
Assessing Family Communication Patterns in Patients of
Hemodialysal Therapy with the Pattern of Kidney Failure
Rr Dinar Soelistyowati and Silvia Nurlaila
Department of Communication Art, University of Bhayangkara Jakarta Raya, Bekasi, Indonesia
Keywords: Kidney Failure Patients, Hemodialysis Therapy, Family Communication, Health Communication.
Abstract: This study aims to examine the pattern of family communication carried out by a husband or wife if their
partner suffers from kidney failure and must do hemodialysis or dialysis and discuss how communication
efforts made by the hospital to be able to make patients feel happy and calm. This study covers how the
interaction of family communication carried out by a husband or wife to their partner who is a patient with
kidney failure before and during hemodialysis therapy and communication efforts made by doctors and
nurses as the hospital in providing information about the development and results obtained to patients. This
research is qualitative by using a combination of Peplau's Interpersonal Relations Theory with the Theory of
Health Belief Models and Behavior Change. The results of this study are expected to be able to bring
behavioral changes and cultural changes between husband or wife to their partners so that the results of this
communication can be socialized and become a reference for families of patients with similar diseases and
as standard operational procedures for doctors and nurses in assisting hemodialysis patients.
1 INTRODUCTION
As a creature that always lives together,
communication is an ability inherent in humans.
Through communication, we can express what is in
our minds. With communication as well, we can
build relationships with many people, be it forming a
network of professional relationships where we
work, building social relationships with people in
the environment where we live, to establish
relationships that are affective and personal like love
and affection with the people we choose as life
partners in creating a happy and prosperous family
both physically and mentally.
Within social boundaries, the family is explained
as an element of a larger kinship network that
connects one's ancestors and descendants (Nam,
2004, p. 2). Whereas from a medical point of view,
the family is defined as a group of people related to
blood or marriage or strong mutual ties, such as
those from the same ancestor, or a husband, wife,
and their children (Miller, Keane, & O'Toole, 2003).
If considered together, these two understandings
have a similarity in which these people can be
considered as families if there is a relationship
between family members, both those from the core
members or from outside parties who have joined to
become part of the family. This means, in the
process of its formation, every member in the family
needs communication activities to channel what will
be discussed in the family.
As in the formation of other communication
networks, the formation of family networks requires
several aspects that are at least worthy of attention
so that the family can be considered a prosperous
family. One important aspect is health. Health itself
has become one of the most important things in
human survival. Various ways have been done by
humans, both in terms of innovation or findings on
drugs, methods, and other medical efforts to
maintain human health both physiologically and
psychologically. However, in a dynamic era like
now, maintaining health seems to be a complex
endeavor for the community, especially in people
with high mobility levels. The density of daily
activities combined with a fluctuating lifestyle
makes it difficult to implement healthy food
consumption patterns. As a result, people are more
likely to turn to fast food that has the potential to
cause various diseases, ranging from external
diseases such as allergies to internal diseases
involving important organs such as stroke and
kidney failure.
The existence of kidney failure in Indonesia is
slowly increasing. Through her seminar, Nila F.
Soelistyowati, R. and Nurlaila, S.
Assessing Family Communication Patterns in Patients of Hemodialysal Therapy with the Pattern of Kidney Failure.
DOI: 10.5220/0009593502850293
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health (ICOH 2019), pages 285-293
ISBN: 978-989-758-454-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
285

Moeloek (2018) also believes that diseases caused
by kidney such as Diabetes Mellitus and its
complications ranks 8th out of 10 causes of death in
Indonesia with a prevalence of 6.7 percent, also
ranks 3rd out of 4 on a national scale of 41,590
deaths in Indonesia with a total of 2,786 people.
While quoted from the results of the Basic Health
Research (Riskesdas) in 2018, the prevalence of
chronic kidney disease (PGK) occurred at 3.8
percent or an increase of 1.8 percent compared to
2013. According to the Director of Prevention and
Control of Non-communicable Diseases the Ministry
of Health of the Republic of Indonesia, Cut Putri
Arianie, an increase in the number of kidney patients
is caused by three factors. First, there is an extension
of the life expectancy of Indonesians to 71 years for
women and 68 for men. Secondly, the occurrence of
technological transition phenomena that makes
people less likely to move so that it can potentially
cause symptoms of diabetes and hypertension and
high blood pressure. Third, there is an economic
transition which has resulted in an increase in the
income of Indonesian people so that they tend to be
reluctant to make their own food and switch to fast
food whose ingredients have the potential to cause
obesity and other physical health disorders. These
diseases can be a major cause of chronic kidney
disease in Indonesia (Novita, 2019).
