
Analysis of Factor Affecting Profitability of State Owned Banks in
Indonesia and Notable Bank in Singapore as Basis for Bank
Management Decision Making to Its Stakeholder
Eddy Winarso
1
and Francis M. Hutabarat
2
1
Accounting Department, Economic Faculty, Widyatama University, Bandung – Indonesia
2
Accouning Department, Economic Faculty Advent Indonesia University, Bandung - Indonesia
Keywords: Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR), Loan to Debt Ratio (LDR), Non Performing Loan (NPL), Retun on Assets
(ROA), Return on Equity (ROE), Notetable Bank
Abstract: Every firm has tendency only to seek profit whereas, the objective of a firm is not only to maximize profit
and maximize their shareholder or owner but also seek to maximize the wealth of their stakeholder. This mean
that a firm needs to benefit their stakeholder and one of the stakeholders of a firm is the community around
the company. The purpose of the study is to analyze the factor affecting return on asset of state owned banks
in Indonesia and notable bank in Singapore combined. The study is descriptive using CAR, NPL and LDR as
their independent variable and ROA and ROE as their dependent variable. The financial used in the study is
for financial data use in the study from annual report and financial statement from year 2013 – 2017. Data
analysis using statistic analysis such as descriptive statistic F test, t test and regression analysis. The result
shows that all state owned banks in Indonesia and notable bank in Singapore are healthy in terms of their
minimum capital, non performing loan and their function well in LDR ratio and in their return on assetin this
study also several ratios have been used and the results are very good, including CAR, NPL, LDR and ROA.
The mean results for CAR are 18.5% for Indonesia and 16% for Singapore banks which is above 8% standard
for minimum capital for a bank. NPL mean result is 2.5% for Indonesia and < 1% for Singapore which is
below the minimum standard of 5% which shows that BUMN bank can manage their non-performing loans.
On the other hand, BUMN bank also shows that they perform their function well in giving loans and receiving
deposits from their customer as shows in LDR ratio of 91.124% for Indonesia and 85% for Singapore which
is between 78-100% standard of Bank Indonesia. The descriptive statistic data also show that ROA has mean
of 2.972% for Indonesia and 1.02% for Singapore that is above 1.5% standard of Bank Indonesia. The result
shows that there is a significant relationship between CAR, NPL, LDR and ROA of state owned banks in
Indonesia and notable bank Singapore combined from year 2013-2017. The results however are not significant
for Return on Equity.
1 INTRODUCTION
Every firm has tendency only to seek profit whereas,
the objective of a firm is not only to maximize profit
and maximize their shareholder or owner but also
seek to maximize the wealth of their stakeholder. This
mean that a firm needs to benefit their stakeholder and
one of the stakeholders of a firm is the community
around the company.
Bank is one institution that needed by the
community in all activities such as transaction
activities and savings and loan activities is Bank.
Bank as an institution becomes a very useful
container for the community, so that even throughout
the world, banks have been trusted to be a solution for
the community regarding their finances. In the
Republic of Indonesia Law Number 10 of 1998
concerning banking industry, it is said that banks are
business entities that collect funds from the public in
the form of deposits and distribute them to the public
in the form of loans and/or other forms in order to
improve the lives of many people. (Kasmir, 2014, p.
24). In order for bank to be beneficial to its
stakeholder and the community, first bank need to
have good financial performance and in other words,
it need to be healthy and function well?
Murhadi (2015) stated that the performance of a
company can be analyzed from its financial
Winarso, E. and Hutabarat, F.
Analysis of Factor Affecting Profitability of State Owned Banks in Indonesia and Notable Bank in Singapore as Basis for Bank Management Decision Making to Its Stakeholder.
DOI: 10.5220/0009258904730479
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 473-479
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
473

statements. Financial statements contain information
about financial position, financial performance, and
changes in financial position that are very useful in
making a decision. It is very important for investors
and shareholders to know the financial condition of a
company. In addition to investors and shareholders
who need these financial statements, the financial
manager also requires financial statements from the
company so that managers can use the information
contained in the financial statements so that decisions
related to Investment, financing, and company
operations can be determined. The ability of banks to
carry out their functions is to receive money from the
public in the form of savings or savings, time deposits
and checking accounts, so that this becomes a fund
collected and channeled back to the community in the
form of loans or loans can be seen from financial
statement analysis. (Kasmir, 2012)
In every business activity carried out, of course,
the first time you want is to get a profit. Various ways
that can be done by a bank to get maximum profit or
profit, one of which is a bank must have large capital.
