
Numerical Simulation of Combustion Characteristics on Tangentially
Fired Boiler with Different Yaw Angle
Rindra Hosanova
1
, Devy Setiorini Sa’adiyah
1,2
and Diniar Mungil Kurniawati
1
1
Insitut Teknologi Kalimantan
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, Kobe University, Japan
Keywords: Computational fluid dynamics, yaw angle, tangentially fired boiler
Abstract: Coal is one of the energy sources that widely used for electricity. Nonetheless, the high demand for coal is
not comparable with the remaining coal in the world, so it is necessary to make a study to reduce the
consumption rate of coal. Increase the efficiency of the tangentially fired boiler with improvement in the
burner is one of the right options. In some cases, because of the uneven distribution of coal type, blended of
mixing coal of higher and lower rank coal is necessary. This condition will affect the combustion behavior in
the boiler, also emission production. This research will study the effect of yaw angle modification to
combustion behavior and emission analysis in the tangentially-fired boiler with the condition of fuel 30%
MRC and 70% LRC. Computational fluid dynamics has been used in this study with validation. The yaw
angle diverse from +5º, 0º, -5º, -10º, dan -15º. The results show that the wider yaw angle increases the
temperature deviation and NOx concentration. Coal burner with -5º has the least temperature deviation and
the lowest NOx emission, which has 83,07 ppm of NOx, then -5º yaw angle is chosen.
1 INTRODUCTION
Coal is one of the most used energy sources,
especially in power plants, according to data obtained
from PT Bukit Asam (Indonesian mining company)
at least 27 percent of the total energy produced in the
world. While coal-fired power plants produce more
than 39 percent of all electricity created in the world,
this is because coal has a relatively easy and
inexpensive extraction process, and infrastructure
requirements are cheaper than other energy resources
(BUMN, 2017). Based on the latest data obtained
from the Geological Agency of the Ministry of
Energy and Mineral Resources (ESDM), Indonesia's
coal reserves amounted to 26.2 billion tons. With coal
production of 461 million in 2017, the remaining coal
reserves are 56 years old if there are no new reserves
found (KESDM, 2016).
The level of coal consumption should reduce, so
further research and innovation are needed. Much
research has been done to reduce the level of coal
consumption by increasing the efficiency of the
boiler. One widely used boiler is a tangentially-fired
boiler because it has the advantage of better
combustion and can be used for broader classes of
coal (Y.C. Liu et al., 2016). Although tangentially
fired boilers have better combustion, there are still
some problems such as carbon that does not burn in
ash, unbalanced heat and there is a temperature
deviation in the super-heater and reheater, numerical
simulations can be successfully used to assess coal
combustion and can observe the behavior of exhaust
emissions from boilers on a large scale (Ho Young
Park et al., 2012).
In coal-production, Indonesia is one of the coal-
producing countries, with the majority of the quality
of coal produced is medium calorie coal, whereas
there are still many old plants that still use low-calorie
coal. Under certain conditions, low-calorie coal
supply cannot meet the needs of the generator, so that
low-calorie coal will be mixed with medium quality
coal, which is more widely available in other
generating units (MEMR, 2016). In a numerical
simulation study, it was shown that tangentially fired
boilers with coal composition of 70% low-calorie
coal with 30% medium calorie coal showed that there
was a high-temperature build-up at the bottom of the
boiler (Sa'adiyah et al., 2017).
To reduce the occurrence of gas temperature
deviations in the boiler can be done by changing the
yaw angle of over-fire water. This is indicated by the
numerical simulation results, which show that
184
Hosanova, R., Saadiyah, D. and Kurniawati, D.
Numerical Simulation of Combustion Characteristics on Tangentially Fired Boiler with Different Yaw Angle.
