
Formulation and Anti Bacterial Activity Test of Liquid Soap Extract
from Cocoa Beans (Theobroma cacao L.) against Staphylococcus
Aureus and Escherichia Coli Bacteria
Dian Ika Perbina Meliala
1
, Vera Estefania Kaban
1
, Christica Ilsanna Surbakti
1
, Wahyudi
1
, Parhan
1
1
Faculty of Pharmacy, Deli Husada Deli Tua Health Institute, Deli Serdang, Indonesia
Email:{dianikaperbinameliala, erastkaban.20, christicailsannas,
Keywords: Extract, Cocoa beans, Natural antibacterial, Cosmetics, Liquid soap
Abstract: Cosmetics are ingredients or materials mixtures that have functions to clean, maintain, add attraction or
change appearance. Antibacterial liquid soap is used to cleanse and soften skin. Many people are not aware
of making antibacterial liquid soap which can be made traditionally by using cocoa beans (Theobroma cacao
L.). This study aimed to formulate liquid soap extracts from cocoa bean extracts which are used as basis for
making liquid soap and tested the antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.
The research method was an experimental method; Simplisia was extracted by using maceration method with
80% ethanol solvent. Testing antibacterial activity used disk diffusion method and statistical analysis used
one way ANOVA test method. The evaluation results of soap formulation quality testing showed that pH and
froth ability had good results and fulfills SNI standard 06-3532-1996. The results showed that formulation III
with concentration of 20 g cocoa bean extract had great antibacterial activity in each bacterium with values
of 12.93 mm and 10.90 mm. In positive control, antibacterial activity showed values of 15.70 mm and 15.26
mm. The statistical analysis results used one way anova test method showed significant results p <0.05, with
significant value of 0.015 found in Staphylococcus aureus bacteria so that the results showed that it affected
the antibacterial activity test. Antibacterial liquid soap containing cocoa bean extract has antibacterial
potential but not as much as antibacterial potential such as Dettol bath soap.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cosmetics are materials or mixtures that rubbed,
glued, poured, sprinkled or sprayed on, put in, it used
on the body or human body parts to clean, maintain
and add the attraction or change the shape, protecting
to keep it in good condition repairing body odor but
it is not intended to treat or cure an illness (Mu and
Sprando., 2010).
Cosmetics have been widely used by the public
and the main purpose of their usage is to beautify
themselves, increase attractiveness, self-confidence,
and protect hair skin from UV damage, pollution and
other environmental factors, prevent aging and help
someone enjoy and appreciate life more (Mu and
Sprando, 2010).
There are many types of cosmetics that used to
protect the skin such as creams, gels, lotions,
ointments, powders and one of them is soap.
Currently in the market there are still many soaps that
use synthetic ingredients such as (diethanolamine
(DEA) and triclosan), but not all usage of active
ingredients in cosmetics are suitable for every skin
condition, which can cause skin irritation (Górnaś and
Rudzińska, 2010).
Today, there are many people do not realize
soap making can also be made traditionally. Cocoa
beans is one of the traditional ingredients used
(Tamarkin et al., 2018). Cocoa plant which has Latin
name Theobroma cacao L. It is tree plantations that
grow in areas that have soil and tropical climate that
are suitable for cultivating cocoa plants (Arzhavitina
and Steckel, 2010). The contents of secondary
metabolites found in cocoa beans are flavonoids,
saponins, and tannins which are chemical compounds
that have potential as antibacterial (Santana et al.,
2016).
Most people know that cocoa beans are only used
in food / beverage processing, but currently cocoa
beans can also be used in the pharmaceutical
(medicine) and cosmetics industries which one of
them in making liquid soap (Brito-vega, 2018).
Meliala, D., Kaban, V., Surbakti, C., Wahyudi, . and Parhan, .
Formulation and Anti Bacterial Activity Test of Liquid Soap Extract from Cocoa Beans (Theobroma cacao L.) against Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli Bacteria.
DOI: 10.5220/0009488502930300
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 293-300
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
293

Liquid soap is a liquid form that is generally made
by using oils or fats intended to clean the skin, made
with additives namely surfactants, preservatives,
foam stabilizers, deodorizers and dyes that are
allowed, and used for bathing without causing
irritation to the skin. Liquid soap has the ability to
emulsify oily dirt so that it can eliminate bacteria and
dirt that sticks to the skin (Foddai, Grant, and Dean.,
2016).
