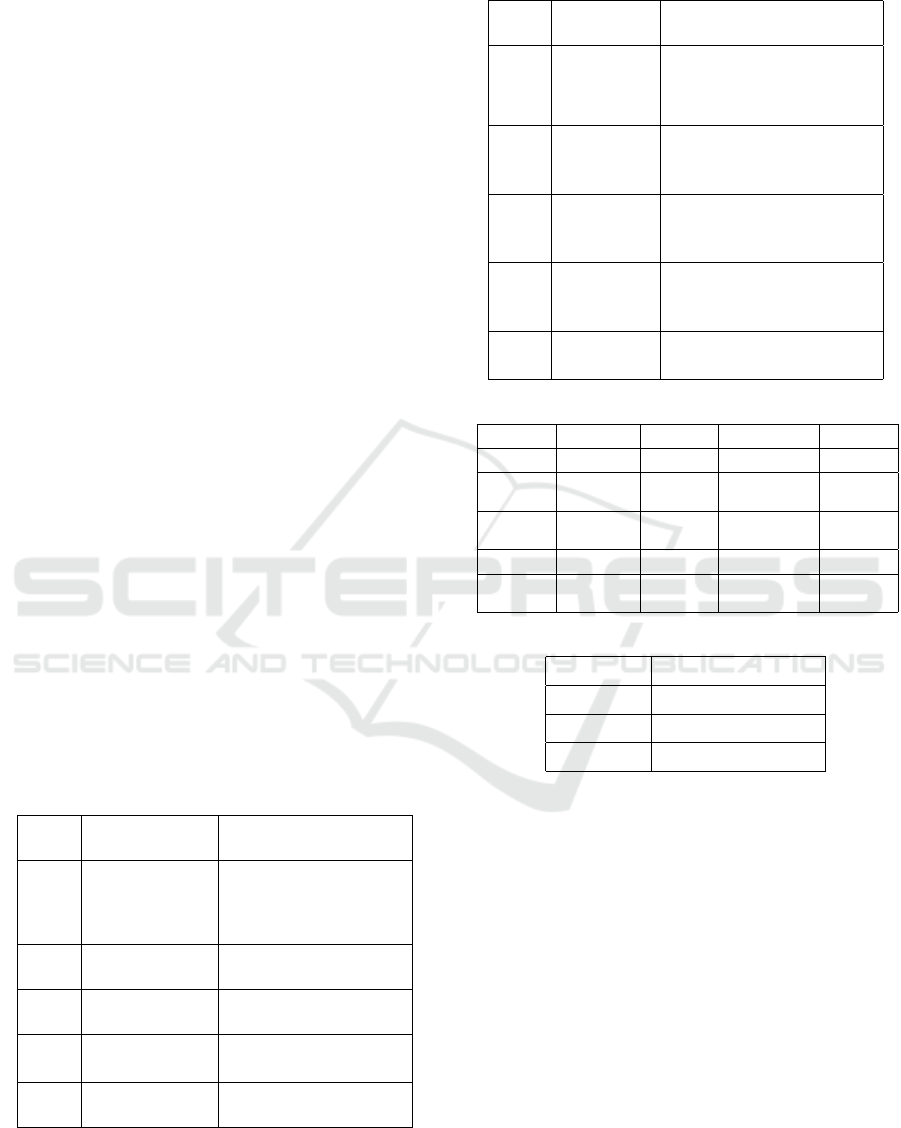
tenance work for the outer spatial and housekeeping
component that are part of the SOP.
5.4 For Answering RQ 6
5.4.1 Risk Identification
The fourth stage of data collection process is carried
out to identify the risks of each activity in each busi-
ness process by conducting a literature study and pro-
ceeding with the validation of the experts. Based on
the results of risk identification with a literature study,
there were 43 risks related to the duration of work that
could affect work efficiency and effectiveness.
After being verified, clarified, and validated by ex-
perts, 24 additional risks were obtained so that the to-
tal risk in the building maintenance and maintenance
work became 67 risks.
5.4.2 Risk Assessment (Qualitative Risk
Analysis)
The previously identified risks are then assessed for
frequency and impact through the fifth stage of data
collection carried out with the survey method of re-
spondents beginning with the pilot survey to deter-
mine whether all identified risks are understood.
