
The Effect of Part and Whole Methods to Improving Shooting
Accuracy in Futsal Players of UNY
Subagyo Irianto
1
, Fitrian Agung Yudhistomo
1
1
Sport Coaching Department, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Jl. Colombo No.1 Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Part Method, Whole Method, Shooting Accuracy
Abstract: This research aims to identify the effects of part and whole method in increasing the shooting accuracy for
the players of UNY Futsal Club. This research’s method is experimental research with two groups pre-test
post-test as its design. The population for this research is 20 players from the UNY male futsal club, and
they were chosen using the total sampling technique. All the samples are given a pretest in the form of
shooting accuracy in order to determine the treatment group, the result of the test was ranked, and then
matched with the A-B-B-A cycle into two groups, consisting of 10 members each. This research uses the
instep as its research instrument, with the validity of 0.978 and reliability of 0.989. This research uses T-test
as its data analysis technique, with the significance level of 5%. The result of this research shows that (1)
there is a significance effects on the use of part method in increasing the shooting accuracy of the players,
with the T-count 6.946 > T-table 2.262, and the significance value 0.000 < 0.05, and the increasing number
of the percentage as much as 28.88%. (2) There is a significance effect on the use of whole method in
increasing the shooting accuracy of the players, with T-count 5.823 > T-table 2.262, and the significance
value 0.000 < 0.05, and the increasing of the percentage as much as 19.46%. (3) The part method is better
than the whole method in increasing the shooting accuracy of the players, with the post-test mean difference
of 1.8.
1 INTRODUCTION
Futsal game is a sports game played by teams that
require teamwork in each group. Futsal game not
only requires teamwork but also individual
techniques. Some aspects of skill mastery in futsal
include technique skills, understanding of tactic,
physical and mental fitness.
Every futsal player has to have good skills in
playing futsal. The basic skills in futsal are not very
different from those in soccer. Those basic skills are
ones with or without the ball. Practice for a kid
under 13 years old has an emphasis on technique
mastery, so the given materials are related to the
techniques that are applied in the game. The basic
techniques that are developed in futsal are also not
very different from those in soccer. Among those
techniques are kicking, passing, keeping, and
shooting the ball to the soccer goal. The smaller size
of the field in futsal, the smaller number of player,
and faster movements make bigger number of goals.
Futsal game puts more emphasis on skills, so the
tactics and strategies are easily applied in this game.
Skills mastery in futsal requires regular and oriented
practice, so futsal players can play well.
Improving futsal skills is certainly not easy. Not
only does it need frequency, but also the right
method. The basic techniques of futsal are not as
many as they are in soccer, but in practice, the
players must have prime skills in order to play this
sport well. Futsal is a type of sports which has rigid
physics rules (Jaya, 2008). Sliding tackle, body
charge, and other harmful aspects in soccer are not
allowed in futsal.
In line with that opinion, futsal is a very fast and
dynamic game (Murhananto, 2006). In terms of a
relatively small field, there is almost no room to
make a mistake. It needs teamwork among the
players for an accurate passing, not just passing by
the opponent. Teamwork among the players is a
necessary factor to support a good team play. During
a futsal game it no longer matters who scores, but
the teamwork and high team collectivity will elevate
a team’s achievement.
Futsal is a branch of sports game adopted from
soccer game, thus having no different techniques
Irianto, S. and Yudhistomo, F.
The Effect of Part and Whole Methods to Improving Shooting Accuracy in Futsal Players of UNY.
DOI: 10.5220/0009303401650170
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 165-170
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
165

from those in soccer games. Among those
techniques are passing, shooting, controlling,
chipping, and dribbling. One of the skills the players
need is a powerful kick and directed to the goal
which is often called ‘shooting’. Shooting towards
the goal is required in order to score in each match.
It has a particular characteristic that is the ball
kicked so hard and fast that it is difficult for the
goalkeeper to anticipate. However, a good shooting
combines power, accuracy and faith and focus to
score a goal. Shooting is an extremely important
technique in a futsal game because the main purpose
of the game is to score a goal. A player with a good
and accurate shooting skill will find it easy to score
a goal especially during penalty. A good shooting
mastery will make it easier to score a goal or to kick
the ball to the opponent’s goal.
