
The Pattern of Development Strategies for Small and Medium
Enterprises in Sleman Regency, Special Region of Yogyakarta
Rini Raharti
1
, Cungki Kusdarjito
2
, Erni Ummi Hasanah
1
, Agnes Ratih Ari Indrayani
1
,
Siti Qomariyah
1
1
Economics Department, Faculty of Economics, Janabadra University, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Agriculture, Janabadra University, Indonesia
sit_qom@gmail.com
Keywords: Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), location quotient, diamond cluster model.
Abstract: Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are potential sectors which need to be developed. The objects of this
research are a number of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Sleman Regency. As for the objectives
are as follows: 1) analizing superior sectors of SMEs which are the most potential to be developed; 2)
identifying the competitive advantage of SMEs; 3) formulating development strategies for superior sectors
of SMEs. The research problem is how to develop strategies of SMEs in Sleman Regency. This research tries
to make a development strategy of SMEs which integrates superiority or local potency of SMEs with its
existing external opportunities. On a macro basis, the strategy formulated in this research is begun with
conducting analysis of potency and problem towards every sector of the existing SMEs, in order to be able to
identify which SMEs sectors are more potential and appropriate to be developed, then it is formulated its
development strategy based on qualitative and quantitative approach. The development strategies of SMEs is
based on integration of two methods, namely location quotient and diamond cluster model. The calculation
result of LQ is obtained that the business sector or scope of SMEs that is superior in Sleman Regency is
business service sector (coefisien of LQ value is 1.6). Next, it is conducted identification of the advantages of
SMEs of business service which refers to Diamond Cluster Model. The result is that several superiority
instruments of SMEs of business service have potency to be developed in the form of input factors, demand
conditions, supporting and related industries, and company strategies and competitors.
1 INTRODUCTION
Development of SMEs becomes a crucial thing in
view of that SMEs have such an important roles for
the economic growth of a country, including
Indonesia (Husband, 1999; Tambunan, 2005). As an
illustration, SMEs in Indonesia have given
contribution towards employment absorption as many
as 99.74% from total of national absorption and given
contribution towards GDP as much as 1.013,5 trillion
rupiah or 56.73%. This big contribution refers that
SMEs have ability to strenghten the structure of
national economy (Tambunan, 2005). Althought
SMEs economically have significant contribution
towards economic growth, however, in their
development, they face up many problems. Based on
this research (Winarni, 2006) and (Situmorang, 2008),
the problems which are faced by SMEs are extracted
as follows: (a) lack of capital, (b) difficulty in
marketing, (c) simple organizational structure with
non-standard divison of labor, (d) low management
quality, (e) limited Human Resources and their low
quality, (g) Most of them do not have financial reports,
(h) weak legality aspects, and (j) low quality of
technology. These problems conduce weak business
network, limited in market penetration ability and
market diversification, economical scale is too small
so that it is difficult to reduce cost, profit margin is
very small, and even farther, SMEs do not have
competitive advantages. Recognizing several
problems faced in developing SMEs, therefore, it is
needed a development strategy for SMEs in order that
development of SMEs in Indonesia is able to run
quickly, problems faced by SMEs are able to be
reduced, and SMEs have more competitive
advantages (Hafsah, 2004). Thus, all problems faced
by SMEs had better to be made as input or
consideration in formulating development strategy so
that it becomes comprehensive strategy and can work
12
Raharti, R., Kusdarjito, C., Ummi Hasanah, E., Ratih Ari Indriyani, A. and Qomariyah, S.
The Pattern of Development Strategies for Small and Medium Enterprises in Sleman Regency, Special Region of Yogyakarta.
DOI: 10.5220/0009200800120015
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Applied Science, Engineering and Social Sciences (ICASESS 2019), pages 12-15
ISBN: 978-989-758-452-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

effectively and efficiently. Various kinds of research
about development strategy of SMEs in Indonesia
have been conducted, among them by (Winarni, 2006;
Situmorang, 2008; Hafsah, 2004). Basically,
strategies of SMEs development that are proposed by
the researchers are not based on its advantages or local
potencies (SMEs potencies) and external
opportunities, as well as the development strategies
proposed are still based on qualitative approach.