Responding to the situation, several efforts have
been socialized and carried out by the government to
the people of Indonesia as a form of preventive
measures in preventing chronic kidney disease, such
as diligently exercising, multiplying activities, and
implementing a drinking pattern of eight glasses of
water every day. However, when it is already
experiencing kidney disease, especially chronic
diseases such as renal failure undergoing
hemodialysis therapy or dialysis, special assistance
is needed, either from the family or from the
hospital, in which each of facilitation required a
strong and intense communication.
In his research related to social studies on health,
Armstrong (Liliweri, 2013, p. 33) states that health
problems and disease problems, and even the
definition of illness, experienced by humans is not
solely derived from individual neglect, family
negligence, negligence of groups or community,
even community neglect in maintaining individual
health. According to him, various social studies on
health actually reported that most of the illnesses
suffered by individuals as well as community
"illnesses" in general stem from ignorance and
misunderstanding of various health information that
they access. Therefore, we need to pay attention to
the flow of health information that is sent and
received by humans. This means we must study
health communication.
Communication at the family level itself also
needs to be considered, especially when
accompanying family members who have certain
diseases. They need to be given special enthusiasm
and motivation given verbally in order to persuade
patients when undergoing a medical process such as
a healing effort. In addition, family communication
also needs to be done to be able to make patients feel
happy and calm when undergoing each of these
medical processes.
Seeing the background picture above, researchers
are interested in reviewing research on family
communication interaction patterns as a form of
mentoring for kidney failure patients undergoing
hemodialysis therapy and communicating
communication efforts undertaken by doctors and
nurses towards patients specifically through the
work of science. Researchers hope the results of this
study can be used as a reference for families of
patients with similar diseases as well as standard
operational procedures for doctors and nurses in
assisting hemodialysis patients.
2 THEORETICAL STUDY
2.1 Communication
In his book entitled Mapping Health
Communication, Gangar defines communication as
the process of delivering and receiving messages
from someone who is shared with others.
Communicating here can be interpreted to help
convey the message to then be known and
understood together. Message in communication is
used in choosing and making decisions.
Communication is defined as such because it is
fundamental in daily life. We cannot live without
communicating. Therefore, communication means
conveying a message from the source of the message
(communicator) to one or more recipients of the
message (audience) using a set of rules or certain
methods. At the simplest level, communication
requires several elements in the form of the sender
of the message, the message itself, the recipient, and
the communication media. However, for each
complex event, the message sender also functions as
the recipient of the message, and other different
messages are sent through different media (2009, p.
4).
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
286

2.2 Family
According to the WHO regional director for the
Southeast Asia region, Dr. Samlee Plianbangchang,
the family is a basic unit on a social level and
provides a basic physical and psychological
environment when children begin to grow and
develop. The family also plays a very important role
in caring for and socializing children as well as
influencing adolescent development (WHO, 2013, p.
3).
The word "family" itself is full of images. In
general, the term "family" refers to the motto or call
to the activities of family members, for example
hard working families, togetherness, or those who
prioritize the welfare of the group over the
individual. Another reason, the word "family"
embodies a set of values that distinguish normal
individuals from abnormal people and right people
from wrong people (Bahfiarti, 2016, p. 65).
2.3 Family Communication
Family communication is important to learn. This is
due to the constitutive relationship between
communication with family. To know the
description of the activities of a family, a social
interaction is needed, in which in the process the
ability to communicate between family members is
needed. Quoted from Hurlock (1997, p. 198), family
communication is defined as the formation of family
life patterns in which there is an element of
education, the formation of attitudes, and behavior
of children that affect the child's development.
From different sources, family communication is
explained as an activity that must occur in family
life. This explanation is obtained because without
communication in the family, life in the family will
become lonely due to the loss of speaking, dialogue,
exchanging ideas so that it will cause vulnerability
between family members. An example of this
explanation is the communication held between
husband and wife, as well as communication
between parents and children need to be built in
harmony in order to build good relationships in the
family (Bahfiarti, 2016, p. 70).