DOI: 10.5220/0009443501840190
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICONIT 2019), pages 184-190
ISBN: 978-989-758-434-3
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
changing the yaw angle of Secondary Over-Fire
Water (SOFA) is a sufficient way to reduce gas
temperature deviation. Numerical simulations show
that changing the angle of SOFA and Closed Couple
Over-Fire Water (CCOFA) can affect gas
temperature and flow in the area around the
superheater and reheater (Ho Young Park et al.,
2015). Horizontal exhaust gas deviation decreases by
changing the yaw angle from SOFA to negative
direction, with Concentric Firing Secondary (CFS)
water at an angle of 22º (Y.C. Liu et al., 2016). To
reduce the occurrence of temperature deviation, it
necessary to optimize airflow in the opposite
direction from the secondary air (Ho Young Park et
al., 2012). So based on this research, it is necessary to
study the effect of the yaw burner angle which is
expected to be able to overcome the temperature
deviation at the bottom of the boiler which can
determine the quality of coal combustion in the boiler
which can affect the exhaust emissions produced, and
also overcome future conditions if Indonesia lacks
low coal calories. So from that, a numerical
simulation study of the combustion characteristics of
tangentially fired boilers with yaw angle variations
was carried out.
2 NUMERICAL METHOD
The numerical simulation in this study using
Computational Fluid Dynamics, which started with
geometry build and meshes formation before setting
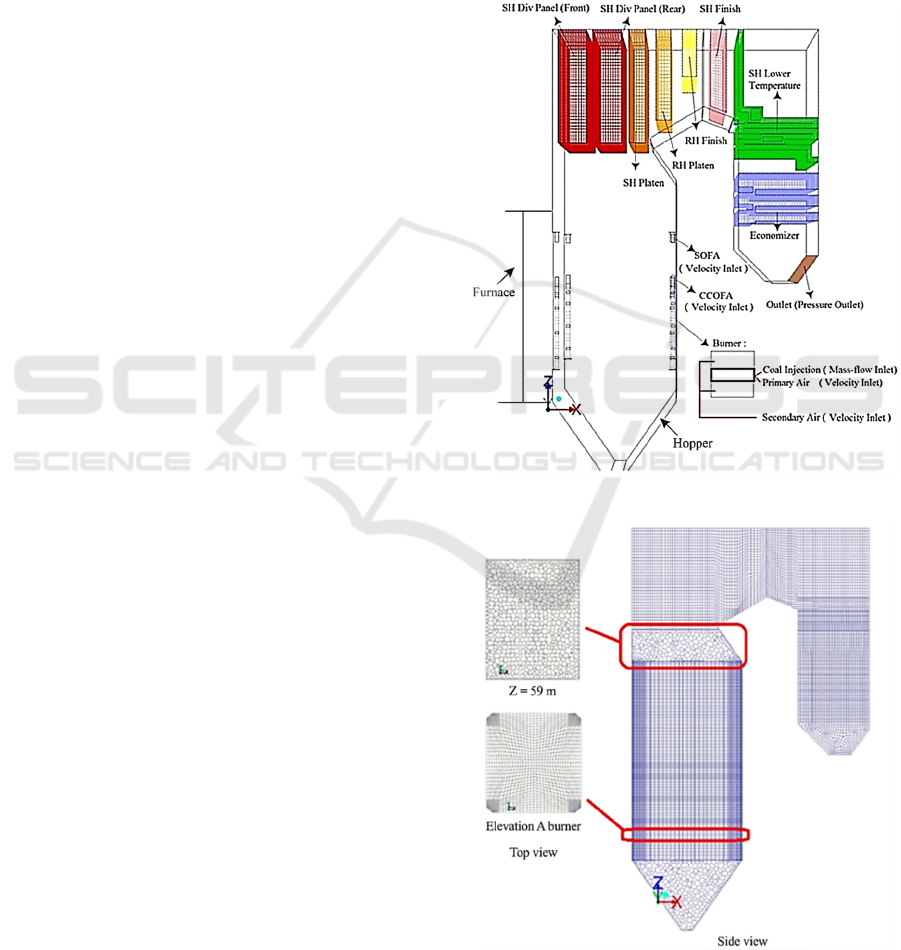
the solving method. The geometry of the tangentially-
fired boiler that will be used in this study is shown in
Fig. 1(a). The furnace section will have 7 (seven)
elevation, namely A, B, C, D, E, F, and G, with 1
(burner) at each corner of the elevation, or it can be
said for each elevation there would be 4 (four) burner.
