
The Financial Inclusion and Its Impact on Society Welfare in
Indonesia
Paidi Hidayat
1
, Raina Linda Sari
1
, Herfita Rizki Hasanah Gurning
1
Department of Development Economics, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Prof. T.M Hanafiah, SH, Kampus USU, Medan,
Indonesia
Keywords: Financial Incluscion, Welfare, Generalized Least Squares.
Abstract: This study aims to analyze the level of financial inclusion and its impact on the welfare of society in Indonesia
using provincial data for 2015-2018. The method used is based on the dimensions of accessibility, availability,
and use of financial services developed by Sarma (2012) to calculate the Index of Financial Inclusion (IFI)
and the generalized least square (GLS) method for estimating panel data. The analysis shows that financial
inclusion in Indonesia is determined by the dimensions of the use and availability of financial services, while
the dimensions of accessibility have a relatively small proportion. Based on the financial inclusion index,
there are 25 provinces included in the category of low financial inclusion, 8 provinces included in the medium
category, and only DKI Jakarta Province included in the category of high financial inclusion. Meanwhile, the
panel data estimation results show that the financial inclusion index has a positive and significant effect on
the welfare of the Indonesian people, which is proxied by the human development index.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the 2000s, financial inclusion has been widely
used as the main focus of policy in many countries
and central banks, to accelerate the development
process. Many empirical studies show a significant
relationship between strengthening the financial
sector, especially formal finance with economic
growth and improving people's welfare. This is
because the financial system can reduce information
costs and transaction costs, increase the allocation of
capital and asset liquidity, and can encourage
investment in activities that have high added value
(Levina, 2007).
To achieve these objectives, must be supported by
a good financial system. Because, a good financial
system will play an important role through the
intermediation function. The role of banks as
intermediaries cannot yet be said to be successful
when the availability of access and financial services
is inadequate. This can be seen from the size of the
financially excluded population. According to Mohan
(2006), financial exclusion signifies lack of access in
the accuracy, affordable costs, fair and safe financial
products and services of service providers. The
causes of financial exclusion or low use of formal
financial products and services include the limited
access to financial service products and services, the
socio-cultural community, and the low level of
financial literacy (OJK, 2016).
The availability of financial services and ease of
access is one of the important aspects to enhance the
role of the financial sector and public involvement in
the economic system in a country. How big is the
opportunity for the community to be able to access
and use financial services that can reflect the level of
financial inclusion in an economy.
Based on the results of surveys and research
conducted by national and international institutions,
it shows that financial inclusion in Indonesia is still
relatively low compared to several countries in
ASEAN. According to the global financial inclusion
index made by the World Bank (2015), only about 40
percent of Indonesians have access to formal financial
institutions and this condition is still lower than
Thailand and Malaysia, which almost reached 80
percent.
OJK survey results (2016) are quite encouraging,
where the level of financial literacy has increased
from 21.84 percent in 2013 to 29.66 percent in 2016.
While the financial inclusion rate also improved from
59.74 percent to 67.82 percent in same period. This
shows that financial inclusiveness in Indonesia is still
Hidayat, P., Sari, R. and Hasanah Gurning, H.
The Financial Inclusion and Its Impact on Society Welfare in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0009314105310536
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 531-536
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
531

low and mutually supportive that Indonesian people's
financial access to formal financial institutions is still
relatively low so that Indonesia's population still has
limited access to the financial services system.
Therefore, given the very important role of financial
inclusion as an effort to accelerate the process of
economic development in Indonesia, studies related
to financial inclusion and its impact on the welfare of
the community are interesting to study.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In Indonesia, financial inclusion or financial inclusion
becomes a national strategy to encourage economic
growth through equitable distribution of income,
poverty reduction, and financial system stability
(Hadad, 2010). The right of every individual is
guaranteed to be able to access the entire range of
quality financial services at an affordable cost. The
target of this policy is very concerned about the poor
low-income, productive poor people, migrant
workers, and people living in remote areas (Bank
Indonesia, 2014).
Regarding financial inclusion, Bank Indonesia
(2014) defines financial inclusion as an effort to
increase public access to financial services by
removing all forms of barriers both price and non-
price. Hannig and Jansen (2010) revealed that
financial inclusion is an effort to include unbankable
people in the formal financial system so that they
have the opportunity to enjoy financial services such
as savings, payments, and transfers.