Based on research conducted by Baharium (2014)
states that ethanol extract of cocoa beans (Theobroma
cacao L.) has an antibacterial effect in inhibiting
Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium which is carried
out in vitro. Therefore, this research conducted on the
formulation and antibacterial activity test of liquid
soap extract from cocoa beans (Theobroma cacao L.)
against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli
bacteria. This research included extracts making from
cocoa beans by maceration and liquid soap
formulation that is tested on Staphylococcus aureus &
Escherichia coli bacteria to determine the inhibitory
power of bacteria to the formulation of liquid soap
preparations from cocoa bean extract with alkali
(KOH), and then testing soap evaluation namely
organoleptic test, pH, foam ability test and irritation
test.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ripe cocoa beans and fresh yellow color are taken
from Lake Rambai Village, Batang Gansal Sub
District, Gansal District, Inhu, Riau. Cocoa beans that
have been taken are sorted to get fresh seeds, then
washed with running water and dried by direct
exposure to sunlight.
2.1 Making Simplicia Powder
Cocoa beans that have been dried are mashed by
pounding them before blend to get more uniform size.
Then the powder is weighed as much as 500 grams,
and then put into a container for extraction purposes
by using the maceration method.
2.2 Research Tools and Materials
The tools used in this study include laboratory
glassware, aluminum foil, autoclaves, 65 mesh
sieves, stirring rods, blenders, bushes, petri dishes,
hotplates, incubators, calipers, ose needles (diameter
1, 78 dm), cotton, disc paper, filter paper, LAF
(Laminar Air Flow), magnetic stirrer, 20 μl
micropipette, microscope, oven, pH meter,
pycnometer, rotary evaporator, digital scales and
vortex. The materials used in this study include stearic
acid, aquadest, cocoa beans, Butyl Hydroxy Toluene
(BHT), 80% ethanol, ethyl acetate, FeCl
3
, glycerin,
H
2
SO
4
, HCl 2N, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose
(HPMC), Ethanol 80%, ethyl acetate, FeC
l3
, glycerin,
H
2
SO
4
, HCl 2N, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose
(HPMC), indicators of phenolphthalein, potassium
hydroxide (KOH) 0.1 N, chloroform, 0.9% NaCl
solution, n-hexane solution, Mueller-Hinton Agar,
coconut oil, castor oil, olive oil, Nutrient agar,
Na
2
SO
4
anhydrous, NaOH 2 N , and Dragendorff
reagent, Lieberman-Bouchardat reagent, lead (II)
acetate 0.4 N. The bacteria used were pure cultures of
Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus bacteria.
2.3 Phytochemical Screening Test
Phytochemical screening is carried out to analyze
bioactive content which is useful as an antibacterial
or as a treatment. The phytochemical screening test of
this cocoa bean powder, namely:
2.3.1 Flavonoids Test
10 g of simplicia powder were added with 100 ml of
hot water. The mixture is then boiled for about 5
minutes, and then filtered when it is hot. As much as
5 ml of filtrate was obtained, added 0.1 g of Mg
powder, 1 ml of concentrated HCL and 2 ml of amyl
alcohol, shaken, and allowed to separate. Flavonoids
are positive if there is red, yellow, or orange color in
the amyl alcohol layer (Cocan et al., 2018; Delazar,
Asgharian, and Asnaashari., 2017).
2.3.2 Tanin Test
0.5 g of simplicia powder sample was added with 10
ml of distilled water. The extraction result is filtered
then the filtrate obtained is diluted with distilled water
until it is colorless. The results of this dilution are
taken as much as 2 ml, and then added with 1-2 drops
of iron (III) chloride. A blue or blackish green color
indicates tannins (Cocan et al., 2018;, Delazar,
Asgharian, and Asnaashari., 2017).
2.3.3 Test of Saponins
As much as 0.5 g of simplicia powder was put into a
test tube and 10 ml of hot aquadest was added, chilled,
then shaken vigorously for no less than 10 minutes to
as high as 1-10 cm of the froth obtained. Furthermore,
with the addition of 2N hydrochloric acid, if the foam
does not disappear, the results obtained indicate the
presence of saponins contained in a simplicia (Cocan
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
294

et al., 2018; Delazar, Asgharian, and Asnaashari.,
2017).
2.3.4 Alkaloide Test
The simplicia powder of cocoa beans was weighed
0.5 g then added 1 ml HCL 2 N and 9 ml aquadest,
heated over water bath for two minutes, cooled and
filtered. The resulting filtrate is used for testing. 10
drops of filtrate are taken into test tube with 2 drops
of Meyer reagent added and white / yellow precipitate
is formed. Next 10 drops of filtrate were added into
test tube and 2 drops of bouchardate reagent were
added to form a brown to black precipitate. Then 10
drops of filtrate were put into test tube and then added
2 drops of dragendrof tuning and an orange to red
brown formed. If at least 2 out of 3 reagents produce
the same precipitate then it positively contains
alkaloids (Cocan et al., 2018; Delazar, Asgharian, and
Asnaashari., 2017).
