
The Effect of Lavender Aromatherapy Giving on Perineum Pain in
Post Partum Mothers
Vitrilina Hutabarat, Stefani Anastasia Sitepu, Megawati Sinambela, G. F. Gustina Siregar
Health Institute of Deli Husada Deli Tua Medan
Street Besar Delitua No. 77 Delitua District Deli Serdang Regency
*Correspondence: Vitrilina Hutabarat
Keywords: Perineum Pain, Lavender Aromatherapy
Abstract: Perineum pain in post-partum mothers is a physiological condition that is experienced by post-partum
mothers, but it can interfere mobilization that causes complications such as post-partum hemorrhage.
Lavender aromatherapy is proven to reduce perineum pain. The purpose of this study was to determine the
effect of lavender aromatherapy giving on perineum pain. This study used quasy experimental method with
pre-test post-test with control group approach with total of 36 research subjects. Subjects were in 2 groups
which there were18 research subjects in each group. The study was conducted twice with pain observation
sheets or VAS (Visual Analogue Scale), i.e. during the active phase. Statistical analysis tests used Wilcoxon
test with Mann Whitney test. There was a difference on perineum pain in post-partum mothers in the
assessment before and after lavender aromatherapy given with p value = 0,000 (p <0.05) whereas pain level
of pre-test in Lavender therapy group majority of severe pain category (72.2%) and after post-test the
majority are moderate pain categories (77.8%).
1 INTRODUCTION
Based on WHO data, there are as many as 99% of
maternal deaths due to childbirth or birth problems
that occur in developing countries. The annual
pregnancy ratio in developing countries is the
highest with 450 maternal deaths per 100,000 live
births when it is compared to the maternal mortality
ratio in 9 developed countries and 51 commonwealth
countries due to complications during pregnancy and
childbirth, and 25% during the postpartum period
(WHO, 2016). The maternal mortality rate in
Indonesia is still high at 359 per 100,000 live births.
The fifth global MDG (Millennium Development
Goals) target is to reduce Maternal Mortality Rate
(MMR) to 102 per 100,000 live births in 2015. It is
referring to current conditions, the potential to
achieve these targets is off track, it means that it
requires hard work and really to achieve it (SDKI,
2012).
One of the efforts that is taken to reduce
maternal mortality is save motherhood program,
which is about post-partum care where there are
often occur complications such as bleeding, sepsis
and perineum trauma. Post-partum care must really
be considered, because 50% of maternal deaths
occur after giving birth (post-partum).
Post-partum is a period of six weeks from the
baby is born until the reproductive organs return to
normal before pregnancy. There are majority of
women who have vaginal delivery experience some
degree of perineum pain after childbirth, both
women who have perineum injury or not due to
episiotomy. Mothers who experience perineum
laceration will feel pain for several days until
healing occurs. Perineum tears or rupture occur in
almost first labor and it is not infrequently in
subsequent deliveries. It is occurred in primiparous
or first-time births when the fetal head comes out.
Episiotomy wounds that are not handled properly
will cause complications, such as blood loss due to
episiotomy too early, infection due to contamination
with urine and feces, dyspareunia, and local
hematomas that cause infections.
According to Smeltzer & Bare (2013), pain is an
unpleasant sensory and emotional experience due to
actual and potential tissue damage. Pain is the main
reason for someone to seek health care assistance.
According to the International Association for the
Study of Pain (IASP) defines pain as a subjective
Hutabarat, V., Sitepu, S., Sinambela, M. and Siregar, G.
The Effect of Lavender Aromatherapy Giving on Perineum Pain in Post Partum Mothers.
DOI: 10.5220/0009514903410347
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 341-347
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
341

sensory and unpleasant emotional experience
associated with actual or potential or damaged tissue
damage felt in events where damage occurred. In
some people, pain can be more troublesome than
other diseases. After giving birth, a mother often
reports pain and trauma to the perineum. Perineum
pain is physiological in post-partum mothers, but
this pain will affect a woman's ability to mobilize so
that it can cause of complications such as post-
partum hemorrhage. Perineum pain due to trauma
such as perineum laceration can cause discomfort
and dyspnoenia (Widayani, 2017).
Vakilian (2015) reports that the lavender
aromatherapy giving can reduce perineum pain on
60 postpartum mothers with spontaneous laceration
and episiotomy, 40% of whom do not feel pain.