In addition, according to Sarma (2012) financial
inclusion is a process that guarantees the ease of
access, availability, and benefits of the formal
financial system for all economic actors. So it can be
concluded that financial inclusion is an effort to
increase public access, especially unbankable people,
into formal financial services by reducing various
kinds of obstacles to access them.
The results of research conducted by Hannig and
Jansen (2010) found that financial inclusion in
addition to addressing income inequality also has the
potential to improve financial stability. This is
because poor people's access to savings from formal
financial institutions can increase the capacity of
households to manage financial vulnerability caused
by the adverse effects of the crisis, diversify the
funding base of financial institutions that can reduce
shocks during a global crisis, increase economic
resilience by accelerating growth, facilitating
diversification, and reducing poverty.
Meanwhile, related to research on the impact of
financial inclusion on development has been carried
out by Sarma and Pais (2011) using the OLS method
and the results of his study found that the level of
human development and financial inclusion has a
positive relationship for several countries in the
world. While the results of the study by Gupta et. al.
(2014), which measures the Index for Financial
Inclusion (IFI) in 28 states and 6 regions in India
using dimensions of penetration, availability and
usage of banking services, empirically found that
financial inclusion indexes and human development
index as a proxy for people's welfare in India have
positive relationship (correlation).
3 METHOD
3.1 Data and Variables
This study uses panel data for the period 2015-2018
at 34 provinces in Indonesia sourced from the Central
Statistics Agency (BPS), the Financial Services
Authority (OJK), and Bank Indonesia (BI). This study
uses the Index of Financial Inclusion (IFI) method
developed by Sarma (2012) in analyzing and
measuring financial inclusion in Indonesia. The
research variables used refer to the IFI measurement
dimensions, namely accessibility (d1), availability
(d2), and usage (d3). Related to the analysis of the
impact of financial inclusion on welfare proxied by
the human development index (HDI), this study uses
several variables as control variables, namely the
number of poor people (PM) and population density
(KP). For operational definitions of all these variables
are as table 1.
3.2 Analysis Method
This study adopts the measurement Index of Financial
Inclusion (IFI) developed by Sarma (2012), in which
to calculate Index of Financial Inclusion (IFI) using
three dimensions, namely accessibility (d1),
availability (d2), and the use of (d3). Accessibility
indicators illustrate the penetration of formal
financial institutions and availibilitas indicator is
indicated by the number of bank branches. While the
usage indicators include the volume of bank lending
to the public. This method is used because it provides
a robust and comprehensive measurements can be
compared between provinces.
Furthermore, this study also uses Data panel to see
the impact of financial inclusion on the welfare of
society, proxied by human development index using
