
The Future and the Challenges of the Indonesian
Banking Industry in the Digital Era
Batara Maju Simatupang and Kevin Bastian Sirait
1Magister Management, Post-Graduate Program, STIE Indonesia Banking School, Jakarta, Indonesia
2Faculty of Economics, Parahyangan Catholic University, Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords: Technology, Digital Culture, Fintech, Indonesian Banking Industry.
Abstract: This article focuses on researching the IT challenges faced by the Indonesian banking industry in the digital
age. The rapid development of technology has provided benefits for the banking sector in integrating
technology to meet the demands of its customers. Although, this advantage comes with its challenges, as with
the emergence of the fintech (financial technology) industry. This study uses an action research method, which
is applied to identify challenges faced by conventional banks and provide solutions to overcome the identified
challenges. Based on the analysis, it was found that conventional banks have a gap between their digital
products and the expectations of their customers; in which majority of the respondent is engaging in the
implementation of open application programming interface (API) to facilitate the digital banking activities of
its customers via the software and the web-service product created by the Indonesian conventional banks. The
implication is that the IT gap between banking services and their customers must be overcome. For this reason,
it is recommended that conventional banks work together in order to meet customer expectations and/or banks
can use a customer-centric approach in product development.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid development and the implementation
of new technologies, all the existing industries have
started to use new technologies to improve their
operational and business activities. Some of the
industries have entered the phase of digitalization,
especially in the case of the banking industry.
According to the report produced by the company of
Frost & Sullivan (2019), it is shown that due to the
rapid development and increases of implementation
of technology in the case of internet penetration and
accessibility, the market revenue of electronic
commerce (e-commerce) is estimated to reach the
value of US$ 45.2 billion in 2019 and US$ 62.3
billion in the following year; to be precise, the aspect
of business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-
consumer (B2C) are said to be increasing in the area
of digital market in Indonesia. In other words, the
Indonesian banking industry may capitalize on this
opportunity to become the facilitator for the customer
in the e-commerce market to handle their digital
transactions, both in the domestic and international
transactions.
Despite the opportunity and the benefits of the
rapid development and implementation of new
technologies, the Indonesian banking industry may
have to consider the potential obstacles and
challenges of these advantages. One of the obstacles
faced by the banks of the digital era is the rise and the
emergence of financial technologies (fintech) firm. In
which, the product that is produced by the fintech
firm has some similarities with the product created by
the conventional banks. In general terms, the product
of the fintech firm has some feature that already exists
in the tradition banking product. Furthermore,
Anagnostopoulos (2018) stated that the product
created by the fintech firm is easier to use and faster
to fulfill the demand of digital transactions of its user
compared to the conventional bank, which means that
the product of the fintech firms creates challenges to
the Indonesian banking industry to facilitate the
domestic and international transaction in the field of
digital transactions.
Furthermore, the banking sector is one of the
sectors that are prone to disruptions (Fichman, et al.,
2014). To be precise, the disruptions which are
triggered by the rapid growth and development of
technologies. These disruptions are putting the
conventional banking industry at risk of maintaining
their position as an intermediary for their customers
in conducting digital transactions, especially in the
Simatupang, B. and Sirait, K.
The Future and the Challenges of the Indonesian Banking Industry in the Digital Era.
DOI: 10.5220/0009198100250033
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 25-33
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
25

case of creating an application that has a better
performance to the fintech firms. These disruptions
are enforced due to the fintech firms has the upper
hand on implementing their technological innovations
to provide better digital financial and banking
services compared to the conventional banks.
In regards to the obstacles and challenges faced
by the Indonesian banking industry, it is considered
naïve to believe that the emergence of fintech firms
solely creates these challenges. The other aspect that
needs to be considered in this matter is the changes in
the digital culture. In other words, it is about how the
banks' customers perceive the implementation and the
benefits of technology in fulfilling their needs in
banking and financial demand in a digital manner. It
is predicted that smartphone users will dominate the
banking market share by the year 2020 in regards to
digital transactions (AT Kearney, 2014; Wirdiyanti,
2018). By this prediction, the Indonesian banking
industry must understand the demands and needs of
its customers. Oshodin et al. (2017) explain that due
to the improvement of technologies enables the firm
to create an application or product in a customer-
centric manner to fulfill the needs and demands of the
customer and the changes in the customer preference
in using a digital product.