According to research that is conducted by Widayani
(2017) there is a decrease in pain intensity of
postpartum perineum suture before and after being
given lavender aromatherapy with inhalation
techniques. It is also supported by Vaziri F (2017)
that lavender aromatherapy that is given to post-
partum mothers has better mood and physicality.
Aromatherapy is a treatment technique by using
odors that come from plants, flowers, trees that
smell nice and delicious (Ali B, 2015). The use of
aromatherapy inhaled can stimulate endorphin
expenditure so that it can reduce pain (Vakilian,
2015). Endorphin substances are chemicals that are
produced by the body as a result of external stimuli
and it produces feelings of calm, pleasure, relaxes,
stimulated and relaxes tense muscles such as pain
and physical exertion (Aprilia, 2015).
Lavender aromatherapy is a therapeutic action
that is beneficial to improve the physical and
psychological condition of maternity mothers.
Physically it is good to be used to reduce pain,
whereas psychologically it can relax the mind,
reduce tension and anxiety and provide calm (Ali B,
2015). Currently the handling used to relieve pain is
complementary therapy aromatherapy with essential
oil of lavender, because lavender has the properties
of anticonvulsant, antidepressant, anxiolytic, and
also soothing. Lavender aromatherapy can be a
complementary alternative therapy to reduce pain in
postpartum women. Ten pleasant odors will
stimulate the thalamus to release encephalin which
have the functions as a natural painkiller and
produces feelings of well-being. Encephalin is same
as endorphins, namely endogenous chemicals
(produced by the body) that have structure similar to
encephalin opioids that are thought to cause
presynaptic barriers (neurons that secrete transmitter
material) and postsynaptic barriers (where the
transmitter works) in the commudorsalis. This
process achieves inhibition by encephalin, the
inhibition of substance P so that pain is reduced to
the brain.
2 METHOD
The research type was quasy experimental design
with pre-test and post-test with control group
approach, this design used two groups where the
first group is given lavender aromatherapy
(treatment group), while the second group as control
was not given lavender aromatherapy and both
groups undergo a test beginning and end. The results
of this study were comparing the groups treated with
control group to determine the effect of lavender
aromatherapy giving on perineum pain in
postpartum mothers in working area of Sibolangit
Public Health Centre, Deli Serdang District. The
population of this study were post-partum mothers in
Sibolangit Health Centre in March until May 2019.
The samples of this study were post-partum mothers
who experienced perineum tears. Inclusion criteria
were mothers during the 1
st
active phase,
physiological deliveries, mothers who had
experienced perineum tears and they were willing to
be respondents. Exclusion criteria were mothers who
gave birth surgically and mothers who had asthma.
The sampling technique in total sampling is done
by taking the case of the entire population of 36
subjects. This research was conducted after
obtaining approval from the head of Public Health
Centre. The study instruments were the observation
sheet of respondents' characteristics (Name, Age,
Ethnicity, Education, occupation) and observation
sheet of Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) pain. While
the tools used in this study were diffuser and
lavender aromatherapy oils for 10 minutes at 10, 30,
and 60 minutes. It is done to find out the decrease in
pain scale by using Visual Analogue Scale (VAS).
With the assessment of pain intensity on a scale of 0
there was no pain, pain intensity on a scale of 1 to 3,
pain such as itching or electric shock or twitching or
twisting or beating or aching or colic. Pain intensity
on a scale of 4 to 6, such as ham or stiff or depressed
or difficult to move or burn or stab. Very painful on
a scale of 7 to 9 but it can still be controlled by the
client. Pain intensity is very severe on a scale of 10
uncontrolled pains.
Substances that are contained in lavender oil
have a lot of potential because it consists of several
ingredients. According to research, in 100 grams of
lavender oil composed of several ingredients, such
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
342
as: essential oils (13%), alpha-pinene (0.22%),
camphene (0.06%), beta-myrcene (5.33%), p-
cymene (0.3%), limonene (1.06%), cineol (0.51%),
linalool (26.12%), borneol (1.21%), terpinen-4-o1
(4, 64%), linet acetate (26.32%), geranyl acetate
(2.14%), and caryophyllene (7.55%). Based on the
data above, it can be concluded that the main content
of lavender is linail acetate and linalool (C10H18O).
This research analysis used univariate and
bivariate. Bivariate analysis is used to prove the
existence of periods before and after each group by
using Wilcoxon test.
