
Increased Performance of the Hypothalamus in Producing
Neurotransmitters in Insomnia through a Combination of Cognitive
Therapy and Muscle Relaxation
Miftahul Zannah, Siti Sarah Bintang, Elsaria Br. Sembiring, Raynald Ignasius Ginting, Isidorus
Jehaman and Sabirin Berampu
Faculty of Nursing and Physiotherapy, Institut Kesehatan Medistra Lubuk Pakam, Indonesia
isidorusjehaman@yahoo.co.id, sabirinbrampu@yahoo.co.id
Keywords: Cognitive Therapy, Muscle relaxation, Hypothalamus and Insomnia.
Abstract: Insomnia is problem on sleep that disorder of hyperaurosal. Insomnia is sleep problem that often occurs
followed by headache, spasm around the head to the neck. These problems cause by delivery of excitatory
neurons that reach muscle is not conveyed properly because transportation of neurotransmitter is not produced
well in the hypothalamus. Hypothalamus is in suprachiasmatic nuclei has long relation, some of the relation
are the limbic system, pineal gland and brain steam which control the aferen and stage of sleep. Physiotherapy
intervention which can give for insomnia is combination of cognitive therapy and muscle relaxation. That
methods effective to improve hypothalamus performance in producing neurotransmitter for the best impulse
conduction for insomnia. This research is use experimental design with one group pre and post test design.
Intervention Cognitive therapy and Muscle Relaxation for 2 weeks with a daily frequency and monitored
sleep disorder before and after intervention. It can be seen the p-value = 0,002 that means less than 0,05 (p <
0,05) so zero hypothesis (Ho) is rejected and alternative hypothesis is accepted. So that Combination of
Cognitive Therapy and Muscle Relaxation effective to improve the performance of hypothalamus in
producing neurotransmitters for insomnia after intervention.
1 INTRODUCTION
Insomnia is one of clinical condition between many
problems such as phsycology and physic, the
problems are difficulties for go to sleep and maintain
it. It can be from nonorganic and nonrestorative that
show like sleep disorders for one month and siesta
time. Sleep disorders nonorganic is primary insomnia,
nonrestortive is secondary insomnia and increase
impaired emotion regulation resulting from sleep loss
may increase the risk of developing emotional
disorders by increasing the use of maladaptive
emotion regulation strategies (Ranum, 2019).
Sleep processing by reticular system just take a
few respons from cerebral cortex and from external
body. Wake up condition occur when reticular system
stimulated with impuls from cerebral cortex, organs
and cells of sense in skin formation. Sleep is cause by
process active inhibition. There is any old theory
about excitatory area in upper brainsteam called
activation reticular system that can be exhaustion
cause many activities a day. The condition is passive
theory of sleep. Sleep is similar to other health
behaviours, in that many aspects of sleep are under
direct behavioural control (Mead and Irish, 2019).
A research by National Sleep Foundation in
America found there are 36% young adult in 18-29
years old got difficulties for wake up compared with
20% in 30-64 years old and 9% in over 65 years old.
(Magoun, 2014). Poor sleep is a significant public
health issue in the United States, with nearly 33% of
adults reporting inadequate sleep duration (CDC,
2016) and > 40% feeling fatigued most days (Mead
and Irish, 2019).
Every years, there are 20%-40% adult got sleep
disorder and 17% among it got serious problems.
Prevalence of sleep disorder can increase every years,
this relevance with increase age and another causes
(Judarwanto, 2015).
Young adult usually get drowsiness, academic
ability, productive creativity and communication
were not decrease. Some job or another logic work,
Zannah, M., Bintang, S., Sembiring, E., Ginting, R., Jehaman, I. and Berampu, S.
Increased Performance of the Hypothalamus in Producing Neurotransmitters in Insomnia through a Combination of Cognitive Therapy and Muscle Relaxation.
DOI: 10.5220/0009465700890096
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 89-96
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
89

pleasure and seize attention could remove drowsiness
till give confusion about mentality. The research
showed, there are drowsiness can easier to remember
but too hard in future to get information with
creativity and constructive. Someone can express the
logic thinking but less than for brilliant (Silber, 2015).