The stages of risk analysis are carried out by re-
ferring to PMBOK 6th Edition as a guideline. Qual-
itative risk analysis is carried out by multiplying the
weighting results of the frequency and impact level,
then categorizing the results of the values according
to the risk criteria. The scale of frequency, impact,
and risk weighting used in this study are displayed in
table 2, 3, 4, and 5. They are:
Table 2: Scale Rating Frequency
Scale Frequency
Level
Remarks
1 Rarely
(rare)
Chance of occuring
is small and only
occur under certain
conditions
2 Few possibili-
ties (unlikely)
Can occur in a
condition
3 Maybe (possi-
ble)
Can occur occasionally
4 Frequent
(likely)
It may occur in many
circumstances
5 Almost certain
(almost certain)
Estimated to occur in
many circumstances
Based on the results of data processing using risk
qualitative analysis, 2 variables of the 67 variables
tested were considered high level risk. According
Table 3: Scale Rating Impact
Scale Impact
Rate
Remarks
1 Not sig-
nificant
(Insignifi-
cant)
Does not cause financial
losses and delays
2 Small Does not cause financial
losses and cause delays of
less than 1 day
3 Moderate Cause moderate financial
losses and cause delays of
less than 1 day
4 Severe A mild-moderate financial
loss and a delay of more
than 1 day
5 Disastrous A high financial loss and a
delay of more than 1 day
Table 4: Weighting frequency and impact
Value Criteria F Weight F Criteria D Weight D
1 Very Low 0,1 No effect 0,05
2 Low 0,3 Less influen-
tial
0,1
3 Moderate 0,5 Pretty Influ-
ential
0,2
4 High 0,7 Influential 0,4
5 Very High 0,9 Very influen-
tial
0,8
Table 5: Risk Category
Risk Score Risk Category (FR)
0,18 – 0,72 High Risk
0,06 – 0,17 Moderate Risk
0,01 – 0,05 Low Risk
to (Tan, 2011), it takes at least 10% of the variable
sample to conduct a further review of a research vari-
able. Therefore, the researcher took 7 risk events
from 67 variables to be followed up. The seven risk
events consist of 2 high level risks and 5 medium level
risks. Those high risk activity in the procedure for
care and maintenance and maintenance of outer spa-
tial and housekeeping components of the government
buildings are displayed in table 6.
5.4.3 Causes and Effects of Risk
The sixth stage of data collection is carried out to
identify the causes, impacts, and risk responses to
high-risk activities. This process is carried out using
literature studies followed by validation on experts.
As for the causes of the risk is displayed in table 7
and the impact of the risk in table 8.
Standard Operational Procedures Development for Government Building’s Care and Maintenance Work of Outer Spatial and Housekeeping
Component to Improve Work Effectiveness and Efficiency using Risk-based Approach
279
N
o
Activities
Implementation
Input
Output
Duratio
n
Remarks
Head of
State
Propert
y
Commitmen
t Officer
Head of
Buildin
g and
Garden
Head of
Building
Subdivisio
n
Civil
Workin
g Group
Thir
d
Party
Work
Inspecto
r
1
Provide a
schedule or
work
instructions /
repairs.
Disposition
Maintenanc
e Work
Schedule
and
Instructions
1 day
Done as
soon as
possible.
2
Making RKS
Implementatio
n of
Maintenance
Works
Maintenance
Work
Schedule and
Instructions
RKS
Concept
Maintenanc
e Work
1 month
3
Making HPS
Maintenance
Work
Implementatio
n
Maintenance
Work
Schedule and
Instructions
HPS
Maintenanc
e Work
Concept
1 month
4
Submitting
RKS for
Implementatio
n of
Maintenance
Works
RKS Concept
Maintenance
Work
RKS
Maintenanc
e Work
1 month
5
Submitting
HPS
Maintenance
Works
HPS
Maintenance
Work Concept
HPS
Maintenanc
e Work
1 month
6
Inform
maintenance
schedule in the
relevant ranks.
Maintenance
Work
Schedule
Schedule
Submission
Report
1 day
Done as
soon as
possible.
7
Prepare work
equipment.