Maximum profit can increase bank capital so that
bank operations can be carried out. And running a
business the bank must be able to achieve company
goals in general, namely to generate profits (Taswan,
2010, p. 151).
Financial ratios are part of financial statements
that show company performance. According to
Kasmir (2003:279), profitability ratio is used to
measure the level of business efficiency and
profitability achieved by the bank concerned. In other
words, profitability ratios are important financial
ratios to determine the ability of banks to earn profits
and measure the performance of a bank. One of the
banking profitability ratios is Return on Assets.
(Taswan, 2010)
Return on assets is the ratio that shows the ratio
between earnings and the total assets of the bank, this
ratio shows the level of efficiency of asset
management carried out by the bank concerned
(Pandia, 2012; Darmawi, 2014). The greater the
Return on Assets (ROA) of a bank, the greater the
bank’s profitability and the better the bank's position
in terms of asset use. In fact, what happens in
companies is that the ROA in small banks has
decreased.
A case stated in Kompas (2017) reported that PT
Bank Bukopin Tbk posted a profit that decreased by
14 percent compared to the previous period. The
report also stated that the capital adequacy ratio
(CAR) increased to 16.34 percent and in addition to
the increase in CAR, the level of liquidity is still well
maintained as loan to deposit ratio or the ratio of
credit to deposits (LDR) is 75.07 percent. On the
other hand, news by Kompas (2018), stated that PT
Bank Tabungan Pensiunan Nasional Tbk (BTPN)
achieved a net profit of Rp 1.2 trillion in 2017. This
figure fell 30 percent compared to the previous year's
achievement. While total funding increased 5 percent
to Rp. 76.5 trillion, with the composition of third
party funds (DPK) up 3 percent to Rp. 67.9 trillion.
Then the company's total assets rose 5 percent to Rp.
95.5 trillion. And it was found that the capital
adequacy ratio (CAR) reached 24.6 percent.
In other cases, Bank is known to also beneficial to
the community by bringing its responsibility in the
form of Scholarship, education endowment, and other
form of fund to the society in Indonesia. (IDN Times,
2018)
Thus from the above case it can be seen that the
condition of changes in CAR and the LDR appear to
have a change in the profit of a bank.Based on the
existing background, the researchers feel the need to
conduct research with the title
Analysis of Factor Affecting Profitability of State
Owned Banks in Indonesia and Notable Bank In
Singapore as Basis for Bank Management Decision
Making to Its Stakeholder
Significant of the Study
The uses of this study are significant for the authors,
in gaining knowledge and the practical experience in
expanding research on different countries as well as
in analyse company's financial statements and their
development. The study also significant for
researcher universities, in supporting the institution
program for their faculty. As additional information,
the study can also be used as a decision-making tool
for companies, investor and other readers.
2 LITERATURE
Financial ratios are numbers obtained from the
comparison of the extracts of one financial statement
post with another that has a relevant and significant
relationship (Harahap, 2004). Whereas according to
Ediningsih (2004) financial ratios are comparisons
between two elements of financial statements that
show an indicator of financial health at a certain time.
Financial ratios are very important for external
analysts who assess a company based on published
financial statements. This assessment includes the
problems of liquidity, solvency, profitability,
management efficiency and prospects for the
company in the future.CAR or often referred to as the
bank’s capital adequacy ratio, is a ratio to shows how
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
474

a bank is able to finance its activities with ownership
of its capital. It is interesting to see how the adequate
capital of banks that can be seen through CAR ratios
can affect banks purpose which it maximize profit
that can be seen through profitability ratio such as
ROA.NPL is a financial ratio that is used as a proxy
against the return credit given to bank depositors in
other words the NPL is the level of bad debts at the
bank. This ratio shows that the bank's management
capabilities in managing troubled credits provided by
the bank. The smaller the Non Performing Loan
(NPL), then the small credit risk borne by the bank.
The bank has a role as the implementation of
monetary policy and the achievement of financial
system stability, so that a healthy, transparent and
accountable banking system is needed. (Indonesian
Banking Booklet 2009) The purpose of the banking
business fundamentals is to obtain optimal benefits by
providing financial services to the public. For
shareholders to invest in the bank aims to earn income
in the form of dividends or get a profit from an
increase in the price of shares owned. (Mudrajad and
Suhardjono, 2002) It is important for banks to always
maintain good performance, especially maintaining a
high level of profitability, being able to distribute
dividends well, business prospects that are always
developing, and able to fulfill prudential banking
regulation provisions well (Mudrajad and
Suhardjono, 2002). If a bank can maintain its
performance well then it can increase the value of
shares in the secondary market and increase the
amount of funds from third parties.