Shooting is a way to score a goal, this is caused
by the fact that every player has a chance to score a
goal and improve the game or the match (Lhaksana,
2011). Shooting can be done in various ways, by
using the top of the foot, the tip of the foot, the inner
side of the foot. However, shooting with the top of
the foot is more effective and more often done by
futsal players. They must be able to shoot well and
accurately under and in a limited time, narrow space,
a tired body, and within the opponent’s guard
(Lhaksana, 2011).
Based on the observation done by the
researchers, futsal players of UNY futsal club have
not mastered the shooting technique yet. The
common problem is that they perform shootings that
are not very accurate and optimal, resulting in a miss
and a less-oriented shot. This could be seen when
they kicked the ball and rarely scored. The problem
was, during a match the players often gave
inaccurate shots, the ball even shoots high upwards.
Shooting is one of the technique that holds an
important role. Because the purpose of shooting is to
get the ball into the opponent’s goal in an attempt to
score a point to change the situation or what is
commonly called a score.
To overcome the problem, a method of practice
needs to be given to improve shooting accuracy. A
method of practice is a procedure and a way of
choosing the type of exercise and its organization
based on the level of complexity and body weight
(Nossek, 1995). The purpose of an exercise planning
to develop an athlete’s skills and performance. The
method of practice used is whole method. It is
generally applied to learn a simple skill. As stated,
“If the taught sports skills are simple and easily
understood, they are better taught as a whole, and
each particular technique is only taught specifically
if the athlete or the subject always makes a mistake
in that particular technique” (Harsono, 2015).
A suitable method of practice is so required to
master the basic skills in futsal that the right method
of practice is needed to fix the basic technique
movements of futsal, which are Part Method and
Whole Method. “Part method is an approach where
in the beginning the students are directed to practice
the whole movements part by part, and only until
each part is mastered do they start practicing the
movement as a whole” (Sugiyanto, 1997).
Part method is expected to help fix and improve
the basic techniques of futsal skills during practice.
“Whole method gives a maximal advantage if simple
movements were to be taught” (Lutan, 2002). Whole
method is basically very suitable or relevant to learn
simple skills. However, if there is some complexity
or a difficult movement in some parts, they could be
taught specifically to students if they often make
mistakes in performing those movements.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
2.1 Research Type
This is an experimental research. Experiment
method is defined as a systematic method in order to
build a causal-effect relationship (Sukardi, 2015).
The design used in this research is “Two Groups
Pretest-Posttest Design”.
2.2 Research Time and Place
The research took place in Badminton Hall of
Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta. It was conducted in
February – March 2019. Treatment was given in 16
meetings, with the frequency of 4 times a week, on
Tuesday, Wednesday, Friday, and Sunday.