2.4 Health Communication
As we all know, health communication is a scientific
field that is growing rapidly in recent decades. As a
scientific field, health communication is a field that
is rich in studies, amazing and relevant to the study
of communication between humans and media
communications relating to health efforts and health
promotion efforts (Junaedi & Sukmono, 2018, p. 2).
Based on the eight points set out in the Toronto
Consensus Statement, Rogers in Harrington (2015,
p. 8) defines health communication as a multi-aspect
and multi-disciplinary approach to reach different
audiences and share information related to health
with the aim of getting involved influence, and
support individuals, communities, health experts,
special groups, policy makers and the public to
defend, introduce, adjust, or maintain behavior,
practices, or policies that will ultimately improve
their health outcomes.
In addition to definitions from experts, the NCA
(National Communication Association) provides a
definition that health communication is the science
of communication related to experts and health
education, including the interaction science of
providing clients, as well as the diffusion of health
information through public health campaigns. While
the ICA (International Communication Association)
explains that health communication is
communication that is primarily involved with the
role of communication theory, practice, and research
in terms of health promotion and health care
(Mulyana, 2018, p. 38).
2.5 Cronic Kidney Disease
Chronic renal failure or what is commonly called
CKD (cronic kidney disease) is a fatal progressive
kidney damage in which the body's ability to
maintain metabolism and fluid and electrolyte
balance, causing azotemia (urea retention and other
nitrogenous waste in the blood). This disease is also
known as end stage renal disease (ESRD). Apart
from the continuation of acute kidney failure,
chronic kidney failure can be caused by several
conditions such as: (1) systemic diseases, especially
Diabetes Mellitus, hypertension, lepitopirosis; (2)
chronic kidney infections (glomerulonephritis,
pyelonephritis); (3) autonomal genetic makeup; (4)
obstruction (disturbance) in the urinary tract; (5)
drugs and nefrotoxic chemicals, and; (6)
environmental factors, such as the presence of
cadmium, mercury, and chrome exposure (Diyono &
Mulyanti, 2019, pp. 43-44).
2.6 Health Belief Model Theory
If interpreted language and separately, this theory
has three main words as concepts, namely health,
beliefs, and models. The word health (health) refers
to the perfect condition that is owned by a person, be
Assessing Family Communication Patterns in Patients of Hemodialysal Therapy with the Pattern of Kidney Failure
287

it physically, mentally, or socially, and is not in a
condition of having a disease or disability (WHO,
2017).
The word belief (belief) means to have a faith, so
that belief can be translated as one's belief in
something that can cause certain behaviors or
actions (Putri, 2016, p. 11). Meanwhile, according to
Hayden, belief (belief) is very closely related to
culture which is one's perception of the right thing
even though it is not a truth. From these two
explanations, it is concluded that belief is a belief in
something that is considered right or wrong that is
influenced by culture so that from that belief will
produce an action or behavior (2017, p. 67).
While the model is generally explained as a
representation (representation) of an object, object,
or ideas in a simplified form of conditions or natural
phenomena. While the model that refers to the
Health Belief Model is interpreted as a
representation of an idea into a condition.
Basically, the Health Belief Model is a
translation of the sociopsychological model. This
model describes four variables that are the size and
attitude of individuals towards health. The four
variables include: (1) understanding vulnerability to
disease, (2) overall understanding of disease, (3) the
benefits of taking action in dealing with disease, and
(4) readiness of individual actions against disease
(Notoatmodjo, 2010, p. 113 -115).
In its application, this model is used as an effort
to explain broadly how the failure of community
participation in the prevention and early detection of
a disease, is also used as the main framework in
behavior related to human health. This model can
also be said as a conceptual formulation to find out
the perceptions of individuals whether they accept or
not about their health, so to find out about individual
perceptions, can be assessed from variables that
include individual desires to avoid pain, their belief
that there is an effort to avoid the disease.
2.7 Behaviour Change Theory
Basically, this theory considers several main theories
about behavior and behavior change that can be a
problem for the development of effective
interventions in driving behavior, including theories
and concepts from the mainstream of psychology,
and branches of science related to health, pleasure,
recreation, physical activity and training in
psychology.