Maintenance
Work
Schedule and
Instructions
Form
checklist
complete
tools
1 day
Work
equipment
prepared by
Building
Managemen
t is limited
to standard
routine
work
equipment.
8
Check
Uniform and
Identification
Completeness.
Schedule and
List of Officer
Names
Form
checklist
completenes
s officer
1 day
9
Conduct
periodic
checks.
Maintenance
Work
Schedule and
Instructions
Form check
list work
1 day
10
Check the zinc
cover
listplank.
1 day
11
Clean the
surface of
GRC with
emery no.2.
1 day
12
Re-paint with
emulsion
paint.
Form check
list previous
work
Form check
list work
1 day
13
Check the
results of
maintenance
work.
Form checklist
work
Maintenanc
e Work
Report
1 day
14
Report the
results of
maintenance
work.
Maintenance
Work Report,
Activity
Documentatio
n, Report
Progress 0%,
50%, and
100%
BA
Submission
of Job
Reports
1 day
NO
NO
YES
YES
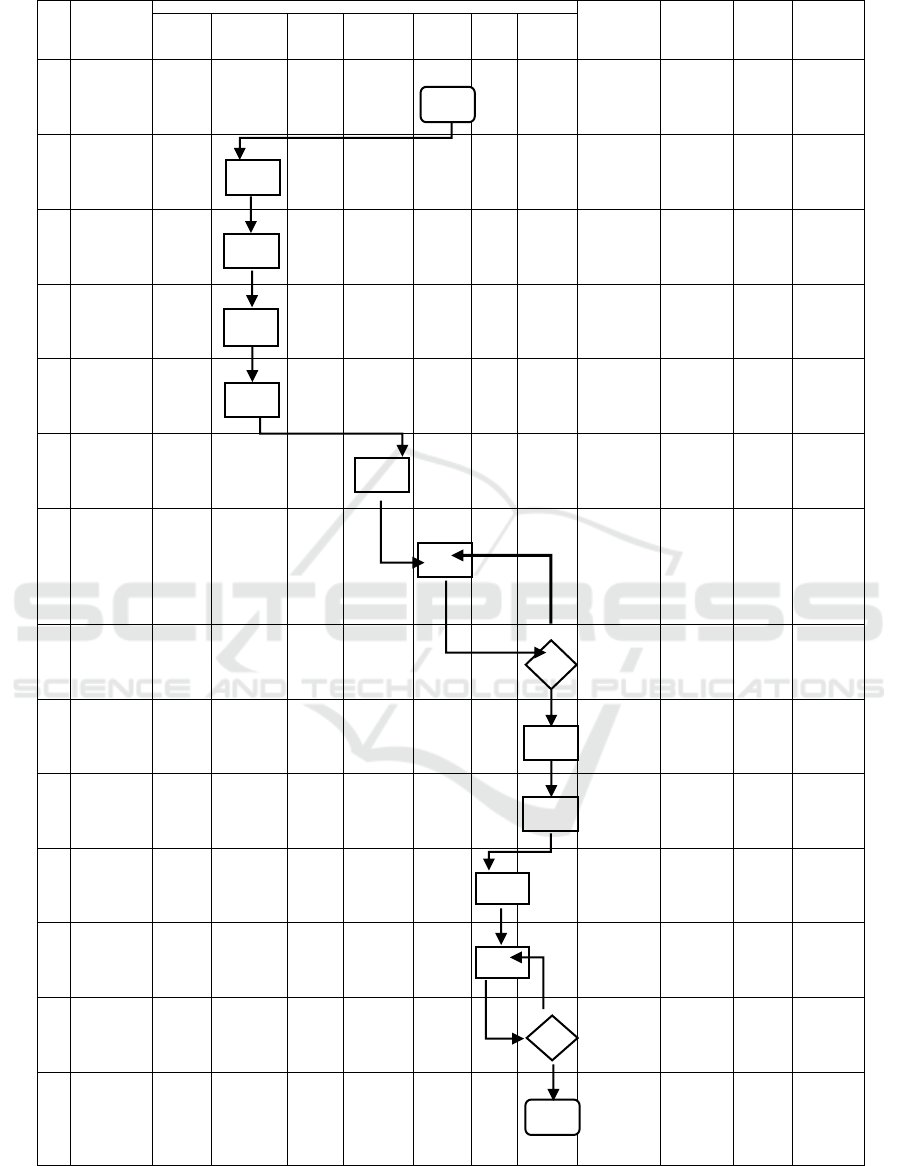
Figure 9: GRC Maintenance List Communication Flowchart
ICoSET 2019 - The Second International Conference on Science, Engineering and Technology
280
Table 6: High Risk Activities
Activities Code Risk Potential Risk
Level
Submitting Technical Proposals and Mainte-
nance Schedule.
