
Literacy of Physical Education Teachers on ICT-based
Instructional Media
Soni Nopembri
1
, Saryono
1
, A. Erlina Listyarini
1
, and Nur Rohmah Muktiani
1
1
Department of Physical Education, Faculty of Sport Sciences, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Colombo Rd No.1,
Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: ICT, Instructional Media, Literacy, PE, Teacher
Abstract: Digital Literacy supports the mandate of the 2013 curriculum that requires teachers to take over Information
Communication Technology (ICT) in the instructional media of Physical Education (PE) classes. Therefore,
this study aims to explore the knowledge and the utilization (literacy) of ICT-based instructional media for
physical education teachers. A descriptive study with survey method was conducted to 371 physical
education teachers of elementary and secondary schools in the Yogyakarta Special Region. The data
collection used knowledge test and utilization of ICT-based instructional media in PE. Quantitative
descriptive analysis was used to process the data obtained. The results showed that the knowledge of PE
teachers on ICT-based instructional media was in low (18.7%), moderate (62.6%), and high (18.7%)
category. Meanwhile, the utilization of ICT-based instructional media in PE class were in low (13.4%),
medium (73.6%), and high (13%) category. Based on the results, it can be concluded that literacy on ICT-
based instructional media of PE teachers needs to be improved with the factors that hinder and support in
gaining knowledge and using it. Therefore, education and training process is needed to increase their
literacy on ICT-based instructional media.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of ICT is a priority in
improving the quality of education. Teachers are
required to master ICT in to develop ICT-based
instructional media and utilize it in the teaching and
learning process. The utilization of ICT starts from
primary, secondary to university, but the variation
and focus of its use varies in each relationship. The
development of ICT has enriched learning resources
and media. Professional teachers must be able to
choose, develop, and utilize various types of
instructional media by utilizing the sophistication of
ICT. The progress of ICT has been also
implemented on various types of learning media. In
addition to enhance skills in using and utilizing ICT
in learning, teachers can also increase the latest
insights and knowledge about learning theories,
methods, and research results. Besides, ICT is used
to discuss and talk about learning problems by
teachers.
The development of ICT is rapidly increasing in
the world of education. Some educational research
findings have proven the benefits of using ICT as a
tool for improving student achievement (Andrea &
Boos, 2004; Gary & O 'Sullivan, 2003; Uwe, 2004).
Clarke and Cronje's (2002) found that the use of
"virtual classrooms" which is a combination of
websites and list server allows for real classroom
imitation with good effects and improves the quality
of messages that can be done in conventional
classrooms. Truell (2001) states that effective
learning, which has useful practical implications,
must support internet-based teaching. In a physical
education setting, Tsangaridou and O'Sullivan
(2003) found that the theory of the relationship
between theories is needed in teacher practice
through web-based learning.
The physical education teachers have the duties
and responsibilities in developing instructional
media. Curriculum 2013 (K-13) requires teachers to
support information and communication technology
in teaching and learning process. One of the factors
that supports it is instructional media that can help
physical education teachers to provide a variety of
materials so that their students can receive well.
ICT-based instructional media in physical education
lesson is not easy to implement because of the
uniqueness given by it. Therefore, good ability of PE
Nopembri, S., Sar yono, ., Listyarini, A. and Muktiani, N.
Literacy of Physical Education Teachers on ICT-based Instructional Media.
DOI: 10.5220/0009211900690072
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 69-72
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
69
teachers in the knowledge and the utilization of ICT
in PE lessons needs to be prepared.
Various debates can be seen from the above
studies. The development of ICT has been very
massive but has not been maximally utilized in the
world of education. Demands for the use of ICT in
the 2013 curriculum have not been fully realized by
teachers, especially PE teachers. The ability of PE
teachers to use ICT as a quality-learning medium
has not been well identified. It can be concluded that
PE teachers are expected to be able to know and use
ICT in instructional media of PE. It is necessary to
research and to explore the extent to which PE
teachers need such assistance. Therefore, the
purpose of this study is to investigate the ability
(literacy) of PE teachers to understand and utilize
ICT in instructional media.
2 METHOD
2.1 Procedure
This research is a quantitative descriptive study
with a survey method. This research began by
making a research instrument which was then
validated. The study continued with determining the
population and research samples. The research
samples were used as the subjects of the research.
The next step was collecting the data from the
research samples based on questionnaires that have
been prepared. Finally, the data were analyzed and
used as the material for writing this article.