Although there are many in number, SMEs
encounter the main problem, namely additional value
of their products is relatively small. It is because of
their small capital so that the opportunity to expand is
limited. Secondly, human resources are relatively
low, thus, level of creativity and product innovation
is low as well. The third, marketing network that they
have is limited. The fourth, the system of organization
management has not work well yet. Therefore, the
process of development and coaching of small and
medium enterprisesis is a must to be carried out by
local government in the era of regional outonomy if it
does not want to be left behind and knocked out from
economic development in the period of upcoming
free market. The objectives of this research are 1)
Analyzing sectors of superior SMEs that are the most
potential to be developed; 2) Identifying competitive
superiority of SMEs; 3) Formulating development
strategies for superior sector of SMEs.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
Types and Data Sources
Data used in this research were subject data, namely
the data that were in formed of opinion, attitude,
experience or character of person or group who
became research subjects (respondents) (Hasanah,
2018). Data sources in this research were primary
data, that was the research data which were obtained
directly from the data sources that were particularly
collected and directly related with the problems
observed. The primary data in this research were
obtained through dividing or distributing
questionnaires that were given to the respondents who
in this case were businessmen in category of micro
small business. Besides that, the data sources in this
research were secondary data, that was, the data that
were generally collected by institution of data
collector and published for data user community
(Kuncoro, 2005). The data collections that were going
to be conducted by using multiple source of evidence,
were interview, archive study and direct observation.
Interview was used as main data sources. The
stakeholders who became respondents in order to gain
the research data were representatives of
Disperindagkop in Sleman Regency, owners,
managers and employees of SMEs.
Population and Sampling
Population in this research were businessmen who
were grouped entreprenuers in the category of SMEs.
The detail in Sleman Regency for the total number of
SMEs were as many as 112 businesses and the total
number of small business were as many as 90
businesses (Disperindagkop, 2014). Determining the
sampling in this research was based on formulation of
Slovin namely n=N/1+Ne
2
in which n is the number
of sampling; N is the number of population and e is
fault tolerence which is set. The smaller fault
tolerance set, the more accurate the sampling
describes the population. By using level of the fault
tolerence as much as 10 percent thus it was obtained
the number of sampling of micro business in Sleman
Regency as many as 52.8 business (rounded to 53).
For the sampling number of Small Business, by using
the same formulation thus it was obtained the
sampling number for small business as many as 47.3
(rounded to 48).
Methodology of Data Collection
Data used in this research were primary data that were
collected by open and closed questionnaires, with the
purposes for getting data about dimension of
developed construction in this research.
Technique of Data Analysis
Location Quotient
Formula of LQ with basic value of GRDP is as
follow:
V
x
R
/V
R
LQ = (1)
V
x
N
/V
N
In which:
V
x
R
= sum of GRDP on a sector x in region
R V
R
= sum of GRDP on all sectors in region R
V
x
N
= sum of GRDP on a sector x in refernce region
N V
N
= sum of GRDP on all sectors in reference
region N
Diamond Cluster Model
Cluster is interpreted as "geographic concentrations of
firms, suppliers, related industries, and specialized
institutions that occur in a particular field in a nation,
state or city." Another definition about clusters is
"geographical concentration of industries that gain
performance advantages through co-location". Cluster
show the relationship among companies which
provide complementary service, including consulting
service, education service provider and training,
The Pattern of Development Strategies for Small and Medium Enterprises in Sleman Regency, Special Region of Yogyakarta
13
financial institutions, professional associations and
goverment institutions (Porter, 1990).
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Data Analysis
The approaches developed in this study are: (a)
identifying the leading sectors in SMEs with the LQ
index; (b) identifying competitive advantages for
SMEs using the Diamond Cluster model. The
competitive advantages are going to include input
factor, demand condition, supporting and related
industry, and strategy company and competitor (c)
classification of competitive advantages of SMEs
becomes internal and external factors. (d) formulating
strategy based on the combination of strength,
weakness, opportunity, and threats, and (e)
Determining development strategy of SMEs, and (f)
implementing strategy chosen (Hasanah, 2018).