X8 There are changes in conditions on the
ground that affect job demand.
High Risk
Submitting Technical Proposals and Mainte-
nance Schedule.
X7 Additional work / change in job demand Moderate
Making HPS Maintenance Work Implemen-
tation
X13 The incompatibility of specifications is deter-
mined by the conditions in the field
Moderate
Making HPS Maintenance Work Implemen-
tation
X11 Calculation error Moderate
Making HPS Maintenance Work Implemen-
tation
X12 Error determining specifications in making
HPS
Moderate
Provide schedules or maintenance work in-
structions
X2 Unclear work instructions Moderate
Submitting Technical Proposals and Mainte-
nance Schedule.
X5 Lack of workforce expertise Moderate
Table 7: Causes of Risk for Duration
Code Cause
P1 Incorrect design information
P2 Investigation of imperfect locations
P3 Bad communication
P4 Imperfect administration of contracts
P5 Uncontrolled external events
P6 Incomplete contract information
P7 Lack of coordination
P8 List of ingredients prices is not appropriate
P9 There is a new government policy
P10 Error math operations when counting
P11 typing / inputting data error
P12 Fatigue conditions when calculating RAB
P13 Job drawing errors as a guideline for
calculations
P14 Deliberately creating confusion for the
benefit of specific groups
P15 Poor ability to present instructions
(communication)
P16 Instructions are not well prepared
P17 Low education level
P18 Not Certified
P19 Not experienced
5.4.4 Risk Response
Based on literature studies and validation by experts,
it can be concluded that there are 14 preventive ac-
tions and 10 corrective actions that are shown in ta-
Table 8: Impact of Risk on Duration
Code Effect
D1 Work late
D2 Change of fees
D3 Work cannot be carried out
D4 There was a change after the technical doc-
ument and the file was created
D5 Late notice regarding changes in
conditions
D6 Price is not up to date
D7 There is a policy misuse
D8 Inaccurate calculations
D9 Invalid data
D10 RAB is wrong
D11 There is a deviation from the calculation
made
D12 Harm certain parties
D13 Inaccurate HPS
D14 Instructions cannot be understood
D15 It is not appropriate to determine the tech-
nical proposal
D16 It is not appropriate to determine the
schedule for carrying out the work
ble 9.
Standard Operational Procedures Development for Government Building’s Care and Maintenance Work of Outer Spatial and Housekeeping
Component to Improve Work Effectiveness and Efficiency using Risk-based Approach
281
Table 9: Preventive Action
Code Preventive Action
TP 1 Check conditions in the field
TP 2 Hold a coordination meeting routinely
TP 3 Providing communication training
TP 4 Check specifications used on HPS
TP 5 Update price lists regularly
TP 6 Adjust to changes
TP 7 Make gradual corrections when doing
calculations
TP 8 Stop working before getting tired
TP 9 Ensure that the image to be calculated has
been approved.
