
Factors Associated with Heat Strains in Workers at the PT
Multikarya Asia Pasifik Raya Workshop in 2019
Erdiana Yuniarti and Putri Handayani
Department of Public Health, Faculty of Health Sciences University of Esa Unggul,
Jl. Arjuna Utara, Kebon Jeruk, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Heat Strain, Heat Pressure, Age, Obesity, Chronic Disease.
Abstract: Heat Strain is an acute or chronic impact caused by exposure to heat stress experienced by a person from
both physical and mental aspects. Preliminary studies conducted on 20 workers using the HSSI (Heat Strain
Score Index) method found that 11 people (55%) did not experience heat strains and 9 people (45%)
experienced heat strains. The physical effects of heat strains range from minor complaints such as skin
rashes to fainting to life-threatening situations when there is a cessation of sweat and heatstroke. This
research was conducted with quantitative research methods with a cross-sectional study design using
primary data on 59 workers. Research variables were analyzed using the chi-square test. The results of the
bivariate analysis found a relationship between heat stress, age, and hydration status with heat strain. While
the variables of obesity and chronic disease have no relationship with heat strain.
1 PRELIMINARY
The heat is a work environment factor that is very
closely related to the health of workers. Various
cases of accidents and diseases caused by work, as
well as other health problems are often caused by
work environment factors that do not meet the
requirements, in addition, there are several other
factors (Budiono, 2003). During activities in the hot
environment, the body will automatically react to
maintain a constant range of environmental heat by
balancing the heat received from outside the body
with heat loss from the body (Tarwaka, 2014).
Heat strain is an acute or chronic impact caused
by exposure to heat stress experienced by a person
from both physical and mental aspects. The physical
effects of heat strains can range from minor
complaints such as skin rashes to fainting to life-
threatening situations when there is a cessation of
sweat and heat stroke (OSHS, 2017). Workers who
experience heat strain will reduce performance
which will also impact on company productivity.
In 2016 in America, the total incidence of heat
strain with a loss of working days of at least one day
was estimated at 1,432 cases. According to case data
due to illness due to heat exposure based on work
per 100,000 workers are in the plantation area (8.13
cases), construction (6.36 cases), mining (5.01
cases), and other work (1.3 cases) (NIOSH, 2016).
In Indonesia, based on the results of a study
conducted by Adiningsih (2013), the results showed
that workers who were in a work environment with a
temperature exceeding NAV experienced complaints
of heat strains such as extreme fatigue of 54.6%,
dizziness 33.3% and stiffness/muscle cramps 12.1%.
There are differences in body temperature, pulse,
blood pressure systole and diastole between before
work and after work with heat exposure, this is
closely related to heat strain (Adiningsih, 2013).
NIOSH (2016) states that environmental factors
affecting heat strain are heat pressure. In addition,
several individual characteristic factors that can also
influence heat strains are age, sex, and obesity.
Other individual characteristic factors that can
influence heat strains are chronic diseases such as
heart disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension.
Hydration status is also one of the main factor
characteristics of individuals who play a role in the
cardiovascular system of the human body (ACGIH,
2007). Apart from that, other individual
characteristic factors that can influence heat strains
are chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes
mellitus, and hypertension (Kenny et al, 2010).
PT Multikarya Asia Pasifik Raya (MKAPR)
established in May 2002 is a company that provides
320
Yuniarti, E. and Handayani, P.
Factors Associated with Heat Strains in Workers at the PT Multikarya Asia Pasifik Raya Workshop in 2019.
DOI: 10.5220/0009595203200327
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health (ICOH 2019), pages 320-327
ISBN: 978-989-758-454-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

products and services for the oil and gas industry in
Indonesia and the regions around Asia and Australia.
Focusing on many lines of business rental services,
repairs/recertifications, general trading and
guaranteed availability of spare parts for contract
outgoing call orders. In the fabrication process at
the Lodan-9 PT MKAPR workshop using machines
and work processes which produce heat.
Based on the results of a preliminary study
conducted on 20 workers in several workshop
locations (namely fabrication area, pump area,
engine area, function test area, radiator transmission
area, and asset area) using the HSSI (Heat Strain
Score Index) method it was found that 11 people
(55%) are in the green zone or do not experience
heat strains and 9 people (45%) have heat strains
with categories in the yellow zone category. Based
on interviews with several workers, there were many
workers who complained such as feeling very
thirsty, sweating, fatigue, muscle aches, and even
once there was a worker who was very weak and
engaged to stop his work.
Based on this, researchers are interested in
conducting research on "Factors related to heat
strains in workers at a workshop at PT Multikarya
Asia Pasifik Raya in 2019”.
2 METHOD
This type of research is quantitative research,
research using bivariate analysis because researchers
want to see whether there is a relationship between
heat stress, age, obesity, chronic disease, and
hydration status with heat strain in workers at a
workshop at PT Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya in
2019.
