
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) User Acceptance Model with
Easy to Use as Intervening Variable
Arifin Lubis, Rustam, and Iskandar Muda
Accounting Departement, Economic & Bussiness Faculty, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Easy to Use, Village Government, Enterprise Resource Planning
Abstract: The purpose of this research is to know the influence of technological resistance, understanding of task,
human resources, financial supporting and training to the successful implementation of the Village
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Base Application with Easy to Use as intervening variable. The type of
this research is descriptive quantitative with the sample respondent of 84 Village Owned Enterprises in
Central Tapanuli Regency, North Sumatera, Indonesia. The statistical tool of this research is with Structural
Equation Modeling with of Smart-PLS software. The results show that financial supporting and training to
the successful implementation of the Village Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Base Application and
technological resistance, understanding of task and human resources are not influence. The Easy to Use as
intervening variable is not influence.
1 INTRODUCTION
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is an integrated
system that supports the core business activities of
an organization which includes manufacturing,
logistics, finance, accounting, sales, marketing, and
humanresources (Nah et al., 2004, Pasaoglu, 2011,
Alsoub et al., 2018). An ERP system will help parts
of an organization to share data and information,
reduce costs, and improve management of business
processes. With the benefits offered by the system,
many companies are tempted to implement it. In
increasing the income of the community and
villages, the Village Government can establish a
Village Owned Enterprise in accordance with the
needs and potential of the village. The establishment
of Village-Owned Enterprises is stipulated by
Village Regulations based on the laws and
regulations. The form of Village-Owned Enterprises
as referred to in paragraph must be a legal entity. In
accordance with the mandate of the Village Law No
6/2014 every village needs to establish a BUMDES,
as one of the efforts to empower the community
while increasing Village Original Revenue (Suriadi
et al., 2015). Furthermore, the Ministry of Villages,
Transmigration and Disadvantaged Regions has
issued Ministerial Regulation No 4/2015 on
BUMDES. Welcoming this the Regional
Governments should also have issued a Regional
Regulation on Procedures for the Formation and
Management of Village-Owned Enterprises.
However, of the many villages that have formed
BUMDES, the level of management and knowledge
of HR capacity has not been maximized.
BUMDES Financial Management is sourced
from state finances (Village Funds), it is necessary
to pay attention to the rules in recording and
reporting accounting standards. If not careful, the
BUMDES manager can be dragged into legal
problems due to not paying attention to the
accounting problems of Bumdes. The main principle
that needs to be considered in the recording and
financial reporting of BUMDES is which accounting
standard will we use as a basis? This is important,
because in the future BUMDES Financial Report
will be audited. The audit process is the process of
comparing notes and reports that are made with
applicable standards. There are several financial
accounting standards (SAK) that can be referred to
for the compilation and recording of BUMDES
accounting, one of which is Entity Accounting
without Public Accountability (ETAP). This ETAP
Financial Accounting Standard is a fairly simple and
practical accounting standard used as a reference for
preparing BUMDES financial statements (Suriadi et
al., 2015).
Lubis, A., Rustam, . and Muda, I.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) User Acceptance Model with Easy to Use as Intervening Variable.
DOI: 10.5220/0009197500090014
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 9-14
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
9

The use of information technology based on
Computer Accounting Applications whose job is to
obtain financial reports automatically, quickly and
has a better level of accuracy than manually
(Amoako et al., 2004, Turetkenet al., 2019,
Youngberget al.,2019 and Zabukovšek et al., 2019).
Have the ability to display data quickly, easily and
efficiently. Having a security system in the form of a
password, can present comparative financial
statements in accordance with the data in the desired
period. Benefits of Computerized Accounting is to
use information technology based on Computer
Accounting Applications whose job is to obtain
financial reports automatically, quickly and have a
better level of accuracy than manually (Widjaja et
al., 2018 and Sternad et al., 2019). Have the ability
to display data quickly, easily and efficiently. Has a
security system in the form of a password, can
present comparative financial reports in accordance
with the data in the desired period. BUMDES
Financial Application, is an application developed to
help the financial management and administrative
management of BUMDES, BUMDES Financial
Applications are developed based on daily
operational needs that will be met when running
BUMDES, by adopting other financial business
entities. So that the flow and reporting meet
financial reporting standards. Althunibat et al (2019)
states that if you want to implement an ERP system,
the infrastructure includes production, payroll, sales,
purchasing and financial reporting. All activities are
integrated as a whole and carried out simultaneously
through one window.