TP
10
Supervise in calculations
TP
11
Establish minimum competency standards
for instructors
TP
12
Checking education background
TP
13
Check worker certification
TP
14
Check worker experience
Table 10: Corrective action
Code Corrective action
TK 1 Review
TK 2 rework
TK 3 Hold a coordination meeting
TK 4 Aligning communication disagreements
TK 5 Recalculation
TK 6 Addendum to work contract / work
instruction
TK 7 There is a calculation adjustment
TK 8 Changes
TK 9 Certification
TK 10 Training
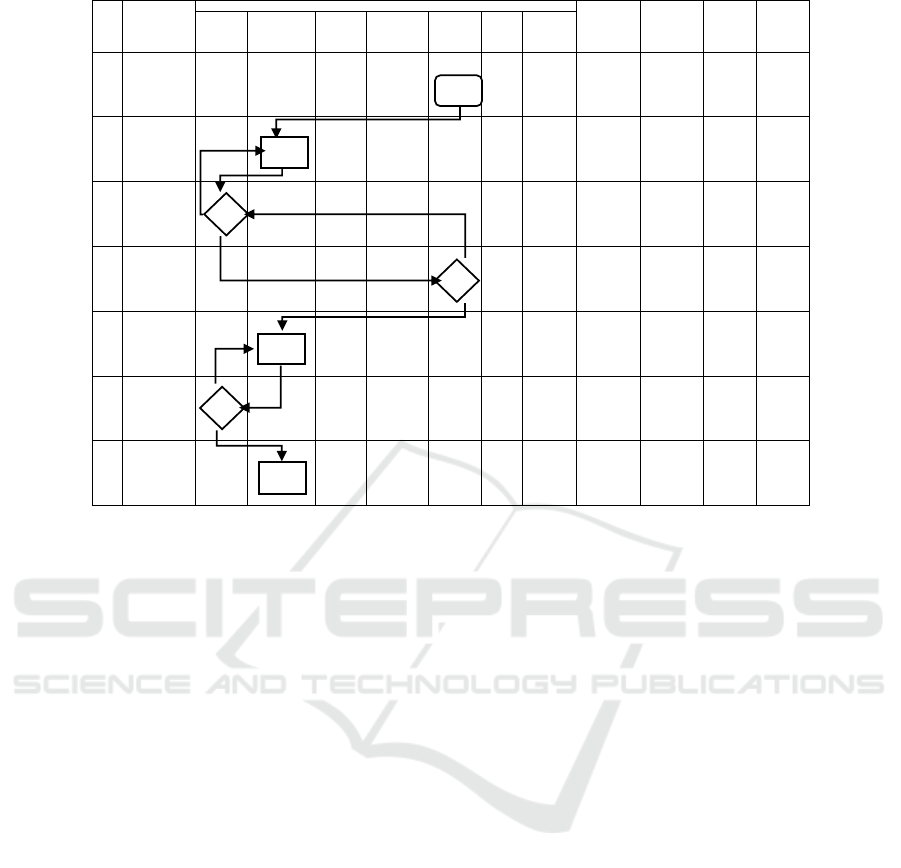
5.5 For Answering RQ 8
5.5.1 Risk-based SOP Development
Based on the results of the collection of risk responses
in the previous discussion, the authors carried out
the development of communication flowcharts for the
care and maintenance work of the outer spatial and
housekeeping components which are part of the SOP
by adding risk control activities.
Of the overall preventive actions and corrective
actions that have been collected, several supervisory
actions are chosen to be used as additional activities.
The results of the identification of risk responses that
are used as additional activities in care and mainte-
nance work are:
• Ensure that the image to be calculated has been
approved.
• Check specifications used on HPS
• Judicial review
• Check conditions in the field
• Hold a coordination meeting
Given that all high-risk activities are classified
as administrative activities, additional activities will
always be the same and are located at the beginning
of the work process. Apart from administrative
activities, there is no additional activity and the SOP
remains the same. Figure 10 shows an example of
developed SOP.
6 CONCLUSION
Based on the research that has been done, there are
several things that can be concluded.
First, it is necessary to adjust the organizational
structure of the Institution’s X State Property Man-
agement Bureau because of work imbalances in cer-
tain parts / sub-sections.
Second, adjustment of job description is required
in the Institution’s X State Property Management Bu-
reau following the adjustment of the organizational
structure.
Third, there are 7 business processes in the outer
space component and 30 business processes in the
housekeeping component of the care and maintenance
work of government buildings.
Forth, the duration of each activity in each busi-
ness process varies according to the level of difficulty
of each activity.
Fifth, inputs and output in each activity studied are
documents that are needed and produced when start-
ing and completing work.
Sixth, there are 67 risks that affect the duration
of all activities in the care and maintenance work of
government buildings.
ICoSET 2019 - The Second International Conference on Science, Engineering and Technology
282
No
Activities
Implementation
Input
Output
Duration
Remarks
Head of
State
Property
Commitment
Officer
Head of
Building
and
Garden
Head of
Building
Subdivision
Civil
Working
Group
Third
Party
Work
Inspector
1
Provide a
schedule or
work
instructions /
repairs.