Figure 1: Research Flowchart
Figure 2: Lavandula officinalis chaix
3 RESULTS
The results showed that there was an influence of
lavender aromatherapy giving on perineum pain in
post-partum mothers. From table 1 it can be seen
that the group which was not given lavender
aromatherapy, the majority of pre-test categories
were moderate pain levels that were 72.2%, the
majority of post-tests were in the category of severe
pain levels namely 88.9%, it can be seen in the
Table 1.
From Table 1 can be known that group were not
given lavender aromatherapy, the pre-test majority
category of moderate pain level is 72.2%, the post-test
majority category of severe pain levels is 88.9%.
Table 1: Distribution of perineum pain without lavender
aromatherapy.
Score
Pain
Level
(VAS)
(Pre)
(Post)
N % N %
0 No pain
0 0 0 0
1-3
Mild
pain
0 0 0 0
4-6
Moderate
pain
13 72,2 2 11,1
7-9
Severe
pain
5 27,8 16 88,9
10
Very
heavy
pain
0 0 0 0
From Table 2 it can be seen that in the group that is
not given lavender aromatherapy, the pre-test pain
level was lower than the post-test pain level, it was
indicated by a median of 3 and 7.5, respectively. At
the time the pre-test, the highest level of pain was
score of 7 (severe pain), and the lowest was score of
5 (moderate pain). Whereas at the time of the post-
Manage research permit
Informed Consent
Responden Sample
Group A
(Intervension)
Subjects who will
meet the inclusion
c
ri
te
ri
a
Group B (Control)
Post Test : Fill in the characteristic
observation sheet, measure the pain
scale with VAS, post test is done
after 2 hours of perineum suturing.
Total
Sampling
Data Processing
Pre-test: Filling in the
characteristic observation
sheet, Pain scale
measurement wi
t
h VA
S
Pre-test: Filling in the
characteristic observation
sheet, Pain scale
measurement with VA
S
Data
Analysis
The Effect of Lavender Aromatherapy Giving on Perineum Pain in Post Partum Mothers
343

test, the highest level of pain was score of 9 (severe
pain), and the lowest was score of 6 (moderate pain).
Table 2: Wilcoxon test for perineal pain levels without
lavender aromatherapy
Median
P Value
(Minimum-Maximum)
Pre Pain
Level
(N=18)
3 (5-7)
0,001
Post Pain
Level
(N=18)
7,5 (6-9)
Based on the Wilcoxon Test results p value
<0.05 means that there are statistically significant
differences in pain levels between pre-test and post-
test in groups that were not given lavender
aromatherapy. It can be concluded that there was an
increase in the level of perineum pain in the group
not given lavender aromatherapy.
From Table 3, it can be seen that in the group
that was given lavender aromatherapy, the majority
pre-test in the category of severe pain level was
72.2%, the majority of post-test in the category of
moderate pain level was 77.8%.
Table 3: The Frequency of perineum pain with lavender
aromatherapy.
Score
Pain
Level
(VAS)
(Pre)
N
%
(Post)
N
%
0 No pain 0 0 0 0
01-
Mar
Mild
pain
0 0 0 0
04-
Jun
Moderate
pain
5 27,8 14 77,8
07-
Sep
Severe
pain
13 72,2 4 22,2
10
Very
heavy
pain
0 0 0 0
From Table 4, it can be seen that the median value
of the group that was given lavender aromatherapy,
the pretest pain level (7.5) was higher than the
posttest pain level (5.5).
Table 4: Wilcoxon test for perineal pain level with
lavender aromatherapy.
Median
P Value
(Minimum-Maximum)
Pre pain
level
(n=18)
7,5 (6-9)
0
Post pain
level
(n=18)
5,5 (4-8)
The Wilcoxon test resulted p value <0.05, it is to
conclude that statistically there were significant
differences in pain levels between pre-test and post-
test, it means that there was a decrease in perineum
pain level after being given lavender aromatherapy.
From Table 5, it can be seen that in the post-test,
most of the groups were not given lavender
aromatherapy experienced severe pain category as
much as 88.9% while those in the groups were given
lavender aromatherapy experienced a category of
moderate pain level that was as much as 77.8%.
Table 5: The Differences on perineum pain in post-partum
mother’s pre-test without and with lavender aromatherapy.