The increase in the value of shares and the amount
of funds from third parties is one indicator of
increasing public trust in the bank concerned. Trust
and loyalty of the owner of the fund to the bank is a
very helpful factor and makes it easier for the bank
management to develop a good business strategy.
Fund owners who lack trust in the bank concerned are
very low in loyalty. This is very unfavorable for the
bank in question, because the owners of funds can
withdraw funds at any time. It is important to evaluate
company performance, both by management,
shareholders, the government, and other parties with
an interest in and related to distributions how that
financial ratios are useful in assessing the financial
condition of a banking company. Financial ratios are
also useful in predicting company profits.
The strength of predictions of financial ratios in
predicting profits so far is indeed very useful in
assessing company performance (performance) in the
future. The strength of financial ratio predictions was
found differently by several researchers. But whether
all existing financial ratios have the ability to predict
profits, someone has already done their research.
Below discussion regarding hypothesis of the study is
comprised of results of previous studies regarding
CAR, NPL, LDR, and ROA.
Hypothesis of the Study
Based on the background description of the problem
above, the hypothesis in this study are as follows:
CAR or often referred to as the bank’s capital
adequacy ratio, is a ratio to shows how a bank is able
to finance its activities with ownership of its capital.
It is interesting to see how the adequate capital of
banks that can be seen through CAR ratios can affect
banks purpose which it maximize profit that can be
seen through profitability ratio such as ROA. (Abba,
Okwa, Soje and Aikpitanyi, 2018)
Moreover, working capital to finance operations,
as an instrument to drive the ratio, and as a tool for
business expansion. Research on the capital aspect of
a bank is more to find out how or the bank's capital is
sufficient to support its needs (Merkusiwati, 2007). In
this study, capital adequacy is studied based on the
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) ratio. Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR) at a certain level determines
that banks have sufficient capital capacity to reduce
risk due to the increase due to an increase or increase
in wealth assets categorized as producing results and
also containing substances (Werdaningtyas, 2002).
Research conducted by Werdaningtyas (2002),
Mawardi (2005) and Suyono (2005) shows the results
that Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) has a positive and
significant influence on Return on Assets (ROA).
Whereas Mawardi (2005) shows that Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR) has a positive and not
significant effect on Return On Assets (ROA) and
Sarifudin (2005) which shows the results of a positive
and not significant Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)
ratio associated with Return On Asset Assets
(ROA)Whereas Mawardi (2005) shows that Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR) has a positive and not
significant effect on Return On Assets (ROA) and
Sarifudin (2005) which shows the results of a positive
and not significant Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)
ratio associated with Return On Asset Assets (ROA).
H
1
: There is a relationship between CAR and
Profitability
NPL is a financial ratio that is used as a proxy against
the return credit given to bank depositors in other
words the NPL is the level of bad debts at the bank.
This ratio shows that the bank's management
capabilities in managing troubled credits provided by
the bank. The smaller the Non Performing Loan
(NPL), then the small credit risk borne by the bank
Analysis of Factor Affecting Profitability of State Owned Banks in Indonesia and Notable Bank in Singapore as Basis for Bank Management
Decision Making to Its Stakeholder
475

hence the aspect of supervision is decreasing, so that
Non-Performing Loans (NPL) are getting bigger or
credit risk is getting bigger (Mawardi, 2005).
Research on the effect of Non Performing Loans
(NPL) shows different results. Among other things,
research conducted by Mawardi (2005) shows that
Non Performing Loans (NPL) has a negative and
significant influence on Return on Assets (ROA).
While the research conducted by, Suyono (2005)
shows the results that Non Performing Loans (NPL)
are negative and not significant to Return on Assets
(ROA).