Furthermore, this boiler also included CCOFA
(Closed-coupled Over-Fire Air) near elevation G and
SOFA (Separated Over-Fire Air) on the higher
elevation.
The formation of boiler meshing is depicted in
Figure 1 (b), which are using hexahedral at the
rectangular shape and polyhedral at the non-
rectangular shape to minimize the error due to
unbalanced mesh size ratio. Meshing is a process of
breaking domains into smaller volumes/forms that
can facilitate stream domain discretization and can
apply control equations to the flow domain. The
domain of the coal burner is mass flow inlet, while
CCOFA, SOFA, primary air, and secondary air are
velocity inlet. The water wall-tubes on wall furnace
are modeled as a heat sink that absorbs heat from flue
gas (heat flux). All heat exchangers, from superheater
to economizer, are modeled as a porous medium that
also absorbs heat (heat generation). The last, the
outlet will be modeled as a pressure outlet.
In this study 70% LRC type coal will be injected
through the elevation of B, D, E, G burners and MRC
type coal with a composition of 30% will be injected
through elevations A and C, as suggested in
Sa’adiyah et al. research, while at elevation F is in
stand by position (deactivated).
(a)
(b)
Figure 1: (a) Boiler geometry and (b) boiler mesh.
Numerical Simulation of Combustion Characteristics on Tangentially Fired Boiler with Different Yaw Angle
185
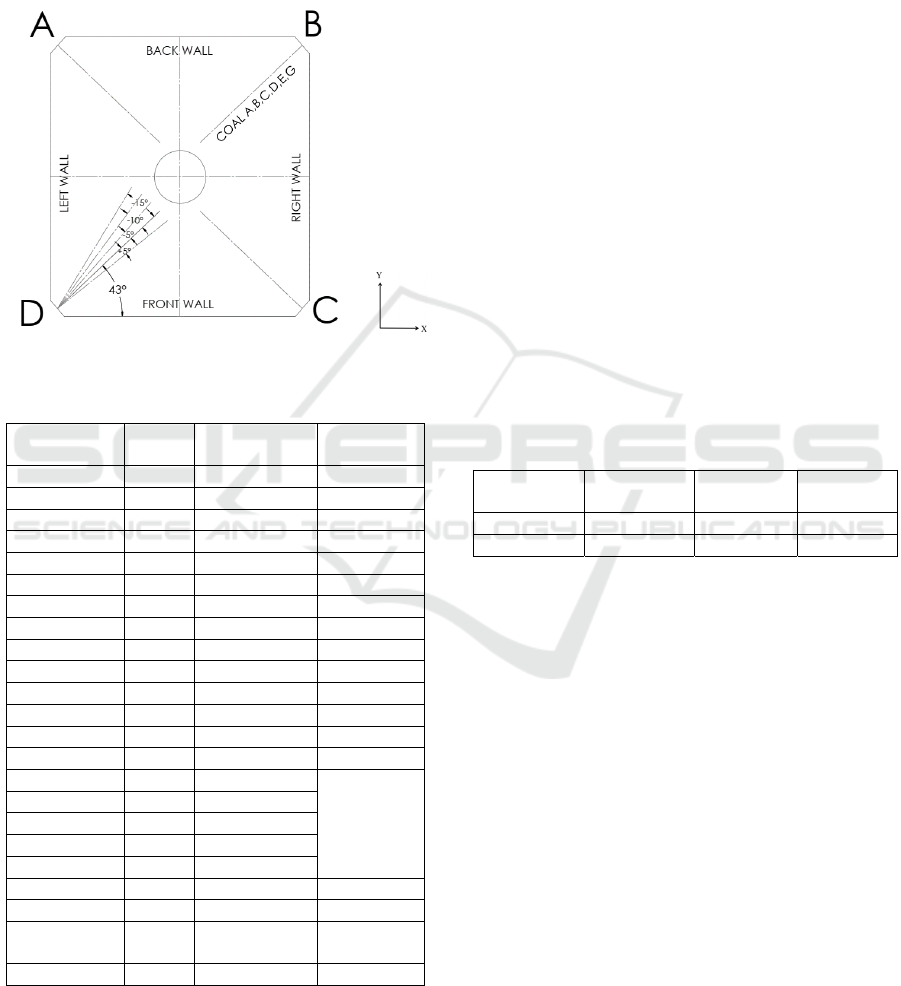
The original angle configuration for each coal
injection and auxiliary air can be seen in figure 2 and
Table 1. The change of yaw angle in this study is
focused on secondary air injection angle, which will
vary from + 5º, 0º, -5º, -10º, and -15º. The specific
condition of coal injection and auxiliary air, including
CCOFA and SOFA, are presented in Table 1.
Figure 2: Yaw angle configuration.
Table 1: Auxiliary Air Boundary Condition.
Auxiliary
Air
Angle
(º)
Temperature
(º C)
Velocity
(m/s)
AA 0 359 59,749
A 0 66 22,8
AB 4.5 359 59,749
B 0 66 22,8
BC1 4.5 359 59,749
BC2 15 359 59,749
C 0 66 22,8
CD1 15 359 59,749
CD2 4.5 359 59,749
CD3 15 359 59,749
D 0 66 22,8