2.3.5 Steroid / Triterpenoida Test
A total of 1 g of simplicia powder was macerated with
20 ml of n-hexane for 2 hours, and then filtered. The
filtrate is evaporated in a vaporizer cup. To remaining
2 drops of anhydrous acetic acid and 1 drop of
concentrated sulfuric acid are added. The purple or
red color then turns green blue indicating the presence
of steroids / triterpenoids (Cocan et al., 2018; Delazar,
Asgharian, and Asnaashari., 2017).
2.3.6 Glycoside Test
Simplisia powder was weighed as much as 3 grams,
then mixed with 30 ml mixture of 7 parts by 80%
ethanol volume and 3 parts by volume of distilled
water (7: 3), refluxed for 10 minutes, chilled and
filtered. To 20 ml filtrate, 25 ml of lead (II) acetate
0.4 N were added, shaken, allowed to stand for 5
minutes and then filtered. The filtrate was extracted 3
times, each time with 20 ml mixture of 3 parts by
volume of chloroform (p) and 2 parts by volume of
isopropanolol (p). To the chloroform layer, sodium
sulfate anhydrous (p) is added to taste, filtered and
evaporated at temperature of no more than 50
0
C.
Dissolve the rest with 2 ml of methanol, then take 0.1
ml of the experimental solution put into test tube,
evaporated on a water bath. To remaining 2 ml of
water added and 5 drops of molish reagent, carefully
added 2 ml of sulfuric acid formed purple ring at
boundary of both liquids indicating the presence of
sugar bonds (Cocan et al., 2018; Delazar, Asgharian,
and Asnaashari., 2017).
2.3.7 Test of Anthraquinic Glycosides
A total of 0.2 g cocoa bean simplex powder was
weighed, and then 5 ml of 2 N sulfuric acid was
added, heated briefly, after being cooled, added 10 ml
of benzene, shaken and allowed to stand. The benzene
layer is separated and filtered, shaken the benzene
layer with 2 ml of NaOH 2N, allowed to stand. The
red water layer and the colorless benzene layer show
anthraquinone (Cocan et al., 2018; Delazar,
Asgharian, and Asnaashari., 2017).
2.4 Making Cocoa Bean Extract
The method of making cocoa bean extract is done by
using cold extraction method, namely maceration.
Simplisia which has been in the form of powder
weighed 500 grams, then macerated by soaking 10
parts of simplicia, then put in a vessel and poured 75
parts of the liquid, then covered and allowed to stand
for 3-5 days in place which is protected from sun
light. Shaken repeatedly, filtered then squeezed. The
pulp from maceration is washed by using 25 parts of
liquid until the juice is obtained. The vessel is closed
and left for 2 days in a cool place and protected from
sunlight, then separated the precipitate obtained. The
filtrate that has been produced is then evaporated by
using rotary evaporator until it thickens slightly, and
then evaporates over water bath to form a thick
extract (Baharium, 2014).
2.5 Sterilization of Tools and Materials
The tools used for antibacterial testing are first
sterilized by heating process carried out to kill all
forms of organisms. Non-glass tools are sterilized by
using an autoclave at 121
0
C for 15 minutes. Whereas
glassware is sterilized using an oven at 170
0
C for 1-
2 hours (Widyaningsih, et al., 2018).
2.6 Soap Formulation
According to Saryanti and Setiawan (2018),
formulations used in making liquid soap preparations
can be seen in Table 1.