Score
Pain
Level
VAS
(post-
test)
Groups
Groups that
were not given
Lavender
Aromatherapy
Groups that
were given
Lavender
Aromatherapy
N % N %
0 No pain 0 0 0 0
01-Mar
Mild
Pain
0 0 0 0
04-Jun
Moderate
Pain
2 11,1 14 77,8
07-Sep
Severe
Pain
16 88,9 4 22,2
10
Very
Heavy
Pain
0 0 0 0
Total 18 100 18 100
From Table 6, it can be seen that the groups were
not given lavender aromatherapy; there were 2
subjects (11.1%) that experienced moderate pain,
and 16 subjects (88.9%) that experienced severe
pain. In the groups that were given lavender
aromatherapy, there were 14 subjects (77.8%) that
experienced moderate pain, and 4 subjects (22.2%)
that experienced severe pain.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
344
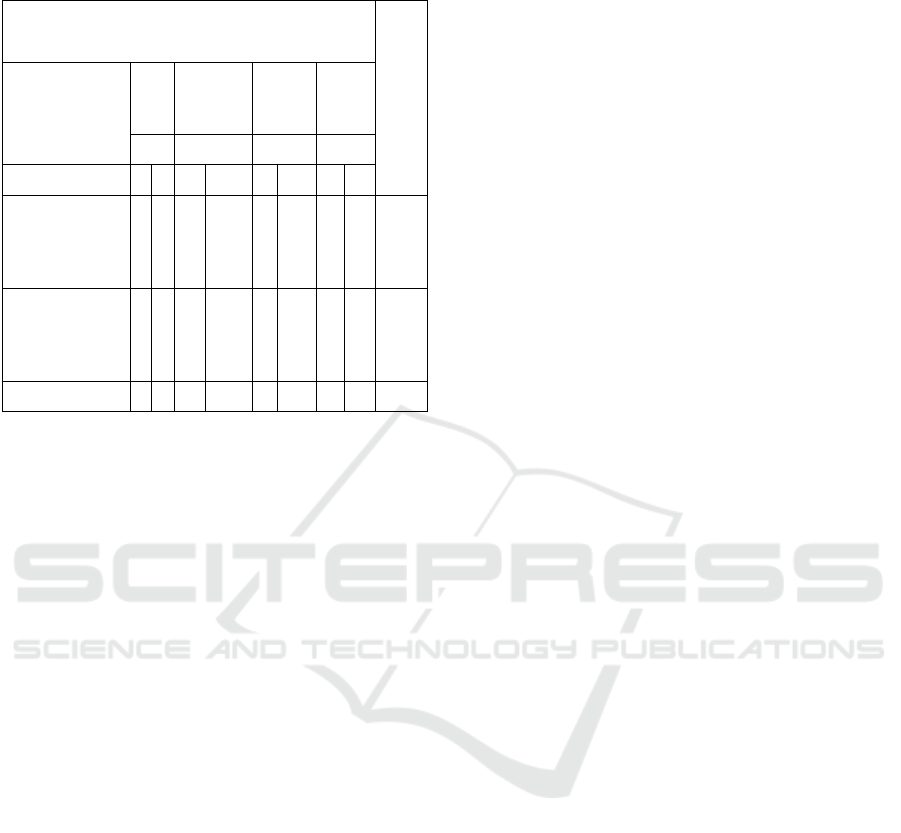
Table 6: Wilcoxon test post-test pain levels without and
with lavender aromatherapy
Pain Level Post-Test
P
Mild
Pain
Moderate
Pain
Severe
Pain
Very
Heavy
Pain
(1-3) (4-6) (7-9) -10
N % N % N % N %
Groups that
were not given
lavender
aromatherapy
0 0 2 11,1 16 88,9 0 0 0.000
Groups that
were given
lavender
aromatherapy
0 0 14 77,8 4 22,2 0 0
Total 0 0 16 44,4 20 55,5 0 0
The Wilcoxon test resulted p value <0.05, it
concluded that statistically there were significant
differences in the level of post-test pain between the
groups that were not given, and the groups were
given lavender aromatherapy. The mean level of
post-test pain in the groups without lavender
aromatherapy was 8.00 while the mean level of pain
in the post-test groups given lavender aromatherapy
was 0.00.
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Perineum Pain Levels with
Lavender Aromatherapy
Changes in the level of pain in the pre-test and post-
test in the groups which are given lavender
aromatherapy was the higher level of pre-test pain
than the level of post-test pain. At the time of pre-
test, the highest level of pain was severe pain, the
lowest was pain moderate. While at the post-test the
highest level of pain was severe pain and the lowest
was mild pain.
