
Analysis of the Influence of Internet of Vehicles on Driverless
Technology
Yunlong Bai
1, a
, Kaixin Yang
1, b
, Xiaowei Chen
1, c
, Jinwei Guo
1, d
and Haibo Dong
1, e
1
Automotive Data CenterChina Automotive Technology&Research Center Co. Ltd, Tianjin 300000, China
e
donghaibo@adcsoft.cn
Keywords: Internet of vehicles, automatic driving, V2X.
Abstract: The Internet of vehicles technology is derived from the Internet of things, which is based on the in-vehicle
network, the inter-vehicle network and the vehicle-mounted mobile Internet, wireless communication and
information exchange are conducted in the car and X (X: car, road, pedestrian and internet, etc.), according
to the agreed communication protocol and data interaction standards. Internet of vehicles technology can
realize intelligent traffic management, intelligent dynamic information service and intelligent vehicle control,
which is a typical application of Internet of things technology in the field of transportation system. With the
development and promotion of communication technology and Internet of vehicles, the future development
of driverless technology is very worth looking forward to. V2X technology, which is indispensable for
driverless driving and smart transportation, has gradually become the research key point of Internet of vehicles
technology, as a specific application of the Internet of things, V2X technology can play a great role in
driverless vehicles. With the continuous development of technology, V2X technology has also been
developed rapidly in China. This paper introduces the key technologies and technical standards of V2X,
summarizes and forecasts the application of V2X technology in driverless technology.
1 INTRODUCTION
Internet of vehicles is the network connection
between vehicles and vehicles, vehicles and roads,
vehicles and people, vehicles and service platforms
through information and communication technology,
which can improve the intelligent level and automatic
driving ability of vehicles. The Internet of vehicles is
typical application of Internet of things in automobile
field (Li Feng, Fang Jiayu, Zhao Li, 2016); its core is
V2X wireless communication technology, including
dedicated short range communication (DSRC), 5G-
V2X, LTE-V2X and so on. With the help of V2X
wireless communication technology, the technical
bottleneck of the automobile in intelligent
development and automatic driving function can be
broken through. At present, the international mature
V2X wireless communication technology has two
technical routes; one is DSRC technology based on
IEEE 802.11p, the other is V2X wireless
communication technology based on LTE (LTE-V2X)
(Liu Fuqiang, Xiang Xueqin, Qiu Dong, 2007; Chen
Qianbin, Chai Rong, Cen Ming, 2015; Cheng Gang,
Guo Da, 2011). There are some shortcomings in the
Internet of vehicles technology based on DSRC, the
Internet of vehicles technology based on 4G network
can provide faster transmission rate and has a good
promotion effect on the development of automatic
driving (Li Zhongdong, 2014).
2 COMMUNICATION
TECHNOLOGY OF INTERNET
OF VEHICLES
2.1 Internet of Vehicles Technology
Based on DSRC
The DSRC consists of the physical layer standard
IEEE 802.11P and the network layer standard
IEEE1609. On this basis, Society of Automotive
Engineers (SAE) issued the SAE J2735 and SAE
J2945 standards and regulated the information
content and structure. The DSRC system includes
Onboard Unit (OBU) and Road Side Unit (RSU), the
two provide two-way transmission of information,
and the RSU transmits traffic information to the back-
128
Bai, Y., Yang, K., Chen, X., Guo, J. and Dong, H.
Analysis of the Influence of Internet of Vehicles on Driverless Technology.
DOI: 10.5220/0009397701280133
In Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Vehicle, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering (ICVMEE 2019), pages 128-133
ISBN: 978-989-758-412-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

end platform (Wang Jianbiao, 2013). The advantages
of DSRC technology are high reliability and strong
real-time transmission, however, since the physical
layer technology of DSRC is the same as the WiFi
commonly used in people's lives, the communication
distance advantage is not obvious, the coverage
distance is short, and large-scale renovation and
investment in roadside facilities is required in
practical applications (Zhao Jing, 2018).
2.2 Internet of Vehicles Technology
Based on LTE
LTE-V2X is based on LTE technology, which is
divided into LTE-V-Cell and LTE-V-Direct. The
former uses existing spectrum and base station for
cellular communication, while the latter AS Ad hoc
network is used for V2X communication in small
scale. The LTE-V2X can reuse existing cellular
infrastructure and spectrum, and operators do not
need to deploy dedicated RSU and provide dedicated
spectrum (Xu Zijian, Yu Mei, 2016). LTE-V2X
mainly solves the problem of shared sensing among
traffic entities, it can expand the vehicle-mounted
detection system from tens of meters to hundreds of
meters or more, and improves effectiveness of AI,
and achieves assisted driving in relatively simple
traffic scenarios. In comparison, DSRC technology
has first-mover advantage, long verification time and
more mature technology, and keeps one step ahead in
network security. The advantage of LTE-V2X is that
it does not require new roadside facilities, its cost is
lower, and network covers longer distances, and can
smoothly evolve to 5G.