Formulation and Anti Bacterial Activity Test of Liquid Soap Extract from Cocoa Beans (Theobroma cacao L.) against Staphylococcus
Aureus and Escherichia Coli Bacteria
295
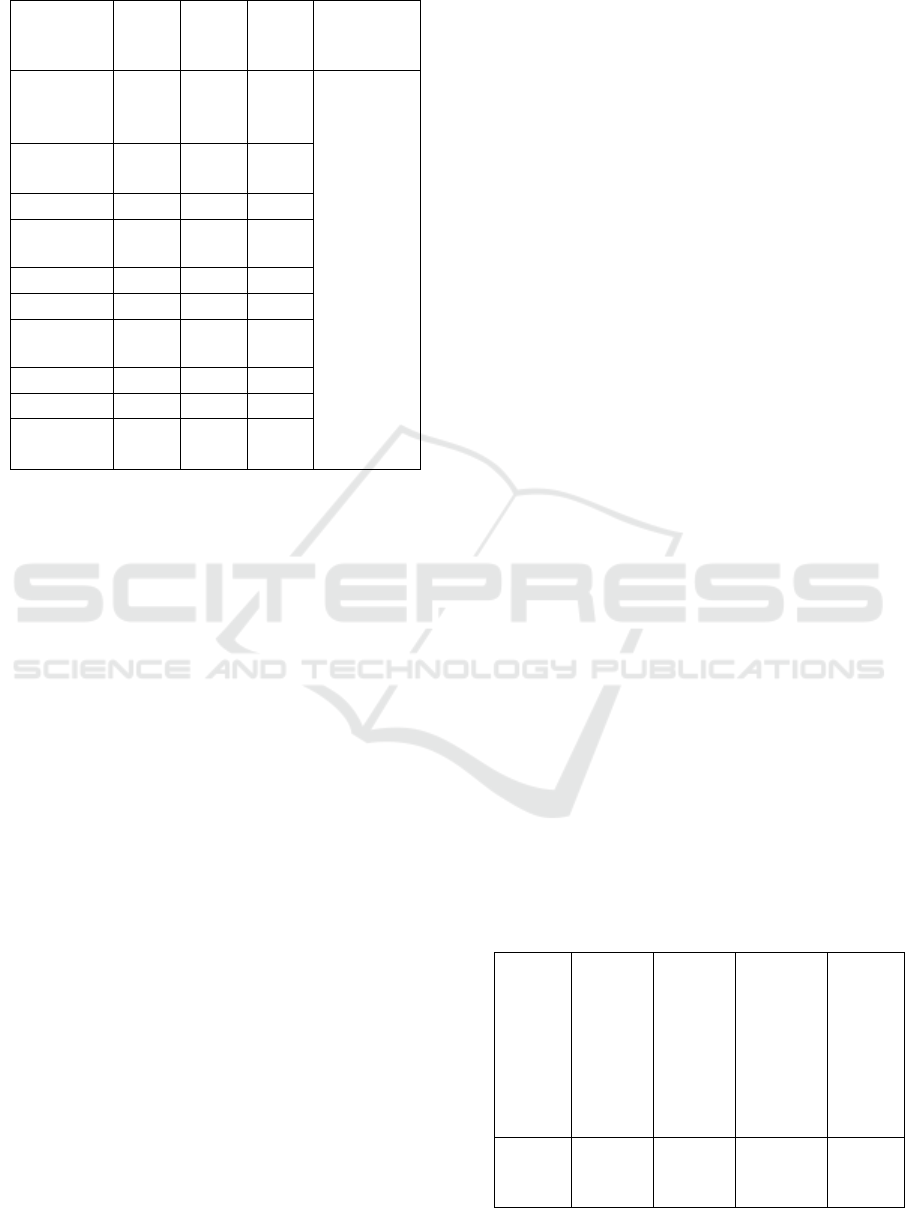
Table 1: Formulations of Liquid Soap
Ingredient FI (g) F
II (g)
F
III
(g)
FIV
(Comparis
on)
Cocoa
bean
extract
5 10 20
Conventio
nal
Castor Oil 10 10 10
Olive Oil 15 15 15
Coconut
Oil
10 10 10
KOH 8 8 8
HPMC 3 3 3
Stearic
acid
2 2 2
Glycerin 18,75 18,75 18,75
BHT 0,02 0,02 0,02
Aquadest ad
100
ad
100
ad
100
2.6.1 Soap Making
Castor oil is first mixed with olive oil and coconut oil,
then stir slowly until homogeneous. Then KOH
solution is added little by little to the oil mixture at
temperature 60-70
0
C to form a paste. Then added
stearic acid and BHT which had previously been
melted, then put into the mixture and stirred until
homogeneous, then put HPMC which has been
developed in hot aquadest into mixture. Furthermore,
glycerin and cocoa bean extract are added and stirred
until homogeneous. Then add up to 100 ml of distilled
water and then stir until homogeneous and put into a
container (Saryanti and Setiawan., 2018).
2.7 Evaluate of Liquid Soap
Preparations
2.7.1 pH Test
Liquid soap pH requirements based on SNI meet the
requirements namely 8 - 11. pH Conditions that are
too low can cause irritation to the skin (Widyaningsih,
et al.,2018)
2.7.2 Irritation Test
The irritation test technique is an open sample test
(Patch Test) on the back of the ear against 20
panelists. A positive irritation reaction is
characterized by redness, itching, or swelling in the
skin area of the inner ear that is treated. The irritation
test parameters include swelling, itching, redness,
peeling and feeling dry with numerical assessment (1)
irritation, (2) slight irritation, (3) absence of irritation.