Based on the Wilcoxon test results in the groups
which were given aromatherapy, it is obtained p
value = 0.001 which was smaller than α = 0.005 thus
there were differences in the level of pain pre-test
and post-test in the groups which were given
aromatherapy lavender. Aromatherapy lavender was
given pre-test and post-test, there were 18 peoples
who experienced an increase and there were 17
peoples experienced an increase in pain levels.
4.2 Changes in Perineum Pain Levels
with Lavender Aromatherapy
A change in the level of pain in the pre-test and post-
test in the groups that were not given lavender
aromatherapy was the higher level of pre-test pain
than the level of post-test pain. At the time of pre-
test, the highest level of pain was the lowest
moderate pain namely severe pain. While in the
post-test the highest level of pain was severe pain
and the lowest was moderate pain.
Based on the Wilcoxon test, it resulted in groups
that were not given lavender aromatherapy p values
= 0.001 which was smaller than α = 0.05 thus there
were differences in the level of pain pre-test and
post-test in the groups that were given lavender
aromatherapy. Lavender aromatherapy was given
pre-test and post-test there were 18 peoples who
experienced an increase and 17 peoples who
experienced an increase in pain levels and who
experienced the same level of pain were as many as
1 person who looked worried because the husband
was absent in labor because the husband was
working.
Aromatherapy is one of the non-pharmacological
methods to reduce pain. Aromatherapy is a healing
process using concentrations of essential oils
extracted from plants to improve the health and
well-being of the body, mind and spirit. The scent is
captured by nasal receptors and then provides further
information to areas in the brain that control
emotions and memory as well as information to the
hypothalamus which is the body's internal system of
immersion, including the sexuality system, body
temperature, and reactions to stress.
Lavender Aromatherapy has bactericidal,
analgesic, and antidepressant, antispasmodic when
aromatherapy is inhaled, the substances contained in
it will stimulate the hypothalamus to release
endorphin hormones because it can relax and calm
the body as well as active substances in the form of
linalool and linalyl acetate in the effects of lavender
as analgesic.
The results showed that lavender aromatherapy
can reduce the intensity of post sectio Caesarea
wound pain and Marni's study (2015) proved that
aromatherapy can reduce labour pain from the pain
scale from 9.58 to 7.30. It is also supported by Nasiri
A (2016) that the administration of Lavender
essential oil can relieve pain in patients with
osteoarthritis of the knee. According to Salamati
(2016) in his research it was found that pain before
and after inhalation of lavender essential oil
significantly affected pain reduction. Lavender
The Effect of Lavender Aromatherapy Giving on Perineum Pain in Post Partum Mothers
345

aromatherapy contains linalyl acetate and linalool
inhaled into the nose that is captured by the olfactory
bulb and then entered through the second branched,
lateral and non-medial olfactory ducts. On the lateral
side, this channel sneaks in the third neuron in the
amygdala, seminular gyrus and gyrus ambiens which
are part of the limbic. The medial side line also
terminates in the limbic system. Limbic is part of the
brain, shaped like the letter C as the centre of
memory, mood, and intellect. Part of the limbic,
namely amygdala is responsible for our emotional
response to its aroma. After limbic aromatherapy
stimulates are exposure encephalin or endorphins to
the hypothalamus gland, and rostral ventromedial
spinal cord. Enkephalin stimulates an area in the
cerebellum called raphe nucleus to secrete serotonin
to create a relaxed, calm and low anxiety effect.
Based on the research result that is conducted at
the health centre, which consists of the treatment and
control group, it can be summarized as follows:
There was an effect of lavender aromatherapy on
perineum pain in post-partum mothers in health
centre with p value of 0,000 <0.05.
4.3 Pain Reduction without and with
Lavender Aromatherapy
Lavender aromatherapy has an effect on reducing
pain level with a proven difference in the average
level of perineum pain as measured by VAS (Visual
Analogue Scale). It can be seen that the pain level in
post-test group that is given lavender aromatherapy
with mean value 24.17 is higher than post-test with
mean value 12.83. From Wilcoxon test results it was
concluded that there were significant differences in
post-test pain levels between groups that were not
given lavender aromatherapy with groups were
given lavender aromatherapy, which was p = 0,000.