2.3 Research Target/Subject
The population of this research is the 20 male futsal
players of UKM UNY. The samples of this research
are male futsal players who were chosen through
total sampling technique. Samples were divided into
two groups, Group A as an experiment group was
given part method of practice and Group B whole
method of practice.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
166
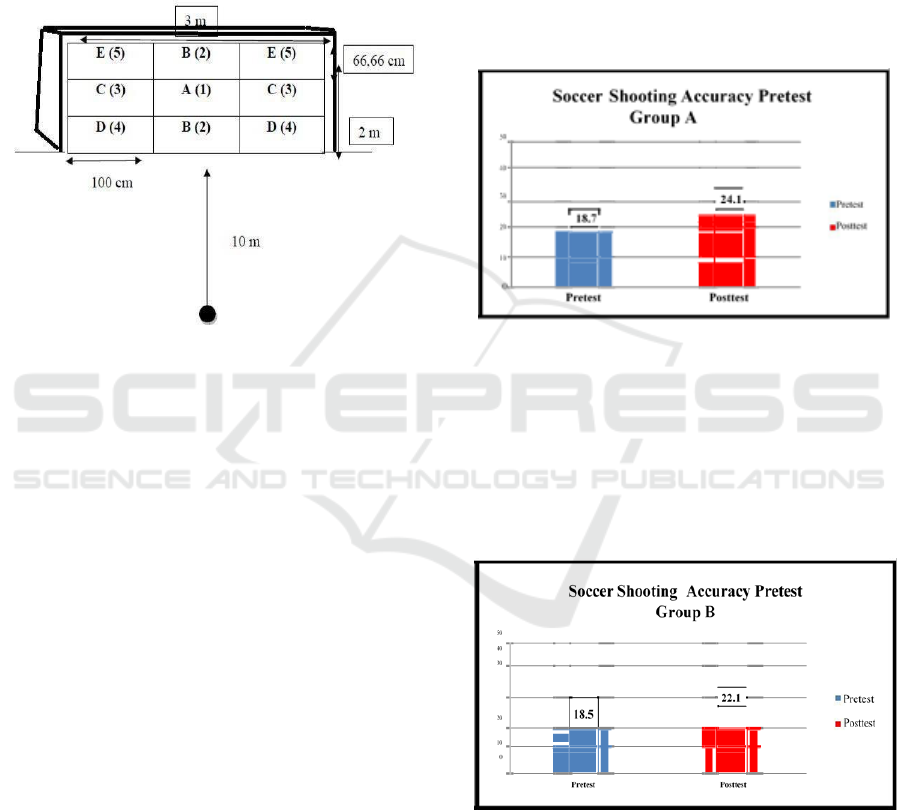
2.4 Data, Instrument, Data Collection
Technique
The test instrument for both pretest and posttest
utilized futsal shooting accuracy test using the top of
the foot, with a validity level of 0.978 and reliability
of 0.989. The figure of shooting accuracy test with
the top of the foot (Maulana, A. T., 2009) can be
seen below.
Figure 1: Shooting accuracy test field. (Source: Maulana,
A. T., 2009)
Shooting was done from the second penalty point
within 10 m from the goal and the ball was kicked
towards the target, which was the futsal goal of 2 m
high and 3 m wide, which was then divided into 9
parts, and each part was 66.66 cm high and 100 cm
wide. Score 1 was for target (A), score 2 was for
target (B), score 3 was for target (C), score 4 for
target (D), and score 5 for target (E). If the kick hit
the goal post and was not in, no score was given and
there was no repetition. Each testee did 10 shots.
2.5 Data Analysis Technique
Before hypothesis testing, precondition testing was
needed. The test of the measurement result data
related to the research result aims to improve the
analysis. Therefore, the normality and homogeneity
of the data were tested.
Hypothesis testing used t-test with the help of
SPSS 16, that is by comparing the mean between the
pretest and the posttest. If the t value is smaller than
t table, Ha is rejected, if t value is bigger than t table,
Ha is accepted.
3 RESEARCH RESULT AND
DISCUSSION
3.1 Research Result
3.1.1 Shooting Accuracy Pretest and
Posttest Group A
The shooting accuracy pretest and posttest of male
futsal players of UKM UNY of part method are
shown in the following figure 2:
Figure 2: Bar chart of shooting accuracy pretest and
posttest of male futsal players of UKM UNY of group A
3.1.2 Shooting Accuracy Pretest and
Posttest Group B
Shooting accuracy pretest and posttest of male
futsal players of UKM UNY of whole method are
shown in the following figure 3:
Figure 3: Bar chart of shooting accuracy pretest and
posttest of male futsal players of UKM UNY of group B
The Effect of Part and Whole Methods to Improving Shooting Accuracy in Futsal Players of UNY
167
3.2 Precondition Testing of Normality
Test Results
Normality test was measured using Kolmogorov-
Smirnov Z formula. The result is shown in the table
1 below:
Table 1: Normality testing.
Group
P
Notes
Pretest Group A
0.660
Normal
Posttest Group A
0.932
Normal
Pretest Group B
0.556
Normal
Posttest Group B
0.925
Normal
From the result in table 1, we can see that all data
have a p value (Sig.) > 0.05. so the variables are
normally distributed. Because all data are normally
distributed, the analysis could be proceeded with
parametric statistics.