H
2
: There is a relationship between NPL and
Profitability
According to Kuncoro and Suhardjono (2002),
financial institutions are very important in economic
development because funds are needed to implement
them.Article 3 of the Banking Law says that the main
function of bank in Indonesia banking is to collect and
channel public funds. (Fahmi, 2014). It is interesting
to see how the function of banks that can be seen
through LDR ratios can affect the its purpose which
it maximize profit that can be seen through
profitability ratio such as ROA. LDR have a positive
and significant effect on bank profits, the results of
the study of Werdaningtyas (2002) is that a Loan to
Deposit Ratio (LDR) has a negative and significant
effect on profitability (ROA). Loan to Deposit Ratio
(LDR) is also defined as how much bank funds are
released into credit (Merkusiwati, 2007). Research on
the effect of the Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR) shows
different results. Among others, research conducted
by Suyono (2005) shows the results of the Loan to
Deposit Ratio (LDR) has a positive and significant
effect on Return on Assets (ROA). Usman (2003)
shows the results of the Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR)
have a positive and significant effect on bank profits.
On the other hand, the result of the study of
Werdaningtyas (2002) is a Loan to Deposit Ratio
(LDR) that has a negative and significant effect on
profitability (ROA).
H
3
: There is a relationship between LDR and
Profitability
CARS, NPL, LDR are ratios that related to the
CAMEL ratio which evaluate the health of a bank
(Simanjuntak & Hutabarat, 2016). CAR or often
referred to as the bank’s capital adequacy ratio, is a
ratio to shows how a bank is able to finance its
activities with ownership of its capital. Loan to
Deposit Ratio (LDR) is defined as how much bank
funds are released into credit, while NPL is the level
of bad debts at the bank. It is interesting to see how
the adequate capital of banks that can be seen through
CAR ratios, bad debt level of bank and how much
bank funds are released into credit can affect banks
purpose which it maximize profit that can be seen
through profitability ratio such as ROA. Previous
studies stated that there is no significant relationship
between CAR and ROA (Hindarto, 2011; Catur
Wahyu Endra Yogianta, 2013; Harun, 2016). On the
other ht there is a relationship between LDR and ROA
(Catur Wahyu and, other study stated that there is a
relationship between CAR and ROA (Edwar, Yokeu,
Bernadin, 2016). Previous study stated that there is no
significant relationship between LDR and ROA
(Edwar, Yokeu, Bernadin, 2016). On the other hand,
other studies stated that Endra Yogianta, 2013;
Hindarto, 2011; Harun, 20160). Previous study stated
that there is no significant relationship between LDR
and ROA (Edwar, Yokeu, Bernadin, 2016). On the
other hand, other studies stated that there is a
relationship between LDR and ROA (Catur Wahyu
Endra Yogianta, 2013; Hindarto, 2011; Harun,
20160) and also between NPL and CAR toward ROA
(Anwar & Murwaningsari, 2017).
H
4
: There is a relationship between CAR, NPL,
LDR, and ROA
3 METHOD OF THE STUDY
To limit the breadth of the discussion in this study,
researchers limit research in terms of the scope and
limitations of research problems. This research was
conducted at state-owned banks listed on the
Indonesian Stock Exchange and notable bank in
Singapore. The study used panel data that was taken
from annual report and financial statement of four
state-owned bank Indonesia and three notable bank in
Singapore of five year data from 2013-2017 with total
sample of 35 data. The use of panel data of two
consecutive years give advantage to measurement of
the changes that take place between points in time
(Cavana et al as seen in Alzahrani Che-Ahmad,
2015). The data taken from the operational variables
used in the study comprise of independent variables
and dependent variables. The independent variables
used in this study are the Capital Adequacy Ratio
(CAR), Non Performing Loan (NPL) and the Loan to
Deposit Ratio (LDR). While the dependent variable
is Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity
(ROE). The sample used in the study from four state-
owned banks that are listed at Indonesia Stock
Exchange are: Bank Mandiri (BMNI), Bank BNI
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
476
(BBNI), Bank BRI (BBRI), and Bank BTN (BBTN),
from Banking sub sector, while the three notable bank
in Singapore are: OCBC Bank, DSB Bank and UOB
Bank.
Analysis of the variables using formula for:
1. Dependent Variable (Profitability)
a. Return on Asset as first dependent variables
with standard
ROA > 1.5%.
b. Return on Equity for the second dependent
variables with standard ROE > 12%.
2. Independent variable
a. Capital Adequacy Ratio, with CAR > 8%
standard.
b. Non Performing Loan, with NPL < 5%
standard
c. Loan to Deposit ratio, with LDR 78-100%
standard.
The statistical analysis is done using Descriptive
statistics of Mean, Standard Deviation, Minimum and
Maximum, Correlation Matrix, Regression analysis,
F-test, t-test, and Kolmogorov-Smirnov.