Bhattacharya et al (2019) discusses The
Effectiveness of the Accounting Information System
Under the Enterprise Resources Planning (ERP)
states that the ERP system will support and create an
effective running of the organization. The research
needs to be followed up on the scale of government
organizations so that it can be seen how effective the
system is capable of creating effectiveness in local
government. Based on the results of research by
Beselga and Alturas (2019) that the success of ERP
implementation is measured by the resulting
financial statements. The success of the system is in
harmony with the perception of its users (users) and
has an impact on service. The conclusion of his
research states that the implementation of ERP
systems can improve the timeliness in publishing
financial reports. These results indicate that the ERP
system is able to shorten the flow of the process of
making financial statements because of its ability to
coordinate and integrate information data across
business processes. A fundamental question is
whether non-profit organizations such as local
governments are ready to run ERP where the local
government is currently implementing Regional
Management Information System where the
component is one of the ERP infrastructure applied.
2 METHOD
This study uses primary data.The hypothesis was
tested by using Structural Equation Modeling with
SMART PLS software 3.0. The data analysis
technique in this research employed Structural
Equation Modeling (SEM). The equationisformed as
follows:
Y = α + b1X1 + b2X2 + b3X3+ b4X4 +
b5X5+b6Z+e
X1 = Technological Resistance
X2 = Understanding
X3 = Human Resources
X4 = Financial Supporting
X5 = Training
Z = Easy to Use
Y = Successful implementation of the
Village Enterprise Enterprise Resource Planning
(ERP) Base Application
b1,….b5 = Coefficient
α = Constant
e = Error
Analysis using SEM requires some suitability
index to measure the correctness of data and models.
3 RESULT
3.1 Result
3.1.1 Evaluation of Structural Model (Inner
Model)
The evaluation of inner model through the
bootstrapping menu also generates t-statistics values.
The criteria are t-statistic> 1.66 (value α = 5%, one
tail). The result of t-statistics value in the table path
coefficients is presented in the following Figure 1 as
a follows :
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
10
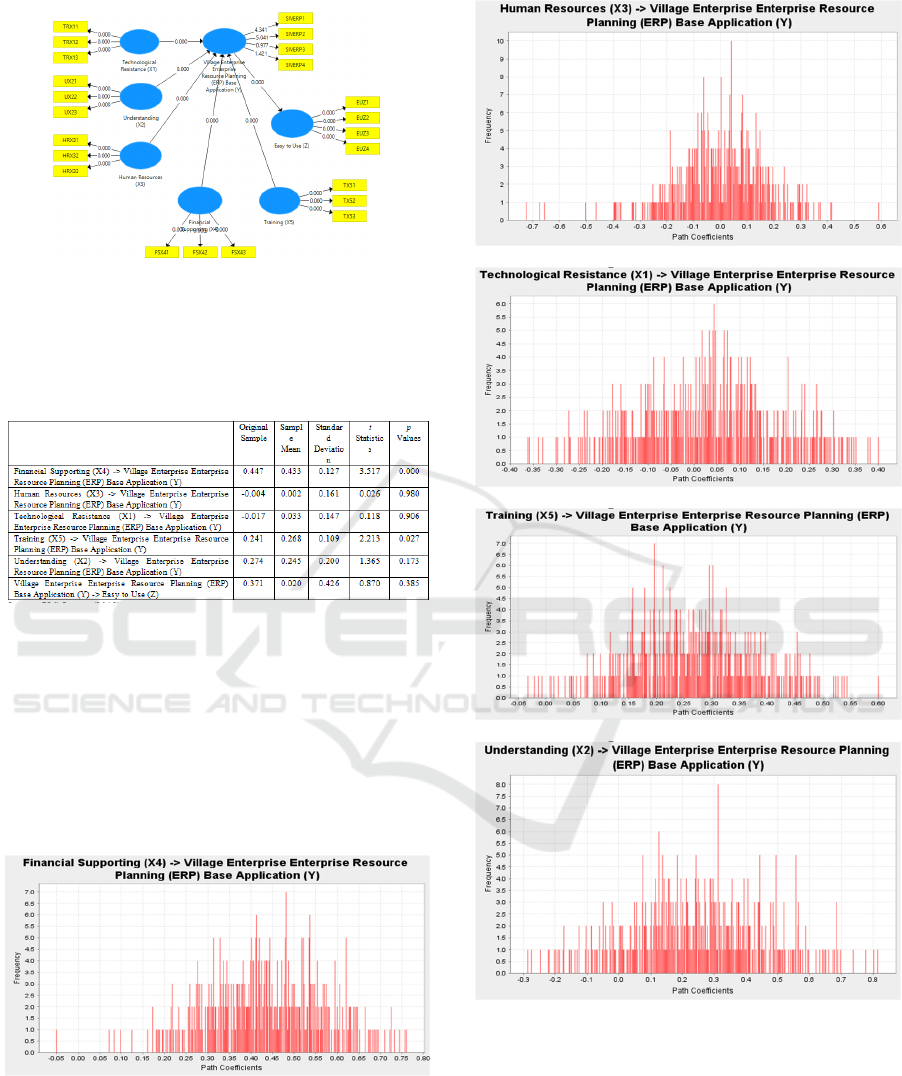
Figure 1. Overall Model with Coefficient
The statistic result of this research in the following
Table1 :
Table 1. Path Coefficients
Source: PLS Output (2019).