In the case of Indonesia, it is reported that the
mobile penetration rate stands at the level of 150%
with the mobile subscriptions reaching 388.04
million people by the year of 2016 alone (Frost &
Sullivan, 2018). By the level of the mobile
penetration rate alone, it is expected for the
Indonesian banking industry to facilitate a better
medium for their customers to conduct digital
transactions. And yet, the fintech firms have the
capability to produce a better digital product
compared to the conventional banks; furthermore,
there is an information and knowledge gap on
utilizing the latest technology to provide a financial
and banking product digitally between the fintech
firm and the conventional banks (Davis, et al., 2017;
Omarini, 2018). In short, the Indonesian banking
industry needs to produce an application or a digital
product that has the same or exceed the quality of the
digital product produced by fintech firms. Based on
the report and the previous research, it can be
indicated that for the Indonesian banking industry to
be able to capitalize the changes in the trend on
conducting digital transactions, then the Indonesian
banking industry must adapt to the changes and the
shifting of preference of its user on regarding the
demands of digital transactions.
In simple terms, the Indonesian banking industry
is forced to cope with the sets of challenges that arise
from the rapid development of technologies; to be
precise, the challenges faced by the Indonesian
banking industry are the emergence of fintech firms
and the changes of digital culture or preference in
their customer on conducting digital transactions. If
the Indonesian banking industry able to capitalize on
the changes and understand the needs of its customers
regarding the demand for digital transactions, then the
Indonesian banking industry will be able to become a
favorable medium for its current and potential
customers in conducting digital transactions.
Based on the introduction above, the primary
objectives of this research are to investigate the
pattern of changes in the digital culture on conducting
digital transactions and providing solutions for the
Indonesian banking industry to be able to cope with
the challenges from the emergence of fintech firms.
With the addition of finding the set of challenges or
obstacles faced by the Indonesian banking industry in
the digital era and determined the future state of the
Indonesian banking industry if those challenges are
handled correctly or not.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In this section, it is provided with the literature
regarding the difference between the conventional
banking industry and the fintech industry, especially
in the context of Indonesia. Furthermore, it is also
included in the literature on the matter of impact due
to the rapid development of technology in the banking
sector.
2.1 Conventional Banking Industry vs.
Fintech Industry
The primary differences between conventional
banking with the fintech industry are solely lying to
the implementation of technology in their financial
and banking products. To be precise, in regards to
fulfilling the demand for digital products to conduct
digital transactions by the current and potential
customers. With the addition of the nature of the
industry, it is known that the fintech industry has the
nature of the "highly-innovative industry";
meanwhile, the conventional banking industry has the
nature of the "highly-regulated industry." In other
words, for the conventional banking industry, all the
banks must follow the regulations that are applied by
the government or standards to conduct any banking
activities; on the other hand, the fintech industry has
greater flexibility to implement their innovation in
technology to their activity to produce a high-quality
product. In which, the fintech industry has a
competitive advantage against the conventional
banking industry in the aspect of technology
utilization and has increased the level of competition
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
26
with conventional banks (Romānova & Kudinska,
2017).
Furthermore, the fintech industry has a diverse
product in its application on fulfilling the demand for
digital banking and financial services (Davis, et al.,
2017). The diversity in the product created by the
fintech firms increases the possibility of the
customers to acquire and use the product easily; in
which, the product can be obtained via the internet. In
the case of the conventional banking industry (also
known as the incumbents), for every digital product
created by the incumbents, it must be validated and
checked by the regulators before the public could
access it. In other words, the regulators check the
digital product produced by the banks to see if the
incumbents meet the criteria and the regulation
applied in the banking sector. Due to the strict
regulations and rules that the incumbents have to
follow, the fintech firms are able to capitalize the gap
within the expectations and the demand of the
banking customer and the fintech firms are able to
create a product that specifically designs to fulfill the
demand with superior advantage in digital product
compared to the incumbents.