The economic model is used to develop a model
of a company’s profitability or its ability to gain
profit. The variable proposed for the model includes
the following functional equation:
ROA it = β0 + β1CAR + β2NPL+β3LDR + ei + uit
. . . . (1)
ROE it = β0 + β1CAR + β2NPL+ β3LDR + ei +
uit . . . . (2)
Where:
ROA it = profitability Return on Asset
ROE it = profitability Return on Equity
CAR = capital adequacy ratio
NPL = non performing loan
LDR = loan to deposit ratio
e = error term
i = indicating data for the i bank
t = time indicator
4 RESULT OF THE STUDY
4.1 Descriptive Statistic
Table 1 shows the characteristic of variables of the
study based on its bank profile whether they are from
Indonesia or Singapore stock exchange origin.
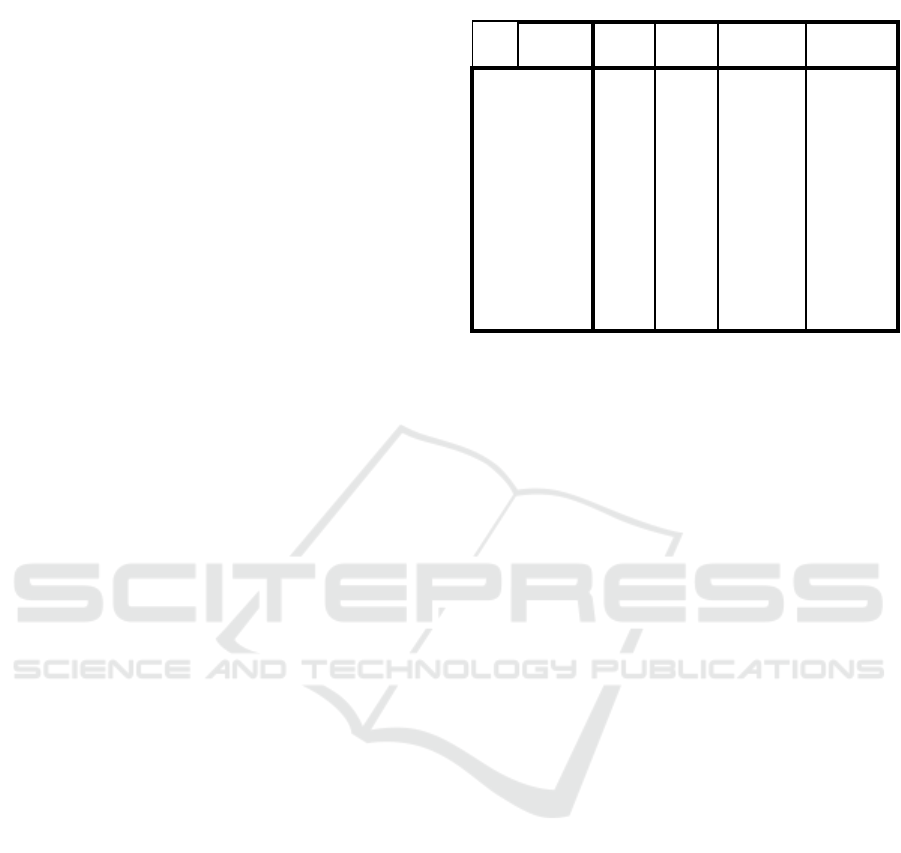
Table 1. Descriptive Statistic
Grou
p
Statistics
Profile
N
Mean Std.
Deviation
Std. Erro
r
Mean
CAR
Indonesia
20 18.5065 2.59021 .57919
Sin
g
a
p
ore 15 16.4267 .85813 .22157
N
PL
Indonesia
20 2.5765 .82675 .18487
Sin
g
a
p
ore 15 .8741 .67207 .17353
LDR
Indonesia
20 91.1390 8.91516 1.99349
Sin
g
a
p
ore 15 85.1738 1.69436 .43748
ROA
Indonesia
20 2.9720 1.08742 .24316
Singapore 15 1.0240 .10398 .02685
ROE
Indonesia
20 20.7400 6.51415 1.45661
Sin
g
a
p
ore 15 11.2400 1.30701 .33747
Based on the table 1 the result shows that the
variables of the study have good mean results.
Generally, the mean results for CAR in Indonesia is
higher than in Singapore with Indonesia at 18.5065%
and Singapore 16.4267% which is both above 8%
standard for minimum capital for a bank. NPL mean
result on the other hand shows that Singapore has
lower non performing loans with .87% than its
Indonesia counterparts which is 2.5765% which is
both below the minimum standard of 5%. This shows
that State-owned bank in Indonesia and notable bank
in Singapore can manage their non-performing loans.