3 DEVELOPMENT HISTORY OF
V2X TECHNOLOGY
In 1986, experts from scientific research institutions,
transportation bureaus, etc. discussed the future
traffic regulations and believed that the future
transportation system must simultaneously ensure
safety, solve congestion and protect the environment.
In 1990, in Texas, the discussion on this issue reached
a climax, participants proposed the concept of IVHS,
namely intelligent vehicle and highway system, later,
and it evolved into the intelligent transportation
system ITS. In 1991, the ITS concept became part of
the Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act
(ISTEA). In addition, ISTEA has invested $6.6
billion in research and testing of ITS systems for the
next six years.
In 1992, the US Department of Transportation
(USDOT) launched the Automated Highway System
in the ITS research to liberate the driver's hands and
feet, the vehicle needs to travel on a road with
magnetic nails, this is the first time in history that the
interconnection of vehicles and highways has been
achieved. After the Automated Highway System test,
the USDOT launched the Intelligent Vehicle
Initiative in 1997 to accelerate the deployment of
anti-collision systems. Based on the smart vehicle
program, USDOT puts forward new demands on
improving traffic congestion and electronic
communication technology. At the 10th ITS World
Congress in Madrid in December 2003, USDOT
announced distribute 75MHz spectrum at 5.9GHz for
DSRC research, and proposed the VII project, the
goal of the project is to apply V2V and V2I
technologies in a small range. In December 2006,
USDOT and the five major automakers jointly tested
the role of V2V and V2I in anti-collision systems and
established new communication-based safety
facilities, including roadside networks and on-board
vehicle equipment. Only when there are enough
vehicles on the road to support V2V communication,
the role of V2V can be fully reflected. To this end, in
August 2014, NHTSA and USDOT proposed the
FMVSS No. 150 Act; this act mandated that new light
vehicles support V2V communication.
The generation of DSRC technology is based on
three standards: the first is IEEE 1609, which defines
the architecture and flow of the network, the second
is SAE J2735 and SAE J2945, which define the
information carried in the message packet, these data
include information from sensors on the car, such as
location, direction of travel, speed and brake
information, the third standard is IEEE 802.11p,
which defines the physical standards for DSRC. The
DSRC top-level protocol stack is developed based on
the IEEE 1609 standard, the V2V information
exchange uses the WAVE Short Message Protocol
instead of WIFI; and the TCP/IP protocol are used for
V2I and V2N information interaction. The DSRC
underlying layer, physical layer, and radio link
control are based on IEEE 802.11p. The IEEE 802.11
standards use the WIFI ecosystem, but WIFI was
originally designed for fixed communication
equipment, and later IEEE 802.11p supported mobile
communication devices.
With the development of cellular communication
technology, the role of cellular communication is
becoming more and more important; at present,
cellular communication technology has changed from
simply transmitting sound to transmitting audio and
data, changes from person-to-person to machine-to-
Analysis of the Influence of Internet of Vehicles on Driverless Technology
129
machine, V2X technology is an application of
machine-to-machine transformation. C-V2X is a
V2X technology based on cellular communication,
which is defined by 3GPP (3rd Generation
Partnership Project), it includes LTE-based and future
5G V2X systems, and it is a powerful complement to
DSRC technology. It uses the existing LTE network
facilities to realize information interaction of V2V,
V2N, V2I, the most attractive features of this
technology are: it can keep up with the changes, adapt
to more complex security application scenarios, meet
low latency, high reliability and bandwidth
requirements.