The design of this study was cross-sectional and
there was no division between the two groups to be
studied. Cross-sectional research is a type of
research that emphasizes the measurement time or
observation of independent and dependent variable
data only once at the time of the study. In this type
of dependent and independent variables are assessed
simultaneously at one time, then there is no follow-
up.
Sources of information in this study were
obtained from primary data which included
observations, examinations, or observations by
questionnaire by interview and direct examination.
The population in this study were workers who
worked in workshops at PT Multikarya Asia Pacific
Raya, amounting to 74 people. The sample used was
using the Prevalence Ratio (PR) formula of 59
respondents using a simple random sampling
technique.
The research instrument used in this study was a
questionnaire or list of statements in the form of a
Heat Strain Score Index which consisted of 18
closed questions and filled in by selecting the
specified option, heat pressure assessment using a
measuring instrument in the form of a Questtemp
Heat Stress Monitor, and several closed questions
with choose the question option on the age, obesity,
chronic illness, and hydration status variables. The
data collection method used by researchers in data
collection is by distributing questionnaires to
workers and by measuring environmental heat
pressures to analyze factors related to heat strains in
workers at a workshop at PT Multikarya Asia
Pacific Raya in 2019. Data analysis was carried out
to obtain factors related to heat strain in workers at
the workshop at PT Multikarya Asia Pasifik Raya
consisted of Univariate and Bivariate analysis.
3 RESULT
3.1 Univariate Analysis
3.1.1 Overview of Heat Strains for Workers
at the PT Multikarya Asia Pacific
Raya Workshop in 2019
The highest proportion was found in workers who
did not experience heat strain, namely as many as 33
people (55.9%) and the lowest proportion was found
in workers who experienced heat strain, namely as
many as 26 people (44.1%).
Table 1: Overview of Heat Strains in Workers.
Heat Strain Frequency Percentage
Heat strain
(≥13,5)
26 44,1%
No heat strains
(<13,5)
33 55,9%
Total 59 100%
3.1.2 Overview of Heat Pressure on
Workers at the PT Multikarya Asia
Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019
The highest proportion is found in workers who
work in areas that do not have heat stress, namely as
many as 39 people (66.1%) and the lowest
proportion is in workers who work in areas of heat
pressure that is as many as 20 people (33.9%).
Factors Associated with Heat Strains in Workers at the PT Multikarya Asia Pasifik Raya Workshop in 2019
321
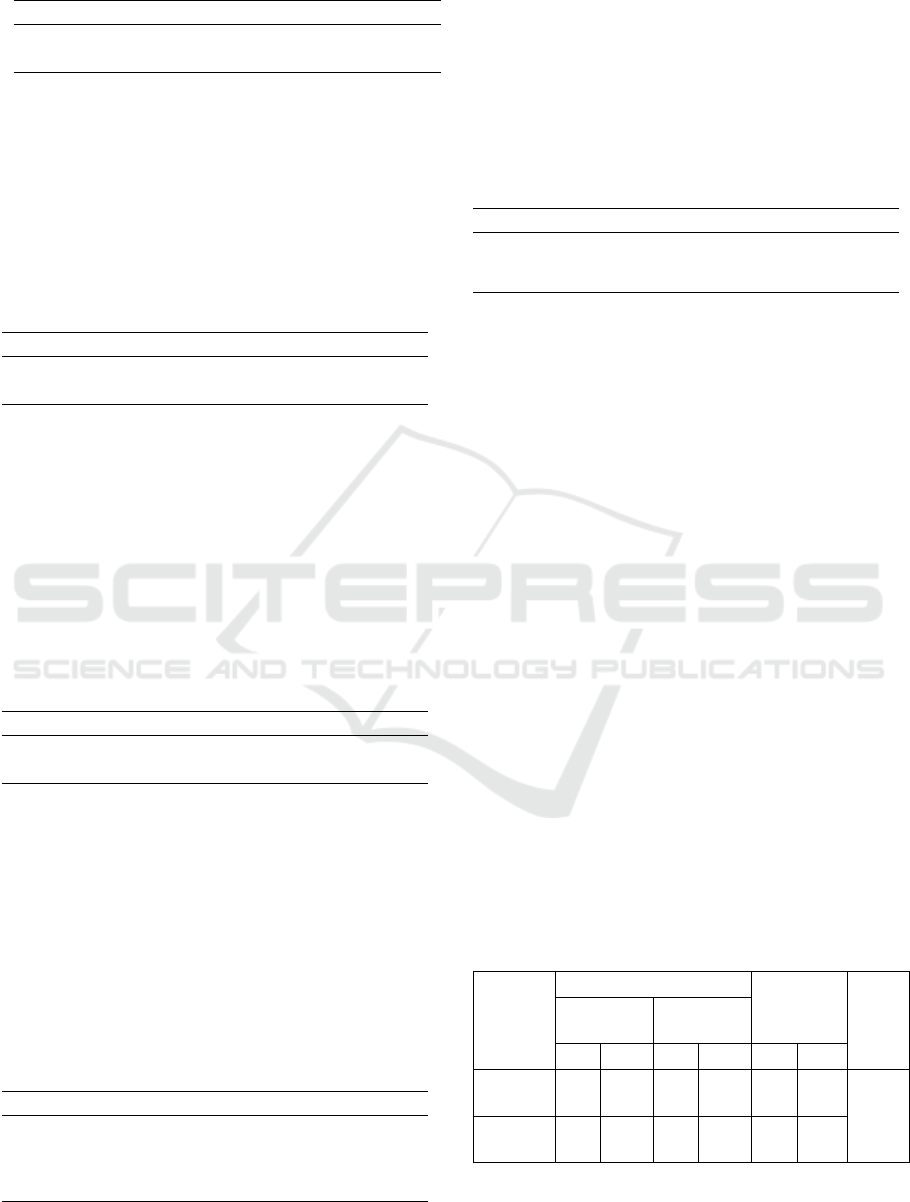
Table 2: Overview of Heat Pressure on Workers.