DE1 15 359 59,749
DE2 4.5 359 59,749
E 0 66 22,8
EF 4.5 359
Not
activated
(assumed
as a wall)
F 0 66
FG1 -20 359
FG2 (LDO) 4.5 359
FG3 -20 359
G 0 66 22,8
GG -25 359 59,749
CCOFA 1 &
2
-25 359 15,438
SOFA 1 & 2 0 359 11,8197
The solution used in this study is using the
SIMPLE (Semi-Implicit Method for Pressure-Linked
Equations) algorithm, where least squares are cell-
based for gradients, standard for pressure, first-order
upwind for turbulent kinetic energy and turbulent
dissipation rate, and second-order upwind for
momentum, lig-vol, O
2
, CO
2
, H
2
O, H
2
, and CO. The
use of these solutions is based on research by
Chungen et al. (2003) and Choi and Kim (2009). The
viscous model to simulates the turbulence flow inside
the boiler is the standard k-ε model, while the coal
combustion process using the species transport
model.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In the numerical simulation, before it can be
continued to do further research, it should be relevant
to the original condition called validation. The
simulation results with the original condition have to
be in the same line with minimal error. However,
because the actual measured results only have CO
2
and O
2
emission percentages, then in this study, Table
2 points out the difference value O
2
and CO
2
concentration at the outlet in both actual and
simulation data/ Computational Fluid Dynamic
(CFD).
Table 2: Auxiliary Air Boundary Condition.
Emission at
boiler exit
Plant Data
(%)
CFD (%) Error
O2 5,4 5,9 9%
CO2 14,8 15,5 4,7%
Table 2 shows that there is a reasonably small
error in CO2 exhaust emissions which is below 5%,
whereas in O2 exhaust emissions there is a difference
of 9%, the simulation results show that the exhaust
emissions data obtained at the outlet is entirely
consistent with the actual data because the error is still
below 10%, this refers to previous research where
errors that occur in exhaust emissions between actual
and simulated data have an error of 16% (Ho Young
Park et al., 2012) and an error of 11% (Tan et al., 2017
) So that this simulation can be used for further
research.