Sufferers of Insomnia in long term cause somatic
symtomps and development illness. The patient can
induce all dimency mentality. Insomnia like an
inability to sleep, sleep or comfortable. Acute and
stress period insomnia can be chronic, fatigue,
extreme anxiety and mental disorders (Culebras,
2016).
Insomnia is generally more frequent and
prolonges at the end of the night when sleep is more
prevalent. Movement are often associated with
vocalisation and tend to be defensive, brief and
undirected, typically involving previous
acquaintances or occupations.
Hypothalamic function for sleep is relationship
with neurotransmitter. Awake or wake up are very
influence with ARAS system (Ascending Reticulary
Activity System. When activity of ARAS increase in
sleep and decrease when go to sleep. ARAS activity
influence by neurotransmitter activity as serotonergic,
noradrenergic, kholonergic and histaminergic systems
(Roth, 2016).
All humans body have a life rhythm who matches
time in a 24-hour cycle. The rhythm along rotation
globe is referred to circadian rhythm. The circadian
rhythm control center lies in the ventral anterior part
of hypothalamus. Experiencing insomnia caused by
influence of hormonal systems. Hormones that affect
sleep system like adrenocorticotropic hormone
(ACTH), Growth hormone (GH), thyroid stimulating
hormone (TSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH)
(Judarwanto, 2015).
These hormone were secreted regularly by
anterior pituitary gland through the hypothalamus
pathway. System regularly affects the production of
neurotransmitter norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin
which are tasked with regulating sleep and wake
mechanisms. The sleep and wake problems are sleep
disorder that interfere with cognitive problems in
individuals (O’Connor, 2013).
This research used intervention cognitive therapy
and muscle relaxation to improve sleep patterns of
individuals experiencing insomnia. Because cognitive
therapy can improve the cognitive distortion in
insomnia, environment, future and to increase
confidence so the feels empowered that still identify
wrong person's attitudes and beliefs about sleep
(Brust, 2014).
Muscle relaxation expected to be able for relaxing
muscles that are experiencing tension thereby
inhibiting course of neurotransmitter to hypothalamus
as hormone producer. Such as interventions of sleep
mechanism to affect the hypothalamus in generating a
sleep cycle regulating hormone (Mehta et al. 2014).
Energy produced by hypothalamus in hormones
that secreted into the central nervous system, muscles
and organs. Many hormones are produced to regulate
performance of body's system, among it hormones
can regulate human sleep patterns such as ACTH, GH,
TSH, and LH. These hormones are secreted regularly
by anterior pituitary gland through the hypothalamus
patway. This system regularly affects production of
neurotransmitter norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin
which are tasked with regulating sleep and wake
mechanisms (Overeem, 2016).
When someone falls asleep, alpha activity begins
to disappear. Beta waves arise frequency more than
14 rounds per second and can be as high as 80 rounds
per second. Stage I is characterized by regular
activities, low voltages and frequency of 3-7 per
second cycles. Stage II is characterized by a pattern
showing the taped-in (spindle-shaped) recording with
frequency of 12-14 per second (sleep spindle) cycle,
slow and trifastic known complex K. Stage III
complex marked with Delta waves Which shows high
voltage activity with a frequency of 0.5-2.5 per second
cycle. Delta waves occur during deep sleep, infants
and severe brain organic diseases. Teta waves have
frequencies between 4 and 7 rounds per second. This
wave occurs in emotional stress on adults, especially
when experiencing disappointment and frustration as
well as brain disorders especially state of brain that is
degeneracy (Zaini, 2015).
Insomnia and severely disturbed sleep are also
increaslingly recognized accompanying features of
limbic encephalitis, a rare disorder in wich fluctuating
confusion, seizure and autonomic symptomology
usually predominate. Delayed sleep phase syndrome
sometimes presents as insomnia unlike the typical
case of primary insomnia by definition, there are also
major problems in waking at several times or hours.