Heat Pressure Frequency Percentage
Yes (> 27,5) 20 33,9%
No (≤ 27,5) 39 66,1%
Total 59 100%
3.1.3 Age at Work in the PT Multikarya
Asia Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019
The highest proportion is in safe workers (aged <40
years), there are 40 people (67.8%) and the lowest
proportion is in workers who are at risk (age ≥ 40
years), there are 19 people (32.2%).
Table 3: Age Descriptions for Workers.
Age Frequency Percentage
Risk (≥ 40 years old) 19 32,2%
Safe (< 40 years old) 40 67,8%
Total 59 100%
3.1.4 Overview of Obesity to Workers at the
PT Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya
Workshop in 2019
The highest proportion is found in workers who are
not Obese (BMI calculation <25), there are 40
people (67.8%) and the lowest proportion is in
Obesity workers (BMI calculation ≥ 25), there are
19 people (32.2%).
Table 4: Overview of Obesity in Workers.
Obesity Status Frequency Percentage
Obesity (≥ 25) 19 32,2%
Not obese (< 25) 40 67,8%
Total 59 100%
3.1.5 Overview of Chronic Disease in
Workers at PT Multikarya Asia
Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019
The highest proportion is found in workers with no
chronic disease, which is as many as 53 people
(89.8%) and the lowest proportion is in workers who
have a chronic disease, there are as many as 6 people
(10.2%).
Table 5: Overview of Chronic Disease in Workers.
Chronic Illness Frequency Percentage
There are chronic
diseases
6 10,2%
There are no chronic
diseases
53 89,8%
Total 59 100%
3.1.6 Overview of Hydration Status of
Workers at PT Multikarya Asia
Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019
The highest proportion is found in hydrated workers,
which is 37 people (62.7%) and the lowest
proportion is in dehydrated workers, there are 22
people (37.3%).
Table 6: Overview of Hydration Status in Workers.
Hydration Status Frequency Percentage
Dehydration 22 37,3%
Hydration 37 62,7%
Total 59 100%
3.2 Bivariate Analysis Results
3.2.1 Relationship between Heat Pressure
and Heat Strain for Workers at the PT
Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya
Workshop in 2019
Workers who experienced the highest proportion of
heat strain were workers who worked in the heat
stress area as many as 18 people (90.0%) and the
lowest proportion were workers who worked not in
the heat pressure area as many as 8 people (20.5%),
among workers those who did not experience the
highest heat strain proportion were workers who
worked in areas that did not work in the heat stress
area as many as 31 people (79.5%) and the lowest
proportion were workers who worked in the area of
heat pressure which was as many as 2 people (10.0
%). Based on the chi-square test results obtained the
value of P = 0,000 (P-value <0.05), which means
that Ho is rejected, statistically showing a
relationship between heat stress and heat strain in
workers at the PT Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya
workshop in 2019.