Moreover, State-owned bank in Indonesia shows
that they perform their function well in giving loans
and receiving deposits from their customer as shows
in LDR ratio of 91.124% which between 78-100%
standard of Bank Indonesia while Singapore notable
bank is at 85%. The descriptive statistic data also
show that ROA in Indonesia state-owned bank has a
mean of 2.972% that is above 1.5% standard of Bank
Indonesia and also above those in notable bank in
Singapore which is 1.02%. The same goes for ROE
in Indonesia 20.7% which is higher than in Singapore
at 11.2%.
Therefore, based on the result of the Descriptive
statistic, state-owned bank in Indonesia shows that
they have good financial performance in comparison
with their notable bank in Singapore.
Analysis of Factor Affecting Profitability of State Owned Banks in Indonesia and Notable Bank in Singapore as Basis for Bank Management
Decision Making to Its Stakeholder
477
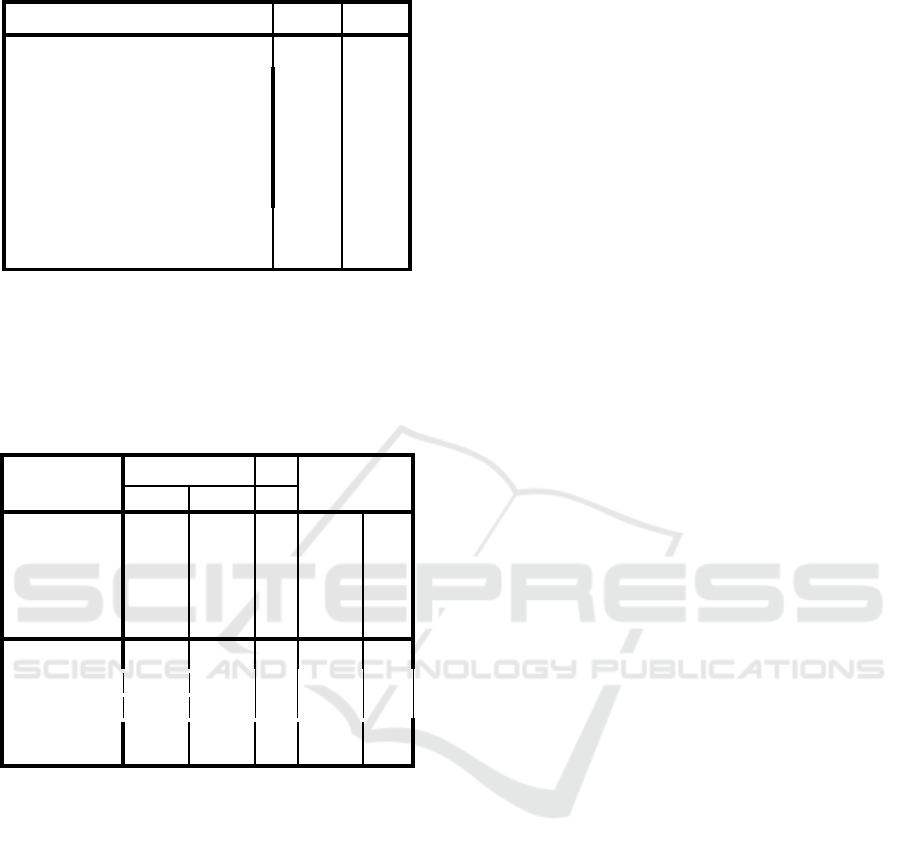
Table 2. Normality Test
ROA ROE
N
35 35
Normal
Parameters
a,b
Mean
2.1371 16.6686
Std.
Deviation
1.27354 6.86795
Most Extreme
Differences
A
bsolute
.219 .195
Positive .219 .195
Negative -.164 -.155
Kolmogorov-Smirnov Z
1.296 1.152
A
symp. Sig. (2-tailed)
.070 .140
Table 2 above show that the test distribution is
normal using kolmogrov -Smirnov normality test for
the dependent variable of the study based on Asyump.
Sig >0.05 Therefore, the data is normally distributed.
Table 3. Regression Model
Coefficients
a
Model Coefficients Coefficient
B T Sig.