3.1 Temperature and Velocity
Distribution
The temperature distribution at the y-center cross-
section is shown in Figure 3. The original case with
default yaw angle 0˚ is depicted in Figure 3 (a). Based
on the default configuration, the fire-ball swirling to
clockwise direction. The injection of MRC to burners
ICONIT 2019 - International Conference on Industrial Technology
186
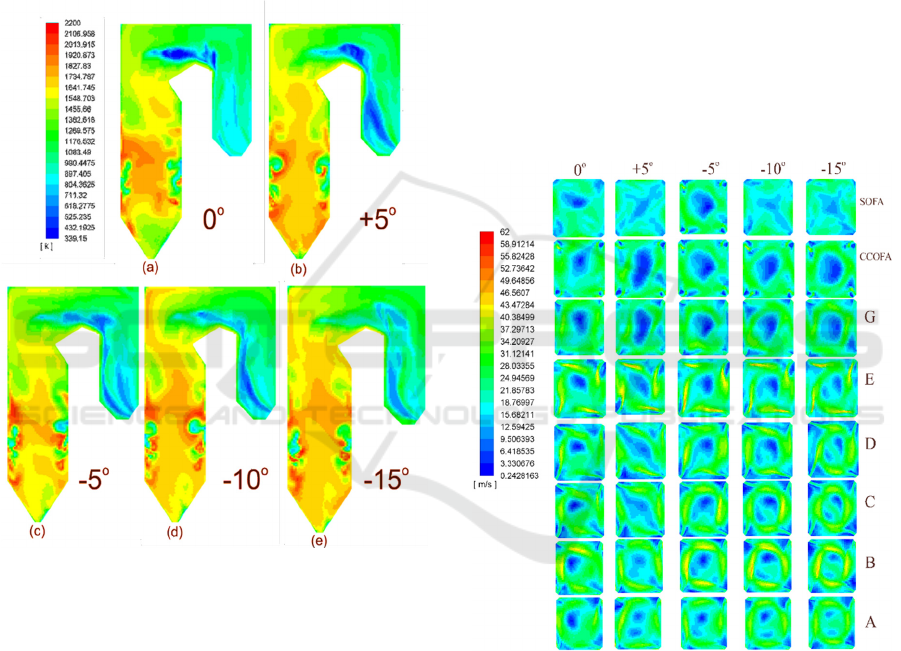
at elevation A and C makes high-temperature
distribution above the hopper zone because MRC has
a high heating value. Then the heat from MRC
combustion accelerates the burning rate of LRC at the
other burner elevation. The high temperature
increases the devolatilization process, so the char of
LRC burned faster. Therefore the combustion process
complete right before entering the superheater and
reheater area. However, the temperature before
entering the superheater area is still relatively high
that needs to be considered to prevent the damage of
the superheater tube from overheated.
Figure 3: Temperature distribution at the y-center cross-
section.
The first case which uses +5˚ yaw angle has the
opposite direction of fire-ball, this condition weakens
the fire-ball. Rather than moving upward, the fire-ball
tends to move to the hopper zone. The combustion
process then also takes place in the hopper zone; that
is why the red color shown in Figure 3 (b). However,
because almost all MRC get burned at hopper zone
and at a lower elevation, the LRC at higher elevation
did not get enough heat to speed up the burning time,
then the uncomplete combustion of LRC moving
upward to superheater area and get burned in that
area.
The observation of temperature distribution with
yaw angle -5˚, -10˚, and -15˚ showed in Figure 3 (c-
e). For these cases, the yaw angle sprays air in the
same direction with fire-ball rotation. The increasing
of yaw angle makes the fire-ball become wider to the
vicinity of wall-burner also decrease the turbulence.