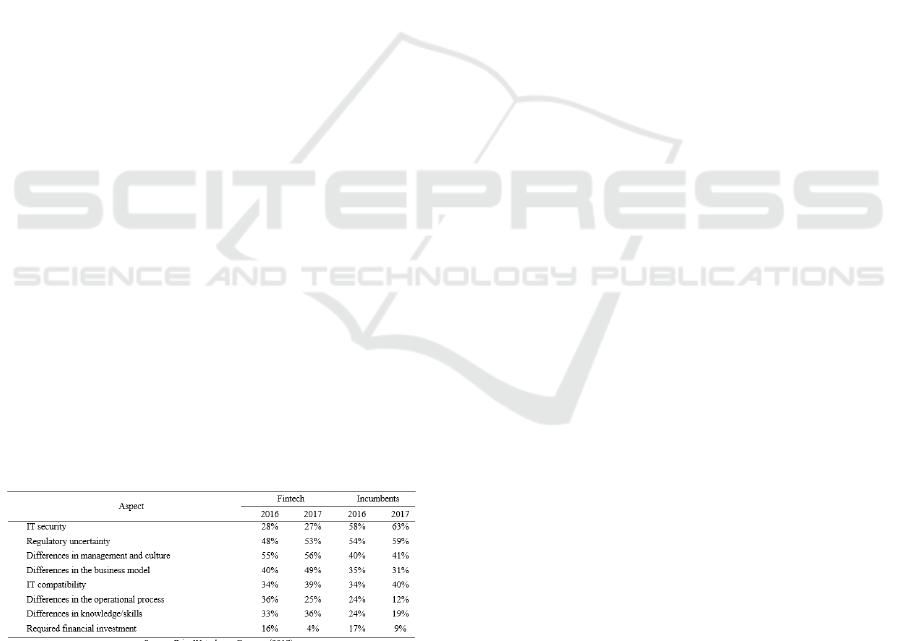
According to the report published by Price
Waterhouse Coopers (2017) which involving 1,308
respondents globally regarding the challenges faced
by the fintech industry and the incumbents, it is found
that the main challenges in the fintech industry are
focuses in the three areas, which are (1) regulatory
uncertainty, (2) differences in management and
culture and (3) the differences within the business
models; meanwhile, in the case of the incumbents, the
main challenges are focuses on (1) information and
technology (IT) security, (2) regulatory uncertainty
and (3) the differences in management and culture.
The overall percentage regarding the challenges
between the two industries is presented in Table 1.
Table 1. The Challenges Between the Fintech Industry and
Conventional Banking Industry
Source: PriceWaterhouseCoopers (2017)
Based on Table 1, it is shown that there is a high
degree of differences in challenges faced by both
industry, especially in the case of the different
management and culture. Based on the difference, the
fintech industry and the conventional banking
industry has an entirely different nature in fulfilling
the demand of digital transactions of its customer. To
be precise, the fintech industry has create six
disruptions to the conventional banking industry:
namely (1) the pace of technological innovation and
adoptions, (2) the disintermediation of financial
services, (3) industry convergence, (4) low cost and
low barriers of entry, (5) borderless platform and (6)
the democratization of investment and financial
services (Brummer & Gorfine, 2014). In simple
terms, the fintech has a different culture and
management style with the conventional banking
industry and capitalize on the benefits of the
development of technologies to gain competitive
advantages against the conventional banking
industry.
2.2 The Impact of Technology in the
Banking Sector
The impact of the rapid development of technologies
is not only focused on the emergence of the fintech
industry, but it also affects the regulators and nations
on how to handling the usage of new technology in
the banking and financial sector. Furthermore, the
impact of the advanced technology is caused by the
combination of three factors, namely (1) regulations,
(2) technological, and (3) economic factors
(Zavolokina, et al., 2016).
In regards to the regulations, due to the rapid
development of technology and its implementation in
the banking and financial sector, regulators are forced
to make regulations that can ensure every company
(fintech and conventional banks) to be prudent. In
which, these companies are forced to make necessary
changes to operate within the law, especially
regarding the code of conduct and regulations in the
matter of providing financial and banking services to
the public. In the case of Indonesia, the regulations
that are applied to the fintech industry are only
focused on the area of (1) lending and borrowing via
the internet and (2) the use of electronic money
(Iman, 2018). In which, the Indonesian regulators still
lack regulations to control any other type of fintech
activities which are operated in Indonesia, such as
cryptocurrencies and blockchain.
In terms of technological factors, the incumbents
are forced to adapt to the latest technology that can be
implemented to increases the quality of their services
in regards to fulfilling the needs and demands of
digital transactions of their current customers.
However, due to the nature of highly regulated
characteristics within the banking industry, the
incumbents must first be checked and validated by the
regulators to ensure their digital product meets the
specified standards. Meanwhile, the fintech industry
has used technological breakthroughs to provide
The Future and the Challenges of the Indonesian Banking Industry in the Digital Era
27

better services or features within the application to
fulfill the demand for digital services of its customers.
In which, there are clear relationships between the
technologies as an input for the fintech industry to
have a transformation in conducting its business
(Zavolokina, et al., 2016). Furthermore, the fintech
industry does not have the same conventional
relationship as the incumbents and its customers, in
which the fintech industry is capable of using
codifiable information to maintain the relationship
with its customers (Vives, 2017). In other words, the
fintech industry is capable of noticing the needs of its
customers in conducting digital transactions.