Prochaska and DiClemente explained that
behavioral changes occur in five stages, including:
a. Pre-contemplation: at this stage, the
individual has no desire to change his
behavior in a predictable future.
b. Contemplation: in this stage, the individual
begins to be aware that a problem has arisen
and to consider several actions in a serious
way to explain the problem. However, at this
stage, the individual has not made a
commitment to take the action.
c. Preparation: includes the desire to change and
some behaviors that are usually minor and
often experience limited success.
d. Action: In this stage, the individual actually
changes his behavior, experience, or
environment in order to get past his problems
or to achieve his goals.
e. Maintenance: individuals who have reached
this stage tend to try to prevent relapses and
strengthen the results obtained at the previous
stage of the action.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study uses descriptive qualitative methods, with
retirees aged 50 years and older as research objects
and case studies as research methods and purposive
sampling as data analysis techniques. These methods
and techniques were chosen to determine the type of
family communication patterns used between
husband or wife who are hemodialysis therapy
patients with their partners when mentoring patients
and implementing communication carried out both
with family members and with doctors and nurses.
In conducting its research, researchers used a
combination of theories between health belief model
theory and behavior change theory.
This study focuses on family interaction patterns
communicated through husband or wife to their
partners who are kidney failure patients undergoing
hemodialysis therapy and health communication
used by doctors and nurses to provide information
and persuasion to patients related to hemodialysis
therapy carried out by patients. In the process of
research, researchers collect data by non-
participatory observation and study of literature and
inquiry.
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
288

4 DISCUSSION & RESULT
4.1 The Situation of Kidney Failure in
Indonesia
Based on the results of research conducted by the
Basic Health Research (Riskesdas) in 2013, there
was an increase in prevalence with age, with a sharp
increase in the age group of 35-44 years compared to
the age group of 25-34 years. Prevalence in men
(0.3%) is higher than women (0.2%), higher
prevalence occurs in rural communities (0.3%), not
going to school (0.4%), self employed, farmers /
fishermen / laborers (0.3%), and the lowest and
lower middle ownership index quintiles of 0.3%
respectively. Whereas the province with the highest
prevalence was Central Sulawesi at 0.5%, followed
by Aceh, Gorontalo and North Sulawesi at 0.4%
each.
Source: Basic Health Research (Riset Kesehatan
Dasar) 2013
Figure 1: Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Failure by
Characteristics in Indonesia in 2013.
Other data was also obtained from the
Indonesian Renal Registry (IRR) in 2017. In its
report, the number of new patients continues to
increase from year to year in line with the increasing
number of HD units, new patients are patients who
first had dialysis in 2017 while active patients are all
patients both new patients in 2017 and old patients
from the previous year who are still undergoing
routine HD therapy and are still alive until
December 31, 2017. In 2017 active patients
increased sharply this shows that more patients can
undergo longer hemodialysis, apparently a factor
JKN has a role in maintaining the continuity of this
therapy (Indonesian Renal Registry, 2017, p. 8).
In the same report, referring to the age category
of patients, the highest proportion of patients was
still in the 45 to 64 years category. When seen in the
table above patients aged less than 25 years
contributed 2.64% to active patients, this shows that
it is time to pay attention to the young age group to
start paying attention to kidney health (Indonesian
Renal Registry, 2017, p. 11).
Source: 10th Report of Indonesian Renal Registry.
Figure 2: Age Distribution Chart for Hemodialysis
Patients in Percent of 2017.
This should be taken seriously, because until now
chronic kidney failure is still incurable, so it still relies
on treatment aimed at slowing the process of
developing kidney failure, reducing complications,
and controlling symptoms of the disease.
4.2 Hemodialysis Therapy as a Fluid
Replacement Treatment for Kidney
Failure Patients
As explained in the previous discussion point that
there is no medical method that can treat kidney
failure holistically (thoroughly). Therefore, if it is
not taken seriously, it will be fatal for patients
because they cannot remove metabolic waste
products and excess fluid that accumulates in the
body when they have entered the final stage of
kidney failure (capacity is only 10% to 15% of
normal kidney function) . In response to these
conditions, it is necessary to replace fluid that is
needed by the patient to survive. One form of
treatment in question is a dialysis method which is
medically better known as hemodialysis.