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
532
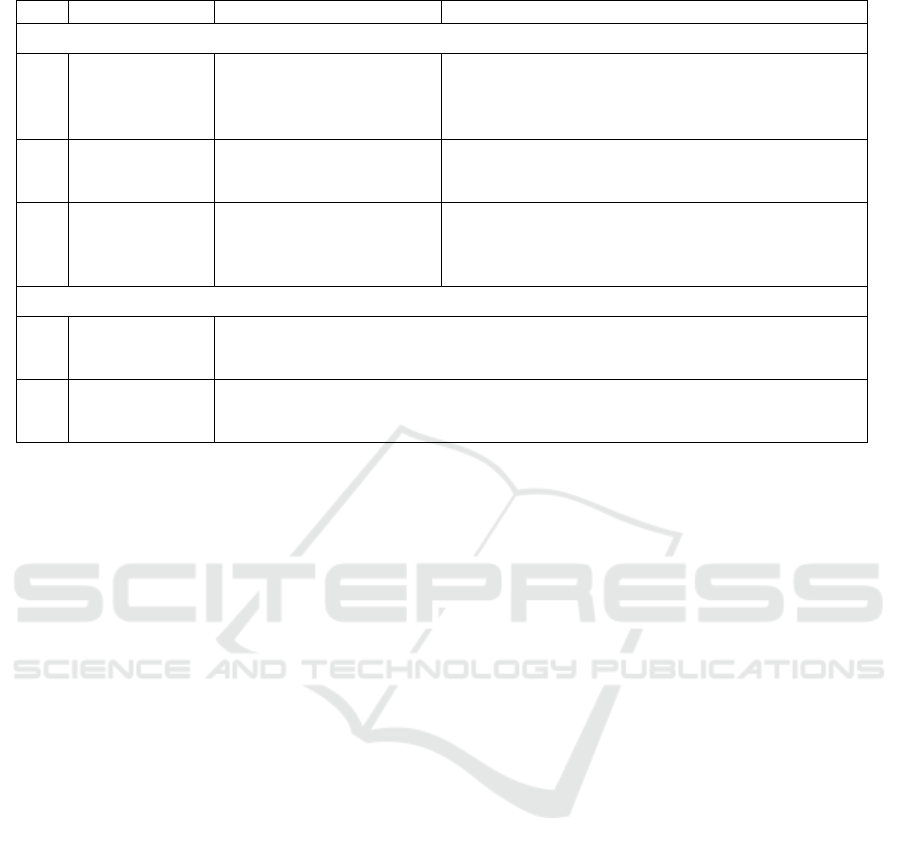
Table 1. Definitions and indicators variable operational research
No. Variables Definition Indicator
Calculation of Financial Inclusion Index (IFI)
1 Accessibility
(d1)
Measuring banking
penetration through the
many users of banking
services
The ratio of the number of bank accounts per 1,000 total
population of adults.
d
1
=(Amount of Bank Account)/(Amount of Adults)
2 Availability (d2) Measuring ability in the use
of formal financial services
The ratio of the number of bank service offices per
100,000 adult population number.
d
2
=
(
Amount of Bank Office
)
/
(
Amount of Adults
)
3 The use (d3) Measuring the extent of use
of banking services by the
community through
financin
g
The ratio of the amount of financing provided banking
to the regional gross domestic product (GDP) in billion
Rupiah.
d
3
=
(
Amount of Bank Financin
g)
/PDRB
Calculating the Impact of Financial Inclusion of the Public Welfare
1 Index of
Financial
Inclusion (IFI)
The index value calculation results of financial inclusion among the provinces in
Indonesia
2 Human
Development
Index
(
HDI
)
The value of the human development index among the provinces in Indonesia as a proxy
to measure the level of social welfare
Source: Sarma
(
2012
)
, BI and CPM
Generalized Least Square (GLS). The research model
specification is:
IPM
it
= α
0
+ α
1
IFI
it
+ α
2
PM
it
+ α
3
KP
it
+µ
it
(1)
HDI is Human Development Index, IFI is Index of
Financial Inclusion, the PM is the number of poor,
and KP is Population Density.
This GLS method can be analyzed through two
models, namely the fixed effects model (FEM) and
the random effects model (REM). Furthermore, from
the two models, the best model was chosen by
conducting the Hausman test (Gujarati, 2008). The
condition is that if the null hypothesis (H0) is
accepted, the model used is the random effect model
(REM). Conversely, if the null hypothesis (H0) is
rejected, the model used is the fixed effect model
(FEM). To process the data in this study, Eviews
Program version 10 was used.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Index of Financial Inclusion (IFI)
in Indonesia
Based on the average value of the Index of Financial
Inclusion (IFI), Indonesia is included in the category
of "moderate" financial inclusion because, having an
average value of the financial inclusion index above
0.3 during the study period. For the grouping between
provinces in Indonesia, there are 25 provinces that fall
into the category of "low" financial inclusion (index
values below 0.3). While there are 8 provinces that
are included in the category of "moderate" financial
inclusion (index value between 0.3-0.6). Only DKI
Jakarta Province is included in the high financial
inclusion category (index value above 0.6, that is,
0.9052).
Provinces in the category of medium financial
inclusion index are Riau Islands Province, DI
Yogyakarta, Banten, Bali, East Nusa Tenggara, East
Kalimantan, North Sulawesi, and West Papua
Province. While the provinces in the category of low
financial inclusion were 25 provinces with the lowest
financial inclusion index, namely West Sulawesi
(0.1782) and Lampung (0.1884).