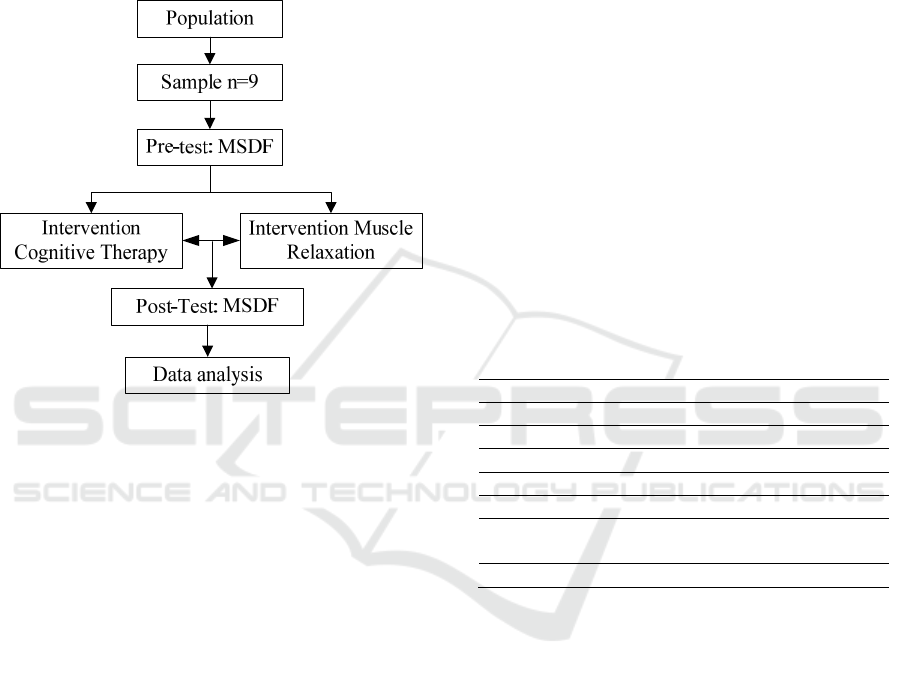
2 METHODOLOGY
This research explain in Figure 1 that used quasi
experimental with one group pre and post test design
in one group consist of 9 young adults in Medan, this
research is measure variables conducted before and
after the intervention of cognitive therapy and muscle
relaxation.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
90
Measurement of hypothalamus performance is
used remonitoring for 2 weeks with sleep disorder
form (MSDF) monitoring in Table 2. MSDF is form
of performance monitoring hypothalamus for sleep
disorders. Calculation of MSDF value after the
intervention is result by calculation duration
headache, impaired activity and stress levels by
insomnia sufferers every day for 2 weeks.
Figure 1: Research plot.
Procedure of screening with MSDF is performed
four times per day within 2 weeks. Respondents asked
to pay attention for activity by giving cross sign (x)
when activities want to sleep, eat and temperature
body. Female respondents the menstrual period
should be considered.
2.1 Cognitive Therapy
Cognitive therapy is part of several techniques
used to reduce chronic insomnia. Stimulus control
therapy states that insomnia is a maladaptive response
such as sleep time factors and sleep environments e.g.
in-reading books in bed from sleep. By giving the
patient instructions on sleep limits, insomnia patients
can learn to increase their sleep time by inducing less
sleep by reducing their time in bed. To avoid it can be
monitoring system or supervision patients using the
standardization of questionnaire (Rains, 2012).
Endorphins have been shown to serve as
modulators of pain in experimental, it has been
suggested they are responsible for decrease pain
perception that some experience during running.
Endorphin system apparently does not function
tonically but influences physiological processes in a
rather
selective
manner only
under
specific environmental conditions of extreme change
in circumstances such as stress (Francis, 2014).
Some of that need to be cared for in insomnia
regarding cognitive therapy can be seen in Table 1.
2.2 Muscle Relaxation
Manual therapy targeting the cervical and head
have been suggested to be the most accepted
therapeutic intervention for management of this
population. Physical therapy management of patients
with insomnia suggest a treatment approach
consisting of both manual therapy management.