Practically, hemodialysis uses a dialiser
(artificial kidney) to remove excess fluid,
electrolytes, and metabolic waste products from the
blood. Blood is drawn from the patient's body
through access to blood vessels such as
arteriovenous fistulas (connections are made
between the arteries and veins in the lower arm) or a
venous catheter is inserted into the main vein in the
neck. Blood is circulated by a dialysis machine at a
speed of around 200cc / minute, passing through an
artificial kidney to filter metabolic waste products
and excess fluid. Blood that has been "cleaned" is
then returned to the patient's body. A patient may
Assessing Family Communication Patterns in Patients of Hemodialysal Therapy with the Pattern of Kidney Failure
289
require 2 to 3 times hemodialysis treatment per
week, and each treatment session will take 4 to 6
hours (Smart Patient, 2016).
4.3 Family Communication Patterns
Between Patients with
Hemodialysis Therapy and
Companions and Its Situation in
Implementing Hemodialysis
Therapy
The form of family communication applied between
one patient's family and another patient's family is
not the same. In general, there are four models of
family communication applied between therapeutic
patients (husband / wife) and their companions. The
four models are:
1. Equality Pattern, where each individual shares
the same rights in communication
opportunities. The role of each person is
carried out equally. Communication runs
honestly, openly, directly, and free from power
sharing. All people have the same rights in the
decision making process. Families get the
highest satisfaction when there is equality.
2. Balance Split Pattern, which is a pattern of
communication in which equality of relations
is maintained, but in this pattern each person
has a different area of authority than the others.
Each person is seen as an expert in a different
field. For example, in a normal / traditional
family, a husband is trusted in business or
political matters. The wife is trusted for
matters of child care and cooking. But the
division of roles based on gender is still
flexible. Conflicts that occur in families are not
seen as a threat because each individual has
their own area and their own expertise.
3. Unbalance Split Pattern, is a communication
pattern where one person dominates, one
person is considered an expert more than
another. One person is in control, this person
usually has higher intellectual intelligence,
wiser, or higher income. Other family
members compensate by submitting to the
person, allowing the dominating person to win
their own arguments and decision making.
4. Monopoly Pattern, which is a communication
pattern that is centered on one person who is
seen as the holder of power. One person is
more giving commands than communicating.
He has the full right to make decisions so
rarely or never ask or ask for opinions from
others. The power of attorney instructs others
what may and may not be done. Then other
family members ask for permission, ask for
opinions, and make decisions based on the
decisions of that person (Saputra, 2014).
Looking at diverse communication patterns like
this, of course there are also some verbal or nonverbal
behaviors that are applied both by the patient and by
the patient's family based on these patterns. The
following is a general description of the patient's
behavior in undergoing the process of hemodialysis
therapy.
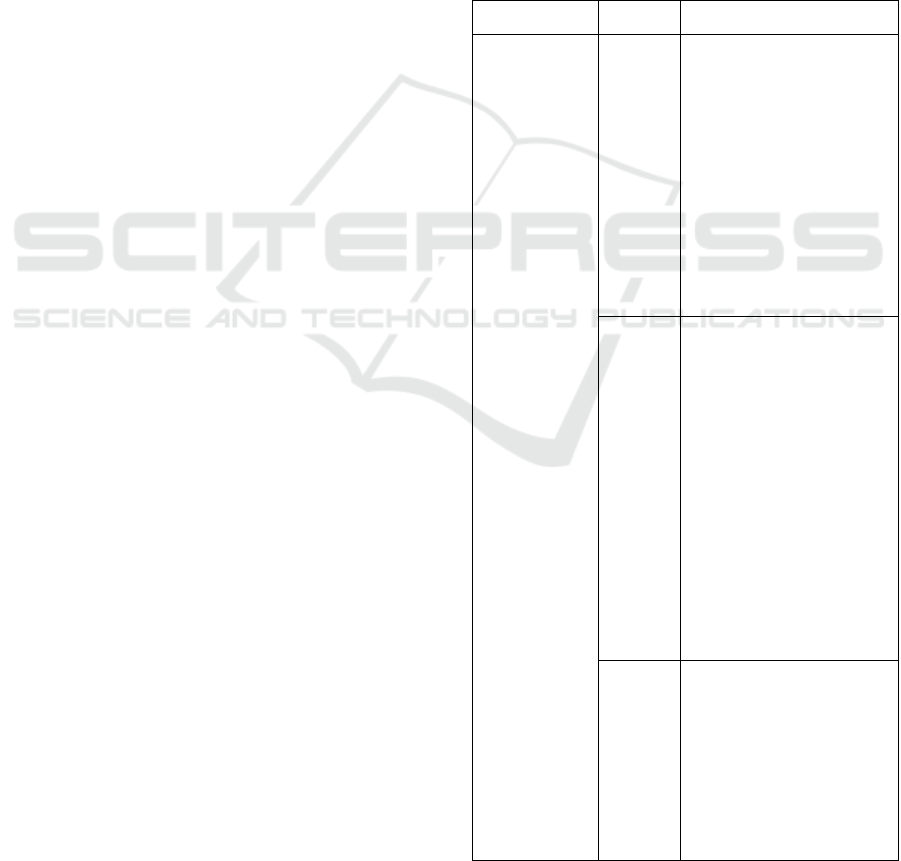
Table 1: Overview of Implementation of Patient
Communication Patterns.