1
(Constant)
5.314 1.401 .171 F 4.078
CAR .139 1.444 .159 Sig. .015
NPL .516 2.037 .050 R .532
LDR
-.074 -2.034 .051 R
Square
.283
2
(Constant)
23.114 .999 .325 F .941
CAR .434 .738 .466 Sig. .433
NPL 1.500 .972 .338 R .289
LDR
-.190 -.854 .399 R
Square
.083
Table 3 above show that the first model on
hypothesis 4 is accepted where CAR, NPL, and LDR
has a significant correlation towards profitability
based on Return on Asset with F-count 4.078 and p-
value 0.015 at α = 5%. On the other hand, the second
model is not accepted since F-count is .941 with p-
value 0.433 at α = 5%, thus there is no significant
relationship between CAR, NPL, and LDR toward
ROE.
Moreover, based on the t-test above H1is
accepted that there is a significant relationship
between CAR and ROA, however H
2
and H
3
is not
accepted that NPL and ROA is not significant and
also between LDR and ROA.
For the regression analysis, based on the table
above, the results show that the regression model for
the study is:
Y = a + b
1
X
1
+ b
2
X
2
+ b
3
X
3
ROA = 5.314 + 0.139 CAR + 0.516 NPL – 0.074
LDR
The regression model indicates that the increase
of CAR by 1 point will increase ROA by 0.139, and
the increase of NPL by 1 point will increase ROA by
0.516, and the increase of LDR by 1 will decrease
ROA by 0.074.
CAR as often referred to as the bank’s capital
adequacy ratio, based on the result shows that state-
owned bank and notable bank in Indonesia and
Singapore are able to finance its activities with
ownership of its capital. The result shows CAR ratios
can affect bank’s ability to gain profit as seen in its
ROA profitability ratio.
The result also shows that the CAR in both
country is at least twice the required standard of 8%
with mean of 18% and 16% respectively for
Indonesia state owned bank and notable bank in
Singapore which indicate they want to have sufficient
capital capacity to reduce risk (Werdaningtyas,
2002). This result is shown to be supported by
previous study such as conducted by Udom and Eze
(2018).
5 CONCLUSION
In this study the researcher found that the effect of
CAR, NPL.LDR on ROA was very good because it
found significant results between these variables. The
mean results for both Indonesian state-owned bank
and notable bank in Singapore are above 8% standard
for minimum capital for a bank. NPL also resulted
below the minimum standard of 5% which shows that
state-owned bank in Indonesia and notable bank in
Singapore can manage their non-performing loans.
On the other hand, state-owned bank in Indonesia and
notable bank in Singapore also shows that they
perform their function well in giving loans and
receiving deposits from their customer as shows in
LDR ratio between 78-100% standard of Bank
Indonesia. The descriptive statistic data also show
that ROA has mean above 1.5% standard of Bank
Indonesia. Hence, the state owned bank in Indonesia
and notable bank in Singapore has good financial
performance from year 2013-2017.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
478

RECOMMENDATION
The researcher saw that the relationship between
CAR, NPL, LDR and ROA was so good that
researchers recommended Indonesia and Singapore
bank investors to hold shares in state-owned
companies and notable bank listed on the Indonesian
and Singapore stock exchange. In terms of
management decision making for their stakeholder,
the banking Industry has supported the community
not only in the business sense but also in humanity
way, in terms of scholarship and also other social
responsibility action. It is best for bank state-owned
bank in Indonesia to always help the community
around and Indonesia as a whole. This is also applied
to Singapore notable bank stakeholder.
REFERENCES
Abba, G. O., Okwa, E., Soje, B., and L. N. Aikpitanyi.
(2018). Determinants of Capital Adequacy Ratio of
Deposit Money Banks in Nigeria. Journal of
Accounting & Marketing, Vol. 7 No. 2. DOI:
10.4172/2168- 9601.1000271.
Anwar, Y., and E. Murwaningsari. (2017). the Effect of
Credit Risk and Capital Adequacy Ratio upon Return
on Asset. The Accounting Journal of
BINANIAGA, Vol. 2 No. 2, December 2017. PISSN:
2527-4309, EISSN: 2580-1481.
Darmawi, H. (2014). Manajemen Perbankan. Jakarta:
PT.BumiAksara.
Ediningsih, S. I. (2004). Rasio Keuangan dan Prediksi
Pertumbuhan Laba: Studi Empiris pada Perusahaan
Manufaktur di BEJ, Wahana, Vol. 7, No. 1.