2.2 Participants
This research was conducted in the Special
Region of Yogyakarta (DIY). The subjects of this
study were 371 physical education teachers of
primary and secondary schools in the region of
Yogyakarta.
2.3 Data Collection
The data were collected by means of a survey
using instruments in the form of a knowledge test
and questionnaires for the use/ the utilization of
ICT-based learning media. The instruments were
compiled by the researchers which were then
distributed to the respondents. So, the data were
collected about the knowledge and the utilization of
ICT-based instructional media by PE teachers. In
this process, the validity and reliability of the
instruments were also carried out based on the data
obtained. PE teachers’ knowledge on ICT-based
instructional media was measured through a
knowledge test consisting of several question items
that must be answered in accordance with the
teacher knowledge. This knowledge test was based
on the cognitive level factors (knowledge) of Bloom
which consist of remembering (C1), understanding
(C2), applying (C3), analyzing (C4), evaluating
(C5), and creating (C6). The utilization of ICT-based
Instructional Media was measured through
questionnaires consisting of series of statements
based on the factors of media use in and outside the
classroom situations, computers, multimedia,
telecommunications, and internet networks.
2.4 Data Analysis
Analysis of the data used in this study is the
percentage that is the result of the division of the
total score of the respondents by the total score that
should be multiplied by one hundred percent
(100%). The knowledge and usage /utilization data
are descriptions of the PE teachers literacy towards
ICT-based learning media.
3 RESULTS
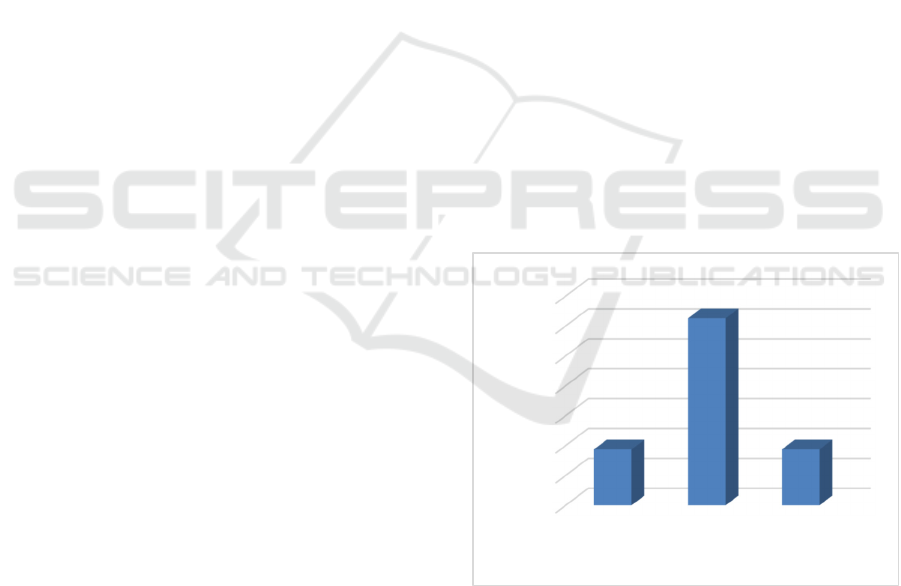
Figure 1: The Level of PE Teachers’ Knowledge on
ICT-based Instructional Media
Figure 1 shows that the level of PE teachers'
knowledge on ICT-based instructional media in
sequence was low (18.7%), moderate (62.6%), and
high (18.7%). Meanwhile, the level of PE teachers’
utilization of ICT-based learning media in sequence
was in the low category (13.4%), moderate (73.6%),
and high (13%) as shown in Figure 2
0,0
10,0
20,0
30,0
40,0
50,0
60,0
70,0
Low Moderate High
Frequency
Categories
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
70
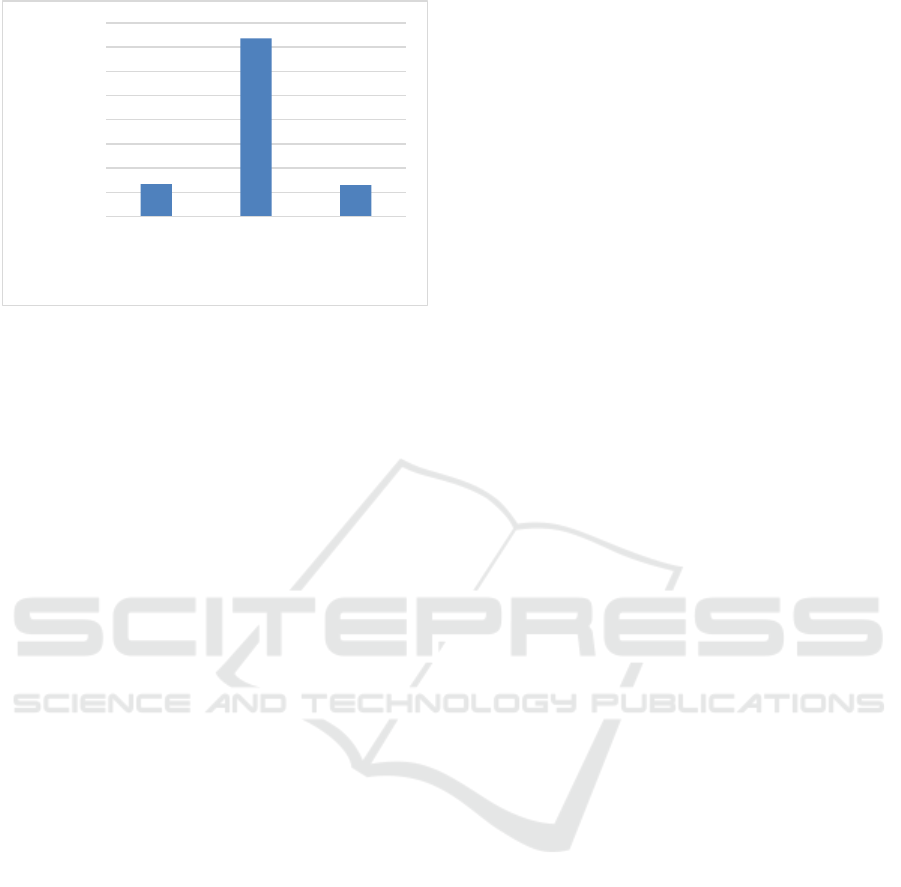
Figure 2: The level of utilization of ICT-based
instructional media by PE teachers.
4 DISCUSSIONS
At this time in schools, the 2013 curriculum have
been enacted. The 2013 curriculum using a scientific
approach is believed to be a golden platform for the
development of students' attitudes, skills, and
knowledge in approaches or work processes that
meet scientific criteria. The 2013 curriculum