Focus Point Informan Implementation
The
Communication
between
Patient and
Doctor
Mr. Y
Patients tend to have an
element of openness with the
doctor, especially regarding
information on the
development of patient
hemodialysis therapy. In
addition, patients have a
stable level of emotions,
high patience and always
have positive thoughts so
that it is easy for doctors to
provide advice and
motivation to patients.
Mrs. H
Patients tend to have an
element of openness with the
doctor, especially regarding
information on the
development of patient
hemodialysis therapy. Have
a slightly more emotional
level so that it needs a little
detailed communication to
avoid miscommunication
with the doctor /. Even so,
patients have a sense of
tolerance and patience that
is good enough so that it is
easy to reduce emotions and
motivate patients regularly.
Mr. P
The patient has an
intermediate level of
emotion so a gradual
explanation of information
is needed from the doctor.
Patients are also proactive
in carrying out therapy so
they can still be able to do
their daily routine.
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
290

Table 1: Overview of Implementation of Patient
Communication Patterns (cont.).
Focus Point Informan Implementation
The
Communication
between
Patient and
Doctor
Mr. W
Have a high level of emotion
and passive activities so that
different communication
approaches are needed and
are carried out in stages in
order to achieve an
interpretation in accordance
with patient expectations.
The
Companion’s
Attempt in
Assisting the
Patient
Mr. Y
In providing assistance to
patients, couples tend to be
faithful to accompany
patients. Couples also
communicate proactively,
both with patients, doctors,
and with other patients'
families.
Mrs. H
Companion tends to actively
accompany the patient when
doing therapy. In addition,
the companion also actively
communicates routinely to
remind and motivate
patients and be selective in
communicating to avoid
conversations that can
discourage the patient.
Mr. P
Companion has a dominant
role in providing assistance
to patients. Almost all
activities related to patient
assistance and routine
patient activities are carried
out independently by the
companion.
Mr. W
In providing assistance to
patients, the companion
tends to communicate
minimally. There are not
many activities that can be
done by the companion
when accompanying the
patient.
The
Companion’s
Skills in
Assisting The
Patient
Mr. Y
The companion carries out
a detailed scheduling to be
adjusted to the patient's
activities in the hospital.
The companion also actively
checks the patient's
condition, especially when
the patient feels
uncomfortable after doing
therapy.
Mrs. H
The companion does leave
to be able to focus on
assisting the patient during
the therapy period.
Although communication
between the companion and
patient is fairly minimal, the
companion is always there
to meet the patient's needs
especially if the patient feels
unwell due to therapy or
starts to think negatively.
Mr. P
The companion is flexible in
accompanying the patient.
In addition, no obstacles
were found between the
chaperone and the patient.
Mr. W
To be able to accompany the
patient, the companion
conducts a shift system with
his assistants. In addition,
although the interaction
between the chaperone and
the patient is fairly passive
and minimal, the chaperone
is proactive in seeking and
broadening his horizons by
talking with the doctor and
other patients' families.
4.4 Health Communication Strategies
Performed by Doctors in
Communicating the Process and
Results of the Development of
Patient Hemodialysis Therapy
As in other fields of science, communication is also
an essential part of health services, especially in
patient safety. Depending on how the health worker
- be it a doctor or nurse - communicates with the
patient, the results of that communication can
threaten the patient's safety but can also prevent the
patient from a health threat. In addition,
communication for health services is often used as a
basis to be able to provide certainty that patients get
the best treatment process, explain the purpose of
treatment and discuss the patient care process with
other professionals involved.