The study results were consistent with the study
of Ghiasi A (2019) that Lavender aromatherapy can
be applied as a complementary therapy to reduce
anxiety during labour. Likewise, the research result
on post-partum post episiotomy mothers that the use
of Lavender oil is effective in reducing perineum
pain due to episiotomy. Supported also by
Ramadhan (2017) Lavender flower (Lavandula
angustifolia) has sedative effect because it contains
linalool (C10H18O). The effect of linalool is
stimulate nucleus raphe, an area in brain and will
secrete serotonin that can make someone sleep or
relax. A review of clinical trial data found that when
lavender is used during labour as aromatherapy,
women reported less pain. Other studies have found
that lavender can reduce pain, nausea, and dizziness
after caesarean section, as well as pain, redness, and
need for topical pain relief after episiotomy when
used in a sitz bath (M.D. Patel. 2018).
The decrease in pain intensity is due to the
subject got the benefits of lavender aromatherapy
that functions which serves to calm. Lavender can
also provide calm, balance, comfort, a sense of
openness and confidence. Besides that, lavender can
also reduce stress, stress, pain, emotional imbalance,
hysteria, frustration, and panic. Lavender can be
useful to reduce pain, and it can provide relaxation
(Vaziri, 2017).
Lavender Aromatherapy contains linalyl acetate
and linalool which are ester compounds that are
formed by combining organic acids and alcohols.
The fragrance produced by lavender aromatherapy
will stimulate the thalamus to release encephalin as a
natural painkiller. Encephalin is a neuromodulator
that functions to inhibit physiological pain.
Enkephalin is a neuromodulator that have functions
to inhibit physiological pain. The fragrance of
lavender will be passed on by the olfactory nerve to
the part of the cerebellum, namely nucleus raphe
which then releases the neurochemical serotonin.
Serotonin works as a neuromodulator to inhibit
nociceptive information in the spinal cord.
This neuromodulator closes the defence
mechanism by inhibiting the release of substance P
in the dorsal horn. The release of the substance P
neurotransmitter causes the transmission of synapses
from the peripheral nerve (sensory) to the
spinothalamic tract nerve. This matter allows the
pain impulses to be transmitted further into the
central nervous system. Inhibition of nerve fibbers
that transmit pain (nociceptive) will make pain
impulses unable to pass through transmission cells
(T cells), so that they cannot be forwarded to higher
processes in the somatosensory, transitional, cortical
cortex, and so on.
Lavender essential therapy positively influences
anxiety, controls insomnia and controls pain.
Serotonin also acts as a neuromodulator to inhibit
nociceptive information in the spinal cord. This
neuromodulator closes the defence mechanism by
occupying receptors in the dorsal horn so as to
inhibit the release of the substance P. The substance
P itself is one example of neurotransmitter with
excitatory action. Inhibition of p substance will
make the impulse of pain unable to pass through the
projection of neurons, so it cannot proceed to a
higher process in the sensory cortex, parietal lobe,
frontal lobe and midbrain so that it cannot be felt as
pain and pain is reduced (Cardia, 2018 ).
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
346

5 CONCLUSION
The conclusion in this study is that there are
significant differences in pain levels in post-partum
mothers who is given lavenderpre and post
aromatherapy (p value = 0,000).
The pre-test pain level in the Lavender therapy
group was in the majority category of severe pain
level (72.2%) and the post-test was in the moderate
pain level category (77.8%).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported By Institut Kesehatan
Deli Husada Delitua Institut Kesehatan Medistra
Lubuk Pakam, Sembiring Hospital Foundation, and
GrandMed Hospital Foundation, Indonesia.
The head of Sibolangit Health Centre and all
medical staffs who work at Sibolangit Health Centre
in Deli Serdang District.
REFERENCES
Afriani A, Rahmawati D. The Effect Of Lavender
Aromatheraphy On Decreasing Of Perineum Paint
Pain in Breast Mothers, February 2019/ page 10-15.
Ali B, Al-Wabel N, Shams S, Ahamad A, Khan S, Anwar
F. Essential oils usep in aromatherapy: A systemic
review. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2015;5(8):601-611.
Aprilia, Yesie dan Ritchmond, B. 2015. Gentle Birth :
Melahirkan Nyaman Tanpa Rasa Sakit. Jakarta : PT
Gramedia Widiasarana Indonesia.
Buckle J. Clinical aromatherapy essential oil in healthcare.
Edisi ke-3. USA: Elsevier Inc.; 2015.
Cardia G, Filho S , Silva E, Uchida N, Cavalcante H.
Effect of Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) Essential
Oil on Acute Inflammatory Response, 2018.