Muscle relaxation can be used to enter sleep
condition by controlling the muscles intentionally will
form a calm and relaxing atmosphere. This
atmosphere is necessary to achieve the Alpha wave
condition that is a condition that needs to enter the
initial sleep phase (Purwanto, 2013).
Table 1: Sleep Hygiene for insomnia.
N
O Esential sleep hygiene
1 Sleep and awake according to the time
2 Avoid to lay down in the afternoon
3 Remove stimulation (caffein, nicotine)
4 Bedroom should be dark
5 Not concumption alcohol
6 Exercise regularly (avoid exercise 5 hours
before go to sleep)
7 Used bed for sleep not for other
Relaxation massage is always used to respond to
skeletal muscles that have an increase in muscle tone
by responding through the relaxation of the the nerve
that conducts the sleep-regulating neurons. Tonus can
be increased in stressful and cold conditions. Massage
can stimulate externally through sensory organs and
increase muscle tone with stimulation. The
sympathical nervous system supplies the delivery of
neurons to muscle spindles that respond to the nervous
system. Massage techniques used are relaxation with
local massage (Holey, 2008).
Increased Performance of the Hypothalamus in Producing Neurotransmitters in Insomnia through a Combination of Cognitive Therapy and
Muscle Relaxation
91
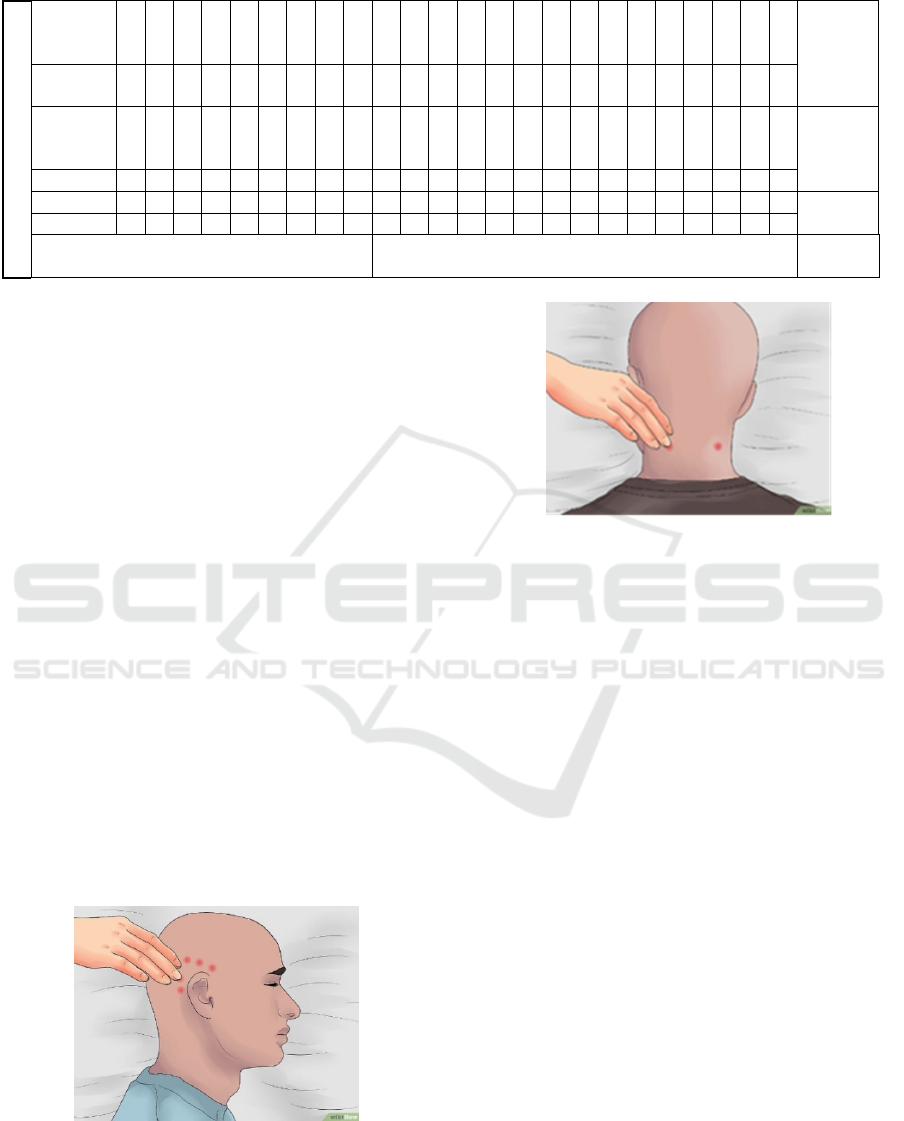
Table 2: Instrument Monitoring Sleep Disorder Form.