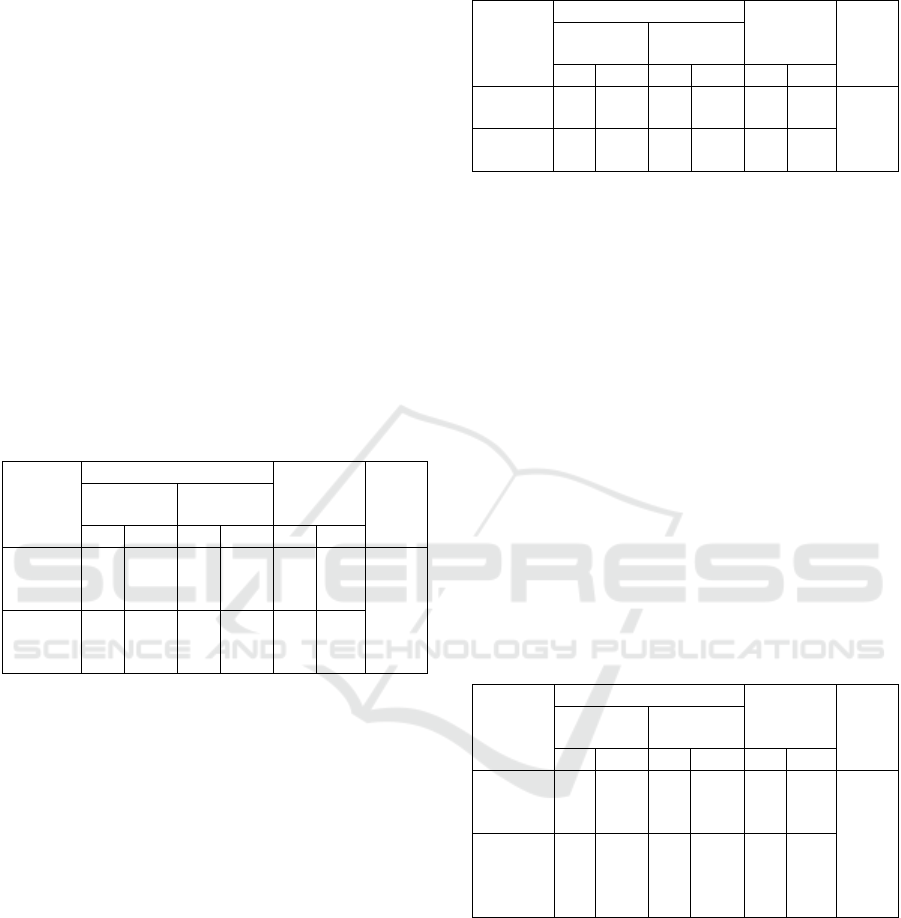
Table 7: Relationship Between Heat Pressure and Heat
Strain in Workers.
Heat
Pressure
Heat Strain
Total
P-
value
Heat
Strain
No Heat
Strain
N % N % N %
Yes
(>27,5)
18 90,0 2 10,0 20 100
0,000
No
(≤27,5)
8 20,5 31 79,5 39 100
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
322
3.2.2 Relationship between Age and Heat
Strain for Workers at PT Multikarya
Asia Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019
Workers who experience heat strain equal
proportions between workers who are safe / have no
risk (aged <40 years) and workers who are at risk (≥
40 years) as many as 13 people (32.5% in the safe
age group, and 68.4% in age group at risk) but for
workers who do not experience heat strain the
highest proportion is found in workers who are safe /
have no risk (aged <40 years) as many as 27 people
(67.5%) and the lowest proportion is in workers who
are at risk as many as 6 people (31.6%). Based on
the chi-square test results obtained P-value = 0.021
(P-value <0.05), which means that Ho is rejected,
which shows the relationship between age and heat
strain in workers at the PT Multikarya Asia Pacific
Raya Workshop in 2019.
Table 8: Relationship Between Age and Heat Strain in
Workers.
Age
Heat Strain
Total
P-
value
Heat
Strain
No Heat
Strain
N % N % N %
Risk
(≥40
Tahun)
13 68,4 6 31,6 19 100
0,021
Safe
(<40
Tahun)
13 32,5 27 67,5 40 100
3.2.3 The Relationship between Obesity and
Heat Strain for Workers at PT
Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya
Workshop in 2019
Workers who experienced the highest heat strain
proportion were workers who were not obese (BMI
calculation results showed <25) as many as 17
people (42.5%) and the lowest proportion was in
obese workers (BMI calculation results showed ≥
25) as many as 9 people (47, 4%), the highest
proportion of workers who did not experience heat
strain were non-obese workers (BMI calculation
results showed <25) as many as 23 people (57.5%)
and the lowest proportion was in obese workers
(BMI calculation results showed ≥ 25) as many as
10 people (52.6%). Based on the chi-square test
results obtained a value of P = 0.943 (Pvalue> 0.05),
which means that Ho is accepted which shows no
significant relationship between obesity and heat
strain in the Workers at the PT Multikarya Asia
Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019.
Table 9: Relationship Between Obesity and Heat Strain for
Workers.