3.3 Test of Homogeneity
Homogeneity principle suggests that if p > 0.05,
then the test is homogenous, if p < 0.05, then the test
is not homogenous. Test of Homogeneity for this
research are shown in the following table 2:
Table 2: Test of homogeneity.
Group
Sig.
Notes
Pretest
0.873
Homogenous
Posttest
0.503
Homogenous
From table two, we can see that pretest-posttest
sig. p > 0.05 so the data is homogenous. “Because
all data are homogenous, the data analysis could be
futsal players of UKM UNY”.
3.4 Hypothesis Testing Result
The first hypothesis reads “There is a significant
effect of part method on shooting accuracy
improvement in futsal players of UKM UNY”, the
data of the analysis result is shown below:
Table 3: T-test of shooting accuracy pretest and posttest
results of part method group.
Mean
t-test for Equality of means
t ht
t tb
Sig.
Difference
%
18.70
6.946
2.262
0.000
5.4
28.88%
24.10
T-test result shows that the t-value of p significance
is 0.000. Because t-value 6.946 > t-table 2.262, and
significance value 0.000 < 0.05, the result shows a
significant difference. Thus, the alternative
hypothesis (Ha) which suggests “There is a
significant effect of part method on shooting
accuracy improvement in futsal players of UKM
UNY”, is accepted.
The second hypothesis suggests “There is a
significant effect of whole method on shooting
accuracy improvement in Futsal players of UKM
UNY.”
Table 4: T-test of shooting accuracy pre-test and post-test
results of whole method group.
Mean
t-test for Equality of means
t ht
t tb
Sig.
Difference
%
18.50
2.753
2.262
0.022
0.8 cm
1,70%
22.10
T-test result shows that the value of p
significance is 0.000. Because t-value 5.823 > t-table
2.262, and significance value 0.000 < 0.05, the result
shows a significant difference. Therefore, the
alternative hypothesis (Ha) which suggests “There is
a significant effect of whole method on shooting
accuracy improvement in futsal players of UKM
UNY”, is accepted.
The third hypothesis which suggests “Part
method is better than whole method in improving
shooting accuracy of futsal players of UKM UNY”
could be determined by the mean difference between
group A and group B. The analysis result is shown
in the following table.
Table 5: T test of group A and group B.
Group
t-test for Equality of means
%
t ht
t tb
Sig,
Difference
Burpee
28.88%
1.812
2.101
0.087
1.80
Depth jump
19.46%
From the t test result table, we can see that the t
value is 1.812 and t-table (df = 18) = 2.101, while
the p-value significance is 0.087. Because t-value
1.812 < t-table = 2.101 and sig, 0.087 > 0.05, there
is no significant difference. The analysis result
demonstrates that the mean value of the posttest
difference in part method exercise and the mean
value of the posttest difference in whole method
exercise was 1.80, with a higher increase of
percentage in part method, 28.88%. Therefore, the
hypothesis (Ha) which suggests “Part method is
better than whole method in improving shooting
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
168

accuracy of futsal players of UKM UNY”, is
accepted.
3.5 Discussion
Based on t-test analysis, we know several things to
draw a conclusion of whether there is an
improvement in shooting accuracy in futsal players
of UKM UNY after part and whole method exercise
for 16 meetings. The research result is further
discussed as follows:
3.5.1 The Effect of Part Method Exercise on
Shooting Accuracy in Futsal Players of
UNY
The research result shows that there is a significant
effect of part method on shooting accuracy
improvement of futsal players of UKM UNY. The
effectiveness of shooting accuracy improvement of
futsal players of UKM UNY before and after part
method exercise is 28.88%. The percentage shows
that the mean of shooting accuracy of futsal players
of UKM UNY during pretest was 18.7 and it
increased during post-test by 24.10. Part method is a
way to practice a sports skill, in this case shooting
technique, done part by part and only until those
parts of skill are mastered are they applied or put
together as a whole. Part method is generally applied
to learn a quite difficult or complex type of skill.