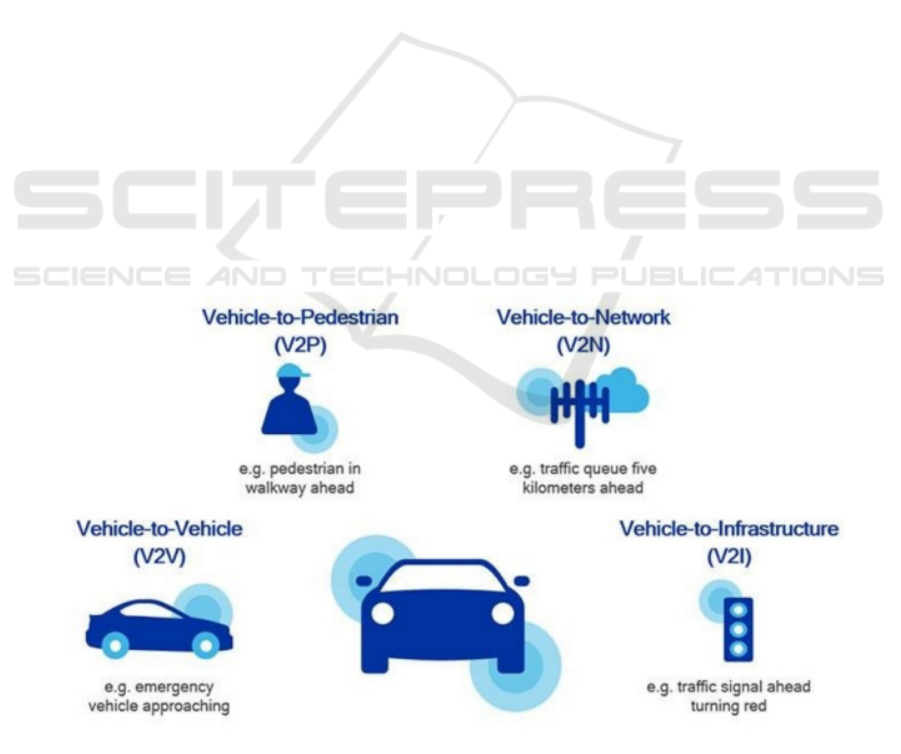
4 CONCEPT OF V2X
TECHNOLOGY
V2X, just as its name implies, is vehicle-to-
everything, which hopes to achieve information
interaction between the vehicles and all entities that
may affect the vehicles, V2X mainly includes
vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), vehicle-to-infrastructure
(V2I), vehicle-to-network (V2N), and vehicle-to-
pedestrian (V2P), as shown in Figure.1. These four
types of cooperation are important links for automatic
driving and smart transportation. Vigorously
developing V2X vehicle networking technology
cannot only reduce the probability of traffic accidents,
improve the safety of road traffic, but also provide
low-cost, easy-to-deploy support and infrastructure
for realizing automatic driving and intelligent
transportation.
V2X was mainly based on DSRC in the early
days; the full name of DSRC is dedicated short range
communication. DSRC has been developed and
tested in the United States for many years, later, with
the development of cellular mobile communication
technology, C-V2X (Cellular V2X, V2X based on
cellular communication technology) technology
emerged. The diagram of C-V2X technology is
shown in Figure.2.
The main purpose of application V2X technology
in smart transportation system is to improve road
safety, solve traffic problems and optimize traffic
management, vehicles needs to communicate with
surrounding roadside units and vehicles, accurately
transmitting vehicle state information collected by
sensors or RFID installed on the vehicle, etc. After
the information is collected, data analysis and
processing are used to extract effective information,
which provides intelligent decision-making basis for
vehicle travel. The key technologies involved in this
process are wireless communication technologies; it
supports real-time reliable communication when the
vehicle is driving at high speed, sensing technology is
used for obtaining accurate position of the vehicle and
mass data processing technology.
Figure 1. V2X classification diagram.
ICVMEE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Vehicle, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering
130

Figure 2. Diagram of C-V2X technology.
Figure 3. Introduction to DSRC and C-V2X technology.
4.1 Wireless Communication
Technology
The V2X network system realizes information
interaction through wireless communication
technologies. The key to the implementation of this
technology lies in the timeliness of wireless
communication technology, namely it is necessary to
ensure that the network access time is the shortest, the
transmission delay is low, and the reliability and
security of information transmission are required as
well. In order to realize inter-vehicle communication
within a certain range, not only the spectrum reuse
should be realized to meet the communication
bandwidth requirements, but also the core network
needs to be established, and the special components
of the system are used to complete the information
transfer and transmission.
4.2 Vehicle Sensing Technology
Real-time and accurate vehicle state sensing
technology is an important foundation for Internet of
vehicles, and it is very important. Sensing
technologies of vehicle state generally include
sensing technology for vehicle motion conditions and
sensing technology for driving environment. Through
these technologies, the motion state of the vehicles
and the surrounding vehicles are sensed, thereby
analysing whether there is a safety hazard or not.
When sensing the motion state of the vehicle, CAN
(Controller Area Network) is used to collect real-time
state data generated by each ECU (electronic control
unit) and sensor equipment in the vehicle, the motion
state of the vehicle is obtained by comprehensive
analysis of the information. Among them, it is
especially important to obtain accurate vehicle
Analysis of the Influence of Internet of Vehicles on Driverless Technology
131

position information by position sense, position sense
is usually divided into absolute position sense and
relative position sense, different position sense
technologies and precision are required to be applied
to different roads.