Obesity
Status
Heat Strain
Total
P-
value
Heat
Strain
No Heat
Strain
N % N % N %
Obesity
(≥25)
9 47,4 10 52,6 19 100
0,943
No
(<25)
17 42,5 23 47,5 49 100
3.2.4 Relationship between Chronic Disease
and Heat Strain in Workers at PT
Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya
Workshop in 2019
Workers who experienced the highest proportion of
heat strains were 22 workers (41.5%) and the lowest
proportion were workers who had chronic illness as
many as 4 people (66.7%), those without heat strain
the highest proportion is workers who have no
chronic disease as many as 31 people (58.5%) and
the lowest proportion is workers who have chronic
illness as many as 2 people (33.3%). Based on the
chi-square test results obtained a value of P = 0.390
(Pvalue> 0.05), which means that Ho is accepted
which shows no significant relationship between
chronic disease and heat strain in Workers at the PT
Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019.
Table 10: The Relationship Between Chronic Disease and
Heat Strain in Workers.
Obesity
Status
Heat Strain
Total
P-
value
Heat
Strain
No Heat
Strain
N % N % N %
There are
chronic
diseases
4 66,7 2 33,3 6 100
0,390
There is
no
chronic
disease
22 41,5 31 58,5 53 100
3.2.5 Relationship between Hydration
Status and Heat Strain for Workers at
PT Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya
Workshop in 2019
Workers who experienced the highest proportion of
heat strain were dehydrated workers as many as 16
people (72.7%) and the lowest proportion were
workers who were hydrated as many as 10 people
(27.0%), among those workers who did not
experience the highest proportion of heat strain that
Factors Associated with Heat Strains in Workers at the PT Multikarya Asia Pasifik Raya Workshop in 2019
323

was hydrated workers 27 people (73.0%) and the
lowest proportion were dehydrated workers as many
as 6 people (27.3%). Based on the chi-square test
results obtained P-value = 0.002 (P-value <0.05),
which means that Ho is rejected which shows the
relationship between hydration status and heat strain
on the Workers at the PT Multikarya Asia Pacific
Raya Workshop in 2019.
Table 11: Relationship between Hydration Status and Heat
Strain in Workers.
Hydration
Status
Heat Strain
Total
P-
value
Heat Strain No Heat
Strain
N % N % N %
Dehydration 16 72,7 6 27,3 22 100
0,002
Hydration 10 27,0 27 73,0 37 100
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Univariate Analysis
The description of heat strain on workers that have
been carried out on 59 workers in the PT Multikarya
Asia Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019, the proportion
of workers who did not experience heat strain was
greater than 44.1% of the proportion of workers who
experienced heat strain which was 55.9%. This is in
line with research conducted by Fadhilah (2014)
which shows that the proportion of workers who do
not experience heat strains is greater than the
proportion of workers who experience heat strains.
The proportion of workers who do not experience
heat strain is greater than workers who do not
experience heat strain, this is because the company
has endeavored that workers are not exposed to
extreme heat from direct exposure to sunlight by
installing a roof especially in work areas that have
heat pressure so that workers do not expose to heat
from direct solar radiation. There are workers who
experience heat strains, this is because workers are
at high ambient heat temperatures, in addition, there
are tools and production machines that continuously
ignite and produce heat to the ambient temperature.
Conditions when conducting research at the Lodan-9
workshop in 6 work areas have been given a roof to
prevent direct exposure to the sun's heat, the pump
and engine area have been given general ventilation
to regulate the ambient temperature so that there is
no heat strain on workers.
The description of heat pressure that has been
carried out environmental measurements of 59
workers in the PT Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya
Workshop in 2019, the proportion of workers who
work in areas that do not have heat stress is greater
that is 66.1% of the proportion of workers who work
in areas that have pressure heat that is equal to
33.9%. This is in line with research conducted by
Septiani (2017) and Fauzi (2013) which shows that
the proportion of workers who work in areas that do
not have heat stress is greater than the proportion of
workers who work in areas that have heat stress. The
high heat pressure can be influenced by several
factors such as the presence of production machines
and working equipment and high air temperatures of
27,950C in the fabrication area. New workers who
are employed at the Lodan-9 workshop on the first
day of work are immediately given a workload with
a high enough heat working environment. This is
done by the company considering the qualifications
imposed by the company are experienced workers in
their fields so that they are considered capable of
working directly at high-risk locations. However,
with the new work environment and possible heat
pressures that are different from previous work on
new workers.
Description of Ages who have done research on
59 workers in the PT Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya
Workshop in 2019, the proportion of workers who
have no risk age / <40 years is greater that is 67.8%
of workers who have at-risk age /> 40 years which is
equal to 32.2%. This is in line with research
conducted by Septiani (2017) which shows that the
proportion of workers who are at risk is greater than
workers who are at risk of age. The proportion of
workers whose age is not at greater risk is due to the
qualifications carried out by the company
determined by the management where the
management places a productive age for work in the
workshop because it is considered as heavy work so
that there are many new workers employed by PT
Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya.