The relatively low financial inclusion index in
Indonesia shows that the distribution and utilization
of banking services is still low. Likewise the
difference in financial inclusion index between
provinces in Indonesia also shows that there is still an
imbalance or inequality for access to banking services
between provinces. This condition occurs in the
provinces of Banten, Bali, and North Sulawesi which
have relatively high of the Index of Financial
Inclusion (IFI) values but the index value of
accessibility dimensions (IA) is relatively low. This
indicates that there are still obstacles in the three
provinces in terms of accessing banking institutions
despite the relatively high availability and use of
banking services.
The Financial Inclusion and Its Impact on Society Welfare in Indonesia
533

Source: Bank Indonesia & BPS (2019)
Figure1: The Average of Index of Financial Inclusion (IFI) on 3 dimensions in Indonesia
Meanwhile, there are also a number of provinces
that have relatively high Index of Financial Inclusion
(IFI) but the index of usage dimension (IP) is
relatively low. This condition occurs in the Riau
Islands, East Kalimantan and West Papua Provinces,
which indicate that the use and use of banking
services is not optimal, although the accessibility and
availability of banking services are relatively good.
This is because in the three provinces the number of
adult residents who have accessed and used banking
services is still relatively small but tends to have more
than 1 bank account.
In addition, it was also found that the province
had a relatively high index of financial inclusion
index but the value of the index of the availability
dimension (IK) of its banking services was relatively
low and this occurred in the Province of East Nusa
Tenggara (NTT). These findings indicate that in East
Nusa Tenggara Province still faces the problem of the
existence of limited bank branch offices in the
regions.
However, there are two provinces that have a
financial inclusion index value and a dimension index
that tends to be relatively evenly distributed, namely
DKI Jakarta Province and DI Yogyakarta Province.
This shows that the people in the two provinces have
a level of financial inclusion that tends to be evenly
distributed, both in terms of the dimensions of
accessibility, the dimensions of availability, and the
dimensions of the use of banking services during
2015-2018. In contrast, provinces that have relatively
low financial inclusion index values and dimensional
indexes occur in Lampung Province and West
Sulawesi Province. These findings indicate that
people in these two provinces are still experiencing
obstacles to accessing and utilizing and using banking
services in the area.
Based on these findings, the average dimension of
banking availability tends to be higher compared to
the dimensions of banking accessibility or
penetration. This means that the number of bank
branch offices is relatively more, but the number of
adult residents who have accounts is still very low.
The low accessibility or penetration of banks can be
made possible even though banks do not have many
customers, but relatively few customers make
transactions with relatively large volumes. The large
transaction volume can be seen from the dimensions
of usage that tend to be large.
In addition, these findings also prove that the low