reaffirms to use the learning approaches by using
teaching methods that further develop thinking skills
and active learning methods that can encourage
students to be more active in seeking answers or
activities. In general, the notion of learning is an
effort made to help a person or a group of people in
such a way so the learning process becomes more
efficient and effective.
The teachers’ knowledge of ICT-based learning
media needs to be improved in order to become a
part of its development. This is in accordance with
the theory of cognitivist perspective which views
that learning is an internal process that includes
memory, retention, information processing,
emotions, and other factors. Among cognitive
learning theories that are often used as the basis of
theory in the use of instructional media is cognitive
theory regarding the stages of development
expressed by Jean Peaget. Heinich (1996: 17)
expresses that with cognitive learning theory from
Peaget, there will be a gradual process in receiving
material to the brain in accordance with students'
abilities. Knowledge construction is also based on
the constructivist perspective, which is a learning
theory with an emphasis on experiences, not merely
cognitive knowledge (Heinich, 1996: 17). In
addition, the knowledge base is also supported by
behavioristic theory which states that learning
principles must be designed to produce behaviors
that can be observed and measured (Neo, 2007).
Some examples are teaching machine learning
programs and learning programs (a forerunner to
multimedia-based learning), and other programs that
use the Stimulus-Response concept and reinforcing
factors.
The utilization of ICT in learning includes tools
or learning media, learning facilities/places, learning
resources, and means of increasing professionalism.
Nowadays, collaborative learning situations often
use learning media. ICT allows students in different
locations to collaborate on problem solving and
online learning. The realization that learning is both
a social and mental process is very important to
understand how media can enhance learning. While
ICT-assisted learning is increasingly popular in
developed countries, this does not mean to be the
most practical. Maybe, other types of media are
more appropriate. Once again, the exact use of
media depends on the needs. Educational
experiences that involve real students and that
provide concrete examples will last longer than
abstract experiences such as listening to teacher
lectures. Learning media help to add elements of
reality - for example, the use of images or computer
simulations during lectures. We have to pay
attention to the submission of good learning
materials, for example; problem solving, intuition,
imagination, and creativity as learning components.