Finally, in terms of the economic factor; the
economic conditions forced the fintech industry and
the conventional banking industry to find the gaps or
areas of improvement to find the state of stability, in
the sense of financial and non-financial state. In the
case of fintech firms, the economic conditions
encourage the fintech firms to find the gaps in the
banking and financial services provided by the
conventional banks and compare them with the
expectations level of their customers. By taking this
step, the fintech firms can capitalize on the weakness
within the conventional banks to provide better digital
services. And, the due to the advancement of
technologies and the flexibility of those technologies,
the fintech industry is able to adopt and implement
the necessary technologies to implementing maintain
an adequate standard to meets the criteria of its
current and potential customers.
3 METHODOLOGIES
In regards to fulfilling the objectives of this research,
the determination of the future state of the Indonesian
banking industry and its challenges are analyzed
using an action research method. Action research is
defined as a scientific process in a specific problem,
in which this process is used to improve the practice
or an understanding given in the problem (McKernan,
1988; Sagor, 2000).
In other words, the action research method is used
to understand the gap between the fintech industry
and incumbents; this step was taken to provide
solutions for old players to overcome the challenges
that arise from the fintech industry. Furthermore, the
action research method is also used to analyze the
impact of changing preferences in digital culture in
connection with the rapid developments in
technology occurring in the financial and banking
sectors.
In terms of understanding the incumbent's views
in the Indonesian banking industry in the digital era,
especially in terms of the impact of technological
advances in the banking sector; The questionnaire
used in this study took a sample of the population of
Commissioners and Directors of the Bank as digital
service practitioners in Indonesia, consisting of
Commissioners, CEOs, and Directors whose main
tasks and functions are related to IT. More precisely,
this questionnaire has presented the views and
opinions of the Indonesian Banking Executives, and
they acted as a "Panel of Experts."
To find IT challenges in Indonesian banking in
the future, then as an analytical tool, the multivariate
regression approach is applied. Multivariate
regression analysis was applied to predict any
changes in the dependent variable in response to
changes in the independent variable (Hair, et al.,
2014). This approach was taken to understand how
incumbents view IT challenges in the future for
Indonesian banks, especially in prioritizing the
application of IT systems in order to meet the
demands of their customers. Furthermore, with the
answers given by the expert panel, we can uncover
the incumbent's priorities for any aspect of the
technological approach in the digital age. And this
method is also used to find the nature of the
relationship between the dependent and the
independent variables. Hence, the regression formula
used in this study is given as follows:
𝑌 = 𝛼 ± 𝛽 𝑋
Based on equation (1), the impact of IT is
presented as Y, and the priority of implementing the
IT to meet the demand of its customer is presented as
X1. The equation (1) can be determined in which
technology the incumbent uses to meet the criteria of
its customers in conducting a digital transaction using
the financial services provided by the conventional
banks. Furthermore, it could map which technologies
the incumbents prioritize in order to cope with
challenges rises from the emergence of the fintech
industry and the shifting of preference of its
customers in the digital era.
One of the research that is using an action
research approach in the banking sector is conducted
by Becker et al. (2010). Becker et al. (2010) found
that banks were dissatisfied in terms of their general-
purpose business models, especially in the case of the
documentation approach taken by banks that are still
considered traditional. Where the traditional
approach taken by banks has an indication of the
inefficiency and deficit of information in the bank,
Becker et al. (2010) stated that banks could use
business process modeling language using semantic
process building blocks to identify weaknesses in the
bank and evaluate the processes within the bank to be
improved. The results of this study indicate a variety
of actions. Specifically, the semantic modeling
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
28

language can be used in designing a system that can
give the capability for the traditional banks in
improving its effectiveness in process-oriented
analysis in their operational activities.
Also, the action research approach is used in the
research conducted by Sudiyatno et al. (2012), it was
found that there was a negative effect on financial
leverage in terms of company performance, (2)
positive effect on financial leverage on firm value, (3)
incentive managers had a positive influence on
company performance and value, (4) capital
expenditure was found to have positive influence on
company performance even though it has a negative
influence on company value and (5) company
performance has a positive influence in terms of
company value. Based on the findings of Sudiyatno
et al. (2012), it is recommended that companies make
policies to maximize the use of debt in their capital
expenditure activities, with the addition of increased
management efforts in order to increase company
values.
Furthermore, the multivariate regression analysis
is used to enrich the analysis of the action research
approach in order to understand the nature of the
specified dependent and independent variables. Also,
the usage of multivariate regression analysis has been
performed in numerous research, such as Sufian &
Chong (2008) and Vintillă & Nenu (2016).