The wider fire-ball expands the combustion area and
let the coal get complete combustion before entering
the next elevation and the superheater area. However,
for numerical simulation with -10˚ shows, the
combustion process delayed until the superheater area
and got worse when using -15˚. This can happen
because after increasing the yaw angle, the air
injection also directing some coal to the wall-furnace
and get burned. The red color occurs in the vicinity of
the burner, which indicated a very high temperature.
While the combustion takes place near the wall
furnace, the intake of air becomes insufficient at the
center, causing uncomplete combustion, the flow
with uncomplete combustion coal moving upward,
and get burned at the superheater area and damage
superheater tubes.
Figure 4: Velocity distribution at each elevation.
The phenomena that happened in the distribution
of temperature at each elevation strengthened with the
distribution of velocity, as shown in Figure 4.
Simulation with +5° yaw angle made the velocity
distribution spread and dispersed the fire ballet
elevation C & D. While on the negative yaw angle,
the velocity distributes evenly from bottom elevation,
elevation A, until SOFA elevation, especially with the
case -5° yaw angle.
Numerical Simulation of Combustion Characteristics on Tangentially Fired Boiler with Different Yaw Angle
187
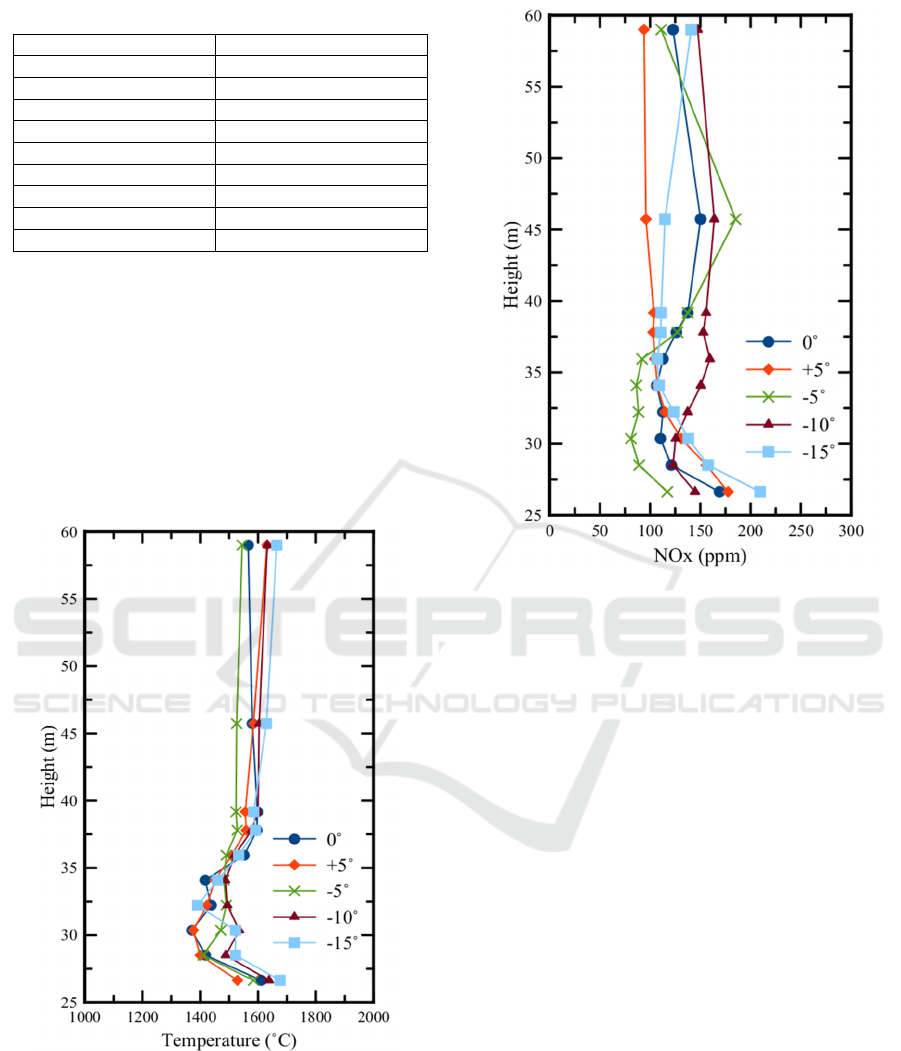
Table 3: Height for each elevation.