Identification of Superior Sector of SMEs
Based on information from the Sleman Regency
Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP) as a basis
for determining the leading sectors for SMEs, there
are some changes in the GRDP calculation carried out
by the Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) which
originally used 2000 base years to be eliminated
starting in February 2015 and as instead, it uses the
2010 base year, so that the classification of sectors or
business fields that were originally 9 sectors becomes
17 sectors or business area.
The following is the identification of the superior
sectors of SMEs consisting of 17 sectors or business
area that are possible to potentially be developed in
Sleman Regency. As for these sectors are (1)
Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishery; 2) Mining and
Excavation 3) Processing Industry; 4) Procurement of
Electricity and Gas; 5) Procurement of Water,
Processing Waste and Recycling Waste; 6)
Construction; 7) Large and Retail Trade, Car and
Motorcycle Repair; 8) Transportation and
Warehousing; 9) Provision of accommodation and
food beverage; 10) Information and communication;
11) Financial Service and Insurance; 12) Real Estate;
13) Business Service; 14) Government
Administration, Defense and Social Security; 15)
Education Service; 16) Health Service and Social
Activity; 17) Other Services. To calculate the
superior or potential SMEs sector from the 17 sectors,
the LQ Index is used. LQ calculations and analysis
basically by comparing the GRDP data of each SMEs
sector with the accumulation of GRDP data in all
sectors in Sleman Regency then compared with the
reference areas, namely the GRDP of Special Region
of Yogyakarta. The GRDP value which is the basis of
the calculation is used by the GDP value with a
constant price of 2010. The results of the calculation
of the LQ value in the form of index values are
presented in table 1.
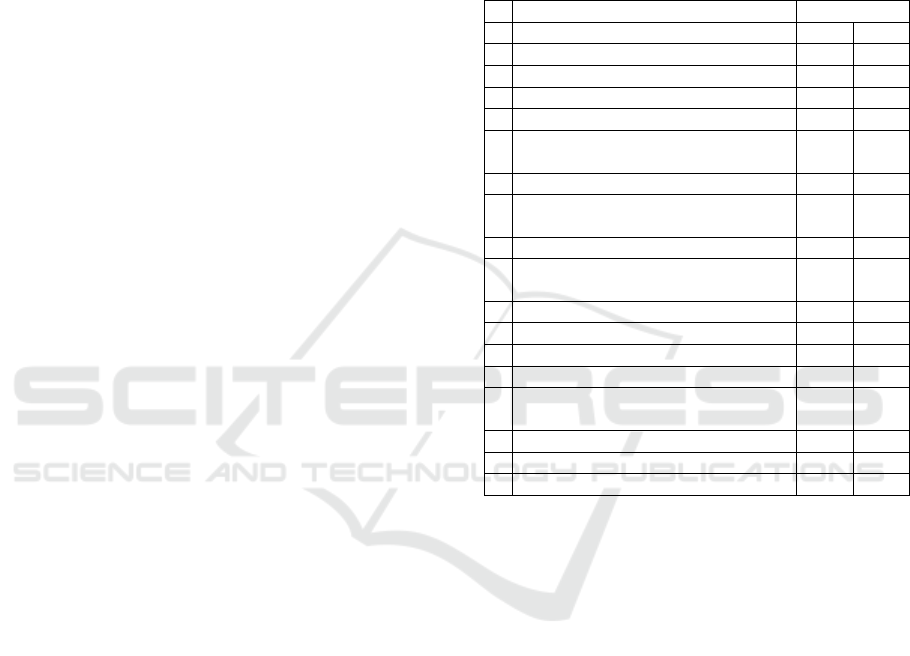
Table 1: Value LQ of Sector/Business Area of GRDP
Sleman Regency in 2013-2014
No Sector/Business Area LQ Value
2013 2014
1A
g
riculture, Forestr
y
and Fisher
y
0.8033 0.7800
2 Mining and Excavation
0.7383 0.7282
3 Processing Industry
1.0180 0.9983
4
Procurement of Electricity and Gas
0.8336 0.8142
5
Procurement of Water, Processing
Waste and Recycling Waste
0.4692 0.4686
6 Construction
1.1816 1.1845
7
Large and Retail Trade Car and
Motorc
y
cle Re
p
ai
r
0.9071 0.0243
8 Transportation and Warehousing
1.1461 1.1582
9
Provision of Accomodation And
Food Bevera
g
e
1.0458 1.0360
10
Information and communication
0.9619 0.9699
11
Financial Service and Insurance
0.8120 0.8263
12
Real Estate
1.1315 1.1353
13
Business Service
1.6413 1.6471
14
Government Administration,
Defense and Social Securit
y
0.8025 0.8061
15
Education Service
0.0305 1.1065
16
Health Service an
d
Social Activit
y
0.9242 0.9253
17
Other Services
0.8660 0.8684
Data processed
4 CONCLUSIONS
The results of the 2014 LQ index calculation (table
1.) that the SMEs sectors that can be developed are
the Corporate Services sector of 1.6471. The
SMEs Services Company LQ index value is the
largest index value compared to other sectors.