In the research conducted by Sufian & Chong
(2008), the multivariate regression analysis is applied
to analyze the return on asset (ROA) in response to
the internal factors and external factors of the
Philippines ' financial institutions. The variables used
by Sufian & Chong (2008) to represent internal
factors are total assets, non-interest income, total
overhead expense and the book value of stockholder;
on the other hand, the external factors are presented
with money supply growth, market capitalization,
annual inflation rate, and gross domestic product.
Sufian & Chong (2008) found that the size of the
bank, credit risk, and expense preference behavior
have negatively related to the bank's profitability;
meanwhile, the non-interest income and
capitalization are positively related to the bank's
profitability. Based on the findings of Sufian &
Chong (2008), it is suggested that the bank-specific
determinant variables are statistically significant to
the banks' profitability, even though the non-interest
income and capitalization have a positive impact on
the bank's profitability.
In terms of the research conducted by Vintillă &
Nenu (2016), multivariate regression analysis is
implemented in order to analyze the ROA and return
on equity (ROE) in response to the quick ratio,
current ratio, leverage, cash conversion, effective tax
rate, and working capital; in which the object of the
research is the companies listed on the Bucharest
Stock Exchange. Based on the findings, it is found
that the variables used in the research of Vintillă &
Nenu (2016) are statistically significant; furthermore,
it is found that there is a negative relationship
between liquidity and firms' financial performance.
Based on the findings, it is indicated that the decrease
in the aspect of liquidity can be excluded as a risk
factor for the Romanian companies.
Based on the explanations regarding the
methodologies used in this research, these
methodologies are used to fulfill the research
objectives. To be precise, these methodologies are
used to determine the challenges faced by the
incumbents, analyze the changes of preference in the
digital culture, and to provide solutions that can be
used by the incumbents to cope with such challenges.
4 FINDINGS
In this section, the methodologies that already
explained in section 3 are applied in order to fulfill
the objectives in this research. The findings of this
research and its analysis are given as follows:
4.1 Multivariate Regression Analysis
Based on the research conducted, it is found that the
IT impact in response to the implementation of IT in
order to fulfill the demand and criteria of its customer
in conducting digital transaction are moving in a
positive manner; in other words, the impact of IT is
directly related to the level of implementation of IT
by the incumbents. The regression equation from the
multivariate regression analysis is presented in
equation (2).
𝑌 = −.801 + 1.067𝑋' (2)
Based on the equation (2), the regression analysis
shows that the impact of IT is dictated by the
movement of the implementation of IT applied by the
incumbents. In other words, the degree of
implementation of IT determined the scale of IT
impact the incumbents may have in their banks,
especially in regards to fulfilling the demand and
criteria of its customers in conducting digital
transactions by using the financial services provided
by the banks.
Furthermore, the linear regression presented in
equation (2), the regression has a p-value of 0.027. In
which, the linear regression of equation (2) is
statistically significant to analyze the movement of
the IT impact in response to the IT implementation of
banks in order to the meet the criteria and
expectations of its customers. In terms of the
The Future and the Challenges of the Indonesian Banking Industry in the Digital Era
29

implementation of IT, it is found that the p-value of
the variable stands at the level of 0.027 (where the p-
value of the variable are below the 0.05 or 5%
threshold); in which, the variable of IT
implementation is statistically significant to describe
the movement of the IT impact to the incumbents.
And finally, in terms of the correlation of the IT
impact and the implementation of IT stands at the
level of 0.765 or 76.5%. The correlation value
indicates that the IT impact and the implementation
of IT has a positive relationship between one and
another. In other words, if one of the variables
increases, then the other variable has the tendency to
be increasing as well and vice versa.
4.2 Action Research Analysis
In regards to the findings using the research action
method, the steps of action research are conducted by
the process defined by Sagor (2000). The analysis of
the challenges faced by the conventional banking
sector (especially for the Indonesian banking sector)
using an action research approach is given as follows.
In accordance with the phenomenon of the emergence
of the fintech industry, the fintech industry is capable
of producing a better application for its customers in
terms of using the application for conducting digital
financial and banking services. In which, these
applications created by the fintech firms consider
better than the conventional banking sector due to the
rapid development and implementation of its product.
As Romānova & Kudinska (2017) explains, the
fintech firms is categorized into two groups, which
are (1) by become the partner for the conventional
banking sector in order to produce a digital banking
and financial for its customers or (2) by creating an
application for its customer to conduct a digital
financial and banking services which are already
provided by the conventional banks. Furthermore,
due there is a gap between the digital product
produced by the conventional banks and the
expectations of its customers in terms of digital
services, the fintech industry are able to complete the
gaps by creating a product the customers, in which the
customers did not acquire in the application created
by the conventional banks (Zavolokina, et al., 2016).