2.7.3 Determination of Antibacterial
Activity
Antibacterial activity test used disc diffusion method,
as much as 15 ml media Nutrient agar (NA) is poured
into the cup until evenly distributed, then
homogenized and allowed to stand at temperature
room until the media is solidified. Then as much as
0.1 ml of Staphylococcus aureus bacterial inoculum
suspension is inserted into sterile petri dish, then put
disc paper into petri dish, then dropped 3 drops of
cocoa bean extract test sample soap with various
formulations (FI, FII, FIII). In this study also used
Aquadest as negative control and Dettol liquid bath
soap as positive control. The cup is left at temperature
room for 10-15 minutes, and then incubated at 37° C
for 24-48 hours, then the diameter of the inhibition
zone around the disc is measured by using calipers.
Tests carried out with three repetitions (triplo). The
same treatment was carried out on Escherichia coli
bacterial inoculums (Ditjen POM, 1995).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1 Phytochemical Screening
Phytochemical screening results of cocoa beans are
carried out to determine the class of secondary
metabolite compounds contained in it. The
examination of secondary metabolites is carried out
on groups of flavonoid compounds, tannins,
saponins, alkaloids, steroids / triterpenoids,
glycosides and anthraquinone glycosides. The results
of phytochemical screening of cocoa beans can be
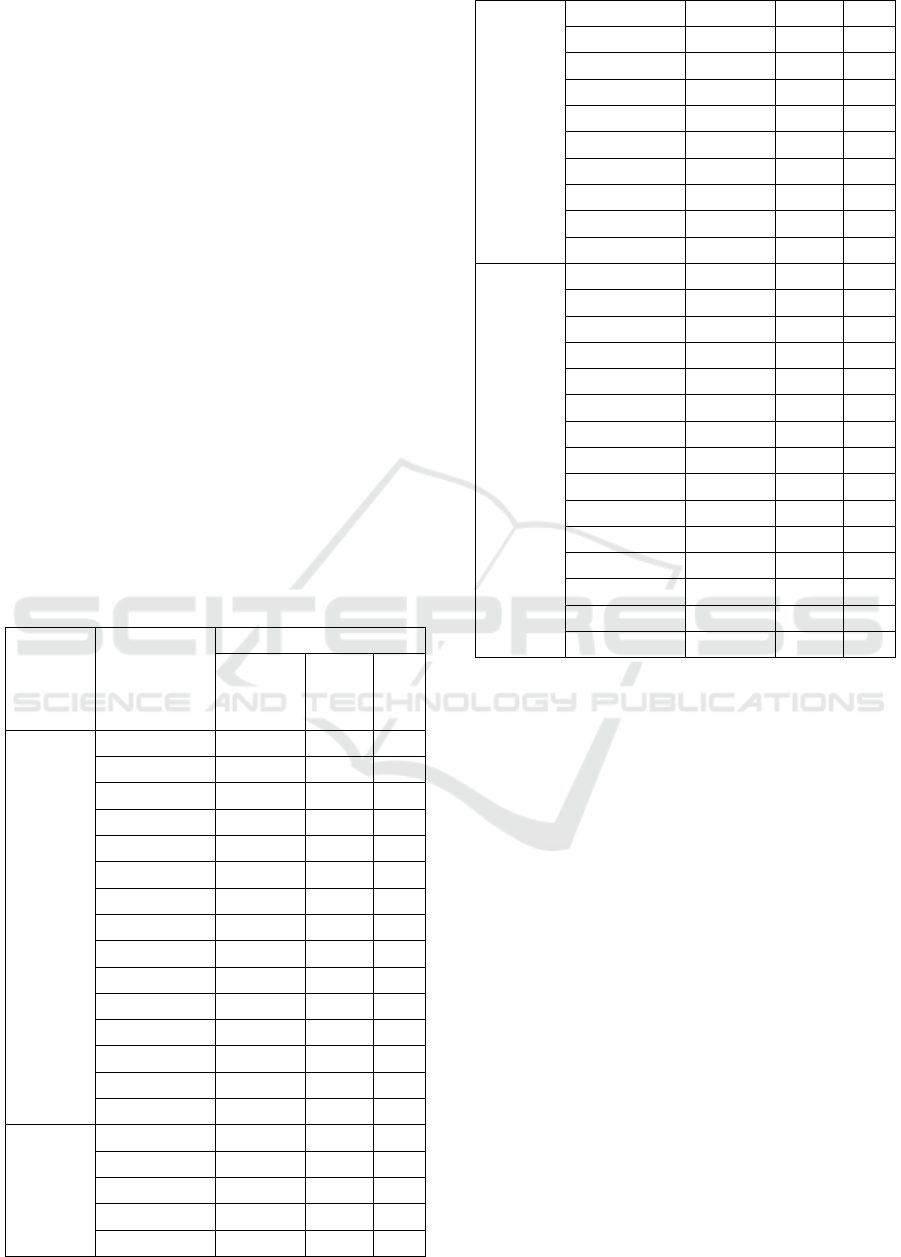
seen in Table 2.