Edwar, Yokeu, Bernadin, (2016).Pengaruh CAR dan LDR
terhadap Return on Assets. Jurnal Ecodemica, Vol. 4,
No 2 (2016)
Fahmi, (2014), Bank dan Lembaga Keuangan Lainnya.
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Fahmi, (2014). Pengantar Perbankan. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Harahap, S. S. (2004.) Analisis Kritis Atas Laporan
Keuangan. Jakarta. PT Raja Grafindo Persada
Harun, U. (2016). Pengaruh Rasio – Rasio Keuangan CAR,
LDR, NIM, NPL, BOPO terhadap ROA. Jurnal Riset
Bisnis dan Manajemen, Vol. 4 No. 1
Hindarto, (2011) Analisis pengaruh CAR, NIM, LDR,
NPL, BOPO dan KAP terhadap Return on Asset. Jurnal
Bisnis Strategic, Vol. 20 No. 20
IDN Times, (2018). Jangan Ketinggalan 4 Beasiswa ini
Menantimu Di Pertengahan Semester. Available at:
https://www.idntimes.com/life/education/ambar-
riyani/jangan-ketinggalan-4-beasiswa-ini-menantimu-
di-pertengahan-semester-c1c2
Kasmir, (2003). Manajemen Perbankan. Jakarta: Grafindo
Persada.
Kasmir, (2012). Manajemen Perbankan. Jakarta: Raja
Grafindo Persada.
Kasmir, (2014). Analisis Laporan Keuangan, Edisi
Pertama, Cetakan Ketujuh. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo
Persada
Kompas, (2017). Semester 1 2017 Laba Konsolidasi Bank
BukopinTurun 14 Percent. Kompas
Kuncoro and Suhardjono (2002). Manajemen Perbankan.
Yogyakarta: Salemba Empat.
Mawardi, W.(2005). Analisis Faktor - Faktor Yang
Mempengaruhi Kinerja Keuangan Bank Umum Di
Indonesia (Studi Kasus Pada Bank Umum dengan Total
Assset Kurang Dari 1 Triliun). Jurnal Bisnis Strategi,
Vol. 14, No. 1, Hal: 83-93, Juli 2005.
Merkusiwati and N. K. L. Aryani. (2007). Evaluasi
Pengaruh CAMEL terhadap Kinerja Perusahaan.
Buletin Studi Ekonomi, Volume 12 No. 1 Tahun 2007
Mudrajad, Kuncoro dan Suhardjono. (2002) Manajemen
Perbankan. Yogyakarta: BPFE
Murhadi, (2015). Analisa Laporan Keuangan. Jakarta:
Salemba Empat.
Pandia, F, (2012). Manajemen Dana dan Kesehatan Bank.
Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Republic of Indonesia Law Number 10 of 1998 concerning
banking industry
Simanjuntak, D., and F. M. Hutabarat, (2016). Bank
Financial Performance Using CAMEL Ratio and
Market Value Tobin’s Q of Banking Sub-Sector Listed
at Indonesian Stock Exchange. 2
nd
International
Multidisciplinary
Conference (IMC) 2016 Proceedings. Universitas
Muhammadiyah Jakarta. Available at
http://jurnal.umj.ac.id
Suyono, A, (2005). Analisis Rasio – rasio bank yang
Berpengaruh Terhadap ROA, Thesis, Program Pasca
Sarjana Magister Manajemen Universitas Diponegoro.
Taswan, (2010). Manajemen Perbankan. Yogyakarta: UPP
STIM YKPM.
Udom, I. S., and O. R. Eze, (2018). Effect of Capital
Adequacy Requirement on the Profitability of
Commercial Banks in Nigeria. International Research
Journal of Finance and Economics, Issue 165 Jannuary
2018. ISSN 1450-2887.
Werdaningtyas, H, (2002). Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi
Profitabilitas Bank Take Over Pramerger Di Indonesia.
Jurnal Manajemen Indonesia, Vol. 1, No. 2, Hal: 24-
39.
Yogianta, C. W. E., (2013). ANALISIS PENGARUH
CAR, NIM, LDR, NPL Dan Bopo Terhadap
Profitabilitas Studi Pada Bank Umum Yang Go Publik
Di Bursa Efek Indonesia Periode Tahun 2002-2010.
Jurnal Bisnis Strategi Vol. 22 No. 2 Desember 2013.
Analysis of Factor Affecting Profitability of State Owned Banks in Indonesia and Notable Bank in Singapore as Basis for Bank Management
Decision Making to Its Stakeholder
479