By noticing the gap between the customer's
expectation and the product created by the
incumbents, the fintech industry is capable on
capitalizing the opportunity by creating a product
with better quality and services compared to the
incumbents due to greater flexibility in implementing
its innovation to its product than the conventional
banking sector.
In terms of the changes of preferences in the
digital era, Das et al. (2016) explains that there are
four disruptions in Indonesia that already happen in
regards to the rapid development and advancement of
technology, which are (1) mobile internet, (2) cloud
technology, (3) internet of things and (4) big data and
advanced analytics. Because of these disruptions, the
customers of the banking industry are expected to
have digital services that enable them to conduct their
digital transactions as smooth and seamless as
possible. In other words, the trends that already
happened in Indonesia is that every digital transaction
can be completed just by using their smartphones or
mobile phones. Furthermore, according to the
Australian Trade and Investment Commission
(2018), the number one reasons the Indonesian
customers conducting digital transaction in 2016
(especially in their purchasing activity in the e-
commerce market) is due to the practicality factor; in
which there are 63% of the respondent engaging in
the digital transactions due to the practicality it
provides.
Figure 1. Indonesian Conventional Banks' IT Engagement
Based on that trend, the incumbents use different
approaches in fulfilling the demands and the needs of
their customers. Specifically, it is found that (1)
37.5% of total respondent is engaging in the
implementation of open application programming
interface (API), (2) 25% of total respondent are
engaging in the implementation of internet of things
(IoT) and (3) 25% of the total respondent are
engaging in the implementation of cloud processing.
To simplify the findings above, Figure 1 is presented
as an overview regarding the Indonesian banks’ IT
engagement in fulfilling the demands and the needs
of its customers. Furthermore, it is found that 62.5%
of the total respondent believes that it is crucial to
collaborate with the fintech firms to improve their
implementation of IT in order to meet the criteria of
its user. Meanwhile, 50% of the total respondent is
considered the implementation of big data analytics
to be important in findings the needs of its customer;
in which the conventional banks may have the
opportunity to produce an application or system to fill
the needs of its customers.
Furthermore, it is indicated that all of the
incumbents have different priorities in regard to the
implementation of IT in order to fulfill the criteria and
the demands of its customers. Also, some of the
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
30

incumbents believe it is essential to collaborate with
the fintech firms in order to produce digital services
That meet the preference of its customer in
conducting the digital transaction; in which, some of
the incumbents working together with the fintech
firms in order to fill the gaps that exist in the digital
era. Also, it is found that not all the incumbents
prioritize the same technology in their business in
order to cope with the challenges that arise in the
digital era; to be precise, in regards to the emergence
of fintech and the changes in the preference of its
customer.
In regards to the challenges faced by the
Indonesian banking sector due to the emergence of
the fintech industry and the changes of preference in
conducting a digital transaction, the Indonesian
banking industry is faced with several problems
relating to the implementation of technology in the
digital era. Some of the problems that are identified
using the action research approach are: (1) the
incumbents are still in struggle to produce an
application or digital financial and banking services
that have the same quality (or better) with the
application with the fintech firms, (2) the incumbents
are restricted in the implementation of the new
technology and implementing its innovations due to
the nature of the industry itself (which are a “highly-
regulated industry”), (3) there are gaps between the
digital product produced by the incumbents and the
expectations of its customer (in which, these gaps are
capitalized by the fintech industry to provide digital
and financial services where the incumbents are not
able to provide to its via technology implementation)
and (4) due to the rapid development of technology,
the banks are needed to provide a better security to
protect theirs and customers data from any
cybersecurity threats that may occurs in any given
time (especially to the data that are used by the
incumbents to implements the new technology in
their digital services for its customer).
Based on the explanations on the challenges faced
by the incumbents, the challenges faced by the
incumbents are oriented on the approach to utilize
their technology to understand and fulfill the
demands, the criteria, and the preferences of its
customers in conducting digital transactions. In
simple terms, the incumbents should either learn from
its competitors (in this case, it is the fintech industry)
in regards to provide better applications for its
customer in doing digital transactions or by
examining the needs of its customers in regards to the
trends that already taken place in this digital era.
4.3 Solutions
Based on the challenges that explained in section 4.2,
several approaches or solutions can be applied by the
incumbents to cope with these challenges (in regards
to the changes of preferences of its customers and the
emergence of the fintech industry). It is identified that
conventional banking customers in need of an
application or software that can make their digital
transactions easier. On the other hand, every customer
has their own preferences or criteria in conducting
digital transactions. In which, the Indonesian
conventional banks should prioritize the necessary
technologies in order to improve the effectiveness of
their application in fulfilling the needs and the criteria
of its customers in conducting digital transactions or
banking activities.