Part method is a form of skill practice done part by
part of the whole skill. It starts with the smallest part
of the skill and eventually builds up as a whole skill
(Prastowo, 2014). Part method is a form of skill
exercise done part by part of the whole skill.
Learning skills are selected to fit more efficient
and simple movements (Putro, 2015). An opinion on
part method, that part method is a method to teach a
movement skill by dividing the movements into
parts before they are put together as a whole
movement (Firdaus, 2014), so in this case, shooting
technique, is broken down into parts and those parts
are then put together after the players have mastered
them in order to make it easier for the players to
understand shooting technique.
Elementary/part method involves
dividing/parsing or grouping of a movement into
functional elements (Syafruddin, 2011). This is
based on the fact that the learned parts of the
movements can be put together as a complex
(whole) movement without losing the quality of the
movement. The application of this method requires
parsing or grouping of a sports technique process
into some functional parts.
3.5.2 The Effect of Whole Method on
Shooting Accuracy of Futsal Players of
UNY
The result shows that there is a significant effect of
whole method on shooting accuracy of futsal players
of UKM UNY. The effectiveness of shooting
accuracy improvement of futsal players of UKM
UNY before and after whole method exercise was
19.46%. The percentage shows that the mean of
shooting accuracy of futsal players of UKM UNY
during pretest was 18.5 and increased during posttest
by 22.10. The whole method was applied by, first of
all, explaining how to shoot properly, including the
first position, movement application, and advanced
movement. Those parts of shooting movements are
explained and demonstrated in details. The next step
is for the players to shoot from the first position to
its advanced movements repeatedly.
Global/whole method, is “global method refers
to the whole movement of a technique and attempts
to find/get the technique through a learning process”
(Syafruddin, 2011). During exercise, the athletes do
not learn the technique separately, but they do the
movements as a whole. “Whole method gives
advantages if simple movements were to be taught”
(Lutan, 2002). Related to whole method stated,
“Whole method is an approach where from the
beginning the students are directed to practice the
series of movements as a whole” (Sugiyanto S. D.,
1997). “Whole method is a method that emphasizes
wholeness of the desired learning materials”
(Suhendro, 2009). Whole method is generally
applied to learn a simple skill.
“If the taught sports skills are simple and easily
understood, they are better taught as a whole, and
each particular technique is only taught specifically
if the athlete or the subject always makes a mistake
in that particular technique” (Harsono, 2015). Global
method or whole method is a way to teach which
moves from general things to specific things
(Mahendra, 2007). In teaching a movement skill or
game, the whole form is taught first and then it is
broken down into smaller parts.
3.5.3 The Comparison of Part Method and
Whole Method Exercise towards
Shooting Accuracy of Futsal Players of
UNY
The analysis result shows that part method is better
than whole method in improving shooting accuracy
of futsal players of UKM UNY, with a mean posttest
difference of 1.8. The percentage of shooting
The Effect of Part and Whole Methods to Improving Shooting Accuracy in Futsal Players of UNY
169

accuracy improvement in part method exercise was
28.88%, while that in whole method group was
19.46%. Exercise methods are ways for a coach to
deliver exercise materials in physical activities and
techniques, in which case the right exercise method
can be seen from how fast players can do the given
exercise materials according to the coach’s
instructions. The research result is supported by
Yulianto, stating that there is a difference in
influence between part and whole methods in
improving soccer shooting skills (Yulianto, 2016).
The effect of part method is better than play
practice. It is also supported by Subarna, in his
research which shows that learning through part
method is significantly more effective than whole
method in improving spike skills in volleyball in
volleyball extracurricular of MA plus Al Munir in
Kabupaten Sumedang (Subarna, 2015).
Part method really helps players who still make
mistakes in learning series of shooting movements.
Anticipating mistakes in shooting requires a
simplification of the movement into parts, from the
starting phase, execution, and follow-through, so
that it is easy for players to learn and understand.
This approach will be good (effective) if parts of the
movements are taught and understood or mastered
before they are put together as a whole movement.