These results show that the financial supporting
and training to the successful implementation of the
Village Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Base
Application andtechnological resistance,
understanding of task and human resources are not
influence. The Easy to Use as intervening variable is
not influence.The path coefficient generated is in the
following Figure as a follow :
Source: PLS Output (2019).
Source: PLS Output (2019).
Source: PLS Output (2019).
Source: PLS Output (2019).
Source: PLS Output (2019).
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) User Acceptance Model with Easy to Use as Intervening Variable
11
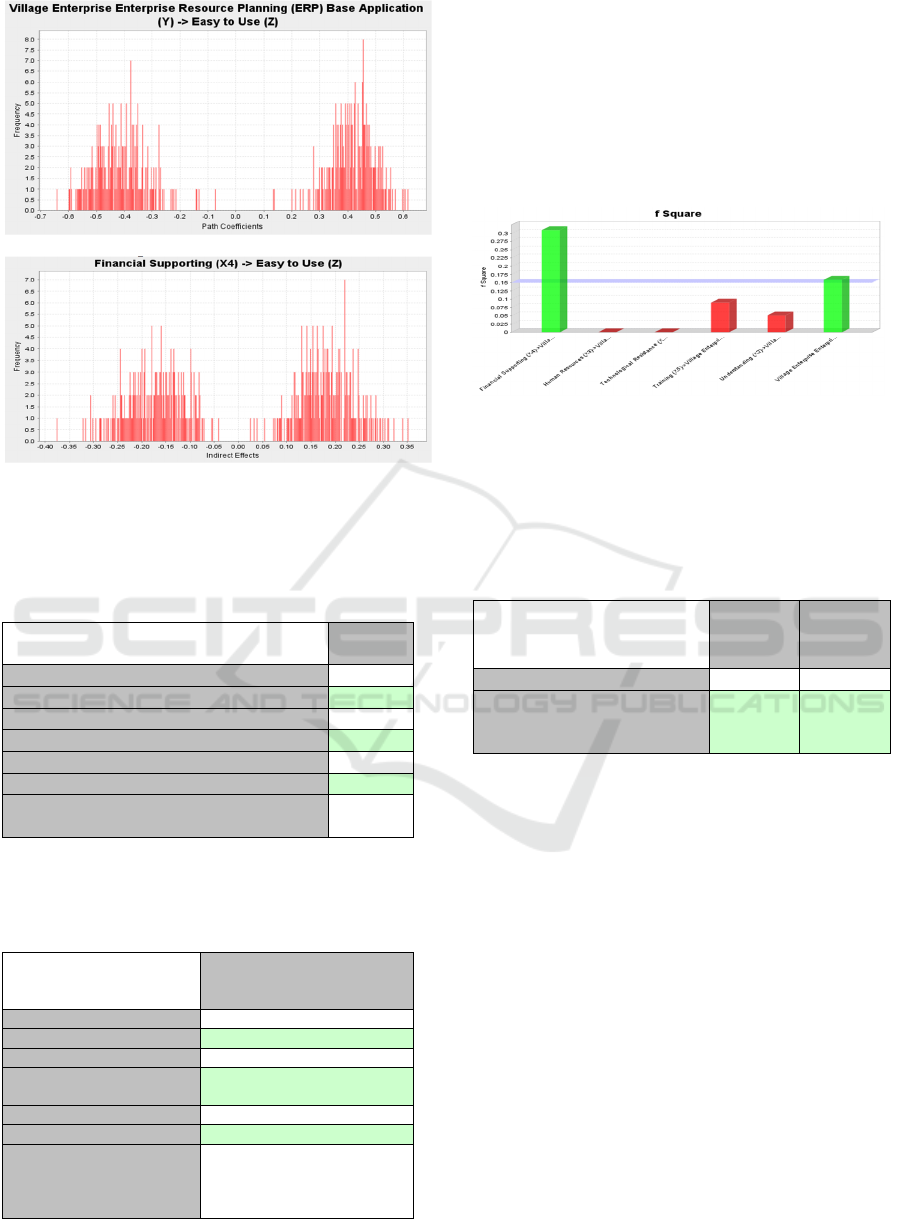
Source: PLS Output (2019).