In this regards, some of the solutions are: (1) the
incumbents could collaborate with the fintech firms
in developing their own digital financial and banking
product to fulfill the demand and the criteria of its
customers, (2) the incumbents could create or develop
their digital banking and financial services using the
customer-centric approach in order to obtain the
information of the needs of its customer and the
incumbents could prioritize which technology to be
implemented to meets the criteria, (3) the incumbents
should have an adequate security to protect the banks
and its customer data in the digital era (especially on
the data which are used to facilitate the customers
digital transactions) and (4) the implementation of
technology by the incumbents should focus on the
aspect of practicality (in which, the application has
the characteristic of seamless and easy-to-use feature)
to be able to keep up with the trend that are already
taken places.
Following the result of the regression analysis
presented in equation (2), the incumbents should
prioritize the technologies that are needed by its
customers. By prioritizing the technologies based on
the criteria and the demands of its customers, the
incumbents are able to keep up with the trends in
conducting digital transactions. Furthermore, by
prioritizing the technology to be implemented based
on the trends, the incumbents are able to develop their
digital product using the customer-centric approach
to maximize the performance and the quality of their
product to meet the criteria and the expectations of its
customers and the trend in the digital culture.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the analysis using the multivariate
regression analysis, it is found that the impact of IT
in response to the implementation of IT in the
Indonesian conventional banks is statistically
significant. Furthermore, the impact of IT is dictated
by the implementation of IT to fulfill the demands of
its customers. Meanwhile, in regards to the analysis
The Future and the Challenges of the Indonesian Banking Industry in the Digital Era
31

using correlation analysis, it is found that the impact
of IT with the IT implementation in terms of meeting
the criteria and the expectation of its customers in
conducting digital banking activities is found to be
positively related. Thus, the more frequent the
conventional banks implementing new technologies,
then the impact of IT will be increasing as well and
vice versa.
In terms of findings using the action research
analysis, it is found that the incumbents are faced with
the following challenges: (1) the incumbents are in
struggle to create an application or digital services
that have the same quality with the product created by
the fintech firms, (2) the incumbents are restricted in
implementing their new technology because to the
nature of the ``highly-regulated industry" in the
conventional banking sector, (3) there are still an
existing gaps between the product created by the
incumbents and the expectations of its customer and
(4) due to the rapid development or advancement
of technologies that are taken places, the incumbents
are needed to provide protection to the cybersecurity
threats that may occur at any given time.
As for the changes in the preferences of the
conventional banks' customers, the majority of the
respondents in this research are engaging in the
development of open API within their system. In
which, this open API system is improved to facilitate
better integration between the software and the web-
services product that is created by the conventional
banks in facilitating the digital banking activities of
its customer. Also, some of the respondents are
focusing on other aspects of IT, such as artificial
intelligence, cloud processing, and IoT. Hence, these
engagements are also focusing on the improvement of
the user's experience of its customers while using the
application created by the Indonesian conventional
banks.
In regards to the solutions that can be applied by
the incumbents to cope with identified challenges
from the action research analysis, the solutions are
given as follows: (1) the incumbents should
collaborate with the fintech firms in developing or
creating their digital product to meet the criteria and
the expectations of its customers, (2) it is advisable
for the incumbents to develop their digital financial
and banking services using a customer-centric
approach to obtain the information regarding the
trend that already taken places in the digital era, (3)
the incumbents should have an adequate security on
protecting the banks and its customers data from the
cybersecurity threats due to the rapid development of
technologies and (4) it is advisable for the incumbents
to develop or create a digital product that is focused
on the aspect of practicality to enhance the experience
of its customers.
The findings, the challenges and the solutions in
this research are in line with the research conducted
by Brummer & Gorfine (2014) and Zavolokina et al.
(2016) in terms of the emergence and the impact of
the fintech industry, with the additions of the changes
in the preference of customers in the digital era. In
simple terms, the challenges created are due to the
advancement of technologies, and the fintech industry
is capable of noticing and capitalizing the gap
between the digital banking product created by the
incumbents and the expectations of its customers to
produce a better-quality application compare to the
conventional banks.
Finally, the limitation of this research is that it
only focuses on the perspectives of the Indonesian
conventional banks in the digital era. Specifically, the
perspectives in this research are only using the expert
panels of individuals that are operated in the banks
that are classified into the category of Book four
banks in terms of the impact of IT and its
implementations in Indonesia. Based on the
conclusion and the explanations above, the future
research regarding the role of IT in the Indonesian
banking industry and the fintech industry will be
including the perspectives of the incumbents and the
fintech in regards to the implementation of
technologies that can be used in creating an
application or digital product that can meet the
criteria and fulfilling the needs of the needs of its
customers in Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Anagnostopoulos, I., 2018. Fintech and regtech: Impact on
regulators and banks. Journal of Economics and
Business, Volume 100, pp. 7-25.