Elevation Height (m)
A 26.64
B 28.5
C 30.36
D 32.22
E 34.08
F 35.94
G 37.8
CCOFA 39.17
SOFA 45.73
3.2 NOx Emission
The special condition of this study is the mixed fuel
that has been used, namely MRC and LRC, which
need modification of yaw angle to reduce the
consumption of coal. Furthermore, the emission also
needs to be considered, called NOx, to offer the best
yaw angle. Figure 5 depicted the average temperature
and NOx concentration. The height shown in the
graph is the height of each elevation, Table 3.
(a)
(b)
Figure 5: Velocity distribution at each elevation.
The higher temperature will have higher NOx
concentration. However, the average value for both
temperature and NOx concentration can not represent
the actual phenomena inside the boiler; the further
observation of NOx is need inside the boiler, Figure
6.
The NOx production relies on temperature and the
amount of nitrogen and oxygen in the flue gas. When
the temperature is higher than 1800K (El-Mahallawy,
2002), the nitrogen from air and coal will react with
oxygen to generate NOx emission. The original case
with 0˚ produced high enough NOx species in the
furnace area, Figure 6 (a). The NOx generation also
occurs until the outlet of the boiler, although only
with a small amount. This indicates still there is
enough heat, nitrogen, and oxygen to produce more
NOx.
The combustion with yaw angle +5˚, as shown in
Figure 6 (b), generated a high amount of NOx in the
hopper zone until the middle of the furnace area, and
this is happening because of the very high
temperature formed due to MRC combustion. Despite
high NOx production at the lower part of the furnace,
the other area includes the heat exchanger area
forming the only little amount of NOx since all
ICONIT 2019 - International Conference on Industrial Technology
188

combustion processes, which produce high heat ends
at the furnace zone.
Figure 6: NOx distribution at the y-center cross-section.
The distribution of NOx with -5˚, -10˚, and -15˚,
which conceived in Figure 6 (c-e), shows that NOx
generation increased as the increasing of yaw angle.
The highest NOx formed at the lower part of the
furnace of -15˚ yaw angle simulation. Regardless of
the highest NOx amount at -15˚ yaw angle,
represented by green color, the simulation with -10˚
yaw angle actually generates more NOx. As can be
seen in Figure 6 (d), NOx formation also happens in
the upper part of the furnace and on the heat
exchanger area. While comparing to all cases with
negative yaw angle, the case with +5° yaw angle
produce a relatively small amount of NOx than
others.
Table 4: NOx emission at boiler exit
Yaw angle NOx (ppm)
0º 113,32
+5º 87,62
-5º 83,07
-10º 145,04
-15º 126,43
Observation of flue gas emission is also taken
place at the boiler exit to know how the yaw angle
variation affected the emission results before going
out to the atmosphere. Table 4 discloses the amount
of each emission for each variation of the yaw angle.
It shows the variation of the yaw angle really affects
the emission, with less emission is provided in -5°
yaw angle case.
4 CONCLUSION
In this study, Computational Fluid Dynamic
modelings were developed to investigate the effect of
the burner yaw angle on the combustion characteristic
and gas emission of a 625 MWe tangentially fired
boiler with mixed coal (70% LRC & 30 % MRC). The
Computational Fluid Dynamic model was validated
against measured results were found to be both
qualitatively and quantitatively consistent. As the
burner yaw angle going wider, the temperature
deviation also higher, which happened on the upper
furnace. The coal burner yaw angle that has the best
temperature distribution is at -5º because it has the
least temperature deviation on the upper furnace,
which minimizes the risk of overheat on superheaters
and reheaters. The least NOx is happened at -5º yaw
angle, with the result is 83,07 ppm because of the
NOx production process at the furnace effect the
results of NOx at the boiler outlet.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thanks to all who help and
support the authors to finish this paper.