Source: PLS Output (2019).
Figure 2. Path Coefficient Figure
The statistic result in the following Table2 :
Table 2. Indirect Effects Total
Easy to
Use (Z)
Easy to Use (Z)
Financial Su
pp
ortin
g
(
X4
)
0.166
Human Resources
(
X3
)
-0.002
Technolo
g
ical Resistance
(
X1
)
-0.006
Training (X5) 0.089
Understanding (X2) 0.101
Village Enterprise Enterprise Resource
Planning (ERP) Base Application (Y)
Source: PLS Output (2019).
The Total Effect show inTable 3 as a follows :
Table 3. Total Effects
Village Enterprise Enterprise
Resource Planning (ERP)
Base Application (Y)
Easy to Use (Z)
Financial Supporting (X4) 0.447
Human Resources (X3) -0.004
Technological Resistance
(X1)
-0.017
Training (X5) 0.241
Understanding (X2) 0.274
Village Enterprise
Enterprise Resource
Planning (ERP) Base
Application (Y)
Source: PLS Output (2019).
The results of the Table show that through the
Financial Supporting variable is the strongest
traversed by the Easy to Use variable. In addition to
hypothesis testing through the bootstrapping menu
that produces t-statistics, inner model evaluation is
also done by reviewing the R-Square value. The R-
square value generated from the inner model
evaluation is presented in the following Figure 3 :
Source: PLS Output, (2019)
Figure 3. F Square
The results show from the Figure 3 show that
financial supporting and training are significant. The
R Square show in Table 3 as a follows :
Table 3. R-Square Value
R
Square
R
Square
Adjusted
Eas
y
to Use
(
Z
)
0.138 0.127
Village Enterprise Enterprise
Resource Planning (ERP)
Base A
pp
lication
(
Y
)
0.452 0.415
Source: PLS Output. (2019).
The results showed a coefficient of determination
equal to 41.5 %.
3.2 Discussion
ERP is part of the entity's infrastructure and is very
important for the survival of the company. Everyone
and the part that will be affected by the ERP must be
involved and provide support. ERP exists to support
business functions and increase productivity, not
vice versa (Calisir et al., 2009, Lim et al., 2005,
Seymour et al., 2007 and Regmi et al., 2019). The
purpose of ERP implementation is to improve the
competitiveness of rural business entities. There are
certain methodologies for ERP implementation that
are more guaranteed success. What needs to be done
is to identify the risks involved in ERP
implementation and then how to manage them. The
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
12

potential for successful implementation will be even
greater if these risks can be minimized.
Strengthen the ability of implementation to
estimate the resources and time needed to carry out
functions in ERP implementation projects. This
inability is generally caused by less detailed
planning, which is usually due to a lack of
experience and knowledge of the project
management team regarding similar work. It could
also be due to the misperception of the implementers
of the scope of work as outlined in the standard for
various reasons (Fiaz et al., 2018, Hasan, 2018, Ding
et al., 2019 and Okcu et al., 2019). Or because the
initial planning was made only for the needs of
fulfilling administrative compliance, for example for
the needs of auction selection, project charter,
billing, and the like
ERP systems tend to replace the old system at
both the tactical and management levels. Everything
must be run consistently which means the way that
is applied in running something must be the same for
all areas. Besides that special treatment will be
carried out in one area will not be realized without
changing the system configuration. Some of the
causes of ERP implementation failures are training.
The biggest difficulty lies in changing the practice of
work that must be done. Besides that training that
involves many modules should be carried out.
Companies must choose between changing business
processes to adjust the system or vice versa, with
implications in terms of cost and time to change the
system. Only a few organizations implement ERP
without consulting a consultant. However,
consultants often do acts that harm their clients by
not sharing responsibility.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The results show that financial supporting and
training to the successful implementation of the
Village Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Base
Application and technological resistance,
understanding of task and human resources are not
influence and Easy to Use as intervening variable is
not influence.
REFERENCES
Alsoub, R. K., Alrawashdeh, T. A., &Althunibat, A. 2018.
User Acceptance Criteria For Enterprise Resource
Planning Software Systems. International Journal Of
Innovative Computing Information And Control,
14(1), 297-307.
Althunibat, A., Zahrawi, A. A., Tamimi, A. A.,
&Altarawneh, F. H. 2019. Measuring the Acceptance
of Using Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) System
in Private Jordanian Universities Using TAM Model.