AT Kearney, 2014. Going Digital: The Banking
Transformation Roadmap, Chicago: AT Kearney.
Australian Trade and Investment Commission, 2018. E-
Commerce in Indonesia: A Guide For Australian
Business, Sydney: Commonwealth of Australia.
Becker, J., Weiß, B. & Winkelmann, A., 2010. Transferring
a domain-specific semantic process modeling language
- Findings from action research in the banking sector.
Pretoria, Association For Information System.
Brummer, C. & Gorfine, D., 2014. Fintech: Building a 21st-
Century Regulator's Toolkit, Santa Monica: Milken
Institute.
Das, K., Gryseels, M., Sudhir, P. & Tan, K. T., 2016.
Unlocking Indonesia's Digital Opportunity, Jakarta:
McKinsey&Company.
Davis, K., Maddock, R. & Foo, M., 2017. Catching up with
indonesia’s fintech industry. Law and Financial
Markets Review.
Fichman, R. G., Dos Santos, B. L. & Zheng, Z., 2014.
Digital Innovation as A Fundamental and Powerful
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
32

Concept in The Information Systems Curriculum.
Management Information Systems, 38(2), pp. 329-353.
Frost & Sullivan, 2018. Digital Market Overview:
Indonesia, Santa Clara: Frost & Sullivan.
Frost & Sullivan, 2019. The Future of Indonesia,
Jakarta: Frost & Sullivan.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J. & Anderson,
R. E., 2014. Multivariate Data Analysis. 7th ed. Harlow:
Pearson.
Iman, N., 2018. Assessing the dynamics of fintech in
Indonesia. Investment Management and Financial
Innovations, pp. 296-303.
McKernan, J., 1988. The Countenance of Curriculum
Action Research: Traditional, Collaborative, and
Emancipatory-Critical Conceptions. Journal of
Curriculum and Supervision, pp. 173-200.
Omarini, A. E., 2018. Banks and Fintechs: How to Develop
a Digital Open Banking Approach for the Bank’s
Future. International Business Research, 11(9), pp. 23-
36.
Oshodin, O., Molla, A., Karanasios, S. & Ong, C. E., 2017.
Is FinTech a disruption or a new eco- system? An
exploratory investigation of banks’ response to FinTech
in Australia. Hobart, Australasian Conference on
Information Systems, pp. 1-11.
PriceWaterhouseCoopers, 2017. Redrawing the lines:
Fintech’s growing influence on Financial Services,
London: PriceWaterhouseCoopers (PWC).
Romānova, I. & Kudinska, M., 2017. Banking and fintech:
A challenge or opportunity?. Contemporary Studies in
Economic and Financial Analysis, Volume 98, pp. 21-
35.
Sagor, R., 2000. Guiding School Improvement with Action
Research. Alexandria: Association for Supervision and
Curriculum Development.
Sudiyatno, B., Puspitasari, E. & Kartika, A., 2012. The
Company's Policy, Firm Performance, and Firm Value:
An Empirical Research on Indonesia Stock Exchange.
American International Journal of Contemporary
Research, 2(12), pp. 30-40.
Sufian, F. & Chong, R. R., 2008. Determinants of bank
profitability in a developing economy: Empirical
evidence from the Philippines. Asian Academy of
Management Journal of Accounting and Finance, 4(2),
pp. 91-112.
Vintillă, G. & Nenu, E. A., 2016. Liquidity and Profitability
Analysis on the Romanian Listed Companies. Journal
of Eastern Europe Research in Business & Economics,
pp. 1-8.
Vives, X., 2017. The Impact of Fintech on Banking. In: G.
B. Navaretti, G. Calzolari, J. M. Mansilla-Fernandez &
A. F. Pozzolo, eds. Fintech and Banking. Friends or
Foes?. Rome: Europeye srl, pp. 97-106.
Wirdiyanti, R., 2018. Digital Banking Technology
Adoption and Bank Efficiency: The Indonesian Case,
Jakarta: Otoritas Jasa Keuangan (OJK).
Zavolokina, L., Dolata, M. & Schwabe, G., 2016. The
FinTech phenomenon: antecedents of financial
innovation perceived by the popular press. Financial
Innovation, 2(1), pp. 1-16.
The Future and the Challenges of the Indonesian Banking Industry in the Digital Era
33