value of the accessibility dimension with the high
value of the availability and usage dimensions
indicates that the public has not optimally utilized
formal financial services as the main source of
financing. People are more likely to use informal
financial services, such as cooperatives and
moneylenders, rather than formal banking facilities.
The dominant role of non-formal financial
institutions in Indonesia, especially in remote areas
shows that the formal financial market in Indonesia is
not functioning properly.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
534
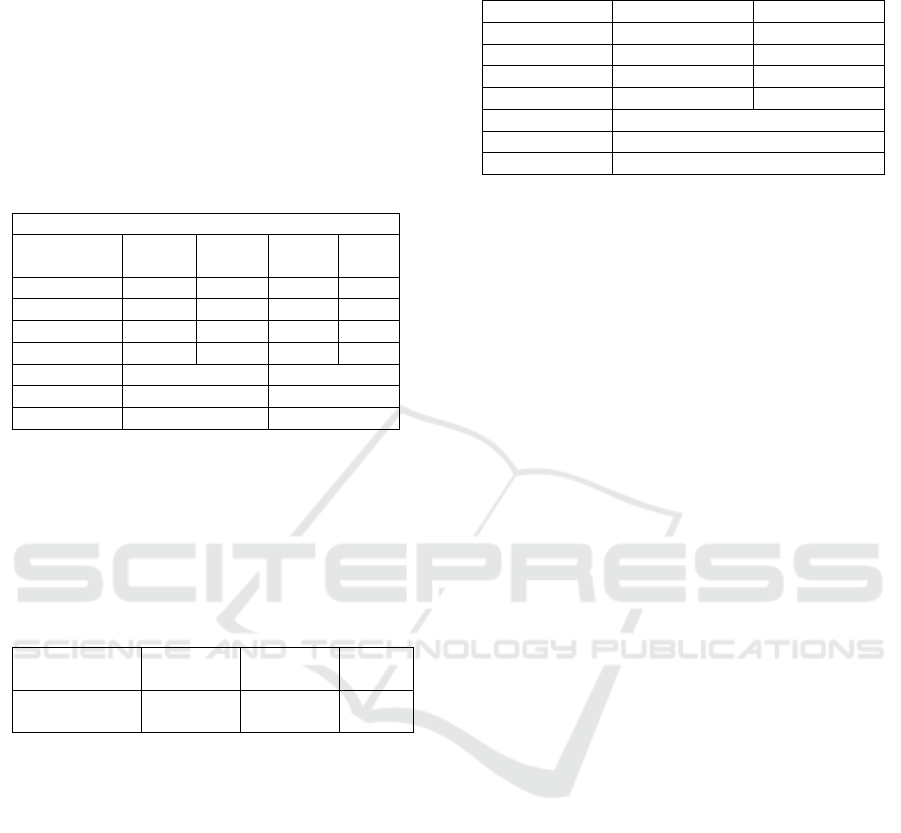
4.2 Panel Data Estimation Results
To see the effect of financial inclusion in the welfare
of society proxied by the human development index
(HDI), the estimate for the panel data methods is
Generalized Least Squares (GLS), Here are the
results estimated using GLS for fixed effect model
(FEM) and random effect model (REM) as shown in
the table 2.
Table 2: Estimation results using the GLS Method.
De
p
endent Variable: Welfare
(
LIPM
)
2015-2018
Independent
Variable
FEM Prob. REM Prob.
C 25.662 0.0000 42.690 0.0000
II
K
0.0898 0.0000 0.1449 0.0000
LPM -0.0366 0.0021 -0.0422 0.0000
LKP 0.3848 0.0000 0.0375 0.0000
Ad
j
. R
2
0.9914 0.4498
Fstat 434.66 37.791
DW
test
13.910 0.9102
Furthermore. to choose the best statistical model
between FEM and REM models for the Generalized
Least Square (GLS) method. it can be done by
Hausman test (Gujarati. 2008) and the results can be
seen based on the chi-square value as shown in the
table 3.
Table 3: The results of Hausman Test.
Test Summary
Chi-Sq.
Statistic
Chi-Sq.
d.f.
Prob.
Cross-section
rando
m
149.13899 3 0.000
Based on the Hausman test results in table 3. the
chi-square value of 149.139 was obtained with a
probability value of 0.0000 which means the null
hypothesis (H0) was rejected. Thus. the best model in
this study is the fixed effects model (FEM). From the
estimation results with FEM model shows that the
coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.9914 which
means that overall the independent variables in the
model (IFI. PM. KP) are quite able to explain
variations in public welfare (HDI) in Indonesia of
99.14 percent and the rest are explained by other
variables not contained in the equation model.
Table 4: Estimation results using Fixed Effects Model
(FEM).
Depvar: LIPM FEM t-stat
C 25.662 13.611
II
K
0.0898 6.053***
LPM -0.0366 -3.160***
LKP 0.3848 12.115***
Ad
j
. R
2
0.9914
Fstat 434.66
DW
test
13.910
Note: *** significant at α = 0,01
The estimation results in table 4 show that the
Index of Financial Inclusion (IFI) has a positive and
significant impact on the level of community welfare
(HDI) in Indonesia at a 99% confidence level. The
coefficient value of 0.089 indicates that every time
there is an increase in the financial inclusion index in
Indonesia by 1 point, ceteris paribus, it will increase
the welfare of the Indonesian people by 0.089 points.
These empirical results support a study by Sarma and
Pais (2011), where the level of human development
and financial inclusion has a positive relationship for
several countries in the world. Likewise the results of
research conducted by Gupta et. al. (2014) where the
index of Financial Inclusion and the Human
Development Index as a proxy for community
welfare in India have a positive correlation.