D
A
Y
Date:
1
2
a
1
a
2
a
3
a
4
a
5
a
6
a
7
a
8
a
9
a
1
0
a
1
1
a
1
2
p
1
p
2
p
3
p
4
p
5
p
6
p
7
p
8
p
9
p
1
0
p
1
1
p
Temper
ature :
Head
ache
Distrupt
ed
activity
Menstr
uation :
Stress
Sleep Sleep
time:
Meal
Medicine (total) : Comment : Sleep
quality:
Massage technique for insomnia (Holey, 2008) :
Effleurage
According to Figure 2, movement along the
parotid gland, until it crosses to the head then
down to side of neck under the chin to
submandibular node
Finger kneading
Starting from the head, forehead, chin and under
the nose or over the lips followed by other facial
muscles. Avoid overstretching of muscles and
skin.
Plucking
Apply tissue picking technique in the same area
followed by finger kneading.
Wringing
According to Figure 3, perform wringing
techniques on an ongoing basis according to the
groove of the head, forehead and chin.
Tapping
The technique is flowing or stimulating muscles.
Vibrations
Used the middle finger, give vibrations around
the ophthalmic foramen (supraorbital foramen),
maxilla (infraorbital foramen) and mandible
(mental foramen) by stimulating the nerve.
Figure 2: Massage relaxation on head.
Figure 3: Massage relaxation on cervical.
2.3 Hypothalamic Performance
The hypothalamus is part of brain that contains a
number of small nuclei. The hypothalamus is located
below the thalamus, just above the brain stem. In
neuroanatomy terminology, it forms the ventral
diencephalon part. The hypothalamus is responsible
for certain metabolic processes and other activities of
the autonomic nervous system that synthesize and
releases neurohormonal, often called the
hypothalamus, releasing hormones that stimulate or
inhibit the secretion of the pituitary hormone
(Pugliese, 2011).
The hypothalamus is a system that regulates
accentuation of individual. Increased activation
systems can deliver stress to the brain and peripheral
centers, which regulate cognitive and bring back
energy to the central nervous system, muscles and
body organs (O'Connor, 2013).
The energy produced by the hypothalamus is
hormones secreted to the central nervous system,
muscles and organs of the body. Many hormones are
produced to regulate the performance of body
systems, including hormones that regulate human
sleep patterns. Like ACTH, GH, TSH, and LH. These
hormones are each secreted regularly by the anterior
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
92

pituitary gland through the hypothalamus patway.
This system regularly influences the release
of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, dopamine,
serotonin which are responsible for regulating sleep
and wake mechanism (Overeem, 2016)
The hypothalamus responds to the coordination
of behavior and emotional responses in the forebrain.
The information is processed and sent via pathway to
brain control centers that mediate metabolic activities
to produce coordination of autonomy and behavior
control. The pathway is the medial part of the
forebrain and the medial periventricular part in
midbrain. While the hypothalamus output that
delivered through network to the forebrain then down
to the brain stem fibers and spinal cord to fibers and
blood vessels to the pituitary (Lynch, 2016).
The hypothalamus has control centers for several
types of unconscious activities of the body, one of that
involves sleeping and wake up. Damage to the
hypothalamus can cause a person to sleep in an
unusually long or long period and sufferers also have
difficulty starting to sleep (Roth, 2016).