The description of obesity that has been
conducted by research on 59 workers in the PT
Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019,
the proportion of non-obese workers is higher at
67.8% of obese workers at 32.2%. This is in line
with research conducted by Fadhilah (2014),
Septiani (2017) in related industries, and Tumbol
(2018) in the construction field which shows that the
proportion of non-obese workers is higher than
obese workers. The proportion of workers who are
obese is smaller than the proportion of workers who
are not obese can be caused by a variety of factors,
including the high physical activity of workers such
as mobilization activities by walking, sometimes
accompanied by lifting weights, and so forth. These
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
324

activities can reduce body fat mass and increase
body muscle mass through burning calories.
The description of chronic diseases that have
been carried out on 59 workers in the PT Multikarya
Asia Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019, the proportion
of workers who did not have chronic illnesses was
higher at 89.8% of workers who had a chronic
illness at 10.2%. This shows the similarity between
research conducted by Tumbol (2018) and Septiani
(2017) which shows that the proportion of workers
who do not have a chronic illness is higher than
workers who have a chronic disease. The high
number of workers who do not have chronic
illnesses can be caused by information bias at the
time of the interview, this is because the retrieval of
research can be done in this variable only through
questionnaires and no physical examination by
medical personnel.
Description of hydration status that has been
carried out on 59 workers in the PT Multikarya Asia
Pacific Raya Workshop in 2019, the proportion of
workers who are hydrated is higher at 62.7% of
workers who are dehydrated at 37.3%. This shows
the similarity between research conducted by
Septiani (2017) which shows that the proportion of
workers who are hydrated is higher than workers
who are dehydrated. The proportion of workers who
experience hydration is higher than workers who are
dehydrated. This is because the company has
provided drinking water for all workers, namely in
the second-floor office area. Based on this study,
there are still workers who are dehydrated. That is
because there are some workers who work in hot
pressure environments.
4.2 Bivariate Analysis
The relationship between heat stress and heat strain,
based on the results of the study the results of
statistical tests indicate that there is a relationship
between heat stress and heat strain. Based on the
results of research conducted, workers in the heat
stress area experienced the most heat strain, this is
because workers who are in the heat pressure area are
jobs related to several production machines such as
cutting tools, welding machines, and other fabrication
machines apart from that mobilization of workers can
also increase core body temperature so there is a
potential for heat strain. The condition when
conducting research in the PT Multikarya workshop
did not have a rest area with cooler room conditions.
The relationship between age and heat strain,
based on statistical test results showed that there was
a significant relationship between age and heat strain
in workers. This is in line with research conducted
by Septiani (2017) and Tumbol (2018) which shows
there is a relationship between age and the incidence
of heat strain. Workers who have age over 40 years
experience the most heat strain (68.4%), this is
because workers with age at risk of having the
ability to pump blood by the heart tend to be worse
so that the body's ability to channel heat from the
body to the surface of the skin also becomes
hampered and the group of workers with age at risk
will increase the indication of the occurrence of heat
strains. The current state of research at PT
Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya's workshops still
employed several workers of high-risk age in areas
of high heat stress because the workers had a good
experience in their fields.
The relationship between obesity and heart
strain, based on the results of the study, the results of
statistical tests showed that there was no significant
relationship between obesity and heart strain. This is
in line with research conducted by Tumbol (2018)
which shows no significant relationship between
obesity and heat strains in workers. the proportion of
obese workers is more likely not to have heat strains.
and there is no difference between obesity and heat
strain, this is because in the obese group and most in
the non-obese group have the workload that tends to
be the same so there is no difference in the heat
strain in the obese group and the non- obese group
so that no difference is found. The situation at the
time of doing research in the workshop of PT
Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya had not yet
implemented a nutrition program both food catering
and canteen for workers.
The relationship between chronic diseases and
heat strains, based on the results of the study showed
that there was no significant relationship between
chronic diseases and heat strains in workers. This is
in line with research conducted by Tumbol (2018)
and Fadhilah (2014) which show no significant
relationship between chronic disease and heat strains
in workers. The proportion of workers who have
chronic diseases is the most among workers who
experience heat strains, but there is no significant
relationship between chronic diseases with heat
strains, this can be due to the least known results in
workers suffering from chronic illnesses, this can
also be due to Other factors are more influential on
workers experiencing heat strains.
The relationship between hydration status and
heat strain, based on the results of the study showed
that there is a relationship between hydration status
and heat strain in workers. This is in line with
research conducted by Septiani (2017) which shows
Factors Associated with Heat Strains in Workers at the PT Multikarya Asia Pasifik Raya Workshop in 2019
325

that there is a relationship between hydration status
and heat strain in workers. the proportion of workers
who were dehydrated the most was workers who
experienced heat strains, and the proportion of
workers who were well hydrated was highest in
workers who did not experience heat strains.
workers at the workshop generally complained of
being tired, having headaches and feeling thirsty.