Disposition
Maintenance
Work
Schedule
and
Instructions
1 day
Done as
soon as
possible.
2
Making RKS
Implementation
of Maintenance
Works
Maintenance
Work
Schedule
and
Instructions
RKS
Concept
Maintenance
Work
1 month
3
Ensure that
the image to
be calculated
has been
approved.
4
Check
specifications
used on HPS
5
Making HPS
Maintenance
Work
Implementation
Maintenance
Work
Schedule
and
Instructions
HPS
Maintenance
Work
Concept
1 month
6
Review
7
Submitting
RKS for
Implementation
of Maintenance
Works
RKS
Concept
Maintenance
Work
RKS
Maintenance
Work
1 month
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
Figure 10: Risk Based SOP
Seventh, There are 7 communication flowcharts
for the outer spatial component and 30 communi-
cation flowcharts for the housekeeping component
in the government building’s care and maintenance
work.
Lastly, in developing SOP for care and mainte-
nance work in government building, the authors use
the integration result of adjusted organizational struc-
ture and job description in Institution’s X State Prop-
erty Management Bureau to delegate the responsibil-
ities of each activity in each of the business processes
obtained. The SOP is presented in the form of docu-
ment communication flow. Activities in each business
process are added with risk prevention activities to an-
ticipate the risks that might occur. The risk prevention
activities are obtained from the risk identification pro-
cess that has been carried out previously.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank the financial support
provided by Universitas Indonesia through PITTA
B funding scheme under grant number NKB –
0803/UN2.R3.1/HKP.05.00/2019 managed by Direc-
torate for Research and Public Services (DRPM) Uni-
versitas Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Asiyanto (2009). Risk Management for Contractors. Pradya
Paramita, Jakarta.
Institute, P. M. (2016). Project Management Book of
Knowledge (PMBOK GUIDE) 6th Edition. PMI In-
donesia Chapter, Jakarta.
Machfudiyanto, R. A., Latief, Y., Soepandji, B. S., and Pu-
tri, P. A. (2018). Improving business processes to de-
velop standard operation procedures on government
building maintenance work in indonesia. In MATEC
Web of Conferences, volume 195, page 06006. EDP
Sciences.
Minister of Administrative Reform and Bureaucratic Re-
form of the Republic Indonesia (2011). Regulation
from Minister of Administrative Reform and Bureau-
cratic Reform of the Republic Indonesia No.12 of
2011.
Minister of Administrative Reform and Bureaucratic Re-
form of the Republic Indonesia (2012). Regulation
from Minister of Administrative Reform and Bureau-
cratic Reform of the Republic Indonesia No.35 of
2012.
Minister of Public Works of the Republic Indonesia (2008).
Regulation from Minister of Public Works of the Re-
public Indonesia No.24 of 2008.
Minister of Research, Technology, and Education of the Re-
public Indonesia (2017). Regulation from Minister of
Research, Technology and Education of The Republic
of Indonesia No. 71 of 2017.
Standard Operational Procedures Development for Government Building’s Care and Maintenance Work of Outer Spatial and Housekeeping
Component to Improve Work Effectiveness and Efficiency using Risk-based Approach
283

Mohammad, A., Resty, A., Marsudi, and Martono (2014).
Maintenance Management Model for Building Archi-
tectural. Semarang State Polytechnics, Semarang.
Paul, H. (2003). The Evolution of Business Process Man-
agement. DCI BPM, New Orelans.
Representative Council of The Republic of Indonesia
(2016). Guidelines for the Preparation of Opera-
tional Standards in Government Administration Pro-
cedures within the Secretariat General and the Exper-
tise Board of the People’s Representative Council of
the Republic Indonesia.
Rosalina (2011). Building Maintenance System Judging
From the Reliability of Buildings (Case Study: Simple
Rental Flats in Cilangkap Regency). Sebelas Maret
University, Surakarta.
Tan, D. W. (2011). Project finance in construction: A struc-
tured guide to assessment. Construction Management
and Economics, 29(10):1074–1075.
ICoSET 2019 - The Second International Conference on Science, Engineering and Technology
284