Reticular formation regulates to delivery impuls
to the brain. The formation rises up through the
medulla, pons, midbrain, then to hypothalamus. The
formation is composed of many nerve cells and nerve
fibers that communicate through synapses. The fibers
have connections that transmit impulses to the brain
and the spinal cord. The reticular formation allows for
reflex and deliberate movements to occur easily, as
well as cortical activities related to the alert state.
Insomnia who experience neuronal delivery disorders
will always in a state of alert so it is difficult to start
sleep (O’Connor, 2013).
At bedtime, the reticular system gets only a little
stimulation from the cerebral cortex (skin of the brain)
and the outer surface of the body. A state of
wakefulness occurs when the reticular system is
stimulated by stimuli from the cerebral cortex and
from the organs and sensing cells in the skin. It is
suspected that the cause of sleep is the active
inhibition process. There is an old theory that states
that the excitatory area in the upper brain stem, called
the "reticular activation system", experiences fatigue
after a day of being awake and, therefore, becomes
inactive. This situation is called the passive theory of
sleep (Choi, 2013).
All living things have a rhythm of life according
the circulation of time in a 24 hour cycle. The rhythm
that goes along with rotation of the globe is called the
circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm control center
is located in ventral anterior part of the hypothalamus.
The part of central nervous system that carries out
synchronization is located in the ventriculo reticularis
medula oblongata substance called the sleep center.
The part of the central nervous system that eliminates
synchronization / desynchronization is found in the
rostral medula oblongata called the aurosal state
(Magoun, 2014).
Activities of disturbed sleep patterns can also be
determined by questionnaire method. Namely by
asking patients directly about their daily sleep diary in
terms of disability, stress levels, amount of sleep and
quality of sleep. Some of these can be calculated
through filling out a questionnaire to find the
categorized as insomnia or not (Mehta et al, 2014).
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Respondent Characteristics
Respondents in this study were 9 young adults with
insomnia with maximum age of 22-25 years with 5
people (55.6%) and the most gender are women
(89.1%) listed in Table 3. Findings the data is in
accordance with research conducted in 2011 in
America by the National Sleep Foundation found that,
more than third (36%) of young adults aged 18-29
years reported having difficulty getting up early
compared with 20% at ages 30-64 years and 9% over
the age of 65 years (Sulistiyani, 2011).
Young adults begin at the age of 18-40 years,
when physical and psychological changes
accompanying reduced reproductive abilities. In
general, classified as young adults will experience a
transition period, both physical transition (physically
trantition) intellectual transition (cognitive transition)
and the transition to social roles (social role transition)
(Physicologymania, 2011).
Table 3: Respondent characteristic.
Characteristic n %
Sex
Man
Women
1
8
11,1
89,1
Age
< 22 years
22 – 25 years
>25 years
2
5
2
22,2
55,6
22,2
Increased Performance of the Hypothalamus in Producing Neurotransmitters in Insomnia through a Combination of Cognitive Therapy and
Muscle Relaxation
93

3.2 Measuring of Monitoring Sleep
Disorder Form Value in Patients
with Insomnia
A description of the characteristics of Sleep Diary
monitoring values before and after the intervention of
a combination of cognitive therapy and muscle
relaxation, can be seen in Table 4.
Table 4: Characteristic of monitoring sleep disorder.
form.
Monitoring Sleep Disorder Form
MSDF Min Max Mean±SD
Pre Test
Post Test
11,12
4,5
48,30
7,50
25,26 ± 12,94
5,96 ± 6,35
The value of Monitoring Sleep Disorder Form
(pre test) the maximum value is 48.30 while the
minimum value is 11.12 with mean of 25.26 and
standard deviation of 12.94. After the intervention, it
is known that the value of monitoring sleep diary is a
maximum value of 7.50 while the lowest value is 4.5
with a mean of 5.96 and a standard deviation of 6.35.