Basically, establishing a relationship with a
patient is very important. Doctors are always
required to be friendly, polite, and show a desire to
help patients by letting patients express what is the
problem for patients. This is done so that the doctor
is able to understand what medical obstacles are
Assessing Family Communication Patterns in Patients of Hemodialysal Therapy with the Pattern of Kidney Failure
291

being experienced by the patient so that he is able to
make an agreement with the patient regarding the
treatment plan that will be given to the patient. In
addition, it is important to ensure that the patient
understands and agrees with the treatment plan and
offers the opportunity to ask questions, confirm a
repeat visit, and provide an emergency contact
number if something unexpected happens before the
consultation time ends. To increase understanding
between doctors and patients, active involvement of
the patient and the patient's family is needed in the
therapy process by giving an informed consent
process.
The consent process is a barometer used to
determine the extent of patient involvement in the
therapy process. Informed consent is not only
limited to giving signatures by patients and their
families, but also a process to provide opportunities
for patients and their families to consider all the
options and risks associated with patient treatment.
Viewed from the professional aspect, doctors are
also encouraged to use evidence-based medicine,
where information that contains the possibility and
failure of a treatment or therapy must be conveyed to
patients to help make decisions. Information that
must be given to patients includes:
1. Diagnosis: includes the diagnostic procedure
and results of the examination. If medical
measures are taken to make a diagnosis, the
diagnostic procedure must be explained.
2. The degree of certainty of diagnosis: Medical
science is a science that has a high degree of
uncertainty, with more symptoms appearing,
the diagnosis can change or can be more
certain.
3. Therapeutic risks: patients need to know the
side effects of therapy, complications due to
therapy or medical treatment, outcomes that
may affect the mental health of patients, the
background of the risk of therapy, the
consequences if not done therapy. Patients
also need to know the available therapeutic
options, not just the type of therapy the doctor
chooses. Patients also need to know the type
of therapy chosen, the expected results, when
therapy should be started, the duration of
therapy and the costs involved.
4. Benefits of therapy and risks if no treatment
is done: some of the treatment prognosis is
poor, so the choice not to provide therapy will
be better.
5. Estimated recovery time: the type of therapy
or medical treatment chosen may affect the
patient's life, such as work, the distance of the
place of treatment from the patient's home if
he must frequently control.
6. Name, position, qualifications, and
experience of health workers who provide
therapy and care: patients need to know
whether the health personnel who will
provide therapy or perform medical treatment
are experienced enough. If not, supervision is
needed from the senior and information about
this supervision must also be given to the
patient.
7. Availability and cost of care after discharge
from the hospital: patients may still need
treatment at home after discharge from the
hospital. Then the information on the
availability of health workers around his
home and the estimated cost of treatment to
recover must also be submitted.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the study found, the
researchers draw the following conclusions:
1. In creating communication interactions
between facilitators and patients in assisting,
there are four communication patterns, namely
equality communication patterns, balanced
split communication patterns, unbalanced split
communication patterns, and monopolistic
communication patterns (monopoly).
2. In relation to the husband / wife's efforts in
assisting patients, referring to the communica-
tion patterns of each informant, there are several
methods pursued by each of the assistants. This
variation in approach between assistants and
patients arises because of several factors such
as: a) division of tasks within the family, b)
gender issues, and c) the ratio of the internal
status ratio of each family member.
3. With regard to the special skills of the
companion in accompanying the patient, the
intensity of communication is a key factor in
the application of verbal interactions, both
internally (between the companion and patient)
and externally (between the patient's family
and the hospital including the doctor, nurse,
OB, and the family of fellow HD therapy
patients.
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
292

Referring to the conclusions that have been
concluded previously, the authors provide some
constructive suggestions as follows:
1. With regard to the many family
communication patterns that are formed from
each patient's family, it helps them try each
type of each of the existing communication
patterns so that they then compare and choose
the best communication pattern to be applied
in their respective families.