The estimation results on the variable number of
poor people (PM) show a negative and significant
effect on the level of community welfare (HDI) in
Indonesia at a 99% confidence level. The coefficient
value of 0.037 means that every 1% increase in the
number of poor people in Indonesia, ceteris paribus,
will cause the level of welfare of the Indonesian
people to decrease by 0.037 points. While the
population density variable (KP) has a positive and
significant effect on the level of community welfare
(HDI) in Indonesia at a 99% confidence level. The
coefficient value of 0.385 indicates that every time
there is an increase in population density in Indonesia
by 1 point, ceteris paribus, it will result in an increase
in the welfare of the Indonesian people by 0.385
points. The results of this estimation are not in line
with the hypothesis which states that there is a
negative and significant effect between population
density and the level of social welfare in Indonesia.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study indicate that Indonesia in the
category of financial inclusion index was during the
study period. Generally. financial inclusion in
The Financial Inclusion and Its Impact on Society Welfare in Indonesia
535

Indonesia tends to be determined by the dimensions
of use and availability. while the dimensions of
accessibility has a relatively smaller proportion.
Proportion of dimensions of use in supporting
financial inclusion in Indonesia is shown by the
ability of people to take advantage of and use of
banking services as savings and financing sources.
For the dimensions of availability (availability)
may be indicated by the increasing number of
branches existing banking area but the existence of
the branch office has not been able to serve all
existing community area. This condition causes the
dimensions of accessibility has a lower index value
than the other dimensions and limitations of this
accessibility that makes many people still can not
access due to geographic barriers banking Indonesian
archipelago so the cost is relatively expensive
establishment of branch offices.
Furthermore. based on the results of the panel data
estimates show that variabel Index of Financial
Inclusion (IFI) positive and significant impact on the
level of social prosperity proxy for the human
development index (HDI). Likewise the population
density variable (KP) positive and significant impact
on the level of welfare in Indonesia. While variable
number of poor (PM) a significant negative effect on
the level of welfare in Indonesia during the study
period.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We gratefully acknowledge that the present research
is supported by Ministry of Research and Technology
and Higher Education Republic of Indonesia. The
support is under the research grant TALENTA USU
2019.
REFERENCES
Berg. H. Van Den. (2001). Economic Growth and
Development. New York: MCGraw-Hill.
Ang JB. (2010). Finance and Inequality: The Case of India.
Shouthern Economic Journal. 76 (3): 738-761.
Bank Indonesia. (2014). Financial Inclusion. Jakarta: Bank
Indonesia.
Beck T. Demirguc-Kunt A. R. Levine. (2007). Finance.
Inequality and the Poor. J Econ Growth. 12: 27-49.
Demirgüç-Kunt. A. And L. Klapper. (2012). Measuring
Financial Inclusion: The Global FINDEX Database.
Policy Research Working Paper. 6025.
Demirgüç-Kunt. A.. T. Beck and P. Honohan. (2008).
Finance for All? Policies and Pitfalls in Expanding
Access. Washington: A World Bank Policy Research
Report.
Gujarati. (2008). Basics of Econometrics. Jakarta: Erland.
Gupta. Anurag. et al. (2014). Financial Inclusion and
Human Development: A State-Wise Analysis From
India. International Journal of Economics. Commerce
and Management. United Kingdom Vol. II. Issue 5.
2014.
Hannig. Alfred and Jansen. Stefan. 2010. Financial
Inclusion and Financial Stability: Current Policy
Issues.Asian Development Bank Institute Working
Paper.
Levine. R. (2007). Financial Development and Economic
Growth: Views and Agenda. Journal of Economic
Literature XXXV p.688-726.
Financial Services Authority (FSA). (2016) National
Survey of Literacy and Financial Inclusion.
Sarma. M. (2008). Index of Financial Inclusion. Icrier
Working Paper. 215.
Sarma. M and Pais. J. (2011). Financial Inclusion and
Development: A Cross Country Analysis. Journal of
International Development 23. 613-628.
Sarma. M. (2012). Index of Financial Inclusion - A measure
of financial sector inclusiveness. Berlin Working
Papers on Money. Finance. Trade and Development. 7.
p.1-34.
Ummah. Bintan Badriatul. (2013). Analysis of Financial
Linkages an inclusive development in Asia. Thesis:
Department of Economics Faculty of Economics and
Management. Bogor Agricultural University.
World Bank. 2015. Financial Inclusion Data/Global
FINDEX.
http://datatopics.worldbank.org/financialinclusion/cou
ntry/indonesia
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
536