3.3 Combination of Cognitive Therapy
and Muscle Relaxation to Improve
Performance of Hypothalamus to
Producing Neurotransmitters in
Insomnia
Hypothesis testing used paired samples t test. Paired
samples t test aims to see changes in treatment by
comparing conditions before and after intervention.
Hypothesis test can be seen in Table 5. Hypothesis test
results show that a combination of cognitive therapy
and effective muscle relaxation to improve the
performance of the hypothalamus patway in
producing neurotransmitters in people with insomnia
after intervention.
Table 5: Hypothesis test with Paired Samples t-test.
Hypothesis test
Characteristic of
MSDF
n t P
Mean ±
SD
Pre Test – Post
Test
9 4,68 0,002
19,30 ±
12,35
Hypothesis testing used paired samples t test. Paired
samples t test aims to see changes in treatment by
comparing conditions before and after intervention.
Hypothesis test can be seen in Table 5. Hypothesis test
results show that a combination of cognitive therapy
and effective muscle relaxation to improve the
performance of the hypothalamus patway in
producing neurotransmitters in people with insomnia
after intervention.
The t value is 4.68 which means that the MSDF value
in insomnia has low sleep quality with a lower
hypothalamic performance before intervention than
after intervention.
3.4 Combination Cognitive Therapy
and Muscle Relaxation
This study aims to look at the effectiveness of a
combination of Cognitive Therapy and Muscle
Relaxation to improve the performance of the
hypothalamus patway in producing neurotransmitters
in young adults with insomnia.
In insomniacs, assessment was carried out which
included history taking in form of sex, age and
examination of the value of sleep disorder using the
monitoring sleep disorder form which was conducted
for 2 weeks. For patients who meet the inclusion
criteria, intervention can be done every day for 2
weeks.
Based on statistical tests paired samples t test on
the MSDF value before and after the intervention on
9 respondents. From the results of data analysis, it was
found that there was an effect of intervention so that
the combination of both cognitive therapy and muscle
relaxation interventions was effective in increasing
the performance of the hypothalamus in producing
neurotransmitters with insomnia in young adults,
which is indicated by the value of p = 0.002, which
means that a p value of less than 0.05 (p <0.05) so the
null hypothesis (Ho) is rejected and alternative
hypothesis (Ha) is accepted.
This is consistent with the theory and purpose of
both methods, Cognitive Therapy is part of several
techniques used to reduce the factors of chronic
insomnia. Stimulus-control therapy states that
insomnia is an maladaptive response such as factors
of sleep time and sleep environment such as the
frequency of reading a book in bed rather than
sleeping. By giving patients guidance on sleep
restrictions, insomniacs can learn to increase their
sleep time by inducing insufficient sleep by reducing
their time in bed. To avoid this, monitoring or
surveillance system for patients can be done by using
a standardized questionnaire (Rains, 2012).
Muscle Relaxation can be used to enter sleep
conditions because by deliberately relaxing the
muscles it will form a calm and relaxed atmosphere.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
94

This atmosphere is needed to reach alpha wave
condition which is a state that is needed by someone
to enter the early sleep phase (Purwanto, 2013). So
that the combination of both can be effective for
increasing the performance of hypothalamus which
decreases in producing neurotransmitters as
regulators of the production of sleep regulating
hormones.
According to several studies of these
interventions. Several studies have suggested that the
touch of a hand can increase hormone production and
reduce the production of cortisol (stress levels) which
keeps a person in a state of guard making it difficult
to start sleeping in young adults. Studies conducted,
massage given is 15 minutes to 10 days with
relaxation massage to increase serotonin and
dopamine levels (Dixon, 2004). Combined with
cognitive therapy several Cognitive Therapy studies
provided an average of 6 sessions with a total time of
5.8 hours per patient. Based on Meta analysis shows
that individual therapy is more effective than group
therapy therapists can provide therapy for 4-6 sessions
of 20-50 minutes each. The result have been reported
when therapy has reached 3-10 sessions (Ralston,
2015).