Table 2: Results of phytochemical screenings
Comp
ound
Class
Reacto
r
Result Conclus
ion
Refere
nce
(Indira
et al.,
2014)
dan
(Dedy,
2016)
Flavo
noid
Mixtur
e 0.1 g
of Mg
Ring is
formed
(+)
Flavono
id
(+)
Flavo
noid
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
296

powder
, 1 mL
HCl
(p), 2
mL
Amil
alcohol
Colour
ed Red
in the
amyl
layer
alcohol
Tanin
FeCl3
(blue
or
blackis
h
green)
Blue
color is
formed
(+)
Tanin
(+)
Tanin
Sapon
in
Aquad
est is
hot
and
whippe
d
strong
Foam
formed
(+)
Saponin
(+)
Sapon
in
With
the
additio
n of 1-
2 drops
of HCl
2N
Froth /
foam is
not lost
Alkal
oids
Meyer
reagent
(sedim
ent
yellow
/
white)
Was
formed
precipi
tate
yellow
/ white
(+)
Alkaloid
(+)
Alkalo
id
Reacto
r
Bouch
ardat
(sedim
ent
brown-
black)
Reacto
r
Bouch
ardat
(sedim
ent
brown-
black)
Steroi
ds
H
2
SO
4
(p)
(purple
and
red,
and or
change
to
green /
blue)
First of
all
purple,
then
change
go
green
(+)
Steroid
(+)
Steroi
d
Glyco
sides
Lead
(II)
acetate
0.4 N
A
purple
ring
forms
at the
second
fluid
bounda
ry
(+)
Glikosid
a
(+)
Glikos
ida
Anthr
acino
ne
Glyco
sides
2 N
sulfuri
c acid,
benzen
e, 2N
NaOH
No red
water
layer
formed
(-)
Anthraci
none
glycosid
es
(-)
Anthr
acinon
e
glycos
ides
3.2 Soap Quality
Soap testing is carried out to determine the physical
appearance and quality of cocoa bean liquid soap
preparations, organoleptic test examinations which
include the shape, odor and color of the preparation,
pH test, foam ability test and irritation test on
volunteers.
3.2.1 pH Test and Froth Capability
pH testing of liquid soap is done because the high and
low pH values of the soap preparations can affect the
absorption rate of the skin. Testing the ability of the
foam is done by fast shaking using a test tube, aiming
to determine the stability of the soap scum caused.
The testing results of pH analysis can be seen in Table
3.
Table 3: pH value and foam stability
NO. Preparation pH Froth
Ability
(cm)
1. Formula I 10,32 6,8
2. Formula II 10,14 7,2
3. Formula III 9,5 7,2
pH testing of liquid soap is done because the high and
low pH values of the soap preparations can affect the
absorption rate of the skin. According to SNI, good
pH of soap is used which is alkaline in the range of 8-
11 to be able to clean the dirt on the skin. The pH
testing result on each formulation of cocoa beans
extract liquid soap has values ranging from 9.5 -
10.25. The addition of strong alkaline KOH can
increase pH value and the addition of high cocoa bean
extract to the formula results in decrease the pH
value. When compared with the comparator Dettol
Formulation and Anti Bacterial Activity Test of Liquid Soap Extract from Cocoa Beans (Theobroma cacao L.) against Staphylococcus
Aureus and Escherichia Coli Bacteria
297
soap which has pH 9 available on the market, the pH
of liquid soap with cocoa bean extract additive is also
close to the commercial standard.
The observations showed that each formula
produced relatively similar foam because it had value
of 6.4 cm while Dettol soap had value of 8.2 cm. The
difference occurred due to the surfactant used by
Dettol soap, namely sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), so
that the resulting bubble foam was more numerous.
The bubbles shape produced in the liquid soap extract
of cocoa beans is very thin so that the rate of decline
in the foam very quickly disappears within ± 180
seconds. Measurement of foam height after 5 minutes
decreases with each formulation. It is due to the small
amount of surfactant that is added to the liquid soap
preparation so that there is no repulsion between
bubbles resulting in lower voltage and the bubbles
break easily (Politova, et al., 2018).