International Journal of Information and Education
Technology, 9(7).
Amoako, G.K., & Salam, A. F. 2004. An extension of the
technology acceptance model in an ERP
implementation environment. Information &
management, 41(6), 731-745.
Beselga, D., & Alturas, B. 2019. Using the Technology
Acceptance Model (TAM) in SAP Fiori. In World
Conference on Information Systems and Technologies
(pp. 575-584). Springer, Cham.
Bhattacharya, M., Wamba, S. F., &Kamdjoug, J. R. K.
2019. Exploring the Determinants of ERP Adoption
Intention: The Case of ERP-Enabled Emergency
Service. International Journal of Technology Diffusion
(IJTD), 10(4), 58-76.
Calisir, F., AltinGumussoy, C., & Bayram, A. 2009.
Predicting the behavioral intention to use enterprise
resource planning systems: An exploratory extension
of the technology acceptance model. Management
research news, 32(7), 597-613.
Ding, Q., Wang, X., Tian, J., & Wang, J. 2019.
Understanding the Acceptance of Teaching Method
Supported by Enterprise WeChat in Blended Learning
Environment. In 2019 International Symposium on
Educational Technology (ISET) (pp. 211-214). IEEE.
Fiaz, M., Ikram, A., & Ilyas, A. 2018. Enterprise Resource
Planning Systems: Digitization of Healthcare Service
Quality. Administrative Sciences, 8(3), 38.
Hasan, B. 2018. Effects of General and ERP Self-Efficacy
Beliefs on the Acceptance of ERP Systems. Journal of
Information & Knowledge Management, 17(03),
1850031.
Lim, E. T., Pan, S. L., & Tan, C. W. 2005. Managing user
acceptance towards enterprise resource planning
(ERP) systems–understanding the dissonance between
user expectations and managerial policies. European
Journal of Information Systems, 14(2), 135-149.
Nah, F. F. H., Tan, X., &Teh, S. H. 2004. An empirical
investigation on end-users' acceptance of enterprise
systems. Information Resources Management Journal
(IRMJ), 17(3), 32-53.
Okcu, S., Koksalmis, G. H., Basak, E., &Calisir, F. 2019.
Factors Affecting Intention to Use Big Data Tools: An
Extended Technology Acceptance Model. In Industrial
Engineering in the Big Data Era (pp. 401-416).
Springer, Cham.
Pasaoglu, D. 2011. Analysis of ERP usage with
technology acceptance model. Global Business and
Management Research, 3(2), 157-165.
Regmi, R., Zhang, Z., Khanal, S., Zhang, H., & Kim, J.
2019. An empirical study on user acceptance of ERP
system by international students in Chinese HEIs: A
TAM approach. International Journal of Higher
Education, 6(1).
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) User Acceptance Model with Easy to Use as Intervening Variable
13

Seymour, L., Makanya, W., &Berrangé, S. 2007. End-
users’ acceptance of enterprise resource planning
systems: An investigation of antecedents. In
Proceedings of the 6th annual ISOnEworld conference
(pp. 1-22).
Suriadi, A, Rudjiman, Mahalli, K,,Achmad, N (2015). The
Applicative Model of The Village_Owned Enterprises
(BUMDES) Development In North Sumatera. Global
Journal of Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences 3(12),
48-62.
Sternad,Zabukovšek, S., Picek, R., Bobek, S.,
ŠišovskaKlančnik, I., &Tominc, P. 2019. Technology
Acceptance Model Based Study of Students’ Attitudes
Toward Use of Enterprise Resource Planning
Solutions. Journal of Information and Organizational
Sciences, 43(1), 49-71.
Turetken, O., Ondracek, J., &IJsselsteijn, W. 2019.
Influential characteristics of enterprise information
system user interfaces. Journal of Computer
Information Systems, 59(3), 243-255.
Widjaja, H. A. E., Larasati, A. P., Respati, R., &Ranaputri,
V. 2018. The Evaluation of Enterprise Resource
Planning (ERP) Financial Accounting and Control
Using Technology Acceptance Model. In 2018
International Conference on Computing, Engineering,
and Design (ICCED) (pp. 69-74). IEEE.
Youngberg, E., Olsen, D., & Hauser, K. 2009.
Determinants of professionally autonomous end user
acceptance in an enterprise resource planning system
environment. International journal of information
management, 29(2), 138-144..
Zabukovšek, S. S., Bharadwaj, S. S., Bobek, S., &Štrukelj,
T. 2019. Technology acceptance model-based research
on differences of enterprise resources planning
systems use in India and the European Union.
Engineering Economics, 30(3), 326-338.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
14