Dehkordi, Z.R., Baharanchi, F.S.H., Bekhradi, R. Effect of
lavender inhalation on the symptoms of primary
Dysmenorrhea and the amount of 1 menstrual
bleeding: A randomized clinical trial. Journal
Complementary Therapies Medicines. 2014.
Frayusi, A. 2015. Pengaruh Pemberian Terapi Wewangian
Bunga Lavender secara Oles Terhadap Skala Nyeri
Pada Klien Infark Miocardium Di CVCU RSUP DR
M Djamil Padang. Jurnal Fakultas Kedokteran
Universitas Andalas.
Ghiasi A, Bagheri L, Haseli A. A Systematic Review on
the anxiolytic effect of aromatherapy during the first
stage of Labor. J of Caring Sci. 2019; 8 (1): 51-60.
Jablonsky, Michal, Ramajova, Helena, Andrea, Katarina,
et al. Comparison of different methods for extraction
from lavender: yield and chemical composition.
Engineering Materials. 2016; 688: 31-7.
Karlina, Dewi S. Pengaruh Pemberian Aromaterapi
Lavender Secara Inhalasi Terhadap Penurunan
Intensitas Nyeri Persalinan Fisiologis Pada Primipara
Inpartu Kala Satu Fase Aktif Di BMP “Fetty
Fathiyah” Kota Mataram, 2016.
Karadag E., Samancioglu Baglama S., The effect of
aromatherapy on fatigue and anxiety in patients
undergoing hemodialysis treatment: A Randomized
Controlled Study. Holist Nurs Pract. 2019;33(44):222-
229.
Lakhan S., Sheafer H., Tepper D. The effectiveness of
Aromatherapy in Reducing Pain: A Systematic Riview
and Meta-Analysis. 2016:8158693.
M.D Patel Shivani. Essential oils: A pain management
alternative for labor and delivery. Obstetrics &
Gynecology. 2018.
McLain,D.E. 2018. Chronic Health Effects Essesment of
Spike Lavender Oil. Walker Doney and Associates,1-
8. Retrieved from
http://www.arttreehouse.com/data/SPIKE.PDF.
Diakses tanggal 09 Desember 2018.
Nasiri A., Mahmodi A M., Nobakht Z. Effect of
aromatherapy massage with lavender essential oil on
pain in patients with oeteoarthritis of the knee: A
randomized controlled clinical trial. Elsevier. 2016;75-
80.
Ramadhan MR. Zettira OZ. Aromaterapi Bunga Lavender
(Lavandula angustifolia) dalam menurunkan risiko
Insomnia. Majority Vol 6 No.2. Maret 2017.
Razaghi N, Hoseini A, Aemi S, Mohebbi T, Boskabadi
H.Efek Aroma Lavender pada Nyeri Pengambilan
Sampel Darah pada Bayi Baru Lahir, April 2015,
Halaman 535-541.
Salamati A, Mashouf S, Sahbaei F, Mojab F. Effects of
Inhalation of Lavender Essential Oil on open-heart
Surgery Pain. Iran J Pharm Res IJPR.
2016;13(4):1257-61.
Sheikhan F, Jahdi F, Khoei EM, Shamsalizadeh N,
Sheikha M, Haghani H. Episiotomy pain relief: use of
lavender oil essence in primiparous Iranian women.
Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2015;18(1):66-70
Stea S, Beraudi A, De Pasquale D. Essential Oils for
Complementary Treatment of Surgical Patients: State
of the Art. Evidance-Based Complement Altern Med.
2016;1-6.
Sudarman E. Efektivitas pemberian aromaterapi lavender
terhadap nyeri kala I persalinan di Rumah Sakit
Pontianak. 2017
Widayani W. Aromaterapi Lavender dapat menurunkan
intensitas nyeri perineum pada ibu post partum. 2016
Vakilian K, Atarha M, Bekhradi R,Chaman R. Healing
advantages of lavender essential oil during episiotomy
recovery: A clinical trial , February 2015, Pages 50-53
Vaziri F, Shiravani M, Najib FS, Pourahmad S, Salehi A,
Yazdanpanahi Z. Effect of Lavender Oil Aroma in the
Early Hours of Postpartum Period on Maternal Pains,
Fatigue, and Mood: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int J
Prev Med. 2017.8:29
The Effect of Lavender Aromatherapy Giving on Perineum Pain in Post Partum Mothers
347