Anido et al., (2004) further explains that placing
teaching material on the web in the form of notes
and assignments at this time is relatively easy and
simple. ICT has at least four educational potentials,
namely as a source of information, learning aids,
media for conducting demonstrations in the
classroom, and effective communication tools that
facilitate student-teacher communication (Weigand,
2002).
Media literacy can be integrated in education in
a number of ways (Friesem 2013; Friesem et al.
2014; Neag 2015). Media literacy plays an important
role in art and music lessons (visual and audio
literacy), language learning with a focus on
communicative media functions (reading and
understanding several types of texts); and in lessons
such as history, geography, and science, which offer
the possibility of promoting media literacy by
searching, analysing, and presenting information. In
addition, media literacy is explicit in the curriculum
by discussing media topics and problems. Simons,
Meeus, and T'Sas (2017) formulated three
competencies to be literate on media. First,
competency-using media is a competence that
0,0
10,0
20,0
30,0
40,0
50,0
60,0
70,0
80,0
Low Moderate High
Frequency
Categories
Literacy of Physical Education Teachers on ICT-based Instructional Media
71

reflects the technical use of media. Second, the
competence in understanding media, namely
competence in the field (critical) understanding of
the media, including analysis, evaluation, and
reflection on media content. Third, the competence
that contributes medially, namely competencies
related to the making and communication of media
messages and participation in using media.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study concludes that the knowledge and the
utilization of ICT-based instructional media on PE
teachers differ from each other, even though most
are in the moderate category. This illustrates that the
literacy of PE teachers on ICT-based instructional
media still has many factors in gaining knowledge
and using ICT-based instructional media. Various
education and training process needed by PE
teachers to increase their literacy on ICT-based
instructional media.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank all teachers who participated in
this study. We also thanks to Faculty of Sport
Science Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta for Research
Group Grants.
REFERENCES
Andrea, M., Boos, M., 2004. Knowledge exchange via
discussion forums in virtual courses or only coffee
klatsch? Available at
www.dgof.de/gor04/index_3.html
Anindo, L., Llamas, M., Fernandez, M.J., 2001. Internet-
based Learning by Doing.
www.ece,msstate.edu/~hagler/May2001/17/Begin.htm
Clarke, P. A., Cronje, J. C. 2002. Teaching on the Internet.
www.jjponline.com/linkbrary/teaching_internet.html.
Friesem, Y., 2013. "Review: Media Literacy in the K-12
Classroom (2012)."Journal of Media Literacy
Education, 5(2), 395-396.
Friesem, Y., Quagliam, D. B, Crane, E., 2014. "Media
Now: A Historical Review of a Media Literacy
Curriculum." Journal of Media Literacy Education,
6(2), 35-55.
Heinich, R., et.al. 1996. Instruction media and
technologies for learning. New Jersey: Englewood
Cliffs.
Gary, K., O’Sullivan, M. 2003. Incidences of Student
Support for and Resistance to a curricular innovation
in High School Physical Education. Journal of
Teaching in Physical Education, 22(3).
Neag, A., 2015."Media Literacy and the Hungarian
National Core Curriculum – A Curate’s Egg," Journal
of Media Literacy Education, 7(1), 35 -45.
Neo, Mai., 2007. “Learning with Multimedia: Engaging
Students in Constructivists Learning”. International
Journal of Instructional Media, 34(2).
Simons, M., Meeus, W., T’Sas, J., 2017. “Measuring
Media Literacy for Media Education: Development of
a Questionnaire for Teachers' Competencies”. Journal
of Media Literacy Education, 9(1), 99-115
Truell, A. D., 2001. “Students Attitudes Towards and
Evaluation of Internet-Assisted Instruction”. Delta Pi
EPSILON Journal, 43(1), 40-49.
Tsangaridou, N., O’Sullivan, M., 2003. Physical
Education Teachers’ Theories of Action and Theories-
in-use. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education,
22(2).
Uwe, M., 2004. The Quality of Information in Knowledge
Exchanging Online Groups: A higher User
Satisfaction with Online Discussions via Offline Social
Networks? Available at
www.dgof.de/gor04/index_3.html
Weigand, H-G., 2002. New Ways of Communicating in
Mathematics Teacher Education: Linking to the
Internet. www.icme-organisers.dk/tsg15/Weigand
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
72