This can be influenced by the environment that is
too hot and will cause the metabolic process of
workers to run faster because workers are more
easily sweating so this if considered will lead to
dehydration in workers, especially in hot pressure
environments so as to increase the risk of
experiencing heat strains. The conditions for
conducting research in the PT Multikarya Asia
Pacific Raya workshop were rarely carried out with
socialization regarding the fulfillment of body fluids
to workers. Generally, the socialization carried out
focused on safety at work.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTION
Based on research conducted on 59 workers in the
PT Multikarya Asia Pacific Raya workshop, the
proportion of workers who did not experience heat
strains was greater than the proportion of workers
who experienced heat strains, the proportion of
workers who worked in areas without heat pressure
was greater than the proportion of workers who
worked in areas of heat stress, the proportion of
workers who are at no age is greater than the
workers who have aged at risk, the proportion of
workers who are not obese is higher than obese
workers, the proportion of workers who do not have
chronic illness is higher than workers who have
chronic illness, the proportion of workers who are
hydrated is higher than workers who are dehydrated,
there is a relationship between heat stress and heat
strain in workers, there is a relationship between
age and heat strain in workers, there is no significant
relationship between obesity and heat strain in
workers, there is no relationship between chronic
disease with heat strains in workers, there is a
relationship between hydration status and heat
strains in workers at the PT Multikarya Asia Pacific
Raya Workshop in 2019.
Suggestions for companies to provide workloads
in heat stress areas for new workers gradually, can
increase routine sports activities such as joint
gymnastics, provide more drinking water in certain
areas, especially in areas that have high heat
pressure and close to the work area so that workers
can meet the needs of fluids, provide a place to rest
with a cooler temperature for workers, consider
workers at risk of age placed in jobs that are at risk
of causing heat strain, and the company should
provide more drinking water that is affordable by
workers and pay attention to aspects of fluid needs
for workers by conducting socialization regarding
fluid needs.
REFERENCES
ACGIH. (2007). American Conference of Govermental
Industrial Hygiene: Evaluation of Heat Stress at a
Glass Bottle Manufacturer, (November). Retrieved
from https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/hhe/reports/pdfs/
2003-0311-3052.pdf
Adiningsih, R. (2013). Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi
Kejadian Heat Strain Pada Tenaga Kerja Yang
Terpapar Panas di PT Aneka Boga Makmur. Retrieved
from http://journal.unair.ac.id/filerPDF/k3c7d9c6fda
afull.pdf
Adisapoetra. (2011). Hubungan Antara Aktivitas Fisik
dengan Status Kegemukan pada Kohort Anak Tahun
2011 di Kota Bogor. Jakarta: Universitas Indonesia.
Budiono, S., Jusuf, & Pusparini, A. (2003). Bunga Rampai
Hiperkes dan Keselamatan Kerja. Semarang: Badan
Penerbit Universitas Diponegoro.
Bureau Labor Statistics (BLS). (2011). Occupational
Outlook Handbook. Washington DC: U.S.:
Department of Labor. Retrieved from https://www.
bls.gov/ooh
Dehghan, Habiballah, E. H. dan P. H. (2013). Validation
of Questionnaire for Heat strain Evaluation in Women
Workers. Queensland University of Technology.
Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub
med/23930180
Departemen Kesehatan Republik Indonesia (Depkes RI).
(2011). No TitleObesitas dan kurang aktivitas fisik.
Retrieved from http://www.depkes.go.id/index.php/
berita/press-release/137-obesitas-dankurang-aktivitas-
fisik-menyumbang-30- kanker.pdf%0A
Fadhilah, R. (2014). Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan
Dengan Heat Strain Pada Pekerja Pabrik Kerupuk di
Wilayah Kecamatan Ciputat Timur Tahun 2014.
Retrieved from http://repository.uinjkt.ac.id/dspace/
bitstream/123456789/25650/3/RIZKI FADHILAH-
FKIK.pdf
Fauzi, Z. A. (2013). Faktor-faktor yang Berhubungan
Dengan Heat Strain Pekerja Pabrik Tahu di
Kecamatan Ciputat Tahun 2013. Retrieved from
http://repository.uinjkt.ac.id/dspace/bitstream/1234567
89/24297/1/Zahro Abdani Fauzi-fkik.pdf
Health and Safety Ontario. (2015). Heat Stress. Retrieved
from https://www.labour.gov.on.ca/english/hs/topics/
heatstress.php
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
326

Hendra. (2009). Tekanan panas dan Metode
Pengukurannya di Tempat Kerja. Smiloka
Keterampilan Pengukuran Bahaya Fisik dan Kimia di
Tempat Kerja.
Hunt, A. P. (2011). Heat Strain, Hydration Status, and
Symptoms of Heat Illness in Surface Mine Workers.