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the results and discussion that has been
done, the conclusion can be drawn is that there is an
average increase in the value of MSDF (Monitoring
Sleep Disorder Form) on 9 respondents, for 1 month
with a value of p = 0.002 (p <0.05). So that the
combination of Cognitive Therapy and Muscle
Relaxation is effective to increased the performance
of the hypothalamus patway in producing
neurotransmitters in young adults with insomnia,
where both interventions simultaneously affect
cognitive and muscle stimulation, thereby delivering
stimulation to the brain and producing
neurotransmitters as regulators of the production of
sleep regulating hormones.
5 SUGGESTION
From the conclusions above, the authors suggest
several things related to this study, including:
Further research needs to be done by using more
samples and longer time to further support and
strengthen the conclusions of this study and to
obtain maximum and satisfying research results.
For physiotherapist, It is expected to be able for
apply intervention method of combining
cognitive therapy and muscle relaxation to
patients with insomnia with the aim of providing
stimulus control therapy and helping patients to
reduce insomnia.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Thank you to all participants who get insomnia that
have been agreed to be a research sample
REFERENCES
Brust, John C.M. 2014. Current diagnosis and treatment
neurology. United States of America: Medical
Publishing division.
Choi, Jenifer H.K and Ted Abel. 2013. Sleep and long term
memory storage. United states of America. Cambridge
University of Press.
Culebras, Antonio. 2
nd
edition. 2007. Sleep disorder and
neurologic disease. United States of America: Informa
healthcare.
Holey, Elizabeth and Eileen cook. 2008. Therapeutic
massage a practical guide for therapists. USA: Elsevier
Judarwanto, Widodo. 2015. Children sleep clinic
information education network. Jakarta: Yudhasmara
foundation.
Lynch, Gary ang Richard granger. 2016. Big brain and
future of human intelligence. United States of America:
Palgrave Macmillan.
Magoun, Horace Winchell. 2014. American Neuroscience
in the twentieth century confluence of the neural
behavioral and communicative streams. Netherlands:
Balkema publishers.
Mehta, Noshir R, et al. 2014. Head, face and neck pain
science evaluation and management. Canada:
Blackwell publishing.
O’connor, et al. 2013. The stress response and the
hypothalamic pituitary – adrenal axis : from molecule to
melancholia. Q.J Med. 93, 323-333.
Overeem, Sebastian and Paul Reading. 2016. Sleep disorder
in Neurology. United Kingdom: Blackwell Publishing
ltd.
Phycologymania. 2011, Jul 12. Psikologi (perkembangan
dewasa awal). Retrieved from
http://www.aktivasiotak.com/fungsi_otak.htm
Pugliese, luca,et al. 2011. The anatomy of extended limbic
pathway in asperger syndrome: a preliminary diffusion
tensor imaging tractography study. Retrieved from
http://www.elsevier.com/locate/ynim
Purwanto, Setiyo. 2013. Mengatasi insomnia dengan terapi
relaksasi. Jurnal kesehatan ISSN 1979 – 7261. 1 (2),
141 – 148.
Increased Performance of the Hypothalamus in Producing Neurotransmitters in Insomnia through a Combination of Cognitive Therapy and
Muscle Relaxation
95

Rains, Jeanetta C and David M.Biondi. 2012. Sleep
disorders and headache. Canada: Blackwell publishing.
Ranum, Bror M. CandPsych, Lars Wichstrom, Stale
Pallesen, Jonas Faich-Madsen, Marte Halse, Sije
Steinsbekk. 2019. Association between objectively
measured sleep duration and symptoms of phychiatric
disorders in middle childhood. JAMA Network Open.
Ralston, George E. 2015. Cognitive–behavioural therapy
for anxiety. USA: Elsevier
Roth, Thomas. 2016, Aug 15. Insomnia: Definition,
prevalence, etiology and consequences. Clinical sleep
medicine. 3, S7 - S10.
Silber, Michael H. 2005, Aug 25. Chronic Insomnia.
English journal med. 353, 803-810.
Zaini, Nurzakiah Binti. 2014. Apa itu insomnia. Insomnia
sleeping disorders.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
96