REFERENCES
Al-Abbas, Audai Hussein., Naser, Jamal., Hussein, Emad
Kamil., 2012. CFD modeling of air-fried and oxy-fuel
combustion in a large-scale furnace at Loy Yang A
brown coal power station. Fuel (2012). Elsevier.
Al-Abbas, Audai Hussein., Naser, Jamal., Hussein, Emad
Kamil., 2012. Numerical simulation of brown coal
combustion in a 500 MW tangentially-fired furnace
under different operating conditions. Fuel (2012).
Elsevier.
BUMN, (2017), Produksi Batubara Indonesia. [online]
available on http:// bumn.go.id/bukitasam/berita/2-
Batubara-di-Indonesia-Produksi-Ekspor-Batubara -
Indonesia- [accessed on July 22, 2018].
Chen, Shinan., He, Boshu., He, Di., Cao, Yang., Ding,
Guangchao., Liu, Xuan., Duan, Zhipeng., Zhang, Xin.,
Song, Jingge., Li, Xuezheng., 2017. Numerical
investigations on different tangential arrangements of
burners for a 600 MW utility boiler. Energy 122 (2017).
Elsevier.
Choi, Choeng Ryul., Kim, Chang Nyung., 2009. Numerical
investigation on the flow combustion and NOx
Numerical Simulation of Combustion Characteristics on Tangentially Fired Boiler with Different Yaw Angle
189

emission characteristics in a 500MWe tangentially fired
pulverized-coal boiler. Fuel 88 (2009). Elsevier.
Chungen, Yin., Rosendahl, Lasse., Condra, Thomas J.,
2003. Further study of the gas temperature deviation in
large-scale tangentially coal-fired boilers. Fuel 82
(2003). Elsevier.
El-Mahallawy, F,. El-Din Habik, S., 2002. Fundamentals
and Technology of Combustion, Elsevier Science Ltd.
Oxford
KESDM., 2016. Laporan Kinerja Direktorat Jenderal
Mineral dan Batubara, KESDM. Jakarta.
Li, D., Lv, Q., Feng, Y., Wang, C., Liu, X., Chen, K., Xu,
K., Zhong, J., Che. D., 2017. Effects of coal blending
and operating conditions on combustion and NOx
emission characteristics in a tangentially-fired utility
boiler. Energy Procedia 105 (2017), Elsevier.
Liu, Y.C., Fan, W.D., 2017. Experimental and numerical
studies on the gas velocity deviation in a 600 MWe
tangentially fired boiler. Applied Thermal Engineering
110 (2017). Elsevier.
Park, Ho Young., Baek Se Hyun., Kim, Young Joo., Kim,
Tae Hyung., Kang, Dong Soo., Kim, Dong Woong.,
2012. Numerical and experimental investigations on the
gas temperature deviation in a large scale, advanced
low NOx, tangentially fired pulverized coal boiler. Fuel
104 (2013). Elsevier.
Park, Ho Young., Baek Se Hyun., Kim, Hyun Hee., Kim,
Young Joo., Kim, Tae Hyung., Lim, Hyun Soo., Kang,
Dong Soo., 2016. Reduction of main steam temperature
deviation in a tangentially coal-fired, two pass boiler.
Fuel 166 (2016). Elsevier.
Sa’adiyah, Devy., Bangga, Galih., Widodo, Wawan.,
Ikhwan, Nur., 2017. Numerical study of flow,
combustion and emissions characteristics in a 625
MWe Tangentially Fired Boiler with the composition
of Coal 70% LRC and 30% MRC. AIP Conference
Proceedings 1867, 020007 (2017). AIP Publishing.
ICONIT 2019 - International Conference on Industrial Technology
190