On the contrary, this method is not effective if the
players directly learn the movement as a whole
(Adiesta & Tuasikal, 2017). From the opinions
above we can conclude that shooting technique is
better taught using part method. Because shooting
techniques have phases of movements which could
be taught separately, when those components or
phases are continuously taught and well-organized,
it will result in a maximum shooting accuracy.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of data analysis, description,
research result testing, and discussion, we can
conclude that: (1) There is a significant effect of part
method on shooting accuracy improvement of futsal
players of UKM UNY, with t value 6.946 > t table
2.262, and significance value 0.000 < 0.05, and a
percentage increase of 28.88%. (2) There is a
significant effect of whole method on shooting
accuracy improvement of futsal players of UKM
UNY, with t value 5.823 > t table 2.262, and
significance value 0.000 < 0.05, and a percentage
increase of 19.46%. (3) Part method is better than
whole method in improving shooting accuracy of
futsal players of UKM UNY, with a mean difference
of posttest of 1.8.
REFERENCES
Adiesta, R., & Tuasikal, A. R. S., 2017. Penggunaan
metode bagian (part method) terhadap hasil
keterampilan dribble dan shooting per menit bola
basket. Jurnal Pendidikan Olahraga dan Kesehatan,
Volume 05, Nomor 03, 483 – 489.
Firdaus, H., 2014. Perbandingan metode pembelajaran
bagian (part-method) dan metode pembelajaran
keseluruhan (whole-method) terhadap kemampuan
siswa dalam melakukan smash bola voli. Jurnal
Pendidikan Olahraga dan Kesehatan. Volume 02
Nomor 02, 363-369.
Harsono, 2015. Kepelatihan olahraga. (teori dan
metodologi). Remaja Rosdakarya. Bandung.
Jaya, A., 2008. Futsal: gaya hidup, peraturan, dan tips-
tips permainan. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Timur.
Lhaksana, J., 2011. Taktik & strategi futsal modern.
Penebar Swadaya Group. Jakarta.
Lutan, R., 2002. Dasar-dasar kepelatihan. Departemen
Pendidikan Nasional. Jakarta.
Mahendra, A., 2007. Modul teori belajar mengajar
motorik. FPOK UPI Bandung. Bandung.
Murhananto, 2006. Dasar-dasar permainan futsal (Sesuai
dengan Peraturan FIFA). PT.Kawan Pustaka. Jakarta.
Nossek, Y., 1995. Teori umum latihan. (Terjemahan: M.
Furqon). Logos: Pan African Press Ltd. (Buku asli
diterbitkan tahun 1992).
Prastowo, G., 2014. Pengaruh metode pembelajaran part
practice terhadap hasil belajar shooting bola basket.
Jurnal Pendidikan Olahraga dan Kesehatan. Volume
02 Nomor 03, 747 – 749.
Putro, B. L., 2015. Perbandingan metode part practice
dengan metode whole practice dalam pembelajaran
shooting bola basket. Jurnal Pendidikan Olahraga dan
Kesehatan. Vol. 02 No. 02, 586-590.
Subarna, 2015. Perbandingan pengaruh metode bagian
dengan metode keseluruhan terhadap hasil
pembelajaran spike dalam permainan bola voli pada
ekstrakurikuler bola voli MA Plus Al Munir
Kabupaten Sumedang. Jurnal Multilateral, Vol. 14,
No. 2.
Sugiyanto S. D., 1997. Perkembangan dan Belajar
Motorik. Depdikbud. Jakarta.
Suhendro, A., 2009. Dasar-dasar kepelatihan. Universitas
Terbuka. Jakarta.
Sukardi, 2015. Evaluasi pendidikan. Bumi Aksara.
Jakarta.
Syafruddin, 2011. Pengantar ilmu melatih. FPOK IKIP.
Padang.
Yulianto, P. F., 2010. Perbedaan pengaruh pendekatan
pembelajaran metode bagian dan keseluruhan terhadap
peningkatan dribble shooting sepakbola ditinjau dari
koordinasi mata-kaki. Jurnal Ilmiah SPIRIT, Vol. 16
No. 1.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
170