3.2.2 Irritation Test
The questionnaire results found that liquid soap
extract of cocoa beans showed no irritation. The
results of irritation testing data on 15 volunteers can
be seen in Table 4.
Table 4: Result of irritation test
Formu
la
Volunteer Skin Condition
Swellin
g
Red
dish
Itc
hin
g
F I I 1 1 1
II 1 1 1
III 1 1 1
IV 1 1 1
V 1 1 1
VI 1 1 1
VII 1 1 1
VIII 1 1 1
IX 1 1 1
X 1 1 1
XI 1 1 1
XII 1 1 1
XIII 1 1 1
XIV 1 1 1
XV 1 1 1
FII I 1 1 1
II 1 1 1
III 1 1 1
IV 1 1 1
V 1 1 1
VI 1 1 1
VII 1 1 1
VIII 1 1 1
IX 1 1 1
X 1 1 1
XI 1 1 1
XII 1 1 1
XIII 1 1 1
XIV 1 1 1
XV 1 1 1
FIII I 1 1 1
II 1 1 1
III 1 1 1
IV 1 1 1
V 1 1 1
VI 1 1 1
VII 1 1 1
VIII 1 1 1
IX 1 1 1
X 1 1 1
XI 1 1 1
XII 1 1 1
XIII 1 1 1
XIV 1 1 1
XV 1 1 1
Irritation testing is done to determine safety when
using antibacterial liquid soap extract of cocoa beans.
The irritation test on liquid soap is done by applying
preparations to the volunteers' inner arms. The inner
arm skin is more sensitive because the horny layer is
thin enough so that the absorption of soap
preparations by the skin is faster (Widyaningsih,
Chasani, and Diastut., 2018). The results of observing
the irritation test by spreading the questionnaire to 15
volunteers gave choice number 1 which indicated that
liquid soap extract of cocoa beans did not cause
irritation in the form of redness, swelling and itching.
It can be attributed to the fact that the liquid soap
extract of cocoa beans is formulated with natural
ingredients that are not harmful so it is safe to use.
3.2.3 Antibacterial Activity Test for Liquid
Soap Cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.)
Extract
The results of antibacterial activity testing on liquid
soap of cocoa bean extracts were carried out by using
three different formulations namely FI 5 g, FII 10 g,
and FIII 20 g. The results of inhibitory zones of liquid
soap extract of cocoa beans on the bacteria
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
298

Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli can be
seen in Figures 1, 2, and Table 5.
Figure 1: Area of circle of inhibition zone of
Staphylococcus aureus
Figure 2: Area of circle of inhibition zone of
Escherichia coli
Table 5: Inhibition Zone of Theobroma Kakao L
Extraction
No. Treatment
Average diameter of
resistance (mm)
Staphylococcus
aureus
Escherichia coli
1.
Aquadest - -
2.
Dettol 15,70 15,26
3.
FI 10,33 9,23
4.
FII 11,70 10,53
5.
FIII 12,93 10,90
The antibacterial activity results of liquid soap
preparations from cocoa bean extracts showed that
diameter of inhibitory zones in Staphylococcus
aureus and Escherichia coli bacteria were categorized
as having strong activity in inhibiting bacterial
growth. Inhibitory zones on positive control of Dettol
soap are 15.70 in Staphylococcus aureus bacteria and
15.26 in Escherichia coli bacteria and are categorized
as having strong inhibitory zone activity and the
results of aquadest as negative control do not form
inhibitory zones because aquadest does not have the
ability to inhibit bacterial growth.
The antibacterial activity of liquid soap extract of
cocoa beans showed that Gram positive testing of
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria had a greater
inhibition zone than Gram negative testing of
Escherichia coli bacteria from several variations of
liquid soap preparation formulas. According to Volk
(1992), it is due to differences in both of bacteria
testing where they have different cell wall
compositions and structures so that gram-positive
bacteria are more susceptible to chemical compounds
than gram-negative.
A Gram-positive bacterium has a simpler cell wall
structure, which is single layer that has low lipid
content (1-4%) so that bioactive materials more easily
enter the cell. While gram-negative bacteria have
more complex cell wall structure, which is three
layers consist of the outer layer of lipoprotein, the
middle layer of lipopolysaccharide that functions as a
barrier to the entry of antibacterial bioactive material,
and the inner layer of peptidoglycan which has high
lipid content (11-12%). In addition, according to
(Arafat and Rahman., 2017) certain antibacterial
compounds can increase their activity from
bacteriostatic to bacteriocidal if a concentration of the
compound in the preparation is increased. The greater
the concentration contained in an antibacterial agent,
the stronger the work activity.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Liquid soap extract contains cocoa beans that have
antibacterial activity but it is not greater than
antibacterial activity of Dettol soap.