Vehicle environmental information sensing
technology is mainly used to obtain information on
the surrounding environment of the vehicles, such as
road line shape, surrounding non-motorized vehicles
and road surface conditions. The route information
can be obtained through the traffic geographic
information system, or on-board equipment uses
pattern recognition technology to complete linear
online recognition. Infrared sensors and on-board
radars can be used to sense information on roadside
pedestrians and non-motorized vehicles. Information
on road conditions, snow and ice, etc. can be detected
and collected by laser, video and infrared
technologies.
4.3 Data Processing Technology
The intelligent assisted driving system based on V2X
can comprehensively analyses and evaluates the mass
data generated by the vehicle through information
fusion and data mining, and then makes intelligent
decisions based on the processing results. Information
fusion is data fusion, it can be summarized as using
computer technology to correlate and analyse the
information collected by sensors from various
information sources, and optimize the information
processing according to the algorithm optimization
criteria, and finally obtain the effective information
needed for intelligent decision-making. In the Internet
of vehicles system, information fusion technology
mainly processes and integrates information from
various parts of the Internet of vehicles, thus
obtaining effective information required by vehicle
travel. Data mining is the basis for processing mass
data that continues to grow; it generally consists of
three steps: find preliminary data, explore data rules
and represent rule.
5. INTERNET OF VEHICLES AND
AUTOMATIC DRIVING
5.1 Traditional Automatic Driving
In the field of existing automatic driving research,
Google, Tesla and other enterprises are generally
based on information input of sensors, radars, and
cameras, the decision of vehicle is made through
artificial intelligence technology, and the vehicle
itself can be driven to a certain extent. However, the
single vehicle has great limitations, in the bad weather
such as night, rain, snow and fog, at the intersections,
corners, etc.; the radar and camera cannot observe
them. Developing more powerful sensors for these
scenarios will need substantial funds that ordinary
consumers can't afford.
5.2 Automatic Driving under the
Internet of Vehicles
In the field of Internet of vehicles and driverless
driving, 1ms may determine the moment of life and
death. 3GPP defines several low-latency scenarios
from 1ms to several ms, which are mainly on
automatic driving. The reaction time such as braking
in automatic driving is a system response time,
including the time for network cloud computing
processing, workshop negotiation processing, and the
vehicle's own system calculation and braking
processing time. If the braking speed of 100km/h is
not more than 0.3m, the overall response time of the
system should not exceed 10ms, and the response
time of the best F1 driver is about 100ms. From the
perspective of security, the system response time is as
low as possible, and the requirements for
communication delay will be higher. In the future,
network can provide good stability while achieving
less than 1ms communication delays. Therefore, the
low-latency scenarios of automatic vehicles require
the cooperation of other parts of the system. In the
realization of vehicle automatic driving scenarios,
V2X is a necessary technology; even if the vehicle
itself can achieve partial automatic driving, the
performance can be further improved Internet of
vehicles technology, it also reduces the cost of
deploying sensors for vehicles and reduces the
reliance on high-precision sensors.
6 CONCLUSIONS
At present, although there are many breakthroughs in
technologies of automatic driving and Internet of
vehicles, the research progress is still little, the
fundamental reason is that the basic technology still
has bottlenecks. The ultimate goal of the Internet of
vehicles is to automatic driving and fully network,
liberates the drivers' hands and feet; and V2X
technology will lay a solid foundation for the
integration of automatic driving and Internet of
vehicles.
ICVMEE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Vehicle, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering
132

REFERENCES
Cheng Gang, Guo Da. Research on the Status and
Development of Internet of Vehicles. Mobile
Communications, 2011, 35(17): 23-26.
Chen Qianbin, Chai Rong, Cen Ming. Future Direction of
Internet of Vehicles. ZTE Technology Journal, 2015,
21(1): 47-51.
Li Feng, Fang Jiayu, Zhao Li. Introduction of Standard and
Technology of LTE-V in 3GPP. Telecommunications
Network Technology, 2016(06): 40-45.
Liu Fuqiang, Xiang Xueqin, Qiu Dong. Research of DSRC
Technology and Communication Mechanism.
Shanghai Auto, 2007(8): 35-38.
Li Zhongdong. V2V System Open New Era of Motor
Vehicle Safety. Automobile Maintenance 2014(23):
28-29.
Xu Zijian, Yu Mei. An Application and Improvement of
V2V Technology in Intelligent Transport System.
Technological Development of Enterprise, 2016,
35(13): 33-36.
Wang Jianbiao. V2X Internet of Vehicles and Its Key
Technologies. Information Technology &
Informatization, 2013(5): 60-64.
Zhao Jing. Current Status and Prospects of V2X
Technology. Guangdong Communication Technology,
2018(1): 6-9.
Analysis of the Influence of Internet of Vehicles on Driverless Technology
133