2. For each companion who wants to provide
assistance to their partners, it should be noted
that they must use consideration when and
where they must communicate based on the
portion of their duties in the family, how they
communicate based on their gender, and for
what communication is used if based on
status position in the family. In addition, to be
able to increase the intensity of
communication, the selection of the right
words needs to be considered so that the
companion can create good quality
communication in order to maintain the hearts
and minds of patients undergoing
hemodialysis therapy.
3. For doctors, especially those who work
directly in handling patient hemodialysis
therapy, it is better to inform patients and
their families of the process and results of
routine therapy. This is needed in ensuring
that patients feel prioritized so as to be able to
bring up motivation for patients to recover.
REFERENCES
Bahfiarti, T. (2016). Komunikasi Keluarga (Suatu
Pendekatan Berkelanjutan Regenerasi Anak Petani
Kakao di Provinsi Sulawesi Selatan). Makassar: Kedai
Buku Jenny.
Diyono, & Mulyanti, S. (2019). Keperawatan Medikal
Bedah: Sistem Urologi. Yogyakarta: Andi Offset.
Gangar, A. (2009). Memetakan Komunikasi Kesehatan.
Bandung: BP2Ki.
Harrington, N. G. (2015). Helath Communication: Theory,
Method, and Application. New York: Routledge.
Hayden, J. A. (2017). Introduction To Health Behaviour
Theory. Burlington: Jones and Bartlett.
Hurlock, E. B. (1997). Psikologi Perkembangan: Suatu
Pendekatan Sepanjang Rentan Kehidupan. Jakarta:
Erlangga.
Indonesian Renal Registry. (2017). 10th Report of
Indonesian Renal Registry. Retrieved from indonesian
renalregistry.or: https://www.indonesianrenalregistry.
org/data/IRR%202017%20.pdf
Junaedi, F., & Sukmono, F. G. (2018). Komunikasi
Kesehatan - Sebuah engantar Komprehensif. Jakarta:
Prenadamedia Group.
Liliweri, A. (2013). Dasar-Dasar Komunikasi Kesehatan.
Yogyakarta: Pustaka Belajar.
Miller, B. F., Keane, C. B., & O'Toole, M. (2003). Miller-
Keane Encyclopedia & Dictionary of Medicine,
Nursing, and Allied Health (7th ed.). Philadelphia:
Saunders.
Moeloek, N. F. (2018). Air Bagi Kesehatan: Upaya
Peningkatan Promotif Preventif Bagi Kesehatan Ginjal
di Indonesia. Jakarta: Menteri Kesehatan RI.
Mulyana, D. (2018). Komunikasi Kesehatan: Pemikiran
dan Penelitian. Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya.
Nam, C. B. (2004). The Concept of Family: Demographic
and Genealogical Perspective. Sociation Today, 2.
Notoatmodjo, S. (2010). Metodologi Penelitian Kesehatan
Edisi Revisi. Jakarta: Bhineka Cipta.
Novita, M. (2019, March 13). Ini Penyebab Pasien
Penyakit Ginjal di Indonesia Meningkat. Retrieved
from Tempo: gaya.tempo.co/read/1184925/ini-penye
bab-pasien-penyakit-ginjal-di-indonesia-meningkat/
full&view=ok
Putri, D. (2016). Gambaran Health Belief Model Pada
Penderita Kanker yang Memilih dan Menjalani
Pengobatan Alternatif. Surabaya: UIN Sunan Ampel.
Rogers, E. M. (1996). The Field of Health Communication
Today: An Up-To-Date Report. Journal of Health
Communication, 15-16.
Saputra, H. (2014, May 14). Pola Komunikasi dalam
Keluarga. Retrieved from https://lumalila
research.com: https://lumalilaresearch.com/2014/05/
14/pola-komunikasi-dalam-keluarga/
Smart Patient. (2016). Gagal Ginjal Kronis. Retrieved
from ha.org.hk: https://www21.ha.org.hk/smartpatient/
EM/MediaLibraries/EM/EMMedia/Chronic-Renal-
Failure-Indonesian.pdf?ext=.pdf
WHO. (2013). Family as Centre of Health Development -
Report of A Regional Meeting. Bangkok: World
Health Organization - Regional Office of South East.
WHO. (2017). Constitution. Retrieved June 20, 2019,
from WHO: https://www.who.int/about/who-we-
are/constitution
Assessing Family Communication Patterns in Patients of Hemodialysal Therapy with the Pattern of Kidney Failure
293