Retrieved from https://eprints.qut.edu.au/44039/1/
Andrew_Hunt_Thesis.pdf
Kementerian Ketenagakerjaan RI. (2018). Peraturan
Menteri Ketenagakerjaan Republik Indonesia Nomor 5
Tahun 2018 Tentang Keselamatan dan Kesehatan
Kerja Lingkungan Kerja. Retrieved from https://
jdih.kemnaker.go.id/data_puu/Permen_5_2018.pdf
Kenny, Glen P, Jane Yardley, C. B. (2010). Heat Stress in
older Individuals and Patients with Common Chronic
Diseases. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.
nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2900329/
Krucik, G. (2014). Medically Reviewed. Retrieved June
30, 2014, from https://clinicalnews.org/2015/06/06/
recognizing-anxiety-symptoms-signs-and- risk-factors/
Kuswana WS. (2014). Ergonomi dan Kesehatan dan
Keselamatan Kerja. Bandung: PT Remaja
Rosdakarya.
Leksana, E. (2015). Strategi Terapi Cairan Pada
Dehidrasi. Semarang: Fakultas Kedokteran
Universitas Diponegoro.
Lundfren, Karin, Kalev Kuklane, I. H. (2006). Effects of
heat stress on Working Populations when Facing
Climate Change. National Institute of Occupational
Safety and Health. Retrieved from https://www.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23411752
N.C. Department of Labor (NCDOL). (2011). A Guide to
Preventing Heat Stress and Cold Stress. North
Carolina: Departement of Labor Occupational Safety
and Health Division. Retrieved from https://safety
resourcesblog.files.wordpress.com/2014/11/a-guide-
to-preventing- heat-stress-and-cold-stress.pdf
NIOSH. (2016). National Institute for Occupational Safety
and Health: Occupational Exposure to Heat and
Hot Environments. Departement of Health and Human
Services. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/
docs/2016-106/pdfs/2016-106.pdf?id=10.26616/NIOS
HPUB2016106
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
(2016). Metabolic Heat Stress. Retrieved from
https://www.osha.gov/dts/osta/otm_iii/otm_iii_4.html#
metabolic%0A
Occupational Safety and Health Service (OSHS). (2017).
Guidelines for The Management of Work in Extreme
of Temperature. Wellington: Occupational Safety and
Health Service Department of Labor.Retrieved from
https://www.osha.gov/SLTC/heatillness/heat_index/pd
fs/all_in_one.pdf
Persons, K. dan D. B. (2002). The Development of a
practical heat stress assement methodology for use in
UK industry. United Kingdom: Loughborough
University. Retrieved from www.hse.gov.uk/research/
rrpdf/rr008.pdf
Rouzier, P. (2003). Muscle Spasms. Retrieved from
https://mmssim.mckesson.com/catalog?node=1376532
+5776749
Septiani. (2017). Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi
Keluhan Heat Strain Pada Pekerja di Unit Fabrik
Processing PT Argo Pantes Tbk Tangerang tahun
2017.Retrieved from http://digilib.esaunggul.ac.id/
faktorfaktor-yang-berhubungan-dengan-keluhan-heat-
strain-pada-pekerja-di-unit-fabric- processing-ptargo-
pantes-tbk-tangerang- tahun-2017-9831.html%0A
Shiel, W. C. (2014). Muscle Cramps. Retrieved from
https://www.emedicinehealth.com/muscle_cramps?
article_em.htm
Stoppler, M. C. (2014). Weakness. Retrieved August 21,
2014, from fernfortuniversity.com/term-papers/swot/
1433/5mckesson.php
Suma’mur. (2009). Higene Perusahaan dan Kesehatan
Kerja (Hiperkes). Jakarata: CV. Agung Seto.
Tarwaka. (2014). Manajemen dan Implementasi K3 di
Tempat Kerja(Edisi II). Surakarta: Harapan Press.
Tumbol, C. M. (2018). Faktor-faktor yang Berhubungan
dengan Kejadian Heat Strain pada Pekerja di Proyek
Apartement Arandra Residences oleh PT. Wika
Gedung Tbk Tahun 2018. Retrieved From https://digi
lib.esaunggul.ac.id/faktorfaktor-yang-berhubungan-de
ngan-kejadian-heat-strain-pada-pekerja-di-proyek-apar
tement-arandra-residence-oleh-pt-wika-gedung-tbk-tah
un-2018- 12629.html
Wan, M. (2006). Assessment of Occupational Heat Strain,
Departemen of Environmental and Occupational
Health. South Florida: College of Public Health.
Retrieved from scholarcommons.usf.edu/cgi/view
content.cgi?article=3744&context=etd
Factors Associated with Heat Strains in Workers at the PT Multikarya Asia Pasifik Raya Workshop in 2019
327