Furthermore, the SMEs sector that has the
potential to be developed is the Transportation and
Warehousing sector at 1.15 and then the Education
Services sector with the LQ index of 1.1065.
Competitiveness Identification of SMEs
The core of Diamond Cluster Model is to effort in
grouping core industries which are related each
others, whether supporting industries, related
industries, supporting service, economic
infrastructure, research, training, education and
others. The cluster is also intended to arrange
ICASESS 2019 - International Conference on Applied Science, Engineering and Social Science
14

several activities of economic development. This
cluster is able to be formed in city, regional distric
and even country.
Before doing identification, it is going to be
explained the intended context of business service.
A business service is a company that does not
produce goods or products, yet it produces output
in the form of service. The business service
characters are as follows:
1. Do not sell goods or products but sell in form of
service.
2. Do not have inventory of goods
3. The purpose is to obtain profit set.
4. Do not determine the cost of goods
5. Do not need in making a report on the cost of
production
Sub-sectors of this business service include
service of lawyer, service of accountant,
architectural bureau, service of data processing,
service of advertisement and others. Identifying
competitive advantages in SMEs area of business
service is in four Diamond Model clusters, namely
input factor, demand condition, supporting and
related industry, company stategy and competitor.
The next stage, the competitive advantage of
SMEs is classified to be internal factors which
consist of its strength and weakness, as well as
external factors including opportunity and threat
factors. The result is that SMEs of business service
are potentially developed.
REFERENCES
Direktori UMKM Disperindagkop Kabupaten Sleman
Tahun 2014.
Hafsah, M.J., 2004.Upaya Pengembangan Usaha Kecil dan
Menengah (UKM), Infokop, Nomor 25 Tahun XX, hal
40–44.
Hasanah, Erni U. (2018), Aplikasi Strategi Samudera Biru
(Blue Ocean Strategy) Untuk Pengembangan UKM Di
Kabupaten Sleman D.I.Yogyakarta, e
journal.janabadra.ac.id
Husband, S. and Purnendu, M., 1999. A Conceptual Model
for Quality Inetgrated Management in Small and
Medium Size Enterprise, International Journal of
Quality & Reliability Management, Vol. 16 No. 7, pp.
699–713.
Kuncoro, M., 2005. Strategi: Bagaimana Meraih
Keunggulan Kompetitif, Erlangga, Jakarta.
Porter, Michael E. (1990). The Competitive Advantage of
Nations. London:The Macmillan Press Ltd.
Prawirokusumo, S., 2001. Ekonomi Rakyat: Konsep,
Kebijakan, dan Strategi, BPPE, Yogyakarta.
Situmorang, J., 2008.Strategi UMKM dalam Menghadapi
Iklim Usaha yang Tidak Kondusif, Infokop, Volume
16, Hal 88–101.
Tambunan, T., 2005. Promoting Small and Medium
Enterprises with a Clustering Approach: A Policy
Experience from Indonesia, Journal of Small Business
Management, Vol 43 No. 2, pp. 138–154.
Winarni, E.S., 2006. Strategi Pengembangan Usaha Kecil
melalui Peningkatan Aksesibilitas Kredit Perbankan,
Infokop Nomor 29, Tahun XXII.
The Pattern of Development Strategies for Small and Medium Enterprises in Sleman Regency, Special Region of Yogyakarta
15