REFERENCES
Arafat, M., & Rahman, N. 2017. Evaluation of antioxidant,
anti-microbial and cytotoxic activity of methanolic
extract of phyllanthus acidus leaves (Doctoral
dissertation, East West University).
Baharum, Z., Akim, A. M., Hin, T. Y. Y., Hamid, R. A., &
Kasran, R. 2016. Theobroma cacao: Review of the
extraction, isolation, and bioassay of its potential anti-
cancer compounds. Tropical life sciences
research, 27(1), 21.
Brito-Vega, H., Salaya-Dominguez, J. M., Gomez-Mendez,
E., Gomez-Vazquez, A., & Antele-Gomez, J. B. 2018.
Physico-chemical properties of soil and pods
(Theobroma cacao L.) in cocoa agroforestry
systems. Journal of Agronomy, 17(1), 48-55.
Formulation and Anti Bacterial Activity Test of Liquid Soap Extract from Cocoa Beans (Theobroma cacao L.) against Staphylococcus
Aureus and Escherichia Coli Bacteria
299

Cocan, I., Alexa, E., Danciu, C., Radulov, I., Galuscan, A.,
Obistioiu, D., ... & Dehelean, C. A. 2018.
Phytochemical screening and biological activity of
Lamiaceae family plant extracts. Experimental and
therapeutic medicine, 15(2), 1863-1870.
Delazar, A., Asgharian, P., & Asnaashari, S. 2017.
Biological and phytochemical screening of
eremostachys azerbaijanica rech. F. Aerial
parts. Jundishapur Journal of Natural Pharmaceutical
Products, 12(3 (Supp)).
Foddai, A. C., Grant, I. R., & Dean, M. 2016. Efficacy of
instant hand sanitizers against foodborne pathogens
compared with hand washing with soap and water in
food preparation settings: A systematic review. Journal
of food protection, 79(6), 1040-1054.
Górnaś, P., & Rudzińska, M. 2016. Seeds recovered from
industry by-products of nine fruit species with a high
potential utility as a source of unconventional oil for
biodiesel and cosmetic and pharmaceutical
sectors. Industrial Crops and Products, 83, 329-338.
Ikotun, A. A., Awosika, O. O., & Oladipo, M. A. 2017. The
African black soap from Elaeis guineensis (Palm kernel
oil) and Theobroma cacao (Cocoa) and its transition
metal complexes. African Journal of
Biotechnology, 16(18), 1042-1047.
Politova, N., Tcholakova, S., Valkova, Z., Golemanov, K.,
& Denkov, N. D. 2018. Self-regulation of foam volume
and bubble size during foaming via shear
mixing. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and
Engineering Aspects, 539, 18-28.
Santana, J. O., Freire, L., de Sousa, A. O., Soares, V. L. F.,
Gramacho, K. P., & Pirovani, C. P. 2016.
Characterization of the legumains encoded by the
genome of Theobroma cacao L. Plant physiology and
biochemistry, 98, 162-170.
Saryanti, D., & Setiawan, I. 2018. Utilization of Secang
(Caesalpinia Sappan L) Wood Extract in Optimization
of Liquid Soap Formulation. Pharmacon: Jurnal
Farmasi Indonesia, 15(1), 1-7.
Tamarkin, D., Friedman, D., & Eini, M. 2018. U.S. Patent
Application No. 15/939,415.
Volk, W.A., dan Wheeler, M.F. 1993. Mikrobiologi Dasar.
Jilid I. Jakarta: Erlangga. Hal. 33-40, 218-219.
Widyaningsih, S., Chasani, M., & Diastuti, H. 2018.
Formulation of Antibacterial Liquid Soap from
Nyamplung Seed Oil (Calophyllum inophyllum L) with
Addition of Curcuma heyneana and its Activity Test on
Staphylococcus aureus. In IOP Conference Series:
Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 349, No. 1, p.
012062). IOP Publishing.
Widyaningsih, S., Chasani, M., Diastuti, H., & Fredyono,
W. N. 2018. Liquid Soap from Nyamplung Seed Oil
(Calophyllum inophyllum L) with Ketapang
(Terminalia catappa L) as Antioxidant and Cardamom
(Amomum compactum) as Fragrance. Molekul, 13(2),
172-17
Yukuyama, M. N., Ghisleni, D. D. M., Pinto, T. D. J. A., &
BouChacra, N. A. 2016. Nanoemulsion: process
selection and application in cosmetics–a
review. International journal of cosmetic
science, 38(1), 13-24.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
300
